Identification of Monilinia yunnanensis Causing Brown Rot in Korla Fragrant Pear and Evaluation of Bacillus siamensis PL55 as a Biocontrol Agent
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Diseased Samples and Isolation, Purification and Pathogenicity Tests of Pathogens
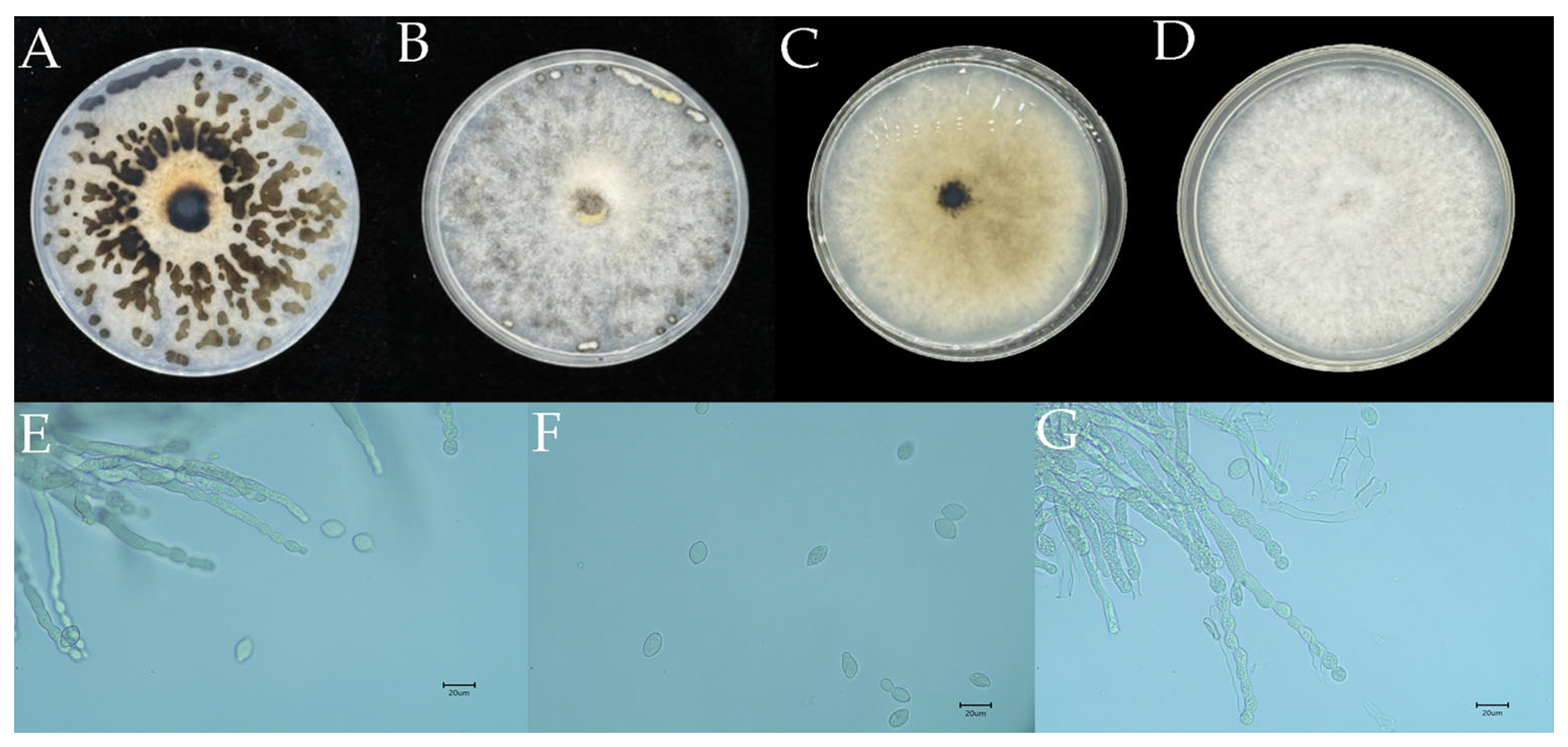
2.2. Morphological Identification of Pathogens
2.3. Molecular Identification of Pathogens
2.4. Isolation and Screening of Biocontrol Strains
2.5. Identification of Biocontrol Strains
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
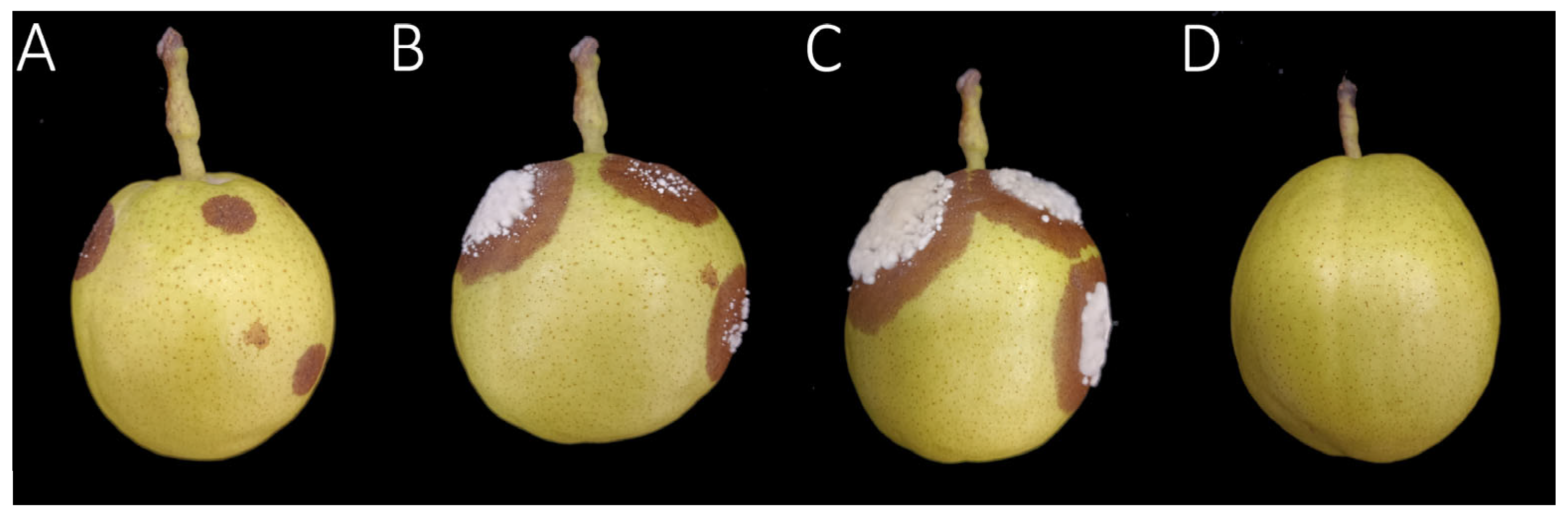
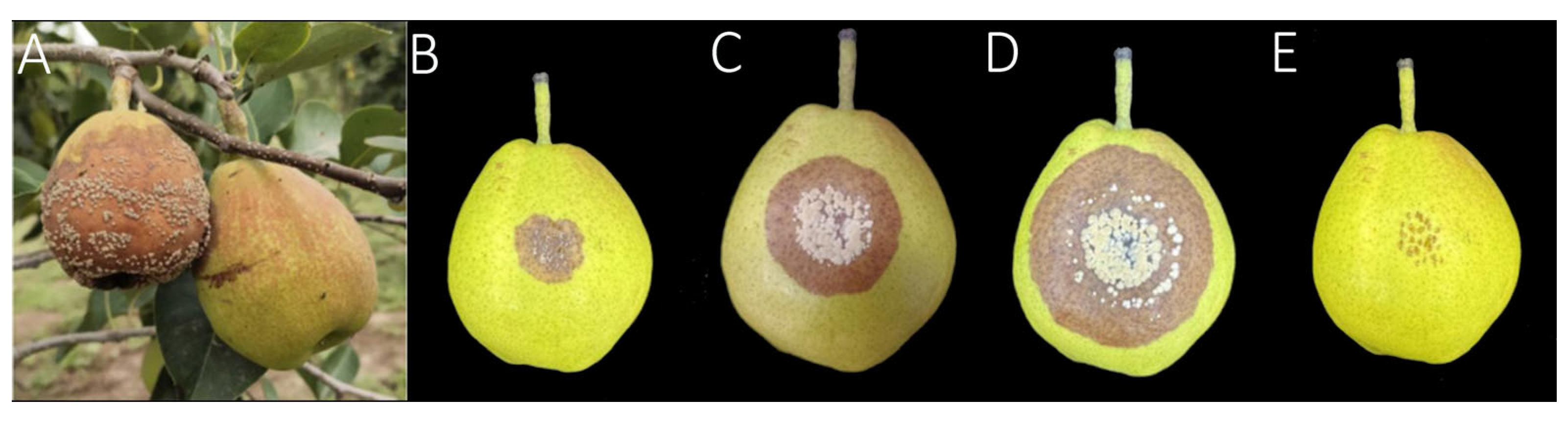
3.1. Symptoms Characterization of Brown Rot in Korla Fragrant Pears
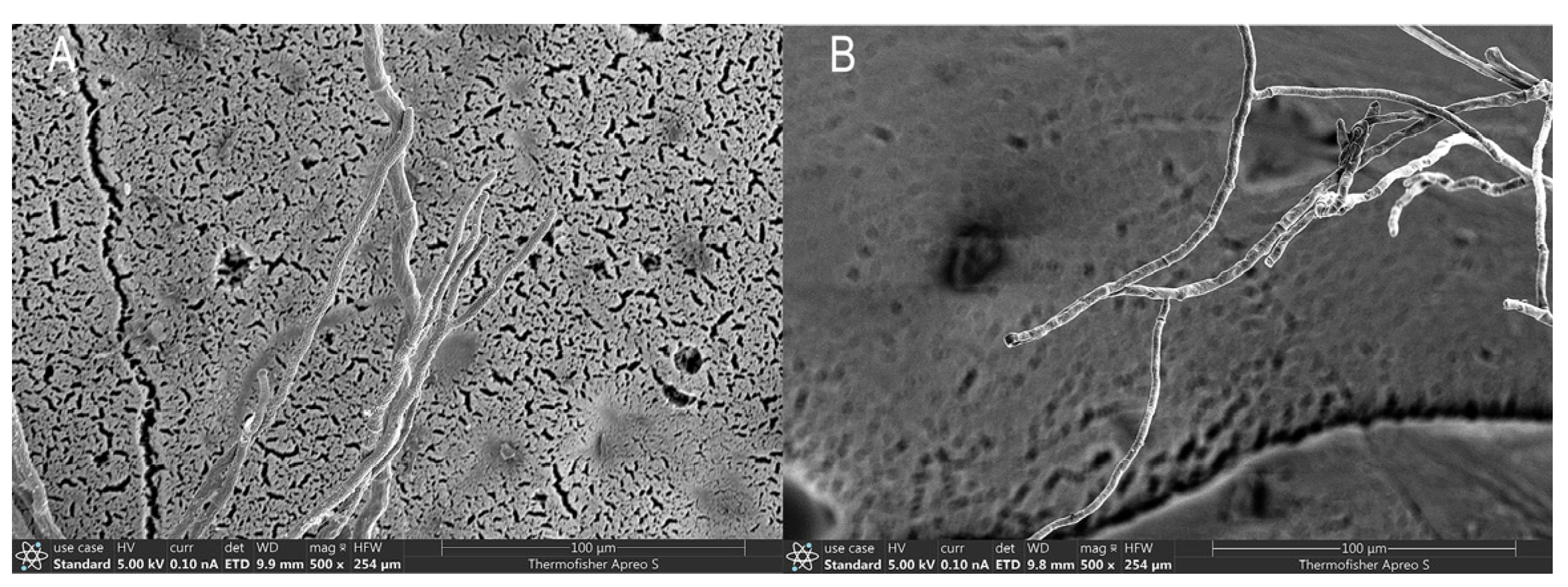
3.2. Identification of Monilinia yunnanensis as the Causal Agent
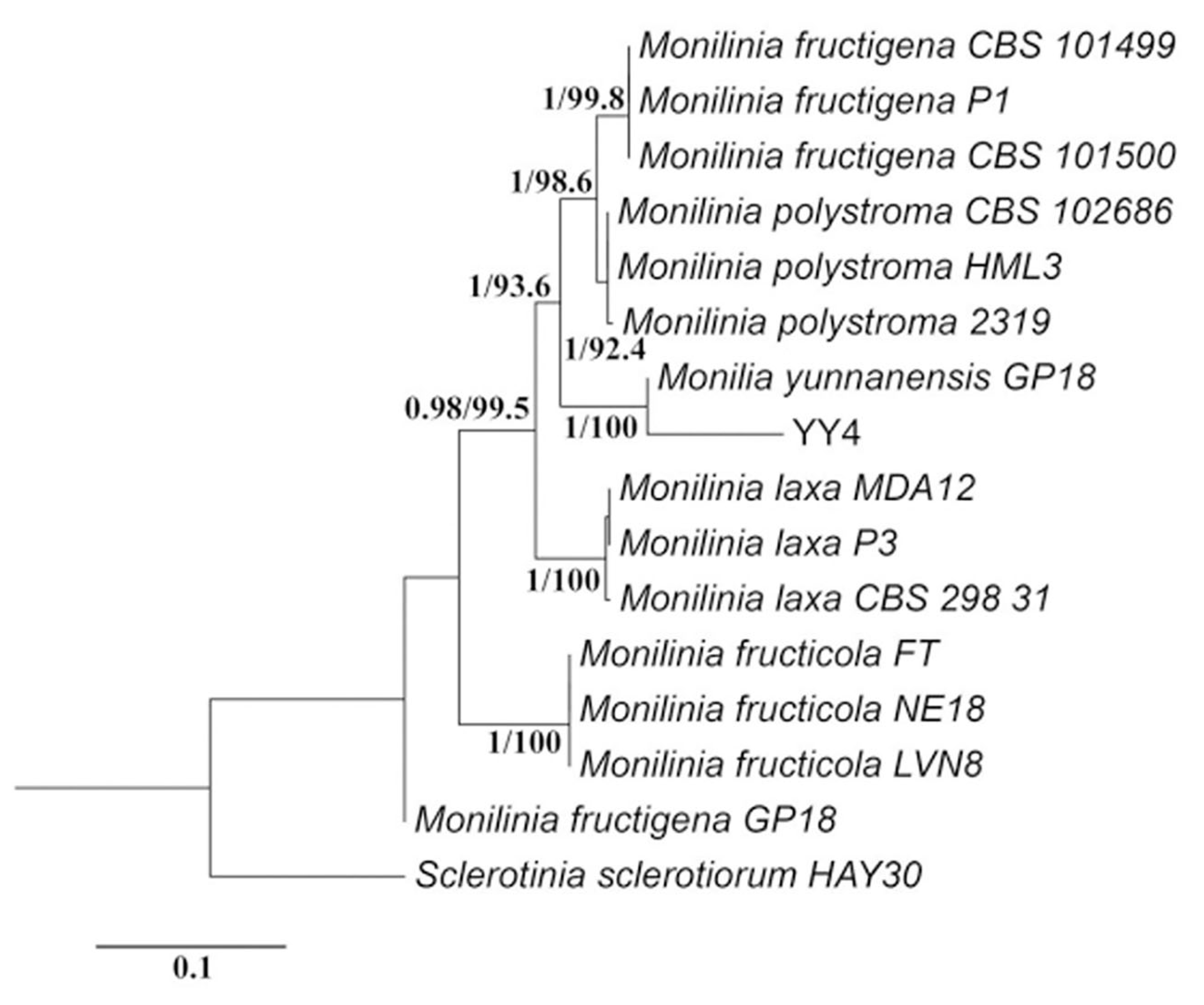
3.3. Confirmation of Monilinia yunnanensis Through Molecular Phylogenetics
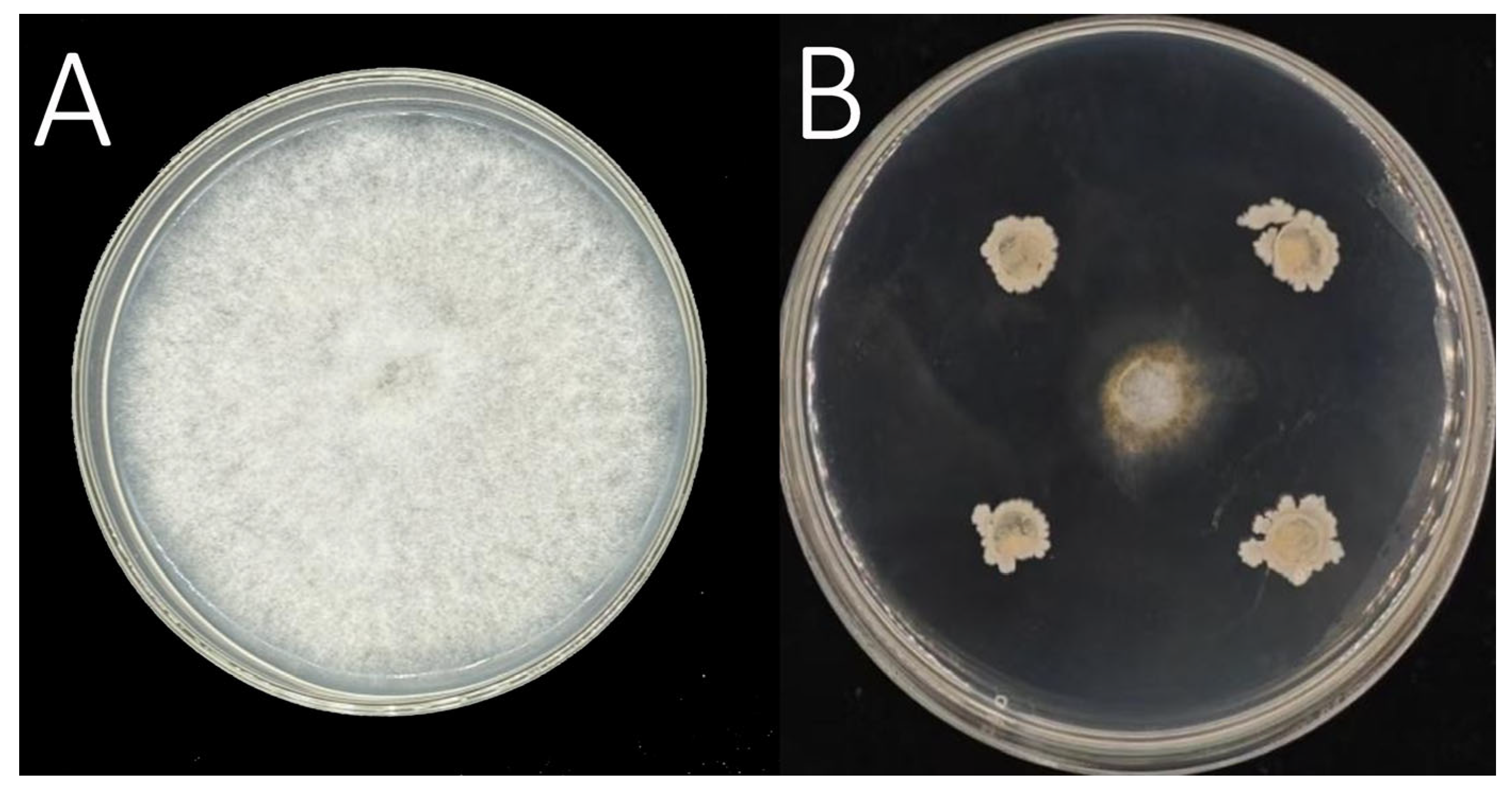
3.4. Selection and Isolation of Effective Biocontrol Strain PL55
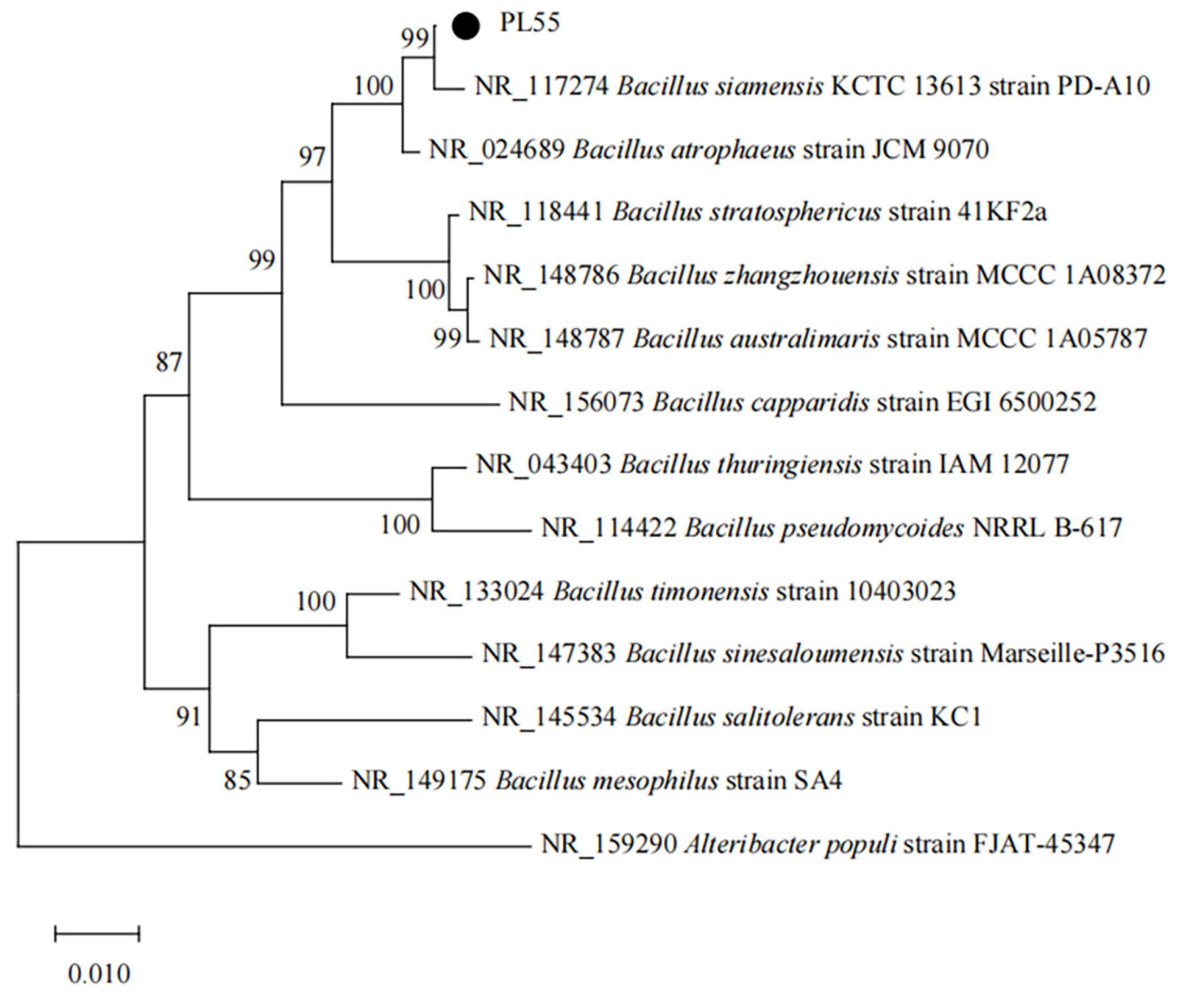
3.5. Molecular Confirmation of Bacillus siamensis Strain PL55
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, X.M.; Yang, Y.Y.; Li, J.K.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Liu, H.X. Effects of 1-MCP treatment on postharvest waxy changes of the peel of Korla fragrant pear. Food Sci. 2015, 36, 262–266. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.; Yan, P.