Research on the Efficient Industrial Scale-Up Cultivation of a Novel Aromatic and Disease-Resistant Mushroom Rhodotus palmatus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
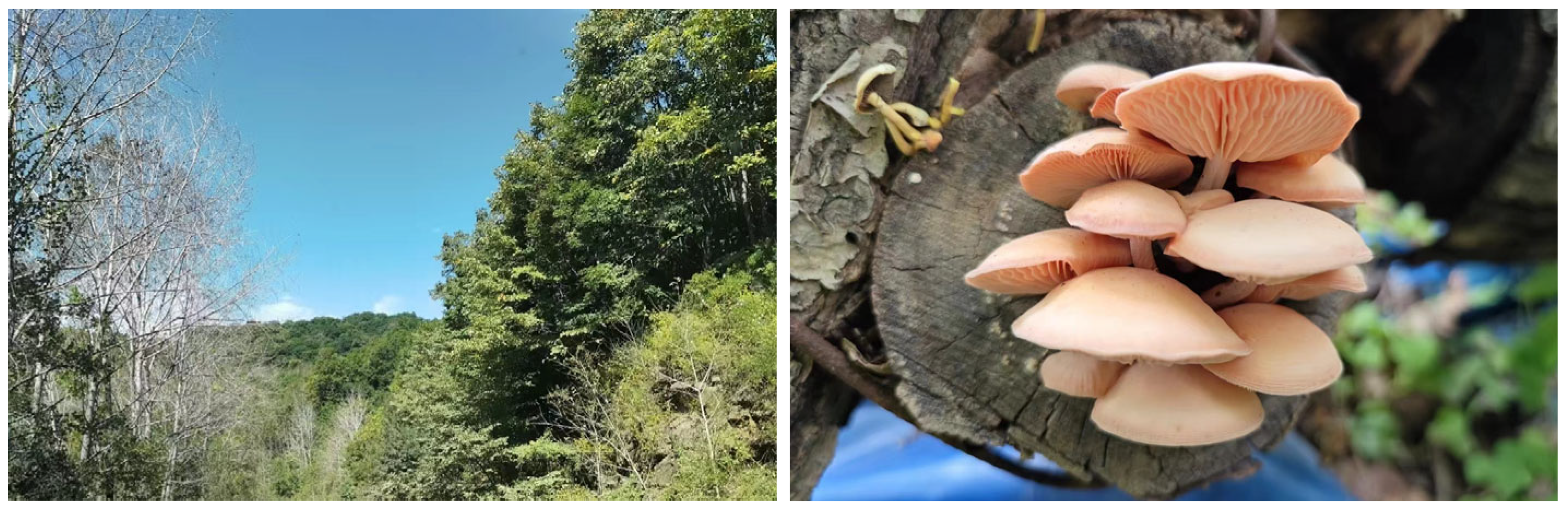
2.1. Strains Collection
2.2. Tissue Isolation and Purification
2.3. Molecular Phylogeny Identification
2.4. Primary and Secondary Screening of Trial Cultivation
2.5. Physiological Performance Determination
- Antagonism Test
- Temperature Gradient Test
