Study on the Nitrogen Response and Low Nitrogen Tolerance Variations in Different Tea Varieties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Experimental Design
2.2. Field Observations, Sample Collection, and Analysis Methods
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
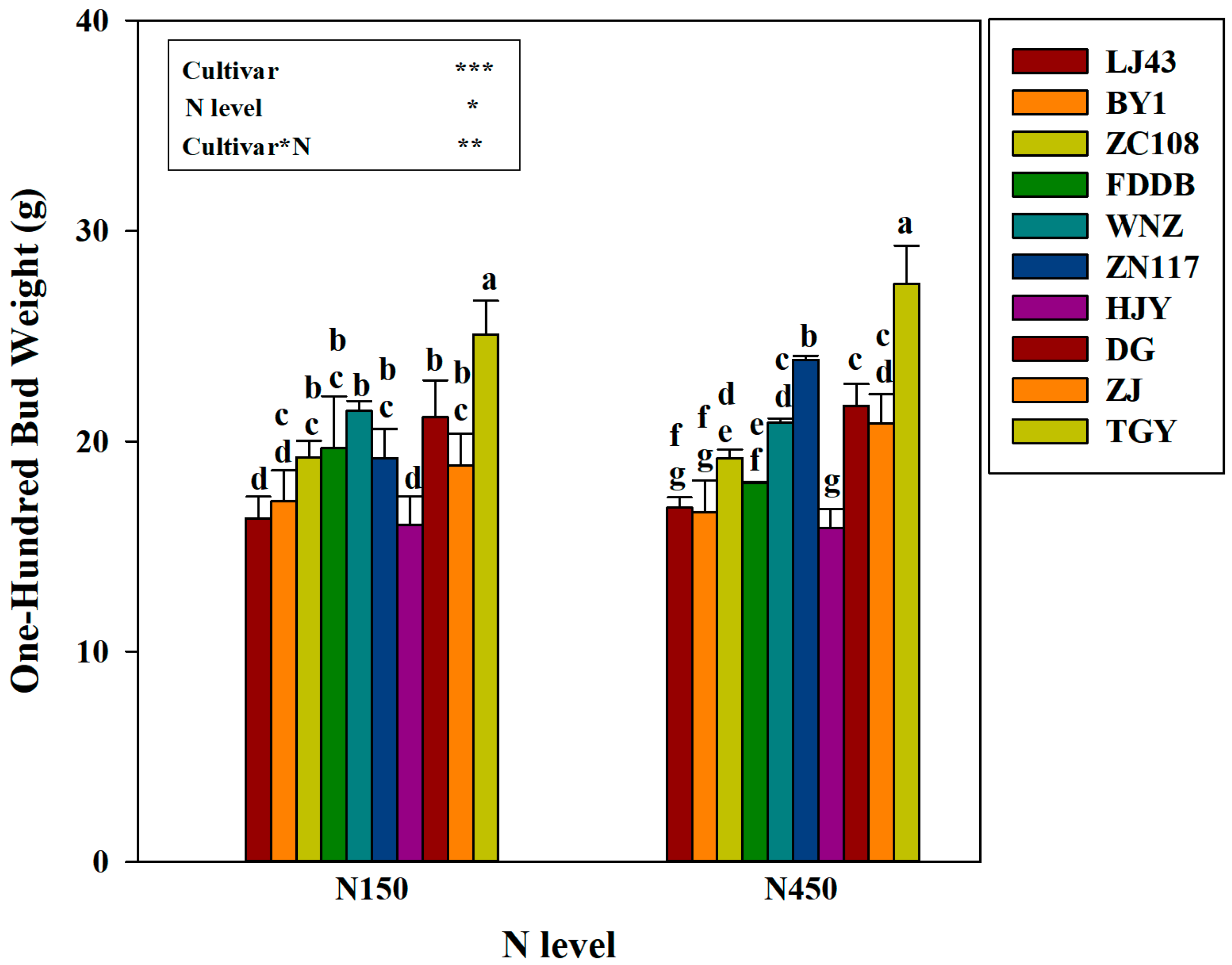
3.1. Plant Growth in Response to Nitrogen Application
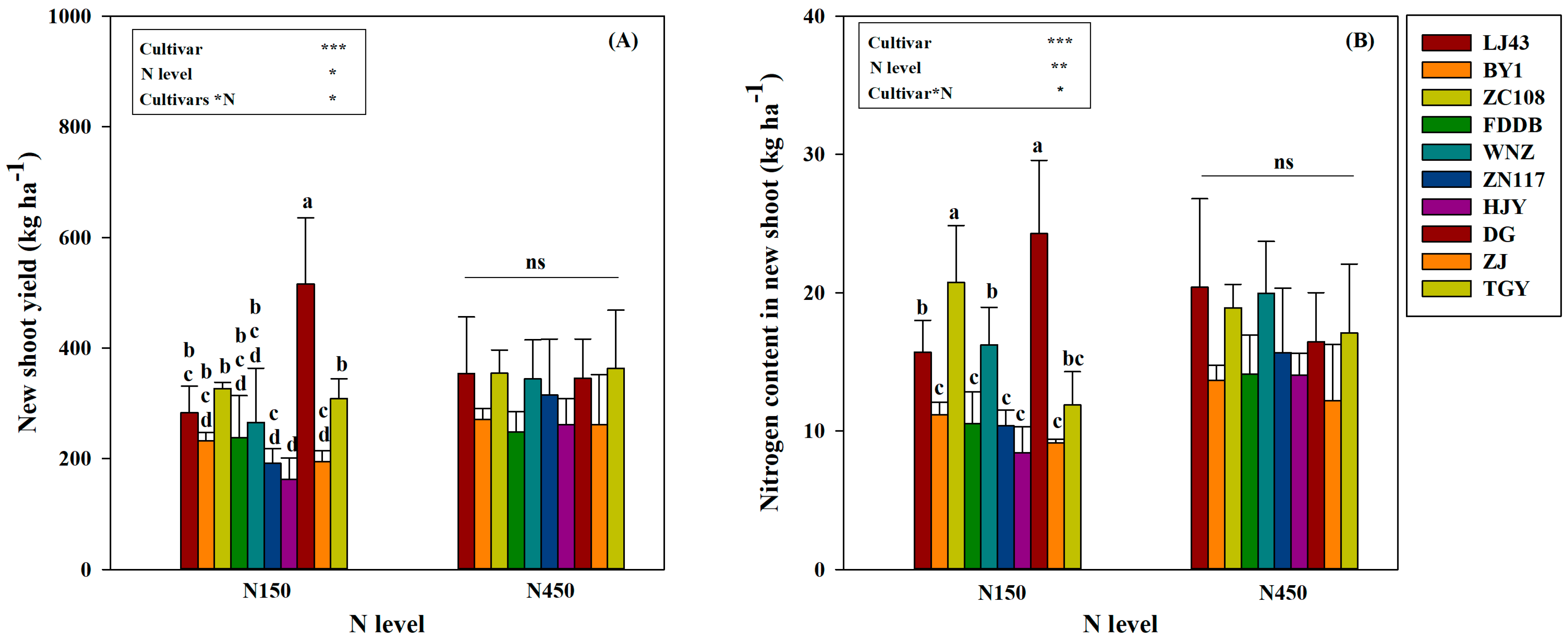
3.2. New Shoot Yield and Its Nitrogen Content in Response to Nitrogen Level
3.3. Pruned Litter Biomass and Its Nitrogen Content in Response to Nitrogen Application
3.3.1. Pruned Litter Biomass and Its Distribution
3.3.2. Nitrogen Content in Pruned Litter and Its Distribution
3.4. Low Nitrogen Tolerance Indexes for Observational Indicators
3.4.1. Tolerance Indexes of Observational Indicators for Low Nitrogen
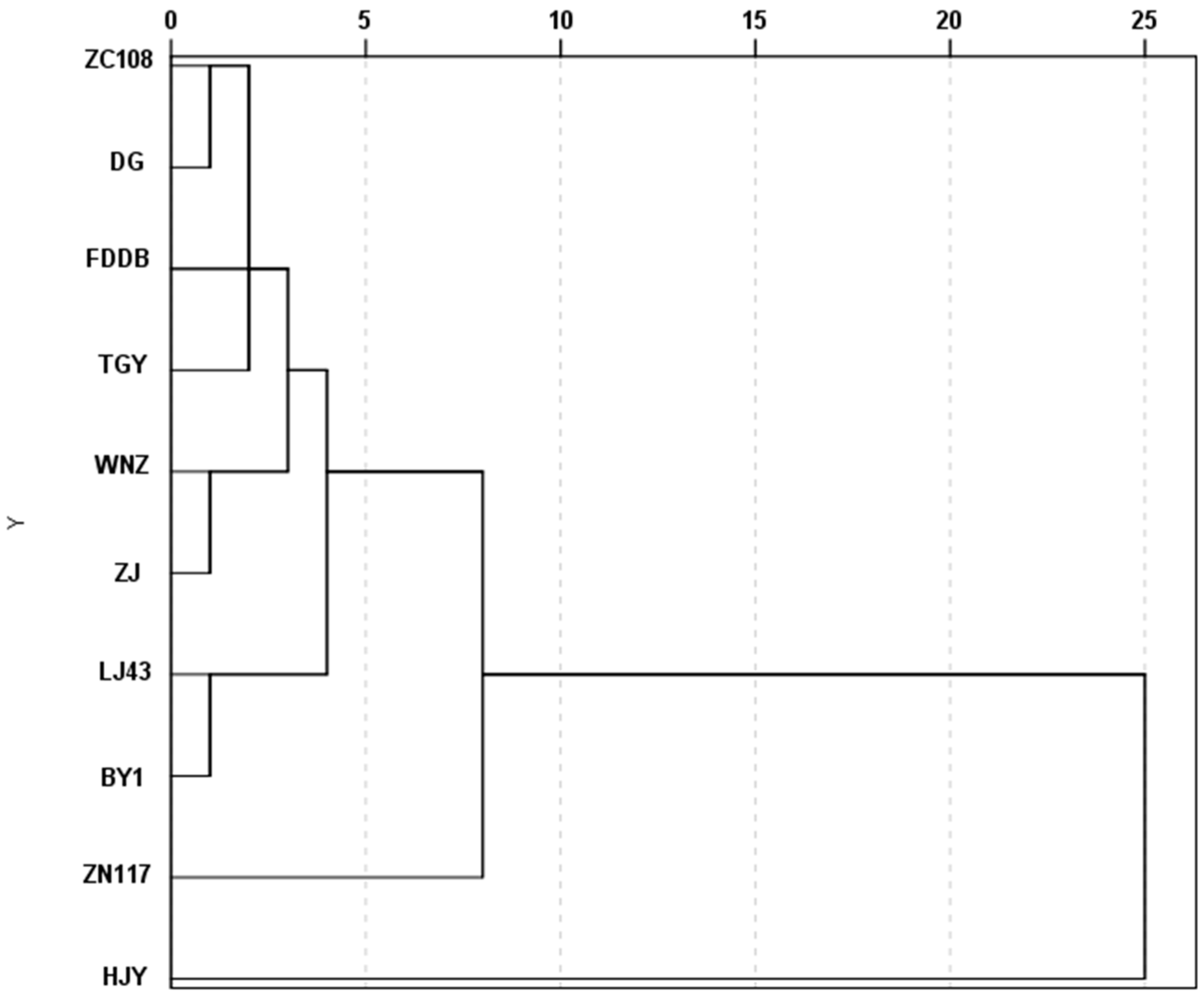
3.4.2. Correlation and Cluster Analysis in Low Nitrogen Tolerance Indexes
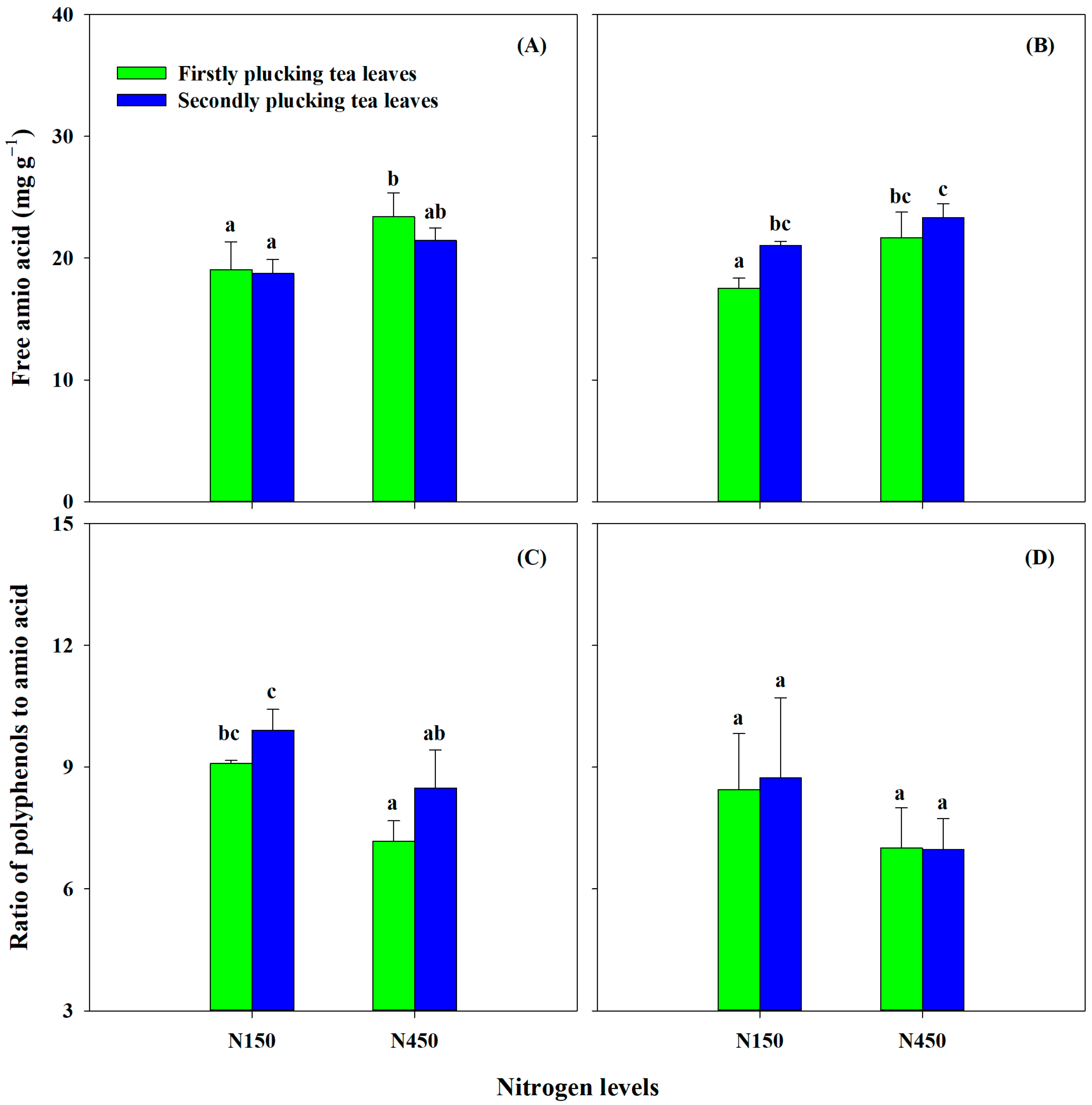
3.4.3. Responses of Tea Quality-Related Components to Nitrogen Supply Levels
4. Discussion
4.1. Determination of Appropriate N Level
4.2. The Effect of Tea-Pruned Litter on the Excessive Nitrogen in Tea Gardens
4.3. Evaluation of Indicators for Screening Low Nitrogen Tea Tree Varieties
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gojon, A. Nitrogen nutrition in plants: Rapid progress and new challenges. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 2457–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Dalmau, J.; Berbel, J.; Ordóñez-Fernández, R. Nitrogen Fertilization. A Review of the Risks Associated with the Inefficiency of Its Use and Policy Responses. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhele, B.; Zhan, X.J.; Yang, G.Z.; Zhang, X.L. Review: Nitrogen assimilation in crop plants and its affecting factors. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2012, 92, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.X.; Hou, Y.L.; Du, N.L. Identification and screening of low-nitrogen tolerant resources in soybean seedlings. J. Plant Genet. Resour. 2023, 24, 408–418. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.R.; Hossain, M.B.; Siddique, A.B.; Rahman, M.T.; Malika, M. Contribution of green manure incorporation in combination with nitrogen fertilizer in rice production. SAARC J. Agric. 