Epidemiology of Xylella fastidiosa in Ibiza and Formentera: A Comprehensive Study of Insect Vectors and Transmission Dynamics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Design
2.2. Insect Vector Sampling
2.3. DNA Extraction from Insects
2.4. Detection of X. fastidiosa Subspecies
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
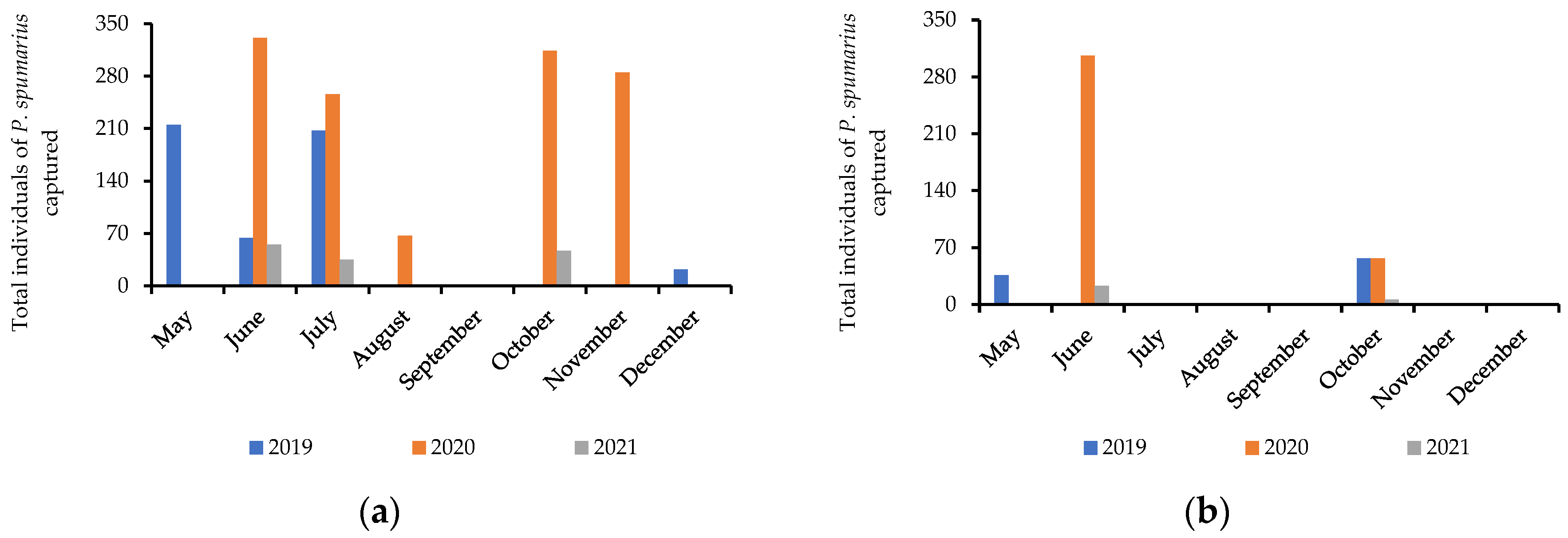
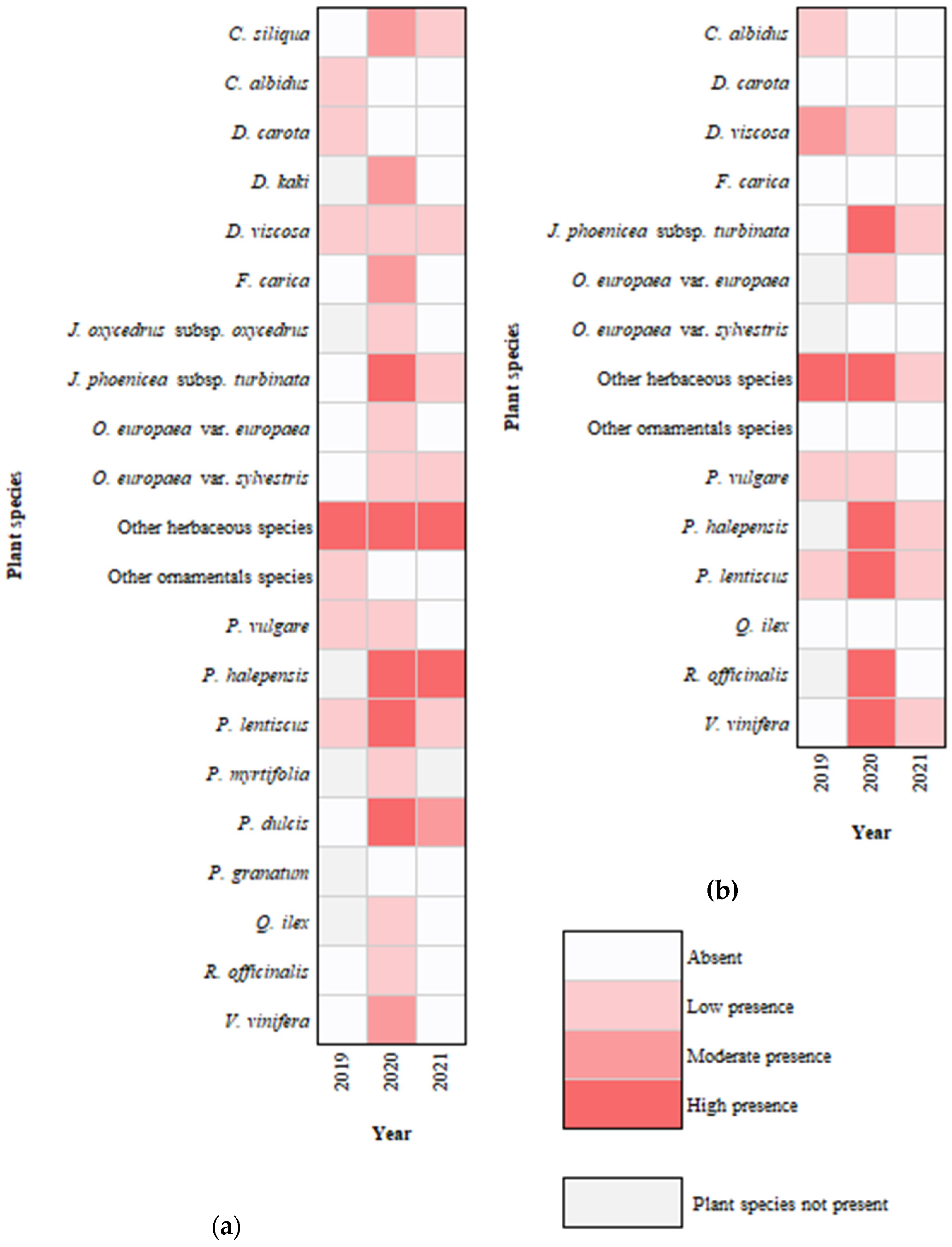
3.1. Aphrophoridae Distribution, Host Plants, and Dynamics
3.2. Detection of X. fastidiosa in the Potential Insect Vectors
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European and Mediterranean Plant Protection Organization (EPPO). PM 7/24 (3) Xylella fastidiosa. EPPO Bull. 2018, 48, 175–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janse, J.D.; Obradovic, A. Xylella fastidiosa: Its biology, diagnosis, control and risks. J. Plant Pathol. 2010, 92, S35–S48. [Google Scholar]
- Krugner, R.; Sisterson, M.S.; Backus, E.A.; Burbank, L.P.; Redak, R.A. Sharpshooters: A review of what moves Xylella fastidiosa. Austral Entomol. 2019, 58, 248–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saponari, M.; Boscia, D.; Nigro, F.; Martelli, G.P. Identification of DNA sequences related to Xylella fastidiosa in oleander, almond and olive trees exhibiting leaf scorch symptoms in Apulia (southern Italy). J. Plant Pathol. 2013, 95, 668. [Google Scholar]
- European and Mediterranean Plant Protection Organization (EPPO). Updated Situation of Xylella fastidiosa in Islas Baleares, Spain; EPPO Reporting Service; EPPO: Paris, France, 2017; p. 083. [Google Scholar]
- European and Mediterranean Plant Protection Organization (EPPO). Xylella fastidiosa in Islas Baleares (ES): More Details and Detection in Grapevine; EPPO Reporting Service; EPPO: Paris, France, 2017; p. 102. [Google Scholar]
- Moralejo, E.; Gomila, M.; Montesinos, M.; Borràs, D.; Pascual, A.; Nieto, A.; Adrover, F.; Gost, P.A.; Seguí, G.; Busquets, A.; et al. Phylogenetic inference enables reconstruction of a long-overlooked outbreak of almond leaf scorch disease (Xylella fastidiosa) in Europe. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olmo, D.; Nieto, A.; Borràs, D.; Montesinos, M.; Adrover, F.; Pascual, A.; Gost, P.A.; Quetglas, B.; Urbano, A.; García, J.d.D.; et al. Landscape Epidemiology of Xylella fastidiosa in the Balearic Islands. Agronomy 2021, 11, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redak, R.A.; Purcell, A.H.; Lopes, J.R.S.; Blua, M.J.; Mizell, R.F., III; Andersen, P.C. The Biology of Xylem Fluid-Feeding Insect Vectors of Xylella fastidiosa and Their Relation to Disease Epidemiology. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2004, 49, 243–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalieri, V.; Altamura, G.; Fumarola, G.; di Carolo, M.; Saponari, M.; Cornara, D.; Bosco, D.; Dongiovanni, C. Transmission of Xylella fastidiosa Subspecies Pauca Sequence Type 53 by Different Insect Species. Insects 2019, 10, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saponari, M.; Loconsole, G.; Cornara, D.; Yokomi, R.K.; De Stradis, A.; Boscia, D.; Bosco, D.; Martelli, G.P.; Krugner, R.; Porcelli, F. Infectivity and Transmission of Xylella fastidiosa by Philaenus spumarius (Hemiptera: Aphrophoridae) in Apulia, Italy. J. Econ. Entomol. 2014, 107, 1316–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conselleria d’Agricultura, Pesca i Medi Natural; Institut de Recerca i Formació Agroalimentària i Pesquera (IRFAP). Estadístiques de l’Agricultura, la Ramaderia i la Pesca a les Illes Balears. 2023; Institut de Recerca i Formació Agroalimentària i Pesquera (IRFAP) i Estadístiques Agràries—Pesqueres: Palma, Spain, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Xylella fastidiosa. Situació Actual a les Illes Balears. Available online: https://apps.caib.es/sites/xf/es/situacian_actual_en_las_illes_balears/ (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- Ribaut, H. Faune de France 57. Homoptères Auchénorhynques. II (Jassidae); Fédération Française des Sociétés de Sciences Naturelles: Paris, France, 1952. [Google Scholar]
- Della Giustina, W. Faune de France 73. Homoptères Cicadellidae: Vol. 3. Compléments aux ouvrages d’Henri Ribaut; Fédération Française des Sociétés de Sciences Naturelles et Institut National de la Recherche Agronomique: Paris, France, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Holzinger, W.E.; Kammerlander, I.; Nickel, H. The Auchenorrhyncha of Central Europe. Die Zikaden Mitteleuropas: Vol. 1. Fulgoromorpha, Cicadomorpha excl. Cicadellidae; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- European and Mediterranean Plant Protection Organization (EPPO). PM 7/24 (4) Xylella fastidiosa. EPPO Bull. 2019, 49, 175–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, S.J.; Ward, L.I.; Clover, G.R.G. Development of LAMP and Real-Time PCR Methods for the Rapid Detection of Xylella fastidiosa for Quarantine and Field Applications. Phytopathology 2010, 100, 1282–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, M.; Lin, H.; La Cabrera-La Rosa, J.C.; Doddapaneni, H.; Civerolo, E.L. Genome-based PCR Primers for Specific and Sensitive Detection and Quantification of Xylella fastidiosa. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2006, 115, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupas, E.; Briand, M.; Jacques, M.A.; Cesbron, S. Novel Tetraplex Quantitative PCR Assays for Simultaneous Detection and Identification of Xylella fastidiosa Subspecies in Plant Tissues. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batarseh, T.N.; Morales-Cruz, A.; Ingel, B.; Roper, M.C.; Gaut, B.S. Using genomes and evolutionary analyses to screen for host-specificity and positive selection in the plant pathogen Xylella fastidiosa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e01220-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM Corp. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 28.0; Released 2023; IBM Corp: Armonk, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Jeger, M.; Bragard, C. The epidemiology of Xylella fastidiosa; a perspective on current knowledge and framework to investigate plant host-vector-pathogen interactions. Phytopathology 2019, 109, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halkka, O.; Raatikainen, M.; Vasarainen, A.; Heinonen, L. Ecology and ecological genetics of Philaenus spumarius (L.) (Homoptera). Ann. Zool. Fenn. 1967, 4, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Raatikainen, M.; Vasarainen, A. Froghoppers (Hom., Cercopidae) in strawberry plantations. Ann. Agric. Fenn. 1970, 9, 290–292. [Google Scholar]
- Yurtsever, S. On the Polymorphic Meadow Spittlebug, Philaenus spumarius (L.) (Homoptera: Cercopidae). Turk. J. Zool. 2000, 24, 447–460. [Google Scholar]
- López, J. Seasonality, Life Cycle and Vectorial Capacity of Xylella fastidiosa Insect Vectors in the Main Crops of the Balearic Islands. Doctoral Thesis, University of Balearic Islands, Palma, Spain, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Miranda, M.A.; Marqués, A.; Sureda, T.; Amore, A.; Paredes-Esquivel, C.; Leza, M.; Beidas, O.; Olmo, D.; Morente, M.; Fereres, A.; et al. Seasonal pattern, hosts and abundance of the potential vectors of Xylella fastidiosa in Mallorca (Balearic Islands, Spain). In Proceedings of the European conference on Xylella fastidiosa: Finding answers to a global problem, Palma, Spain, 13–15 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bodino, N.; Cavalieri, V.; Dongiovanni, C.; Saladini, M.A.; Simonetto, A.; Volani, S.; Plazio, E.; Altamura, G.; Tauro, D.; Gilioli, G.; et al. Spittlebugs of Mediterranean Olive Groves: Host-Plant Exploitation throughout the Year. Insects 2020, 11, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodino, N.; Cavalieri, V.; Dongiovanni, C.; Simonetto, A.; Saladini, M.A.; Plazio, E.; Gilioli, G.; Molinatto, G.; Saponari, M.; Bosco, D. Dispersal of Philaenus spumarius (Hemiptera: Aphrophoridae), a Vector of Xylella fastidiosa, in Olive Grove and Meadow Agroecosystems. Environ. Entomol. 2021, 50, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosopoulos, S.; Maryańska-Nadachowska, A.; Kuznetsova, V.G. The Mediterranean: Area of origin of polymorphism and speciation in the spittlebug Philaenus (Hemiptera, Aphrophoridae). Zoosyst. Evol. 2010, 86, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizell, R.F., III; Tipping, C.; Andersen, P.C.; Brodbeck, B.V.; Hunter, W.B.; Northfield, T. Behavioral Model for Homalodisca vitripennis (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae): Optimization of Host Plant Utilization and Management Implications. Environ. Entomol. 