Isolation of Bacteria from Agricultural Soils and Evaluation of Their Degradative Capacity for Organochlorine and Organophosphorus Pesticides
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
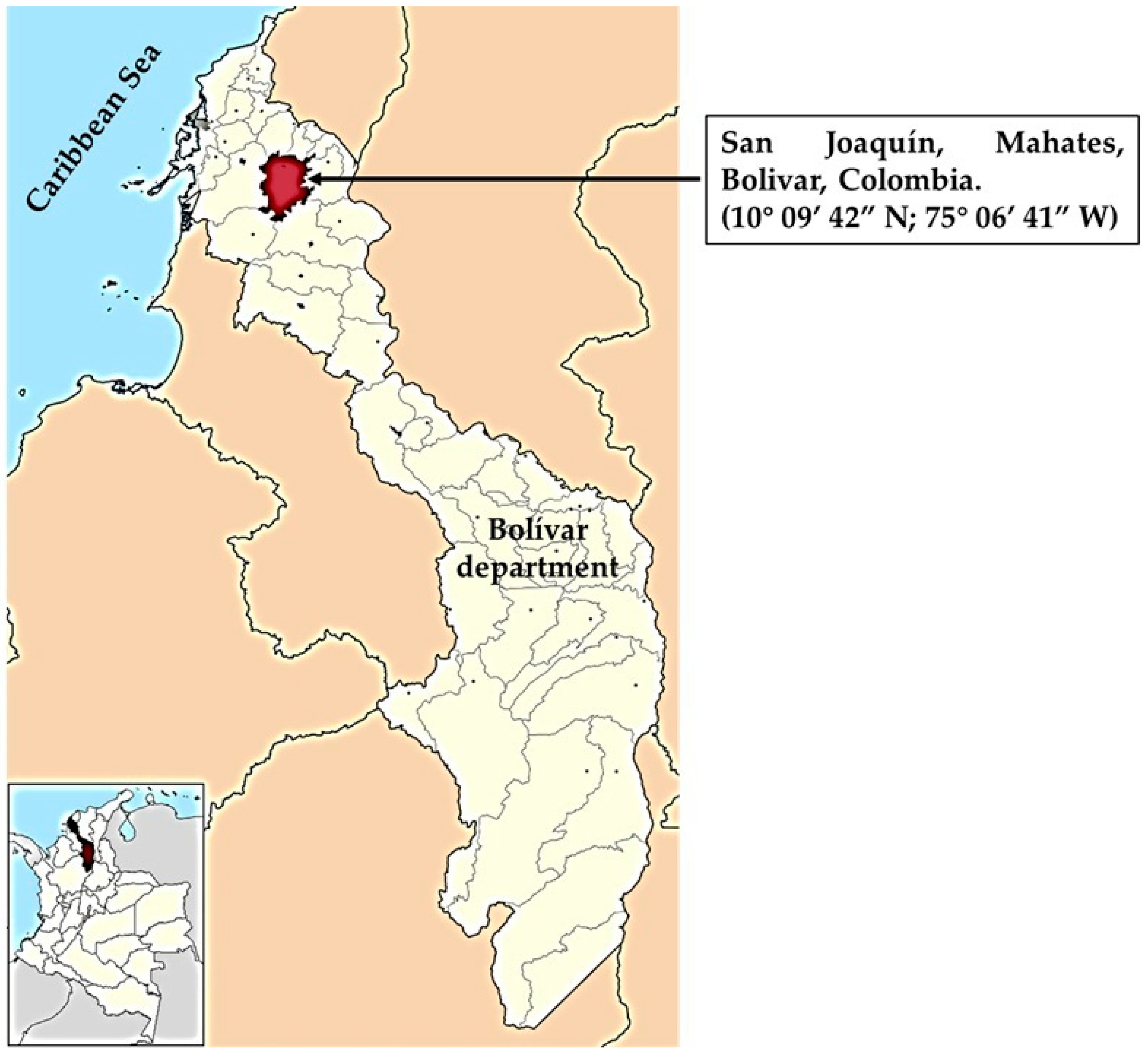
2.1. Soil Sample Collection
2.2. Chemicals and Microbial Culture Medium
2.3. Preparation of Soil Samples and Activation of Pesticide-Degrading Metabolism in Bacterial Colonies
2.4. Isolation of Native Bacterial Colonies from Agricultural Soils
2.5. Biochemical and Molecular Identification of Isolated Bacterial Colonies
2.6. Quantification of Pesticide Concentration and Determination of Bacterial Biomass, During Biodegradation Process
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
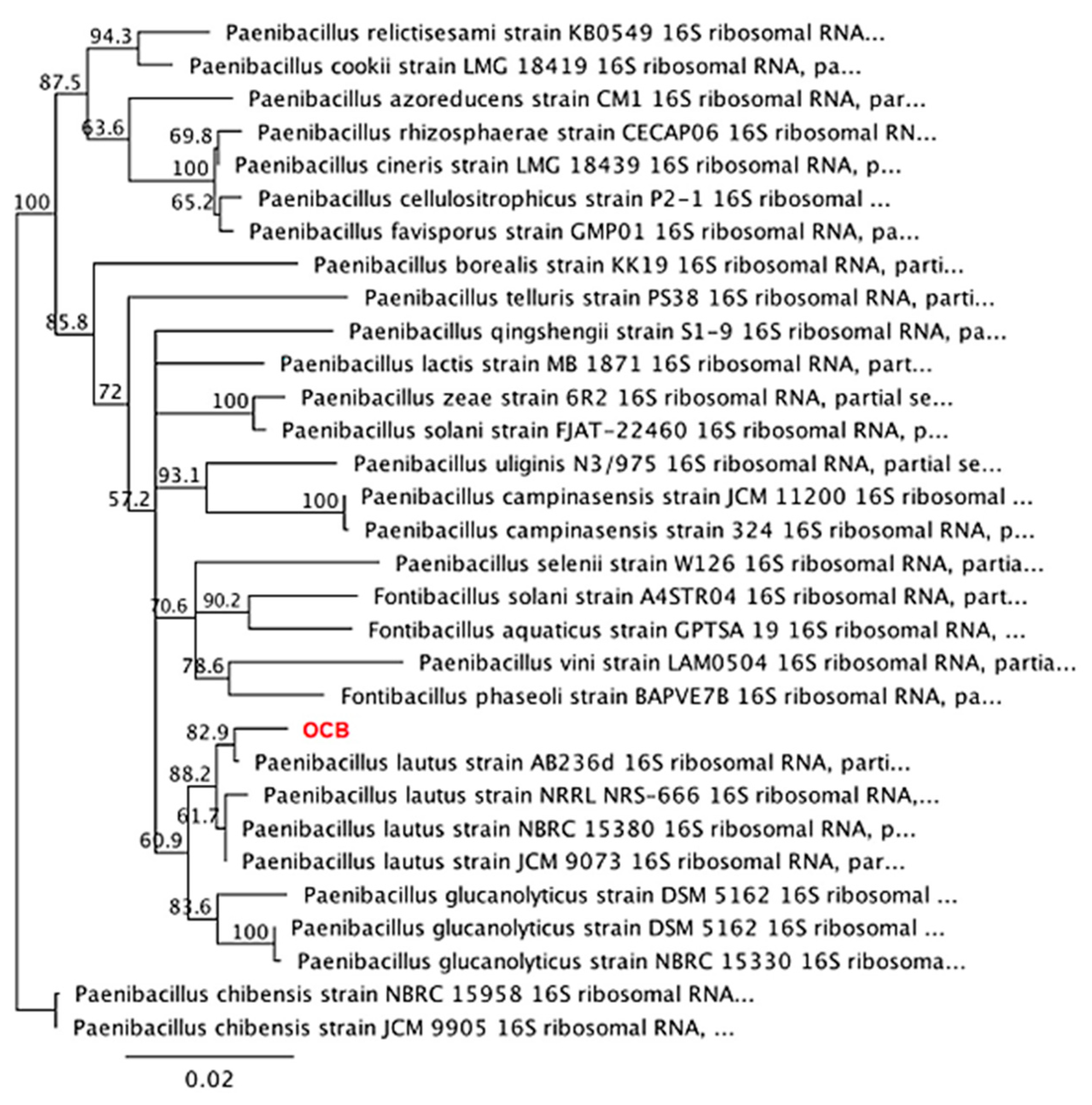
3.1. Isolation and Identification of Native Bacterial Colonies from Soils
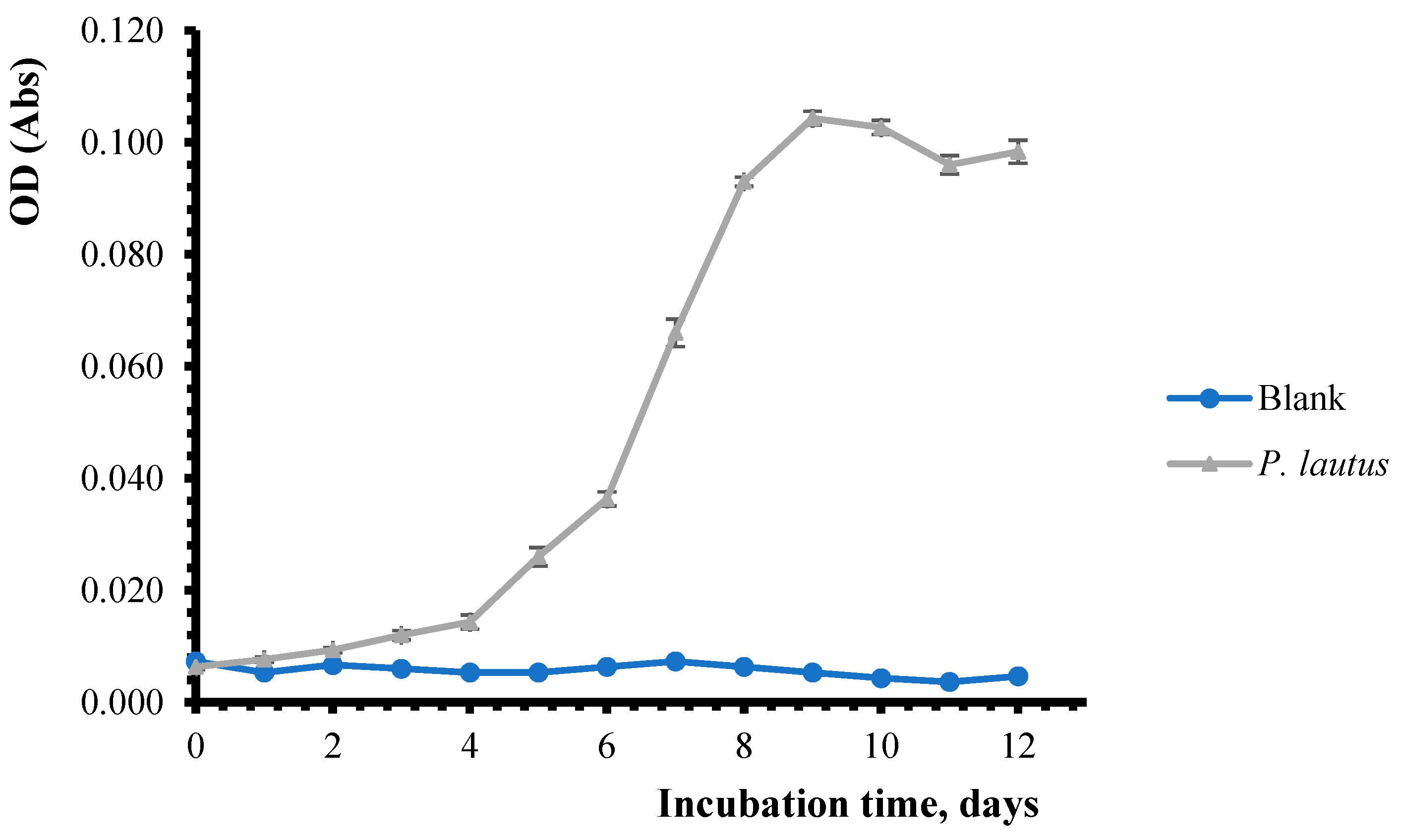
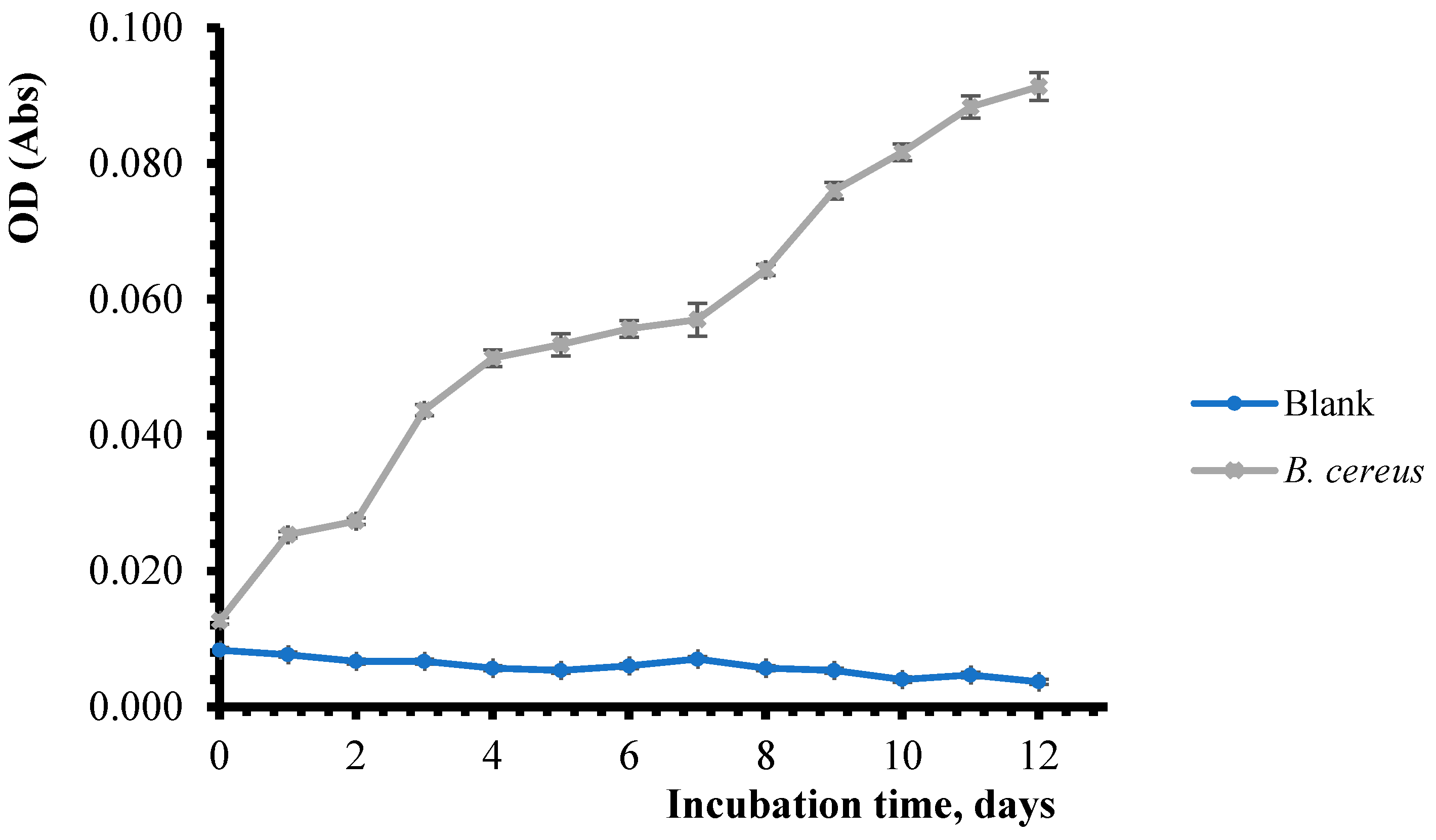
3.2. Determination of Bacterial Biomass During Pesticide Biodegradation Process
3.3. Analysis of Quantification of Pesticide Biodegradation by Gas Chromatography
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OP | Organophosphorus pesticide |
| OC | Organochlorine pesticide |
| OD | Optical density |
| GC-MS | Gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry |
References
- Nasiri, M.; Ahmadzadeh, H.; Amiri, A.H. Biodegradation and metabolic fate of organophosphorus pesticides in well water using Dunaliella salina. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Li, K.; Yan, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Qiao, C.; Yang, T.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, B. A novel chlorpyrifos hydrolase CPD from Paracoccus sp. TRP: Molecular cloning, characterization, and catalytic mechanism. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 31, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Jiménez, S.; Casado, N.; García, M.A.; Marina, M.L. Enantiomeric analysis of pyrethroids and organophosphorus insecticides. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1605, 360345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovecka, P.; Pacovska, I.; Stursa, P.; Vrchotova, B.; Kochankova, L.; Demnerova, K. Organochlorinated pesticide degrading microorganisms isolated from contaminated soil. New Biotechnol. 2015, 32, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishag, A.E.S.A.; Abdelbagi, A.O.; Hammad, A.M.A.; Elsheikh, E.A.E.; Elsaid, O.E.; Hur, J.-H.; Laing, M.D. Biodegradation of Chlorpyrifos, Malathion, and Dimethoate by Three Strains of Bacteria Isolated from Pesticide-Polluted Soils in Sudan. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 8491–8498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.K.R.; Nagaraju, R.; Rajini, P.S. Insights into the mechanisms mediating hyperglycemic and stressogenic outcomes in rats treated with monocrotophos, an organophosphorus insecticide. Toxicology 2012, 294, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Agriculture. Prohibition on the Use and Sale of Organochlorine Insecticides. Ministry of Agriculture, Bogotá–Colombia. 