Path Analysis on the Meteorological Factors Impacting Yield of Tartary Buckwheat at Different Sowing Dates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Time and Location of the Experiment
2.2. Experimental Materials
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Investigation and Determination Items
2.4.1. Investigation of Growth Period and Growth Stages
2.4.2. Investigation of Meteorological Data
2.4.3. Yield
2.4.4. Quality Determination
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Growth and Development Situations of Tartary Buckwheat Under Different Sowing Dates
3.2. Influence of Sowing Dates on Yield and Yield Components
3.3. Effect of Sowing Date on Quality
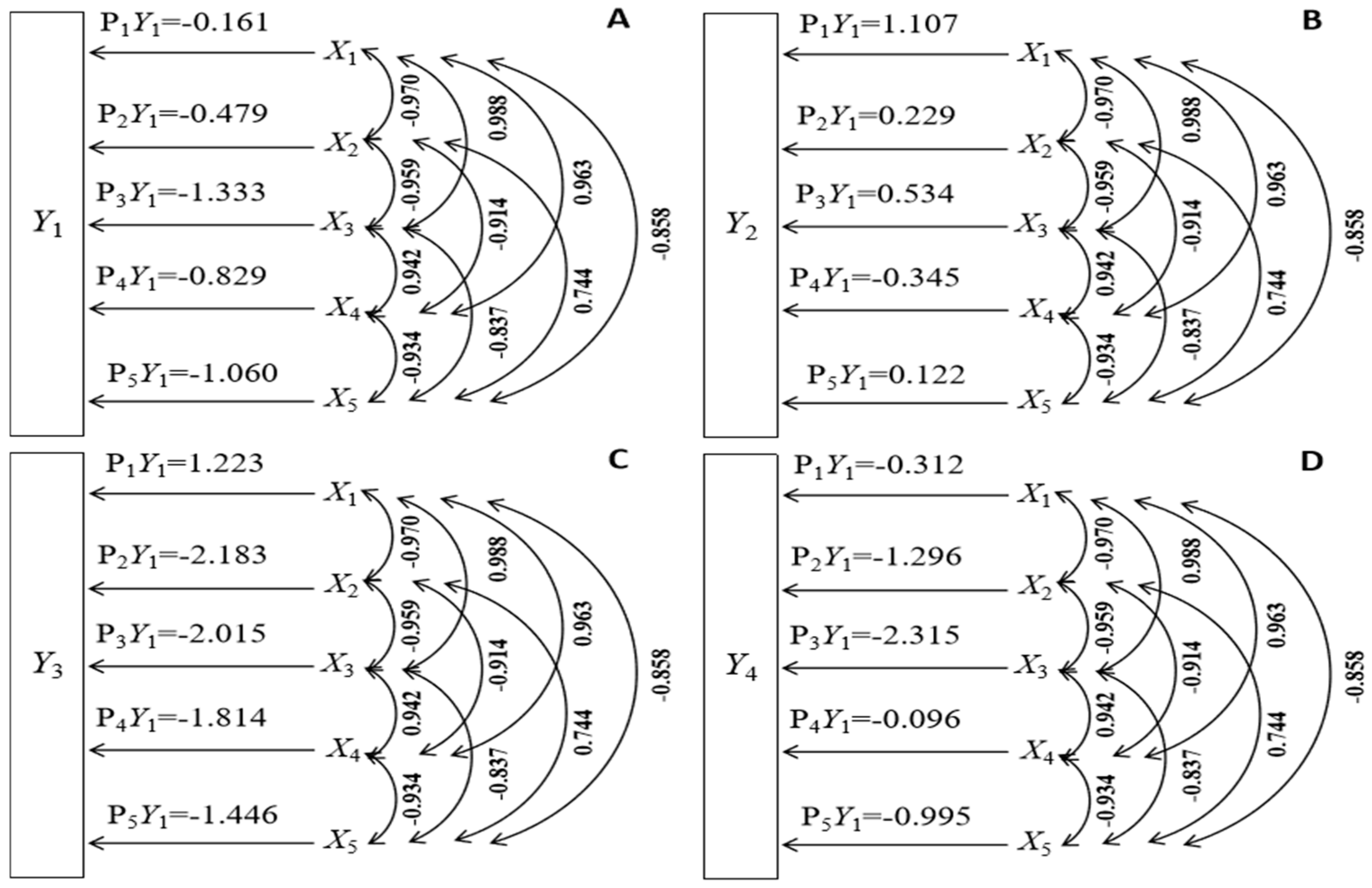
3.4. Path Analysis of Thousand-Grain Weight, Number of Grains per Plant, and Setting Rate with Meteorological Factors
3.5. Path Analysis of Quality Indicators and Meteorological Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Performance of Yield and Growth Period of Tartary Buckwheat Under Different Sowing Dates
4.2. Relationship Between Yield and Its Components and Meteorological Factors
4.3. Relationship Between Grain Quality and Meteorological Factors
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jha, R.; Zhang, K.; He, Y.; Mendler-Drienyovszki, N.; Magyar-Tábori, K.; Quinet, M.; Germ, M.; Kreft, I.; Meglič, V.; Ikeda, K.; et al. Global nutritional challenges and opportunities: Buckwheat, a potential bridge between nutrient deficiency and food security. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 145, 104365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Zhang, J.Y.; Cheng, T.; Guo, Y.Y.; Zhang, L.; Han, X.; Liu, C.Y.; Wan, Y.; Ye, X.L.; Cao, X.N.; et al. New Strategies to Address World Food Security and Elimination of Malnutrition: Future Role of Coarse Cereals in Human Health. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1301445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, R.; Kumar, S.; Awasthi, C.P.; Verma, M.L. Biochemical Evaluation of Tartary Buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum Gaertn.) Genotypes of Cold Desert of Himachal Pradesh. Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Asia 2017, 14, 821–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Feng, S.; Qu, Y.; Gong, X.; Luo, Y.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Dang, K.; Gao, X.; Feng, B. Identifying the primary meteorological factors affecting the growth and development of Tartary buckwheat and a comprehensive landrace evaluation using a multi-environment phenotypic investigation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 6104–6116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Mao, Y.; Tang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, A.; Li, C.; Wu, H.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, H. Rutin distribution in Tartary buckwheat: Identifying prime dietary sources through comparative analysis of post-processing treatments. Food Chem. 2025, 464, 141641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivan, K.; Spela, M.; Mateja, G.; Vekoslava, S. Impact of Selenium on Mitochondrial Activity in Young Tartary Buckwheat Plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 63, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinová, J.; Dadáková, E. Influence of Sowing Date and Stand Density on Rutin Level in Buckwheat. Cereal Res. Commun. 