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Y. Changes in the metabolome and nutritional quality of pulp from three types of Korla fragrant Pears with different appearances as revealed by widely targeted metabolomics. Plants 2023, 12, 3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Tang, Y.; Lan, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, Y.; Niu, H.; Jin, X.; Liu, Y. Construction method of quantitative evaluation model for the maturity of Korla fragrant pear. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2022, 15, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.Y.; Wang, H.Y. Current status, problems, and countermeasures of the fragrant pear industry development in Korla City. Shanxi Agric. Econ. 2024, 192–194. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, L.F.; Cai, M.L.; Du, S.F.; Luo, C.X. Identification of two Monilia species from apricot in China. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 2496–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.F.; Chen, S.N.; Chen, G.K.; Schnabel, G.; Du, S.F.; Chen, C.; Li, G.Q.; Luo, C.X. Identification and characterization of three Monilinia species from plum in China. Plant Dis. 2015, 99, 1775–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morca, A.U.; Teksür, P.K.; Eğerci, Y. Morphological and molecular identification of Monilinia spp. causing blossom blight and fruit rot on sweet cherries in the Aegean region of Turkey. Phytoparasitica 2022, 50, 527–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Duan, W.; Hu, M.; Guo, L. Research progress on the pathogens of brown rot in stone and pome fruits. Acta Mycol. 2022, 41, 331–348. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.Z.; Chen, Y.; Yi, T.Y. Research progress on peach brown rot. J. Biol. Disaster Sci. 2025, 48, 286–293. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.J.; Cox, K.D.; Schnabel, G.; Luo, C.X. Monilinia species causing brown rot of peach in China. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.Q.; Niu, C.W.; Chen, X.Y.; Guo, L.Y. Monilinia species associated with brown rot of cultivated apple and pear fruit in China. Plant Dis. 2016, 100, 2240–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, J.Q.; Shi, Y.N.; Huang, M.L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Li, Y.P. Identification of brown rot pathogens and selection of control agents for green crisp plum. J. Shanxi Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2024, 44, 88–94. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.J.; Zhou, Z.X.; Du, H.; Lü, Z.L.; Li, J.P.; Wang, Y. Isolation and identification of brown rot pathogens in apple from some regions of Gansu, and screening of antagonistic bacteria. Biotechnol. Bull. 2023, 39, 209–218. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, C.X.; Schnabel, G.; Hu, M.; De Cal, A. Global distribution and management of peach diseases. Phytopathol. Res. 2022, 4, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabke, A.; Hu, M.J.; Luo, C.X.; Bryson, P.K.; Schnabel, G. First report of brown rot of apple caused by Monilinia fructicola in Germany. Plant Dis. 2011, 95, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.W.; Wang, S.L.; Liu, B.Y.; Du, J.F.; Wang, Y.Z. Population identification and pathogenicity analysis of peach brown rot pathogens in Shandong province. J. Fruit Sci. 2023, 40, 327–339. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Rungjindamai, N.; Jeffries, P.; Xu, X.M. Epidemiology and management of brown rot on stone fruit caused by Monilinia laxa. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2014, 140, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidorova, T.M.; Asaturova, A.M.; Homyak, A.I. Biologically active metabolites of Bacillus subtilis and their role in the control of phytopathogenic microorganisms. Agric. Biol. 2018, 53, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Li, P.; Wu, S.; Zhao, P.; Gao, H. Bacillus subtilis CF-3 volatile organic compounds inhibit Monilinia fructicola growth in peach fruit. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avan, M.; Kotan, R.; Albastawisi, E.M.; Erarslan, G. Biological control of blossom blight and brown rot caused by Monilinia laxa by using a Bacillus subtilis strain TV-6F. Erwerbs-Obstbau 2023, 65, 2399–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.Y.; Zong, Z.F. Plant Pathology Experimental Techniques; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, M.; Liu, J.F.; Zheng, X.F.; Liu, Y.L.; Hu, H.T. Isolation of Anoectochilus roxburghii stalk rot pathogens and a preliminary screening of its antagonistic bacteria. J. Zhejiang Agric. Sci. 2022, 63, 2354–2358, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lü, Z.L.; Jiang, J.J.; Li, J.P.; Zhai, Y.Q.; Hui, N.N.; Wang, L.; Ma, S.B.; Zheng, G.; Qi, Y.H.; Wang, S.S.; et al. Isolation and identification of brown rot pathogens in apple fruits. Northwest Agric. J. 2023, 32, 488–494. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.Y.; Wang, L.N.; Yang, G.Z.; Zhang, W.; Shu, Q.; Su, J.; Yunnan Academy of Agricultural Sciences Horticultural Crops Research Institute. Identification of the pathogen of anthracnose on Yunnan Caiyunhong pear. Plant Pathol. J. 2024, 54, 1248–1251. [Google Scholar]
