Stem-Leaf Segmentation and Morphological Traits Extraction in Rapeseed Seedlings Using a Three-Dimensional Point Cloud
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Experimental Design
2.2. Point Cloud Data Acquisition Methodology
2.2.1. Point Cloud Data Acquisition
- (1)
- Open the control cabinet installed on the right side of the vehicle with the key and turn on the main switch to power on the entire system. (After scanning, power off the entire system.)
- (2)
- After entering the Weijing Intelligent HPPC local control software, connect the IP addresses of the four stereo cameras and connect the devices.
- (3)
- Release the emergency stop status of the vehicle, enable the vehicle to automatically exit, and then manually reset the X-axis and Z-axis of the scanning mechanism to avoid errors in the distance traveled by the vehicle.
- (4)
- To detect the ROI for each camera, the specific method is to first define the left eye ROI (note: The designated ROI must include all laser lines on the surface of the test object. Based on this, the smaller the ROI, the higher the frame rate.) Then, the ROI for the right eye is delineated using the same method. Click “Apply” or “OK” to take effect.
- (5)
- After setting the location of the community, move the vehicle to the community. When the vehicle movement is over, confirm whether the crop to be photographed is under the camera, and then adjust the position of the scanning mechanism, especially the scanning height. In this experiment, the height of the scanner was set at about one meter from the top of the crop. If the scanning height is too high or too low, the target point cloud will be missing.
- (6)
- When the scanning mechanism is running, if the point cloud image effect is not good, check whether the laser line is in the camera. If not, redefine the ROI.
