Impacts of Converting Native Grassland into Arable Land and an Avocado Orchard on Soil Hydraulic Properties at an Experimental Farm in South Africa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Soil Sampling and Laboratory Procedures
2.3. Determination of the Soil Water Retention Curve and Pore Size Distribution
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Soil Particle Size Distribution and Soil Organic Carbon
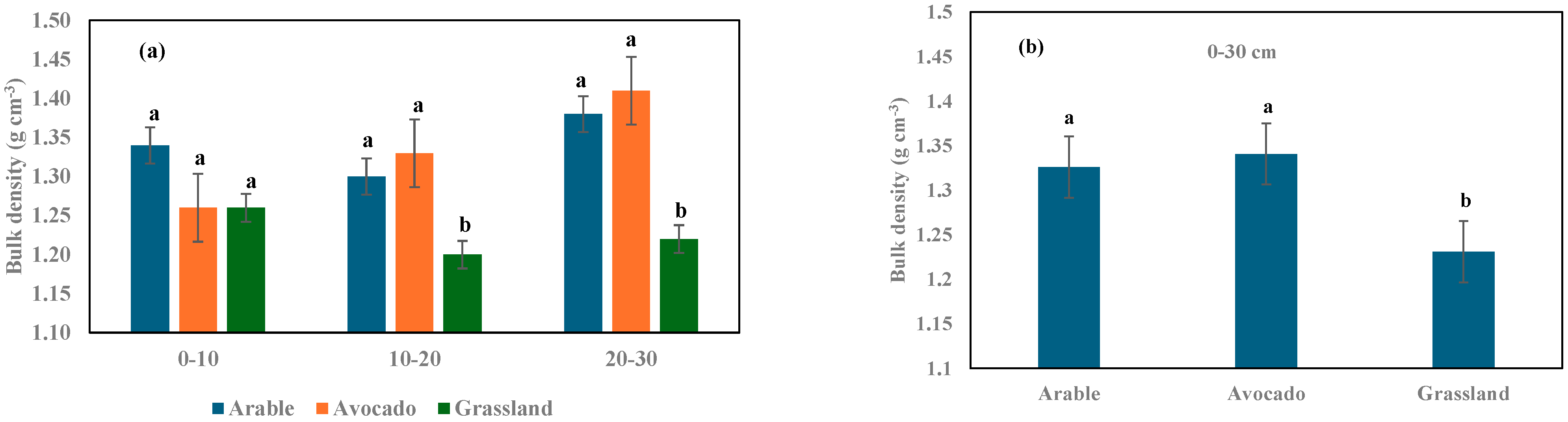
3.2. Soil Bulk Density
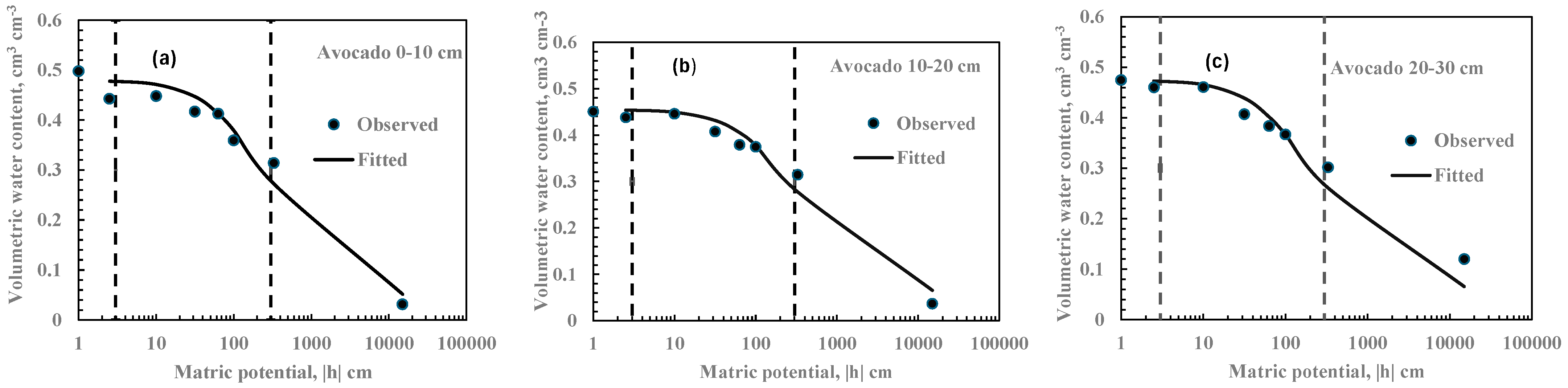
3.3. Soil Water Retention Curve and Fitted vG Model Parameters
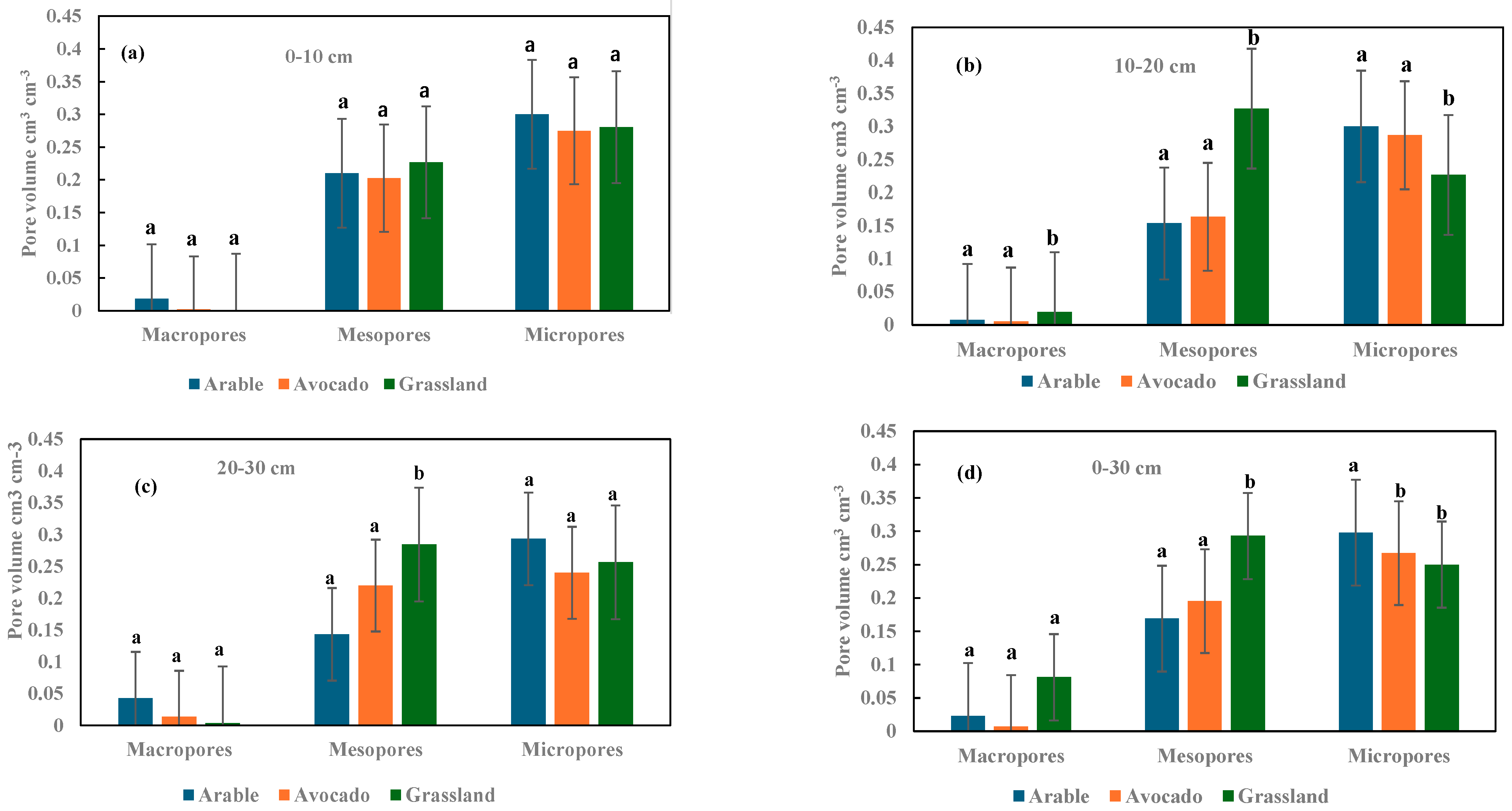
3.4. Soil Pore Size Distribution
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brearley, F.Q.; Thomas, A.D. Land-use Change Impacts on Soil Processes in Tropical and Savannah Ecosystems: An Introduction. In Land-Use Change Impacts on Soil Processes-Tropical and Savannah Ecosystems; Brearley, F.Q., Thomas, A.D., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, UK; Boston, MA, USA, 2025; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Z.; Hu, W.; Beare, M.; Thomas, S.; Carrick, S.; Dando, J.; Langer, S.; Müller, K.; Baird, D.; Lilburne, L. Land use effects on soil hydraulic properties and the contribution of soil organic carbon. J. Hydrol. 2021, 602, 126741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Dong, L.; Li, A.; Lv, W.; Wu, J.; Zhang, H.; Bai, R.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Shangguan, Z.; et al. Soil physicochemical properties and crusts regulate the soil infiltration capacity after land-use conversions from farmlands in semi-arid areas. J. Hydrol. 2023, 626, 130283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horel, A.; Tóth, E.; Gelybó, G.; Kása, I.; Bakacsi, Z.; Farkas, C. Effects of Land Use and Management on Soil Hydraulic Properties. Open Geosci. 2015, 7, 742–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajic, K.; Kresovic, B.; Tolimir, M.; Zivotic, L.; Lipovac, A.; Gajic, B. Hydraulic properties of fine-textured soils in lowland ecosystems of Western Serbia vary depending on land use. Geoderma Reg. 2023, 32, e00603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eze, S.; Dougill, A.J.; Banwart, A.J.; Hermans, T.D.G.; Ligowe, I.S.; Thierfelder, C. Impacts of conservation agriculture on soil structure and hydraulic properties of Malawian agricultural systems. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 201, 104639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indoria, A.K.; Sharma, K.L.; and Reddy, K.S. Hydraulic properties of soil under warming climate. In Climate Change and Soil Interactions; Prasad, M.N.V., Pietrzykowski, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 473–508. [Google Scholar]
- Hillel, D. Introduction to Soil Physics; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1980; pp. 57–89. [Google Scholar]
- Rabot, E.; Wiesmeier, M.; Schlüter, S.; Vogel, H.-J. Soil structure as an indicator of soil functions: A review. Geoderma 2018, 314, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzel, K.; Carrick, S.; Wahren, A.; Feger, K.-H.; Bodner, G.; Buchan, G. Soil hydraulic properties of recently tilled soil under cropping rotation compared with two-year pasture. Vadose Zone J. 2011, 10, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabro, J.D.; Stevens, W.B. Soil-water characteristic curves and their estimated hydraulic parameters in no-tilled and conventionally tilled soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 219, 105342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yimer, F.; Messing, I.; Ledin, S.; Abdelkadir, A. Effects of different land use types on infiltration capacity in a catchment in the highlands of Ethiopia. Soil Use Manag. 2008, 24, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, J.A.; Giraldez, J.V.; Pastor, M.; Fereresa, E. Effects of tillage method on soil physical properties, infiltration and yield in an olive orchard. Soil Tillage Res. 1999, 52, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, W.D.; Bowman, B.T.; Drury, C.F.; Tan, C.S.; Luc, X. Indicators of good soil physical quality: Density and storage parameters. Geoderma 2002, 110, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebb, C.; Schoderbek, D.; Hernandez-Ramirez, G.; Hewins, D.; Carlylec, C.N.; Bork, E. Soil physical quality varies among contrasting land uses in northern prairie regions. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 240, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormann, H.; Klaassen, K. Seasonal and land-use dependent variability of soil hydraulic and soil hydrological properties of two Northern German soils. Geoderma 2008, 145, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owuor, S.O.