- Lane, C.R. A synoptic key for differentiation of Monilinia fructicola, M. fructigena and M. laxa, based on examination of cultural characters. EPPO Bull. 2002, 32, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.C. Handbook of Fungal Identification; Shanghai Scientific & Technical Press: Shanghai, China, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, C.W.; Wang, J.R.; Zhu, X.Q.; Li, J.; Zhao, W.S.; Li, B.H. Species of brown rot pathogens in wild fruit forests in Xinjiang. Acta Mycol. 2016, 35, 1514–1525. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Feng, H. Study on Pathogenesis of Cytospora pyri in Korla Fragrant Pear Trees (Pyrus sinkiangensis). J. Fungi 2025, 11, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, A.H.; Brubaker, C.L.; Wendel, J.F. A rapid method for extraction of cotton (Gossypium spp.) genomic DNA Suitable for RFLP or PCR analysis. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 1993, 11, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.J.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990; Volume 18, pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Glass, N.L.; Donaldson, G.C. Development of primer sets designed for use with the PCR to amplify conserved genes from filamentous ascomycetes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.Y.; Ji, B.Z.; Yin, W.X.; Luo, C.X. First Report of brown rot caused by Monilinia yunnanensis on sweet cherry in China. Plant Dis. 2024, 108, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F. Population Structure and Pathogenicity of Monilinia in Shanxi Province. Master’s Thesis, Shanxi Agricultural University, Jinzhong, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Weon, H.Y.; Sang, M.K.; Song, J. Complete genome sequence of Bacillus velezensis M75, a biocontrol agent against fungal plant pathogens, isolated from cotton waste. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 241, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, L.Q.; Zhang, S.K.; Chen, Y.S.; Zhou, Y.N.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Xin, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, P. Isolation of ‘Mei Zao’ sweet cherry brown rot pathogens and identification of endogenous antagonistic bacteria. Food Ferment. Ind. 2020, 46, 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.X.; Zhang, Y.M.; Zhu, H.L.; Ren, L.; Zhang, B.J. Antifungal activity of volatile organic compounds from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens XJ5 and control effect against Monilinia fructigena. Chin. J. Biol. Control. 2020, 36, 575–580. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Wang, D.; Han, D.; Zhang, D.D.; Li, R.; Kong, Z.Q.; Dai, X.F.; Subbarao, K.V.; Chen, J.Y. Characterization of the endophytic Bacillus subtilis KRS015 strain for its biocontrol efficacy against Verticillium dahliae. Phytopathology 2024, 114, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. Antifungal Activities Od Volatile Compounds and Component Analysis of Volatile Compounds Produced by Endophytic Bacillus subtilis Y8 Against Curvularia lunata. Master’s Thesis, Anhui Agricultural