Assessing the Influences of Grassland Degradation on Soil Quality Through Different Minimum Data Sets in Southwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling Design and Soil Analysis
2.3. Constructing Soil Quality Index
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Soil Indicators
3.2. Establishing the MDS and SMDS
3.3. Constructing the Soil Quality Indexes
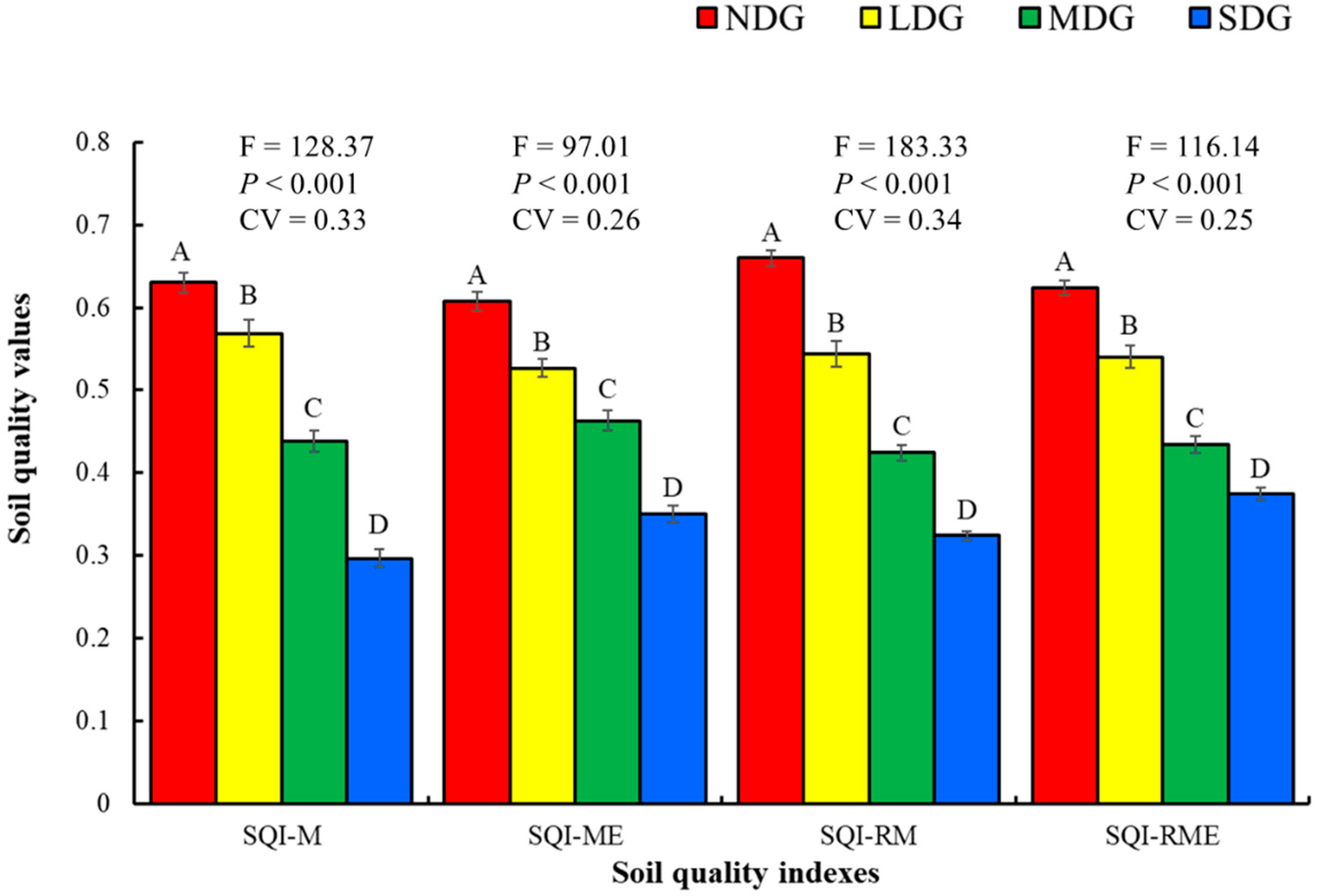
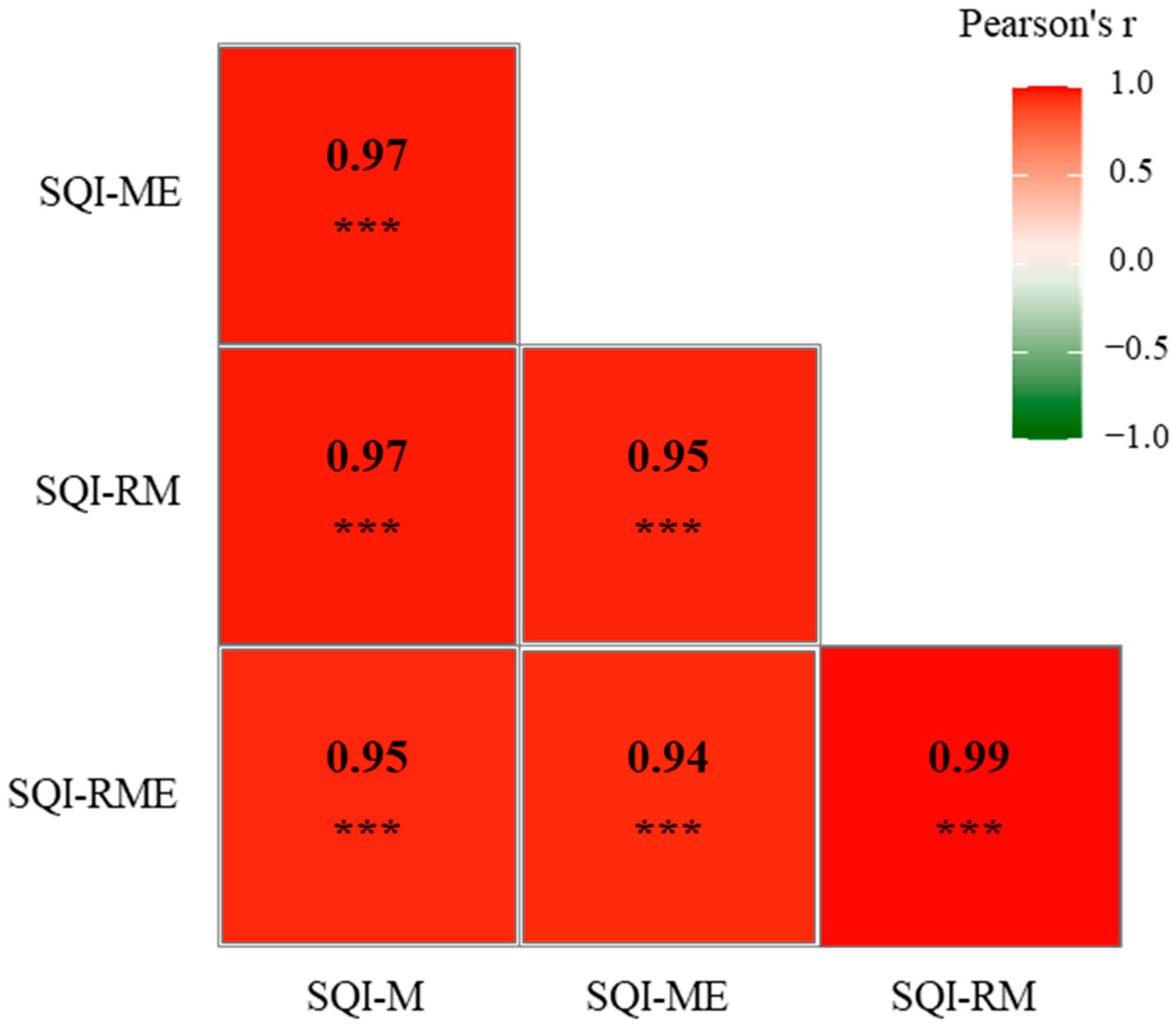
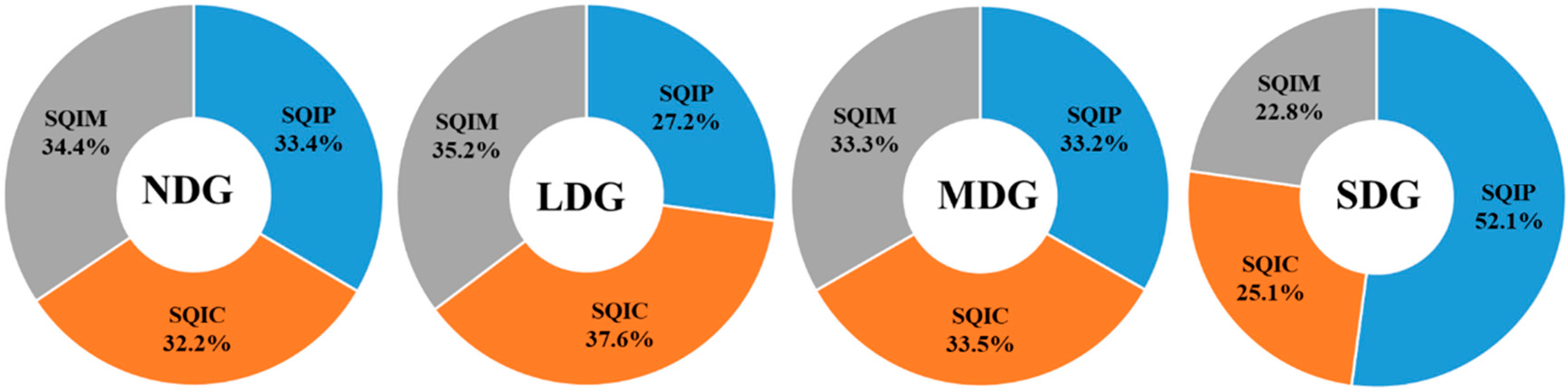
3.4. Assessing the Soil Quality Under Different Grasslands
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Grassland Degradation on Soil Properties
4.2. Assess the Influences of Grassland Degradation on Soil Quality
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferreira, C.S.S.; Seifollahi-Aghmiuni, S.; Destouni, G.; Ghajarnia, N.; Kalantari, Z. Soil degradation in the European Mediterranean region: Processes, status and consequences. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 805, 150106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Yi, X.Y.; Zheng, H.T.; Ni, K.; Ma, Q.X.; Cai, Y.J.; Ma, L.F.; Shi, Y.Z.; Yang, X.D.; et al. Partially replacing chemical fertilizer with manure improves soil quality and ecosystem multifunctionality in a tea plantation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 378, 109284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraamwinkel, C.T.; Beaulieu, A.; Dias, T.; Howison, R.A. Planetary limits to soil degradation. Commun. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laik, R.; Singh, S.K.; Pramanick, B.; Kumari, V.; Nath, D.; Dessoky, E.S.; Attia, A.O.; Hassan, M.M.; Hossain, A. Improved method of boron fertilization in rice (Oryza sativa L.)