Evaluation of the Symbiotic Effects of Bradyrhizobium elkanii Y63-1 Inoculation on Soybean Zhongdou 63
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions in Pot Experiments
2.2. Preparation of Rhizobial Inoculant
2.3. Culture Medium and Reagents
2.4. Determination of Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium Content in Soil
2.5. Pot Experiments in Three Soil Types
2.6. Pot Experiments Under Different Nitrogen Levels
2.7. Field Experiment Design and Indicator Measurement
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
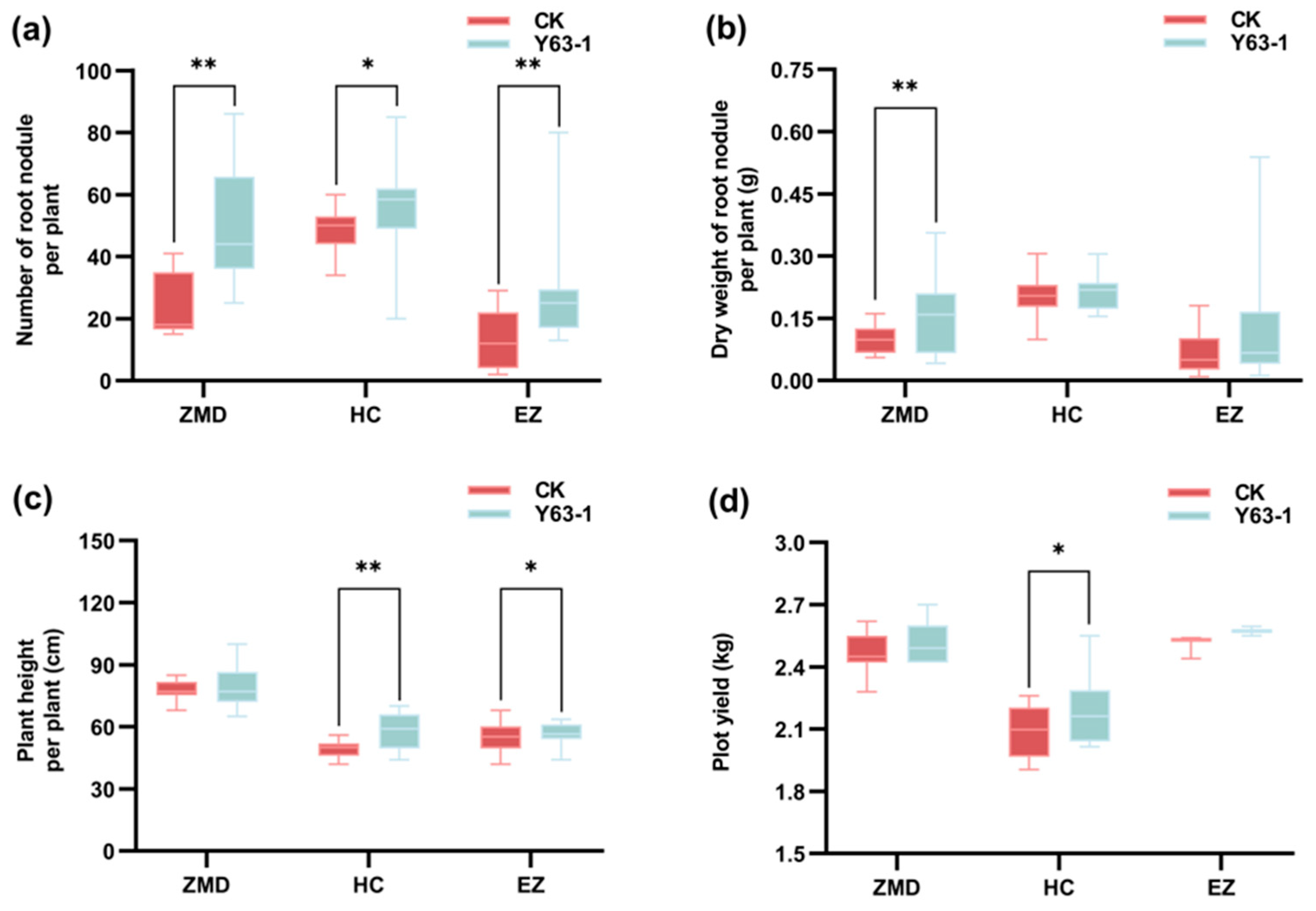
3.1. The Nodulation Phenotype of Soybean ZD63 Was Significantly Improved After Inoculation with Y63-1 in Three Soil Types from Different Regions
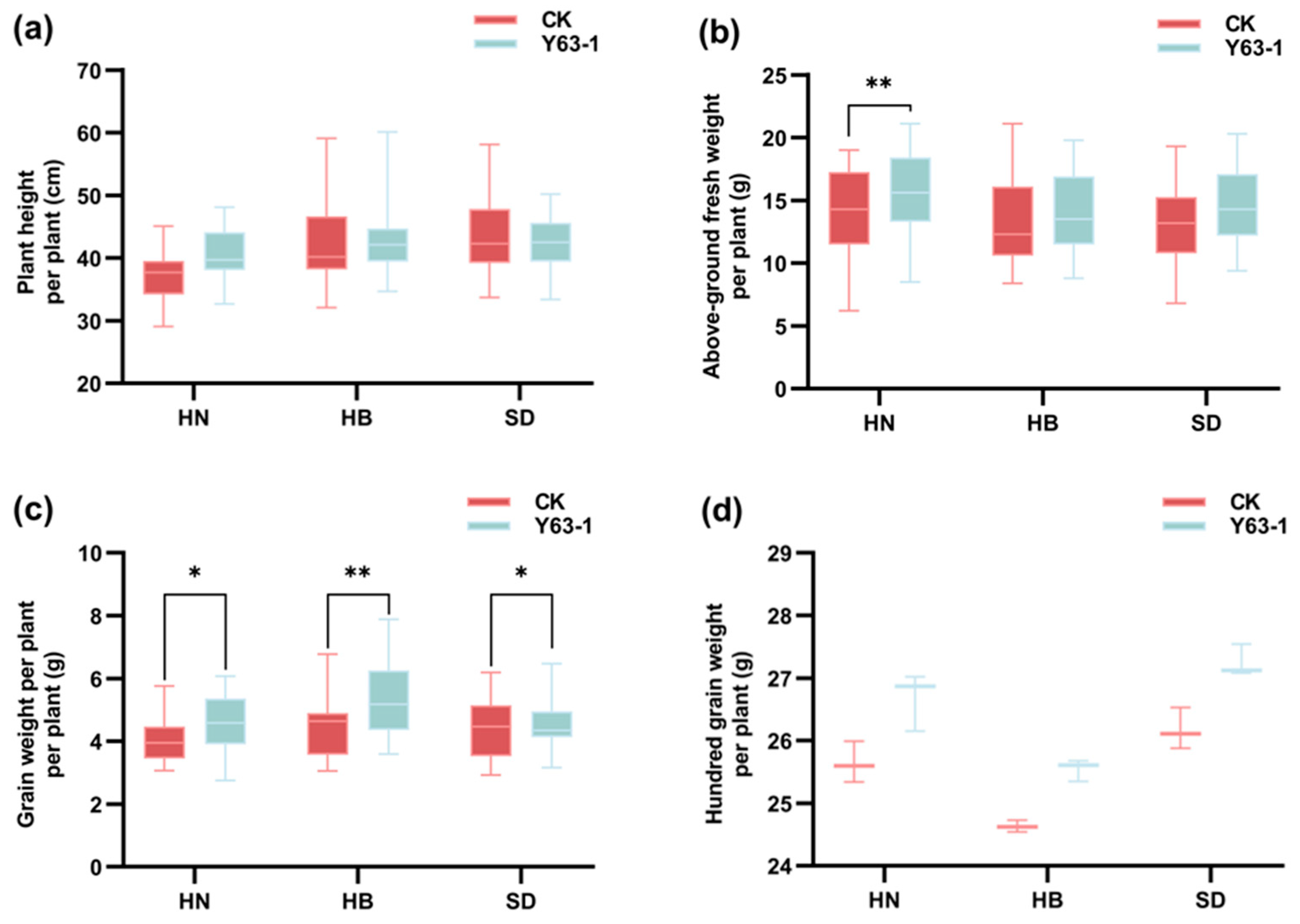
3.2. The Yield-Related Traits of Soybean ZD63 Were Improved After Inoculation with Y63-1 in Three Soil Types from Different Regions