- Antifungal Interaction Assay
2.6. Intermediate Cultivation Test
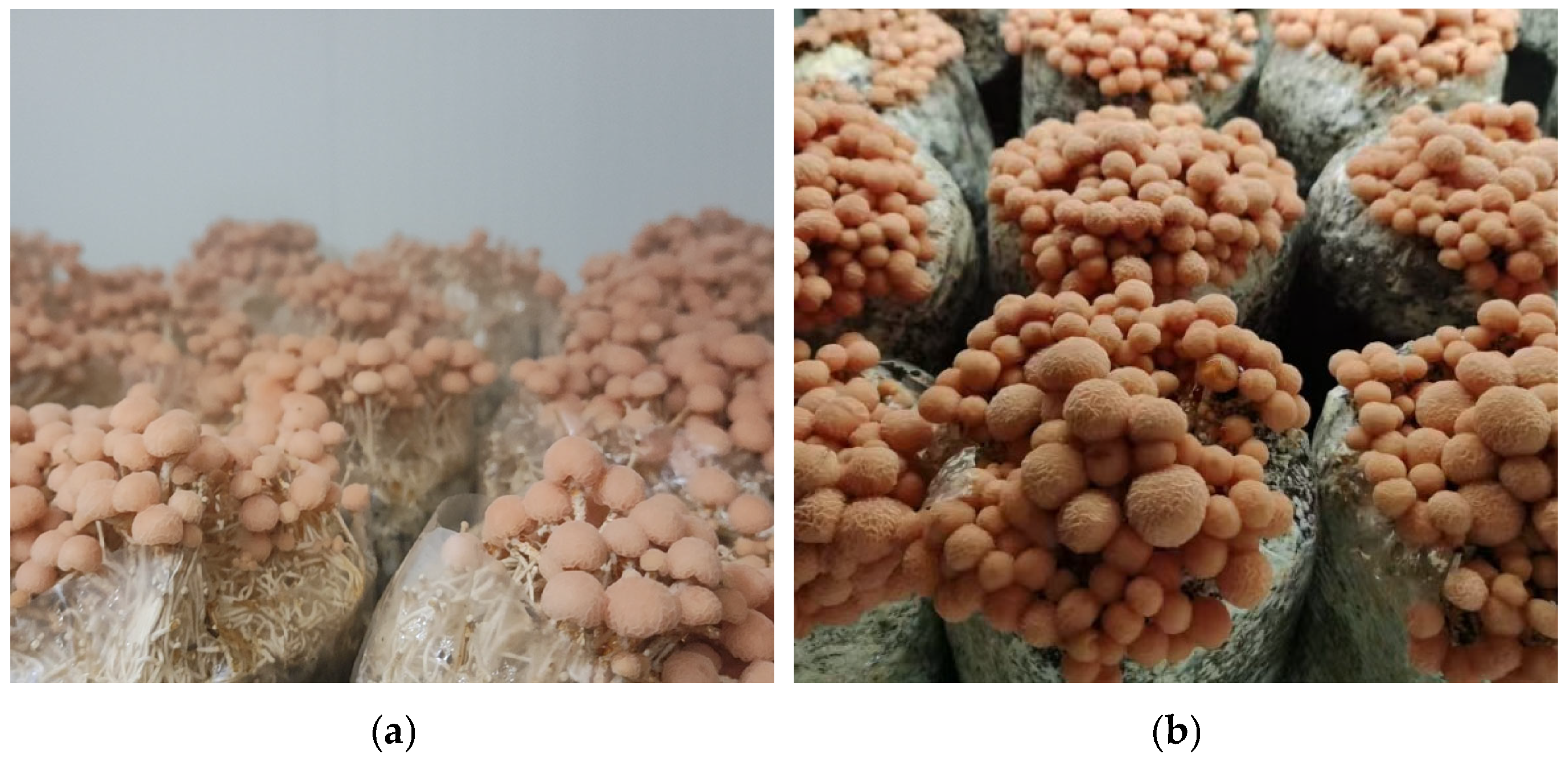
2.7. Demonstration of Commercial Cultivation
2.8. Determination of Nutrient Contents in Fruiting Body
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Phylogenetic Analysis
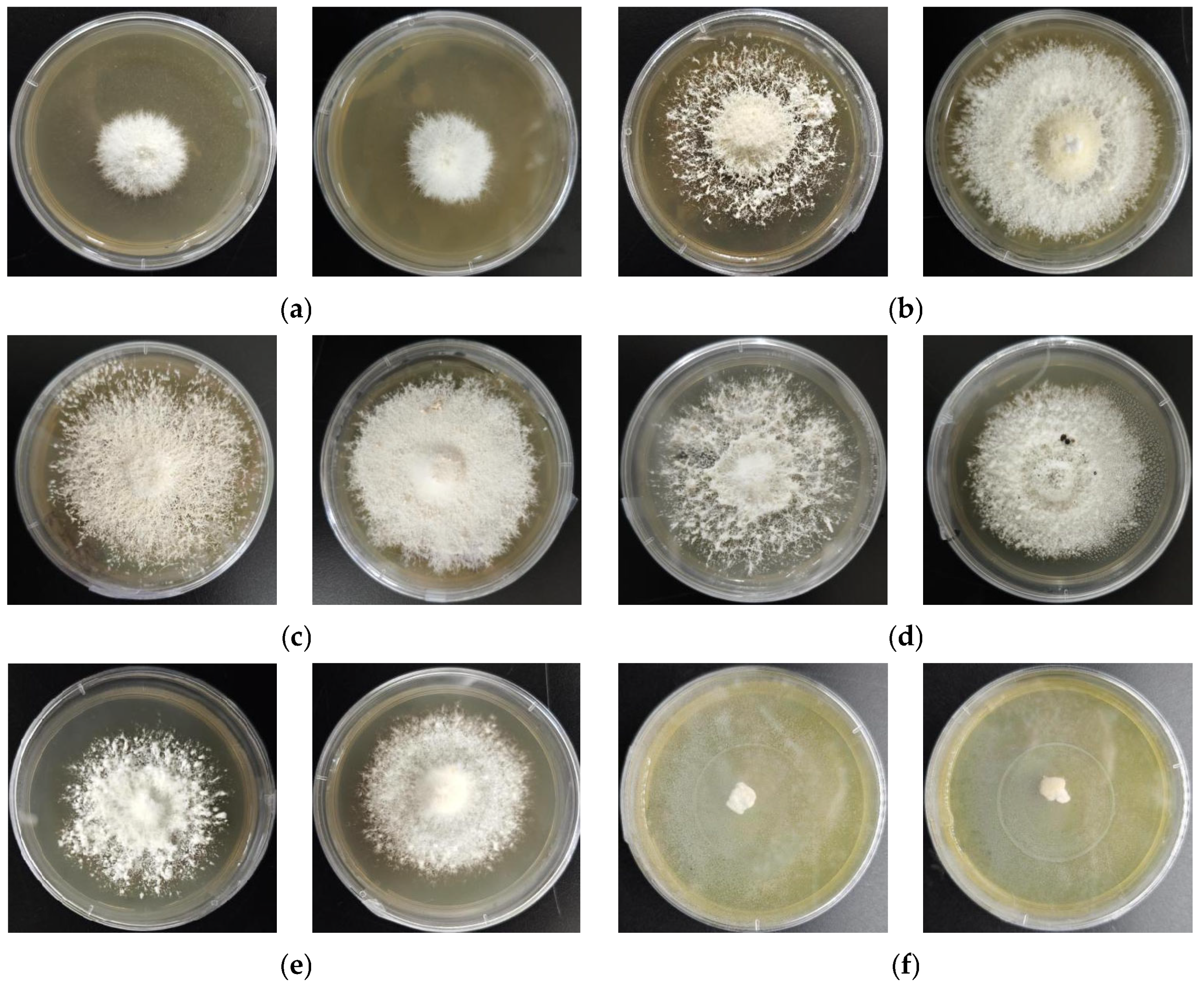
3.2. Results of Primary and Secondary Screening
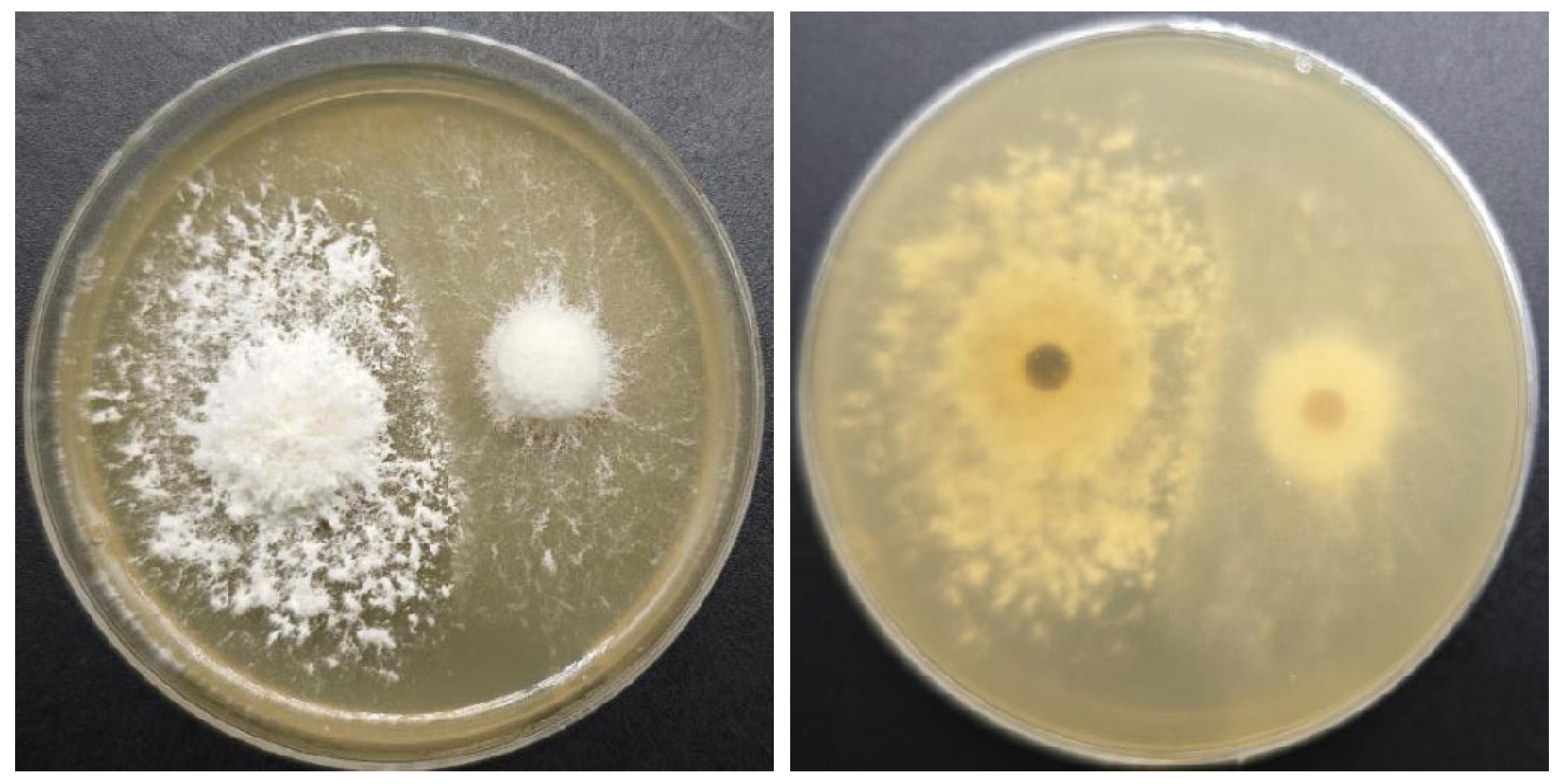
3.3. Results of Antagonistic Reaction
3.4. Results of Temperature Gradient Test
