Synergistic Effects of Mineralization Degree and Sodium Adsorption Ratio on the Rhizosphere Bacterial Community and Soil Nutrients of Upland Cotton Under Saline Water Irrigation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Test Area
2.2. Experiment Design
2.3. Determination Items and Methods
2.3.1. Soil Moisture Content and Sodium Adsorption Ratio Determination
2.3.2. Soil Nutrients and pH Determination
2.3.3. Collection of Rhizosphere Bacterial
2.3.4. Determination of Rhizosphere Bacterial Community Diversity [41,42,43]
- Sample DNA Extraction and Detection: Nucleic acids were extracted using the OMEGA Soil DNA Kit (D5635-02) (Omega Bio-Tek, Norcross, GA, USA). The extracted DNA was subjected to 0.8% agarose gel electrophoresis to assess molecular size and quantified using a Nanodrop.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction Amplification: The V3-V4 variable region of the 16S rRNA gene was amplified by PCR using a forward primer 338F (5′-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG-3′), which carries a barcode sequence, and a reverse primer 806R (5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′).
- Library Construction for Sequencing: Libraries were constructed using the TruSeq Nano DNA LT Library Prep Kit from Illumina (San Diego, CA, USA).
- Sequencing: For qualified libraries, perform paired-end sequencing on the Illumina NovaSeq (PE250) instrument (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA).
2.3.5. Data Processing
- Using QIIME2 version 2022.11 and following the official tutorial, the biological information of the microbiome was analyzed. The raw sequence data were decoded using the “demux” plugin, and the primers were removed using the “cutadapt” plugin. Then, sequence quality filtering, denoising, merging, and chimera removal were performed using the DADA2 plugin. The resulting sequences were clustered at 100% sequence similarity to generate the ASV (Amplicon Sequence Variant) representative sequences and the corresponding abundance table.
- Amplicon Sequence Variant Classification and Taxonomic Assignment: The Amplicon Sequence Variant (ASV) representative sequences were compared with the reference sequences in the Silva 138.1 database to obtain the taxonomic information for each ASV. All Amplicon Sequence Variants with abundance values below 0.001% of the total sequencing volume of all samples were removed, and the abundance matrix after removing rare ASVs was used for subsequent analysis. In the R 4.3.3 language environment, the VennDiagram package is used to draw petal diagrams; the ggplot2 package is used to draw bar charts and box plots; the vegan and dplyr packages are used for non-metric multidimensional scaling analysis and permutational multivariate analysis of variance, Redundancy analysis, and Mantel test correlation analysis; the RColorBrewer, igraph, psych, stringr, and dplyr packages are used for co-occurrence network analysis, and statistical analysis and visualization are conducted in Gephi 0.10; the LEfSe package in Python 3.9 and the ggtree package in R are used for Linear discriminant analysis Effect Size analysis.
3. Results
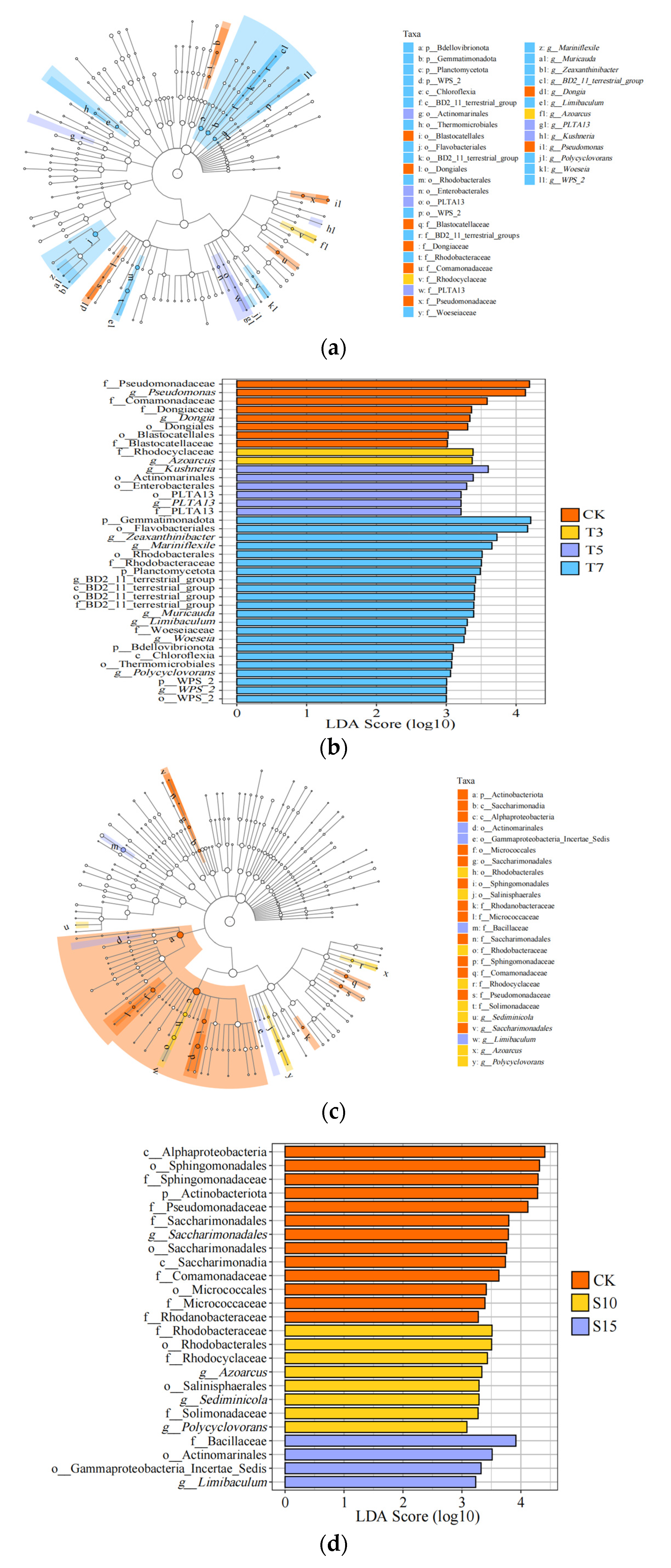
3.1. Influence of Saline Water Irrigation on the Structure of Rhizosphere Bacterial Communities
3.2. Impact of Saltwater Irrigation on Rhizosphere Bacterial Co-Occurrence Networks
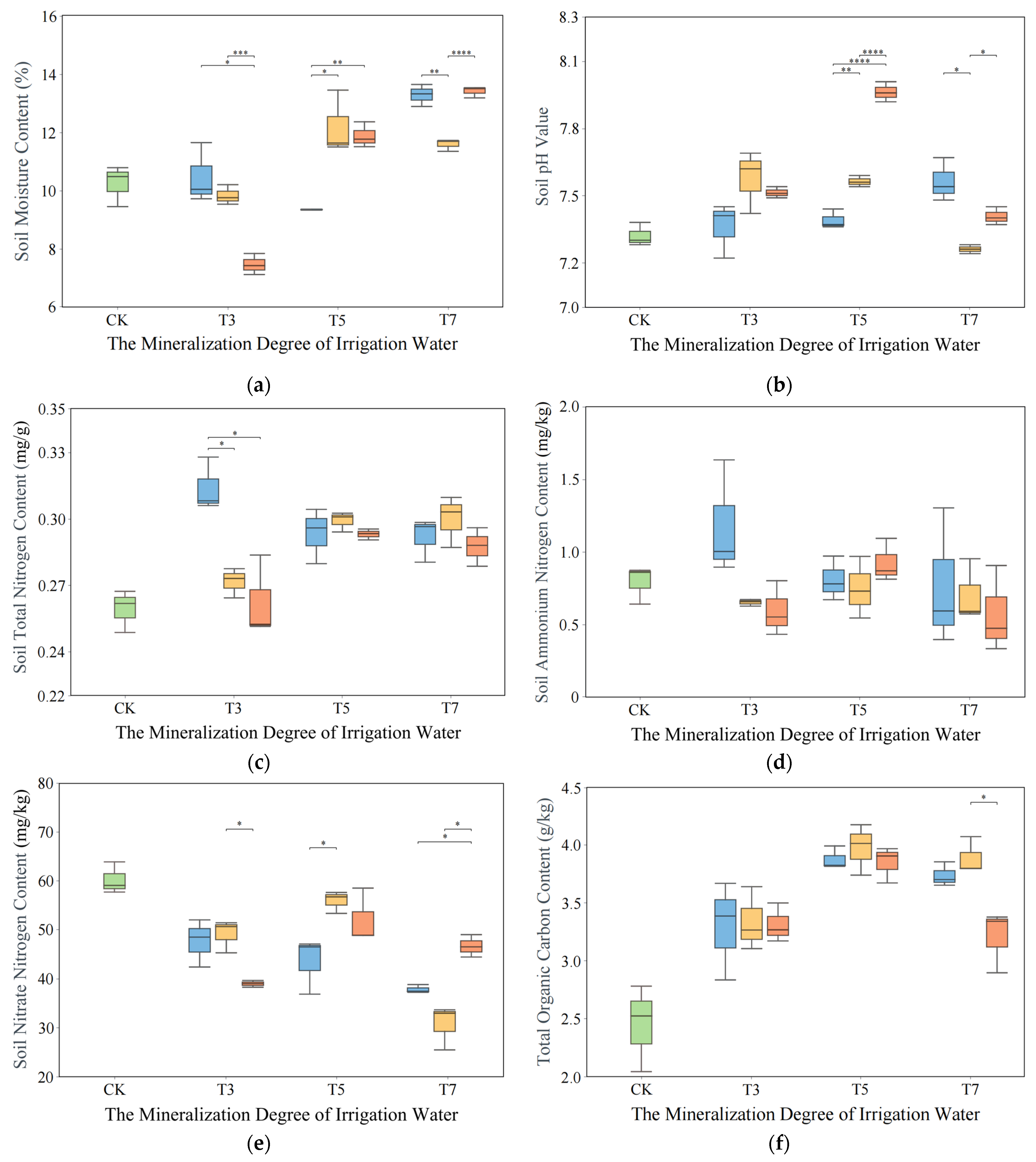
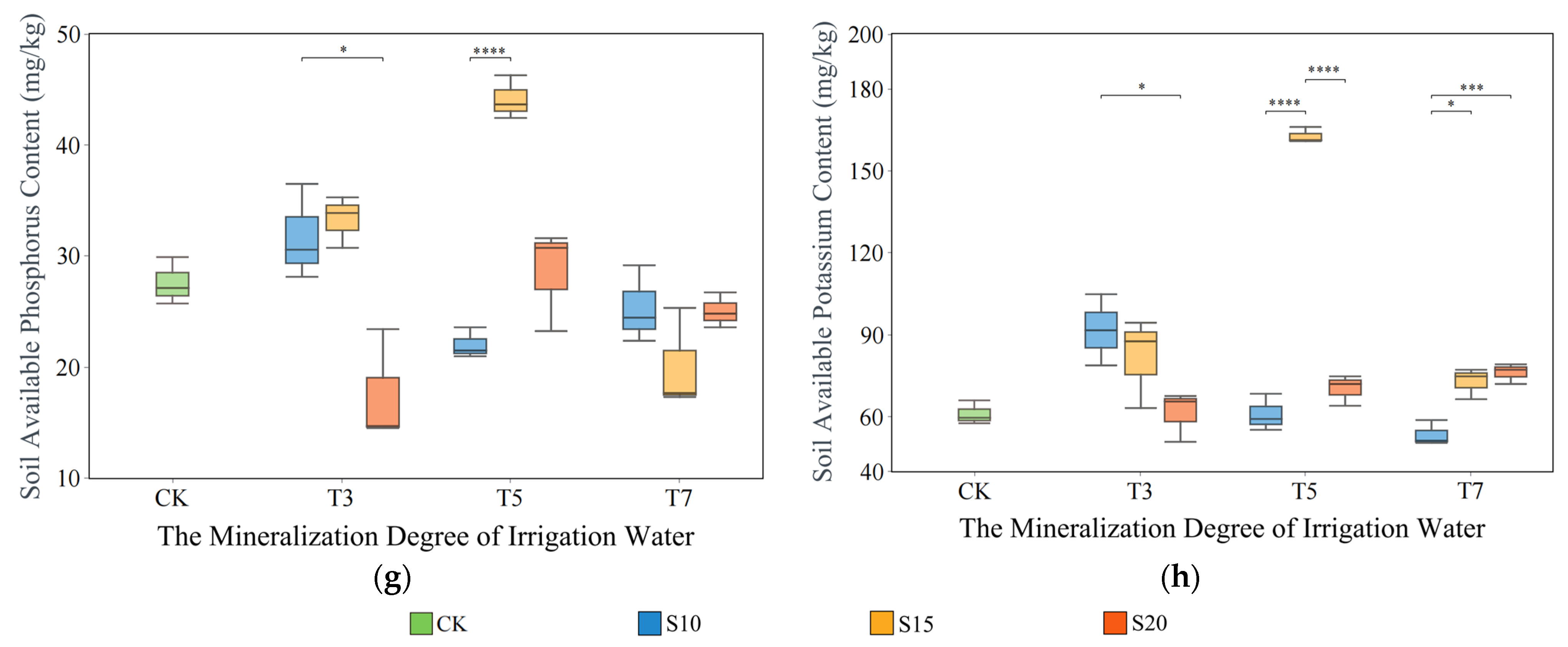
3.3. Impact of Saltwater Irrigation on Soil Environment
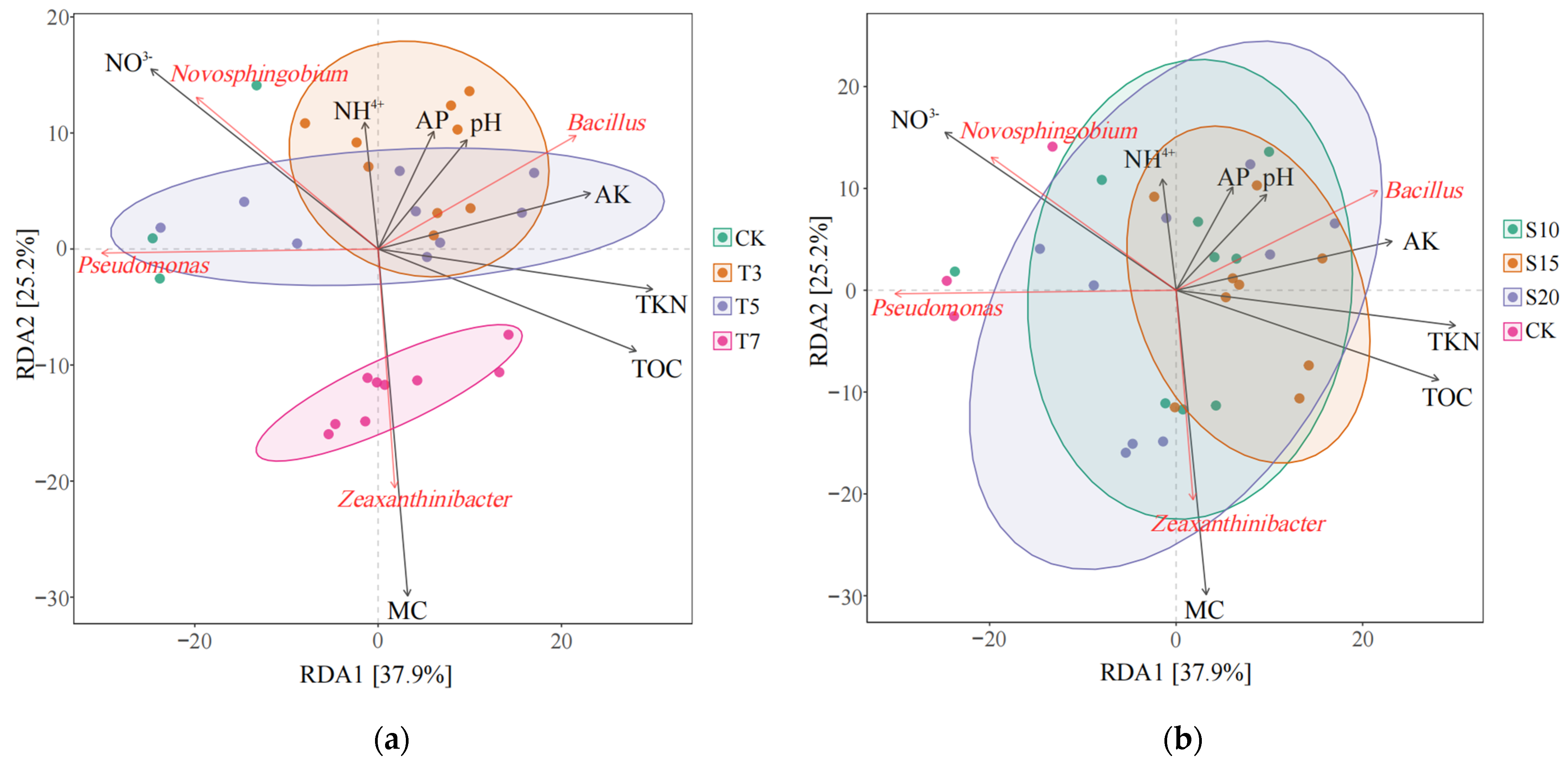
3.4. Relationship Between Rhizosphere Bacterial Community Structure and Soil Environmental Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of Irrigation Water Ion Composition on the Structure and Composition of Rhizosphere Bacteria in Cotton
4.2. Influence of Irrigation Water Ion Composition on the Topological Properties of Co-Occurrence Networks of Cotton Rhizosphere Bacterial Communities
4.3. Relationship Between the Composition of Bacterial Communities in the Rhizosphere of Cotton and Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AK | available potassium |
| AP | available phosphorus |
| ASVs | Amplicon Sequence Variants |
| LEfSe | Linear discriminant analysis Effect Size |
| LDA | Linear discriminant analysis |
| MC | soil moisture content |
| MD | mineralization degree |
| NH4+-N | ammonium nitrogen |
| NMDS | non-metric multidimensional scaling |
| NO3−-N | nitrate nitrogen |
| PERMANOVA | permutational multivariate analysis of variance |
| RDA | Redundancy analysis |