2015, 12, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.F.; Dou, Z.X.; He, P.; Ju, X.T.; Powlson, D.; Chadwick, D.; Norse, D.; Lu, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; et al. New technologies reduce greenhouse gas emissions from nitrogenous fertilizer in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8375–8380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Fan, X.; Miller, A.J. Plant nitrogen assimilation and use efficiency. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2012, 63, 153–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, F.; Yang, Z.; Huang, H.; Yang, F.; Zhu, L.; Han, D. Nitrogen fertilization in soil affects physiological characteristics and quality of green tea leaves. HortScience 2018, 53, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Guo, Y. Analysis of Characteristics, Problems and Countermeasures of China’s Tea Export Trade. China Tea 2024, 47, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, C.; Xu, B.; Han, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Zhao, X. Synthetic nitrogen fertilizers alter the soil chemistry, production and quality of tea. A meta-analysis. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 38, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.Y.; Wu, X.; Shi, Y.Z.; Ma, L.F. Nutrient input and evaluation of fertilization efficiency in typical tea areas of China. In Nutrient Management in China. Part I. Nutrient Balances and Nutrient Cycling in Agro-Ecosystems; International Potash Institute: Basel, Switzerland, 2004; pp. 367–375. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.J.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, W.J. Research on main factors of fertilizer efficiency. Tea Sci. Technol. 1992, 135, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.L.; Wang, L.Y.; Cheng, H.; Wei, K.; Wu, L.Y. The effects of nitrogen levels on important agronomic traits and chemical composition in tea plants. Tea Sci. 2017, 37, 383–391. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.J.; Liao, W.Y.; Ding, Y.; Wang, H.S.; Xia, X.J. Effects of nitrogen fertilization on yield and quality of tea. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2011, 17, 1430–1436. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.Y.; Burgos, A.; Ma, L.F.; Zhang, Q.F.; Tang, D.D.; Ruan, J.Y. Lipidomics analysis unravels the effect of nitrogen fertilization on lipid metabolism in tea plant (Camellia sinensis L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Hu, J.H.; Shi, Y.Z.; Liu, M.Y.; Zhang, Q.F.; Ruan, J.Y. Effects of nitrogen supply on flavonol glycoside biosynthesis and accumulation in tea leaves (Camellia sinensis). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 138, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, J.; Haerdter, R.; Gerendas, J. Impact of nitrogen supply on carbon/nitrogen allocation: A case study on amino acids and catechins in green tea [Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze] Plants. Plant Biol. 2010, 12, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Yang, X.; Shi, Y.; Yi, X.; Ji, L.; Cheng, Y.; Ruan, J. Response of tea yield, quality and soil bacterial characteristics to long-term nitrogen fertilization in an eleven-year field experiment. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 166, 103976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Liao, W.Y.; Yi, X.Y.; Niu, S.Y.; Ma, L.F.; Shi, Y.Z.; Zhang, Q.F.; Liu, M.Y.; Ruan, J.Y. Fertilization status and reduction potential in tea gardens of China. J. Plant Nutr. Sci. 2019, 25, 421–432. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.Z.; Li, Y.; Fu, X.Q.; Shen, J.L.; Chen, D.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.L.; Xiao, R.L.; Wei, W.X.; Wu, J.S. Effect of controlled-release fertilizer on N2O emissions and tea yield from a tea field in subtropical central China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 25580–25590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.T.; Geng, Y.B.; Liang, T. Optimization of reduced chemical fertilizer use in tea gardens based on the assessment of related environmental and economic benefits. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xin, W.; Wang, W.; Zhao, S.; Xu, L.; Jiang, X.; Wang, J. Mapping of Candidate Genes in Response to Low Nitrogen in Rice Seedlings. Rice 2022, 15, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Ren, W.; Wang, P.; Chen, F.; Yuan, L.; Pan, Q.; Mi, G. Evaluation of maize root growth and genome-wide association studies of root traits in response to low nitrogen supply at seedling emergence. Crop J. 2021, 9, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Gong, X.; Wang, H.; Dang, K.; Deng, X.; Feng, B. Low-nitrogen tolerance comprehensive evaluation and physiological response to nitrogen stress in broomcorn millet (Panicum miliaceum L.) seedling. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 151, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, C.L.; Wan, H.P.; Wu, X.M.; Dai, X.G.; Chen, J.D.; Ji, Q.Q.; Qian, F. Genome-wide association study of low nitrogen tolerance traits at the seedling stage of rapeseed. Biol. Plant. 