2008, 37, 1049–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, P.C.; Brodbeck, B.V.; Mizell, R.F., III; Oden, S. Abundance and Feeding of Homalodisca coagulata (Hemiptera: Auchenorrhyncha: Cicadellidae) on Vitis Genotypes in North Florida. Environ. Entomol. 2005, 34, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodbeck, B.V.; Andersen, P.C.; Mizell, R.F. Nutrient mediation of behavioral plasticity and resource allocation in a xylem-feeding leafhopper. Oecologia 2011, 165, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, J.R.S.; Landa, B.B.; Fereres, A. A survey of potential insect vectors of the plant pathogenic bacterium Xylella fastidiosa in three regions of Spain. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2014, 12, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morente, M.; Cornara, D.; Plaza, M.; Durán, J.M.; Capiscol, C.; Trillo, R.; Ruiz, M.; Ruz, C.; Sanjuan, S.; Pereira, J.A.; et al. Distribution and Relative Abundance of Insect Vectors of Xylella fastidiosa in Olive Groves of the Iberian Peninsula. Insects 2018, 9, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lago, C.; Morente, M.; De las Heras-Bravo, D.; Martí-Campoy, A.; Rodríguez-Ballester, F.; Plaza, M.; Moreno, A.; Fereres, A. Dispersal of Neophilaenus campestris, a vector of Xylella fastidiosa, from olive groves to over-summering hosts. J. Appl. Entomol. 2021, 145, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodino, N.; Cavalieri, V.; Dongiovanni, C.; Plazio, E.; Saladini, M.A.; Volani, S.; Simonetto, A.; Fumarola, G.; Di Carolo, M.; Porcelli, F.; et al. Phenology, seasonal abundance and stage-structure of spittlebug (Hemiptera: Aphrophoridae) populations in olive groves in Italy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornara, D.; Bosco, D.; Fereres, A. Philaenus spumarius: When an old acquaintance becomes a new threat to European agriculture. J. Pest Sci. 2018, 91, 957–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoni, V. Contribution to the knowledge of the Auchenorrhyncha (Hemiptera Fulgoromorpha and Cicadomorpha) of Tuscany (Italy). Redia 2005, 88, 85–102. [Google Scholar]
- Generalitat Valenciana; Servicio de Sanidad Vegetal; D. G. Agricultura, Ganadería y Pesca. Situación de Xylella fastidiosa en la Comunitat Valenciana; D. G. Agricultura, Ganadería y Pesca: Valencia, Spain, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Xylella fastidiosa (XYLEFA). Hosts. Available online: https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/XYLEFA/hosts (accessed on 30 January 2024).
