Effect of Fertilization Timing on Nitrogen Uptake in Spring Tea of Different Sprouting Phenological Cultivars: A Field Trial with 15N Tracing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Field Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Weather Recording
2.4. Plant and Soil Sampling
2.5. Measurements of 15N, Soil Properties and Tea Quality
2.6. Calculations and Statistics
2.6.1. Calculations
2.6.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Temperature and Rainfall During the Experiment
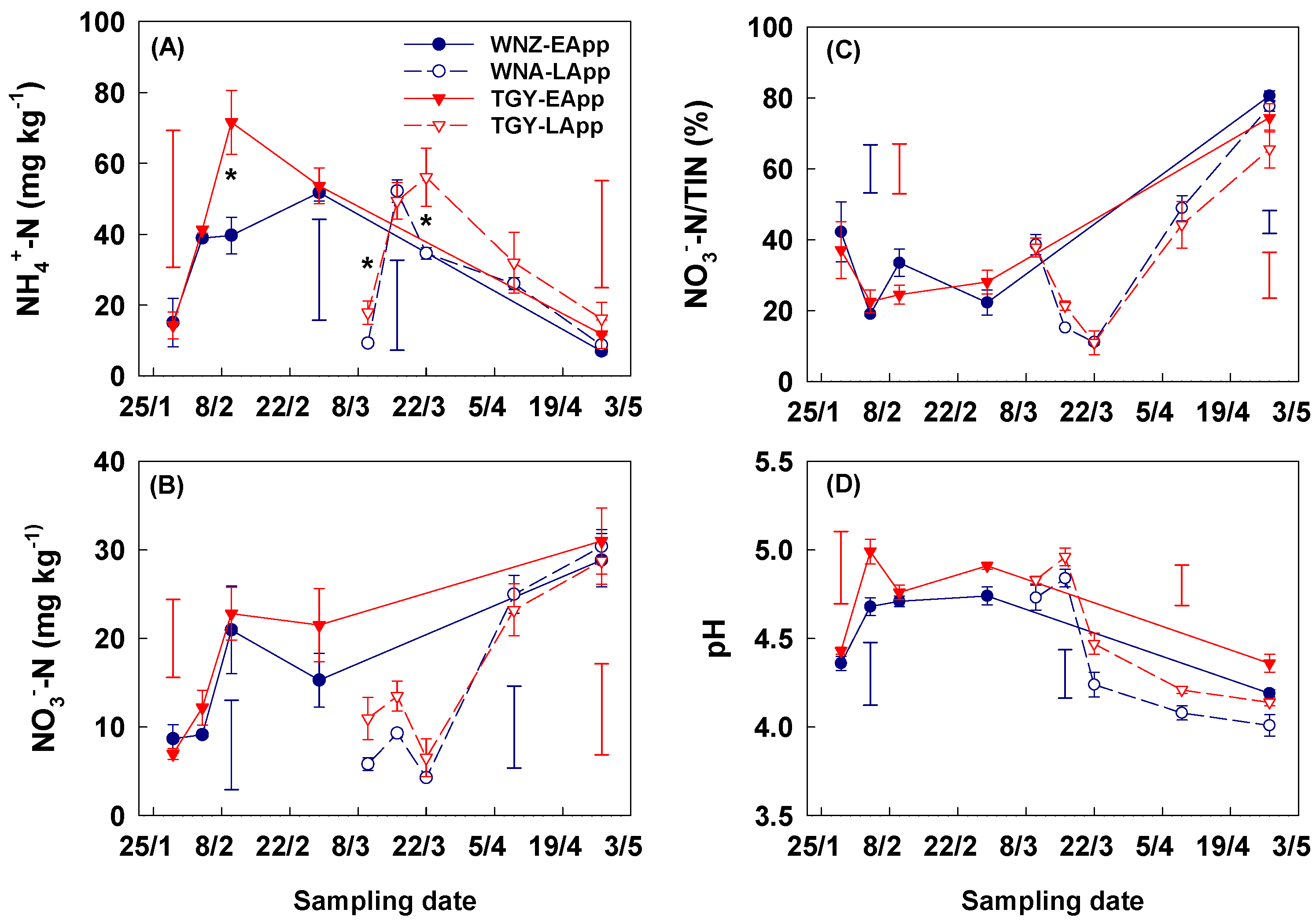
3.2. Soil Properties
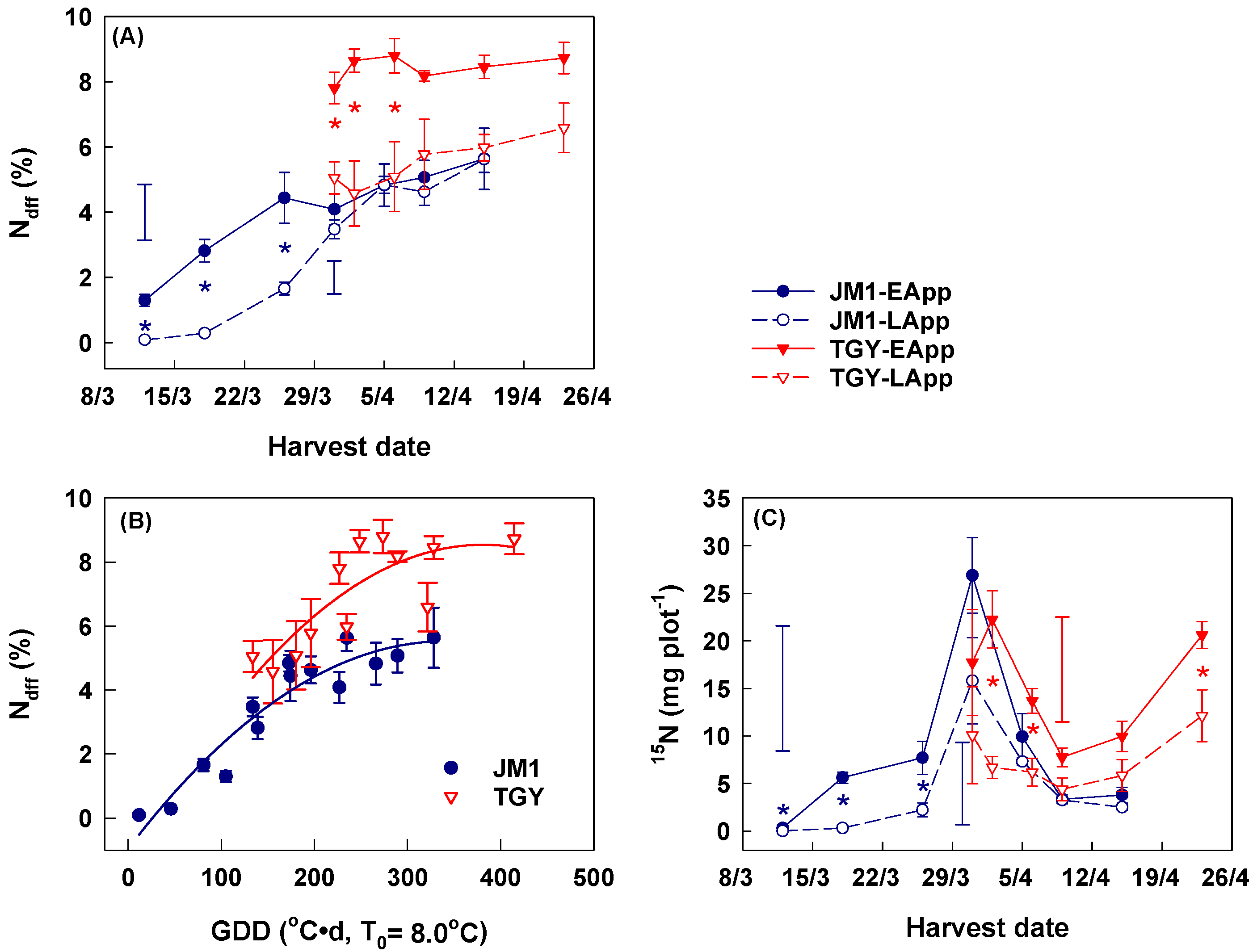
3.3. 15N in Mature Leaves
3.4. Dynamic Change in 15N in Young Spring Shoots
3.5. Ndff and 15N Content in Pruned Material
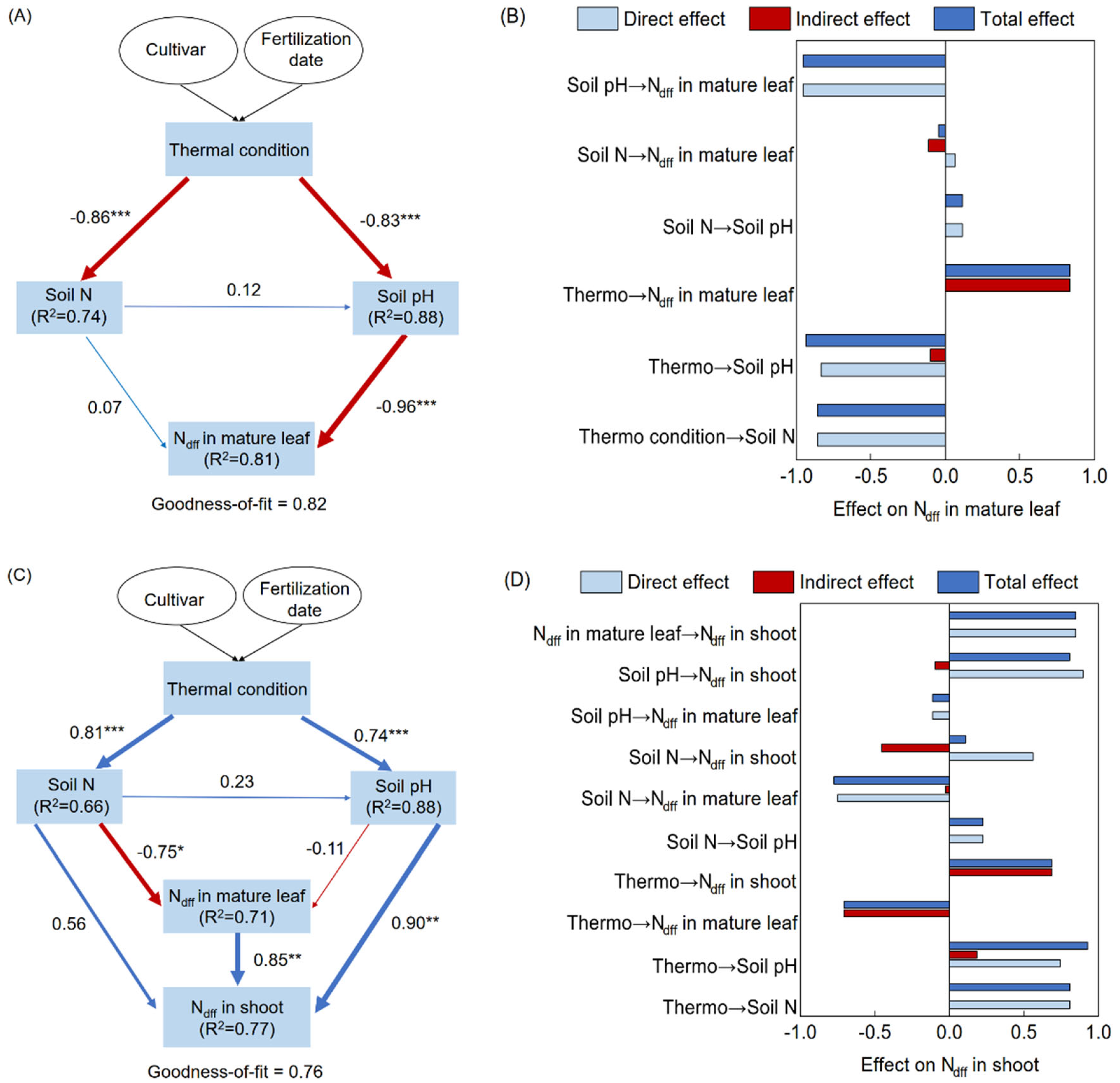
3.6. Partial Least Squares Path Modeling
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of N Topdressing Timing on N in Young Spring Shoots of Early- and Late-Sprouting Cultivars
4.2. Role of Soil N Transformation in N Uptake of Tea Trees in Response to Topdressing Timing
4.3. The Quality and Economic Value of Spring Tea in Response to Topdressing Timing
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ndff | N derived from fertilizer |
| NO3−-N | Nitrate |
| NH4+-N | Ammonium |
| TIN | Total inorganic nitrogen |
| TN | Total nitrogen |
| GDD | Growing degree days |
| JM1 | Jia-ming 1 |
| TGY | Tie-guan-yin |
| EApp | Early application |
| LApp | Late application |
References
- Tang, S.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, N.; Li, Y.; Ma, Q.; Xiao, H.; Zhou, X.; Xu, X.; Jiang, T.; He, P.; et al. Temporal variation in nutrient requirements of tea (Camellia sinensis) in China based on QUEFTS analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Fu, H.R.; Pan, W.K.; Zhou, J.J.; Xu, M.; Han, K.F.; Chen, K.J.; Ma, Q.X.; Wu, L.H. Improving tea (Camellia sinensis) quality, economic income, and environmental benefits by optimizing agronomic nitrogen efficiency: A synergistic strategy. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 142, 126673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okano, K.; Matsuo, K. Seasonal changes in uptake, distribution and redistribution of 15N-nitrogen in young tea (Camellia sinensis L.) plants. Jpn. J. Crop Sci. 1996, 65, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, F.; Zhang, E.; Khattak, W.A.; Li, J.; Ilyas, M.; Deng, X.; Ihtisham, M.; Guo, F.; Wang, P.; Wang, M.; et al. Natural variations and dynamics of macronutrients for 87 tea plant (Camellia sinensis) varieties throughout the growing seasons in Wuhan. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 306, 111425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, M.; Ma, L.; Shi, Y.; Ruan, J. Metabolomic analyses reveal distinct change of metabolites and quality of green tea during the short duration of a single spring season. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 3302–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Dong, C.; Yang, T.; Ma, J.; Zhang, S.; Wei, C.; Wan, X.; Zhang, Z. Seasonal theanine accumulation and related gene expression in the roots and leaf buds of tea plants (Camellia sinensis L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Liao, W.; Yi, X.; Niu, S.; Ma, L.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, M.; Ruan, J. Fertilization status and reduction potential in tea gardens of China. J. Plant Nutr. Fer. 2019, 25, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Chen, H.; Shan, Y.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, G.; Wu, L.; Ruan, J.; Lv, J.; Shi, Y.; Pan, L.; et al. Status and suggestions of tea garden fertilization on main green tea-producing counties in Zhejiang province. J. Tea Sci. 2013, 33, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pregitzer, K.S.; King, J.S. Effects of soil temperature on nutrient uptake. In Nutrient Acquisition by Plants: An Ecological Perspective; BassiriRad, H., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 277–310. ISBN 978-3-540-27675-3. [Google Scholar]
- Quartieri, M.; Millard, P.; Tagliavini, M. Storage and remobilisation of nitrogen by pear (Pyrus Communis L.) trees as affected by timing of N supply. Eur. J. Agron. 2002, 17, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccuzzo, G.; Scandellari, F.; Allegra, M.; Torrisi, B.; Stagno, F.; Mimmo, T.; Zanotelli, D.; Gioacchini, P.; Millard, P.; Tagliavini, M. Seasonal dynamics of root uptake and spring remobilisation of nitrogen in field grown orange trees. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 226, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Jiang, S.; Deng, M.; Lv, L.; Xu, Z.; Ruan, J. Thermo condition determines the uptake of autumn and winter applied nitrogen and subsequent utilization in spring tea (Camellia sinensis L.). Horticulturae 2021, 7, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hao, X.; Ma, C.; Cao, H.; Yue, C.; Wang, L.; Zeng, J.; Yang, Y. Identification of differential gene expression profiles between winter dormant and sprouting axillary buds in tea plant (Camellia sinensis) by suppression subtractive hybridization. Tree Genet. Genomes 2014, 10, 1149–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, F.; Liu, H.; Fu, H.