-m (Brassica juncea L.) cropping system in upland calcareous soils. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Restoring soil quality to mitigate soil degradation. Sustainability 2015, 7, 5875–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.L.; Wang, C. Multiple soil quality assessment methods for evaluating effects of organic fertilization in wheat-maize rotation system. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 150, 1269299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obade, V.P.; Lal, R. A standardized soil quality index for diverse field conditions. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 541, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiesi, F.; Beheshti, A. Evaluating forest soil quality after deforestation and loss of ecosystem services using network analysis and factor analysis techniques. CATENA 2022, 208, 105778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.J.; Liu, J.L.; Tang, H.Y.; Sun, X.Z.; Liu, S.W.; Tang, X.G.; Ding, Z.; Ma, M.G.; Ci, E. Establishing a soil quality index to evaluate soil quality after afforestation in a karst region of Southwest China. CATENA 2023, 230, 107237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marion, L.F.; Schneider, R.; Cherubin, M.R.; Colares, G.S.; Wiesel, P.G.; Costa, A.B.; Lobo, E.A. Development of a soil quality index to evaluate agricultural cropping systems in southern Brazil. Soil. Tillage. Res. 2022, 218, 105293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuite, Z.; Demessie, A.; Abebe, T. Land use effect on soil quality and its implication to soil carbon storage in Aleta Chuko, Ethiopia. Geoderma Reg. 2025, 40, e00917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.J.; Liu, S.W.