University, Hefei, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Wu, Z.; Tian, C.; Liang, Y.; You, C.; Chen, L. Identification and characterization of the endophytic bacterium Bacillus atrophaeus XW2, antagonistic towards Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. Ann. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 1361–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Collection Time | Collection Location and Coordinates | Number of Collected Specimens |
|---|---|---|
| 2024.05 | Tamen Town, Aral City, First Division 80°39′51″, 40°37′20″ | 11 |
| 2024.05 | Tarim University, Aral City, First Division 81°17′22″, 40°32′53″ | 15 |
| 2024.05 | Xinjingzi Town, Aral City, First Division 81°37′26″, 40°40′40″ | 13 |
| 2024.08 | Korla City, Bayingolin Mongol Autonomous Prefecture 86°0′31″, 41°36′50″ | 16 |
| 2024.08 | Korla City, Bayingolin Mongol Autonomous Prefecture 86°5′39″, 41°40′45″ | 11 |
| 2024.08 | Tumxuk City, Third Division 79°8′24″, 39°49′34″ | 18 |
| Inoculation Days (d) | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lesion Area (cm2) | 4.56 ± 1.15 c | 16.88 ± 0.83 b | 33.04 ± 0.82 a |
| Strain Name | Inhibition Rate (%) | Strain Name | Inhibition Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PL55 | 88.18 ± 3.43 a | PL22 | 73.82 ± 1.38 b |
| PL12 | 68.31 ± 1.15 cd | PL17 | 62.43 ± 1.73 e |
| PL36 | 39.46 ± 2.34 j | PL29 | 44.24 ± 1.96 i |
| VP15 | 29.55 ± 2.71 l | VP61 | 31.54 ± 1.66 l |
| VP12 | 73.96 ± 3.15 b | VP62 | 46.95 ± 1.41 i |
| VP11 | 58.08 ± 2.37 fg | XL63 | 31.36 ± 1.19 l |
| XL12 | 63.15 ± 1.26 e | XL64 | 71.03 ± 2.36 bc |
| LH12 | 56.13 ± 2.03 gh | LH18 | 59.74 ± 00.41 ef |