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, P.; Li, W. Effect of combined nitrogen application time on the growth and quality of tea. J. Tea Commun. 2014, 41, 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Ye, X.; Zhang, X.; Huang, W.; Zhao, H. Natural variations and dynamic changes of nitrogen indices throughout growing seasons for twenty tea plant (Camellia sinensis) varieties. Plants 2020, 9, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congreves, K.A.; Otchere, O.; Ferland, D.; Farzadfar, S.; Williams, S.; Arcand, M.M. Nitrogen use efficiency definitions of today and tomorrow. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 637108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.Z.; Close, D.C.; Quin, P.R.; Swarts, N.D. Nitrogen use efficiency, allocation, and remobilization in apple trees: Uptake is optimized with pre-harvest N supply. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 657070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.G.; Isaac, M.E. Nitrogen dynamics in agroforestry systems: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 42, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Ma, J.; Xue, K.; An, Z.; Luo, W.; Sheng, Y. Effects of temperature and humidity on soil gross nitrogen transformation in a typical shrub ecosystem in Yanshan mountain and hilly region. Life 2023, 13, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Müller, C.; Cai, Z. Temperature sensitivity of gross N transformation rates in an alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, X.; Chen, Z.; Dai, S.; He, X.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, J.; Müller, C. Effects of changing temperature on gross N transformation rates in acidic subtropical forest soils. Forests 2019, 10, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Chen, S.; Meng, L.; Dan, X.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Q.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, J.; Nardi, P.; Müller, C. Maize genotypes regulate the feedbacks between maize nitrogen uptake and soil nitrogen transformations. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 188, 109251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Harindintwali, J.D.; Cui, H.; Yao, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, F.; Yang, J. Warm growing season activates microbial nutrient cycling to promote fertilizer nitrogen uptake by maize. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 290, 127936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Ni, K.; Ji, L.; Zhao, C.; Chai, H.; Yi, X.; He, W.; Ruan, J. Estimation of evapotranspiration and crop coefficient of rain-fed tea plants under a subtropical climate. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhu, Y.; Geng, S.; Ruan, J. Response of nutritional status and tea quality to the rate and substitution of chemical fertilizers with organic manure. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Shi, Y.; Ruan, J. Nitrogen absorption by field-grown tea plants (Camellia sinensis) in winter dormancy and utilization in spring shoots. Plant Soil 2019, 442, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowogrodzki, A. How climate change might affect tea. Nature 2019, 566, S10–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, D.; Xu, R. Effects of urea and (NH4)2SO4 on nitrification and acidification of ultisols from southern China. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ni, K.; Shi, Y.; Yi, X.; Ji, L.; Ma, L.; Ruan, J. Heavy nitrogen application increases soil nitrification through ammonia-oxidizing bacteria rather than archaea in acidic tea (Camellia sinensis L.) plantation soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuypers, M.M.M.; Marchant, H.K.; Kartal, B. The Microbial nitrogen-cycling network. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Gao, Y.; Nicol, G.W.; Campbell, C.D.; Prosser, J.I.; Zhang, L.; Han, W.; Singh, B.K. Links between ammonia oxidizer community structure, abundance, and nitrification potential in acidic soils. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2011, 77, 4618–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Yu, M.; Chen, H.; Zhao, H.; Huang, Y.; Su, W.; Xia, F.; Chang, S.X.; Brookes, P.C.; Dahlgren, R.A.; et al. Elevated temperature shifts soil N cycling from microbial immobilization to enhanced mineralization, nitrification and denitrification across global terrestrial ecosystems. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 5267–5276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Min, H.; Li, Z.; Dell, B.; Chen, L. Differential responses of soil nitrogen forms to climate warming in Castanopsis hystrix and Quercus aliena forests of China. Forests 2024, 15, 1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, L.; Wei, K.; Wang, L.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, F.; Wu, L.; Bai, P.; Zhang, C. Characteristics of NH4+ and NO3− fluxes in tea (Camellia sinensis) roots measured by scanning ion-selective electrode technique. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, L.; Shi, Y.; Ruan, J. Preferential assimilation of NH4+ over NO3− in tea plant associated with genes involved in nitrogen transportation, utilization and catechins biosynthesis. Plant Sci. 2020, 291, 110369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; He, H. Soil acidification associated with changes in inorganic forms of N reduces the yield of tea (Camellia sinensis). Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2023, 69, 1660–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Ma, J.; Apostolides, Z.; Chen, L. Metabolomics for a millenniums-old crop: Tea plant (Camellia sinensis). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 6445–6457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Zhong, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Fu, H.; Yang, B.; Zhang, L. Metabolomics in quality formation and characterisation of tea products: A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 4001–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Yao, J.; Ma, C.; Pu, L.; Peng, Y.; Lei, Z. Positive effects of nitrogen fertilization on the flavor ingredients of tea (Wuniuzao), soil physicochemical properties, and microbial communities. Environ. Technol. Innovation. 2025, 37, 103911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Qiu, Q.; Fan, D.; Wang, X.; Zheng, X. Influence of different nitrogen sources on carbon and nitrogen metabolism and gene expression in tea plants (Camellia sinensis L.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 167, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, N.; Hu, Z.; Luo, W.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Zhuang, J. Nitrogen forms and nitrogen deficiency regulate theanine accumulation patterns in tea plants (Camellia sinensis) during winter dormancy. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cao, Q.; Granato, D.; Xu, Y.; Ho, C. Association between chemistry and taste of tea: A review. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2020, 101, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Cultivar | Treatment | FAA (%) | TP (%) | TP/FAA | Density (Shoots Plot−1) | Yield (g Plot−1) | N Content (mg Plot−1) | Ndff (%) | 15N Content (mg Plot−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JM1 | EApp | 4.92 ± 0.09 a | 17.35 ± 0.36 c | 3.53 ± 0.13 b | 1461 ± 75 a | 25.17 ± 1.47 a | 1429 ± 114 a | 4.11 ± 0.46 bc | 57.55 ± 4.15 ab |
| LApp | 5.10 ± 0.09 a | 19.03 ± 0.57 b | 3.73 ± 0.10 b | 992 ± 189 ab | 16.73 ± 3.03 b | 948 ± 186 b | 3.37 ± 0.23 c | 31.38 ± 5.65 b | |
