Abstract
At present, maize production is facing the challenge of balancing stalk lodging caused by stalk rot with maintaining a good grain yield potential. Improving the basal internode properties by optimizing nitrogen (N) management is an effective strategy to reduce the stalk rot incidence and stalk lodging rate, whilst simultaneously achieving a stable grain yield. A two-year field study was conducted to evaluate the basal internode characteristics under natural field conditions and inoculation with Fusarium pseudograminearum, the causative pathogen of stalk rot, and also to measure the ultimate grain yield with four different N fertilizer application rates (0, 120, 180, and 240 kg N ha−1). Rapid injection inoculation and histochemical staining technologies were employed to assess the stalk rot and lodging resistance. The results showed that reducing N rates improved the basal internode qualities (i.e., shorter internode length, larger cross-sectional area, improved internode plumpness and sclerenchyma tissue, and higher lignified degree and vascular number in sclerenchyma tissue) and enhanced the infection resistance. The lodging rate and stalk rot incidence all gradually declined with reduced N rates. Furthermore, pathogen diffusion degree which was indicated by infection index was decreased with reducing N rates. Ultimately, the mechanical strength of the N0, N120, N180, and N240 plants decreased by 5.31%, 5.83%, 5.01%, and 11.21% compared with that of the control, respectively. These results suggested that the stalk quality was improved through optimal nitrogen application, and also that the stalk rot and lodging resistance increased. The grain yield of the N180 plants was superior to that of those receiving the other treatments. Overall, 180 kg N ha−1 is recommended to balance the stalk lodging resistance and grain yield in the research region. Additionally, breeding cultivars with improved stalk quality is likely to be required to counter the escalating lodging risks arising from stalk rot occurrence.
1. Introduction
Maize (Zea mays L.) is one of the most important cereal crops. It is unlikely that further expansions of the agricultural farmland it currently occupies will be needed. Therefore, increasing the yield per unit area is urgently required to satisfy the ever-increasing food, feed, and industrial processing demands [1,2,3]. However, maize stalk lodging has become a critical limiting factor for improving the grain yield in modern production scenarios [4,5]. It reduces the maize yield by approximately 5~25%—up to 75% in severe cases—and leads to a completely diminished yield [6,7]. Lodging also results in grain quality reduction and harvesting difficulties [8]. Furthermore, extreme weather events, including gales and torrential rain, occur frequently in the context of climate change, and are one of the primary external causes of stalk lodging [9]. Hence, enhancing maize lodging resistance has become a key goal for increasing and/or maintaining the grain yield per unit area.
Maize basal internode properties play a vital role in improving the stalk lodging resistance [10,11]. Many researchers have shown that the maize lodging resistance strongly depends on the morphological characteristics, anatomical structure, and mechanical strength of the basal internodes [12,13,14]. A wind tunnel simulation experiment revealed that the plant height and basal internode anatomy traits were key factors for maize stalk lodging resistance [15]. A meta-analysis also indicated that the dry weight of biomass, cellulose and lignin content, and anatomical structure were all identified as important indicators of lodging stress tolerance [16]. The stalk diameter, dry weight, lignin and cellulose content, and bending strength of the basal internodes are all significantly positively correlated with the maize stalk lodging resistance. That is to say, high-quality basal internodes possess a larger stalk diameter, higher dry weight per unit length, thicker sclerenchyma tissues, stronger bending strength, and so on. Thus, improving the basal internode quality could decrease the lodging risk and ensure a stable grain yield.
Lower stalk quality is a direct cause of lodging. However, stalk rot, a devastating soil-borne disease, is an indirect factor causing stalk lodging [17,18]. Stalk rot is recognized by irregular longitudinal brown spots at the basal internodes of the stalk; then, constriction, softening or hardening, and loosening of the stalk interior occur at a later stage of the disease, which is related to the senescence of stalk pith cells [19]. Fusarium (F.) pseudograminearum is the main pathogen causing maize stalk rot in the North China Plain. Conidiums of F. pseudograminearum can infect the plant through the root and/or wounds caused by mechanical injury. Stalk rot leads to vascular bundle damage and then reduces the stalk’s mechanical strength [20]. Therefore, the decomposition of the maize stalk after infection by this pathogen causes a decrease in the stalk quality and thus increases the risk of lodging. Statistically, the incidence of stalk rot in the field reaches 5–30% in China [21]. The causative pathogen spreads and infects plants mainly through the soil; therefore, applying fungicides is ineffective at completely curing stalk rot. A convenient and effective strategy is urgently needed, e.g., crop management optimization for enhancing plants’ resistance and then reducing maize stalk rot occurrence and the lodging rate.
N is one of the most important nutrients for plant growth and improving grain yield. Moderate N fertilizer application could optimize photosynthate allocation to the basal internodes, improving internode formation and, thus, the stalk quality [22]. Therefore, N application is the most accessible and effective measure that improves the lodging resistance of maize. Many studies have shown that excess N application leads to plant over-growth, increases plant height and internode length, thins internodes, and lowers the stalk filling degree, which increases plants’ susceptibility to stalk lodging [23,24,25]. Furthermore, previous studies have reported that the chemical composition of basal internodes, comprising lignin and cellulose, could be significantly affected by the N application rate, and therefore change the internode toughness and rigidity [26,27]. However, there is limited research on the effects of N application rates on lodging resistance through the regulation of pathogen infection and stalk rot spread as well as the relationship between them.
Based on the above, we hypothesized that moderate N application could increase maize’s lodging resistance by regulating its stalk rot resistance. In this study, we conducted two field trials of different N application rates, examining the basal third internode characteristics under natural field conditions and inoculation with a pathogen in the growing seasons of 2019 and 2020. The morphological characteristics, anatomical structure, basal third internode mechanical strength, and final grain yield were analyzed. Also, the pathogen infection process and its extent were also observed after inoculation. The main objectives of this study were as follows: (1) to analyze the growing dynamics of indicators relating to the mechanical strength of the basal third internodes with different N application rates; (2) to clarify the regulating effects of N application rates on the lodging resistance under natural conditions and inoculation; and (3) to recommend a N application level that balances the lodging resistance and grain yield.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site Description
The field experiment was established in 2019 and 2020 at Dishang Experimental Station, Hebei province, China (114°72′ E, 37°94′ N; 65 m asl), which represents the agricultural production and climate conditions of the North China Plain in China. The experimental site experiences a warm, temperate zone, semi-humid, and monsoon climate. Figure 1 presents the average monthly precipitation and air temperatures in 2019 and 2020 growing seasons. The soil at the experimental site is light loam, and the soil characteristics at the 0–20 cm soil layer were shown in Table 1. The assay standardized methods of soil organic matter, total N, total K, available N, available P, and available K were the Walkley–Black method, Kjeldahl method, Sodium bicarbonate extraction, Sodium hydroxide melting, Sodium hydroxide extraction, and Ammonium acetate extraction, respectively [28].