- (7)
- After the scanning is completed, the device will be stored and the system will be shut down.
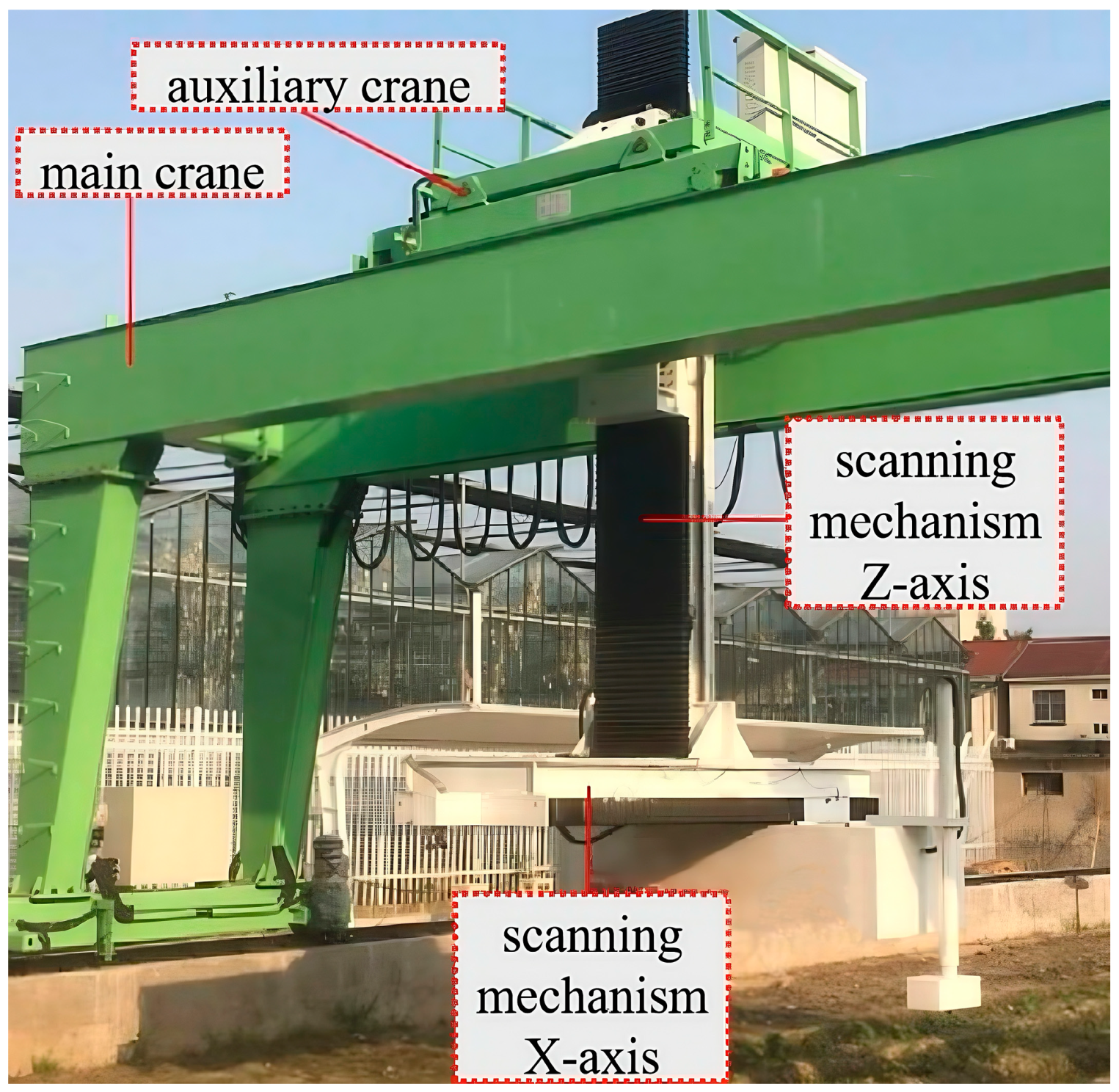

2.2.2. Target Point Cloud Extraction
2.3. Methodology for Extraction of Morphological Structural Parameters of Rapeseed
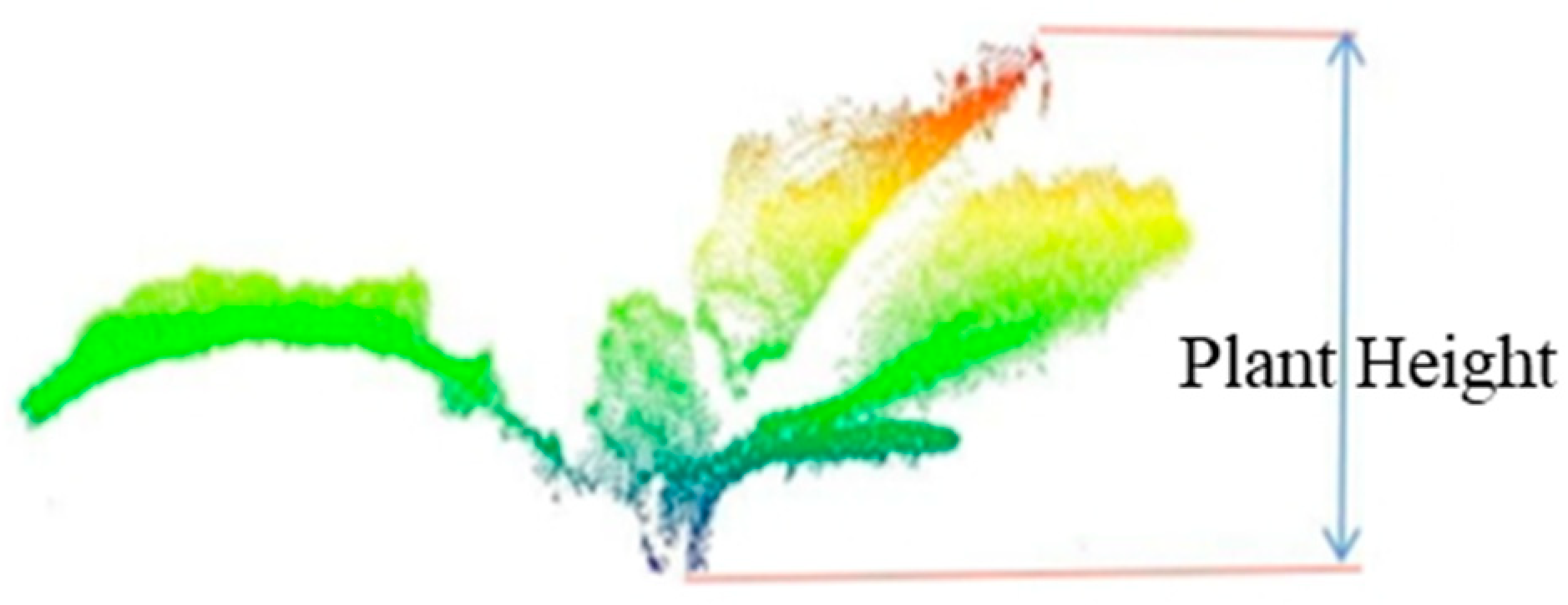
2.3.1. Plant Height Extraction
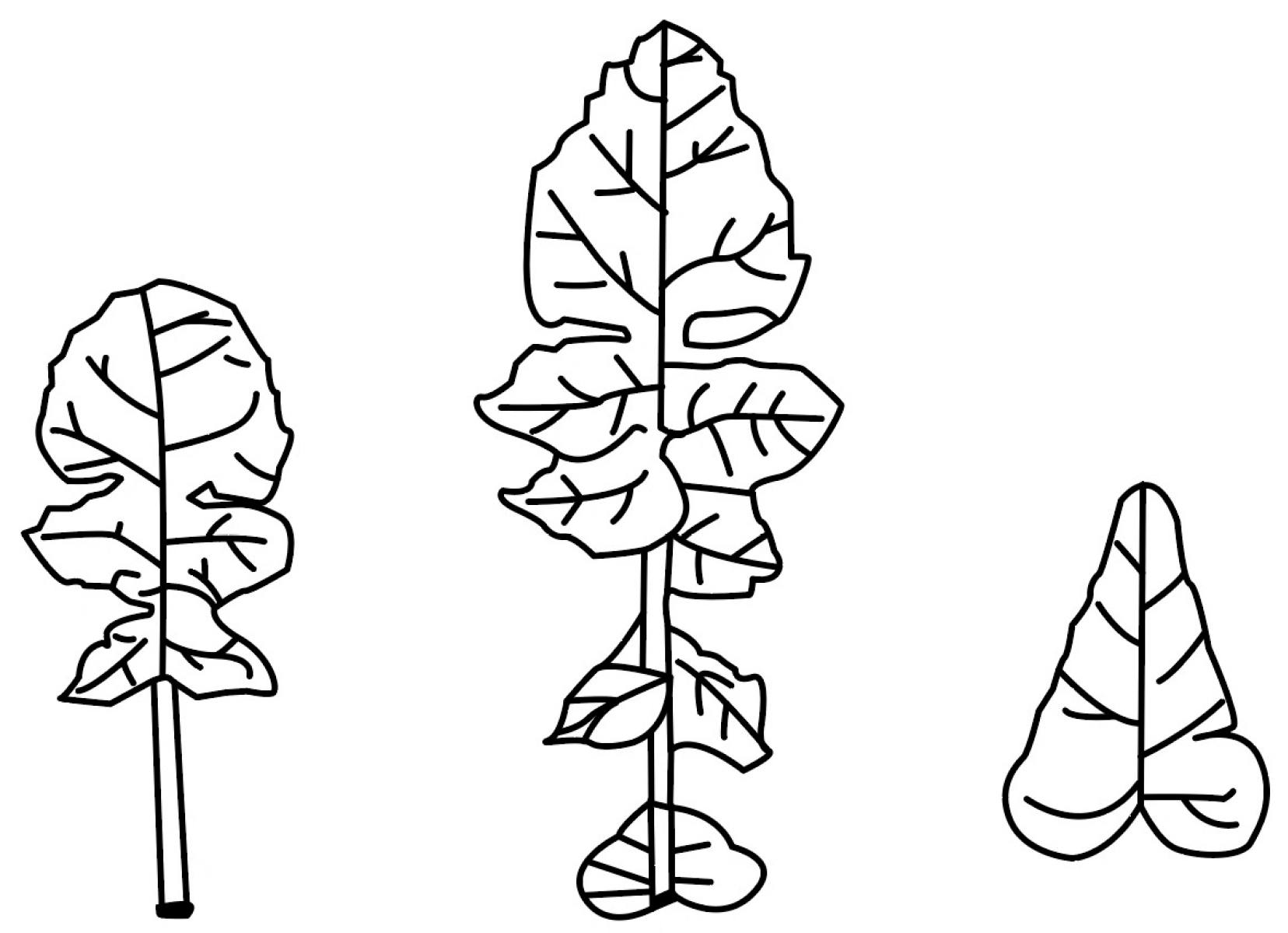
2.3.2. Leaf Length and Width Extraction

2.3.3. Leaf Area Extraction
2.4. Accuracy Assessment
2.5. Data Processing and Analysis
2.6. Technology Roadmap
3. Results
3.1. Agronomic Parameters at Seedling Stage
3.2. Estimation of Plant Height
3.2.1. Plant Height Measurement
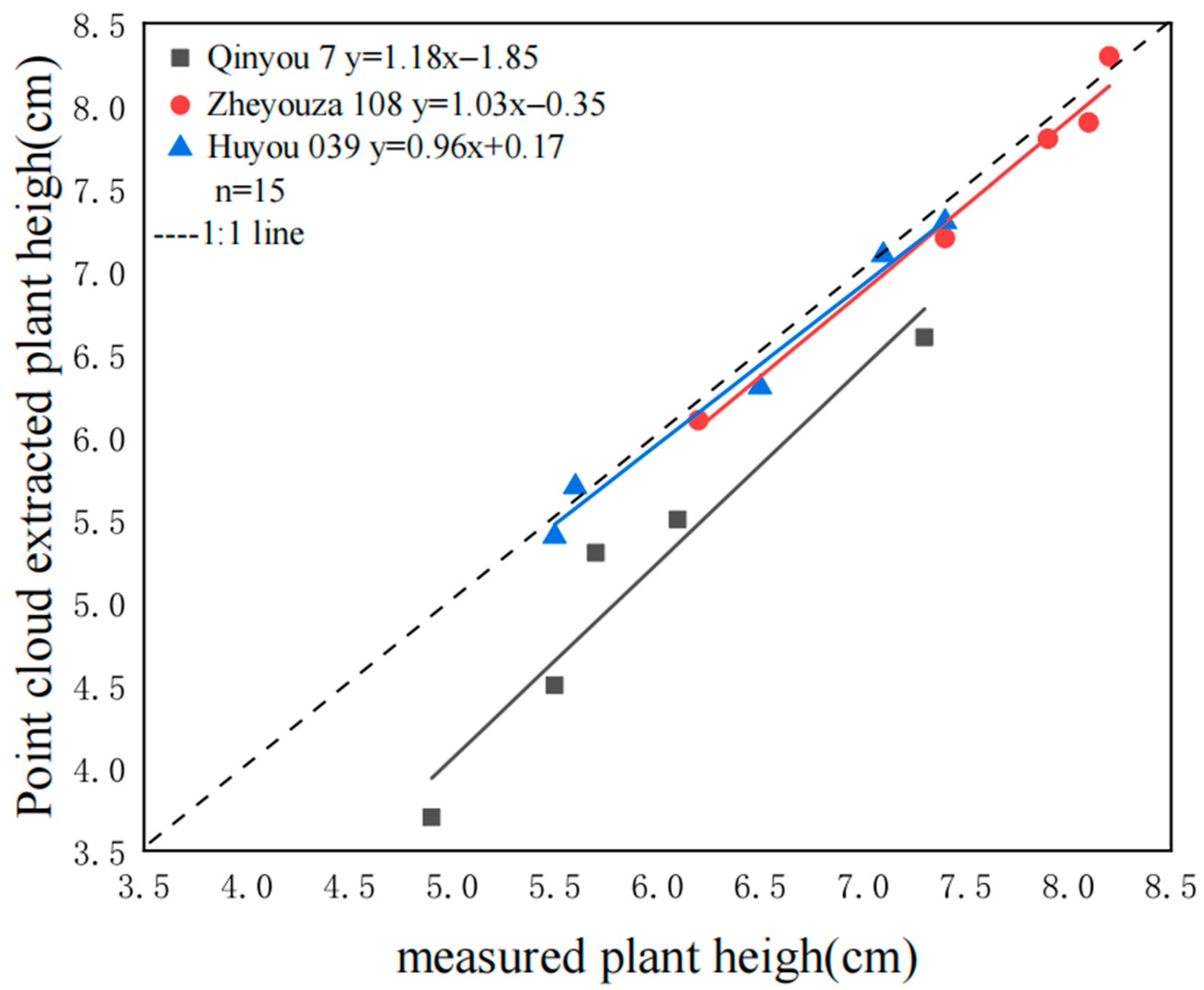
3.2.2. Evaluation of Plant Height Extraction Accuracy
3.3. Estimation of Leaf Length, Leaf Width, and Leaf Area Parameters
3.3.1. Extraction of Leaf Length and Width
3.3.2. Evaluation of Leaf Length and Width Extraction Accuracy
3.3.3. Extraction of Leaf Area
3.3.4. Evaluation of Leaf Area Extraction Accuracy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, S.; Liu, X.; Tan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, B. Sensors, systems and algorithms of 3D reconstruction for smart agriculture and precision farming: A review. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 224, 109229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegewald, H.; Wensch-Dorendorf, M.; Sieling, K.; Christen, O. Impacts of break crops and crop rotations on oilseed rape productivity: A review. Eur. J. Agron. 2018, 101, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Yang, L.; Mu, J.; Yu, X.; He, Y. Global Analysis of the Genetic Variations in miRNA-Targeted Sites and Their Correlations With Agronomic Traits in Rapeseed. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 741858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Liu, K. Worldwide rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) research: A bibliometric analysis during 2011–2021. Oil Crop Sci. 2022, 7, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodacre, R.; Roberts, L.; Ellis, D.I.; Thorogood, D.; Reader, S.M.; Ougham, H.; King, I. From phenotype to genotype: Whole tissue profiling for plant breeding. Metabolomics 2007, 3, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.M.; Ludwig, E.; Gutierrez, J.; Gehan, M.A. Deep Learning in Image-Based Plant Phenotyping. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2024, 75, 771–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafa, S.; Mondal, D.; Panjvani, K.; Kochian, L.; Stavness, I. Explainable deep learning in plant phenotyping. Front. Artif. Intell. 2023, 6, 1203546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Su, Y.; Wu, F.; Pang, S.; Gao, S.; Hu, T.; Liu, J.; Guo, Q. Stem–Leaf Segmentation and Phenotypic Trait Extraction of Individual Maize Using Terrestrial LiDAR Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 1336–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Hu, L.; He, R.; He, Y. Research on methods of plant 3D information acquisition. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2012, 28, 142–147. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Wen, W.; Gou, W.; Lu, X.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, C.; Xiang, Z.; Chen, L.; Guo, X. A miniaturized phenotyping platform for individual plants using multi-view stereo 3D reconstruction. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 897746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Hao, Y.; Zhao, M.; Lv, Z.; Hu, X.; Li, F. Plant phenotype analysis based on 3D reconstruction technology. Internet Things Technol. 