2013, 41, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakaei, M.; Farshadfar, M. Studies on Genetic Parameters, Heritability, and Path Analysis Under Irrigated and Rainfed Conditions in Chickpea. Plant Mol. Biol. Reprod. 2025, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, W.J.d.S.; Neto, F.d.A.; Al-Qahtani, W.H.; Okla, M.K.; Al-Hashimi, A.; Vieira, P.F.d.M.J.; Gravina, G.d.A.; Zuffo, A.M.; Dutra, A.F.; Carvalho, L.C.B.; et al. Correction: Yield of soybean genotypes identified through GGE biplot and path analysis. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0320098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obua, T.; Sserumaga, J.P.; Tukamuhabwa, P.T.; Namara, M.; Awio, B.; Mugarra, J.; Tusiime, G.; Chigeza, G. Unravelling Yield and Yield-Related Traits in Soybean Using GGE Biplot and Path Analysis. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.Q.; Yin, M.; Wang, M.J.; Ma, H.Y.; Chu, G.; Liu, Y.H.; Xu, C.M.; Zhang, X.F.; Zhang, Y.B.; Wang, D.Y.; et al. Effects of Meteorological Factors on Quality of Late Japonica Rice During Late Season Grain Filling Stage Under ‘Early Indica and Late Japonica’ Cultivation Pattern in Southern China. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2023, 56, 46–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, S. Assessing the Agronomic Subfield Variability by Sentinel-2 NDVI Time-Series and Landscape Position. Agronomy 2023, 13, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, Q.; Chen, S.; Sun, S.; Liu, L. Reduced actual vapor pressure exerts a significant influence on maize yield through vapor pressure deficit amid climate warming. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2024, 68, 2041–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhong, D.; Chen, X.; Niu, Z.; Cao, Q. Impact of climate change on rice growth and yield in China: Analysis based on climate year type. Geogr. Sustain. 2024, 5, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Lu, H.F.; Qiao, D.M. Integrated effects of meteorological factors, edaphic moisture, evapotranspiration, and leaf area index on the net primary productivity of Winter wheat- Summer maize rotation system. Field Crops Res. 2023, 302, 109080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyomugabo, P.; MacCarthy, D.S.; Adiku, S.G.K. Growth and yield of rice as influenced by different levels of temperature, water and nitrogen under greenhouse condition. Cogent Food Agric. 2024, 10, 2374620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vida, G.; Cséplő, M.; Rakszegi, M.; Bányai, J. Effect of Multi-Year Environmental and Meteorological Factors on the Quality Traits of Winter Durum Wheat. Plants 2022, 11, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Chen, S.; Shao, L.; Sun, H. Selecting traits to increase winter wheat yield under climate change in the North China Plain. Field Crops Res. 2017, 207, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Li, M.; Liu, X.Z.; Chen, R.J.; Ma, G.M.; Wang, P.; Zhang, J. Correlation Analysis of Meteorological Factors with Miaze Yield and Its Components. Crop Res. 2023, 37, 343–348. [Google Scholar]
