Preliminary Evaluation of the Biocontrol Potential of Stethorus punctillum, a Key Natural Enemy of Spider Mites in Northwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Insect Sources
2.2. The Functional Response of S. punctillum on T. urticae in Laboratory Trials
2.3. Spider Mite Control by S. punctillum on Different Crops in the Field
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Functional Response of Larvae and Adults of S. punctillum in the Laboratory
3.2. Impacts of S. punctillum on Caged Cohorts of Spider Mites on Three Crops in the Field
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adesanya, A.W.; Lavine, M.D.; Moural, T.W.; Lavine, L.C.; Walsh, D.B. Mechanisms and management of acaricide resistance for Tetranychus urticae in agroecosystems. J. Pest Sci. 2021, 94, 639–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migeon, A.; Nouguier, E.; Dorkeld, F. Spider Mites Web: A Comprehensive Database for the Tetranychidae. In Trends in Acarology; Sabelis, M.W., Bruin, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; Volume 17, pp. 557–560. [Google Scholar]
- Jakubowska, M.; Dobosz, R.; Zawada, D.; Kowalska, J. A review of crop protection methods against the two spotted spider mite—Tetranychus urticae Koch (Acari: Tetranychidae)—With special reference to alternative methods. Agriculture 2022, 12, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, N.; Shi, Z.; Harwood, J.D.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, S.; Desneux, N.; Zhao, J.; Ren, W. Laboratory and field evaluation of maize resistance to the two-spotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae. J. Pest Sci. 2024, 97, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.; Kerns, D.L.; Gore, J.; Lorenz, G.; Stewart, S. Susceptibility of two spotted spider mites (Tetranychus urticae) to abamectin in midsouth cotton. Crop Prot. 2017, 98, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhmanov, A. Tetranychus urticae Koch biology on apple trees. Bull. Sci. Pract. 2024, 10, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attia, S.; Grissa, K.L.; Lognay, G.; Bitume, E.; Hance, T.; Mailleux, A.C. A review of the major biological approaches to control the worldwide pest Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae) with special reference to natural pesticides: Biological approaches to control Tetranychus urticae. J. Pest Sci. 2013, 86, 361–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandeep, V.; Chinmayi, S.; Bellanki, A. Two-spotted spider mite: Biology, damage symptoms and integrated pest management in crop ecosystem. Vigyan Varta 2024, 5, 163–165. [Google Scholar]
- Marcic, D. Acaricides in modern management of plant-feeding mites. J. Pest Sci. 2012, 85, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathipour, Y.; Maleknia, B. Chapter 11-Mite Predators. In Ecofriendly Pest Management for Food Security; Omkar, Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; Volume 11, pp. 329–366. [Google Scholar]