| LH24 | 61.33 ± 2.21 ef | LH33 | 73.46 ± 1.42 b |
| ZT13 | 39.11 ± 1.09 jk | ZT21 | 59.66 ± 2.43 ef |
| ZT12 | 61.15 ± 1.29 ef | ZT31 | 67.02 ± 1.38 d |
| ZT19 | 67.59 ± 0.96 d | XT15 | 54.62 ± 1.53 h |
| XT13 | 69.42 ± 1.16 cd | XT22 | 36.12 ± 2.33 k |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, Q.; Tang, Y.; Li, Z.; Yu, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Feng, H. Identification of Monilinia yunnanensis Causing Brown Rot in Korla Fragrant Pear and Evaluation of Bacillus siamensis PL55 as a Biocontrol Agent. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2678. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122678
Xue Q, Tang Y, Li Z, Yu J, Wang Z, Wang L, Feng H. Identification of Monilinia yunnanensis Causing Brown Rot in Korla Fragrant Pear and Evaluation of Bacillus siamensis PL55 as a Biocontrol Agent. Agronomy. 2025; 15(12):2678. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122678
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Qinyuan, Yuxin Tang, Ziying Li, Jiahui Yu, Zhe Wang, Lan Wang, and Hongzu Feng. 2025. "Identification of Monilinia yunnanensis Causing Brown Rot in Korla Fragrant Pear and Evaluation of Bacillus siamensis PL55 as a Biocontrol Agent" Agronomy 15, no. 12: 2678. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122678
APA StyleXue, Q., Tang, Y., Li, Z., Yu, J., Wang, Z., Wang, L., & Feng, H. (2025). Identification of Monilinia yunnanensis Causing Brown Rot in Korla Fragrant Pear and Evaluation of Bacillus siamensis PL55 as a Biocontrol Agent. Agronomy, 15(12), 2678. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122678