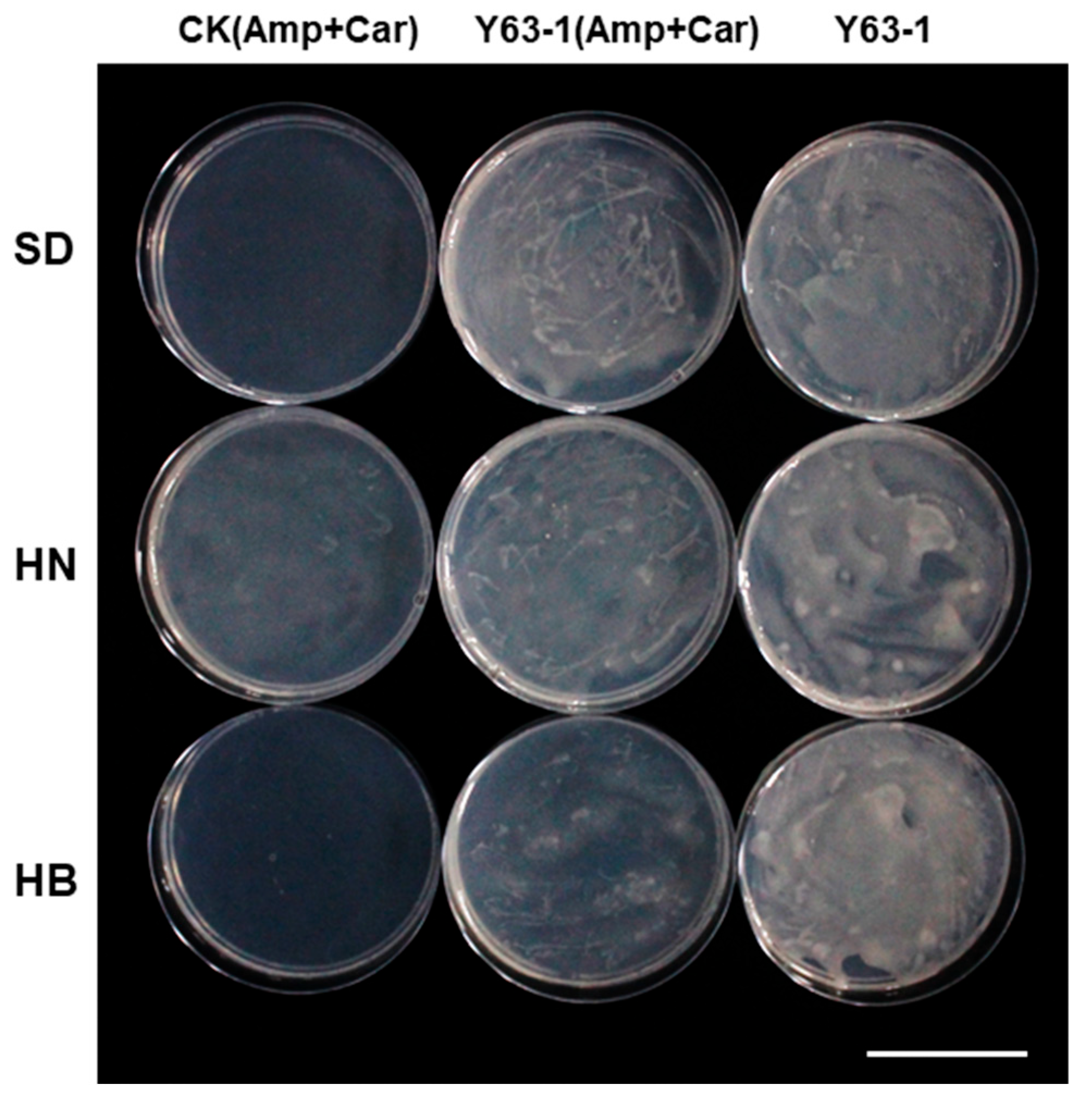
3.3. Y63-1 Strain Is More Competitive in Nodulation of Soybean ZD63 Compared to Indigenous Rhizobia of the Three Soil Types from Different Regions
3.4. Symbiotic Effects and Plot Yields of Soybean ZD63 Were Improved After Inoculation with Y63-1 in Three Areas with Different Nitrogen Levels
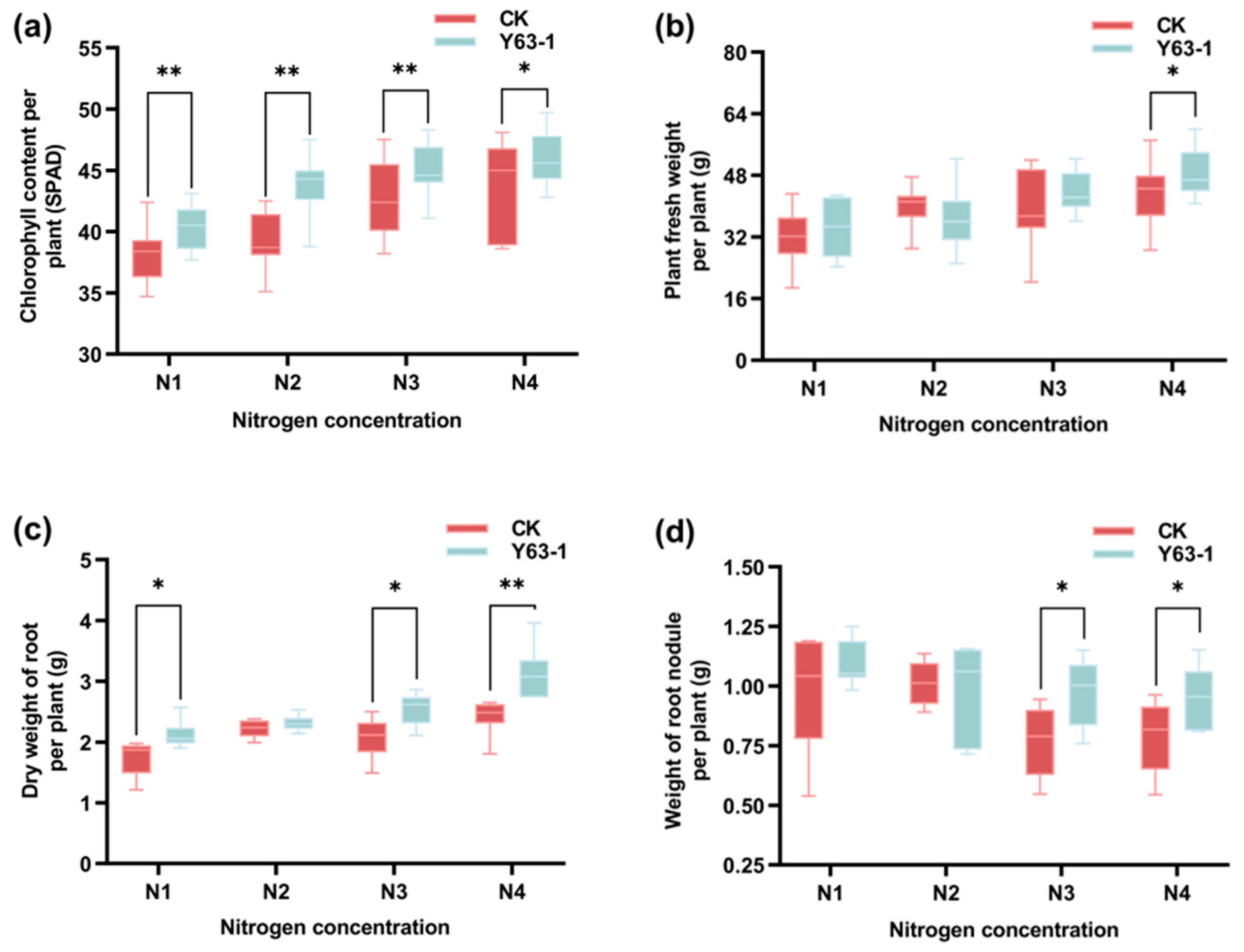
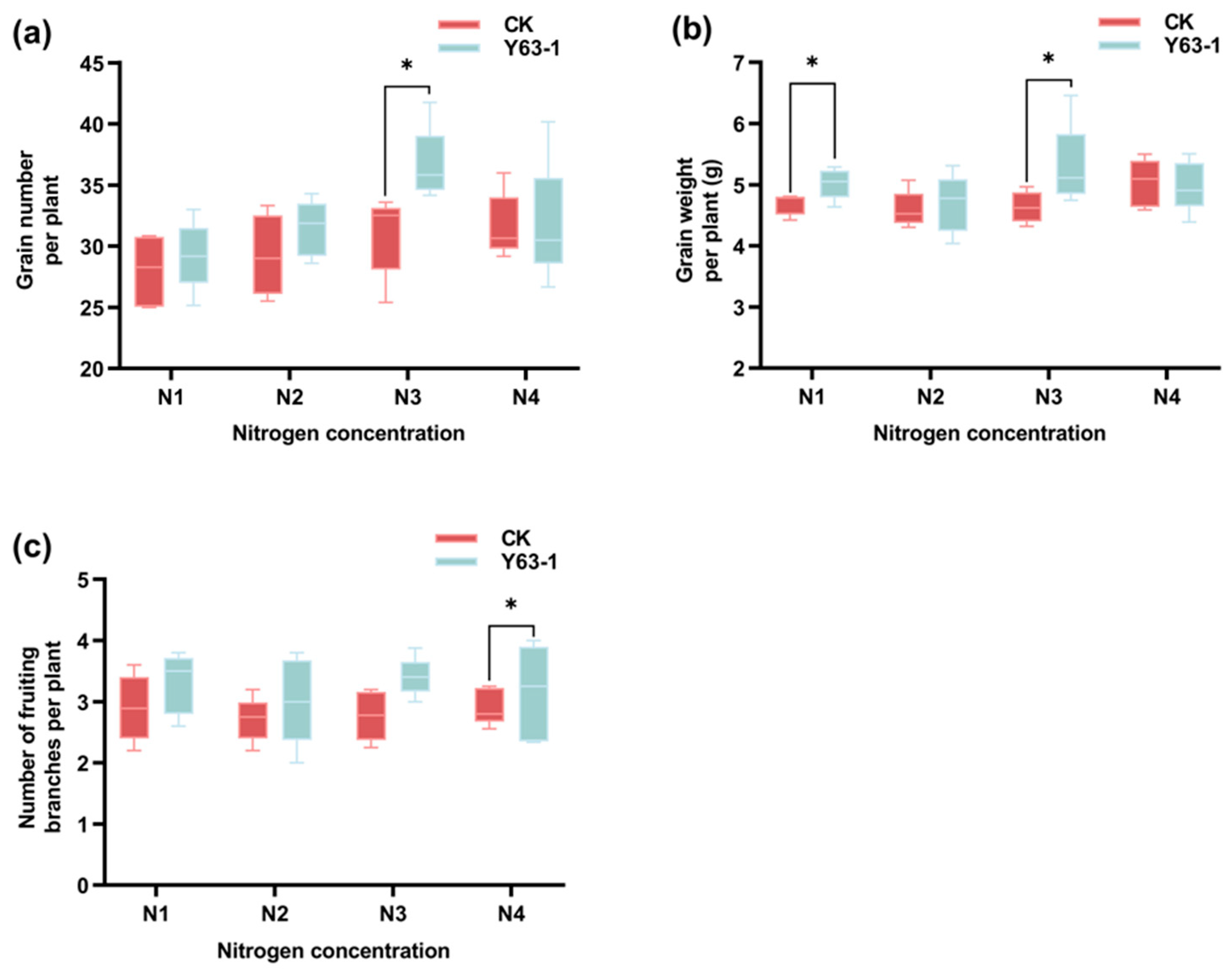
3.5. Symbiotic Effects of Y63-1 Inoculation on Soybean ZD63 Grown in Greenhouse Under Different Nitrogen Levels
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ZD63 | Zhongdou 63 |
| YMA | Yeast Extract Mannitol Agar |
| SNF | Symbiotic nitrogen fixation |
| Car | Carbenicillin |
| Cep | Cephalosporin |
| Amp | Ampicillin |
| Rif | Rifampicin |
| HB | Hubei |
| HN | Henan |
| SD | Shandong |
| ZMD | Zhumadian |
| HC | Hanchuan |
| EZ | Ezhou |
References