- Ratnadass, A.; Fernandes, P.; Avelino, J.; Habib, R. Plant species diversity for sustainable management of crop pests and diseases in agroecosystems: A review. Agron. Sustain Dev. 2012, 32, 273–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, G.; Islam, W.; Haque, M. Biology and predation of Stethorus punctillum Weise (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) feeding on Tetranychus urticae Koch. J. Bio-Sci. 2007, 15, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapur, A.P. On the old world species of the Genus Stethorus Weise (Coleoptera, Coccinellidae). Bull. Entomol. Res. 1948, 39, 297–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putman, W.L. Bionomics of Stethorus punctillum Weise (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in Ontario. Can. Entomol. 1955, 87, 9–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.; Brodeur, J.; Cloutier, C. Seasonal activity of the spider mite predators Stethorus punctillum (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) and Neoseiulus fallacis (Acarina: Phytoseiidae) in raspberry, two predators of Tetranychus mcdanieli(Acarina: Tetranychidae). Biol. Control 2005, 34, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Shen, M.; Xiong, J.; Guo, Z. Approaches to enhance the effectiveness of biocontrol of Panonychus citri (Acari: Tetranychidae) with Stethorus punctillum (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in citrus orchards in Guizhou. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 1996, 1, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raworth, D.A. Development, larval voracity, and greenhouse releases of Stethorus punctillum (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Can. Entomol. 2001, 133, 721–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rott, A.S.; Ponsonby, D.J. Improving the control of Tetranychus urticae on edible glasshouse crops using a specialist coccinellid (Stethorus punctillum Weise) and a generalist mite (Amblyseius californicus McGregor) as biocontrol agents. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2000, 10, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adly, D. Evaluate the efficiency of releasing two predatory species at their optimal temperature for controlling Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae) in a croton greenhouse. Pers. J. Acarol. 2023, 12, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, D.; Pu, J. Main crops structural change and its climate background in Gansu Province during the past two decades. J. Nat. Resour. 2012, 27, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworski, C.C.; Thomine, E.; Rusch, A.; Lavoir, A.-V.; Wang, S.; Desneux, N. Crop diversification to promote arthropod pest management: A review. Agric. Commun. 