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); Delbianco, A.; Gibin, D.; Pasinato, L.; Morelli, M. Update of the Xylella spp. host plant database—Systematic literature search up to 30 June 2019. EFSA J. 2021, 18, e07726. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Moussa, I.E.; Valentini, F.; Lorusso, D.; Mazzoni, V.; Digiaro, M.; Varvaro, L.; D’Onghia, A.M. Evaluation of “Insect Spy” approach for monitoring Xylella fastidiosa in symptomless olive orchards in the Salento peninsula (Southern Italy). IOBC-WPRS Bull. 2015, 121, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- European Food Safety Authority. Xylella fastidiosa. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/topics/topic/xylella-fastidiosa (accessed on 21 December 2023).
- Xylella fastidiosa (XYLEFA). Distribution. Available online: https://gd.eppo.int/taxon/XYLEFA/distribution (accessed on 9 December 2023).
- Ministerio de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación (MAPA). SIGPAC. Datos por CCAA y Usos; Ministerio de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación (MAPA): Madrid, Spain, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cruaud, A.; Gonzalez, A.A.; Godefroid, M.; Nidelet, S.; Streito, J.C.; Thuillier, J.M.; Rossi, J.P.; Santoni, S.; Rasplus, J.Y. Using insects to detect, monitor and predict the distribution of Xylella fastidiosa: A case study in Corsica. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Onghia, A.M. CIHEAM/IAMB innovative tools for early surveillance and detection of Xylella fastidiosa. In Xylella fastidiosa & the Olive Quick Decline Syndrome (OQDS). A Serious Worldwide Challenge for the Safeguard of Olive Trees; D’Onghia, A.M., Brunel, S., Valentini, F., Eds.; CIHEAM: Bari, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega, J. Identificació de Vectors i Hostes Potencials de Xylella fastidiosa a Diferents Àrees Fructícoles i Vinícoles de Catalunya. Bachelor’s Thesis, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, Barcelona, Spain, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sabaté, J. Philaenus spumarius (Vector de Xylella fastidiosa): Cicle Vital i Control; Generalitat de Catalunya, Departament d’Agricultura, Ramaderia, Pesca i Alimentació: Barcelona, Spain, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Halkka, O.; Raatikainen, M.; Halkka, L.; Lokki, J. Factors determining the size and composition of island populations of Philaenus spumarius (L.) (Homoptera). Acta Entomol. Fenn. 1971, 28, 83–100. [Google Scholar]
- Wiegert, R.G. The Ingestion of Xylem Sap by Meadow Spittlebugs, Philaenus spumarius (L.). Am. Midl. Nat. 1964, 71, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereres, A. Insect vectors as drivers of plant virus emergence. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015, 10, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markheiser, A.; Cornara, D.; Fereres, A.; Maixner, M. Analysis of vector behavior as a tool to predict Xylella fastidiosa patterns of spread. Entomol. Gen. 2020, 40, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard, A.; Zeilinger, A.R.; Vanhove, M.; Schartel, T.E.; Beal, D.J.; Daugherty, M.P.; Almeida, R.P. Xylella fastidiosa: Insights into an Emerging Plant Pathogen. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2018, 56, 181–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| ID/Island | Name | Location | Crop | Vegetation of the Surroundings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plot 1 1 | Bodega Ibizkus | 38°52′ N 01°15′ E | V. vinifera | C. siliqua, C. albidus, E. arborea, J. phoenicea, J. oxycedrus, P. halepensis, P. lentiscus, P. dulcis, and R. officinalis |