- Yeganeh, M.B.; Nassiri, S.M.; Zare, D.; Shirzadifar, A.M.; Fazaeli, M.; Nosrati, M. Evaluating the influence of air temperature and far-infrared radiation on the physicochemical characteristics of dried rice. Discov. Food 2025, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.P.; Xiao, Y.J.; Guo, L.; Shan, B.X.; Liu, X.K.; Duan, X.Y.; Rehman, A.-U.; Guo, C.; Zhang, W.J.; Li, H.S.; et al. Effect of High Nighttime Temperatures on Growth, Yield, and Quality of Two Wheat Cultivars During the Whole Growth Period. Plants 2024, 13, 3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.Q.; Cao, N.; Li, Y.Y.; Hou, Y.L.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, T.L.; Cui, J.H.; Li, B.; Shi, W.L.; et al. Rational reduction of planting density and enhancement of NUE were effective methods to mitigate maize yield loss due to excessive rainfall. Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 160, 127326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.Y.; Xu, S.W.; Li, G.Q.; Zhang, Y.G.; Wu, J.Z.; Liu, J.J. The Influence of Meteorological Factors on Wheat and Rice Yields in China. Crop Sci. 2018, 58, 1440–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virili, A.; Petris, R.; Miceli, F. Late summer sowing positively affects yield of lowland buckwheat in Northeastern Italy. Ital. J. Agron. 2024, 19, 100022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.L.; Liu, Y.H.; Liu, S.C.; Wang, R.Y.; Qiao, Z.J.; Cao, X.N. Effect of sowing date on physicochemical properties of waxy and non-waxy proso millet (Panicum miliaceum L.) starches. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 303, 140626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Gupta, A.K.; Gupta, S.K.; Kaur, N. Effect of Sowing Time on Protein Quality and Starch Pasting Characteristics in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Genotypes Grown under Irrigated and Rain-Fed Conditions. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M. Fayyaz-ul-Hassan Response of Spring Wheat (Triticum Aestivum L.) Quality Traits and Yield to Sowing Date. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coventry, D.R.; Gupta, R.K.; Yadav, A.; Poswal, R.S.; Chhokar, R.S.; Sharma, R.K.; Yadav, V.K.; Gill, S.C.; Kumar, A.; Mehta, A. Wheat Quality and Productivity as Affected by Varieties and Sowing Time in Haryana, India. Field Crops Res. 2011, 123, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampurlanés, J.; Angás, P.; Cantero-Martínez, C. Root Growth, Soil Water Content and Yield of Barley under Different Tillage Systems on Two Soils in Semiarid Conditions. Field Crops Res. 2001, 69, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Xu, H.; Khan, S.; Equiza, M.A.; Lee, S.H.; Vaziriyeganeh, M.; Zwiazek, J.J. Plant Water Transport and Aquaporins in Oxygen-Deprived Environments. J. Plant Physiol. 2018, 227, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Abadie, C.; Carroll, A.; Lamade, E.; Tcherkez, G. Responses to K Deficiency and Waterlogging Interact via Respiratory and Nitrogen Metabolism. Plant Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Cui, W.; Xu, K.; Gao, H.; Wei, H.; Zhang, H. Effects of Early- and Late-Sowing on Starch Accumulation and Associated Enzyme Activities During Grain Filling Stage in Rice. Rice Sci. 2021, 28, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.J.; Burrell, M.M.; Emes, M.J.; Tetlow, I.J. Effects of Post-Anthesis High-Temperature Stress on Carbon Partitioning and Starch Biosynthesis in a Spring Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Adapted to Moderate Growth Temperatures. Plant Cell Physiol. 