2021, 65, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Shi, F.; Li, W.; Zhong, M.; Li, C.; Chen, S. Comprehensive screening of low nitrogen tolerant maize based on multiple traits at the seedling stage. PeerJ 2022, 10, e14218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, B.S.; Foulkes, J.; Singh, G.; Sareen, S.; Kumar, P.; Broadley, M.R.; Singh, G.P. Identification of wheat cultivars for low nitrogen tolerance using multivariable screening approaches. Agronomy 2020, 10, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Ling, F.; Jia, D.; Cui, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, C.; Dou, J. Effects of low nitrogen on seedling growth, photosynthetic characteristics and antioxidant system of rice varieties with different nitrogen efficiencies. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.Y.; Wang, X.P.; Cui, S.Z.; Yao, G.K. Research on the differences and mechanisms of nitrogen nutrition between tea varieties. China Tea 1993, 15, 35–37. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.C.; Yang, Y.J.; Chen, L.; Ruan, J.Y. Study on nitrogen efficiency differences of different tea varieties. J. Tea Sci. 2004, 24, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.C.; Yang, Y.J.; Chen, L.; Ruan, J.Y. A preliminary study on physiological and biochemical indicators related to nitrogen utilization efficiency of tea plants. Acta Agron. Sin. 2005, 31, 926–931. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.Y.; Chen, C.S.; Lin, Z.H.; Wei, K.; Wu, L.Y.; Feng, S.H.; Cheng, H. Response differences of tea plant growth to nitrogen concentration among different varieties. Tea Sci. 2015, 35, 423–428. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, J.Y.; Ma, L.F.; Shi, Y.Z. Potassium management in tea plantations: Its uptake by field plants, status in soils, and efficacy on yields and quality of teas in China. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2013, 176, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.F. Research on Nitrogen Absorption and Utilization of Tea Plants and Nitrogen Fertilizer Application Techniques. Ph.D. Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, F.F.; Qi, X.B.; Li, P.; Du, Z.G.; Guo, W. Groundwater depth and nitrogen application amount jointly regulate the water and residual soil nitrate accumulation in agricultural soil profile. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuda, S.; Hayatsu, M. Nitrous oxide flux from a tea field amended with a large amount of nitrogen fertilizer and soil environmental factors controlling the flux. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2004, 50, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Zhang, J.; Meng, T.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Muller, C.; Cai, Z. Tea plantation destroys soil retention of NO3− and increases N2O emissions in subtropical China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 73, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ma, L.; Ji, L.; Shi, Y.; Yi, X.; Yang, Q.; Ruan, J. Long-term nitrogen fertilization indirectly affects soil fungi community structure by changing soil and pruned litter in a subtropical tea (Camellia sinensis L.) plantation in China. Plant Soil 2019, 444, 409–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, V.S.; Herrmann, L.; Hudek, L.; Nguyen, T.B.; Bräu, L.; Lesueur, D. How application of agricultural waste can enhance soil health in soils acidified by tea cultivation: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 813–839. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, X.X.; Wang, J.A.; Dang, J.Y.; Zhang, D.Y. Study on screening indexes of low-nitrogen tolerance genotypes in wheat. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. Sci. 2007, 1, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, L.; Han, P.P.; Chang, H.B.; Gu, C.M.; Huang, W.; Li, Y.S.; Liao, X.S.; Xie, L.H.; Liao, X. Screening of low-nitrogen tolerant germplasm and evaluation of green manure application potential in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Acta Agron. Sin. 2022, 48, 1488–1501. [Google Scholar]
- Muchow, R.C.; Davis, R. Effect of nitrogen supply on the comparative productivity of maize and sorghum in a semi-arid tropical environment II. Radiation interception and biomass accumulation. Field Crops Res. 1988, 18, 17–30. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.Y.; Cheng, H.; Wei, K.; Wu, L.Y.; Zhang, C.C.; Ruan, L. A Method for Identification of Tea Tree Tolerant to Poor Resources. CN 201410118557.5, 30 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.J.; Mi, G.H.; Chun, L.; Liu, J.A.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, F.S. Analysis of heterosis in nitrogen efficiency of maize. Acta Agron. Sin. 2004, 29, 1014–1018. [Google Scholar]
| Treatment | Plant Height (cm) | Plant Width (cm) | LAI | SPAD | Bud Density (per 0.1 m−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cultivar | |||||