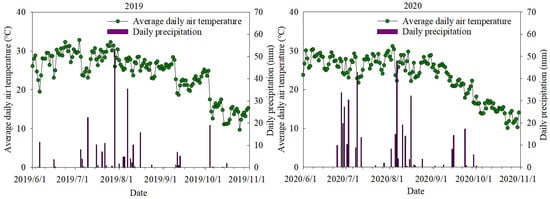
Figure 1.
The average daily air temperature and daily precipitation in 2019 and 2020 growing seasons.

Table 1.
The soil characteristics at the 0–20 cm soil layer of the experiment site.
2.2. Experimental Material and Design
Experiment 1 was designed to explore the effects of N application rates on maize stalk quality, lodging rate and stalk rot incidence in 2019 and 2020. The maize hybrid Zhengdan 958 (ZD958) was selected as the experimental material, which was applied widely in the research region. The planting density was 7.5 × 104 plants ha−1. The experiment adopted a completely random design. Each treatment was arranged for three replications, and the plot area was 56.3 m2 (7.5 m × 7.5 m). Four N fertilizer application rates (0, 120, 180, and 240 kg ha−1) were designed, which were denoted by N0, N120, N180, and N240, respectively. The application rates of the phosphorus (P2O5) and potassium (K2O) for each treatment were 120 kg ha−1 and 150 kg ha−1. The N, P, and K fertilizers were all applied once at sowing according to the general management mode in the research region.
Experiment 2 was designed with a rapid injection inoculation technology undertaking to evaluate the regulating effects of N application rates on resistance to pathogen expansion of stalk rot. The fifty plants per plot with uniform growth and no pests and diseases were selected to mark using tags at tasseling stage. The main pathogen of F. pseudograminearum causing stalk rot at the research region was inoculated on Potato Dextrose Agar plate medium (200 g potato, 20 g glucose, 20 g agar, 1000 mL water) and cultured for 7 days till the hyphae took over the entire plate. Then, the agar and F. pseudograminearum were mixed with a concentration of 2.0 × 106 mL−1 for inoculation. Before inoculation, a drill with a diameter of 3 mm was used for opening a hole in the middle of the third basal internode above the soil of selected plants at 7 days after silking, into which 0.5 mL of mixture was injected at the four N treatments. Then, petroleum jelly was smeared on the hole to prevent rainwater from flowing into the hole. Healthy maize plants of each N treatment served as controls.
2.3. Measuring Items and Methods
2.3.1. Natural Stalk Lodging Rate and Stalk Rot Incidence
Plants were considered stalk-lodged when they broke at or below the ear-bearing node. The number of stalk lodging plants in each plot was recorded. The stalk lodging rate was calculated by dividing the number of stalk-lodged plants by the total number of plants. The stalk rot incidence was calculated by dividing the number of stalk rot plants by the total number of plants.
2.3.2. Morphological Characteristics of Basal Third Internode
Sampling occurred at V12 (twelve-unfolded leaves), VT (tasseling), R4 (dough stage), and R6 (physiological maturity) in 2019 and added R2 (blister stage) and R5 (dent stage) in 2020. Five representative plants in each plot were sampled to measure mechanical properties of basal third internode and anatomical features.
The lengths of the basal third internodes (L, cm) were measured with a ruler. The major axis (A1, mm) and short axis (A2, mm) of the basal third internodes were measured using a digital vernier caliper. The cross sectional area (CSA, mm2) was calculated by Formula (1) [29].
The basal third internodes were dried at 75 °C in a drying oven to a constant weight and then weighted using a balance scale (DW, mg). The internode plumpness (mg/cm DW), referring to the dry weight per length of basal third internode, was calculated by Formula (2).
Internode plumpness = DW/L
2.3.3. Histochemical Staining of Transverse
About 1 cm of tissue was cut from the basal third internodes with a sharp blade at the R2 stage and then put into FAA solution (70% ethanol, acetic acid, 38% formaldehyde) quickly for at least 48 h. To observe the lignified cell walls, safranin O-fast green staining was performed according to standard protocols. The area and number of vascular bundles and the thickness of sclerenchyma tissue were quantified using CaseViewer software 2.3.2 (3DHISTECH Ltd., Budapest, Hungary).
2.3.4. Mechanical Property
The mechanical strength (N) of basal third internodes was determined using a stalk strength tester (Zhengjiang Top Instrument Co., Ltd., Hangzhou, China) at each sampling stage. The test probes (“U” type and pin type) of the tester were vertical and uniform and acted on the middle of the internodes, and then the maximum force required to break or pierce the stem was displayed on the screen of the tester.
2.3.5. Infection Index
After measuring the mechanical strength of the internode, the stalk was longitudinally split to inspect the pith for discoloration, and then the length of discoloration of internodes (DL) was measured with a ruler. The total length of the internode (L) was also recorded (Figure 2). The internode infection index was calculated according to Formula (3) [13].
Infection index (%) = DL/L × 100%
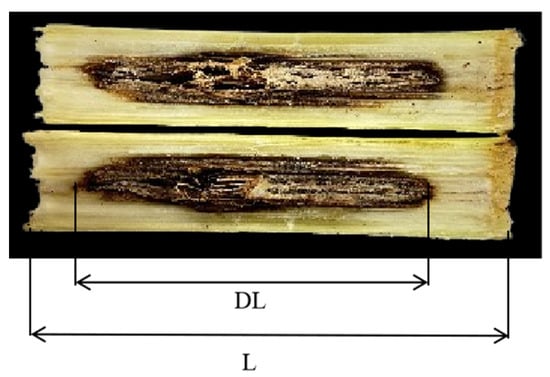
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram for measuring infection index of basal third internode.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed for the stalk morphological characteristics, mechanical properties, cell wall components, and grain yield using IBM SPSS Statistics 19.0 software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Comparisons among different treatments were separated using the least significant differences (LSD) test at p ≤ 0.05. The figures in this experiment were plotted using SigmaPlot 14.0 (Systat Software, Inc., SanJose, CA, USA).