2023, 64, 729–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wassmann, R.; Jagadish, S.V.K.; Sumfleth, K.; Pathak, H.; Howell, G.; Ismail, A.; Serraj, R.; Redona, E.; Singh, R.K.; Heuer, S. Chapter 3 Regional Vulnerability of Climate Change Impacts on Asian Rice Production and Scope for Adaptation. Adv. Agron. 2009, 102, 91–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkin, O.K.; Loveys, B.R.; Atkinson, L.J.; Pons, T.L. Phenotypic Plasticity and Growth Temperature: Understanding Interspecific Variability. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Tetlow, I.J.; Nawaz, S.; Iqbal, A.; Mubin, M.; Nawaz ul Rehman, M.S.; Butt, A.; Lightfoot, D.A.; Maekawa, M. Effect of High Temperature on Grain Filling Period, Yield, Amylose Content and Activity of Starch Biosynthesis Enzymes in Endosperm of Basmati Rice. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 2237–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhash, B.; Yadav, G.S.; Raghavendra, S.; Avasthe, R.K.; Anup, D.; Mohapatra, K.P.; Tahashildar, M.; Kamlesh, K.; Prabha, M.; Thoithoi, D.M.; et al. Production technology and multifarious uses of buckwheat (Fagopyrum spp.): A review. Indian J. Agron. 2018, 63, 415–427. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.; Gao, D.; Liao, S.; Cheng, S.; Jia, J.; Xu, W. Identification of a pleiotropic QTL cluster for Fusarium head blight resistance, spikelet compactness, grain number per spike and thousand-grain weight in common wheat. Crop J. 2023, 11, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Li, Q.; Chen, H.; Zeng, Y.; Li, B.; Zhong, X.; Wang, L.; Ren, W. Relationship between chalkiness and the structural and thermal properties of rice starch after shading during grain-filling stage. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 252, 117212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ji, Y.; Li, E.; Gilbert, R.G. Interactions between leached amylose and protein affect the stickiness of cooked white rice. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 135, 108215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senphan, T.; Benjakul, S.; Sukketsiri, W.; Chotphruethipong, L.; Sriket, C. Comparative studies on characterizations and cytotoxicity of oil extracted from Lingzhi (Ganoderma lucidum) G2 spore using Soxhlet extraction and microwave-assisted extraction. Appl. Food Res. 2024, 4, 100483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Xiang, D.B.; Yan, L.; Song, Y.; Zhao, G.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, B.L. Changes in Seed Growth, Levels and Distribution of Flavonoids during Tartary Buckwheat Seed Development. Plant Prod. Sci. 2016, 19, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loman, M.H.; Sible, C.N.; Below, F.E. Soybean planting date affects the relationships between soil test values and grain yield. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2024, 88, 2194–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, X.Y.; Xiang, D.B.; Shu, H.; Liao, M.; Zhao, G.; Shua, R.L.M.; Hai, L.J.M.; Lou, F.H. Effects of Different Sowing Dates on Growth and Yield of Buckweat. J. Henan Agric. Sci. 2013, 42, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.J.; Zhao, X.M.; Zuo, J.; Song, B.; Hu, C.F.; Chen, S.Y.; Zuo, J. Effects of Different Sowing Date on Agronomic and Economic Trait, and Yield of Diffeerent Sorghum Varieties and Their