1974. Available online: https://www.minagricultura.gov.co/convocatorias/Documents/Apertura_Registro_2016_2018/Anexo_4_listado_de_plaguicidas_prohibidos_en_Colombia.pdf (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- Girones, L.; Oliva, A.L.; Marcovecchio, J.E.; Arias, A.H. Spatial Distribution and Ecological Risk Assessment of Residual Organochlorine Pesticides (OCPs) in South American Marine Environments. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2020, 7, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte-Restrepo, E.; Noguera-Oviedo, K.; Butryn, D.; Wallace, J.S.; Aga, D.S.; Jaramillo-Colorado, B.E. Spatial distribution of pesticides, organochlorine compounds, PBDEs, and metals in surface marine sediments from Cartagena Bay, Colombia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 14632–14653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ubaque, C.A.; García-Ubaque, J.C.; Vaca-Bohórquez, M.L. Persistent organic compounds in Colombia: Quantification and diagnostics for organochlorine pesticides. Tecnura 2015, 19, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, V.B.; Estrella, L.F.; Alves, M.G.R.; Gallistl, C.; Vetter, W.; Silva, T.T.C.; Malm, O.; Torres, J.P.M.; Finco, F.D.B.A. Residues of legacy organochlorine pesticides and DDT metabolites in highly consumed fish from the polluted Guanabara Bay, Brazil: Distribution and assessment of human health risk. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2020, 55, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabzevari, S.; Hofman, J. A worldwide review of currently used pesticides’ monitoring in agricultural soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 152344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ore, O.T.; Adeola, A.O.; Bayode, A.A.; Adedipe, D.T.; Nomngongo, P.N. Organophosphate pesticide residues in environmental and biological matrices: Occurrence, distribution, and potential remedial approaches. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2023, 5, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, M.C.O.; Rocha, B.A.; Adeyemi, J.A.; Nadal, M.; Domingo, J.L.; Barbosa, F. Legacy and emerging pollutants in Latin America: A critical review of occurrence and levels in environmental and food samples. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 848, 157774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzanetou, E.N.; Karasali, H. A Comprehensive Review of Organochlorine Pesticide Monitoring in Agricultural Soils: The Silent Threat of a Conventional Agricultural Past. Agriculture 2022, 12, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte-Restrepo, E.; Jaramillo-Colorado, B.E.; Duarte-Jaramillo, L. Effects of chlorpyrifos on the crustacean Litopenaeus vannamei. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliva, A.L.; Girones, L.; Recabarren-Villalón, T.V.; Ronda, A.C.; Marcovecchio, J.E.; Arias, A.H. Occurrence, behavior and the associated health risk of organochlorine pesticides in sediments and fish from Bahía Blanca Estuary, Argentina. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 185, 114247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wołejko, E.; Jabłońska-Trypuć, A.; Wydro, U.; Butarewicz, A.; Łozowicka, B. Soil biological activity as an indicator of soil pollution with pesticides—A review. App. Soil Ecol. 2020, 147, 103356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echeverri-Jaramillo, G.; Jaramillo-Colorado, B.; Sabater-Marco, C.; Castillo-López, M. Cytotoxic and estrogenic activity of chlorpyrifos and its metabolite 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol. Study of marine yeasts as potential toxicity indicators. Ecotoxicology 2021, 30, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Khan, M.S. Ecotoxicological implications of residual pesticides to beneficial soil bacteria: A review. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 188, 105272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldas-Vargas, A.; Van der Vooren, T.; Rijnaarts, H.H.M.; Sutton, N.B. Biostimulation is a valuable tool to assess pesticide biodegradation capacity of groundwater microorganisms. Chemosphere 2021, 280, 130793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Mao, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, P.; Wu, C.; Xie, J.; Yu, B.; Sial, M.U.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Modified Biochar as a More Promising Amendment Agent for Remediation of Pesticide-Contaminated Soils: Modification Methods, Mechanisms, Applications, and Future Perspectives. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pischedda, A.; Tosin, M.; Degli-Innocenti, F. Biodegradation of plastics in soil: The effect of temperature. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2019, 170, 109017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondo, E.E.; Aparicio, J.D.; Bigliardo, A.L.; Fuentes, M.S.; Benimeli, C.S. Enhanced bioremediation of lindane-contaminated soils through microbial bioaugmentation assisted by biostimulation with sugarcane filter cake. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 190, 110143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, P.R.S.; Birolli, W.G.; Ferreira, I.M.; Porto, A.L.M. Biodegradation pathway of the organophosphate pesticides chlorpyrifos, methyl parathion and profenofos by the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sydowii CBMAI 935 and its potential for methylation reactions of phenolic compounds. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 166, 112185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Singh, J.; Ramamurthy, P.C.; Kumar, V.; Bhardwaj, S.; Garg, V.K. Biodegradation of monocrotophos by indigenous soil bacterial isolates in the presence of humic acid, Fe (III) and Cu (II) ions. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2021, 15, 100778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geed, S.R.; Sawarkar, A.N.; Singh, R.S.; Rai, B.N. New approach for biodegradation of Malathion pesticide by Bacillus sp. isolated from agricultural field: Bioreactor and kinetics. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govarthanan, M.; Ameen, F.; Kamala-Kannan, S.; Selvankumar, T.; Almansob, A.; Alwakeel, S.; Kim, W. Rapid biodegradation of chlorpyrifos by plant growth-promoting psychrophilic Shewanella sp. BT05: An eco-friendly approach to clean up pesticide-contaminated environment. Chemosphere 2020, 247, 125948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, H.R.M.; Argolo, C.S.; Argôlo-Filho, R.C.; Loguercio, L.L. A 16S rDNA PCR-based theoretical to actual delta approach on culturable mock communities revealed severe losses of diversity information. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Yadav, A.N.; Saxena, R.; Paul, D.; Tomar, R.S. Biodiversity of pesticides degrading microbial communities and their environmental impact. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 31, 101883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangola, S.; Bhatt, P.; Kumar, A.J.; Bhandari, G.; Joshi, S.; Punetha, A.; Bhatt, K.; Rene, E.R. Biotechnological tools to elucidate the mechanism of pesticide degradation in the environment. Chemosphere 2022, 296, 133916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangola, S.; Sharma, A.; Joshi, S.; Bhandari, G.; Prakash, O.; Govarthanan, M.; Kim, W.; Bhatt, P. Novel mechanism and degradation kinetics of pesticides mixture using Bacillus sp. strain 3C in contaminated sites. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 181, 104996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Shentu, J.; Ma, B.; Lu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Xu, J.; He, Y. Microbial and abiotic factors of flooded soil that affect redox biodegradation of lindane. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, B.; Chaudhuri, S. Removal of lindane in liquid culture using soil bacteria and toxicity assessment in human skin fibroblast and HCT116 cell lines. Environ. Technol. 2023, 44, 1213–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansouri, A.; Cregut, M.; Abbes, C.; Durand, M.-J.; Landoulsi, A.; Thouand, G.; Mansouri, A.; Cregut, M.; Abbes, C.; Durand, M.-J.; et al. The Environmental Issues of DDT Pollution and Bioremediation: A Multidisciplinary Review. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 181, 309–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morillo, E.; Villaverde, J. Advanced technologies for the remediation of pesticide-contaminated soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 576–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kaushik, G.; Dar, M.A.; Nimesh, S.; López-Chuken, U.J.; Villarreal-Chiu, J.F. Microbial Degradation of Organophosphate Pesticides: A Review. Pedosphere 2018, 