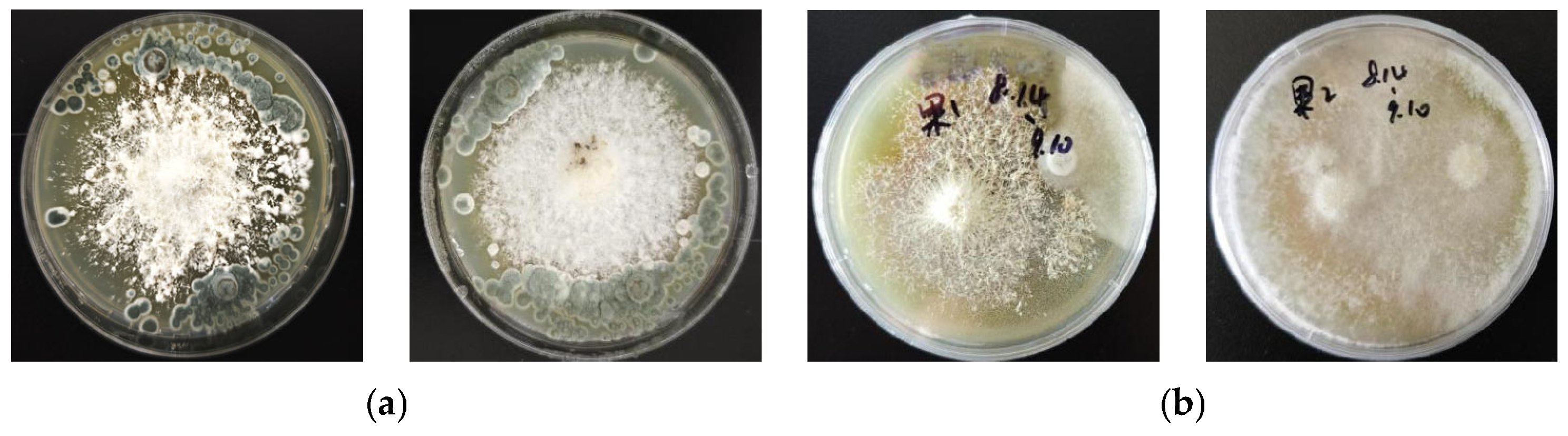
3.5. Results of Antifungal Interaction Assay
3.6. Results of Intermediate Test
3.7. Results of Demonstration Cultivation
3.8. Nutrient Contents of ZJGWG001 and GGR-001 Fruiting Bodies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Tolgor, B. Chinese Changbai Mountain Mushrooms; China Science Publishing: Beijing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.L.; Qin, J.; Guo, T.; Hao, Y.J. The phylogeny and evolution of the Physalacriaceae family. Abstract Collection of Papers from the 2016 Academic Annual Conference of the Chinese Mycological Society. 2016, pp. 181–182. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=8XsFQqBkIey2jFvGvQ0v4b5MD0yq_QDNeLNaeh-hwJoySLRbWmB0zsQUaeJwgv27XP2DuTYyX_lSNpq5vqVrA03tDH_oH99kz9P3NvilP4QWdgmrG29DVh0t_hB3OnRnnLiBGzSjnCTMg18EytYEc7b2lrTBiFFwPkAdVUXeGNg5vmzh9mxbSFzv820zy2eo&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 9 December 2025).