| LJ43 | 88.21 ± 5.67 d | 109.00 ± 6.01 abc | 8.63 ± 0.90 ab | 71.26 ± 4.98 cd | 168.00 ± 14.46 a |
| BY1 | 77.58 ± 4.13 e | 95.46 ± 6.02 d | 8.31 ± 1.03 ab | 58.73 ± 2.50 e | 148.11 ± 11.97 c |
| ZC108 | 103.33 ± 7.88 a | 110.29 ± 5.62 abc | 8.65 ± 0.68 ab | 74.13 ± 2.75 bc | 152.61 ± 5.42 bc |
| FDDB | 100.00 ± 4.08 ab | 118.58 ± 9.81 a | 9.12 ± 1.03 a | 62.36 ± 3.03 e | 140.56 ± 5.00 cd |
| WNZ | 92.08 ± 4.40 bcd | 116.38 ± 8.02 ab | 8.65 ± 1.03 ab | 60.11 ± 4.74 e | 154.06 ± 11.61 abc |
| ZN117 | 92.17 ± 6.36 bcd | 105.38 ± 7.14 c | 8.31 ± 0.85 ab | 76.48 ± 5.83 ab | 144.94 ± 10.24 c |
| HJY | 79.58 ± 6.08 e | 104.79 ± 9.32 c | 7.68 ± 1.06 b | 34.19 ± 4.18 f | 126.78 ± 18.97 de |
| DG | 95.42 ± 2.43 abcd | 111.21 ± 7.47 abc | 8.96 ± 0.45 a | 72.69 ± 3.86 bc | 165.71 ± 10.59 ab |
| ZJ | 98.42 ± 10.67 abc | 107.42 ± 4.85 bc | 7.64 ± 1.06 b | 67.76 ± 3.79 d | 92.21 ± 10.73 f |
| TGY | 90.54 ± 7.59 cd | 108.96 ± 8.54 abc | 7.49 ± 0.87 b | 80.15 ± 2.24 a | 120.99 ± 17.93 e |
| N level | |||||
| N450 | 93.68 ± 10.86 a | 109.99 ± 10.40 | 8.53 ± 1.00 | 66.20 ± 12.65 | 147.13 ± 24.45 a |
| N150 | 89.78 ± 8.51 b | 107.50 ± 7.78 | 8.16 ± 0.99 | 65.37 ± 13.79 | 134.11 ± 26.11 b |
| ANOVA | |||||
| Cultivar | <0.001 *** | 0.002 ** | 0.036 * | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** |
| N level | 0.02 * | 0.237 | 0.127 | 0.435 | <0.001 *** |
| Cultivar × N level | 0.743 | 0.996 | 0.687 | 0.739 | 0.589 |
| Treatment | Pruned Litter Biomass (kg ha−1) | Pruned Stem Biomass (kg ha−1) | Pruned Leaves Biomass (kg ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cultivar | |||
| LJ43 | 9190.89 ± 913.38 a | 5319.36 ± 638.09 a | 3871.53 ± 576.17 a |
| BY1 | 5934.90 ± 945.71 c | 3394.74 ± 802.46 c | 2540.16 ± 296.42 c |
| ZC108 | 8723.41 ± 937.40 ab | 5384.59 ± 581.41 a | 3338.83 ± 458.68 ab |
| FDDB | 8819.72 ± 1832.31a | 5313.99 ± 1349.05 a | 3505.73 ± 722.48 ab |
| WNZ | 8956.20 ± 1220.44 a | 5062.72 ± 968.84 a | 3893.48 ± 381.15 a |
| ZN117 | 7953.88 ± 1605.91 ab | 4210.48 ± 1348.53 abc | 3743.41 ± 503.68 a |
| HJY | 3662.24 ± 1304.68 d | 1994.46 ± 663.36 d | 1667.78 ± 641.32 d |
| DG | 8566.77 ± 1361.41 ab | 4737.29 ± 1076.92 ab | 3829.48 ± 657.72 a |
| ZJ | 6015.07 ± 1027.84 c | 2909.02 ± 971.91 cd | 3106.06 ± 318.38 bc |
| TGY | 7149.10 ± 1292.67 bc | 3701.24 ± 872.12 bc | 3447.86 ± 796.86 ab |
| N level | |||
| N450 | 8333.91 ± 1844.34 a | 4655.40 ± 1340.82 a | 3678.51 ± 747.18 a |
| N150 | 6846.87 ± 2026.19 b | 3823.50 ± 1396.38 b | 3023.37 ± 787.70 b |
| ANOVA | |||
