Effect of Film-Mulching on Soil Evaporation and Plant Transpiration in a Soybean Field in Arid Northwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site Description
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Observations and Data Collection
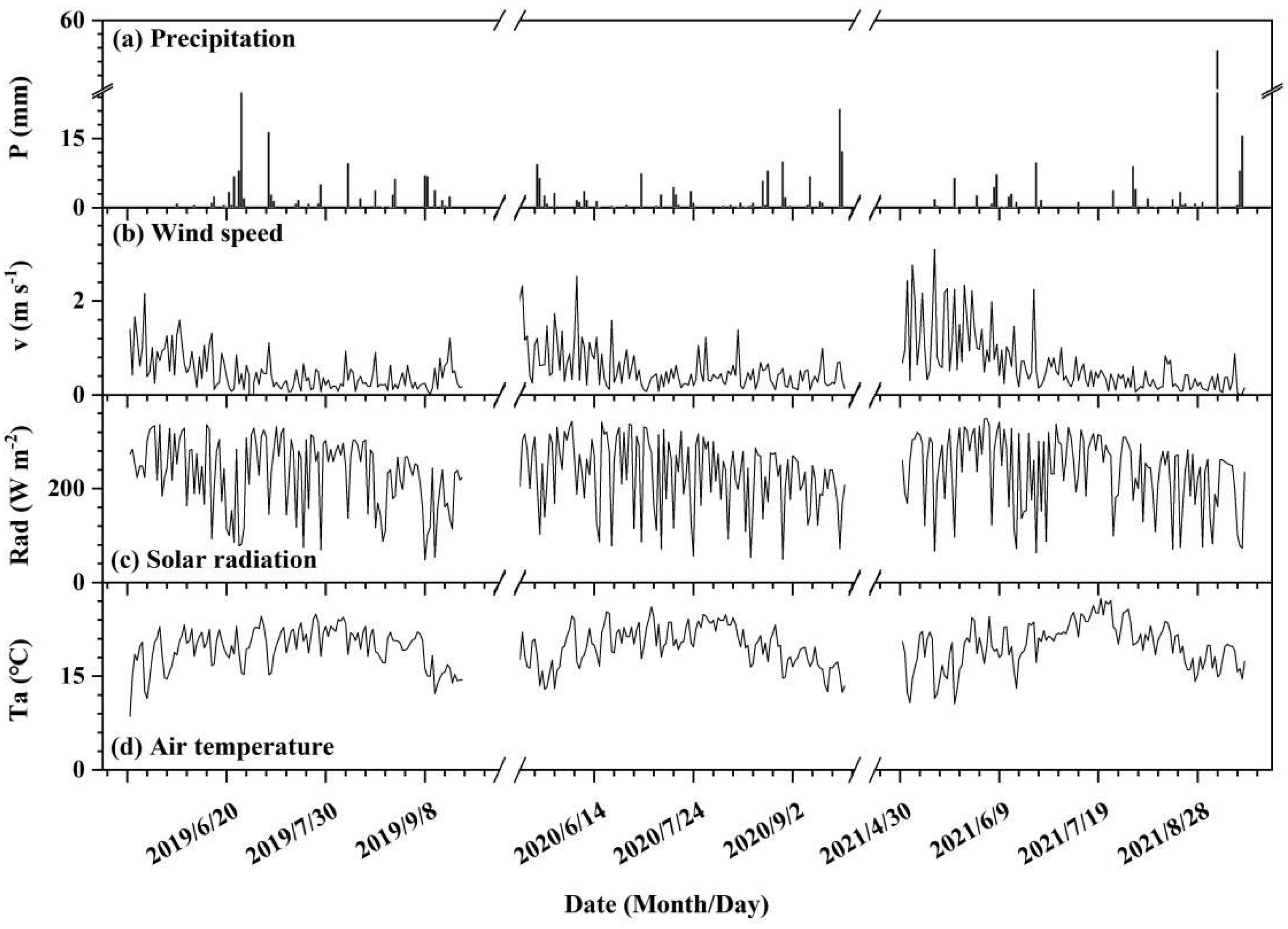
2.3.1. Meteorological Data
2.3.2. Water and Heat Fluxes
2.3.3. Soil Evaporation
2.3.4. Physiological Indicators
2.4. MSW Model Description
2.5. Model Evaluation Indicators
3. Results
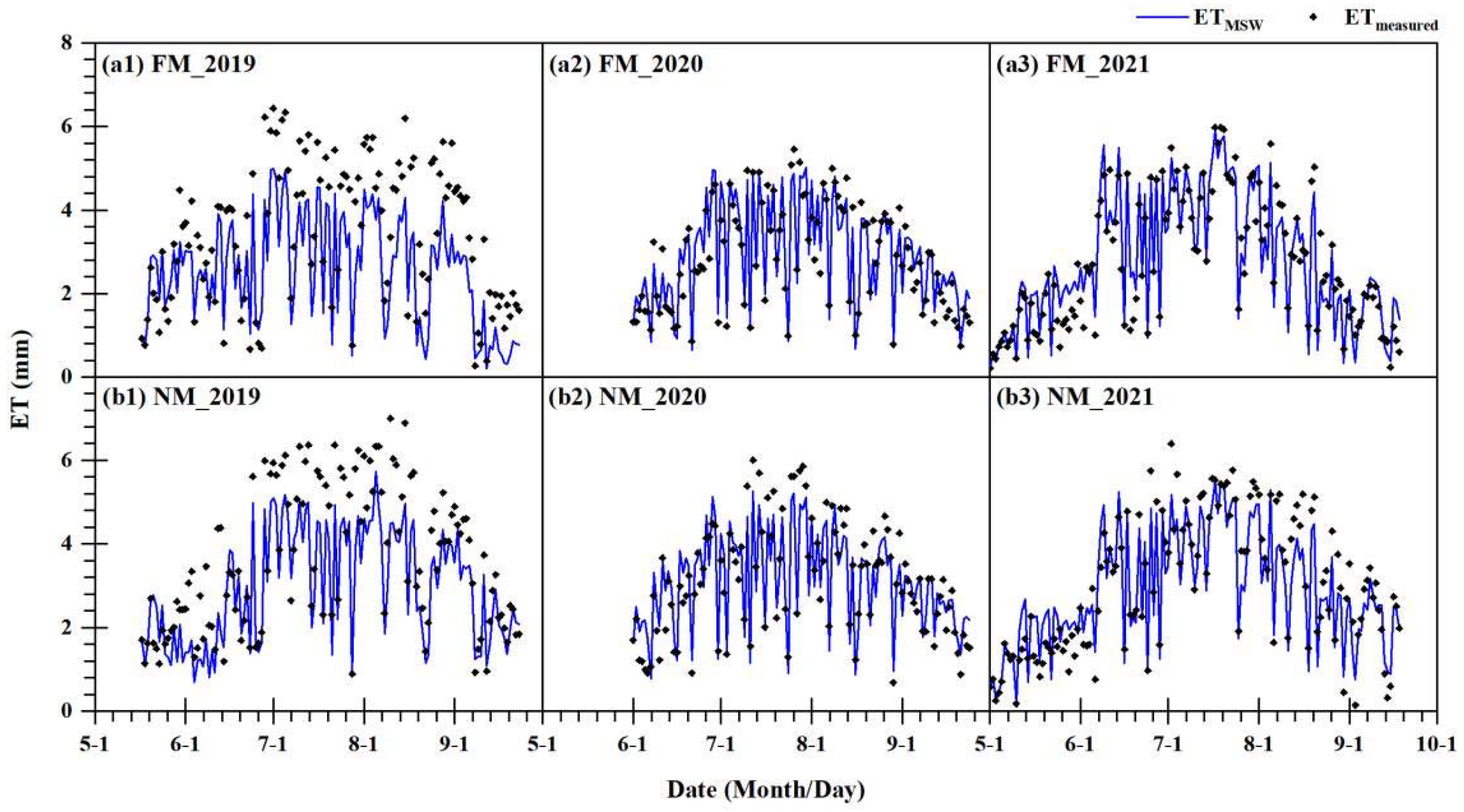
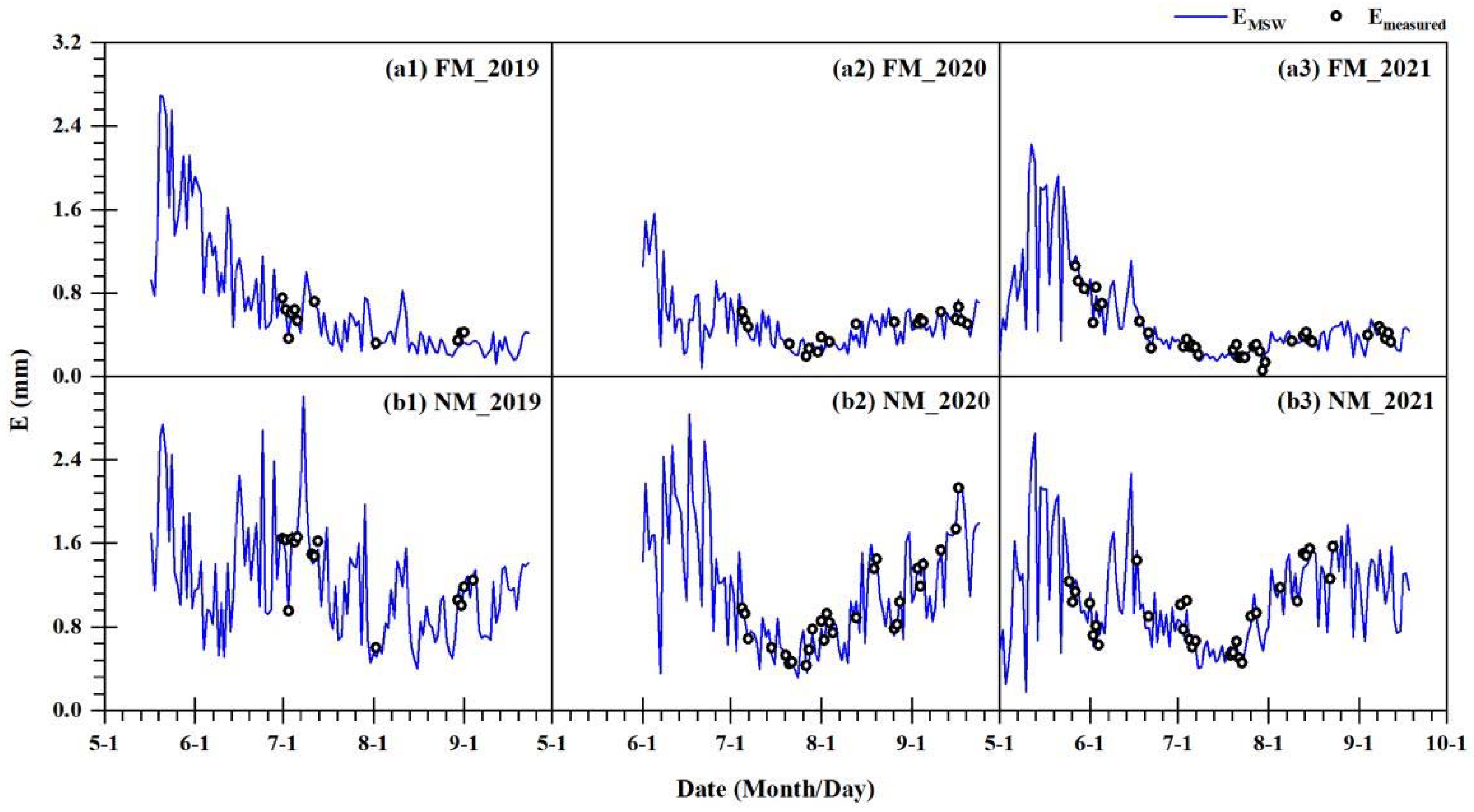
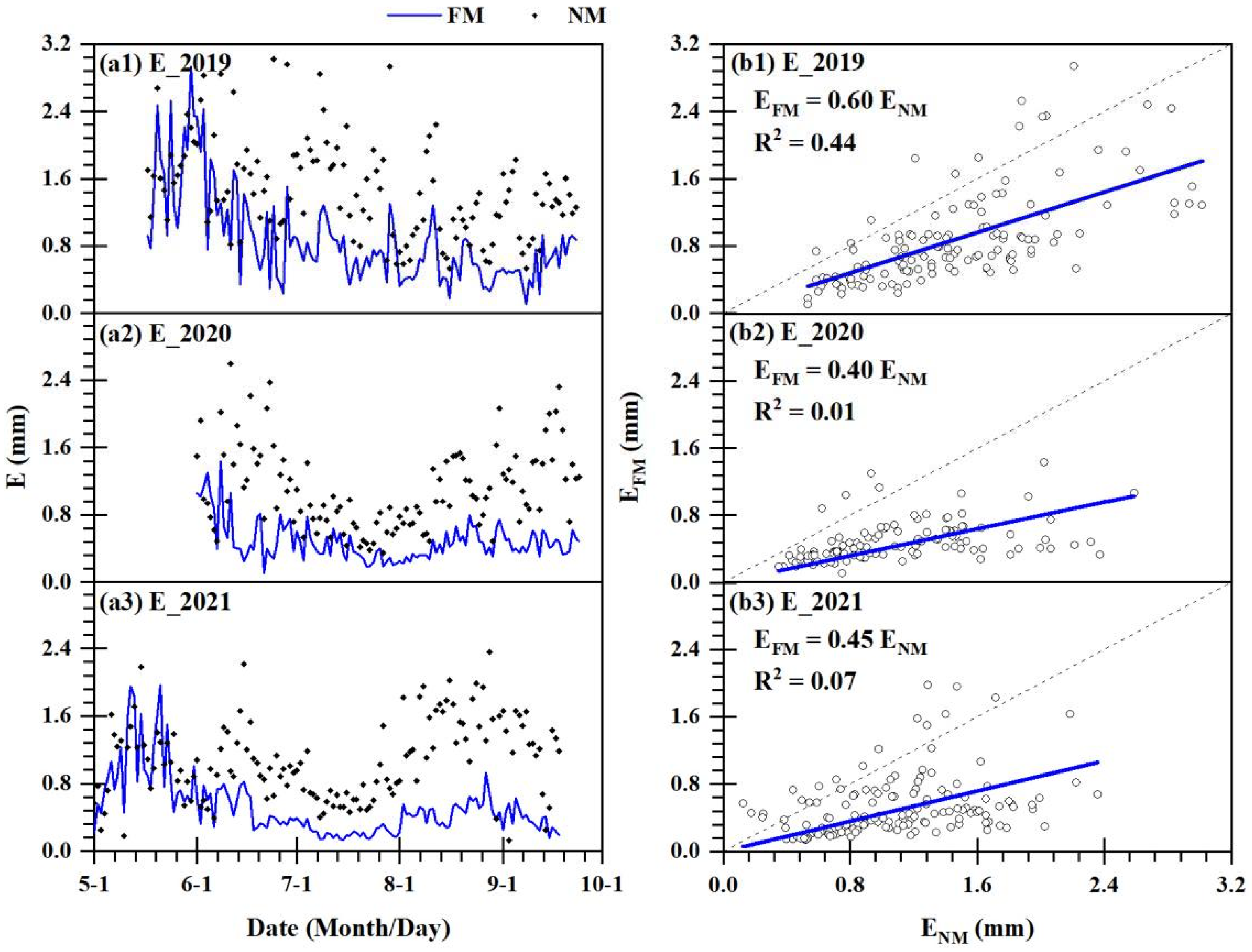
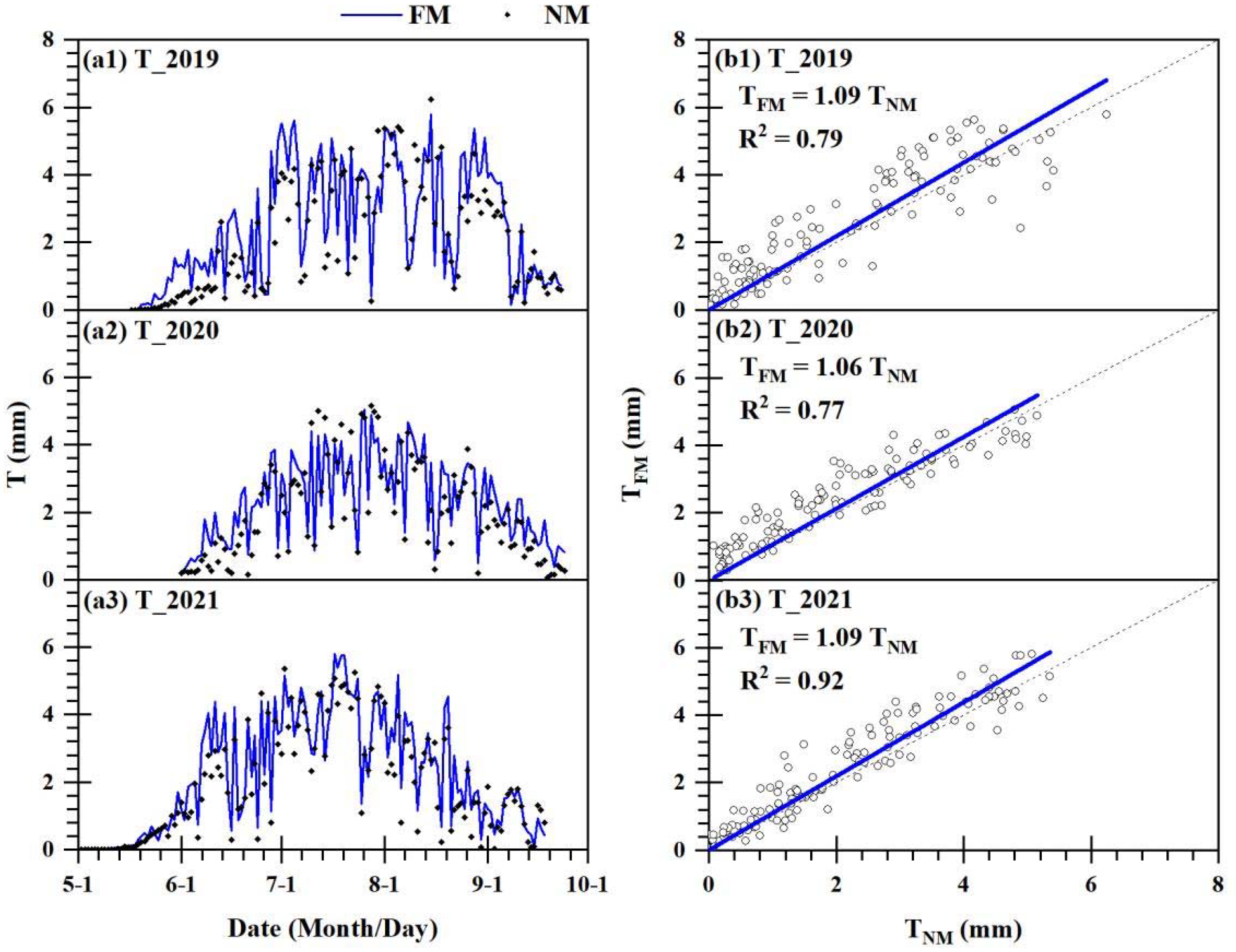
3.1. Simulation Effect of the MSW Model
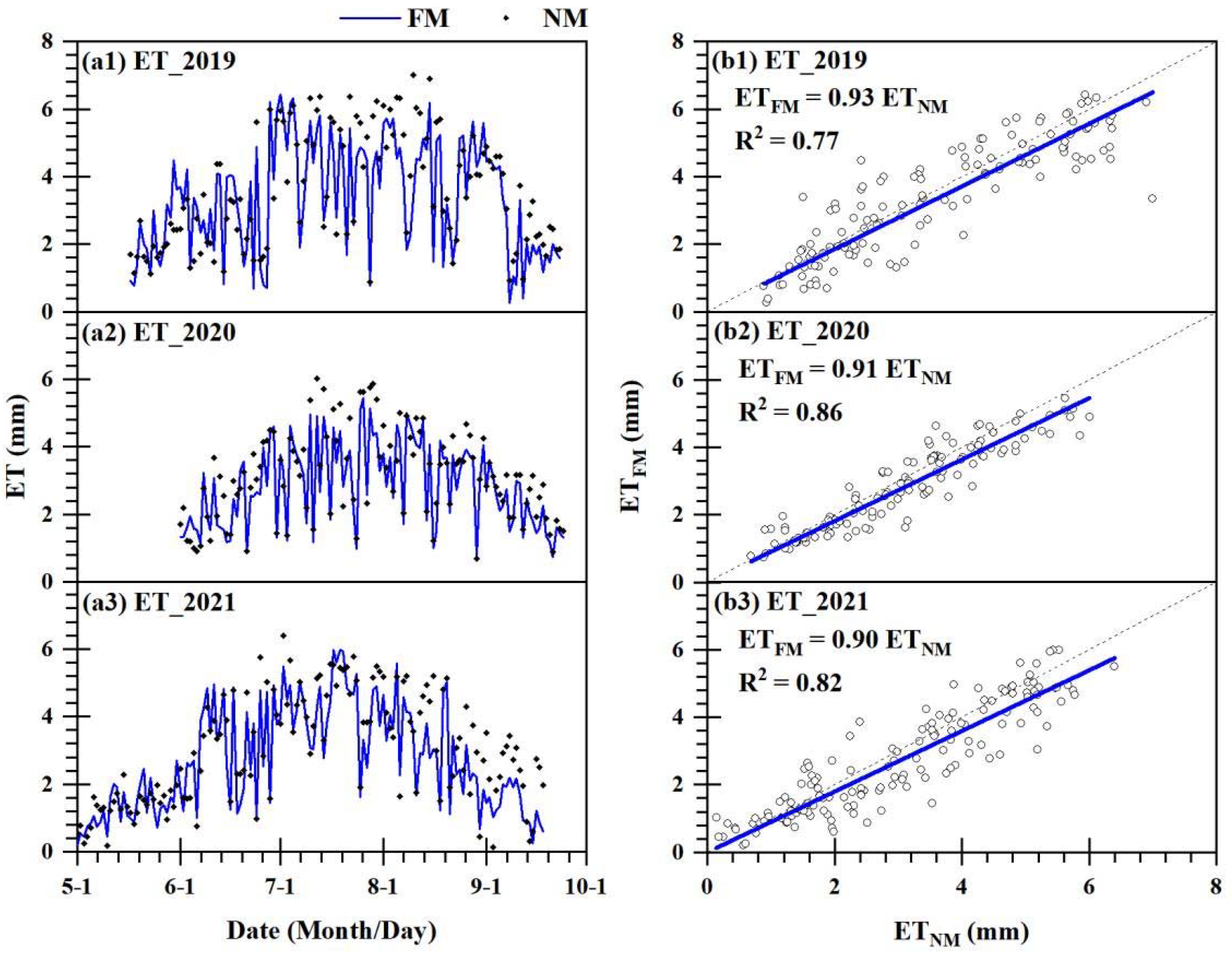
3.2. Comparison of ET, E, and T Under Different Irrigation Conditions
3.3. Comparison of Yield and WUE Under Different Irrigation Conditions
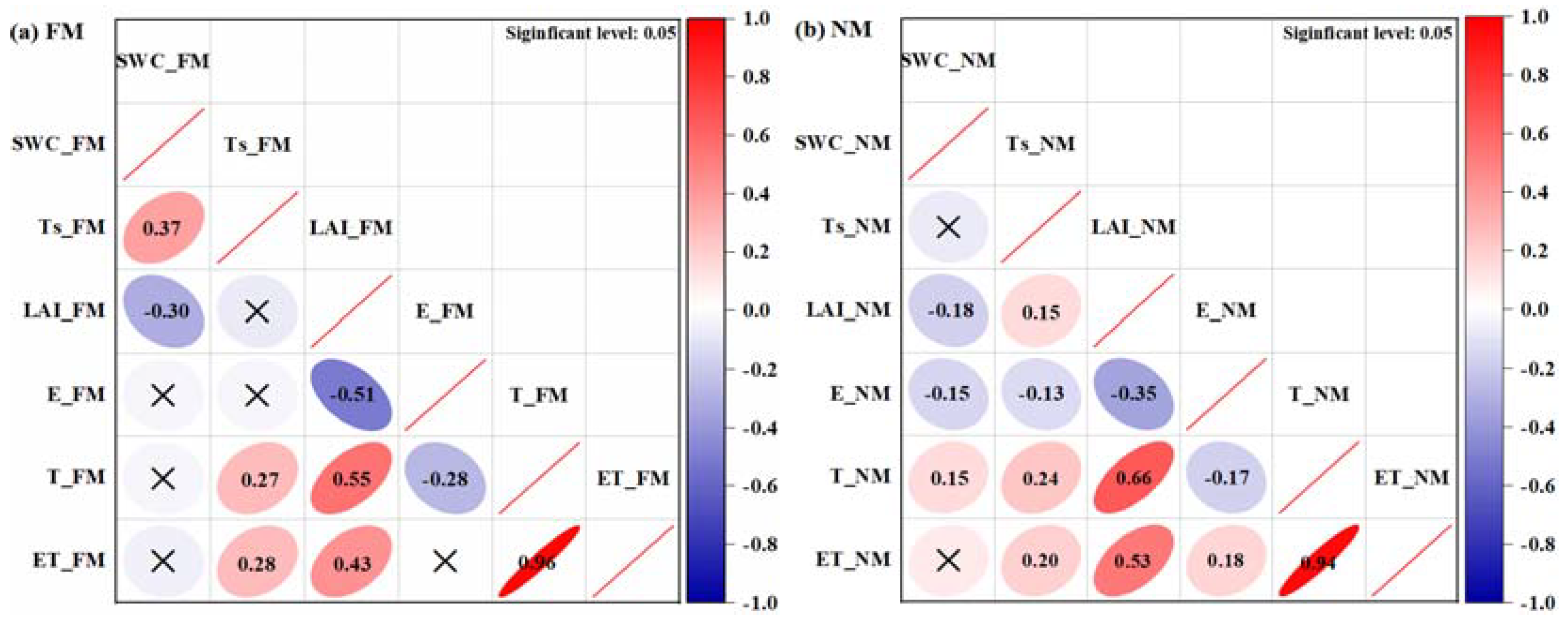
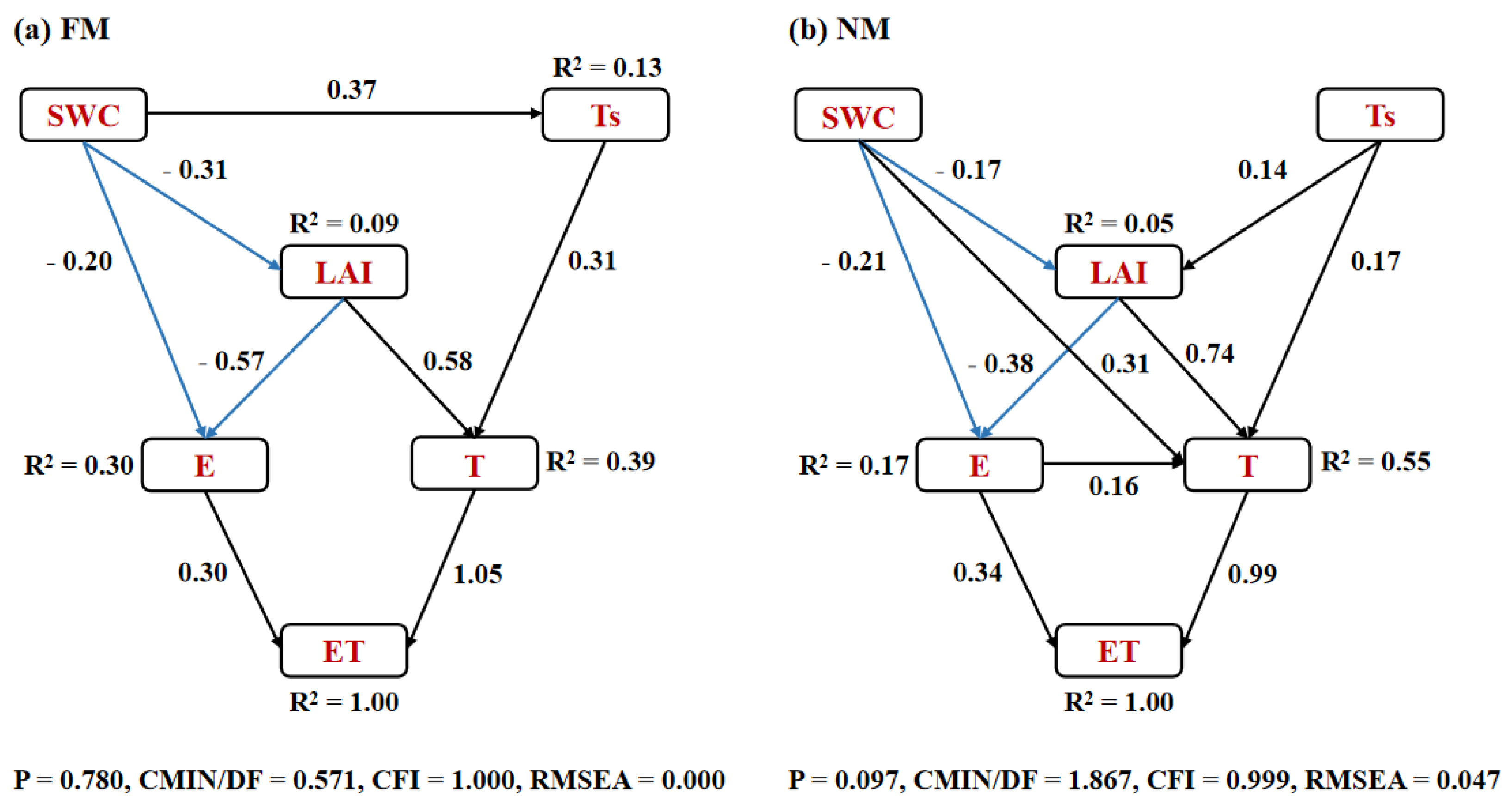
3.4. Effect from Soil Temperature/Humidity and Crop Growth on Field Evapotranspiration
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ding, Y.; Chen, D.; Qin, D.; Zhai, P. Understanding human influence on climate change in China. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2022, 9, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.Z.; Hao, X.M.; Du, T.S.; Tong, L.; Su, X.L.; Lu, H.N.; Li, X.L.; Huo, Z.L.; Li, S.E.; Ding, R.S. Improving agricultural water productivity to ensure food security in China under changing environment: From research to practice. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 179, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, J.; Wang, J.D.; Gong, S.H.; Xu, D.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Qin, Q.M. Assessment of maize yield-increasing potential and optimum N level under mulched drip irrigation in the Northeast of China. Field Crops Res. 2018, 215, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Oki, T. Water pricing reform for sustainable water resources management in China's agricultural sector. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 275, 108045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.T.; Du, G.F.; Tian, J.S.; Jiang, C.D.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang, W.F. Mulched drip ir-rigation increases cotton yield and water use efficiency via improving fine root plasticity. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 255, 106992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, H.; Zhang, W.; Siddique, K.H.M. Response of plastic film mulched maize to soil and atmospheric water stresses in an arid irrigation area. Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 154, 127080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q.; Shi, H.B.; Li, R.P.; Miao, Q.F.; Feng, Y.Y.; Wang, N.; Li, J.W. Evaporation of maize crop under mulch film and soil covered drip irrigation: Field assessment and modelling on West Liaohe Plain, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 253, 106894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Ji, Q.Y.; Zhang, F.C.; Li, Y.; Fan, J.L.; Hou, X.H.; Yan, F.L.; Liu, X.Q.; Gong, K.Y. Effects of various soil water potential thresholds for drip irrigation on soil salinity, seed cotton yield and water productivity of cotton in northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 279, 108172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, J.D.; Gong, S.H.; Xe, D.; Sui, J.; Wu, Z.D.; Mo, Y. Effects of film mulching on evapotranspiration, yield and water use efficiency of a maize field with drip irrigation in Northeastern China. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 205, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Liu, W.; Zhou, S.; Liu, C. Influence of plastic film mulch on maize water use efficiency in the Loess Plateau of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 224, 105710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.D.; Xia, Z.Q.; Fu, Y.F.; Wang, Q.; Xue, J.Q.; Chu, J. Response of soil temperature, moisture, and spring maize (Zea mays L.) root/shoot growth to different mulching materials in semi-arid areas of northwest China. Agronomy 2020, 10, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, R.