- Tian, Y.; Wang, M.J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Li, S.N.; Zhao, W.X.; Jia, Y.P. Effects of Rhizobial Inoculation on Growth and Physiology of Gorage Soybean at Different Nitrogen Levels. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2025, 1–11. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.3362.S.20250508.1712.002 (accessed on 15 October 2025).
- La Menza, N.C.; Monzon, J.P.; Lindquist, J.L.; Arkebauer, T.J.; Knops, J.M.H.; Unkovich, M.; Specht, J.E.; Grassini, P. Insufficient nitrogen supply from symbiotic fixation reduces seasonal crop growth and nitrogen mobilization to seed in highly productive soybean crops. Plant Cell Environ. 2020, 43, 1958–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, P. Isolation, Identification and Application of Rhizobium y63. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China, 2024. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.27630/d.cnki.gznky.2024.000598 (accessed on 15 October 2025).
- Ju, X.T.; Zhang, F.S. Thinking about nitrogen recovery rate. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2003, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampitti, I.A.; de Borja Reis, A.F.; Córdova, S.C.; Castellano, M.J.; Archontoulis, S.V.; Correndo, A.A.; Antunes De Almeida, L.F.; Moro Rosso, L.H. Revisiting biological nitrogen fixation dynamics in soybeans. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 727021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.S.; Chen, X.P.; Vitousek, P. An experiment for the world. Nature. Nature 2013, 497, 33–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.L.; Lin, M.; Ping, S.Z. Biological nitrogen fixation and its application in sustainable agriculture. Biotechnol. Bull. 2008, 18, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Santi, C.; Bogusz, D.; Franche, C. Biological nitrogen fixation in non-legume plants. Ann. Bot. 2013, 111, 743–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Q.; Sheng, J.D.; Pan, L.Y.; Cao, H.Y.; Li, C.C.; Lambers, H.; Wang, X.R. Soil property determines the ability of rhizobial inoculation to enhance nitrogen fixation and phosphorus acquisition in soybean. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 171, 104346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, B.J.R.; Boddey, R.M.; Urquiaga, S. The success of BNF in soybean in Brazil. Plant Soil 2003, 252, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.X.; Gao, J.F.; Cao, P.P.; Gao, Q.; Hua, F.J.; Wang, C.Y.; Zhu, G.X. Effects of nitrogen reducing and inoculation with rhizobium agents on the growth, yield and economic benefit of high protein summer soybean in huang-huai-hai region. J. Hebei Agric. Sci. 2022, 26, 72–77+82. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Leng, P.; Yang, S.Q.; Zhou, S.X.; Zhang, C.J.; Huang, Y.; Shan, Z.H.; Yang, Z.L.; Hao, Q.N.; Chen, S.L.; et al. Isolation and identification of soybean rhizobium Y63 strain. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci. 2024, 46, 920–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.W.; Li, J.; Cao, F.M.; Shen, D.L.; Jiang, X. Application of Soybean Rhizobial Inoculants in China: Existing Problems and Countermeasures. In Proceedings of the 11th National Symposium on Soil Microbiology, the 6th National Symposium on Soil Biology and Biochemistry, and the 4th National Symposium on Microbial Fertilizer Production Technology, Changsha, China, 18 October 2010; Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CPFD&filename=TRXH201010001062 (accessed on 15 October 2025).