| Cultivar | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** |
| N level | <0.001 *** | 0.002 ** | <0.001 *** |
| Cultivar × N level | 0.608 | 0.801 | 0.306 |
| Treatment | Nitrogen in Pruned Litters (kg ha−1) | Nitrogen Content in Pruned Stems (kg ha−1) | Nitrogen Content in Pruned Leaves (kg ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cultivar | |||
| LJ43 | 172.11 ± 21.99 a | 57.46 ± 7.15 ab | 114.76 ± 16.35 a |
| BY1 | 112.02 ± 23.88 c | 36.40 ± 12.07 d | 73.62 ± 12.80 b |
| ZC108 | 166.68 ± 30.47 a | 65.03 ± 13.47 a | 101.65 ± 17.55 a |
| FDDB | 160.04 ± 39.18 a | 55.27 ± 18.33 ab | 104.77 ± 24.03 a |
| WNZ | 159.15 ± 53.08 a | 48.70 ± 19.13 bc | 110.45 ± 35.13 a |
| ZN117 | 153.66 ± 38.13 ab | 52.79 ± 19.95 b | 105.82 ± 22.54 a |
| HJY | 75.01 ± 43.14 d | 20.74 ± 11.47 e | 54.28 ± 12.22 c |
| DG | 150.52 ± 54.52 ab | 36.14 ± 10.95 d | 112.66 ± 30.14 a |
| ZJ | 103.16 ± 22.11 c | 24.11 ± 12.14 e | 81.38 ± 8.32 b |
| TGY | 125.60 ± 24.56 bc | 40.42 ± 7.79 cd | 83.38 ± 18.51 b |
| N level | |||
| N450 | 166.20 ± 39.23 a | 52.92 ± 18.05 a | 110.95 ± 24.78 a |
| N150 | 111.49 ± 35.05 b | 34.64 ± 15.04 b | 77.90 ± 21.77 b |
| ANOVA | |||
| Cultivar | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** |
| N level | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** | <0.001 *** |
| Cultivar × N level | 0.311 | 0.183 | 0.127 |
| Varieties | Indicator’s Tolerance Index | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant Height | Plant Width | One-Hundred-Bud Weight | Bud Density | LAI Value | SPAD Value | Aboveground Biomass | Aboveground Accumulated Nitrogen Content | |
| LJ43 | 0.90 ± 0.03 c | 1.05 ± 0.03 ab | 1.01 ± 0.04 abc | 0.84 ± 0.02 a | 0.85 ± 0.06 abc | 0.98 ± 0.02 a | 0.88 ± 0.11 a | 0.89 ± 0.12 a |
| ZC108 | 0.89 ± 0.02 c | 0.97 ± 0.03 bcd | 0.98 ± 0.01 abc | 0.97 ± 0.02 a | 0.94 ± 0.07 ab | 0.95 ± 0.01 a | 0.87 ± 0.09 a | 0.69 ± 0.18 abcd |
| FDDB | 0.99 ± 0.05 a | 1.09 ± 0.08 a | 1.02 ± 0.04 ab | 0.94 ± 0.03 a | 0.95 ± 0.01 ab | 0.96 ± 0.01 a | 0.78 ± 0.10 a | 0.68 ± 0.10 abcd |
| WNZ | 0.96 ± 0.06 abc | 0.94 ± 0.02 cd | 1.03 ± 0.02 a | 0.86 ± 0.00 a | 0.93 ± 0.01 ab | 0.91 ± 0.07 a | 0.94 ± 0.02 a | 0.64 ± 0.01 bcd |
| ZN117 | 0.91 ± 0.04 abc | 1.06 ± 0.06 ab | 0.78 ± 0.02 d | 0.89 ± 0.04 a | 0.90 ± 0.12 ab | 0.99 ± 0.09 a | 0.67 ± 0.10 a | 0.56 ± 0.06 de |
| BY1 | 0.98 ± 0.02 ab | 0.97 ± 0.01 bcd | 1.05 ± 0.06 a | 0.88 ± 0.06 a | 0.84 ± 0.01 bc | 1.03 ± 0.01 a | 0.92 ± 0.09 a | 0.80 ± 0.07 ab |