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Zhou, D.W. Selecting the minimum data set and quantitative soil quality indexing of alkaline soils under different land uses in northeast China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 616, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.F.; Zhang, X.S.; Zhao, Y.; Song, M.J.; Liang, J. Soil quality assessment of reclaimed land in the urban-rural fringe. CATENA 2023, 220, 106692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Z.; Si, B.C.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Z.M.; Lu, Z.C.; Chen, X.; Han, X.Z.; Zhu, Y.C.; Zou, W.X. Divers of soil quality and maize yield under long-term tillage and straw incorporation in Mollisols. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 246, 106360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.J.; Haider, M.F.; Ali, Z.; Akhtar, W.; Alam, S. Evaluation of soil quality through simple additive soil quality index (SQI) of Tehsil Charsadda, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2024, 23, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Si, H.T.; Li, M.Y.; Li, C.; Zhu, D.X.; Mao, Z.; Yan, Y.L.; Jiang, K.; Yu, P.J. Influence of land use types on soil properties and soil quality in karst regions of Southwest China. Agronomy 2024, 14, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temjen, W.; Singh, M.R.; Ajungla, T. Effect of shifting cultivation and fallow on soil quality index in Mokokchung district, Nagaland. India. Ecol. 2022, 11, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.K.; Wen, L.; Li, Y.Y.; Wang, X.X.; Zhu, L.; Li, X.Y. Soil quality effects of grassland degradation and restoration on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 76, 2256–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, G.S.; Ji, Y.H.; Bai, Y.F. Spatiotemporal