- Wang, B.; Zhang, M.J. A new record species of the genus Rhodotus. Microbiol. China 1992, 19, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujakiewicz, A. Gloiodon strigosus (Swartz: Fr.) P. Karst. (Bondarzewiaceae) in Poland. Acta Mycol. 2007, 42, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Volobuev, S.V.; Popov, E.S.; Bolshakov, S.Y.; Tsutsupa, T.A. Species of fungi recommended for inclusion in the 2nd edition of the Red Data Book of Oryol Region. Разнooбразие растительнoгo мира 2021, 3, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.K.; Park, Y.J.; Choi, S.K.; Lee, J.O.; Choi, J.H.; Sung, J.M. Some unrecorded higher fungi of the seoraksan and odaesan national parks. Mycobiology 2006, 34, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tang, L.P.; Hao, Y.J.; Cai, H.Q.; Tolgor, B.; Yang, Z.L. Morphological and molecular evidence for a new species of Rhodotus from tropical and subtropical Yunnan, China. Mycol. Prog. 2014, 13, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrici, A.; Legon, N. BMS Day Foray Reports. Mycologist 1999, 13, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundberg, W.J.; Methven, A.S.; Monoson, H.L. Rhodotus palmatus (Basidiomycetes, Agaricales, Tricholomataceae) in Illinois. Mycotaxon 1997, 65, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X. A new species and a new record of Tricholomataceae from China. Acta Mycol. Sin. 1992, 11, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.G. Studies on Conservation Biology of Endangered Macrofungi in Changbai Mountain Nature Reserve. Master’s Thesis, Jilin Agricultural University, Changchun, China, June 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Elkhateeb, W.A.; Daba, G.M. The wild non edible mushrooms, what should we know so far. Int. J. Adv. Biochem. Res. 2022, 6, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandargo, B.; Michehl, M.; Stadler, M.; Surup, F. Antifungal sesquiterpenoids, rhodocoranes, from submerged cultures of the wrinkled peach mushroom, Rhodotus palmatus. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 83, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandargo, B.; Michehl, M.; Praditya, D.; Steinmann, E.; Stadler, M.; Surup, F. Antiviral meroterpenoid rhodatin and sesquiterpenoids rhodocoranes A–E from the wrinkled peach mushroom, Rhodotus palmatus. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 3286–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Cao, R.K.; Bao, H.Y. Effects of Rhodotus palmatus polysaccharide on immunodeficient mice induced by cyclophosphamide. Acta Edulis Fungi 2023, 30, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolgor, B.; Fan, Y.G. Study on domesticaion of Rhodotus palmatus. Edible Fungi China 2008, 27, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commercial cultivation of mushrooms (Rhodotus palmatus) has been achieved. Edible Med. Mushrooms 2024, 32, 210.
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.L.; Wu, Z.Q. Ceriporiopsis kunmingensis sp. nov. (Polyporales, Basidiomycota) evidenced by morphological characters and phylogenetic analysis. Mycol. Prog. 2017, 16, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user–friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, M.A.; Holder, M.T.; Vos, R.; Midford, P.E.; Liebowitz, T.; Chan, L.; Hoover, P.; Warnow, T. The CIPRES Portals. CIPRES. Available online: www.phylo.org/sub_sections/portal (accessed on 8 July 2024).
- GB/T 21125-2007; Technical Inspection for Mushroom Selecting and Breeding. National Standardization Administration: Beijing, China, 2007.
- NY/T 1845-2010; Identification of Distinctness for Edible Mushroom Cultivar by Antagonism. Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of China: Beijing, China, 2010.
- GB5009.5-2016; Determination of Protein in Food of National Standard for Food Safety. China Food and Drug Administation: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB5009.124-2016; Determination of Amino Acids in Food of National Standard for Food Safety. China Food and Drug Administation: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB/T 15672-2009; Determination of Total Saccharide in Edible Mushroom. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- SN/T 4260-2015; Determination of Crude Polysaccharides in Plant Source Foods for Export-Phehol-Sulfuric Acid Colorimetry. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2015.