3. Results
3.1. The Morphological Parameters of Basal Third Internodes
There were significant differences in the internode length, cross-sectional area, and internode plumpness as growing progressed (Figure 3). The internode length showed a stable trend from V12 with each N treatment (Figure 3a,b). However, the cross-sectional area exhibited an increase with development and reached its maximum at R1, then became stable (Figure 3c,d). The basal third internode plumpness presented a unimodal curve, reached its maximum value at the R4 stage, and then gradually decreased (Figure 3e,f).
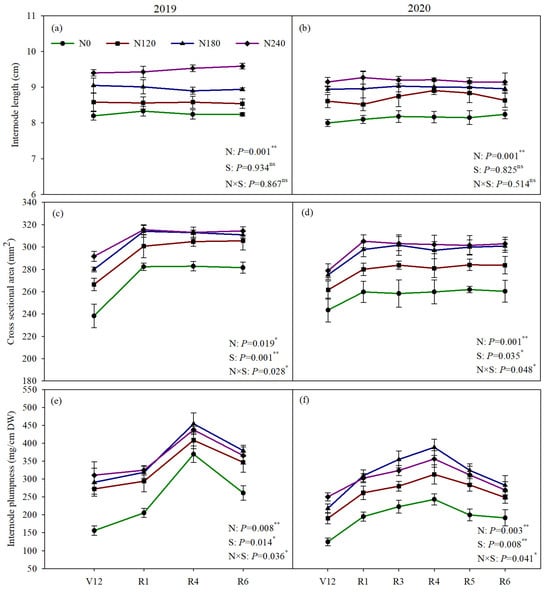
Figure 3.
Dynamics of maize basal third internode morphological characteristics during 2019 and 2020 growing seasons. (a,c,e) represent the internode length, cross sectional area and internode plumpness, respectively, in 2019, and (b,d,f) represent those characters in 2020. N0, N120, N180, and N240 represent N application amounts of 0, 120, 180, and 240 kg N ha−1, respectively. V12, twelfth leaf; R1, silking; R3, milk; R4, dough; R5, dent; R6, mature. Error bars represent the standard error of means. * and ** indicate significance at p < 0.05 and p < 0.01.
The N application rates had significant effects on the internode length, cross-sectional area, and internode plumpness. With decreasing N application rates, both the internode length and cross-sectional area showed a trend of decreasing gradually over the two growing seasons. Compared with those of N240, the internode length and cross-sectional area of the N0, N120, and N180 plants decreased by 12.20%, 7.46%, and 3.81%, and 13.03%, 5.64%, and 1.28%, respectively. It was observed that there was no significant change in the internode length from V12 to R6. The cross-sectional area increased with the N rates, but that of the N180 and N240 plants showed no significant difference during the R1-R6 period. In the V12-R1 period, the internode plumpness tended to decrease with decreasing N application, but in the R1-R6 period, the internode plumpness of the N180 plants was the highest. These results indicate that moderate N application (180 kg ha−1) could reduce the basal internode length, maintain a relatively high stalk diameter, and improve the internode plumpness of maize basal stalks during the filling stage.
3.2. The Anatomical Structure of Basal Third Internodes
The N application rates had significant effects on the vascular bundle diameter per unit visual field of the maize basal third internode (Figure 4). With decreasing N application rates, the bundle diameter per unit visual field showed an increasing trend. That of the plants receiving the N0 treatment was significantly higher than those under other treatments, but there was no significant difference between the plants receiving the N180 and N240 treatments.
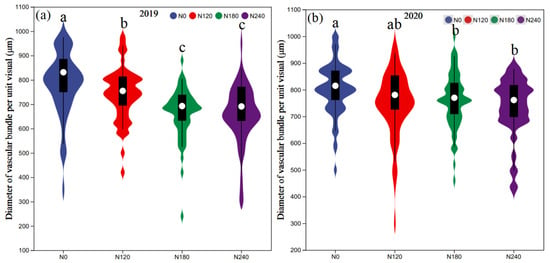
Figure 4.
The diameter of vascular bundle per unit visual under different N treatments. (a) represent diameter of vascular bundle per unit visual in 2019 and (b) represent that in 2020. The violin plots show the value distribution during the two growing seasons. The black bars represent the 25 and 75 percentiles, and the white dots within the plots indicate the median. N0, N120, N180, and N240 represent N application rates of 0, 120, 180, and 240 kg N ha−1, respectively. Different lowercase letters denote significant differences between the N treatments at p < 0.05.
The effect of the N application rate on the vascular bundle number in the sclerenchyma and parenchyma of the maize basal third internode was different (Table 2). The number of vascular bundles in the sclerenchyma decreased with decreasing N, while the number of vascular bundles in the parenchyma had the opposite trend. The effect of the N application rate on the total vascular bundle number was inconspicuous, except for that with N0, which was significantly lower than that with the other treatments.

Table 2.
Number of vascular bundles under different N application rates.
To investigate the basal internode quality in more detail, the anatomical characteristics were measured using paraffin sections (Figure 5). The N application rates had a significant effect on the micro-structure and lignification degree of the maize basal internodes. With increasing N application, the sclerenchyma thickness first increased (from 655.20 μm at N0 to 1074.90 μm at N180) and then decreased (from 1074.90 μm at N180 to 725.80 μm at N240). The lignification degree of the sclerenchyma, parenchyma, and vascular bundle increased with decreasing N. The results showed that moderately reducing the N amount could improve the lignification degree of the maize basal stalks and improve the stalk quality.