2019, 9, 84–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, J. Plant phenotype analysis based on 3D reconstruction technology. Internet Things Technol. 2021, 42, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Nie, C.; Shi, L. Crop phenotypic trait identification technology promotes the development of smart agriculture. In Proceedings of the 19th Annual Conference of the Chinese Crop Society, Wuhan, China; 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Lu, S.; Guo, X.; Wen, W. Surfaces reconstruction of plant leaves based on point cloud data. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2012, 28, 184–190. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Mao, H.; Li, P.; Le, Z. 3D visualization of plant leaves based on laser scanning point cloud data. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2011, 39, 20239–20241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wen, W.; Guo, X.; Zhao, C. 3D reconstruction of plant leaves based on point cloud data. J. Chin. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2014, 16, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Lin, B.; Lin, T.; Shi, X.; Zhang, D.; Xu, Z.; Yan, H.; Shi, X. Measurement and visual modelling of the three-dimensional structure of oilseed rape plants. Zhejiang Agric. J. 2013, 25, 926–932. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.Y.; Huang, H.; Mei, G.U.; Guan, C.Y. Research progress toward the ideal type of rapeseed plant. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci. 2023, 45, 4–16. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H. Practical Rapeseed Cultivation; Shanghai Science and Technology Press: Shanghai, China, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; Yao, J.; Zhang, X.; Fan, B.; Li, X.; Hai, Y.; Fan, X. Three-dimensional reconstruction and phenotype measurement of maize seedlings based on multi-view image sequences. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 974339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wen, W.; Wu, S.; Wang, C.; Yu, Z.; Guo, X.; Zhao, C. Maize Plant Phenotyping: Comparing 3D Laser Scanning, Multi-View Stereo Reconstruction, and 3D Digitizing Estimates. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Li, M. Method for extracting three-dimensional phenotypic information of maize seedlings at the leaf scale. Prog. Laser Optoelectron. 2023, 60, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Wei, B.; Guan, H.; Cheng, Y.; Zhuo, Z. A method for calculating and simulating phenotype of soybean based on 3D reconstruction. Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 154, 127070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Sun, K.; Yan, Z.; Yan, X.; Yu, J.; Shi, J.; Hu, Z.; Jiang, H.; Xin, D.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Analysing the phenotype development of soybean plants using low-cost 3D reconstruction. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Liu, S.; Hou, C.; Liu, Q.; Li, F.; Zhang, W. Organ segmentation and phenotype analysis of soybean plants based on 3D point cloud. China Agric. Sci. Technol. Her. 2023, 25, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paproki, A.; Sirault, X.; Berry, S.; Furbank, R.; Fripp, J. A novel mesh processing based technique for 3D plant analysis. BMC Plant Biol. 2012, 12, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Shao, K.; Xiao, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, J.; Wang, R.; Meng, L.; Ma, Y. Segmentation of Individual Leaves of Field Grown Sugar Beet Plant Based on 3D Point Cloud. Agronomy 2022, 12, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Feng, H.; Yang, W.; Duan, L.; Chen, G.; Xiong, L.; Liu, Q. High-throughput