Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of bHLH Transcription Factors and Their Expression Profile in Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification and Characterization of bHLHs
2.2. Analysis of Conserved Motif Distribution and Gene Structure
2.3. Gene Expression Profile Analysis
2.4. Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis (WGCNA)
2.5. Isolation of RNA and Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Characterization of StbHLH Genes
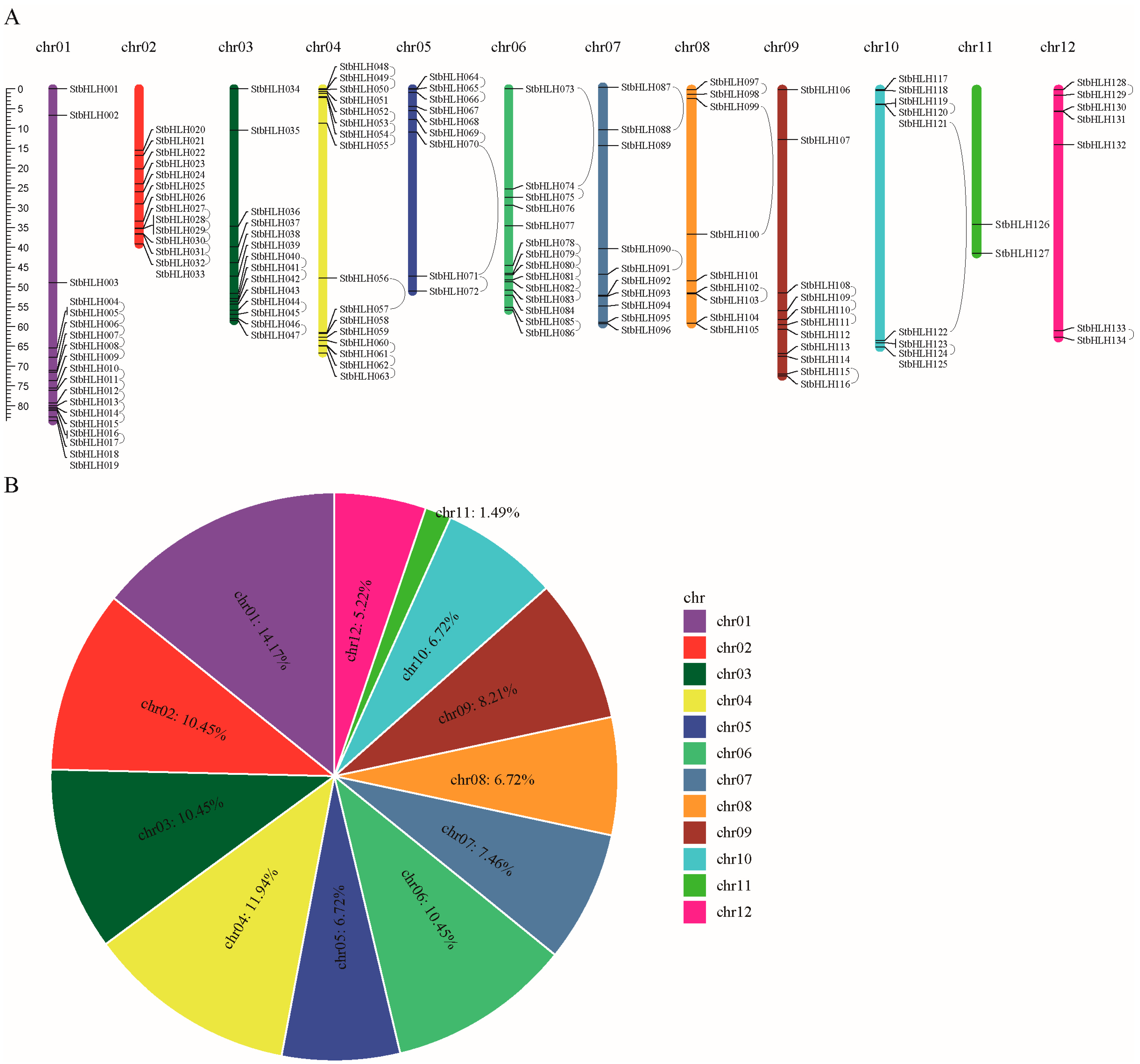
3.2. Chromosome Distribution and Gene Replication of StbHLH Family Genes
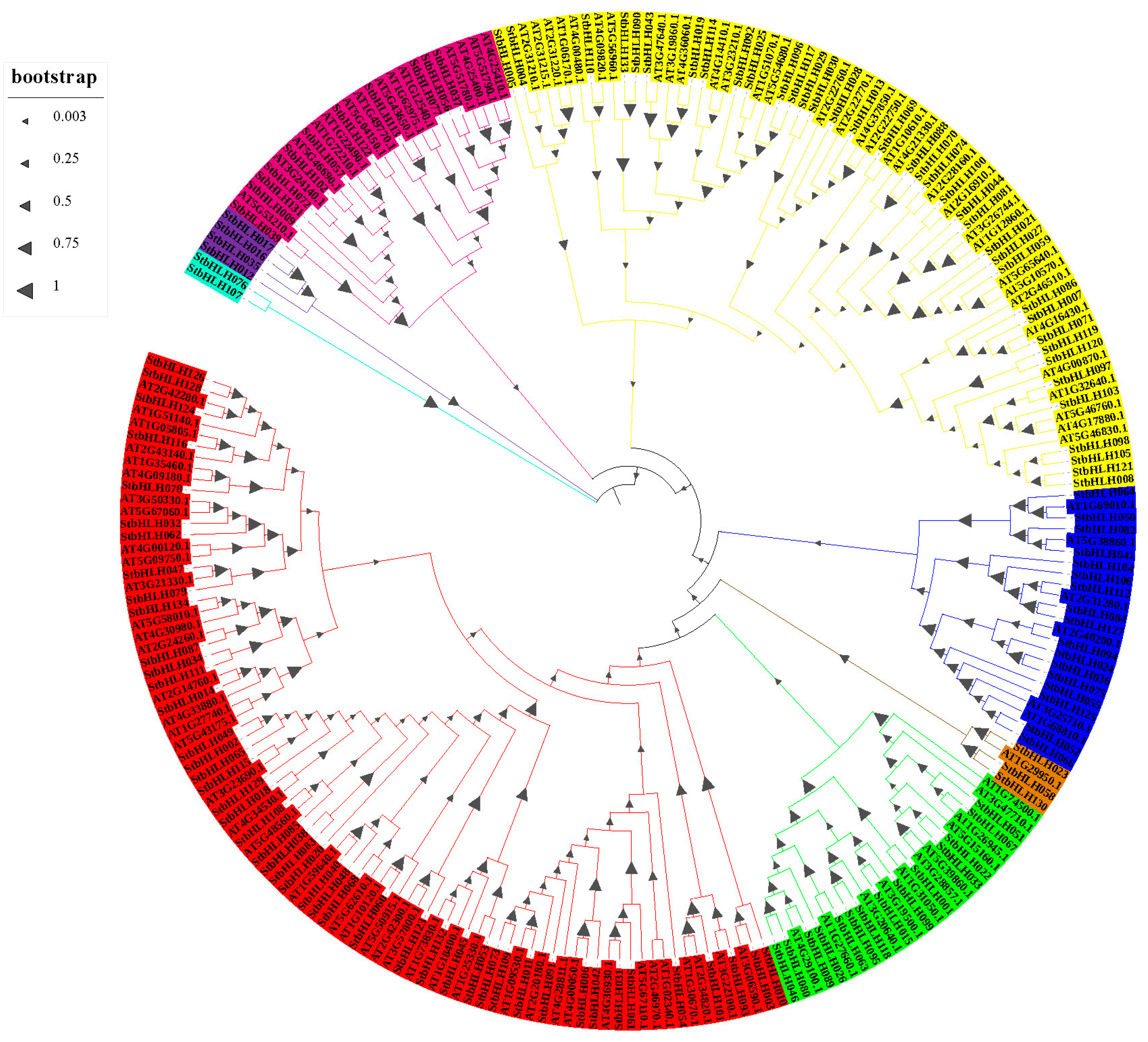
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of StbHLH Genes
3.4. Gene Structure, Motif Composition and Protein Interaction Analysis of StbHLH Genes
3.5. Analysis of the Promoter Region Cis-Regulatory Element
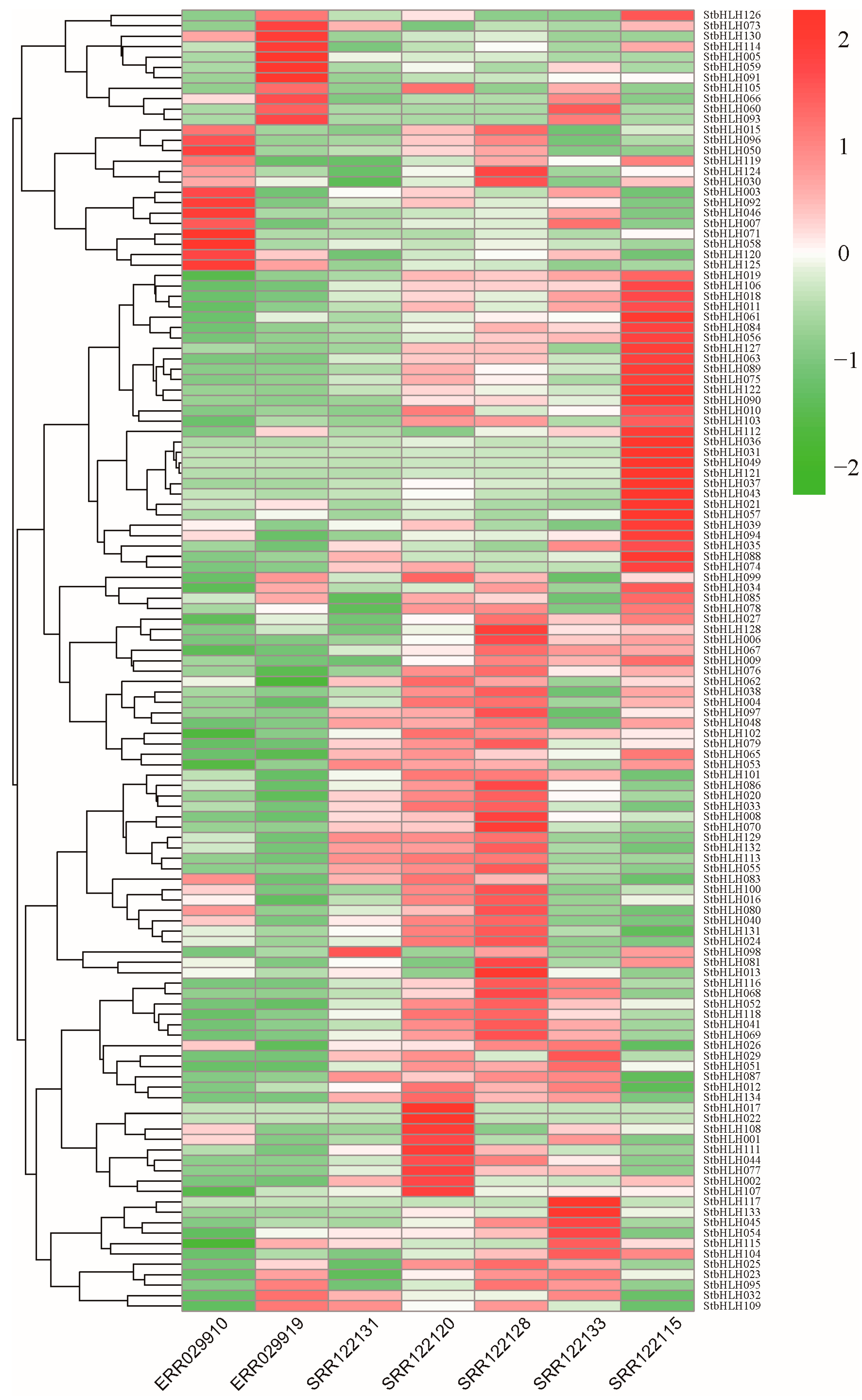
3.6. Expression Patterns of bHLH Genes in Potato Plant Under Different Tissues
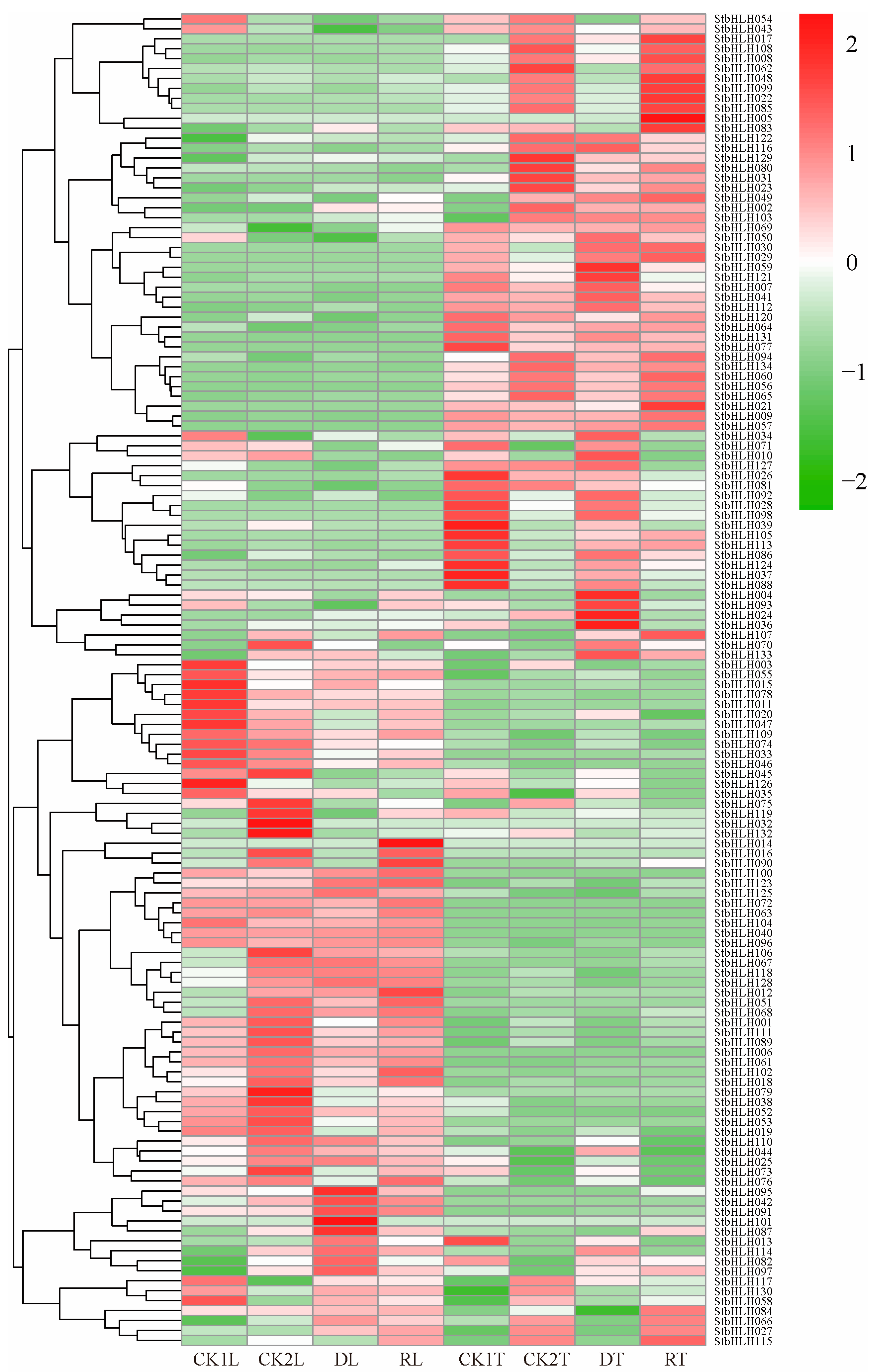
3.7. Expression Patterns of StbHLH Genes in Potato Plant Under Abiotic Stress
3.8. Expression Profiles of StbHLHs Under Drought and Re-Watering Treatment
3.9. StbHLH025 Regulates Tissue Development and Stress Response in Potato
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wagg, C.; Hann, S.; Kupriyanovich, Y.; Li, S. Timing of short period water stress determines potato plant growth, yield and tuber quality. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 247, 106731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Zhang, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Yang, X.; Wu, L.; Chen, M.; Wang, H.; Jing, Q.; Shen, J.; et al. Drought priming at seedling stage improves photosynthetic performance and yield of potato exposed to a short-term drought stress. J. Plant Physiol. 