| SAR | sodium adsorption ratio |
| TOC | total organic carbon |
| TKN | total nitrogen |
References
- USDA Foreign Agricultural Service. Cotton: World Markets and Trade. 11 February 2025. Available online: https://usda.library.cornell.edu/concern/publications/kp78gg36g?locale=en (accessed on 17 March 2025).
- Rao, S.S.; Tanwar, S.P.S.; Regar, P.L. Effect of deficit irrigation, phosphorous inoculation and cycocel spray on root growth, seed cotton yield and water productivity of drip irrigated cotton in arid environment. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 169, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Soothar, R.K.; Shar, S.U.; Alharthi, B.; Shaikh, I.A.; Laghari, M.; Das, S.J.; Samoon, A.; Jamali, N.A.; Fiaz, S.; et al. Responses of cotton yield and water productivity to irrigation management: Assessment of economic costs, interactive effects of deficit irrigation water and soil types. Discov. Life 2025, 55, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ding, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Tan, J.; Ge, X. Spatial heterogeneity response of soil salinization inversion cotton field expansion based on deep learning. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1437390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL/visualize (accessed on 17 March 2025).
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. Announcement on Cotton Production in 2024. National Bureau of Statistics of China. 25 December 2024. Available online: https://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/zxfb/202412/t20241225_1957879.html (accessed on 2 March 2025).
- Wu, Q.; Liang, Y.; Gao, F.; Du, M.L.; Wu, B.; Liu, J. Analysis of chemical characteristics, distribution and cause of formation of brackish water in Alar City, Xinjiang. Environ. Chem. 2021, 40, 737–745. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Global Status of Salt-Affected Soils—Main Report; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhao, L.; Wang, C.; Huang, H.; Zhuang, M. Synergistic improvement of carbon sequestration and crop yield by organic material addition in saline soil: A global meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 891, 164530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghassemi, F. Salinisation of Land and Water Resources: Human Causes, Extent, Management and Case Studies; University of New South Wales Press Ltd.: Sydney, Australia, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Litalien, A.; Zeeb, B. Curing the earth: A review of anthropogenic soil salinization and plant-based strategies for sustainable mitigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavi, I.; Thevs, N.; Priori, S. Soil Salinity and Sodicity in Drylands: A Review of Causes, Effects, Monitoring, and Restoration Measures. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 712831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Nan, L.; Li, B.; Cao, S. Effects of solute types and degree of mineralization on salt ions in soil release solution. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Mojtaba, M.; Mohsen, F.; Naser, B. Adsorption Isotherms of Boron in Soil: The effects of Sodium Adsorption Ratio (SAR), pH and Ionic strength. Majallah-I Āb Va Khāk 2017, 30, 1954–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, G.d.O.; Martins Filho, S.; Reis, E.F.d.; Moraes, W.B.; Nazário, A.d.A. Chemical changes in two soils irrigated with saline water. Ciên. Agron. 2008, 39, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, S.; Arshad, S.; Bashir, B.; Ata, B.; Al-Dalahmeh, M.; Alsalman, A.; Ali, H.; Alhennawi, S.; Kiwan, S.; Harsanyi, E. Evaluating machine learning performance in predicting sodium adsorption ratio for sustainable soil-water management in the eastern Mediterranean. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCleskey, R.B.; Cravotta, C.A.; Miller, M.P.; Tillman, F.; Stackelberg, P.; Knierim, K.J.; Wise, D.R. Salinity and total dissolved solids measurements for natural waters: An overview and a new salinity method based on specific conductance and water type. Appl. Geochem. 2023, 154, 105684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Moayedi, H.; Salari, M.; Le, B.N.; Ahmadi Dehrashid, A. Assessment of sodium adsorption ratio (SAR) in groundwater: Integrating experimental data with cutting-edge swarm intelligence approaches. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2024, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Feng, D.; Cao, C.; Zheng, C.; Dang, H.; Li, K.; Gao, Y.; Sun, C. Evaluating the impacts of long-term saline water irrigation on soil salinity and cotton yield under plastic film mulching: A 15-year field study. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 293, 108703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavi, M.S.; Sanderman, J.; Chittleborough, D.J.; Cox, J.W.; Marschner, P. Sorption of dissolved organic matter in salt-affected soils: Effect of salinity, sodicity and texture. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 435, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Zhang, A.; Zhu, C.; Dang, H.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, J.; Cao, C. Saline Water Irrigation Changed the Stability of Soil Aggregates and Crop Yields in a Winter Wheat–Summer Maize Rotation System. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, M.T.; Majeed, S.; Rana, I.A.; Ali, Z.; Jia, Y.; Du, X.; Hinze, L.; Azhar, M.T. Impact of salinity stress on cotton and opportunities for improvement through conventional and biotechnological approaches. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, N.; Dong, Q.; Luo, T.; Zhang, X.; Song, M.; Wang, X.; Ma, X. New developments in understanding cotton’s physiological and molecular responses to salt stress. Plant Stress 2025, 15, 100742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghbel, F.; Fazel, F.; Aguilar, J.; Mostafazadeh-Fard, B.; Mosaedi, A.; Howell, N. Maintaining Silage Corn Production Under Sodic Irrigation Water Conditions in a Semi-Arid Environment. Agronomy 2025, 15, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.H.; Adhikari, M.; Jeong, S.S.; Lee, S.P.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, G.S.; Park, D.H.; Kim, H.; Yang, J.E. Microbial diversity of soils under different land use and chemical conditions. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2024, 67, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Bai, Y.; Guo, S.; He, Z.; Wang, B.; Liu, H.; Zhai, J.; Cao, H. Effect of Irrigation Water Salinity on Soil Characteristics and Microbial Communities in Cotton Fields in Southern xinjiang, China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, X.; Jin, M.; Wang, R.; Chen, J.; Guo, S. Reduced co-occurrence and ion-specific preferences of soil microbial hub species after ten years of irrigation with brackish water. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 199, 104599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Sun, C.; Cai, S.; Liu, F.; Xie, H.; Xiong, Q. Research progress in crop root biology and nitrogen uptake and use, with emphasis on cereal crops. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukun, G.; Jianghui, C.; Genzeng, R.; Shilin, W.; Puyuan, Y.; Congpei, Y.; Hongkai, L.; Jinhua, C. Changes in the root-associated bacteria of sorghum are driven by the combined effects of salt and sorghum development. Environ. Microbiome 2021, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hnini, M.; Aurag, J. Genetic diversity, stress tolerance and phytobeneficial potential in rhizobacteria of Vachellia tortilis subsp. raddiana. Environ. Microbiome 2024, 19, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; La, S.; Zhang, X.; Gao, L.; Tian, Y. Salt-induced recruitment of specific root-associated bacterial consortium capable of enhancing plant adaptability to salt stress. ISME J. 2021, 15, 2865–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; He, G.; Yang, T.; Kong, C. Effects of different fertilization treatments on coffee bean quality and rhizosphere microorganisms. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2025, 71, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, N.; Khalil, S.; Cardinale, M.; Rasheed, A.; Zhao, F.; Abideen, Z. A comprehensive evaluation of the potential of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria for applications in agriculture in stressed environments. Pedosphere 2025, 35, 229–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark Ibekwe, A.; Ors, S.; Ferreira JF, S.; Liu, X.; Suarez, D.L. Seasonal induced changes in spinach rhizosphere microbial community structure with varying salinity and drought. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1485–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Guo, X.-W.; Yang, M.-Q.; Min, W.; Guo, H.-J. Microbial Community Structure and Functional Genes of Phosphorus Cycling in Cotton Field Soil Under Long-term Saline Drip Irrigation. Huanjing Kexue 2025, 46, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Feng, X.; Liu, X.; Ju, Z. Long-term freezing saline water irrigation and cotton cultivation improved soil properties and maintained low salinity in the root zone of coastal saline soil. Soil Use Manag. 