volumetric reconstruction for 3D wheat plant architecture studies. J. Innov. Opt. Health Sci. 2016, 9, 1650037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.H.; Jiang, L.Y.; Mason, A.S.; Xiao, M.L.; Zhu, L.R.; Li, L.Z.; Zhou, Q.H.; Shen, C.J.; Huang, C.H. Research progress and strategies for multifunctional rapeseed: A case study of China. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 1673–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Chen, B.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, F.; Xie, T.; Xu, K.; Gao, G.; Yan, G.; Li, H.; Li, L.; et al. Genomic selection and genetic architecture of agronomic traits during modern rapeseed breeding. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 694–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Ruifang, Z.; Pujuan, S.; Pengfei, W. Segmentation of crop organs through region growing in 3D space. In Proceedings of the 2016 Fifth International Conference on Agro-Geoinformatics (Agro-Geoinformatics), Tianjin, China, 18–20 July 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Lu, K.; Pan, L.; Liu, T.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, B. Three-dimensional reconstruction of oilseed rape branches based on RGB-D camera with angiosperm identification and localisation. J. Agric. Mach. 2019, 50, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Wen, W.; Peng, Y.; Guo, X.; Lu, S.; Du, J. Research on geometric modelling of oilseed rape at seedling stage. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2011, 39, 14005–14007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, X. Three-Dimensional Reconstruction of Oilseed Rape Plants Based on RGB-D Camera and Algorithm for Carex Phenotype Detection. Bachelor’s Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, P. Research