2024, 292, 154157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasir, M.W.; Toth, Z. Effect of drought stress on potato production: A review. Agronomy 2022, 12, 635–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obidiegwu, J.E. Coping with drought: Stress and adaptive responses in potato and perspectives for improvement. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 542–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payyavula, R.S.; Singh, R.K.; Navarre, D.A. Transcription factors, sucrose, and sucrose metabolic genes interact to regulate potato phenylpropanoid metabolism. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 5115–5131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, N.; Dolan, L. Origin and diversification of basic-helix-loop-helix proteins in plants. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 862–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feller, A.; Machemer, K.; Braun, E.L.; Grotewold, E. Evolutionary and comparative analysis of MYB and bHLH plant transcription factors. Plant J. 2011, 66, 94–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchers, A.; Pieler, T. Programming pluripotent precursor cells derived from Xenopus embryos to generate specific tissues and organs. Genes 2023, 1, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Duan, X.; Jiang, H.; Sun, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Guo, J.; Liang, W.; Chen, L.; Yin, J.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factor family in rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 1167–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo-Ortiz, G.; Huq, E.; Quail, P.H. The Arabidopsis basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factor family. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 1749–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Lv, W.; Zhang, H.; Ma, L.; Li, P.; Ge, L.; Li, G. Genome-wide analysis of the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factor family in maize. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, P.; Jiang, Y.X.