| Plot 2 1 | Can Benet | 38°55′ N 01°18′ E | O. europaea and V. vinifera | C. siliqua, C. albidus, E. arborea, J. phoenicea, O. europaea, P. vulgare, P. halepensis, P. lentiscus, and R. officinalis |
| Plot 3 1 | Bodega Can Rich | 38°59′ N 01°20′ E | O. europaea and V. vinifera | A. donax, C. siliqua, D. kaki, O. europaea, P. vulgare, and P. dulcis |
| Plot 4 1 | Can Secorrat | 39°00′ N 01°21′ E | C. siliqua, O. europaea, and V. vinifera | C. albidus, E. arborea, J. phoenicea, J. oxycedrus, P. halepensis, P. lentiscus, and Q. ilex |
| Plot 5 1 | Pla de Corona | 39°02′ N 01°20′ E | P. dulcis | C. siliqua, J. phoenicea, O. europaea, P. halepensis, and P. lentiscus |
| Plot 6 1 | Pla d’Albarca | 39°02′ N 01°22′ E | V. vinifera | - |
| Plot 7 1 | Camí de Cas Vidals | 39°04′ N 01°28′ E | C. siliqua | C. albidus, D. viscosa, J. phoenicea., O. europaea, P. lentiscus, and R. officinalis |
| Plot 8 1 | Can Tixedó | 39°04′ N 01°29′ E | Non-crop areas | C. albidus, J. phoenicea, P. vulgare, P. lentiscus, and R. officinalis |
| Plot 9 1 | Crtra. de Sant Joan | 39°00′ N 01°29′ E | Non-crop areas | D. viscosa, J. phoenicea, P. lentiscus L., and P. vulgare |
| Plot 10 1 | Can Miquel Guasch | 38°59′ N 01°28′ E | O. europaea | C. siliqua L., D. viscosa, J. oxycedrus, O. europaea, P. vulgare, P. halepensis, P. lentiscus, P. dulcis, and R. officinalis |
| Plot 11 1 | Can Marquet | 39°01′ N 01°29′ E | Citrus sp. and O. europaea | C. siliqua, C. albidus, D. viscosa, J. regia, J. phoenicea, J. oxycedrus, L. nobilis, N. oleander, P. halepensis, P. lentiscus, Q. ilex, and R. officinalis |
| Plot 12 1 | Necrópolis des Puig des Molins | 38°54′ N 01°25′ E | Urban | D. viscosa and P. vulgare |
| Plot 13 1 | Es viver | 38°54′ N 01°25′ E | Urban | C. australis, C. siliqua, L. dentata, O. europaea, P. halepensis, P. myrtifolia, and R.officinalis |
| Plot 14 1 | Agrotourism Can Planells | 39°02′ N 01°25′ E | Citrus sp. and P. americana | C. siliqua, C. albidus, E. arborea, J. phoenicea, J. oxycedrus, P. halepensis, O. europaea, P. lentiscus, Q. ilex, and R. officinalis |
| Plot 15 2 | Bodega Terramoll | 38°40′ N 01°32′ E | V. vinifera | P. lentiscus |
| Plot 16 2 | Vénda des Pi des Català | 38°41′ N 01°26′ E | Non-crop areas | J. phoenicea and P. lentiscus |
| Plot 17 2 | El Pilar de la Mola | 38°40′ N 01°34′ E | V. vinifera | D. viscosa, J. phoenicea, P. halepensis, P. lentiscus, R. officinalis |
| Plot 18 2 | Pol. 2 Parc. 157 | 38°41′ N 01°23′ E | O. europaea | J. phoenicea, and P. lentiscus |
| Plot 19 2 | Bodega Cap de Barberia | 38°39′ N 01°24′ E | V. vinifera | C. albidus, J. phoenicea, O. europaea, and R. officinalis |
| Plot 20 2 | Pol. 1 Parc. 297 | 38°40′ N 01°24′ E | O. europaea | J. phoenicea and P. lentiscus |
| Plot 21 2 | Pol. 1 Parc. 144 | 38°40′ N 01°25′ E | O. europaea | J. phoenicea and R. officinalis |
| Plot 22 2 | Pol. 2 Parc. 197 | 38°41′ N 01°25′ E | O. europaea | P. vulgare |
| Plot 23 2 | Pol. 14 Parc. 178 | 38°39′ N 01°34′ E | O. europaea | D. viscosa and P. vulgare |