Correlations with Mian Metorological Factors. Guizhou Agric. Sci. 2023, 51, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.F.; Zhang, X.S.; Tang, Z.H.; Hong, D.F.; Ma, Y.; Wei, F.; Li, J.W.; Li, Z. Effect of rainy and less sunshine weather on maize yield in middle and late filling stage. China Seed Ind. 2013, 2, 46–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Yang, B.; Chen, J.; Liu, S.; Tang, J. The impact of climate change on agronomic traits of winter wheat in Yangzhou. BIO Web Conf. 2024, 142, 02010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Zhu, Y.M.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, M.S.; Xu, M.Y. Yield formation of different single-season rice (Oryza sativa L.) types and its relationships with meteorological factors in Yunnan Province of Southwest China. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao 2013, 24, 2831–2842. [Google Scholar]
- Shilo, S.; Lensky, I.M.; Bonfil, D.J. Using Satellite Data to Optimize Wheat Yield and Quality under Climate Change. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.H.; Zeng, Y.Y.; He, X.B.; Zhou, N.D.; Chen, J. Response of Grain Yield and Quality if High Quality Ruce to Climate Factors at Different Soeing Dates in Southeastern Zhejiang Province, China. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis 2023, 35, 736–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.B.; Song, Y.; Song, C.; Wan, Y.; Ye, X.L.; Liu, C.Y.; Liang, C.C.; Zhao, G. Seed setting and its spatial characteristics in Tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum). Phyton-Int. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 91, 1659–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Fan, Y.; Cui, L.; Li, C.; Guo, C. Cold Stress Response Mechanisms in Anther Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loitongbam, B.; Chandra, K.; Bisen, P.; Namrata; Thakur, P.; Sandhya. Breeding for Low Temperature Stress Tolerance in Reproductive Stage of Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Int. J. Bio-Resour. Stress Manag. 2017, 8, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.M.; Li, Y.C.; Xue, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.C.; Ma, X.; Han, X.; Ju, H.; Zhang, Q.Y. Spatial and Temporal Variations of Winter Wheat Quality and Key Meteorological Factors in China. J. Triticeae Crops 2023, 43, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Q.; Yu, X.F.; Gao, J.L.; Ma, D.L.; Guo, H.H.; Hu, S.P. Patterns of Influence of Meteorological Elements on Maize Grain Weight and Nutritional Quality. Agronomy 2023, 13, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingos, I.F.N.; Bilsborrow, P.E. The effect of variety and sowing date on the growth, development, yield and quality of common buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench). Eur. J. Agron. 2021, 126, 126264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, K.Y.; Li, K. Detection of Meteorological Influence on Bread Wheat Quality in Hebei Province, China Based on The Gradient Boosting Decision Tree. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1083665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Shen, X.Q.; Han, Y.J.; Guo, K.J. Analysis of Key Meteorological Factors for Planting Quality Reaching the Standardof Strong Gluten Wheat in Henan Province. Chin. J. Agrometeorol. 