2023, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyckhuys, K.A.G.; Pozsgai, G.; Ben Fekih, I.; Sanchez-Garcia, F.J.; Elkahky, M. Biodiversity loss impacts top-down regulation of insect herbivores across ecosystem boundaries. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 930, 172807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Hu, J. Decomposition and calculation of contribution factors of pesticide use increase in China: Based on the perspective of cropping structure adjustment. J. Ecol. Rural 2020, 36, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Gupta, A.; Waswani, H.; Prasad, M.; Ranjan, R. Impact of Pesticides on the Ecosystem. In Agrochemicals in Soil and Environment: Impacts and Remediation; Naeem, M., Bremont, J.F.J., Ansari, A.A., Gill, S.S., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; Volume 2, pp. 157–181. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Duan, M.; Yu, Z. Agricultural landscapes and biodiversity in China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 166, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontijo, L.M. Engineering natural enemy shelters to enhance conservation biological control in field crops. Biol. Control 2019, 130, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyckhuys, K.A.G.; Abram, P.K.; Barrios, E.; Cancino, J.; Collatz, J.; Fancelli, M.; Klein, A.-M.; Lindell, C.A.; Osterman, J.; Pinto, M.; et al. Orchard systems offer low-hanging fruit for low-carbon, biodiversity-friendly farming. BioScience 2025, biae140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyckhuys, K.A.G.; Gu, B.; Ben Fekih, I.; Finger, R.; Kenis, M.; Lu, Y.; Subramanian, S.; Tang, F.H.M.; Weber, D.C.; Zhang, W.; et al. Restoring functional integrity of the global production ecosystem through biological control. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlong, M.J.; Zalucki, M.P. Exploiting predators for pest management: The need for sound ecological assessment. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2010, 135, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfadyen, S.; Davies, A.P.; Zalucki, M.P. Assessing the impact of arthropod natural enemies on crop pests at the field scale. Insect Sci. 2015, 22, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira de Sousa Neto, E.; Filgueiras, R.M.C.; Mendes, J.A.; Melo, J.W.d.S. Functional and numerical responses of Neoseiulus idaeus and Neoseiulus californicus to eggs of Tetranychus urticae. Int. J. Acarol. 2019, 45, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holling, C.S. Some characteristics of simple types of predation and parasitism. Can. Entomol. 1959, 91, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, M.E.; Kristensen, K.; van Benthem, K.J.; Magnusson, A.; Berg, C.W.; Nielsen, A.; Skaug, H.J.; Maechler, M.; Bolker, B.M. GlmmTMB balances speed and flexibility among packages for zero-inflated generalized linear mixed modelling. R J. 2017, 9, 378–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S. An R Companion to Applied Regression, 3rd ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing, version 4.2.1; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022; Available online: http://www.R-project.org (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- Jin, P.; Tian, L.; Chen, L.; Hong, X. Spider mites of agricultural importance in China, with focus on species composition during the last decade (2008–2017). Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2018, 23, 2087–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Naranjo, S.E.; Wu, K. Biological control of cotton pests in China. Biol. Control 2014, 68, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Yu, Y.; Tan, X.; Chen, A.; Feng, J. Biological control of insect pests in apple orchards in China. Biol. Control 2014, 68, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, B.A.; Nadeem, M.A.; Nawaz, H.; Amin, M.M.; Abbasi, G.H.; Nadeem, M.; Ali, M.; Ameen, M.; Javaid, M.M.; Maqbool, R.; et al. Pesticides: Impacts on agriculture productivity, environment, and management strategies. In Emerging Contaminants and Plants: Interactions, Adaptations and Remediation Technologies; Aftab, T., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 5, pp. 109–134. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez Bayo, F. Indirect effect of pesticides on insects and other arthropods. Toxics 2021, 9, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matter, M.M.; El-Shershaby, M.M.A.; Farag, N.A.; Gesraha, M.A. Impact of temperature and prey density on the predacious capacity and behaviour of Stethorus punctillum Weise. Arch. Phytopath. Plant 2011, 44, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.; Hou, F.; Ni, Z.; Guo, J. Predatory functional response of female adult amblyseius herbicolus to Polyphagotarsonemus Latus. J. Mt. Agric. Biol. 2023, 42, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasap, I.; Atlihan, R. Consumption rate and functional response of the predaceous mite Kampimodromus Aberrans to two-spotted spider mite Tetranychus urticae in the laboratory. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2011, 53, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotoh, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; Mori, K. Effect of Temperature on life history of the predatory mite Amblyseius (Neoseiulus) Californicus (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2004, 32, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Fadamiro, H.Y. Functional responses and prey-stage preferences of three species of predacious mites (Acari: Phytoseiidae) on citrus red mite, Panonychus citri (Acari: Tetranychidae). Biol. Control 2010, 53, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiftikçi, P.; Kök, Ş.; Kasap, İ. Biological control of two spotted spider mites [Tetranychus urticae Koch (Acari: Tetranychidae)] using Phytoseiulus persimilis Athias-Henriot (Acari: Phytoseidae) at different ratios of release on field-grown tomatos. Biol. Control 2020, 151, 104404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente Orta, G.; Álvarez, H.A.; Madeira, F.; Albajes, R. The influence of planting periods on herbivore and natural enemy abundance on yellow sticky traps in Bt maize fields. Insects 2022, 13, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