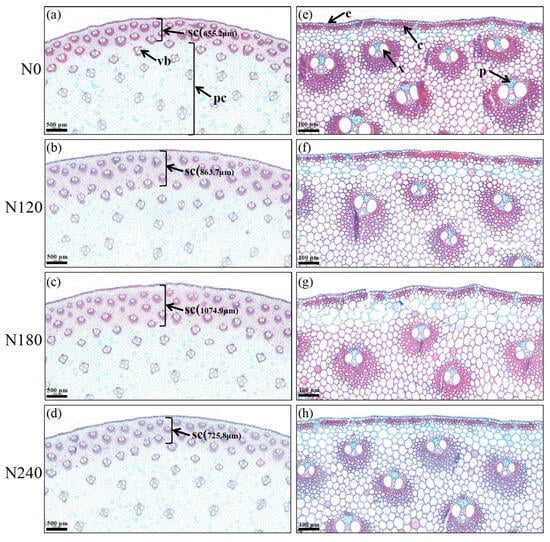
Figure 5.
Transverse sections of internodes stained with sarranine-O-fast green for lignification. Left column images under 2× ocular lens; right column images under 10× ocular lens. sc, sclerenchyma tissues; pc, parenchyma tissues; e, epidermis; c, cortex; x, xylem; p, phloem; vb, vascular bundle. N0, N120, N180, and N240 represent N application rates of 0, 120, 180, and 240 kg N ha−1, respectively. Bars = 500 μm (a–d) and 100 μm (e–h). The cells are stained red, and the deeper the stain, the more lignified they are.
3.3. The Mechanical Strength of Basal Third Internodes
The N application levels and growing stages had significant effects on the mechanical strength of the basal third internode (Table 3). The mechanical strength showed a trend of first increasing and then decreasing with basal third internode development. The mechanical strength increased to its maximum value at R3–R4, and then decreased gradually. The increasing N application rates contributed to improving the mechanical strength of the basal internode, but excessive N application (such as 240 kg ha−1) had the opposite effect. The average values at the investigated stages were 279.6, 313.0, 328.4, and 282.7 at N0, N120, N180, and N240, respectively (the mean value of two seasons and growing stages). It was observed that N180 was the optimal N application treatment and led to the highest mechanical strength of the basal third internode.

Table 3.
Effect of N application levels on mechanical strength of basal third internodes at V12, R1, R3, R4, R5, and R6 in two growing seasons.
3.4. Stalk Lodging Rate and Stalk Rot Incidence and Relationship Between Them
With the decreasing N application rate, the stalk lodging rate showed a decreasing trend during the two growing seasons (Figure 6a,b). The stalk lodging rate of the N0 plants was significantly lower than that of the plants subjected to the other N treatments. However, that of the N240 plants was significantly higher than that of the plants receiving the other treatments. The stalk lodging rate of the N0, N120, and N180 plants decreased by 85.38%, 65.62%, and 59.11% compared to that of N240 plants (mean value of two seasons and growing stages). By investigating the stalk rot incidence, it was found that its trend was basically the same as that of the stalk lodging rate under different N application rates (Figure 6c,d). Compared with the stalk rot incidence of the N240 plants, that of the N0, N120, and N180 plants was decreased by 74.97%, 54.03%, and 41.95% (mean value of two seasons and growing stages), respectively. The results indicated that the stalk lodging rate and stalk rot incidence of maize could be significantly reduced by reducing the N application rate.
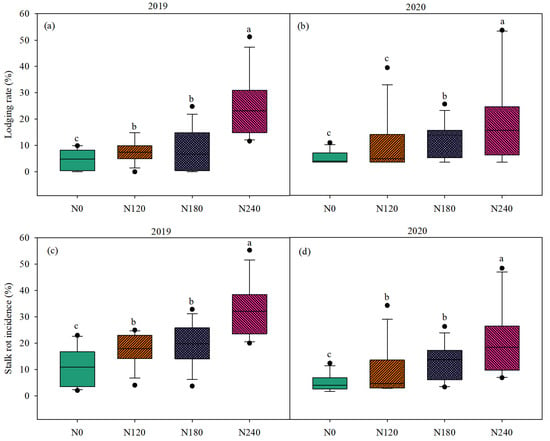
Figure 6.
Stalk lodging rate and stalk rot incidence under different N treatments in 2019 and 2020. (a,b) show the stalk lodging rate, and (c,d) exhibit the stalk rot rate. The box plots show spanning 25 and 75 percentiles meeting at the median. The solid line in the box indicates the mean value. The dark spots indicate the outlier. Different lowercase letters denote significant differences among the N levels at p < 0.05.
The stalk rot incidence was significantly positively correlated with the stalk lodging rate under natural conditions (Figure 7). According to the coefficient of determination (R2) of the fitting equation over the two growing seasons, the percentage of stalk lodging caused by stalk rot disease reached 70.74%. Moreover, per 0.37% increase in stalk lodging, there was an increase in stalk rot by 1%. This indicated that stalk rot was an important factor affecting maize lodging.
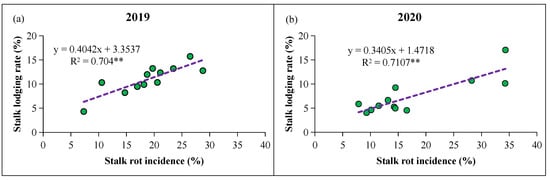
Figure 7.
Relationship between natural stalk rot incidence and stalk lodging rate of different N application levels in two growing seasons. (a,b) represent correlation analysis between stalk lodging rate and stalk rot incidence in 2019 and 2020, respectively. Green circles and purples represent the correlation coefficient and regression line, respectively. ** indicates significance at p < 0.01.
3.5. Infection Process and Infection Index Under Different N Rates
The disease spots showed a gradual increasing trend as the infection progressed. Different N application rates had significant effects on the stalk rot severity, which was indicated by the infection index (Figure 8). As the infection time advanced, the infection index also increased. Decreasing the N application rate could help reduce the infection index. Compared with the infection index of the N240 plants, that of the N0, N120, and N180 plants was, on average, reduced by 24.51%, 15.16%, and 11.04%. This result indicated that reducing the N application levels appropriately could alleviate the degree of stalk rot infection.