dynamic simulation of grassland carbon storage in China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2016, 59, 1946–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.J.; Wang, H.Q.; Hu, J.; Shi, W.Y.; Xia, X.Y.; Sun, X.Z.; Tang, H.Y.; Huang, Y.X. Vegetation degradation reduces aggregate associated carbon by reducing both labile and stable carbon fraction in Northeast China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2024, 954, 176789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.D.; Song, Z.L.; Zhang, D.B.; Wu, Y.T.; Zwieten, L.V.; Sun, S.B.; Wang, W.Y.; Liu, H.Y.; Wang, Y.D.; Wang, H.L. Soil properties and anthropogenic influences control the distribution of soil organic carbon in grasslands of northern China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.K.; Zhao, G.J.; An, Z.F.; Mu, X.M.; Jiao, J.Y.; An, S.S.; Tian, P. Effect of grazing intensity on alpine meadow soil quality in the eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huangfu, J.Y.; Mao, F.X.; Lu, X.S. Analysis of grassland resources in southwest China. Acta Pratacult. Sin. 2012, 21, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.Y.; Geng, X.Q.; Zhao, X.; Shen, H.H.; Hu, H.F. How many areas of grasslands are there in China? Chin. Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 1731–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuyunga; Wulantuya; Zhang, W.Q.; Siqinchaoketu; Gaosuriguga; Bao, M.S. Analysis of the evolution of the grassland degradation evaluation index system in China based on CiteSpace. Chin. J. Grassl. 2023, 45, 125–136. [Google Scholar]
- GB 19377-2003; Parameters for Degradation, Sandification and Salification of Rangelands. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2003.