2024, 40, e13117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Wang, L.; Xie, Y.; Sun, J.; Ning, H.; Han, Q.; Kanneh, J.E.; Liu, H. Optimizing canopy structure through equal row spacing and appropriate irrigation enhances machine-harvested seed cotton yield and quality. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 216, 118799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Ning, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, W.; Xu, P.; Song, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, X.; Liu, H. Reducing the Sodium Adsorption Ratio Improves the Soil Aggregates and Organic Matter in Brackish-Water-Irrigated Cotton Fields. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tianqi24.com. (n.d.). Alar Temperature: Monthly Temperature Trends for Alar City in 2024. Available online: https://www.tianqi24.com/alaer/history2024.html (accessed on 16 March 2025).
- Guo, K.; Liu, X. The successive infiltration of various saline waters accelerates the infiltration processes and enhances the salt leaching in a coastal saline soil. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 5083–5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Subramanian, S.; Faith, J.J.; Gevers, D.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R.; Mills, D.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing. Nat Methods 2013, 10, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Druzhinina, I.S.; Pan, X.; Yuan, Z. Microbially mediated plant salt tolerance and microbiome-based solutions for saline agriculture. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 1245–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, C.; Feng, Q.; Wei, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Li, H. Shifts in soil microbial metabolic activities and community structures along a salinity gradient of irrigation water in a typical arid region of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhou, T.; Huang, G.; Xiong, Y. Soil microbial community and associated functions response to salt stresses: Resistance and resilience. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamim, A.; Sanka Loganathachetti, D.; Chandran, S.; Masmoudi, K.; Mundra, S. Salinity of irrigation water selects distinct bacterial communities associated with date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) root. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, N.; Marschner, P.; Burns, R.G. Soil microbial activity and community composition: Impact of changes in matric and osmotic potential. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Du, S.; Guo, H.; Min, W. Long-term saline water drip irrigation alters soil physicochemical properties, bacterial community structure, and nitrogen transformations in cotton. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 182, 104719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Shi, Y.; Cui, X.; Yue, P.; Li, K.; Liu, X.; Tripathi, B.M.; Chu, H. Salinity is a key determinant for soil microbial communities in a desert ecosystem. Msystems 2019, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Miao, S.; Song, Y.; Wang, X.; Jin, F. Biochar application reduces saline–alkali stress by improving soil functions and regulating the diversity and abundance of soil bacterial community in highly saline–alkali paddy field. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousk, J.; Bååth, E.; Brookes, P.C.; Lauber, C.L.; Lozupone, C.; Caporaso, J.G.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Soil bacterial and fungal communities across a pH gradient in an arable soil. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Guo, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Ren, M.; Zhao, P.; Huang, Z.; Jia, H.; Wang, J.; Lin, A. Effective strategies for reclamation of saline-alkali soil and response mechanisms of the soil-plant system. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drabesch, S.; Lechtenfeld, O.J.; Bibaj, E.; León Ninin, J.M.; Lezama Pachecco, J.; Fendorf, S.; Friedrich-Planer, B.; Kappler, A.; Muehe, E.M. Climate induced microbiome alterations increase cadmium bioavailability in agricultural soils with pH below 7. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-G.; Bian, X.-M.; Li, Y.-B.; Zhang, W.; Li, S. Effects of long-term continuous cropping of cotton and returning cotton stalk into field on soil biological activities. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2008, 19, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar]