| HJY | 0.97 ± 0.04 abc | 0.90 ± 0.02 d | 0.93 ± 0.03 c | 0.82 ± 0.23 a | 0.74 ± 0.00 c | 0.96 ± 0.01 a | 0.38 ± 0.23 b | 0.37 ± 0.13 e |
| DG | 0.99 ± 0.02 a | 0.91 ± 0.04 cd | 0.94 ± 0.08 bc | 0.89 ± 0.02 a | 0.94 ± 0.01 ab | 0.93 ± 0.02 a | 0.83 ± 0.08 a | 0.73 ± 0.10 abcd |
| ZJ | 0.95 ± 0.02 abc | 0.99 ± 0.03 bc | 0.93 ± 0.01 c | 0.76 ± 0.03 a | 0.88 ± 0.01 ab | 0.94 ± 0.01 a | 0.93 ± 0.29 a | 0.58 ± 0.05 cde |
| TGY | 0.93 ± 0.01 abc | 1.00 ± 0.01 bc | 0.93 ± 0.02 c | 0.76 ± 0.04 a | 0.97 ± 0.07 a | 0.99 ± 0.01 a | 0.82 ± 0.04 a | 0.77 ± 0.09 abc |
| Average value | 0.95 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 0.86 | 0.89 | 0.96 | 0.80 | 0.67 |
| CV(%) | 3.75 | 6.10 | 7.73 | 7.59 | 7.36 | 3.42 | 20.00 | 20.57 |
| Low Nitrogen Tolerance Coefficient | Plant Height | Plant Width | One-Hundred-Bud Weight | Bud Density | LAI Value | SPAD Value | Aboveground Biomass |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant width | −0.325 | ||||||
| One-hundred-bud weight | 0.323 | −0.119 | |||||
| Bud density | 0.025 | 0.165 | 0.186 | ||||
| LAI value | −0.110 | 0.320 | 0.010 | 0.253 | |||
| SPAD value | −0.144 | 0.372 | −0.061 | −0.053 | −0.257 | ||
| Aboveground biomass | −0.111 | 0.192 | 0.468 | 0.054 | 0.589 | −0.087 | |
| Aboveground accumulated nitrogen content | −0.191 | 0.339 | 0.478 | 0.119 | 0.45 | 0.318 | 0.735 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, S.; Ni, K.; Chai, H.; Ning, Q.; Cheng, C.; Kang, H.; Liu, H.; Ruan, J. Study on the Nitrogen Response and Low Nitrogen Tolerance Variations in Different Tea Varieties. Agronomy 2025, 15, 815. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040815
Zheng S, Ni K, Chai H, Ning Q, Cheng C, Kang H, Liu H, Ruan J. Study on the Nitrogen Response and Low Nitrogen Tolerance Variations in Different Tea Varieties. Agronomy. 2025; 15(4):815. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040815
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Shenghong, Kang Ni, Hongling Chai, Qiuyan Ning, Chen Cheng, Huajing Kang, Hui Liu, and Jianyun Ruan. 2025. "Study on the Nitrogen Response and Low Nitrogen Tolerance Variations in Different Tea Varieties" Agronomy 15, no. 4: 815. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040815
APA StyleZheng, S., Ni, K., Chai, H., Ning, Q., Cheng, C., Kang, H., Liu, H., & Ruan, J. (2025). Study on the Nitrogen Response and Low Nitrogen Tolerance Variations in Different Tea Varieties. Agronomy, 15(4), 815. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040815