- Cao, Y.; Xiong, K.N. Soil quality assessment under different vegetation restoration strategies in the karst rocky deserted area of Southwestern China. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 3249–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedifar, M. Assessing alteration of soil quality, degradation, and resistance indices under different land sues through network and factor analysis. CATENA 2023, 222, 106807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Rosa, D.D.; Liakos, L.; Labouyrie, M.; Borrelli, P.; Callabio, B. Soil bulk sensity assessment in Europe. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 364, 108907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, W.T.; Zheng, H.; Chi, Y.; Ren, W.B.; Zhang, H.X.; Zhang, W.Y.; Yuan, F.; Liu, Y.L. Reseeding restoration significantly improves the physical and chemical properties of degraded grassland soil in China—A meta analysis. CATENA 2025, 252, 108849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.W.; Dai, L.C.; Li, Q.; Qian, D.W.; Cao, G.M.; Zhou, H.K.; Du, Y.G. Light grazing significantly reduces soil water storage in Alpine grasslands on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.Y.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Zhu, B.; Qiang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Pang, X.Y. Phosphourus addition decreases plant lignin but increases microbial necromass contribution to soil organic carbon in a subalpine forest. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 4194–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Yu, P.J.; Li, G.D.; Zhou, D.W.; Chen, X.Y. Overlooking soil erosion induces underestimation of the soil C loss in degraded land. Quat. Int. 2014, 349, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.X.; Wei, T.X.; Sha, G.L.; Zhu, Q.K.; Liu, Z.; Ren, K.; Yang, C. Soil enzyme activities of typical plant communities after vegetation restoration on the Loess Plateau, China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 170, 104292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pausch, J.; Kuzyakov, Y. Carbon input by roots into the soil: Quantification of rhizodeposition from root to ecosystem scale. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartemink, A.E.; Barrow, N.J. Soil pH—Nutrient relationships: The diagram. Plant Soil 2023, 486, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.M.; Wang, S.P.; Jiang, L.L.; Zhang, L.R.; Cui, S.J.; Meng, F.D.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y. Changes of soil microbial community under different degraded gradients of alpine meadow. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 222, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunemann, E.K.; Bongiorno, G.; Bai, Z.G.; Creamer, R.E.; Deyn, G.D.; Goede, R.; Fleskens, L.; Geissen, V.; Kuyper, T.W.; Mader, P.; et al. Soil quality—A critical review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 120, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepehya, S.; Mehta, D.