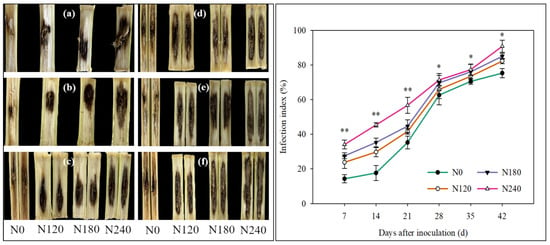
Figure 8.
The plot on the left shows the infection process of Fusarium gramineum on maize basal stalk under different N treatments. (a–f) indicate the 7th day, 14th day, 21st day, 28th day, 35th day, and 42nd day after inoculation, respectively. The plot on the right shows the infection index during the inoculation process. ** and * indicate significance at p < 0.01 and p < 0.05.
3.6. The Mechanical Strength of Basal Third Internodes Inoculated by Pathogen Under Different N Rates
Compared with the mechanical strength of the non-inoculated stalks, that of the inoculated stalks exhibited a decreasing trend (Figure 9). Also, as the infection duration increased, reductions in the strength intensified gradually. Compared with the controls, the reduction in the stalk mechanical strength decreased from 2.70% to 10.78% (mean value of N application rates) from 7 to 42 days after inoculation. The different N application rates had significant effects on the stalks’ mechanical strength after inoculation. Increasing the N application rate contributed to improving the stalk mechanical strength, but excessive N, for example, 240 kg ha−1, had the opposite effect. The fluctuations in the stalk mechanical strength in the plants receiving the N240 treatment were significantly higher than those receiving the other N treatments (average of each sampling period). The mechanical strength of the N0, N120, N180, and N240 plants decreased by 5.31%, 5.83%, 5.01%, and 11.21% compared with that of the control, respectively. From 7 to 21 days after inoculation, the mechanical strength of the plants receiving the N0 treatment was not significantly different from that of the control plants, while that of the plants receiving the other N treatments was significantly reduced. The results showed that moderately reducing the N application rate could reduce the decreasing fluctuations in the stalk mechanical strength, slowing down the decline in the stalk quality in the case of infection.
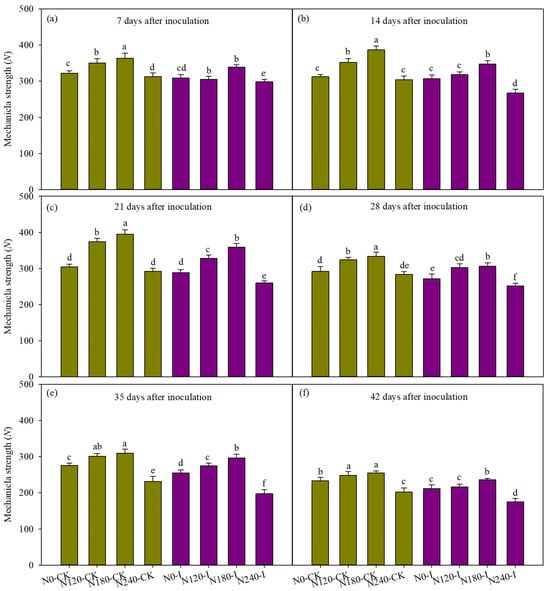
Figure 9.
The mechanical strength of the basal third internode under natural conditions and inoculation conditions. (a–f) indicate 7, 14, 21, 28, 35 and 42 days after inoculation, respectively. CK represents control. I represents inoculation with pathogen. N0, N120, N180, and N240 represent N application rates of 0, 120, 180, and 240 kg ha−1, respectively. Different lowercase letters denote significant differences between the N levels at p < 0.05.
3.7. Grain Yield Under Different N Application Levels
The N application rates had significant effects on the maize yield and its constituent factors (Table 4). Among the yield’s components, the ear numbers exhibited little change with alterations in the N rates. However, the kernel number per ear and 1000-kernel weight increased with an increase in N application rates, while those of the N180 and N240 plants had no significant difference. Compared with the kernel number per ear and 1000-kernel weight of the N0 plants, those of the N120, N180, and N240 plants increased by 5.87%, 9.73%, and 10.41% (average of two years), respectively. The grain yield of the N0 and N120 plants was reduced by 9.76% and 5.61%, respectively, compared with that of N240. Ultimately, the grain yield performance of the plants receiving the N180 and N240 treatments exhibited no significant difference but was significantly higher than that of the N0 and N120 plants. The results showed that moderately reducing N could lead to a higher yield by improving the three components of grain yield together. N180 was the optimal N fertilizer application strategy for maintaining a relatively higher grain yield.

Table 4.
Effect of different N application rates on grain yield and yield components.
4. Discussion
4.1. Moderately Reducing N Optimized Basal Internodes Morphogenesis and Achieved Stable Grain Yield
The evidence from the 2-year field experiment demonstrated that a moderately reduced N application strategy could improve the basal internode quality and increase the lodging resistance. In terms of morphological characteristics, previous studies have shown that the internode length, stalk diameter, and filling degree of the basal internode are pivotal indicators of the stalk mechanical strength [14,29]. Significantly decreasing the basal internode length and increasing the stalk diameter and filling degree could contribute to improving plants’ lodging resistance [30]. This research is fully consistent with former results. In this study, based on the morphological characteristics of basal third internode, we estimated that the internode length, cross-sectional area, and internode filling plumpness increased with increasing N application rates. However, excessively high N application rates (such as over 180 kg ha−1) also significantly increased the internode length, which reduces the lodging resistance. There was no significant difference between the N180 and N240 plants regarding the cross-sectional area and internode plumpness. That is to say, the cross-sectional area and plumpness of the basal third internode could reach a high level, and a suitable internode length could be maintained under the application of 180 kg N ha−1; continuing to increase N was redundant and wasteful.
Regarding anatomical characteristics, it has been reported that the sclerenchyma cells in the mechanical tissues under the epidermis are very important for mechanical strength [31,32]. Also, a previous study indicated that stabilizing the cell structure, preventing intracellular space expansion, and reinforcing the cell wall were key targets to increase the stalk rot resistance of maize [33]. In this study, the micro-structure observations of the transverse sections of the basal third internode revealed that the sclerenchyma tissue width increased with increasing N application, but excessive N application led to a reduced sclerenchyma tissue thickness under the application of 240 kg ha−1. A noteworthy aspect of the anatomical traits was that the degree of lignification of the sclerenchyma tissues and vascular bundles increased with decreased N application rate. Vascular bundles play a vital role in mechanical support. Therefore, the vascular bundles in plant stalk tissues provide hardness and toughness and can be regulated by cultivation management. It might be that mechanical support was sufficiently regulated by moderate nitrogen application rates.