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Guzha, A.C.; Jacobs, S.; Merbold, L.; Rufino, M.C.; Pelster, D.E.; Díaz-Pinés, E.; Breuer, L. Conversion of natural forest results in a significant degradation of soil hydraulic properties in the highlands of Kenya. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 176, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangiabadi, M.; Gorji, M.; Khavari Khorasai, S.; Saadat, S. Effect of soil pore size distribution on plant-available water and least limiting water range as soil physical quality indicators. Pedosphere 2020, 30, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimmo, J.R. Porosity and Pore Size Distribution. In Encyclopedia of Soils in the Environment; Hillel, D., Ed.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2004; Volume 3, pp. 295–303. [Google Scholar]
- Negassa, W.C.; Guber, A.K.; Kravchenko, A.N.; Marsh, T.L.; Hildebrandt, B.; Rivers, M.L. Properties of Soil Pore Space Regulate Pathways of Plant Residue Decomposition and Community Structure of Associated Bacteria. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutlek, M. Soil hydraulic properties as related to soil structure. Soil Tillage Res. 2004, 79, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namugize, J.N.; Jewitta, G.; Graham, M. Effects of land use and land cover changes on water quality in the uMngeni river catchment, South Africa. Phys. Chem. Earth 2008, 105, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources. In International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps, 4th ed.; International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS): Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Fey, M. Soils of South Africa; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010; pp. 105–115. [Google Scholar]
- Mzezewa, J.; Van Rensburg, L.D. Effects of tillage on runoff from a bare clayey soil on a semi-arid ecotope in the Limpopo Province of South Africa. Water SA 2011, 37, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Palmer, A.R.; Ainslie, A.M. Grasslands of South Africa. Available online: https://www.fao.org/4/y8344e/y8344e08.htm (accessed on 17 January 2025).