28, 190–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbe, C.C.; Oyetibo, G.O.; Ilori, M.O. Ecological impact of organochlorine pesticides consortium on autochthonous microbial community in agricultural soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 207, 111319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geed, S.R.; Kureel, M.K.; Shukla, A.K.; Singh, R.S.; Rai, B.N. Biodegradation of malathion and evaluation of kinetic parameters using three bacterial species. Resour. Effic. Technol. 2016, 2, S3–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tan, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Ni, H.; Li, L. Complete biodegradation of chlorpyrifos by engineered Pseudomonas putida cells expressing surface-immobilized laccases. Chemosphere 2016, 157, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilani, R.A.; Rafique, M.; Rehman, A.; Munis, M.F.; Rehman, S.U.; Chaudhary, H.J. Biodegradation of chlorpyrifos by bacterial genus Pseudomonas. J. Basic Microbiol. 2016, 56, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Pandey, V.; Yadav, S.K.; Khare, P. Comparative evaluation of biodegradation of chlorpyrifos by various bacterial strains: Kinetics and pathway elucidation. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2024, 203, 105989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, A.; Bhardwaj, K.K.; Shaiza, M.; Gupta, R. Isolation, characterization and identification of pesticide degrading bacteria from contaminated soil for bioremediation. Biol. Fut. 2021, 72, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dar, M.A.; Chanwala, J.; Meena, P.R.; Singh, A.P.; Kaushik, G. Biodegradation of malathion by Micrococcus sp. strain MAGK3: Kinetics and degradation fragments. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; You, M. Isolation, identification and characterization of a novel triazophos-degrading Bacillus sp. (TAP-1). Microbiol. Res. 2012, 167, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, R.; Verma, S.; Chatterjee, S. Biodegradation of organophosphorus pesticide profenofos by the bacterium Bacillus sp. PF1 and elucidation of initial degradation pathway. Environ. Technol. 2023, 44, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, S.; Liaquat, F.; Khan, Q.M.; Khalid, Z.M.; Iqbal, S. Biodegradation of chlorpyrifos and its hydrolysis product 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol by Bacillus pumilus strain C2A1. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthukumaravel, S.; Sivalaxmi, B.; Nagarajan, S.A.; Sivakumar, N.; Kumar, A.; Hoti, S.L. Biodegradation of Organophosphorus Insecticides by Bacillus Species Isolated from Soil. J. Basic Microbiol. 2024, 2024, e2400597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannahi, M.; Radha, R. Biodegradation of Methyl Parathion by Bacillus species. IJPPR. Hum. 2018, 11, 143–154. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Chen, X.; Shi, Y.; Su, Z.C. Bacterial Degradation of Chlorpyrifos by Bacillus cereus. Adv. Mat. Res. 2011, 356–360, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambreen, S.; Yasmin, A. Novel degradation pathways for Chlorpyrifos and 3,5,6-Trichloro-2-pyridinol degradation by bacterial strain Bacillus thuringiensis MB497 isolated from agricultural fields of Mianwali, Pakistan. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 172, 104750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, M.; Ahmad, M.; Kanwal, A.; Butt, Z.A.; Khan, Q.F.; Raza, S.A.; Qayyum, H.; Wahid, A. Biodegradation of chlorpyrifos using isolates from contaminated agricultural soil, its kinetic studies. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaramillo Colorado, B.E.; Bermúdez Tobón, A.; Tirado Ballestas, I. Organophosphorus pesticides degrading bacteria present in contaminated soils. Rev. Cienc. Técnicas Agropecu. 2016, 25, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uniyal, S.; Sharma, R.K.; Kondakal, V. New insights into the biodegradation of chlorpyrifos by a novel bacterial consortium: Process optimization using general factorial experimental design. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 209, 111799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, A.B.; Chaabane, H.; Ghazouani, T.; Caboni, P.; Coroneo, V.; Devers, M.; Béguet, J.; Martin-Laurent, F.; Fattouch, S. Evidence for enhanced dissipation of chlorpyrifos in an agricultural soil inoculated with Serratia rubidaea strain ABS 10. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 29358–29367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cycoń, M.; Wójcik, M.; Piotrowska-Seget, Z. Biodegradation of the organophosphorus insecticide diazinon by Serratia sp. and Pseudomonas sp. and their use in bioremediation of contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2009, 76, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthivel, S.; Dhanapal, A.R.; Palaniswamy, R.; Dhandapani, S.; Kathiravan, M.N. Biodegradation of Endosulfan-a Chlorinated Cyclodiene Pesticide by Indigenous Pseudomonas sp. MSCAS BT01. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol 2022, 194, 2747–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barragán-Huerta, B.; Costa-Pérez, C.; Peralta-Cruz, J.; Barrera-Cortés, J.; Esparza-García, F.; Rodríguez-Vázquez, R. Biodegradation of organochlorine pesticides by bacteria grown in microniches of the porous structure of green bean coffee. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2007, 59, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Shi, H.; Liang, Y.; Qin, L.; Zeng, H.; Song, X. Degradation Characteristics and Remediation Ability of Contaminated Soils by Using β-HCH Degrading Bacteria. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oro, C.E.D.; Saorin Puton, B.M.; Venquiaruto, L.D.; Dallago, R.M.; Tres, M.V. Effective Microbial Strategies to remediate contaminated agricultural soils and conserve functions. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, R.; Brady, N. The Nature and Properties of Soils, 15th ed.; Pearson Education: Columbus, OH, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ferris, R.A.; Palmer, B.A.; Borlee, B.R.; McCue, P.M. Ability of Chromogenic Agar, MALDI-TOF, API 20E and 20 Strep Strips, and BBL Crystal Enteric and Gram-Positive Identification Kits to Precisely Identify Common Equine Uterine Pathogens. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2017, 57, 3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáez-Nieto, J.; Medina-Pascual, M.; Carrasco, G.; Garrido, N.; Fernandez-Torres, M.; Villalón, P.; Valdezate, S. Paenibacillus spp. isolated from human and environmental samples in Spain: Detection of 11 new species. New Microbes New Infect. 2017, 19, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffa, C.M.; Chiampo, F. Bioremediation of Agricultural Soils Polluted with Pesticides: A Review. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sundar, L.S.; Chao, Y.Y. Potential of Purple Non-Sulfur Bacteria in Sustainably Enhancing the Agronomic and Physiological Performances of Rice. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leskovac, A.; Petrovi, S. Pesticide Use and Degradation Strategies: Food Safety, Challenges and Perspectives. Foods 2023, 12, 2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara-Moreno, A.; Morillo, E.; Merchán, F.; Madrid, F.; Villaverde, J. Chlorpyrifos Removal in an Artificially Contaminated Soil Using Novel Bacterial Strains and Cyclodextrin. Evaluation of Its Effectiveness by Ecotoxicity Studies. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabbier; Singh, M.; Maiti, S.; Kumar, S.; Saha, S.K. Removal enactment of organo-phosphorous pesticide using bacteria isolated from domestic sewage. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 263, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, J.; Silambarasan, S.; Logeswari, P. Simultaneous degradation of organophosphorus and organochlorine pesticides by bacterial consortium. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 2590–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, Y.; Zang, P.; Zhao, Y.; He, Z.; Zhu, H.; Song, S.; Zhang, L. Study on the simultaneous degradation of five pesticides by Paenibacillus polymyxa from Panax ginseng and the characteristics of their products. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 168, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


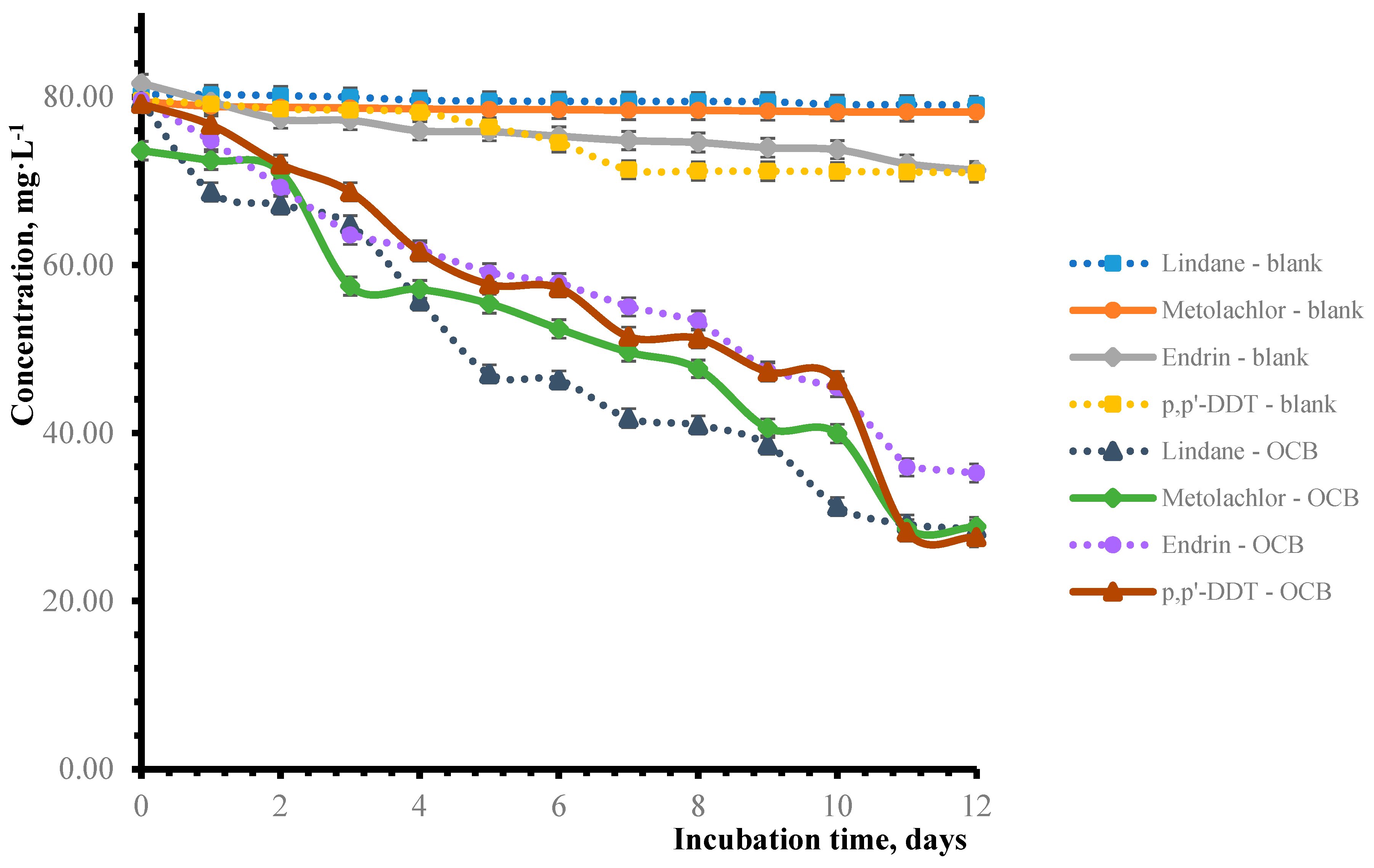
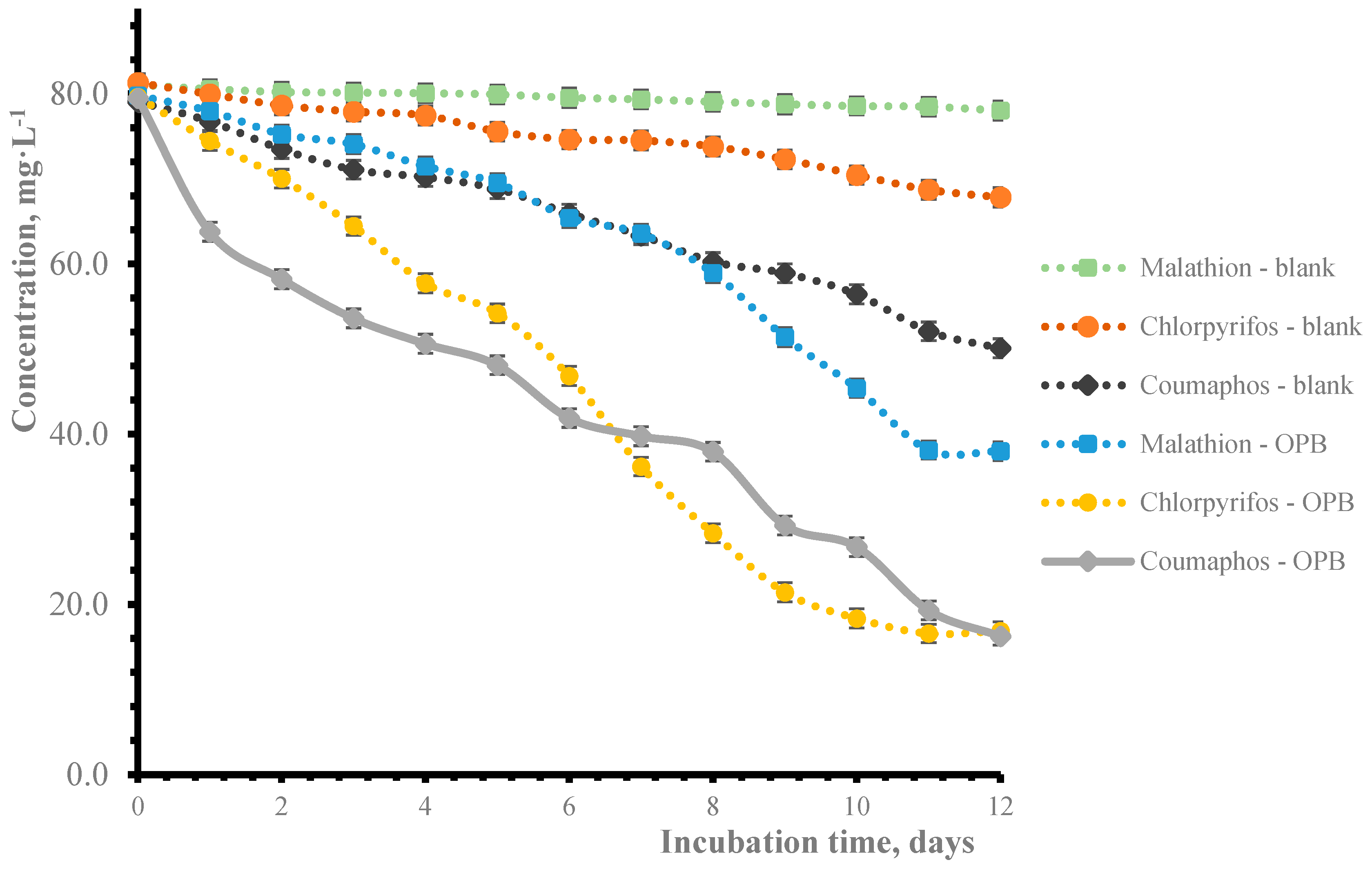
| Incubation Time | Control—Blank OC | Paenibacillus lautus | Control—Blank OP | Bacillus cereus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Days) | (Abs) | (Abs) | (Abs) | (Abs) |
| 0 | 0.007 ± 4.1 × 10−4 | 0.060 ± 4.7 × 10−4 | 0.008 ± 9.4 × 10−4 | 0.013 ± 1.2 × 10−3 |
| 1 | 0.005 ± 4.2 × 10−4 | 0.080 ± 4.1 × 10−4 | 0.008 ± 1.2 × 10−3 | 0.025 ± 1.3 × 10−3 |
| 2 | 0.007 ± 4.7 × 10−4 | 0.090 ± 4.2 × 10−4 | 0.007 ± 4.7 × 10−4 | 0.027 ± 1.2 × 10−3 |