on Point Cloud Data Processing Method for Automatic Measurement of Phenotypic Parameters in Mature Oilseed Rape. Bachelor’s Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Cho, S.I. High-Resolution 3D Crop Reconstruction and Automatic Analysis of Phenotyping Index Using Machine Learning. Agriculture 2021, 11, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Yang, H.; Liu, D.; Wang, X. Research on automatic 3D reconstruction of plant phenotype based on Multi-View images. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 220, 108866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xia, H.; Liu, Y.; Ji, K.; Huo, L.; Ni, C. Research on Morphological Indicator Extraction Method of PinusmassonianaLamb. Based on 3D Reconstruction. Forests 2023, 14, 1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, K.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J.; Peng, S.; Li, J.; Wang, M. 3D Point Cloud on Semantic Information for Wheat Reconstruction. Agriculture 2021, 11, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


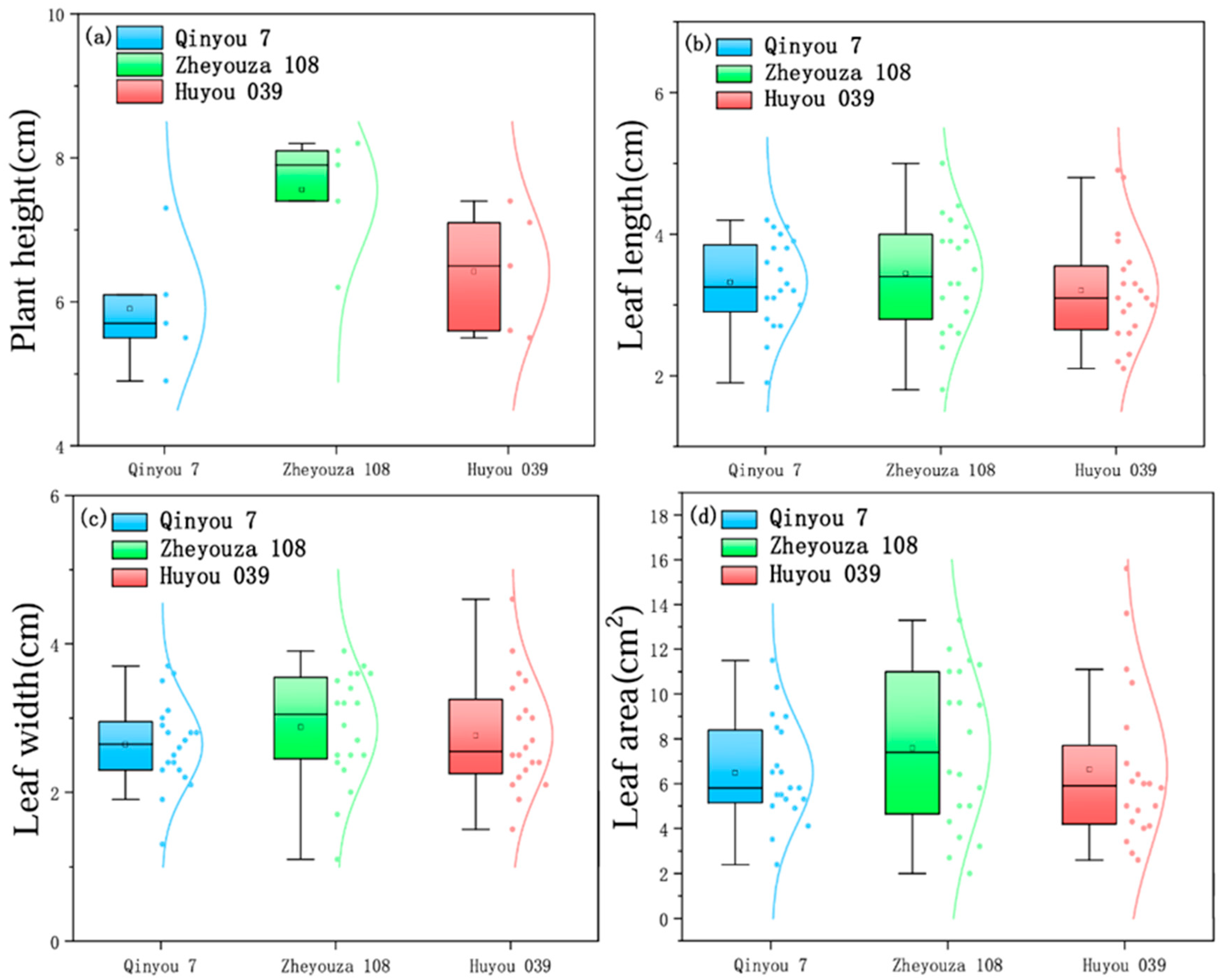

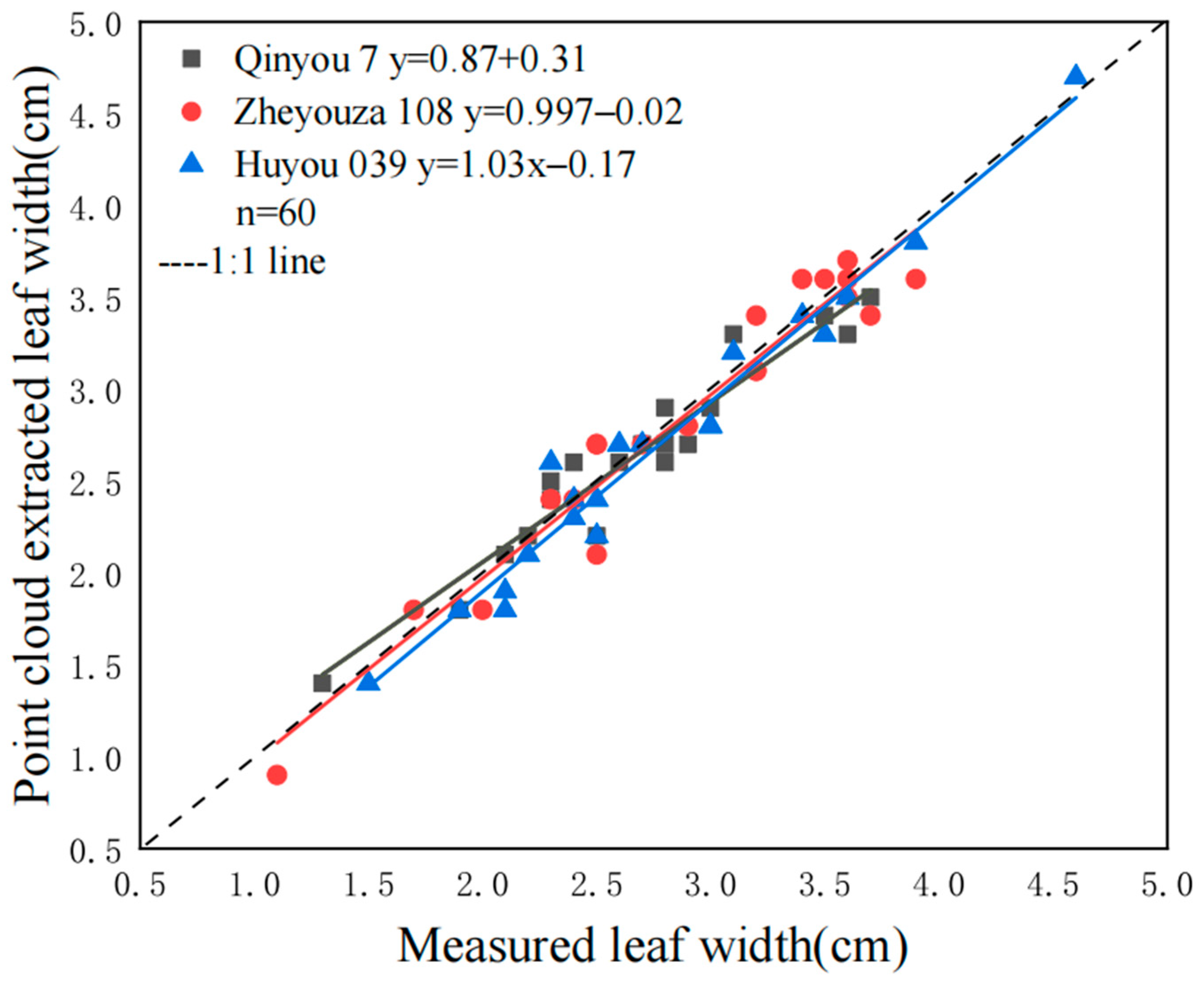
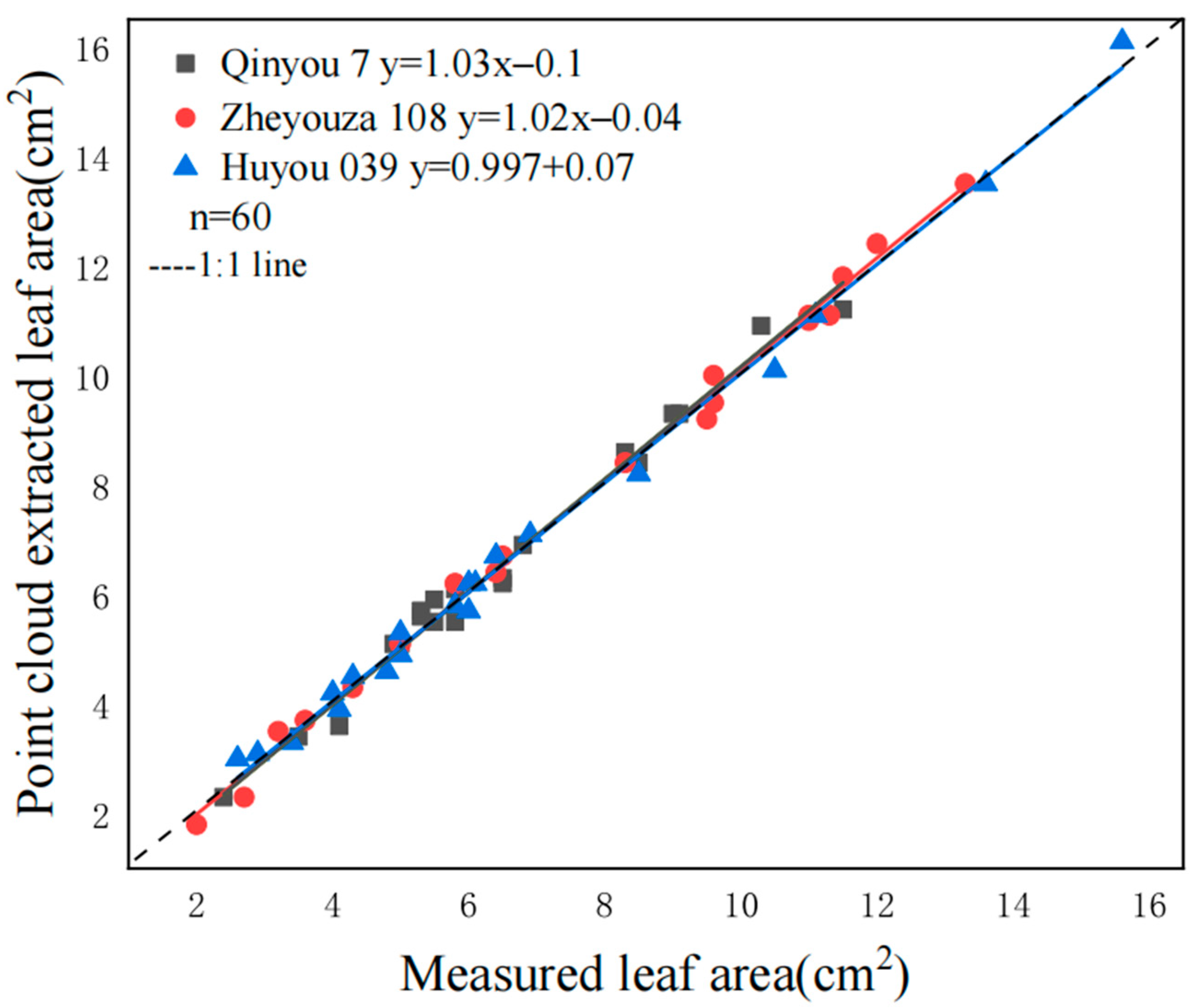
| Group | Leaf Length | Leaf Width | Leaf Area | Plant Height |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qinyou 7 | 3.32 ± 0.63 a | 2.65 ± 0.58 a | 6.48 ± 2.32 a | 5.90 ± 0.89 b |
| Zheyouza 108 | 3.44 ± 0.80 a | 2.88 ± 0.75 a | 7.58 ± 3.53 a | 7.56 ± 0.82 a |
| Huyou 039 | 3.21 ± 0.76 a | 2.77 ± 0.75 a | 6.63 ± 3.53 a | 6.42 ± 0.86 ab |
| Variety | Plant Height (cm) | Difference (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3D Extraction Value | Manual Measurement Value | ||
| Qinyou 7 | 5.9 | 5.12 | 13.3 |
| Zheyouza 108 | 7.56 | 7.46 | 1.3 |
| Huyou 039 | 6.42 | 6.36 | 0.9 |