- Subramanian, P.; Kim, K.; Krishnamoorthy, R.; Sundaram, S.; Sa, T. Endophytic bacteria improve nodule function and plant nitrogen in soybean on co-inoculation with Bradyrhizobium japonicum MN110. Plant Growth Regul. 2015, 76, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.h.; Gao, H.; Wang, H.; Guo, Y.; He, M.; Peng, Y.; Wang, X.L. GSK3-mediated stress signaling inhibits legume-rhizobium symbiosis by phosphorylating GmNSP1 in soybean. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 488–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, F.; Bhuiyan, M.A.H.; Alam, S.S.; Waghmode, T.R.; Kim, P.J.; Lee, Y.B. Effect of Rhizobium sp. BARIRGm901 inoculation on nodulation, nitrogen fixation and yield of soybean (Glycine max) genotypes in gray terrace soil. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2015, 79, 1660–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiori, A.K.; de Oliveira Gutuzzo, G.; dos Santos Sanzovo, A.W.; de Souza Andrade, D.; de Oliveira, A.L.M.; Rodrigues, E.P. Effects of rhizobium tropici azide-resistant mutants on growth, nitrogen nutrition and nodulation of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Rhizosphere 2021, 18, 100355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.Q.; Xu, X.P.; Wang, W.; Ma, J.C.; Wei, D.; He, P.; Pampolino, M.F.; Johnston, A.M. Estimating nutrient uptake requirements for soybean using QUEFTS model in China. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, S.; Zhai, L.; Wang, H.; Lei, Q.; Ren, T.; Yin, C. Row ratios of intercropping maize and soybean can affect agronomic efficiency of the system and subsequent wheat. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogino, P.; Banchio, E.; Bonfiglio, C.; Giordano, W. Competitiveness of a Bradyrhizobium sp. strain in soils containing indigenous rhizobia. Curr. Microbiol. 2008, 56, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.X.; Shen, H.L.; Zheng, B.; Yang, L.; Dong, Z.Y.; Wan, C.X. Biodiversity of indigenous rhizobia from soybean nodules in Xinjiang and its matching relationship with different soybean varieties. Xinjiang Agric. Sci. 2025, 1–23. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/65.1097.S.20250224.1248.002 (accessed on 15 October 2025).