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, R.; Sharma, D.; Sharma, A. Concept and assessment methodology of soil quality: A review. Int. J. Plant. Soil. Sci. 2024, 36, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.J.; Han, D.L.; Liu, S.W.; Wen, X.; Huang, Y.X.; Jia, H.T. Soil quality assessment under different land uses in an alpine grassland. CATENA 2018, 171, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobink, T.; Greiner, L.; Keller, A.; Gret-Regamey, A. Soil quality indicators—From soil functions to ecosystems services. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 94, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Huang, X.D.; Qiao, N.; Geng, Q.L.; Liu, Y.Z.; Song, H.Q.; Yang, Z.L.; Liu, C.; Wang, G. Effects of mowing and fertilization on soil quality in a semiarid grassland of North China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 32, 1656–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Soil Properties Type | Soil Properties | Standard Analytical Methods | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical properties | pH | 1:5 soil-to-water ratio | Liu et al., 2025 [2] |
| SOC (g kg−1) | Dry combustion C and N analyzer | Liu et al., 2025 [2] | |
| TN (g kg−1) | Dry combustion C and N analyzer | Liu et al., 2025 [2] | |
| TP (g kg−1) | Digestion, spectrophotometer detection | Liu et al., 2025 [2] | |
| AN (mg kg−1) | Alkaline hydrolysis diffusion method | Liu et al., 2025 [2] | |
| AP (mg kg−1) | Sodium bicarbonate extraction, colorimetric detection | Liu et al., 2025 [2] | |
| Microbial properties | LAP (nmol h−1 g−1) | Microplate fluorescence method | Cao et al., 2024 [27] |
| NAG (nmol h−1 g−1) | Microplate fluorescence method | Cao et al., 2024 [27] | |
| AG (nmol h−1 g−1) | Microplate fluorescence method | Cao et al., 2024 [27] | |
| BG (nmol h−1 g−1) | Microplate fluorescence method | Cao et al., 2024 [27] | |
| BX (nmol h−1 g−1) | Microplate fluorescence method | Cao et al., 2024 [27] | |
| CBH (nmol h−1 g−1) | Microplate fluorescence method | Cao et al., 2024 [27] | |
| ACP (nmol h−1 g−1) | Microplate fluorescence method | Cao et al., 2024 [27] | |
| Physical properties | MWD (mm) | Wet sieving and calculation | Yu et al., 2023 [9] |
| GMD (mm) | Wet sieving and calculation | Yu et al., 2023 [9] | |
| Clay (%) | Using mastersizer 2000 | Yu et al., 2023 [9] | |
| Sand (%) | Using mastersizer 2000 | Yu et al., 2023 [9] | |
| BD (g cm−3) | Cutting ring method | Liu et al., 2025 [2] | |
| SWC (%) | Oven-drying method | Yu et al., 2023 [9] |
| NDG | LDG | MDG | SDG | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 6.77 (±0.06) c | 7.07 (±0.12) b | 6.97 (±0.10) bc | 7.69 (±0.04) a | <0.001 |
| SOC (mg g−1) | 54.81 (±1.43) a | 52.86 (±2.17) a | 37.22 (±1.02) b | 25.41 (±1.15) c | <0.001 |
| TN (mg g−1) | 2.99 (±0.12) a | 2.74 (±0.08) a | 1.96 (±0.12) b | 1.88 (±0.14) b | <0.001 |
| TP (mg g−1) | 0.71 (±0.02) b | 0.80 (±0.02) a | 0.61 (±0.03) c | 0.59 (±0.03) c | <0.001 |
| AN (mg kg−1) | 137.4 (±5.29) a | 122.71 (±4.64) b | 99.12 (±5.21) c | 86.11 (±3.71) c | <0.001 |
| AP (mg kg−1) | 4.77 (±0.10) a | 4.85 (±0.11) a | 3.71 (±0.15) b | 3.2 (±0.06) c | <0.001 |