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhang, J.Z.; Li, W.H. The response of photosynthetic capacity and yield of cotton to various mulching practices under drip irrigation in Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 249, 106814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, A.H.; Al-Ghobari, H.M.; Zin El-Abedin, T.K.; Alrasasimah, M.S.; El-Shafei, A.A. Impact of partial root drying and soil mulching on squash yield and water use efficiency in arid. Agronomy 2021, 11, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.H.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, K.P.; Qin, R.Z.; Zhang, W.J.; Sun, G.J.; Huang, J. Effects of soil mulching on staple crop yield and greenhouse gas emissions in China: A meta-analysis. Field Crops Res. 2022, 284, 108566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durgam, M.; Mailapalli, D.R.; Singh, R. Prediction of soil temperature in wheat field using machine learning models. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2024, 22, 3510–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, W. Irrigation-induced crop growth enhances irrigation cooling effect over the North China Plain by increasing transpiration. Water Resour. Res. 2023, 59, e2022WR034142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Othman, A.A.; Mattar, M.A.; Alsamhan, M.A. Effect of mulching and subsurface drip irrigation on soil water status under arid environment. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2020, 18, e1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, G.Y.; Mo, Y.; Zhang, D.; Xu, X.H.; Wilkerson, C.J.; Hoogenboom, G. Evaluation of subsurface, mulched and non-mulched surface drip irrigation for maize production and economic benefits in northeast China. Irrig. Sci. 2020, 39, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.D.; Yang, L.C.; Xue, X.K.; Kamran, M.; Ahmad, I.; Dong, Z.Y.; Liu, T.N.; Jia, Z.K.; Zhang, P.; Han, Q.F. Plastic film mulching stimulates soil wet-dry alternation and stomatal behavior to improve maize yield and resource use efficiency in a semi-arid region. Field Crops Res. 2019, 233, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhao, P.; Kang, S.Z.; Li, S.; Tong, L.; Ding, R.S.; Lu, H.N. Surface soil water content dominates the difference between ecosystem and canopy water use efficiency in a sparse vineyard. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 226, 105817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, E.F.; Santos, D.L.; de Lima, L.W.F.; Castricini, A.; Barros, D.L.; Filgueiras, R.; Da Cunha, F.F. Water regimes on soil covered with plastic film mulch and relationships with soil water availability, yield, and water use efficiency of papaya trees. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 269, 107709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knipper, K.; Anderson, M.; Bambach, N.; Kustas, W.; Gao, F.; Zahn, E.; Hain, C.; Mcelrone, A.; Belfiore, O.R.; Castro, S.; et al. Evaluation of partitioned evaporation and transpiration estimates within the DisALEXI modeling framework over irrigated crops in California. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.E.; Kang, S.Z.; Zhang, L.; Ortega-Farias, S.; Li, F.S.; Du, T.S.; Tong, L.; Wang, S.F.; Ingman, M.; Guo, W.H. Measuring and modeling maize evapotranspiration under plastic film-mulching condition. J. Hydrol. 2013, 503, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, I.S. The ratio of heat losses by conduction and by evaporation from any water surface. Phys. Rev. 1926, 27, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, P.J.; Castellvi, F.; Ibañez, M.; Rosell, J.I. Assessment of reliability of Bowen ratio method for partitioning fluxes. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1999, 97, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Kang, S.; Li, F.; Zhang, L. Comparison of three evapotranspiration models to Bowen ratio-energy balance method for a vineyard in an arid desert region of northwest China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2008, 10, 1629–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuttleworth, W.J.; Wallace, J.S. Evaporation from sparse crops: An energy combination theory. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1985, 111, 839–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buakum, B.; Limpinuntana, V.; Vorasoot, N.; Pannangpetch, K.; Bell, R.W. Rooting patterns of four crop legumes in response to seed-placement depths in the dry season. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B-Soil Plant Sci. 2012, 62, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Mao, X.M.; Shukla, M.K. A modified SWAP model for soil water and heat dynamics and seed-maize growth under film mulching. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 292, 108127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Wang, F.; Han, J.; Kang, S.; Feng, S. Duration of plastic mulch for potato growth under drip irrigation in an arid region of Northwest China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2010, 150, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Mao, X.; Li, S.; Huang, X.; Che, J.; Ma, C. A review of plastic film mulching on water, heat, nitrogen balance, and crop growth in farmland in china. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arredondo, T.; Delgado-Balbuena, J.; Kimball, B.; Luna-Luna, M.; Yepez-Gonzalez, E.; Hu-ber-Sannwald, E.; Garcia-Moya, E.; Garatuza-Payan, J. Late sowing date as an adaptive strategy for rainfed bean production under warming and reduced precipitation in the Mexican Altiplano? Field Crops Res. 2020, 255, 107903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, M.; Skalicky, M.; Garai, S.; Hossain, A.; Sarkar, S.; Banerjee, H.; Kundu, R.; Brestic, M.; Barutcular, C.; Erman, M.; et al. Supplementing nitrogen in combina-tion with rhizobium inoculation and soil mulch in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) production system: Part II. Effect on phenology, growth, yield attributes, pod quality, profitability and nitrogen use efficiency. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, A.J.B.; Cristofani-Yaly, M.; Da Conceicao, P.M.; Devite, F.T.; Bastianel, M.; Romero, P.V.S.; Padilha, P.H.B.; de Azevedo, F.A. Physiological and productivity responses of Tahiti acid lime grafted onto dwarfing rootstocks under different planting and mulching practices. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2025, 9, 1489291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nendel, C.; Reckling, M.; Debaeke, P.; Schulz, S.; Berg-Mohnicke, M.; Constantin, J.; Fronzek, S.; Hoffmann, M.; Jaksic, S.; Kersebaum, K.; et al. Future area expansion outweighs increasing drought risk for soybean in Europe. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2023, 29, 1340–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, C.; Liang, M.; Chen, P.; Anwar, S.; Fan, M.Y.; Xie, G.M.; Wang, C.Y. Exploring the influence of planting densities and mulching types on photosynthetic activity, antioxidant enzymes, and chlorophyll content and their relationship to yield of maize. Plants 2024, 13, 3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, C.; Park, J.; Mansoor, S.; Chung, Y.S.; Kim, K. Drought Stress Restoration Frequencies of Phenotypic Indicators in Early Vegetative Stages of Soybean (Glycine max L.). Sustainability 2023, 15, 4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Irrigation Method | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FM | NM | FM | NM | FM | NM | |
| Planting date (Month/Day) | 05/12 | 05/06 | 05/01 | |||
| Harvesting date (Month/Day) | 09/20 | 09/23 | 09/23 | 09/17 | 09/13 | 09/16 |
| Year | Irrigation Date (Month/Day) | Single Irrigation Volume (mm) | Total Irrigation Amount (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 06/10, 06/25, 07/15, 07/29, 08/11, 08/24, 09/03 | 45 (26) | 296 |