Previous studies have shown that mechanical strength is a pivotal indicator of maize lodging resistance [34,35]. Appropriate N application could promote maize growth and the development of basal stalks, thus improving the maize lodging resistance. In this study, the basal internode mechanical strength increased with increased N application rates, but excessive N application, i.e., at 240 kg ha−1, had the opposite effect on the mechanical strength. In real-life production, the balance between lodging resistance and grain yield should be considered. It is generally believed that the risk of lodging is higher under high-yielding conditions and is much more pronounced under excessive N application. Previous studies have demonstrated that crop lodging is only observed in plots where higher grain yields are obtained [36,37]. The higher the N application rate, the higher the lodging risk [38]. This study is fully in agreement with these findings. Increasing the N application contributed to improving the grain yield; however, an excessive N application rate carried with it a higher lodging risk. In this study, the grain yield of the N180 and N240 plants showed no significant difference, but the lodging resistance of the N180 plant was significantly higher than that of the N240 plant. Although the N0 and N120 plants had a lower lodging rate and stalk rot incidence, their grain yield was also reduced significantly. Therefore, optimizing N fertilizer management could improve the morphological traits and dry matter accumulation of basal internodes and thus increase their mechanical strength and enable a higher grain yield to be achieved. A moderate N application rate of 180 kg ha−1 is recommended for maize production under the tested environmental conditions, with the yield performance and lodging resistance considered simultaneously.
4.2. Moderately Reducing N Enhanced Resistance to Pathogen Infection and Reduced the Lodging Rate
One reason for reduced lodging rates with moderate N application is the reduction in stalk rot incidence under natural conditions. N is involved in plant developmental processes but is also an energy source required for pathogen infection [39]. There is evidence that N fertilizer increases the stalk rot severity, especially if at an excessive dosage. When plants are supplied with excessive N, pathogens are able to reproduce at a high rate and invade plant tissues. The main symptom of stalk rot is that the internodes become soft and the pith becomes hollow; thus, the plant is susceptible to lodging under adverse weather conditions [40]. Hence, maintaining a moderate N supply to prevent or alleviate stalk rot and stalk lodging needs more attention in maize management. This study’s findings are in full agreement with this statement. In the current study, the maize stalk rot prevalence and lodging rate with four different N application rates were evaluated under natural conditions. The stalk rot and lodging rate all decreased with reduced N application rates. In addition, the stalk rot incidence was significantly positively correlated with the stalk lodging rate under natural conditions. Based on the coefficient of determination (R2) of the fitting equation, the percentage of stalk lodging induced by stalk rot was 70.74%. Moreover, per increase in stalk lodging of 0.37%, the stalk rot increased by 1%. This indicated that stalk rot was a very important factor affecting stalk lodging. Therefore, reducing stalk rot infection through moderate nitrogen management is an effective strategy for reducing the lodging rate.
4.3. Moderately Reducing N Improved Resistance to Pathogen Expansion and Maintained Relatively High Stalk Mechanical Strength
Another contributing factor to enhancing lodging resistance through moderate N application is the resistance to pathogen spread with inoculation. This study utilized a rapid injection inoculation technique to evaluate how N application rates regulated the resistance to stalk rot spread under field conditions. In this research, the lesion area spread from the parenchymatous tissues to the sclerenchyma tissues with the inoculation treatment, which can be explained by the parenchymatous tissues being more susceptible to infection and the sclerenchyma tissues having a degree of resistance against pathogen spread during the inoculation process. This finding was consistent with previous research and indicated that a higher proportion of the sclerenchyma tissue functioned similarly as a hard, protective defense against pathogen spread [41]. The infected internodes softened, thus reducing their mechanical strength, which eventually led to stalk lodging. The infection index reflects the degree of longitudinal spread of the pathogen. Moderately reducing the N application increased the pathogen spread resistance, which could be expressed as a reduction in the infection index.
This research also indicated that, compared with the control, the inoculation treatment reduced the mechanical strength of the basal third internodes. Moderate N application could mitigate the degree of mechanical strength loss and reduce the lodging risk. In addition, stalk rot resistance is related to the degree of lignification of the internode. A previous study has shown that a higher content of cell wall structural carbohydrates, such as lignin and cellulose, in the internodes leads to stronger stalk rot resistance [42]. These carbohydrates can act as structural barriers against the adaptation of plants to disease stress [43]. Therefore, increasing the stalk quality, sclerenchyma tissue proportion, and lignification could increase the stalk rot resistance, which can be achieved through moderate N application, at 180 kg ha−1.
This study has clarified the regulatory effects of moderate N application on improving properties related to lodging and also enhancing resistance to infection and expansion of stalk rot. However, in-depth research is required to reveal the defense mechanism of N’s regulation of stalk rot and lodging resistance. For example, plant cell walls are changeable structures, the elements of which can be altered in response to stalk rot. This will trigger adaptive responses (such as in plant metabolism processes, hormone levels, signaling pathways, and so on) during stalk development and infection, which is worthy of elucidation in the future.