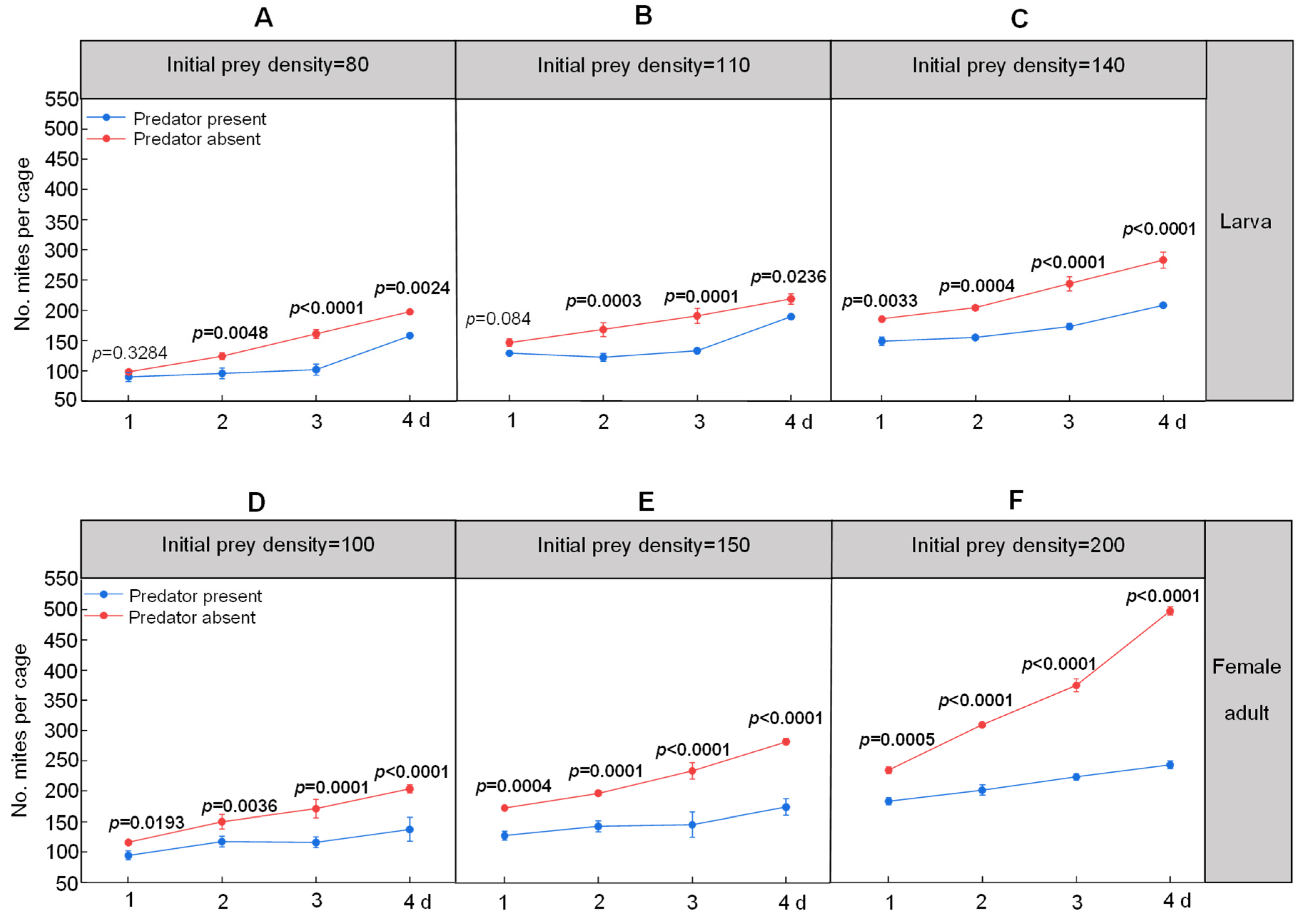

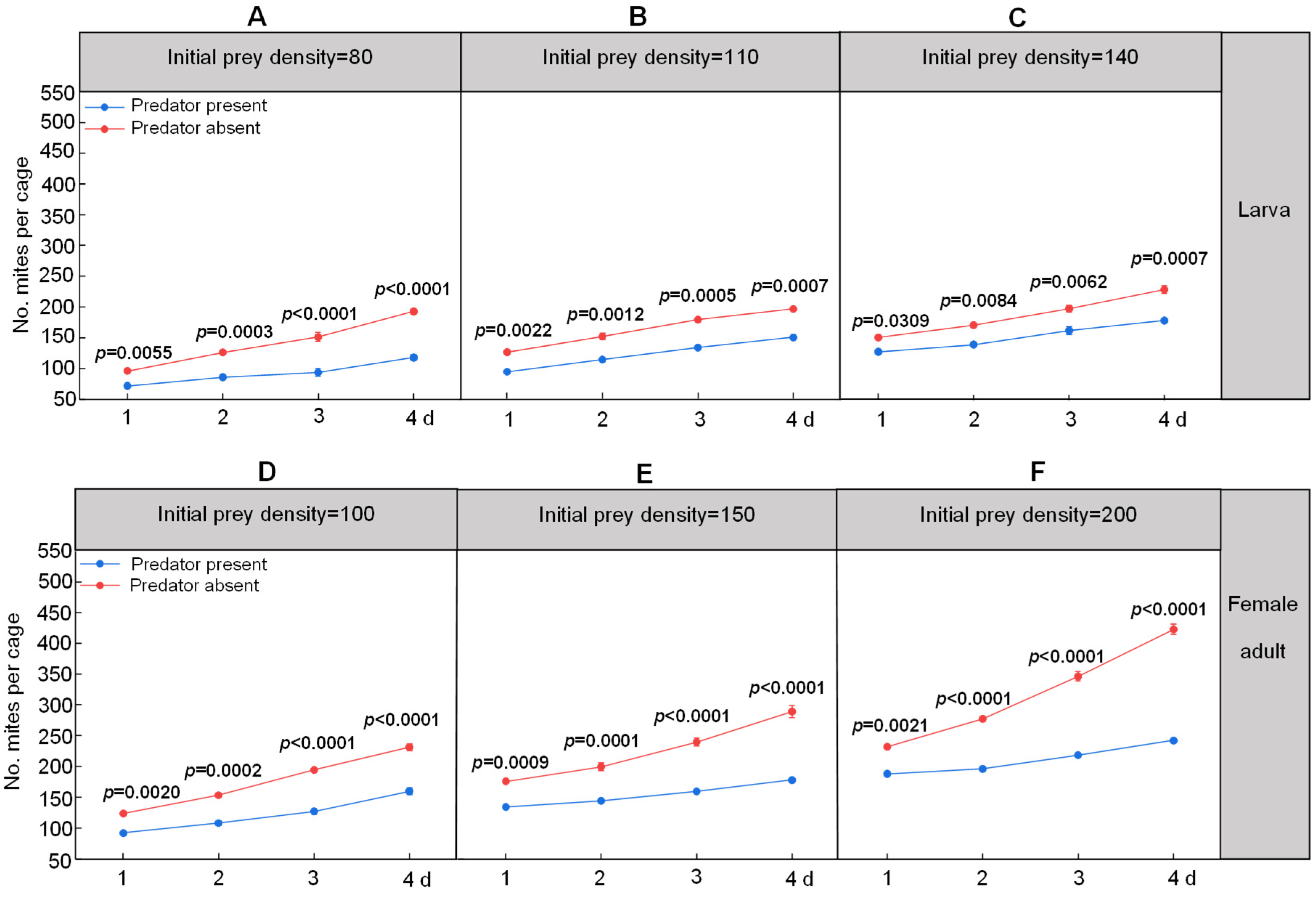
| Ladybeetle Life Stage | Prey Density | Consumed Numbers of Prey | ANOVA Statistics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Third-instar larva | 40 | 32 ± 1.53 e | F4,10 = 155.62 p < 0.001 |
| 80 | 58.33 ± 2.33 d | ||
| 120 | 72.67 ± 3.76 c | ||
| 160 | 93 ± 2.52 b | ||
| 200 | 116.67 ± 2.33 a | ||
| Female adult | 50 | 47.33 ± 1.86 e | F4,10 = 294.58 p < 0.001 |
| 100 | 94.67 ± 0.67 d | ||
| 150 | 129.67 ± 3.84 c | ||
| 200 | 153.67 ± 4.48 b | ||
| 250 | 181.67 ± 2.73 a | ||
| Male adult | 50 | 47.33 ± 1.45 d | F4,10 = 194.06 p < 0.001 |
| 100 | 85.33 ± 2.73 c | ||
| 150 | 125.67 ± 2.60 b | ||
| 200 | 140.67 ± 2.40 b | ||
| 250 | 166.67 ± 5.93 a |
| Ladybeetle Life Stage | Functional Response Equation | R2 | χ2 | Instant Attack Rate (a) | Handling Time (Th)/(d) | Maximum Daily Consumption (1/Th) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Third-instar larva | Na = 0.7978N0/(1 + 0.0020N0) | 0.972 | −0.0497 | 0.7978 | 0.0026 | 391.26 |
| Female adult | Na = 1.1389N0/(1 + 0.0023N0) | 0.989 | −0.0172 | 1.1389 | 0.0020 | 498.07 |
| Male adult | Na = 1.1120N0/(1 + 0.0027N0) | 0.980 | −0.0179 | 1.1120 | 0.0024 | 413.95 |
| Ladybeetle Life Stage | Predator–Prey | PRSR of Spider Mites on Day 4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maize | Cotton | Apple | ||
| larvae | 1:80 | 20.08% ± 1.12% | 21.99% ± 2.21% | 38.88% ± 1.93% |
| 1:110 | 13.16% ± 3.98% | 23.74% ± 2.04% | 23.48% ± 1.01% | |
| 1:140 | 26.21% ± 4.52% | 43.19% ± 2.04% | 21.27% ± 3.53% | |
| adults | 1:100 | 31.99% ± 11.64% | 25.28% ± 4.95% | 30.86% ± 3.32% |
| 1:150 | 38.52% ± 5.66% | 38.24% ± 1.18% | 38.36% ± 1.78% | |
| 1:200 | 51.47% ± 1.90% | 40.02% ± 2.24% | 42.69% ± 0.59% | |
| Ladybeetle Life Stage | Initial Prey Densities | Fixed Effect | χ2 | df | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Larva | 80 | Treatment | 52.30 | 1 | <0.001 |
| Day | 180.62 | 3 | <0.001 | ||
| Treatment × Day | 11.86 | 3 | 0.0079 | ||
| 110 | Treatment | 52.12 | 1 | <0.001 | |
| Day | 96.63 | 3 | <0.001 | ||
| Treatment × Day | 10.12 | 3 | 0.0176 | ||
| 140 | Treatment | 100.38 | 1 | <0.001 | |
| Day | 109.05 | 3 | <0.001 | ||
| Treatment × Day | 2.25 | 3 | 0.5225 | ||
| Adult | 100 | Treatment | 82.87 | 1 | <0.001 |
| Day | 93.19 | 3 | <0.001 | ||
| Treatment × Day | 5.29 | 3 | 0.1517 | ||
| 150 | Treatment | 176.71 | 1 | <0.001 | |
| Day | 108.84 | 3 | <0.001 | ||
| Treatment × Day | 7.29 | 3 | 0.0632 | ||
| 200 | Treatment | 410.40 | 1 | <0.001 | |
| Day | 294.69 | 3 | <0.001 | ||