| Variety | Leaf Length (cm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaf 1 | Leaf 2 | Leaf 3 | Leaf 4 | |
| Qinyou 7 | 3.4 | 2.94 | 3.48 | 3.5 |
| Zheyouza 108 | 2.74 | 3.72 | 3.6 | 3.5 |
| Huyou 039 | 3.14 | 3.4 | 3.46 | 2.8 |
| Variety | Leaf Width (cm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaf 1 | Leaf 2 | Leaf 3 | Leaf 4 | |
| Qinyou 7 | 2.48 | 2.52 | 2.8 | 2.68 |
| Zheyouza 108 | 2.04 | 3.1 | 3.12 | 3.12 |
| Huyou 039 | 2.62 | 2.9 | 3 | 2.24 |
| Variety | Leaf Area | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaf 1 | Leaf 2 | Leaf 3 | Leaf 4 | |
| Qinyou 7 | 5.52 | 5.9 | 7 | 7.76 |
| Zheyouza 108 | 6.8 | 6.8 | 7.1 | 9.92 |
| Huyou 039 | 6.24 | 7.34 | 7.42 | 5.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, B.; Zain, M.; Zhang, L.; Han, D.; Sun, C. Stem-Leaf Segmentation and Morphological Traits Extraction in Rapeseed Seedlings Using a Three-Dimensional Point Cloud. Agronomy 2025, 15, 276. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15020276
Sun B, Zain M, Zhang L, Han D, Sun C. Stem-Leaf Segmentation and Morphological Traits Extraction in Rapeseed Seedlings Using a Three-Dimensional Point Cloud. Agronomy. 2025; 15(2):276. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15020276
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Binqian, Muhammad Zain, Lili Zhang, Dongwei Han, and Chengming Sun. 2025. "Stem-Leaf Segmentation and Morphological Traits Extraction in Rapeseed Seedlings Using a Three-Dimensional Point Cloud" Agronomy 15, no. 2: 276. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15020276
APA StyleSun, B., Zain, M., Zhang, L., Han, D., & Sun, C. (2025). Stem-Leaf Segmentation and Morphological Traits Extraction in Rapeseed Seedlings Using a Three-Dimensional Point Cloud. Agronomy, 15(2), 276. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15020276