- Gee, G.W.; Bauder, J.W. Particle size analysis. In Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 1, Monogr. 9, 2nd ed.; Klute, A., Ed.; ASA and SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1986; pp. 383–411. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommer, L.E. Total Carbon, Organic Carbon and Organic Matter. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2. Chemical and Microbiological Properties, 2nd ed.; ASA-SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 539–579. [Google Scholar]
- van Genuchten, M.T.; Leij, F.J.; Yates, S.R. The RETC Code for Quantifying the Hydraulic Functions of Unsaturated Soils; Version 1.0. EPA Report 600/2-91/065; U.S. Salinity Laboratory, USDA-ARS: Riverside, CA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Luxmore, R.J. Micro-, meso-, microporosity of soil. Letter to the editor. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1981, 45, 671–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, Y.; Kosugi, K.; Mizuyama, T. Changes in pore size distribution and hydraulic properties of forest soil resulting from structural development. J. Hydrol. 2006, 331, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, R.; Vesh, R.; Thapab, A.C.; Acosta-Martinezc, V. Soil organic matter and microbial community responses to semiarid croplands and grasslands management. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 141, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Elliott, E.T.; Paustian, K. Soil macroaggregate turnover and microaggregate formation: A mechanism for C sequestration under no-tillage agriculture. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 2099–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buruso, F.H.; Adimassu, Z.; Sibali, L.L. Effects of land use/land cover changes on soil properties in Rib watershed, Ethiopia. Catena 2023, 224, 106977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, N.; Koestel, J.; Messing, I.; Moeys, J.; Lindahl, A. Influence of soil, land use and climatic factors on the hydraulic conductivity of soil. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 5185–5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.W.; Johnston, M.A.; Lorentz, S.A. The effect of soil compaction on the water retention characteristics of soils in the forest plantations. S. Afr. J. Plant Soil 2001, 18, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myeni, L.; Mdlambuzi, T.; Paterson, D.G.; De Nysschen, G.; Moeletsi, M.E. Development and Evaluation of Pedotransfer Functions to Estimate Soil Moisture Content at Field Capacity and Permanent Wilting Point for South African Soils. Water 2021, 13, 2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R.; Shukla, M.K. Principles of Soil Physics; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lipiec, J.; Kus, J.; Slowinska-Jurkiewicz, A.; Nosalewicz, A. Soil porosity and infiltration as influenced by tillage methods. Soil Tillage Res. 2006, 89, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Layer (cm) | Land Use | Particle Size Distribution (%) | SOC (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand | Silt | Clay | |||
| 0–10 | Arable | 23.6 a ±3.0 | 20.1 ±2.5 | 56.3 a ±3.6 | 1.48 ±0.58 |
| Avocado | 26.2 a ±2.3 | 25.3 ±2.3 | 48.5 b ±1.8 | 1.34 ±0.19 | |
| Grassland | 27.3 b ±3.9 | 25.4 ±2.0 | 47.3 b ±3.3 | 1.30 ±0.63 | |
| 10–20 | Arable | 25.0 ±2.5 | 23.0 a ±3.6 | 52.0 a ±4.7 | 1.38 ab ±0.42 |
| Avocado | 25.1 ±2.4 | 19.1 b ±2.8 | 55.8 a ±2.8 | 1.19 a ±0.15 | |
| Grassland | 25.6 ±3.0 | 24.7 a ±1.4 | 49.7 b ±0.7 | 1.55 b ±0.25 | |
| 20–30 | Arable | 24.2 a ±1.7 | 20.3 a ±3.2 | 55.5 a ±5.8 | 1.24 ±0.18 |