| Treatment × Day | 44.38 | 3 | <0.001 |
| Ladybeetle Life Stage | Initial Prey Densities | Fixed Effect | χ2 | df | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Larva | 80 | Treatment | 65.92 | 1 | <0.001 |
| Day | 180.07 | 3 | <0.001 | ||
| Treatment × Day | 4.65 | 3 | 0.1995 | ||
| 110 | Treatment | 93.38 | 1 | <0.001 | |
| Day | 108.27 | 3 | <0.001 | ||
| Treatment × Day | 6.80 | 3 | 0.0787 | ||
| 140 | Treatment | 229.39 | 1 | <0.001 | |
| Day | 117.31 | 3 | <0.001 | ||
| Treatment × Day | 11.35 | 3 | 0.0100 | ||
| Adult | 100 | Treatment | 100.72 | 1 | <0.001 |
| Day | 150.74 | 3 | <0.001 | ||
| Treatment × Day | 2.14 | 3 | 0.5439 | ||
| 150 | Treatment | 103.60 | 1 | <0.001 | |
| Day | 106.46 | 3 | <0.001 | ||
| Treatment × Day | 15.05 | 3 | 0.0018 | ||
| 200 | Treatment | 284.55 | 1 | <0.001 | |
| Day | 201.62 | 3 | <0.001 | ||
| Treatment × Day | 8.17 | 3 | <0.001 |
| Ladybeetle Life Stage | Initial Prey Density | Fixed Effect | χ2 | df | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Larva | 80 | Treatment | 121.98 | 1 | <0.001 |
| Day | 136.81 | 3 | <0.001 | ||
| Treatment × Day | 3.93 | 3 | 0.2689 | ||
| 110 | Treatment | 67.47 | 1 | <0.001 | |
| Day | 94.89 | 3 | <0.001 | ||
| Treatment × Day | 0.10 | 3 | 0.9924 | ||
| 140 | Treatment | 42.11 | 1 | <0.001 | |
| Day | 82.15 | 3 | <0.001 | ||
| Treatment × Day | 0.84 | 3 | 0.8395 | ||
| Adult | 100 | Treatment | 116.91 | 1 | <0.001 |
| Day | 171.15 | 3 | <0.001 | ||
| Treatment × Day | 1.76 | 3 | 0.6231 | ||
| 150 | Treatment | 162.74 | 1 | <0.001 | |
| Day | 110.98 | 3 | <0.001 | ||
| Treatment × Day | 7.26 | 3 | 0.0640 | ||
| 200 | Treatment | 259.31 | 1 | <0.001 | |
| Day | 192.40 | 3 | <0.001 | ||
| Treatment × Day | 24.95 | 3 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Zhang, D.; Guo, H.; He, X.; Liu, B.; Wang, S.; Lu, Y. Preliminary Evaluation of the Biocontrol Potential of Stethorus punctillum, a Key Natural Enemy of Spider Mites in Northwest China. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051092
Wang H, Zhang D, Guo H, He X, Liu B, Wang S, Lu Y. Preliminary Evaluation of the Biocontrol Potential of Stethorus punctillum, a Key Natural Enemy of Spider Mites in Northwest China. Agronomy. 2025; 15(5):1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051092
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Haoyu, Dawei Zhang, Huan Guo, Xiaoling He, Bing Liu, Senshan Wang, and Yanhui Lu. 2025. "Preliminary Evaluation of the Biocontrol Potential of Stethorus punctillum, a Key Natural Enemy of Spider Mites in Northwest China" Agronomy 15, no. 5: 1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051092
APA StyleWang, H., Zhang, D., Guo, H., He, X., Liu, B., Wang, S., & Lu, Y. (2025). Preliminary Evaluation of the Biocontrol Potential of Stethorus punctillum, a Key Natural Enemy of Spider Mites in Northwest China. Agronomy, 15(5), 1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051092