5. Conclusions
This study systematically analyzed the regulating effects of N rates on lodging resistance of maize under natural field conditions and after inoculation. The results indicated that moderately reducing the N application to 180 kg ha−1 improved the morphological characteristics (such as decreasing the internode length and increasing the cross-sectional area and filling degree of the basal internode), reinforced the anatomical structure (such as increasing the degree of lignification of the internodes and sclerenchyma tissue proportion), and enhanced the mechanical strength of the maize plants. These changes all contributed to increasing the lodging and stalk rot resistance compared to with excessive N application, at 240 kg ha−1. Also, reducing N alleviated the fluctuations in the decline in mechanical strength after inoculation. A moderate 180 kg ha−1 N treatment could balance the stalk lodging resistance and grain yield and, overall, is recommended for increasing the maize stalk lodging and stalk rot resistance and for maintaining a higher grain yield performance in the present experimental region. This research might provide a theoretical foundation for reducing stalk rot and increasing lodging resistance through optimal N management.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.Z. and J.Z.; methodology, M.Z.; software, Y.C.; validation, Y.S.; formal analysis, M.Z.; investigation, L.L.; resources, L.L.; data curation, M.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, M.Z.; writing—review and editing, M.Z.; visualization, J.Z.; supervision, Y.S.; project administration, J.Z.; funding acquisition, J.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by S&T Program of Hebei (22326404D), National Key Research and Development Plan (2023YFD190260404), and Science and Technology Innovation Project, Hebei Academy of Agricultural and Forestry Science (2022-KJCXZX-LYS-8).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Jingjing Jin (Institute of Cereal and Oil Crops, Hebei Academy of Agricultural and Forestry Science) for providing Fusarium pseudograminearum.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Chen, X.P.; Cui, Z.L.; Vitousek, P.M.; Cassman, K.G.; Matson, P.A.; Bai, J.S.; Meng, Q.F.; Hou, P.; Yue, S.C.; Romheld, V.; et al. Integrated soil-crop system management for food security. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 6399–6404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilman, D.; Clark, M. Food, Agriculture & the Environment: Can We Feed the World & Save the Earth? Daedalus 2015, 144, 8–23. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.L.; Zhang, H.Y.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, C.C.; Ma, W.Q.; Huang, C.D.; Zhang, W.F.; Mi, G.H.; Miao, Y.X.; Li, X.L.; et al. Pursuing sustainable productivity with millions of smallholder farmers. Nature 2018, 555, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.T.; Zhang, S.; Lv, Y.J.; Ning, F.F.; Cao, Y.B.; Liao, S.H.; Wang, P.; Huang, S.B. Optimizing ear-plant height ratio to improve kernel number and lodging resistance in maize (Zea mays L.). Field Crops Res. 2022, 276, 108376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Nie, C.W.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.X.; Ming, B.; Xue, J.; Yang, H.Y.; Xu, H.G.; Meng, L.; Cui, N.B.; et al. Evaluating how lodging affects maize yield estimation based on UAV observations. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13, 979103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Ma, W.; Peng, J.Y.; Chen, Z.M. Study on yield loss of summer maize due to lodging at the big flare stage and grain filling stage. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2015, 48, 3952–3964. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Gu, X.H.; Chen, L.P.; Qu, X.Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, J.P.; Pan, Y.C. Hyperspectral estimation of maize (Zea mays L.) yield loss under lodging stress. Field Crops Res. 2023, 302, 109042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.F.; Ming, B.; Hou, L.Y.; Xue, J.; Wang, K.R.; Xie, R.Z.; Hou, P.; Wang, Z.G.; Ma, D.L.; Gao, J.L.; et al. Improving maize quality from mechanical grain harvesting by matching maize varieties with accumulated temperature in northeast China. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 5061–5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.L.; Liu, F.; Li, X.L.; Yin, P.J.; Lan, T.Q.; Feng, D.J.; Song, B.; Lei, E.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.L.; et al. Ecological factors regulate stalk lodging within dense planting maize. Field Crops Res. 2024, 317, 109529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.L.; Xie, R.Z.; Liu, X.; Niu, X.K.; Hou, P.; Wang, K.R.; Lu, Y.L.; Li, S.K. Lodging-related stalk characteristics of maize varieties in China since the 1950s. Crop Sci. 2014, 54, 2805–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Gu, S.C.; Wang, Y.Y.; Yang, R.M.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Sheng, D.C.; Cui, T.; Huang, S.B.; Wang, P. Morphological and mechanical variables associated with lodging in maize (Zea mays L.). Field Crops Res. 2021, 269, 108178. [Google Scholar]
- Sekhon, R.S.; Joyner, C.N.; Ackerman, A.J.; McMahan, C.S.; Cook, D.D.; Robertson, D.J. Stalk bending strength is strongly associated with maize stalk lodging incidence across multiple environments. Field Crops Res. 2020, 249, 107737. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.; Gao, S.; Hou, L.Y.; Li, L.L.; Ming, B.; Xie, R.Z.; Wang, K.R.; Hou, P.; Li, S.K. Physiological influence of stalk rot on maize lodging after physiological maturity. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, D.J.; Brenton, Z.W.; Kresovich, S.; Cook, D.D. Maize lodging resistance: Stalk architecture is a stronger predictor of stalk bending strength than chemical composition. Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 219, 124–134. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.M.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, S.H.; Wen, W.L.; Lu, X.J.; Guo, X.Y. Identifying key factors influencing maize stalk lodging resistance through wind tunnel simulations with machine learning algorithms. Artif. Intell. Agric. 2025; in press, corrected proof. [Google Scholar]
- Ghorbani, M.; Amirahmadi, E. Biochar and soil contributions to crop lodging and yield performance—A meta-analysis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 215, 109053. [Google Scholar]