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, M.Q.; Ji, X.M.; Ma, L.; Jin, G.Z.; Li, J.X.; Zhang, S.B.; Kong, D.X.; et al. Functions of basic helix–loop–helix (bHLH) proteins in the regulation of plant responses to cold, drought, salt, and iron deficiency: A comprehensive review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 10692–10709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enamul, H.; Peter, H.Q. PIF4, a phytochrome-interacting bHLH factor, functions as a negative regulator of phytochrome B signaling in Arabidopsis. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 2441–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.Q.; Zhao, P.; Kong, N.N.; Lu, R.Z.; Pei, Y.; Huang, C.X.; Ma, H.L.; Chen, Q. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the potato bHLH transcription factor family. Genes 2018, 9, 54–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wu, X.; Li, N.; Nie, H.; Ma, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, Y. The StbHLH47 transcription factor negatively regulates drought tolerance in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorrips, R.E. MapChart: Software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J. Hered. 2002, 93, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Debarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.H.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H.; et al. MCScanX: A toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhao, X.Q.; Wang, J.; Wong, G.K.S.; Yu, J. KaKs_calculator: Calculating Ka and Ks through model selection and model averaging. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2006, 4, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y. TBtools-II: A “one for all, all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant 2023, 11, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: An R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, P.; Martin, C.; Toledo-Ortiz, G. Update on the basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 2497–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Javed, T.; Zaheer, U.; Zhou, J.R.; Huang, M.T.; Fu, H.Y.; Gao, S.J. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of the bHLH transcription factor gene family in Saccharum spontaneum under Bacterial Pathogen Stimuli. Trop. Plant Biol. 2021, 14, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Kim, H.S.; Yu, T.; Zhang, A.; Yang, Y.; Liu, M.; Yu, W.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, Q.; et al. Identification and function analysis of bHLH genes in response to cold stress in sweetpotato. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 169, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Song, J.; Liu, S.; Chen, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Xiao, Y.; Cao, B.; Lei, J.; Zhu, Z. Genome-wide identification of the Capsicum bHLH transcription factor family: Discovery of a candidate regulator involved in the regulation of species-specific bioactive metabolites. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Qiao, H.; Ma, M.; Wang, X.; Tian, Y.; Bai, S.; Hasi, A. Genome-wide identification and characterization of melon bHLH transcription factors in regulation of fruit development. Plants 2021, 10, 2721–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Meng, X.Q.; Hong, H.T.; Liu, S.Y.; Yu, J.; Huang, C.; Dong, T.T.; Geng, H.X.; Li, Z.Y.; Zhu, M.K. Systematic identification and expression analysis of bHLH gene family reveal their relevance to abiotic stress response and anthocyanin biosynthesis in sweetpotato. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.W.; Lu, D.D.; Yu, Y.L.; Li, L.; Dong, W.; Xu, L.J.; Yang, Q.; Wan, X.F.; Liang, H.Z. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the bHLH gene family and its response to abiotic stresses in Carthamus tinctorius. Plants 2023, 12, 3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Lai, D.; Yang, H.; Xue, G.; He, A.; Chen, L.; Feng, L.; Ruan, J.; Xiang, D.; Yan, J.; et al. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the bHLH transcription factor family and its response to abiotic stress in foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.). BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Li, X.; Han, P.; Liu, H.; Gong, J.C.; Zhou, W.J.; Shi, B.x.; Liu, A.; Xu, L. Genome-wide investigation of bHLH genes and expression analysis under different biotic and abiotic stresses in Helianthus annuus L. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 189, 72–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, G.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J. Genome-wide identification of basic helix–loop–helix (bHLH) family in peanut: Potential regulatory roles in iron homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, P.F.; Li, C.L.; Zhao, X.R.; Li, M.F.; Zhao, H.X.; Guo, J.Y.; Cai, Y.; Chen, H.; Wu, Q. Overexpression of a tartary buckwheat gene, FtbHLH3, enhances drought/oxidative stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 625–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waseem, M.; Rong, X.; Li, Z. Dissecting the role of a basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor, SlbHLH22, under salt and drought stresses in transgenic Solanum lycopersicum L. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wu, M.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, W.; Ren, X.; Liang, E.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, C.; Xiao, N.; Li, Y.; et al. A maize phytochrome-interacting factors protein ZmPIF1 enhances drought tolerance by inducing stomatal closure and improves grain yield in Oryza sativa. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 1375–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Hir, R.; Castelain, M.; Chakraborti, D.; Moritz, T.; Dinant, S.; Bellini, C. AtbHLH68 transcription factor contributes to the regulation of ABA homeostasis and drought stress tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Physiol. Plant 2017, 160, 312–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Wang, C.; Han, X.; Tang, S.; Liu, S.; Xia, X.; Yin, W. A novel bHLH transcription factor PebHLH35 from Populus euphratica confers drought tolerance through regulating stomatal development, photosynthesis and growth in Arabidopsis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 450, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Seomun, S.; Yoon, Y.; Jang, G. Jasmonic Acid in Plant Abiotic Stress Tolerance and Interaction with Abscisic Acid. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1886–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.S.; Joo, J.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, Y.K.; Nahm, B.H.; Song, S.I.; Cheong, J.J.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, J.K.; Choi, Y.D. OsbHLH148, a basic helix-loop-helix protein, interacts with OsJAZ proteins in a jasmonate signaling pathway leading to drought tolerance in rice. Plant J. 2011, 65, 907–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leivar, P.; Monte, E. PIFs: Systems integrators in plant development. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 56–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gong, J.; Zhang, L.C.; Shen, H.; Chen, G.P.; Xie, Q.L.; Hu, Z.L. Overexpression of SlPRE5, an atypical bHLH transcription factor, affects plant morphology and chlorophyll accumulation in tomato. J. Plant Physiol. 2022, 273, 153698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
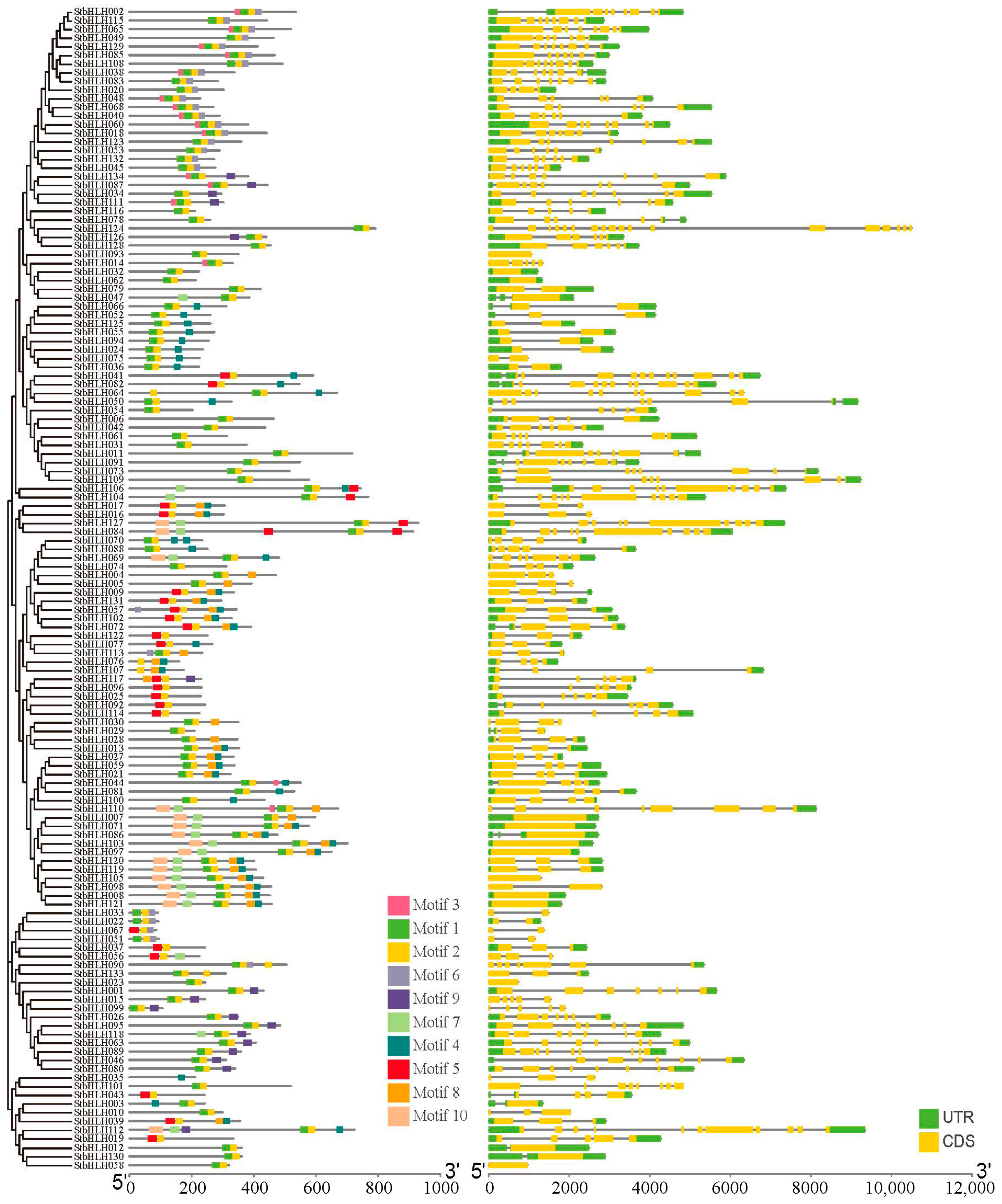


| Motif | Length (aa) | Amino Acid Conserved Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Motif 1 | 27 | HSLAERRRREKJNERMKALQELVPNCN |
| Motif 2 | 21 | KTDKASMLDEAINYIKELQEQ |