| Avocado | 24.0 a ±1.6 | 20.0 a ±2.2 | 56.0 a ±2.2 | 0.79 ±0.38 | |
| Grassland | 24.1 a ±4.4 | 28.2 b ±4.5 | 48.7 b ±1.3 | 0.94 ±0.63 | |
| Depth (cm) | Land Use | θs (cm3 cm−3) | θr (cm3 cm−3) | n | α (cm−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–10 | Arable | 0.528 ±0.02286 | 0.0006 ±0.00044 | 1.3538 a ±0.05198 | 0.0133 ±0.00956 |
| Avocado | 0.487 ±0.01465 | 0.0005 ±0.00038 | 1.3824 a ±0.05361 | 0.0130 ±0.00481 | |
| Grassland | 0.5355 ±0.03223 | 0.0452 ±0.03498 | 1.6549 b ±0.0391 | 0.0081 ±0.00115 | |
| 10–20 | Arable | 0.4892 a ±0.01616 | 0.0005 ±0.00020 | 1.3507 ±0.04708 | 0.0099 a ±0.00162 |
| Avocado | 0.4548 a ±0.00550 | 0.0006 ±0.00020 | 1.3993 ±0.08577 | 0.0107 a ±0.00601 | |
| Grassland | 0.5726 b ±0.02506 | 0.0001 ±0.00015 | 1.3428 ±0.03364 | 0.0465 b ±0.01153 | |
| 20–30 | Arable | 0.4791 ±0.08140 | 0.0002 ±0.00017 | 1.3856 ±0.17952 | 0.0567 ±0.09140 |
| Avocado | 0.4737 ±0.00576 | 0.0007 ±0.00025 | 1.3696 ±0.03211 | 0.0142 ±0.00269 | |
| Grassland | 0.5448 ±0.00366 | 0.0025 ±0.00416 | 1.4270 ±0.04545 | 0.0160 ±0.00162 |
| Depth (cm) | Land Use | Total Porosity | FC | PWP | PAW | AC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cm3 cm−3 | ||||||
| 0–10 | Arable | 0.528 ±0.02286 | 0.3119 a ±0.02795 | 0.0867 ±0.01198 | 0.2252 ±0.02837 | 0.1931 ±0.08093 |
| Avocado | 0.487 ±0.01465 | 0.2719 b ±0.01084 | 0.0662 ±0.00925 | 0.2056 ±0.01949 | 0.2069 ±0.04360 | |
| Grassland | 0.5355 ±0.03223 | 0.2684 b ±0.01176 | 0.0359 ±0.00549 | 0.2325 ±0.00929 | 0.2671 ±0.05833 | |
| 10–20 | Arable | 0.4892 ±0.01616 | 0.3095 a ±0.01308 | 0.0864 ±0.01881 | 0.2231 a ±0.00670 | 0.1797 a ±0.00744 |
| Avocado | 0.4548 ±0.00550 | 0.2775 b ±0.01606 | 0.0654 ±0.01622 | 0.2121 a ±0.03071 | 0.1773 a ±0.01806 | |
| Grassland | 0.5726 b ±0.02506 | 0.2257 c ±0.01450 | 0.0559 ±0.01839 | 0.1698 b ±0.01242 | 0.3469 b ±0.01557 | |
| 20–30 | Arable | 0.4791 ±0.08140 | 0.3079 ±0.03651 | 0.0856 ±0.04355 | 0.2223 ±0.07705 | 0.1712 ±0.10898 |
| Avocado | 0.4737 ±0.00576 | 0.2613 ±0.00459 | 0.0473 ±0.0230 | 0.2141 ±0.02737 | 0.2124 ±0.00450 | |
| Grassland | 0.5448 ±0.00366 | 0.2636 ±0.00755 | 0.0554 ±0.00858 | 0.2082 ±0.00284 | 0.2812 0.01031 | |
| Average across 3 depths | ||||||
| 0–30 | Arable | 0.4988 ±0.04852 | 0.3098 a ±0.02397 | 0.0862 a ±0.02447 | 0.2235 ±0.04121 | 0.1813 a ±0.06864 |
| Avocado | 0.4691 ±0.01376 | 0.2702 b ±0.01223 | 0.0596 b ±0.01748 | 0.2106 ±0.02848 | 0.1988 a ±0.02245 | |
| Grassland | 0.5510 ±0.0264 | 0.2526 b ±0.02261 | 0.0491 b ±0.01442 | 0.2035 ±0.04848 | 0.2984 b ±0.04384 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mzezewa, J. Impacts of Converting Native Grassland into Arable Land and an Avocado Orchard on Soil Hydraulic Properties at an Experimental Farm in South Africa. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051039
Mzezewa J. Impacts of Converting Native Grassland into Arable Land and an Avocado Orchard on Soil Hydraulic Properties at an Experimental Farm in South Africa. Agronomy. 2025; 15(5):1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051039
Chicago/Turabian StyleMzezewa, Jestinos. 2025. "Impacts of Converting Native Grassland into Arable Land and an Avocado Orchard on Soil Hydraulic Properties at an Experimental Farm in South Africa" Agronomy 15, no. 5: 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051039
APA StyleMzezewa, J. (2025). Impacts of Converting Native Grassland into Arable Land and an Avocado Orchard on Soil Hydraulic Properties at an Experimental Farm in South Africa. Agronomy, 15(5), 1039. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051039