2023, 44, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.S.; Li, L.; Feng, Y.J.; Wang, T.; Li, C.L.; Wu, H.L.; Hu, Y.F.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, H.X. Impact of heat stress on the development, physiological and biochemical characteristics of Tartary buckwheat flowers, and its transcriptomic analysis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2025, 220, 109535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Y.; Yi, Y.; Liang, H.; Wei, S.Q.; Jiang, L.G.; Ali, I.; Ullah, S.; Zhao, Q. Effects of Meteorological Factors on the Yield and Quality of Special Rice in Different Periods after Anthesis. Agric. Sci. 2019, 10, 451–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Year | Sowing Date | X1 (°C) | X2 (d) | X3 (h) | X4 (mm) | X5 (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | 6/15 | 16.7 | 12 | 338.5 | 19.8 | 6.8 |
| 6/26 | 15.3 | 17 | 332.7 | 24.4 | 5.4 | |
| 7/6 | 11.8 | 29 | 318.5 | 8.4 | 6.6 | |
| 7/17 | 8.9 | 30 | 309.0 | 1.6 | 9.1 | |
| 2023 | 6/19 | 16.8 | 11 | 333.6 | 24.4 | 5.7 |
| 6/30 | 15.3 | 18 | 329.5 | 24.2 | 5.4 | |
| 7/10 | 10.7 | 27 | 316.6 | 10.2 | 7.3 | |
| 7/21 | 9.0 | 31 | 307.3 | 2.0 | 9.0 |
| Year | Sowing Date | Emergence Stage | Squaring Period | Full-Bloom Stage | Maturity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | 6/15 | 7/21 | 8/13 | 9/8 | 10/5 |
| 6/26 | 8/3 | 8/18 | 9/11 | 10/11 | |
| 7/6 | 8/14 | 9/7 | 9/24 | 10/30 | |
| 7/17 | 8/27 | 9/19 | 9/31 | 11/18 | |
| 2023 | 6/19 | 7/24 | 8/18 | 9/14 | 10/10 |
| 6/30 | 8/6 | 8/22 | 9/14 | 10/15 | |
| 7/10 | 8/18 | 9/10 | 9/28 | 11/3 | |
| 7/21 | 9/5 | 9/25 | 10/4 | 11/21 |
| Year | Sowing Date | Yield kg·hm2 | 1000-Seeds Weight (g) | Seeds per Plant | Seed Weight per Plant (g) | Seed Setting Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | 6/15 | 2187.7 ± 78.6 a | 22.69 ± 0.39 a | 183.9 ± 4.7 a | 4.17 ± 0.06 a | 21.84 ± 0.55 a |
| 6/26 | 1810.1 ± 174.3 b | 22.30 ± 0.71 a | 161.7 ± 9.4 a | 3.61 ± 0.29 b | 17.00 ± 0.49 b | |
| 7/6 | 660.0 ± 62.4 c | 17.05 ± 0.36 b | 105.5 ± 5.4 b | 1.80 ± 0.11 c | 11.40 ± 0.74 c | |
| 7/17 | 415.8 ± 60.4 c | 14.73 ± 0.59 c | 87.7 ± 1.9 c | 1.29 ± 0.07 d | 8.62 ± 0.55 d | |
| 2023 | 6/19 | 1983.5 ± 167.0 a | 22.92 ± 0.12 a | 175.4 ± 3.4 a | 6.43 ± 0.16 a | 21.49 ± 0.92 a |
| 6/30 | 1746.2 ± 189.9 a | 22.64 ± 0.52 a | 155.7 ± 14.2 a | 5.64 ± 0.52 a | 16.48 ± 0.82 ab | |
| 7/10 | 596.3 ± 116.6 b | 15.38 ± 0.87 b | 104.8 ± 12.5 b | 2.59 ± 0.43 b | 11.17 ± 0.59 bc | |
| 7/21 | 364.4 ± 89.1 b | 13.73 ± 0.59 b | 83.0 ± 9.0 c | 1.83 ± 0.28 b | 7.84 ± 0.53 c |
| Year | Sowing Date | Flavonoid Content (%) | Protein Content (%) | Starch Content (%) | Lipid Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | 6/15 | 1.719 ± 0.043 c | 10.65 ± 0.118 c | 74.43 ± 0.97 a | 2.470 ± 0.128 a |
| 6/26 | 1.813 ± 0.041 bc | 11.26 ± 0.070 b | 71.77 ± 0.51 b | 2.350 ± 0.070 ab | |
| 7/6 | 1.870 ± 0.049 ab | 12.35 ± 0.111 a | 68.80 ± 0.36 c | 2.243 ± 0.093 bc | |
| 7/17 | 1.890 ± 0.038 a | 12.33 ± 0.078 a | 65.83 ± 0.45 d | 2.103 ± 0.067 c | |
| 2023 | 6/19 | 1.864 ± 0.017 c | 11.25 ± 0.086 c | 73.37 ± 1.11 a | 2.650 ± 0.089 a |
| 6/30 | 2.039 ± 0.017 bc | 11.85 ± 0.082 b | 70.57 ± 1.25 b | 2.520 ± 0.072 ab | |
| 7/10 | 2.076 ± 0.012 ab | 12.69 ± 0.050 b | 66.50 ± 0.66 c | 2.377 ± 0.085 bc | |
| 7/21 | 2.109 ± 0.027 a | 12.77 ± 0.025 a | 64.47 ± 1.11 d | 2.247 ± 0.078 c |
| Meteorological Factor | Y1 | ||||