- Petermann, B.J.; Acosta-Martinez, V.; Laza, H.E.; Lewis, K.; Steffan, J.; Slaughter, L.C. Soil bacterial and fungal microbiomes under cotton production are more sensitive to tillage and cover crops than irrigation level in a semi-arid sandy soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 204, 105711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, A.; Wan, W.; Luo, X.; Zheng, L.; He, G.; Huang, D.; Chen, W.; Huang, Q. High salinity inhibits soil bacterial community mediating nitrogen cycling. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e01366-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Wang, Z.; Hu, L.; Wang, L.; Fang, J.; Liu, R. Comparative Genomics Reveal Distinct Environment Preference and Functional Adaptation Among Lineages of Gemmatimonadota. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, H.; Yue, Y.; Nair, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Adaptive traits of Planctomycetota bacteria to thrive in macroalgal habitats and establish mutually beneficial relationship with macroalgae. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2024, 9, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.M.; Zhou, Y.L.; Wei, Z.F.; Wang, Y. Phylogenomic insights into distribution and adaptation of Bdellovibrionota in marine waters. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xie, J.; Yang, M.; Cai, R.; Cai, C.; Gan, Y.; Aweya, J.J.; Cai, G.; Wang, H. Marine Flavobacteriaceae produce zeaxanthin via the mevalonate pathway. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2025, 7, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Jeong, H.I.; Jeong, S.E.; Jeon, C.O. Zeaxanthinibacter aestuarii sp. nov., isolated from estuary sediment and emended description of the genus Zeaxanthinibacter Asker et al. 2007. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 3264–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanenko, L.; Bystritskaya, E.; Savicheva, Y.; Eremeev, V.; Otstavnykh, N.; Kurilenko, V.; Velansky, P.; Isaeva, M. Description and whole-genome sequencing of Mariniflexile litorale sp. nov., isolated from the shallow sediments of the sea of Japan. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.P.; He, Y.Y.; Li, J.H.; Lü, Z.L.; Zhang, Y.W.; Li, Y.H.; Li, J.L.; Zhang, M.X.; Cao, Y.H.; Zhang, J.L. Planting halophytes increases the rhizosphere ecosystem multifunctionality via reducing soil salinity. Environ. Res. 2024, 261, 119707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, K.; Bienhold, C.; Buttigieg, P.L.; Knittel, K.; Laso-Pérez, R.; Rapp, J.Z.; Boetius, A.; Offre, P. Diversity and metabolism of Woeseiales bacteria, global members of marine sediment communities. ISME J. 2020, 14, 1042–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zhang, X.; Luan, S.; Zhou, H.; Liu, L.; Qu, Y. Diversity and structure of soil bacterial community in intertidal zone of Daliao River estuary, Northeast China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 163, 111965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Liang, J.; Wang, R.; Chi, L.; Wang, W.; Tan, J.; Shi, H.; Song, X.; Cui, Z.; Xie, Q.; et al. Response of bacterial community metabolites to bacterial wilt caused by Ralstonia solanacearum: A multi-omics analysis. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 14, 1339478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, M.L.; Liu, L.M.; Guo, Y.S.; Chen, J.F. Effects of Fertilizers Applied on Growth of Kandelia obovata Seedlings and Microbial Community in Soil. Fujian J. Agric. Sci. 2024, 39, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zuo, X.; Wei, G.; Wang, H.; Gao, Y.; Ling, W. Immobilized Pseudomonas spp. for bioremediation of soils contaminated with emerging organic pollutants. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 204, 105717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, T.; Singh, R.; Singh, H.; Bhanwaria, R.; Gandhi, S.G.; Bhardwaj, R.; Gandhi, S.G.; Bhardwaj, R.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, P. Pseudomonas consortium improves soil health and alleviates cadmium (Cd) toxicity in Brassica juncea L. via biochemical and in silico approaches. Plant Stress 2024, 14, 100611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.X.; Luo, B.J.; Guo, H.R.; Cen, S.J.; Zhang, H.Q.; Ge, T.D.; Wu, J.X.; Fan, X.L. Soil ecological effects of soil fumigation and microbial agents controlling continuous melon barrier in high tunnel. Soils Crops 2024, 13, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakor, R.; Mistry, H.; Bariya, H. Isolation and Identification of Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria: Azoarcus Species. In Practical Handbook on Agricultural Microbiology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, H.; Prandoni, N.; Fernández-Pascual, M.; Fajardo, S.; Morcillo, C.; Diaz, E.; Carmona, M. Azoarcus sp. CIB, an anaerobic biodegrader of aromatic compounds shows an endophytic lifestyle. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.H.; Sung, H.; Kim, H.S.; Tak, E.J.; Kang, W.; Lee, J.Y.; Hyun, D.W.; Kim, P.S.; Bae, J.W. Complete genome sequence of the halophile bacterium Kushneria konosiri X49 T, isolated from salt-fermented Konosirus punctatus. Stand. Genom. Sci. 2018, 13, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.X.; Chen, M.; Zhang, W.; Tang, J.H.; Li, Y.T.; Gu, P.; Lu, Y. Characterization of bacterial communities in freshwater and seawater of the Yellow River estuary by 16S rRNA gene high-throughput absolute abundance quantification. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2024, 64, 4338–4357. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Jin, Z.; Wang, X.; George, T.S.; Feng, G.; Zhang, L. Simulated root exudates stimulate the abundance of Saccharimonadales to improve the alkaline phosphatase activity in maize rhizosphere. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 170, 104274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, H.F.; Lesaulnier, C.; Pelikan, C.; Gutierrez, T. Visualisation of the obligate hydrocarbonoclastic bacteria Polycyclovorans algicola and Algiphilus aromaticivorans in co-cultures with micro-algae by CARD-FISH. J. Microbiol. Methods 2018, 152, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.T.; Nakagawa, Y.; Harayama, S. Sediminicola luteus gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel member of the family Flavobacteriaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 841–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Zhu, G.; Pascual-Garcia, A.; Dini-Andreote, F.; Zheng, J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, S.; Jiang, Y. Unraveling the diversity dynamics and network stability of alkaline phosphomonoesterase-producing bacteria in modulating maize yield. Imeta 2024, 3, e260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Jin, J.; Lu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, Z. Bacterial diversity loss weakens community functional stability. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 202, 105536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, H.; Reich, P.B.; Banerjee, S.; van der Heijden, M.G.; Sadowsky, M.H.; Ishii, S.; Jia, X.; Shao, M.; et al. Erosion reduces soil microbial diversity, network complexity and multifunctionality. ISME J. 2021, 15, 2474–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Jiang, L.; Li, W.; Li, E.; Lv, G. Structural Characteristics and Assembly Mechanisms of Soil Microbial Communities under Water–Salt Gradients in Arid Regions. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, R.; Wang, Z. Rationale saline-water irrigation also serves as enhancing soil aggregate stability, regulating carbon emissions, and improving water use efficiency in oasis cotton fields. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 223, 120144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mougi, A. pH Adaptation stabilizes bacterial communities. NPJ Biodivers. 2024, 3, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zeng, J.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, X. pH is the primary determinant of the bacterial community structure in agricultural soils impacted by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollution. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rengasamy, P. World salinization with emphasis on Australia. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Zeng, W.; Hou, M.; Wang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Lei, G.; Zhou, B.; Huang, J. Responses of the soil microbial community to salinity stress in maize fields. Biology 2021, 10, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, S.; Wang, W.; Song, X.; Guo, D.; Lawi, A.S. Soil bacterial community characteristics and its effect on organic carbon under different fertilization treatments. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1356171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Chen, P.; Li, Z.G.; Li, L.Y.; Zhang, R.Q.; Hu, W.; Liu, Y. Soil aggregate-associated organic carbon mineralization and its driving factors in rhizosphere soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 186, 109182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, W.; Li, L.; Zhao, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Q.; Wei, L.; Wang, K.; Jiang, J. A critical review of effects, action mechanisms and mitigation strategies of salinity in anaerobic digestion. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 208, 115095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surey, R.; Schimpf, C.M.; Sauheitl, L.; Mueller, C.W.; Rummel, P.S.; Dittert, K.; Kaiser, K.; Böttcher, J.; Mikutta, R. Potential denitrification stimulated by water-soluble organic carbon from plant residues during initial decomposition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 147, 107841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Tang, T.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Neher, D.A.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, J.; Xiao, D.; Hu, P.; Wang, K.; et al. Nitrogen fertilization increases the niche breadth of soil nitrogen-cycling microbes and stabilizes their co-occurrence network in a karst agroecosystem. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 374, 109177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Fanin, N.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Du, G.; Hu, F.; Jiang, L.; Hu, S.; Liu, M. Nutrient-induced acidification modulates soil biodiversity-function relationships. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Frey, B.; Li, D.; Liu, X.; Chen, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Sui, X.; Li, M.H. Effects of organic nitrogen addition on soil microbial community assembly patterns in the Sanjiang Plain wetlands, northeastern China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 204, 105685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.Y.; Wang, Y.; Quan, X.; Tang, X.H.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Qu, L.P.; Yan, X.L. Ammonium and Nitrate Nitrogen Alter Bacterial Community in the Rhizospheres and Root Surfaces with Seedling Growth of Two Tree Species. Forests 2024, 15, 2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.; Wang, M.; Sui, X.; Frey, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Ni, H.; Li, M. High ammonium addition changes the diversity and structure of bacterial communities in temperate wetland soils of northeastern China. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kessel, M.A.; Speth, D.R.; Albertsen, M.; Nielsen, P.H.; Op den Camp, H.J.; Kartal, B.; Jetten, M.S.; Lücker, S. Complete nitrification by a single microorganism. Nature 2015, 528, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Berg, B.; Sun, T.; Wang, Z.; Han, X. Response of fine root decomposition to different forms of N deposition in a temperate grassland. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 147, 107845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, N.; Rai, A.K.; Krishnamurthy, S.L.; Singh, R.K.; Sundha, P.; Patel, S.; Bedwal, S.; Sharma, P.C. Nutrients availability in salt-affected soils varies with the ionic composition of solid and solution phases of inland and coastal agroecosystems of India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şentürk, E.; Atasoy, G.; Şanlıbaba, P. Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacteria: Biochemical and Molecular Characteristics. In Anammox Technology in Industrial Wastewater Treatment; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Shen, L.; Li, Y.; Cao, H.; Chen, C.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Z.; Lu, Y. Insights into the nitrogen transformation mechanism of Pseudomonas sp. Y15 capable of heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification. Environ. Res. 2024, 240, 117595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.J.; Jeon, Y.J.; Ko, M.S. Influence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa-based biopolymer on mitigating soil erosion and heavy metal dispersion. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 955, 176889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
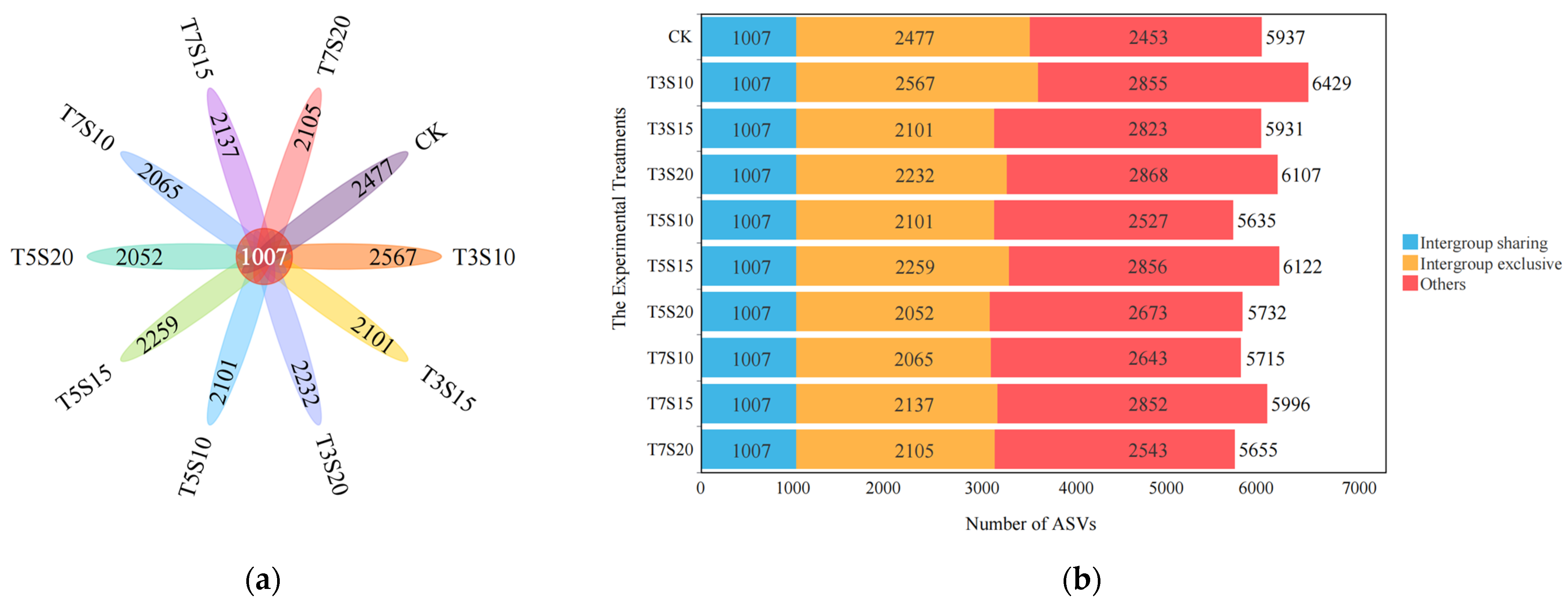
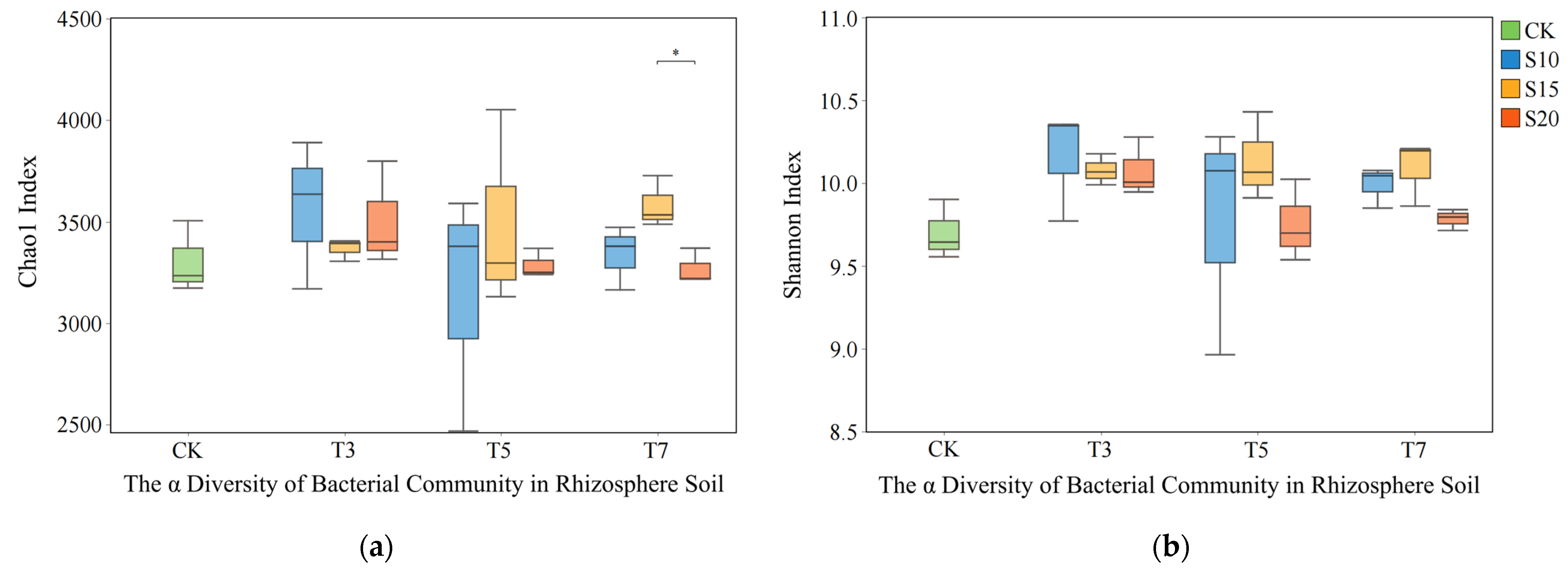
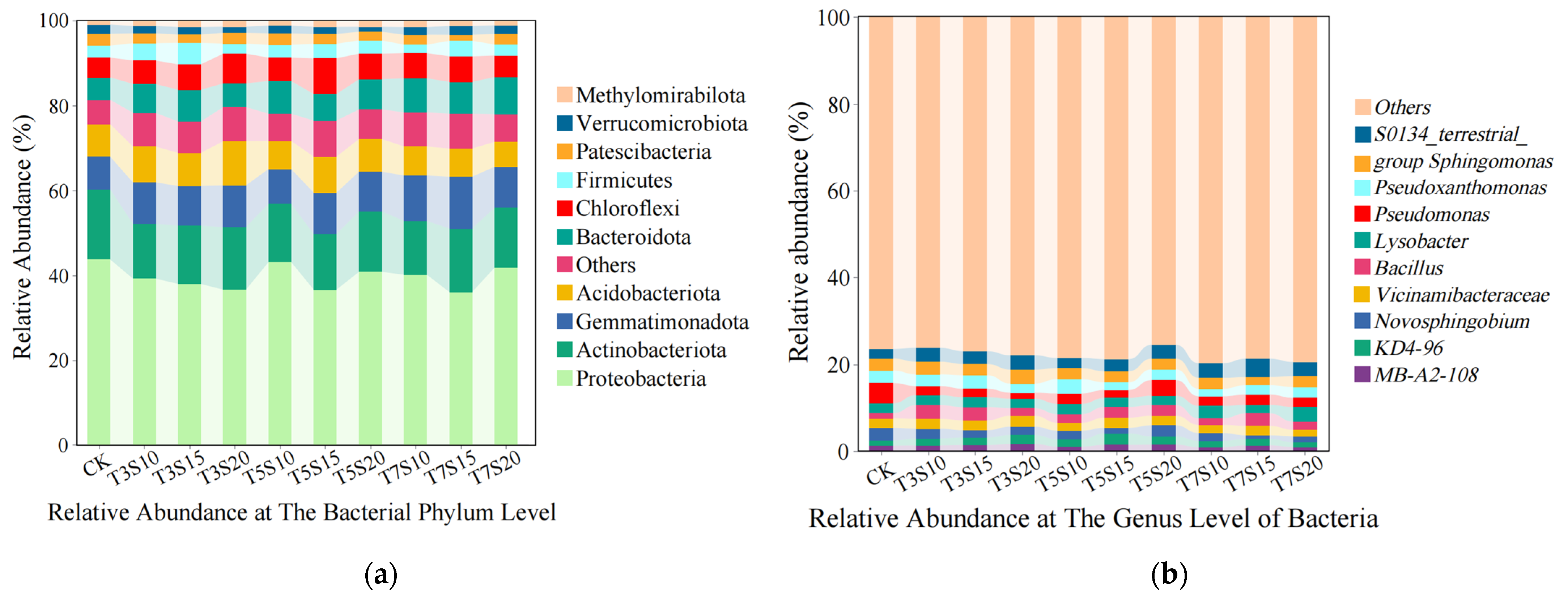
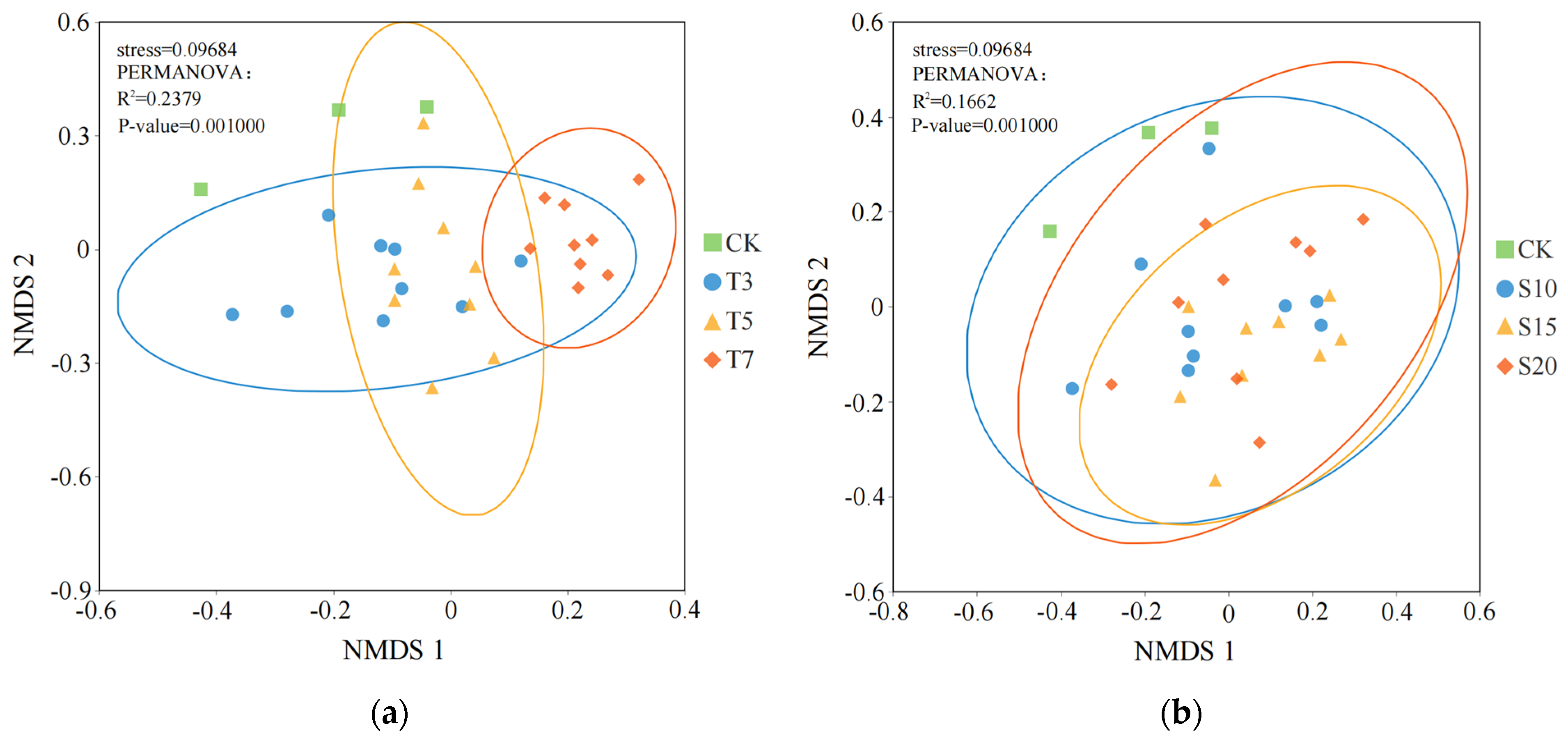

| Soil Depth (cm) | Na+ (g/kg) | Ca2+ (g/kg) | Mg2+ (g/kg) | Clay Particle (%) | Silt (%) | Sand (%) | Dry Bulk Density (g/cm3) | Field Capacity (cm3/cm−3) | Organic Matter (g/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0-20 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.37 | 17.05 | 82.58 | 1.6 | 0.26 | 5.66 |