| 2020 | 06/24, 07/09, 07/23, 08/06, 08/22, 09/06 | 35 (21) | 196 |
| 2021 | 06/14, 06/30, 07/16, 07/31, 08/18 | 35 | 175 |
| Meteorological Indicator | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | Mean Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total precipitation during the growing period (mm) | 128.8 | 131.8 | 149.0 | 136.5 |
| Wind speed (m s−1) | 0.40 | 0.61 | 0.64 | 0.55 |
| Solar radiation (W m−2) | 231.95 | 231.45 | 238.69 | 234.03 |
| Air temperature (°C) | 19.5 | 19.5 | 20.0 | 19.7 |
| Observation Indices | Probe Model | Manufacturer | Installation Location | Observed Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air temperature and humidity | HMP155 | Vaisala, Vantaa, Finland | 0.5 m and 1 m above the canopy | 10 min |
| Soil temperature | 109L | Campbell Scientific, Inc., Logan, UT, USA | 20 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm, 80 cm, and 100 cm below the surface | 10 min |
| Soil water content | CS616 | 10 min | ||
| Soil flux | HFP01 | Hukseflux, Almere, The Netherlands | 5 cm below the surface | 10 min |
| Radiation | CNR4 | Kipp & Zonen, Almere, The Netherlands | 1.5 m above the canopy | 10 min |
| Year | Irrigation Method | N | Fitted Equation | R2 | MAE (mm d−1) | RMSE (mm d−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | FM | 130 | ETMSW = 0.75·ETmeasured | 0.83 | 0.95 | 1.10 |
| NM | 130 | ETMSW = 0.81·ETmeasured | 0.85 | 0.74 | 0.91 | |
| 2020 | FM | 116 | ETMSW = 1.02·ETmeasured | 0.86 | 0.36 | 0.45 |
| NM | 116 | ETMSW = 0.97·ETmeasured | 0.80 | 0.43 | 0.51 | |
| 2021 | FM | 141 | ETMSW = 1.00·ETmeasured | 0.88 | 0.40 | 0.52 |
| NM | 141 | ETMSW = 0.93·ETmeasured | 0.86 | 0.44 | 0.57 | |
| 2019–2021 | FM | 387 | ETMSW = 0.90·ETmeasured | 0.76 | 0.57 | 0.75 |
| NM | 387 | ETMSW = 0.89·ETmeasured | 0.81 | 0.54 | 0.69 |
| Year | Irrigation Method | N | Fitted Equation | R2 | MAE (mm d−1) | RMSE (mm d−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | FM | 11 | EMSW = 0.92·Emeasured | 0.91 | 0.05 | 0.06 |