| Motif 3 | 15 | DYIHVRARRGQATDS |
| Motif 4 | 21 | RLMEALESLGLDVLHANISTV |
| Motif 5 | 29 | RSSHIAVERNRRKKMNELFSELRSLLPPS |
| Motif 6 | 20 | VEFLSMKLATVNPRLDFNJD |
| Motif 7 | 29 | VCIPTPSGVVELGSTEVIPENLELVQQVK |
| Motif 8 | 26 | PEIEVKIIGDDAMIRVQSEKKPGPLL |
| Motif 9 | 27 | EEAMQDLRSRGLCLVPISCTTAISSST |
| Motif 10 | 42 | NVTDTEWFYLMSMAQSFPVGEGLPGKAFSSGSHIWLTGAQEL |
| Gene Name | Forward Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| StEfla (reference gene) | CAAGGATGACCCAGCCAAG | TTCCTTACCTGAACGCCTGT |
| StbHLH025 | AATGCTCAATGGCCCTCCAA | CCCTGCGCATTTTCTCCCTA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Diao, Y.; Yin, L.; Deng, X.; Wang, S. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of bHLH Transcription Factors and Their Expression Profile in Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Agronomy 2025, 15, 1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051070
Ye J, Zhang L, Liu S, Diao Y, Yin L, Deng X, Wang S. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of bHLH Transcription Factors and Their Expression Profile in Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Agronomy. 2025; 15(5):1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051070
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Jiali, Lingzhi Zhang, Shuaikang Liu, Yi Diao, Lina Yin, Xiping Deng, and Shiwen Wang. 2025. "Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of bHLH Transcription Factors and Their Expression Profile in Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.)" Agronomy 15, no. 5: 1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051070
APA StyleYe, J., Zhang, L., Liu, S., Diao, Y., Yin, L., Deng, X., & Wang, S. (2025). Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of bHLH Transcription Factors and Their Expression Profile in Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Agronomy, 15(5), 1070. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051070