| TGY | EApp | 3.49 ± 0.19 b | 25.93 ± 0.60 a | 7.50 ± 0.47 a | 933 ± 89 b | 20.57 ± 2.26 ab | 1077 ± 110 ab | 8.50 ± 0.26 a | 91.97 ± 10.99 a |
| LApp | 3.45 ± 0.09 b | 25.88 ± 0.13 a | 7.52 ± 0.21 a | 674 ± 26 b | 16.08 ± 1.77 b | 856 ± 94 b | 5.50 ± 0.73 b | 45.24 ± 3.49 ab | |
| p-Value | Cultivar | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.003 | 0.258 | 0.115 | <0.001 | 0.004 |
| Time | 0.580 | 0.097 | 0.700 | 0.007 | 0.013 | 0.020 | 0.002 | <0.001 | |
| Cultivar × Time | 0.388 | 0.081 | 0.738 | 0.366 | 0.389 | 0.340 | 0.032 | 0.153 |
| Cultivar | Treatment | Mass (g Plot−1) | N Content (g Plot−1) | Ndff (%) | 15N Content (mg Plot−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JM1 | EApp | 93.9 ± 20.5 b | 2.23 ± 0.47 ab | 2.78 ± 0.07 a | 61.6 ± 12.3 ab |
| LApp | 65.9 ± 12.4 b | 1.63 ± 0.31 b | 2.77 ± 0.21 a | 43.6 ± 6.9 b | |
| TGY | EApp | 167.0 ± 22.6 a | 3.23 ± 0.54 a | 2.91 ± 0.21 a | 96.2 ± 21.3 a |
| LApp | 111.0 ± 12.5 b | 2.21 ± 2.69 ab | 1.93 ± 0.26 b | 40.7 ± 3.4 b | |
| p-Value | Cultivar | 0.006 | 0.079 | 0.242 | 0.100 |
| Time | 0.035 | 0.072 | 0.015 | 0.029 | |
| Cultivar × Time | 0.446 | 0.062 | 0.172 | 0.034 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Ni, K.; Yang, X.; Long, L.; Ma, L.; Su, Y.; Ruan, J. Effect of Fertilization Timing on Nitrogen Uptake in Spring Tea of Different Sprouting Phenological Cultivars: A Field Trial with 15N Tracing. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1090. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051090
Zhang Y, Ni K, Yang X, Long L, Ma L, Su Y, Ruan J. Effect of Fertilization Timing on Nitrogen Uptake in Spring Tea of Different Sprouting Phenological Cultivars: A Field Trial with 15N Tracing. Agronomy. 2025; 15(5):1090. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051090
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yongli, Kang Ni, Xiangde Yang, Lizhi Long, Lifeng Ma, Youjian Su, and Jianyun Ruan. 2025. "Effect of Fertilization Timing on Nitrogen Uptake in Spring Tea of Different Sprouting Phenological Cultivars: A Field Trial with 15N Tracing" Agronomy 15, no. 5: 1090. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051090
APA StyleZhang, Y., Ni, K., Yang, X., Long, L., Ma, L., Su, Y., & Ruan, J. (2025). Effect of Fertilization Timing on Nitrogen Uptake in Spring Tea of Different Sprouting Phenological Cultivars: A Field Trial with 15N Tracing. Agronomy, 15(5), 1090. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051090