| LAP (nmol h−1 g−1) | 37.25 (±0.90) a | 35.5 (±1.18) a | 26.85 (±1.77) b | 21.26 (±0.77) c | <0.001 |
| NAG (nmol h−1 g−1) | 27.45 (±1.38) a | 25.78 (±1.28) a | 20.66 (±1.72) b | 21.45 (±1.60) b | 0.011 |
| AG (nmol h−1 g−1) | 4.26 (±0.13) a | 3.63 (±0.15) b | 4.02 (±0.20) ab | 2.24 (±0.09) c | <0.001 |
| BG (nmol h−1 g−1) | 49.03 (±2.62) a | 52.47 (±2.51) a | 36.17 (±1.22) b | 26.24 (±1.18) c | <0.001 |
| BX (nmol h−1 g−1) | 4.69 (±0.17) a | 3.81 (±0.17) b | 2.96 (±0.06) c | 1.82 (±0.10) d | <0.001 |
| CBH (nmol h−1 g−1) | 6.10 (±0.22) a | 4.69 (±0.29) b | 4.78 (±0.13) b | 2.63 (±0.14) c | <0.001 |
| ACP (nmol h−1 g−1) | 61.49 (±2.74) ab | 66.43 (±3.30) a | 60.53 (±2.25) ab | 56.1 (±2.68) b | 0.104 |
| MWD (mm) | 3.30 (±0.08) a | 2.54 (±0.17) c | 2.69 (±0.14) bc | 2.93 (±0.07) ab | 0.002 |
| GMD (mm) | 2.16 (±0.12) a | 1.3 (±0.18) b | 1.31 (±0.13) b | 1.61 (±0.09) b | <0.001 |
| Clay (%) | 4.44 (±0.21) c | 6.85 (±0.17) a | 6.78 (±0.32) a | 5.76 (±0.24) b | <0.001 |
| Sand (%) | 23.72 (±3.29) a | 4.06 (±0.54) c | 13.32 (±1.81) b | 10.79 (±1.30) b | <0.001 |
| BD (g cm−3) | 1.08 (±0.04) b | 1.14 (±0.05) b | 1.45 (±0.07) a | 1.40 (±0.05) a | <0.001 |
| SWC (%) | 69.67 (±2.60) a | 38.79 (±1.87) b | 37.21 (±2.03) b | 38.34 (±1.20) b | <0.001 |
| Soil Indicators | Minimum Data Set | Separate Minimum Data Set | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | Chemical | Microbial | Physical | ||||
| PC1 | PC2 | PC1 | PC2 | PC1 | PC2 | |||||
| pH | −0.75 | 0.17 | −0.51 | 0.07 | −0.75 | 0.58 | ||||
| SOC | 0.94 | −0.25 | −0.04 | 0.01 | 0.97 | 0.01 | ||||
| TN | 0.87 | 0.02 | −0.26 | 0.20 | 0.89 | 0.18 | ||||
| TP | 0.67 | −0.44 | −0.27 | 0.10 | 0.79 | 0.44 | ||||
| AN | 0.88 | −0.02 | −0.01 | 0.21 | 0.87 | −0.18 | ||||
| AP | 0.88 | −0.29 | −0.18 | −0.06 | 0.93 | 0.08 | ||||
| LAP | 0.93 | −0.22 | −0.01 | −0.03 | 0.94 | 0.08 | ||||
| NAG | 0.59 | −0.12 | −0.26 | −0.64 | 0.60 | 0.76 | ||||
| AG | 0.70 | −0.11 | 0.59 | 0.20 | 0.80 | −0.48 | ||||
| BG | 0.85 | −0.35 | −0.09 | 0.24 | 0.88 | −0.02 | ||||
| BX | 0.94 | −0.10 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.95 | −0.07 | ||||
| CBH | 0.89 | −0.03 | 0.36 | −0.15 | 0.93 | −0.08 | ||||
| MWD | 0.31 | 0.86 | −0.08 | 0.32 | 0.87 | 0.37 | ||||
| GMD | 0.45 | 0.80 | −0.15 | 0.29 | 0.91 | 0.22 | ||||
| Clay | −0.45 | −0.81 | 0.16 | 0.13 | −0.93 | 0.01 | ||||
| Sand | 0.43 | 0.71 | 0.31 | −0.38 | 0.81 | 0.09 | ||||
| BD | −0.77 | 0.04 | 0.48 | 0.12 | −0.47 | 0.86 | ||||
| SWC | 0.77 | 0.57 | 0.02 | −0.15 | 0.92 | −0.19 | ||||
| Eigenvalues | 10.18 | 3.44 | 1.37 | 1.02 | 4.54 | 0.60 | 4.42 | 0.82 | 4.15 | 0.96 |
| Variance (%) | 56.54 | 19.09 | 7.62 | 5.66 | 75.61 | 10.03 | 73.65 | 13.71 | 69.20 | 16.05 |
| Cumulative | 56.54 | 75.63 | 83.25 | 88.91 | 75.61 | 85.64 | 73.65 | 87.37 | 69.20 | 85.25 |
| Indicator | pH | SOC | TN | TP | AN | AP | LAP | ANG | AG | BG | BX | CBH | MWD | GMD | Clay | Sand | BD | SWC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| SOC | *** | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| TN | ** | *** | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| TP | * | *** | *** | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| AN | *** | *** | *** | ** | 1 | |||||||||||||