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | |
| X1 | −0.5234 | 0.5197 | 0.6995 | 0.0430 | |
| X2 | −0.7297 | 0.4905 | 0.6294 | 0.0324 | |
| X3 | −0.7561 | −0.5118 | 0.6689 | 0.0409 | |
| X4 | −0.7192 | −0.4641 | 0.4726 | 0.0509 | |
| X5 | −0.5705 | −0.3077 | 0.3729 | 0.6574 | |
| Meteorological Factor | Y2 | ||||
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | |
| X1 | −0.2453 | 0.4859 | 0.2661 | 0.1511 | |
| X2 | 0.1359 | 0.4585 | 0.2394 | 0.1137 | |
| X3 | 0.1408 | −0.2399 | 0.2544 | 0.1437 | |
| X4 | 0.1340 | −0.2176 | 0.4418 | 0.1790 | |
| X5 | 0.1063 | −0.1443 | 0.3487 | 0.2500 | |
| Meteorological Factor | Y3 | ||||
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | |
| X1 | −0.6588 | 0.0916 | −0.5947 | −0.1272 | |
| X2 | 0.6361 | 0.0864 | −0.5351 | −0.0957 | |
| X3 | 0.6592 | −0.6443 | −0.5687 | −0.1210 | |
| X4 | 0.6268 | −0.5842 | 0.0833 | −0.1507 | |
| X5 | 0.4973 | −0.3873 | 0.0657 | −0.5589 | |
| Meteorological Factor | Y1 | ||||
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | |
| X1 | −0.4506 | −1.2997 | −0.7690 | −0.7798 | |
| X2 | −0.1516 | −1.2267 | −0.6919 | −0.5865 | |
| X3 | −0.1571 | −0.4407 | −0.7353 | −0.7417 | |
| X4 | −0.1494 | −0.3996 | −1.1819 | −0.9237 | |
| X5 | −0.1185 | −0.2650 | −0.9327 | −0.7226 | |
| Meteorological Factor | Y2 | ||||
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | |
| X1 | 0.2156 | 0.5209 | −0.3197 | 0.0901 | |
| X2 | 1.0416 | 0.4917 | −0.2877 | 0.0677 | |
| X3 | 1.0792 | 0.2108 | −0.3057 | 0.0857 | |
| X4 | 1.0265 | 0.1911 | 0.4737 | 0.1067 | |
| X5 | 0.8143 | 0.1267 | 0.3738 | −0.3004 | |
| Meteorological Factor | Y3 | ||||
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | |
| X1 | −2.0541 | −1.9643 | −1.6819 | −1.0637 | |
| X2 | 1.1513 | −1.8540 | −1.5133 | −0.8000 | |
| X3 | 1.1930 | −2.0089 | −1.6081 | −1.0118 | |
| X4 | 1.1346 | −1.8215 | −1.7863 | −1.2601 | |
| X5 | 0.9001 | −1.2080 | −1.4097 | −1.5804 | |
| Meteorological Factor | Y4 | ||||
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | |
| X1 | −1.2199 | −2.2571 | −0.08870 | −0.7321 | |
| X2 | −0.2931 | −2.1304 | −0.07981 | −0.5506 | |
| X3 | −0.3037 | −1.1930 | −0.08480 | −0.6964 | |
| X4 | −0.2889 | −1.0817 | −2.0526 | −0.8673 | |
| X5 | −0.2292 | −0.7172 | −1.6198 | −0.08335 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Sun, J.; Chen, H.; Yan, Z.; Liu, S.; Liu, L.; Cao, X. Path Analysis on the Meteorological Factors Impacting Yield of Tartary Buckwheat at Different Sowing Dates. Agronomy 2025, 15, 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040950
Zhang J, Sun J, Chen H, Yan Z, Liu S, Liu L, Cao X. Path Analysis on the Meteorological Factors Impacting Yield of Tartary Buckwheat at Different Sowing Dates. Agronomy. 2025; 15(4):950. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040950
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jin, Jing Sun, Hong Chen, Zhiming Yan, Sichen Liu, Longlong Liu, and Xiaoning Cao. 2025. "Path Analysis on the Meteorological Factors Impacting Yield of Tartary Buckwheat at Different Sowing Dates" Agronomy 15, no. 4: 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040950
APA StyleZhang, J., Sun, J., Chen, H., Yan, Z., Liu, S., Liu, L., & Cao, X. (2025). Path Analysis on the Meteorological Factors Impacting Yield of Tartary Buckwheat at Different Sowing Dates. Agronomy, 15(4), 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040950