- Khokhar, M.; Hooda, K.S.; Singh, V. Open access post flowering stalk rot complex of maize present status and future prospects. Maydica 2014, 59, 226–242. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Xue, J.; Chen, J.G.; Fan, Y.H.; Zhang, G.Q.; Xie, R.Z.; Ming, B.; Hou, P.; Wang, K.R.; Li, S.K. Key indicators affecting maize stalk lodging resistance of different growth periods under different sowing dates. J. Integr. Agric. 2020, 19, 2419–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goszczyska, T.; Botha, W.J.; Venter, S.N.; Coutinho, T.A. Isolation and identification of the causal agent of brown stalk rot, a new disease of maize in South Agrica. Plant Dis. 2007, 91, 643–773. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.J.; Saravanakumar, K.; Xia, H.; Gao, J.X.; Fu, K.H.; Sun, J.N.; Dou, K.; Chen, J. Occurrence and virulence of Fusarium spp. Associated with stalk rot of maize in North-East China. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2017, 98, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Wang, B.; Sun, X.F.; Qi, X.B.; Zhao, C.H.; Chang, X.L.; Khaskheli, M.L.; Gong, G.S. Symptoms and pathogens diversity of corn Fusarium sheath rot in Sichuan Province, China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2835. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Gu, S.C.; Wang, Y.Y.; Xu, C.C.; Zhao, Y.T.; Liu, X.L.; Wang, P.; Huang, S.B. The relationships between maize (Zea mays L.) lodging resistance and yield formation depend on dry matter allocation to ear and stem. Crop J. 2023, 11, 258–268. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, J.; Zhang, Y.M.; Zhang, G.Q.; Tian, M.; Xie, R.Z.; Ming, B.; Hou, P.; Wang, K.R.; Xue, J.; Li, S.K. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer management on stalk lodging resistance traits in summer maize. Agriculture 2022, 12, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Batyrbek, M.; Ikram, K.; Ahmad, S.; Kamran, M.; Khan, R.S.; Hou, F.J.; Han, Q.F. Nitrogen management improves lodging resistance and production in maize (Zea mays L.) at a high plant density. J. Integr. Agric. 2023, 2, 417–433. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Zhou, F.; Wang, X.L.; Zhan, X.X.; Guo, Z.X.; Liu, Q.L.; Wei, G.; Lan, T.Q.; Feng, D.J.; Kong, F.L.; et al. Optimizing nitrogen management enhances stalk lodging resistance and grain yield in dense planting maize by improving canopy light distribution. Eur. J. Agric. 2023, 148, 126871. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Liu, X.G.; Yang, J.; Wang, H.Q.; Fu, C.X.; Li, W.X. MicroRNA528 affects lodging resistance of maize by regulating lignin biosynthesis under N-luxury conditions. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 806–814. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Gao, F.; Ren, B.Z.; Dong, S.T.; Liu, P.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, J.W. Lignin metabolism regulates lodging resistance of maize hybrids under varying planting density. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 2077–2089. [Google Scholar]
- Cater, M.R.; Gregorich, E.G. Soil Sampling and Methods of Analysis, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, X.X.; Kong, F.L.; Lium, Q.L.; Lan, T.Q.; Liu, Y.Q.; Xu, J.Z.; Ou, Q.; Chen, L.; Kessel, G.; Kempenaar, C.; et al. Maize basal internode development significantly affects stalk lodging resistance. Field Crops Res. 2022, 286, 108611. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Zheng, S.; Gui, J.S.; Fu, C.J.; Yu, H.S.; Song, D.L.; Shen, J.H.; Qin, P.; Liu, X.M.; Han, B.; et al. Shortened basal intenodes encodes a gibberenllin 2-oxidase and contributes to lodging resistance in rice. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 288–299. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, E.Y.; Liu, D.C.; Guo, X.L.; Yang, W.L.; Sun, J.Z.; Li, X.; Zhan, K.H.; Cui, D.Q.; Lin, J.X.; Zhang, A.M. Anatomical and chemical characteristics associated with lodging resistance in wheat. Crop J. 2013, 1, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M.C.; Lin, C.H.; Jiang, Z.R.; Yan, F.Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Tang, X.N.; Yang, F.; Ding, Y.F.; Li, W.W.; Liu, Z.H.; et al. Uniconazole enhances lodging resistance by increasing structural carbohydrate and sclerenchyma cell wall thickness of japonica rice (Oryza sativa L.) under shading stress. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2023, 206, 105145. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.J.; He, P.; Jin, J.Y. Effect of potassium on ultrastructure of maize stalk pith and young root and their relation to stalk rot resistance. Agric. Sci. China 2019, 9, 1467–1474. [Google Scholar]
- Kamran, M.; Ahmad, I.; Wang, H.Q.; Wu, X.R.; Xu, J.; Liu, T.N.; Ding, R.X.; Han, Q.F. Mepiquat choloride application increases lodging resistance of maize by enhancing stem physical strength and lignin biosynthesis. Field Crops Res. 2018, 224, 148–159. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.; Li, Z.Z.; Zhang, X.; Xi, Y.L.; Shaik, M.R.; Khan, M. How do novel plant growth regulators and cultivation models strategies affect mechanical strength, lodging resistance and maize productivity in semi-arid regions? Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 295, 108790. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Ma, B.L. Understanding the trade-off between lodging resistance and seed yield, and developing some non-destructive methods for predicting crop lodging risk in canola production. Field Crops Res. 2022, 288, 108691. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Gao, G.D.; Xu, L.S.; Wang, Z.K.; Wang, C.Y.; Yang, T.H.; Kuai, J.; Wang, B.; Xu, Z.H.; Zhao, J.; et al. Reducing nitrogen application at high planting density enhances secondary cell wall formation and decreases stem lodging in rapeseed. Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 156, 127162. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.J.; Liu, F.C.; Wu, W. Optimizing nitrogen management strategies to minimise lodging risk while sustaining high seed yield in rapeseed. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 142, 126671. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.F.; Li, X.Y.; Chen, S.C.; Jin, B.J.; Wu, C.Y.; Li, G.; Sun, C.L.; Zhou, Y.G.; Lin, X.Y. Nitrogen fertilization modulates rice phyllosphere functional genes and pathogens through fungal communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 929, 172622. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Wang, B.B.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.M.; Zhou, T.W.; Li, M.Q.; Duan, X.C. Advances in studies of maize stalk rot. J. Plant Genet. Resour. 2019, 20, 1118–1128. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.; Gao, S.; Fan, Y.H.; Li, L.L.; Ming, B.; Wang, K.R.; Xie, R.Z.; Hou, P.; Li, S.K. Traits of plant morphology, stalk mechanical strength, and biomass accumulation in the selection of lodging-resistance maize cultivars. Eur. J. Agron. 2020, 117, 126073. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.J.; Wang, Y.Z.; Zhang, X.R.; Cheng, Z.Q.; Song, Y.H.; Li, H.M.; Wang, N.; Liu, S.; Cao, Z.J.; Li, H.X.; et al. Transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses reveal the role of phenylalanine metabolism in the maize response to stalk rot caused by Fusarium proliferatum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, A.; Sánchez-Vallet, A.; Jordá, L.; Carrasco-López, C.; Rodríguez-Herva, J.J.; López-Solanilla, E. Plant cell walls: Source of carbohydrate based signals in plant-pathogen interactions. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2024, 82, 102630. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).