| 3 | 0.006 ± 8.6 × 10−4 | 0.012 ± 8.1 × 10−4 | 0.007 ± 4.7 × 10−4 | 0.044 ± 4.7 × 10−4 |
| 4 | 0.005 ± 4.2 × 10−4 | 0.014 ± 1.2 × 10−3 | 0.006 ± 4.7 × 10−4 | 0.051 ± 1.3 × 10−3 |
| 5 | 0.005 ± 4.1 × 10−4 | 0.026 ± 1.6 × 10−3 | 0.005 ± 4.7 × 10−4 | 0.053 ± 4.7 × 10−4 |
| 6 | 0.006 ± 4.1 × 10−4 | 0.036 ± 1.3 × 10−3 | 0.006 ± 8.2 × 10−4 | 0.056 ± 9.4 × 10−4 |
| 7 | 0.007 ± 4.0 × 10−4 | 0.066 ± 2.4 × 10−3 | 0.007 ± 8.1 × 10−4 | 0.057 ± 1.6 × 10−3 |
| 8 | 0.006 ± 4.2 × 10−4 | 0.093 ± 8.2 × 10−4 | 0.006 ± 9.4 × 10−4 | 0.064 ± 1.7 × 10−3 |
| 9 | 0.005 ± 4.1 × 10−4 | 0.104 ± 1.2 × 10−3 | 0.005 ± 4.7 × 10−4 | 0.076 ± 1.6 × 10−3 |
| 10 | 0.004 ± 4.3 × 10−4 | 0.103 ± 1.3 × 10−3 | 0.004 ± 8.1 × 10−4 | 0.082 ± 1.3 × 10−3 |
| 11 | 0.004 ± 4.7 × 10−4 | 0.096 ± 1.6 × 10−3 | 0.005 ± 4.7 × 10−4 | 0.088 ± 2.1 × 10−3 |
| 12 | 0.005 ± 4.3 × 10−4 | 0.098 ± 2.0 × 10−3 | 0.004 ± 4,6 × 10−4 | 0.091 ± 1.2 × 10−3 |
| % Degradation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incubation Time (Days) | Lindane | Metolachlor | Endrin | p,p′-DDT |
| 5 | 40.8 ± 0.13 | 24.7 ± 0.23 | 25.8 ± 0.23 | 27.1 ± 0.13 |
| 8 | 48.4 ± 0.24 | 35.2 ± 0.27 | 32.9 ± 0.27 | 35.2 ± 0.26 |
| 10 | 60.6 ± 0.29 | 45.7 ± 0.10 | 42.9 ± 0.24 | 41.5 ± 0.22 |
| 12 | 64.0 ± 0.19 | 60.8 ± 0.11 | 55.7 ± 0.18 | 65.1 ± 0.17 |
| % Degradation | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Incubation Time (Days) | Malathion | Chlorpyrifos | Coumaphos |
| 2 | 5.7 ± 0.12 | 12.0 ± 0.26 | 26.7 ± 0.02 |
| 4 | 10.4 ± 0.34 | 27.4 ± 0.18 | 36.3 ± 0.19 |
| 9 | 35.5 ± 0.29 | 73.0 ± 0.16 | 63.1 ± 0.24 |
| 12 | 52.3 ± 0.17 | 78.7 ± 025 | 79.5 ± 0.27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez-Orozco, V.A.; Duarte-Restrepo, E.; Jaramillo-Colorado, B.E. Isolation of Bacteria from Agricultural Soils and Evaluation of Their Degradative Capacity for Organochlorine and Organophosphorus Pesticides. Agronomy 2025, 15, 814. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040814
Rodríguez-Orozco VA, Duarte-Restrepo E, Jaramillo-Colorado BE. Isolation of Bacteria from Agricultural Soils and Evaluation of Their Degradative Capacity for Organochlorine and Organophosphorus Pesticides. Agronomy. 2025; 15(4):814. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040814
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez-Orozco, Victor A., Edisson Duarte-Restrepo, and Beatriz E. Jaramillo-Colorado. 2025. "Isolation of Bacteria from Agricultural Soils and Evaluation of Their Degradative Capacity for Organochlorine and Organophosphorus Pesticides" Agronomy 15, no. 4: 814. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040814
APA StyleRodríguez-Orozco, V. A., Duarte-Restrepo, E., & Jaramillo-Colorado, B. E. (2025). Isolation of Bacteria from Agricultural Soils and Evaluation of Their Degradative Capacity for Organochlorine and Organophosphorus Pesticides. Agronomy, 15(4), 814. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040814