- GB5009.14-2017; National Food Safety Standards, Determination of Zinc in Food. People’s Republic of China National Health and Family Planning Commission, National Food and Drug Administration: Beijing, China, 2017.
- GB5009.90-2016; National Food Safety Standards, Determination of Iron in Food. People’s Republic of China National Health and Family Planning Commission, National Food and Drug Administration: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB5009.92-2016; National Food Safety Standards, Determination of Calcium in Food. People’s Republic of China National Health and Family Planning Commission, National Food and Drug Administration: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB5009.84-2016; National Food Safety Standards, Determination of Vitamin B1 in Food. The National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB5009.85-2016; National Food Safety Standards, Determination of Vitamin B2 in Food. The National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China, National Food and Drug Administration: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB5009.86-2016; National Food Safety Standards, Determination of Ascorbic Acid in Food. The National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB5009.296-2023; National Food Safety Standards, Determination of Vitamin D in Food. National Health Commission, State Administration for Market Regulation: Beijing, China, 2023.
- Vu, D.; Groenewald, M.; de Vries, M.; Gehrmann, T.; Stielow, B.; Eberhardt, U.; Al-Hatmi, A.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Cardinali, G.; Houbraken, J.; et al. Large–scale generation and analysis of filamentous fungal DNA barcodes boosts coverage for kingdom fungi and reveals thresholds for fungal species and higher taxon delimitation. Stud. Mycol. 2019, 92, 135–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.J.; Lu, H.; Xu, Z.; Song, C.Y.; Tan, Q.; Liu, J.Y.; Shang, X.D. A new variety of Flammulina velutipes, ‘Shangyan 1820’, was developed through single-spore hybridization. Mycosystema 2023, 42, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Lu, S.J.; Sun, J.M.; Xu, Z.Q.; Qi, J.; Liu, P.; Huang, J.Z. Analysis and evaluation on nutritional components of 26 common edible fungi in market. Edible Fungi China 2021, 40, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q. The development history of edible fungus cultivation. Acta Edulis Fungi 2024, 31, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.R.; Yu, H.L.; Jiang, N.; Li, Y.; Zhou, F.; Shang, X.D.; Song, C.Y.; Tan, Q. The current status and trends of the development of industrialized production of edible mushrooms in China. Edible Med. Mushrooms 2024, 32, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.Y. Re search