| Treatments | MD (g/L) | SAR (mmol/L)1/2 | Na⁺ (mg/L) | Ca²⁺ (mg/L) | Cl⁻ (mg/L) | Mg²⁺ (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CG | 1.44 | 8.74 | 419.09 | 103.60 | 648.10 | 87.54 |
| T3S10 | 3 | 10 | 759.08 | 356.69 | 1616.02 | 87.54 |
| T3S15 | 3 | 15 | 918.27 | 209.40 | 1604.10 | 87.54 |
| T3S20 | 3 | 20 | 1013.00 | 121.78 | 1597.01 | 87.54 |
| T5S10 | 5 | 10 | 1077.46 | 789.42 | 2864.91 | 87.54 |
| T5S15 | 5 | 15 | 1350.00 | 536.00 | 2844.47 | 87.54 |
| T5S20 | 5 | 20 | 1532.23 | 368.69 | 2830.87 | 87.54 |
| T7S10 | 7 | 10 | 1344.74 | 1269.42 | 4117.63 | 87.54 |
| T7S15 | 7 | 15 | 1727.97 | 914.87 | 4088.95 | 87.54 |
| T7S20 | 7 | 20 | 1991.32 | 671.24 | 4069.24 | 87.54 |
| Treatments | Proportion of Positive Correlation Edges (%) | Proportion of Negatively Correlated Edges (%) | Average Degree | Network Density | Average Clustering Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CG | 58.01 | 41.99 | 113.207 | 0.379 | 0.983 |
| T3S10 | 51.85 | 48.15 | 104.22 | 0.349 | 0.986 |
| T3S15 | 51.05 | 48.95 | 112.993 | 0.378 | 0.976 |
| T3S20 | 50.43 | 49.57 | 103.94 | 0.348 | 0.988 |
| T5S10 | 54.60 | 45.40 | 114.147 | 0.382 | 0.985 |
| T5S15 | 54.51 | 45.49 | 103.513 | 0.346 | 0.993 |
| T5S20 | 56.12 | 43.88 | 128.993 | 0.431 | 0.987 |
| T7S10 | 52.54 | 47.46 | 108.993 | 0.365 | 0.986 |
| T7S15 | 52.07 | 47.93 | 104.307 | 0.349 | 0.990 |
| T7S20 | 57.39 | 42.61 | 115.96 | 0.388 | 0.983 |
| Treatments | Proteobacteria | Actinobacteriota | Acidobacteriota | Gemmatimonadota | Bacteroidota | Chloroflexi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CG | 43.67 | 17.67 | 8.00 | 7.33 | 5.67 | 5.00 |
| T3S10 | 40.33 | 16.00 | 7.67 | 10.33 | 7.00 | 5.67 |
| T3S15 | 41.00 | 16.00 | 6.67 | 9.67 | 8.00 | 6.33 |
| T3S20 | 38.33 | 19.00 | 8.00 | 10.67 | 5.67 | 7.00 |
| T5S10 | 42.33 | 15.67 | 6.00 | 8.67 | 8.67 | 5.67 |
| T5S15 | 41.33 | 15.00 | 7.00 | 9.00 | 5.00 | 8.67 |
| T5S20 | 41.33 | 18.00 | 7.00 | 9.00 | 5.67 | 6.33 |
| T7S10 | 41.33 | 15.67 | 6.00 | 11.67 | 6.33 | 6.00 |
| T7S15 | 37.00 | 17.00 | 6.33 | 13.00 | 6.00 | 6.33 |
| T7S20 | 41.00 | 16.33 | 4.67 | 11.33 | 8.00 | 5.33 |
| Environmental Factors | RDA 1 | RDA 2 | R2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MC | −0.236 | −0.972 | 0.5227 | 0.001 |
| TOC | −0.988 | −0.154 | 0.3413 | 0.006 |
| NO3−-N | 0.936 | 0.352 | 0.3163 | 0.006 |
| TKN | −0.100 | −0.027 | 0.2741 | 0.010 |
| AK | −0.919 | 0.395 | 0.0987 | 0.230 |
| NH4+-N | 0.320 | 0.947 | 0.0250 | 0.699 |
| AP | 0.070 | 0.998 | 0.0236 | 0.716 |
| pH | −0.408 | 0.913 | 0.0096 | 0.898 |
| Bacterial Genus-Level Species | Environmental Factors | r | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Novospingobium | NO3−-N | 0.1855 | 0.017 |
| Novospingobium | TOC | 0.1979 | 0.029 |
| Pseudomonas | NO3−-N | 0.1668 | 0.022 |
| Pseudomonas | TKN | 0.1574 | 0.048 |
| Pseudomonas | TOC | 0.3064 | 0.007 |
| Bacillus | NO3−-N | 0.2787 | 0.009 |
| Bacillus | TOC | 0.3721 | 0.004 |
| Zeaxanthinibacter | TOC | 0.3899 | 0.002 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Yang, G.; Ning, H.; Xie, Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, J. Synergistic Effects of Mineralization Degree and Sodium Adsorption Ratio on the Rhizosphere Bacterial Community and Soil Nutrients of Upland Cotton Under Saline Water Irrigation. Agronomy 2025, 15, 895. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040895
Zhang C, Yang G, Ning H, Xie Y, Song Y, Wang J. Synergistic Effects of Mineralization Degree and Sodium Adsorption Ratio on the Rhizosphere Bacterial Community and Soil Nutrients of Upland Cotton Under Saline Water Irrigation. Agronomy. 2025; 15(4):895. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040895
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Chenfan, Guang Yang, Huifeng Ning, Yucai Xie, Yinping Song, and Jinglei Wang. 2025. "Synergistic Effects of Mineralization Degree and Sodium Adsorption Ratio on the Rhizosphere Bacterial Community and Soil Nutrients of Upland Cotton Under Saline Water Irrigation" Agronomy 15, no. 4: 895. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040895
APA StyleZhang, C., Yang, G., Ning, H., Xie, Y., Song, Y., & Wang, J. (2025). Synergistic Effects of Mineralization Degree and Sodium Adsorption Ratio on the Rhizosphere Bacterial Community and Soil Nutrients of Upland Cotton Under Saline Water Irrigation. Agronomy, 15(4), 895. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040895