| AP | ** | *** | *** | *** | *** | 1 | ||||||||||||
| LAP | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | 1 | |||||||||||
| NAG | 0.05 | ** | ** | ** | * | ** | ** | 1 | ||||||||||
| AG | *** | *** | ** | * | *** | ** | *** | 0.17 | 1 | |||||||||
| BG | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | * | ** | 1 | ||||||||
| BX | *** | *** | *** | ** | *** | *** | *** | ** | *** | *** | 1 | |||||||
| CBH | *** | *** | *** | ** | *** | *** | *** | ** | *** | *** | *** | 1 | ||||||
| MWD | 0.43 | 0.35 | 0.07 | 0.35 | 0.10 | 0.45 | 0.32 | 0.43 | 0.26 | 0.38 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 1 | |||||
| GMD | 0.33 | 0.13 | * | 0.44 | * | 0.24 | 0.15 | 0.32 | 0.17 | 0.16 | * | 0.09 | *** | 1 | ||||
| Clay | 0.26 | 0.16 | * | 0.50 | * | 0.17 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 0.32 | 0.39 | 0.07 | 0.06 | *** | *** | 1 | |||
| Sand | * | 0.15 | 0.11 | 0.26 | 0.10 | 0.26 | 0.13 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.48 | 0.07 | ** | ** | ** | *** | 1 | ||
| BD | * | *** | *** | ** | *** | *** | *** | ** | 0.14 | *** | *** | ** | 0.24 | 0.07 | ** | 0.16 | 1 | |
| SWC | ** | ** | *** | 0.09 | ** | ** | ** | * | * | * | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | ** | 1 |
| Indicators | Scoring Curve | Parameters | Weight for MDS | Weight for SMDS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Slope | Variance | Equal | Variance | Equal | ||
| SOC | More is better | 42.57 | −2.5 | 0.64 | 0.25 | 0.30 | 0.17 |
| MWD | More is better | 2.86 | −2.5 | 0.22 | 0.25 | ||
| AG | More is better | 3.54 | −2.5 | 0.08 | 0.25 | ||
| NAG | More is better | 23.84 | −2.5 | 0.06 | 0.25 | 0.05 | 0.17 |
| Clay | Less is better | 5.96 | 2.5 | 0.27 | 0.17 | ||
| BD | Less is better | 1.27 | 2.5 | 0.06 | 0.17 | ||
| pH | Less is better | 7.12 | 2.5 | 0.04 | 0.17 | ||
| BX | More is better | 3.32 | −2.5 | 0.28 | 0.17 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Bai, X.; Lv, D.; Zou, S.; He, B.; Feng, T. Assessing the Influences of Grassland Degradation on Soil Quality Through Different Minimum Data Sets in Southwest China. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051091
Li W, Bai X, Lv D, Zou S, He B, Feng T. Assessing the Influences of Grassland Degradation on Soil Quality Through Different Minimum Data Sets in Southwest China. Agronomy. 2025; 15(5):1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051091
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wangjun, Xiaolong Bai, Dongpeng Lv, Shun Zou, Bin He, and Tu Feng. 2025. "Assessing the Influences of Grassland Degradation on Soil Quality Through Different Minimum Data Sets in Southwest China" Agronomy 15, no. 5: 1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051091
APA StyleLi, W., Bai, X., Lv, D., Zou, S., He, B., & Feng, T. (2025). Assessing the Influences of Grassland Degradation on Soil Quality Through Different Minimum Data Sets in Southwest China. Agronomy, 15(5), 1091. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051091