| Plot 24 2 | Sa Figuera (Pol. 2 Parc. 95) | 38°41′ N 01°25′ E | F. carica | P. lentiscus |
| Plot 25 2 | Figueres Can Toni Mestre | 38°41′ N 01°29′ E | F. carica | P. lentiscus |
| Plot 26 2 | Bellotera de Can Vicent d’es Torrent | 38°42′ N 01°26′ E | Non-crop areas | Q. ilex and D. viscosa |
| Host Plant Species of Adult P. spumarius Captured | qPCR Detection 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | Total | |
| P. myrtifolia | 0+/0 | 2+/4 (50.00) | 0+/0 | 2+/4 (50.00) |
| C. siliqua | 0+/0 | 3+/32 (9.38%) | 1+/7 (14.29%) | 4+/39 (10.26%) |
| D. kaki | 0+/0 | 0+/28 (0.00%) | 0+/0 | 0+/28 (0.00%) |
| D. viscosa | 2+/13 (15.38%) | 0+/0 | 0+/1 (0.00%) | 2+/14 (14.29%) |
| F. carica | 0+/0 | 1+/19 (5.26%) | 0+/0 | 1+/19 (5.26%) |
| J. phoenicea subsp. turbinata | 0+/0 | 0+/62 (0.00%) | 0+/5 (0.00) | 0+/67 (0.00%) |
| D. viscosa | 2+/13 (15.38%) | 0+/0 | 0+/1 (0.00%) | 2+/14 (14.29%) |
| O. europaea var europaea | 0+/0 | 0+/5 (0.00%) | 0+/0 | 0+/5 (0.00%) |
| O. europaea var sylvestris | 0+/0 | 0+/0 | 0+/1 (0.00%) | 0+/1 (0.00%) |
| Other herbaceous species | 23+/705 (3.26%) | 9+/446 (2.02%) | 9+/45 (20.00%) | 41+/1196 (3.43%) |
| Other ornamentals species | 9+/14 (64.29%) | 0+/0 | 0+/0 | 9+/14 (64.29%) |
| Other woody species | 0+/0 | 0+/6 (0.00%) | 0+/0 | 0+/6 (0.00%) |
| P. halepensis | 0+/0 | 9+/278 (3.24%) | 2+/51 (3.92%) | 11+/329 (3.34%) |
| P. lentiscus | 0+/4 (0.00%) | 13+/158 (8.23%) | 1+/9 (11.11%) | 14+/171 (8.19%) |
| P. dulcis | 0+/0 | 10+/196 (5.10%) | 1+/18 (5.55%) | 11+/214 (5.14%) |
| Q. ilex | 0+/0 | 0+/1 (0.00%) | 0+/0 | 0+/1 (0.00%) |
| V. vinifera | 0+/0 | 0+/18 | 0+/0 | 0+/18 (0.00%) |
| GLM: total captures | AIC | 1353.750 | ||
| p (host plant species) | 0.000 | |||
| p (plot) | 0.000 | |||
| p (year) | 0.000 | |||
| GLM: number of positives (+) | AIC | 231.244 | ||
| p (host plant species) | 0.191 | |||
| p (plot) | 0.008 | |||
| p (year) | 0.486 | |||
| Pearson correlation: total captures and number of positives (+) | r | 0.639 ** | ||
| p | <0.001 | |||
| Chi-square test: percentage of positives for XF | r | 114.013 | ||
| p | <0.001 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Llompart, M.; Cifre, J.; Olmo, D.; Juan, A.; Castellà, F.; Jiménez, S.; Sabaté, J. Epidemiology of Xylella fastidiosa in Ibiza and Formentera: A Comprehensive Study of Insect Vectors and Transmission Dynamics. Agronomy 2025, 15, 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15020329
Llompart M, Cifre J, Olmo D, Juan A, Castellà F, Jiménez S, Sabaté J. Epidemiology of Xylella fastidiosa in Ibiza and Formentera: A Comprehensive Study of Insect Vectors and Transmission Dynamics. Agronomy. 2025; 15(2):329. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15020329
Chicago/Turabian StyleLlompart, Miquel, Josep Cifre, Diego Olmo, Andreu Juan, Francesc Castellà, Sergio Jiménez, and Jordi Sabaté. 2025. "Epidemiology of Xylella fastidiosa in Ibiza and Formentera: A Comprehensive Study of Insect Vectors and Transmission Dynamics" Agronomy 15, no. 2: 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15020329
APA StyleLlompart, M., Cifre, J., Olmo, D., Juan, A., Castellà, F., Jiménez, S., & Sabaté, J. (2025). Epidemiology of Xylella fastidiosa in Ibiza and Formentera: A Comprehensive Study of Insect Vectors and Transmission Dynamics. Agronomy, 15(2), 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15020329