on Brand Promotion of Yunnan Wild Edible Fungus in A Company. Master’s Thesis, Yunnan Normal University, Kunming, China, December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yunnan Provincial Environmental Protection Bureau. List of Biological Species in Yunnan Province (2016 Edition); Yunnan Science and Technology Press: Kunming, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.J.; Zhang, C.X.; He, M.X.; Liang, Z.Q.; Deng, X.H.; Zeng, N.K. Buchwaldoboletus xylophilus and Phlebopus portentosus, two non–ectomycorrhizal boletes from tropical China. Phytotaxa 2021, 520, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

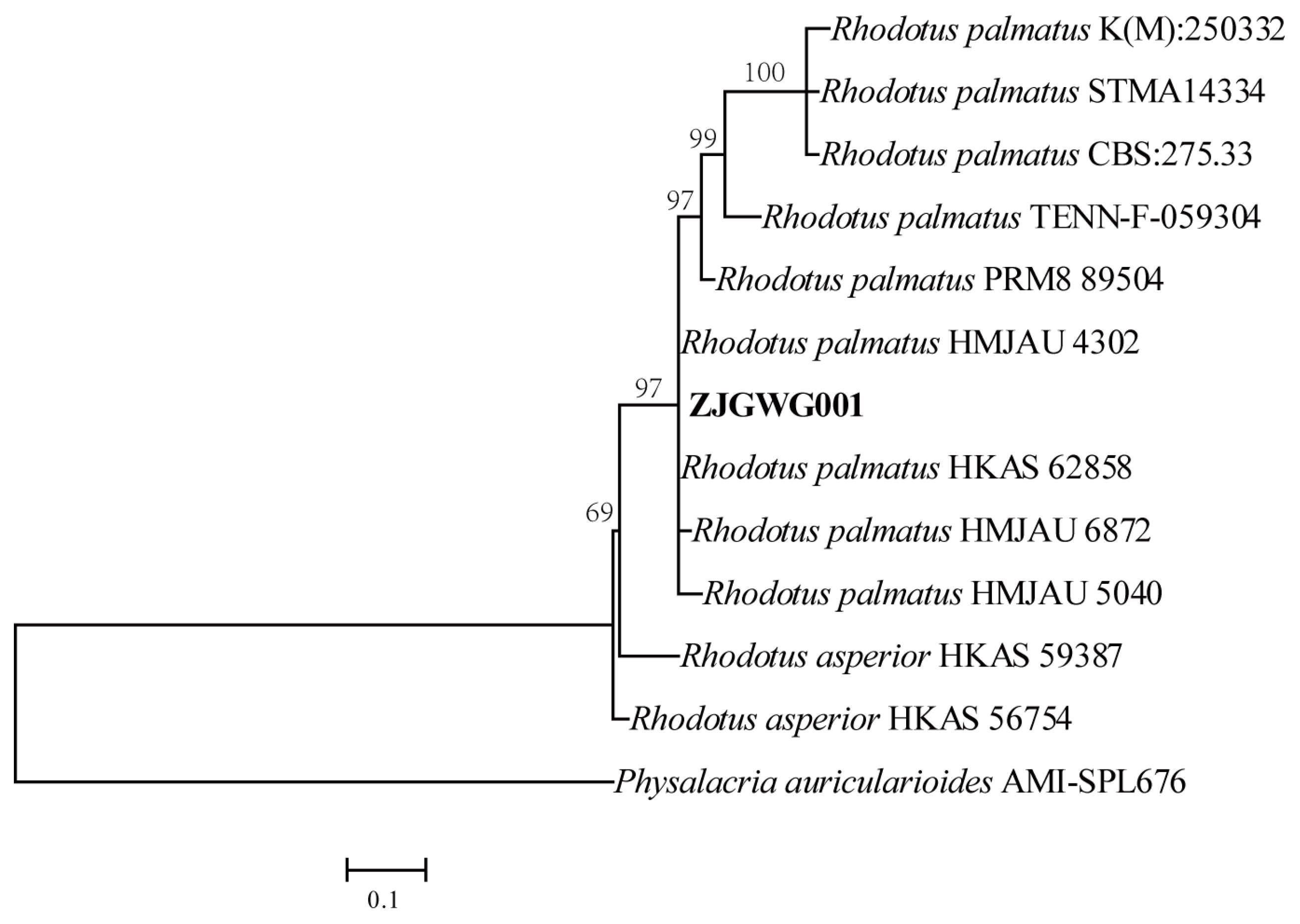




| Species Name | Sample No. | GenBank Accessions No. | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rhodotus palmatus | K(M):250332 | MZ159700 | Unpublished |
| R. palmatus | HKAS 62858 | KC179738 | [7] |
| R. palmatus | PRM8 89504 | KC179739 | [7] |
| R. palmatus | HMJAU 4302 | KC179740 | [7] |
| R. palmatus | HMJAU 5040 | KC179741 | [7] |
| R. palmatus | HMJAU 6872 | KC179742 | [7] |
| R. palmatus | STMA14334 | MK287617 | [14] |
| R. palmatus | CBS:275.33 | MH855439 | [35] |
| R. palmatus | TENN-F-059304 | PV688318 | Unpublished |
| R. palmatus | ZJGWG001 | PV839816 | This study |
| R. asperior | HKAS 59387 | KC179736 | [7] |
| R. asperior | HKAS 56754 | KC179737 | [7] |
| Physalacria auricularioides | AMI-SPL676 | OM964475 | Unpublished |
| Stage | Growth Period/Day | Stipe Traits | Pileus Traits | Yield/(g·bag−1) | Biological Efficiency/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Color | Length/ (cm) | Color | Diameter /(cm) | ||||
| Primary | 25 | Pinkish | 2.80 ± 0.25 | Orange red | 2.11 ± 0.36 | 131.21 ± 8.21 | 43.7 ± 2.74 |
| Secondary | 25 | Pinkish | 3.07 ± 0.19 | Orange red | 2.30 ± 0.18 | 136.34 ± 7.88 | 45.4 ± 2.63 |
| Strain | 5 °C/(cm) | 10 °C/(cm) | 15 °C/(cm) | 20 °C/(cm) | 25 °C/(cm) | 30 °C/(cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZJGWG001 | 1.2 | 2.4 | 3 | 2.9 | 2.3 | 0.1 |
| GGR-001 | 1.1 | 2.7 | 2.7 | 2.2 | 2.3 | 0.1 |
| Stage | Growth Period/(Day) | Stipe Traits | Pileus Traits | Yield/(g·bag−1) | Biological Efficiency/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Color | Length/(cm) | Diameter /(mm) | Color | Diameter /(cm) | ||||
| Secondary screening | 25 | Pinkish | 3.07 ± 0.19 b | \ | Oranged red | 2.30 ± 0.18 | 136.34 ± 7.88 b | 45.4 ± 2.63 b |
| Intermediate test | 25 | Pinkish | 5.97 ± 0.25 a | 3.42 ± 0.14 | Pink | 2.63 ± 0.15 | 156.45 ± 7.10 a | 52.2 ± 2.37 a |
| Strain | Growth Period/(Day) | Buds Number * | Stipe Traits | Pileus Traits | Yield/(g·bag−1) | Biological Efficiency/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Color | Length/(cm) | Diameter /(mm) * | Color | Diameter /(cm) | |||||