| NM | 14 | EMSW = 0.99·Emeasured | 0.96 | 0.06 | 0.07 | |
| 2020 | FM | 19 | EMSW = 0.95·Emeasured | 0.88 | 0.05 | 0.06 |
| NM | 27 | EMSW = 1.01·Emeasured | 0.98 | 0.06 | 0.07 | |
| 2021 | FM | 37 | EMSW = 0.98·Emeasured | 0.95 | 0.05 | 0.06 |
| NM | 29 | EMSW = 0.98·Emeasured | 0.94 | 0.08 | 0.09 | |
| 2019–2021 | FM | 67 | EMSW = 0.96·Emeasured | 0.93 | 0.05 | 0.06 |
| NM | 70 | EMSW = 0.99·Emeasured | 0.97 | 0.07 | 0.08 |
| Year | Irrigation Method | ET (mm) | E (mm) | T (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | FM | 439.6 | 113.5 | 326.1 |
| NM | 465.9 | 190.4 | 275.5 | |
| 2020 | FM | 330.7 | 55.9 | 274.8 |
| NM | 361.1 | 128.2 | 232.9 | |
| 2021 | FM | 382.7 | 73.3 | 309.4 |
| NM | 423.9 | 152.6 | 271.3 | |
| Mean value | FM | 384.3 | 80.9 | 303.4 |
| NM | 416.9 | 157.0 | 259.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, D.; Wang, C.; Guo, Z.; Li, S.; Sun, Y.; Hou, X.; Wang, Z. Effect of Film-Mulching on Soil Evaporation and Plant Transpiration in a Soybean Field in Arid Northwest China. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1089. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051089
Yang D, Wang C, Guo Z, Li S, Sun Y, Hou X, Wang Z. Effect of Film-Mulching on Soil Evaporation and Plant Transpiration in a Soybean Field in Arid Northwest China. Agronomy. 2025; 15(5):1089. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051089
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Danni, Chunyu Wang, Zhenyu Guo, Sien Li, Yingying Sun, Xiandong Hou, and Zhenhua Wang. 2025. "Effect of Film-Mulching on Soil Evaporation and Plant Transpiration in a Soybean Field in Arid Northwest China" Agronomy 15, no. 5: 1089. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051089
APA StyleYang, D., Wang, C., Guo, Z., Li, S., Sun, Y., Hou, X., & Wang, Z. (2025). Effect of Film-Mulching on Soil Evaporation and Plant Transpiration in a Soybean Field in Arid Northwest China. Agronomy, 15(5), 1089. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051089