| ZJGWG001 | 23 | 62.25 ± 6.73 a | Pinkish | 8.50 ± 1.39 | 2.64 ± 0.57 b | Pink | 3.83 ± 0.69 | 177.43 ± 10.08 | 59.1 |
| GGR-001 | 24 | 52.95 ± 6.00 b | Pinkish | 8.48 ± 1.22 | 4.75 ± 1.18 a | Pink | 3.69 ± 0.80 | 174.46 ± 10.74 | 58.2 |
| Item | Unit | ZJGWG001 | GGR-001 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asp | g/100 g | 1.21 | 0.99 |
| Thr | g/100 g | 0.59 | 0.49 |
| Ser | g/100 g | 0.61 | 0.50 |
| Glu | g/100 g | 2.06 | 1.93 |
| Pro | g/100 g | 0.41 | 0.31 |
| Gly | g/100 g | 0.58 | 0.51 |
| Ala | g/100 g | 0.66 | 0.74 |
| Val | g/100 g | 0.49 | 0.51 |
| Met | g/100 g | 0.16 | 0.17 |
| Ile | g/100 g | 0.49 | 0.41 |
| Leu | g/100 g | 0.78 | 0.66 |
| Tyr | g/100 g | 0.49 | 0.37 |
| Phe | g/100 g | 0.49 | 0.38 |
| His | g/100 g | 0.81 | 0.49 |
| Lys | g/100 g | 0.68 | 0.54 |
| Arg | g/100 g | 0.69 | 0.53 |
| Trp | g/100 g | 0.17 | 0.13 |
| Cys | g/100 g | 0.16 | 0.15 |
| Total amino acids | g/100 g | 11.53 | 9.81 |
| Zn | mg/kg | 32.9 | 32.1 |
| Fe | mg/kg | 32.1 | 23.8 |
| Ca | mg/kg | 13.5 | 17.1 |
| Protein | g/100 g | 14.0 | 13.6 |
| Crude fiber | g/100 g | 0.6 | 1.7 |
| Total sugar | % | 54.1 | 18.3 |
| Polysaccharide | % | 2.57 | 15.07 |
| Crude fat | g/100 g | 1.1 | 0.57 |
| VB1 | mg/100 g | 0.129 | - |
| VB2 | mg/100 g | 0.422 | - |
| VC | mg/100 g | 22.2 | - |
| VD2 | μg/100 g | 21.2 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, X.; Liu, S.; Zhou, F.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.; Liu, C.; Wang, L.; Hua, R.; Sun, D. Research on the Efficient Industrial Scale-Up Cultivation of a Novel Aromatic and Disease-Resistant Mushroom Rhodotus palmatus. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2882. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122882
Luo X, Liu S, Zhou F, Li J, Zhang J, Liu Q, Liu C, Wang L, Hua R, Sun D. Research on the Efficient Industrial Scale-Up Cultivation of a Novel Aromatic and Disease-Resistant Mushroom Rhodotus palmatus. Agronomy. 2025; 15(12):2882. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122882
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Xi, Shaoxiong Liu, Fan Zhou, Jianying Li, Junbo Zhang, Qimeng Liu, Chunli Liu, Lei Wang, Rong Hua, and Dafeng Sun. 2025. "Research on the Efficient Industrial Scale-Up Cultivation of a Novel Aromatic and Disease-Resistant Mushroom Rhodotus palmatus" Agronomy 15, no. 12: 2882. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122882
APA StyleLuo, X., Liu, S., Zhou, F., Li, J., Zhang, J., Liu, Q., Liu, C., Wang, L., Hua, R., & Sun, D. (2025). Research on the Efficient Industrial Scale-Up Cultivation of a Novel Aromatic and Disease-Resistant Mushroom Rhodotus palmatus. Agronomy, 15(12), 2882. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122882