- Guo, J.; Yang, F.; Han, J.C.; Wei, S.J.; Zhang, X.X. Isolation, identification, evaluation of soybean rhizobia from saline-alkali soil in Yellow River Delta. Soil Fertil. Sci. China 2025, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, P.; Jin, F.X.; Li, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, C.J.; Shan, Z.H.; Yang, Z.L.; Chen, L.M.; Cao, D.; Hao, Q.N.; et al. High efficient broad-spectrum Bradyrhizobium elkanii Y63-1. Oil Crop Sci. 2023, 8, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, J.; Guan, W.; Liu, Z.; He, G.; Zhang, D.; Liu, X. Soil fertility evaluation and spatial distribution of grasslands in Qilian Mountains Nature Reserve of eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. PeerJ 2021, 9, e10986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Helios, W.; Serafin-Andrzejewska, M.; Kozak, M.; Lewandowska, S. Impact of nitrogen fertilisation and inoculation on soybean nodulation, nitrogen status, and yield in a central European climate. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, P.; Jin, F.X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, C.J.; Chan, Z.H.; Yang, Z.L.; Yuan, S.L.; Chen, H.F. Screening and optimization of culture medium for Bradyrhizobium elkanii Y63-1. Soybean Sci. 2024, 43, 641–647. [Google Scholar]
- Unay, J.; Perret, X. Synthetic plasmids to challenge symbiotic nitrogen fixation between rhizobia and legumes. In Methods in Rhizosphere Biology Research; Reinhardt, D., Sharma, A.K., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.J.; Zeng, Q.F.; Wei, X.D.; Wang, J.C.H.; Wei, X.; Chen, C. The rhizobia of wild legume forage in guizhou tailings areas and determination of resistance. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2022, 30, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.L.; Huo, X.X.; Zhang, H.; Huang, Y.H.; Hao, Y.R.; Li, Z.; Zheng, Z.H.; Guo, K. Isolation, identification and field application of soybean rhizobia in saline-alkali land of the Yellow River Delta. Shandong Agric. Sci. 2023, 55, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovino, R.S.; da Silva, T.R.; Rodrigues, R.T.; de Sá Carvalho, J.R.; Cunha, J.B.A.; de Lima, L.M.; Dos Santos, R.C.; Santos, C.E.; Ribeiro, P.R.; de Freitas, A.D. Elite Bradyrhizobium strains boost biological nitrogen fixation and peanut yield in tropical drylands. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2022, 53, 1623–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Zhong, Z.D.; Fan, W.; Peng, Y.Q.; Du, S.; Chen, D.S.; Wang, X.L.; Li, Y.G. Symbiotic compatibility among eight elite soybean rhizobia strains and twenty-seven soybean cultivars from different planting regions. Soybean Sci. 2017, 36, 405–418. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, X.J.; Jin, Y.L.; Yao, T.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, J.G.; Li, C.N.; Yang, X.M.; Chen, J.G. Isolation, identification and screening of rhizobium strains from white clover in Lanzhou. Grassl. Turf. 2022, 42, 132–138. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Y.Z.; Zhang, W.; Tang, Z.J.; Fu, J.Y.; Li, Z.J.; Zhang, F.C. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer reduction and rhizobia inoculation on physiological growth, nitrogen use efficiency and yield of soybean. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2024, 55, 340–351. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Han, W.X.; Tang, A.H.; Shen, J.L.; Cui, Z.L.; Vitousek, P.; Erisman, J.W.; Goulding, K.; Christie, P.; et al. Enhanced nitrogen deposition over China. Nature 2013, 494, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.X.; Liu, S.Y.; Wang, W.F.; Zheng, F.; Han, L.L.; Zhang, L.M. Diversity of soybean rhizobia in Northeast China and their application. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2024, 35, 1850–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.X.; Xu, Y.; Li, L.; Huang, X.J.; Wang, D.S.; Wu, Q.Z.; Cheng, G.D.; Zhai, Y.L. Effect of Nitrogen Fertilizer and Rhizobium Inoculation on Nodulation and Growth of Southern Xinjiang Spring Soybean. Soybean Sci. 2021, 40, 241–248. [Google Scholar]
- Basile, L.A.; Lepek, V.C. Legume–rhizobium dance: An agricultural tool that could be improved? Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 14, 1897–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, P.K.; Bisht, S.C.; Mishra, S.; Selvakumar, G.; Bisht, J.K.; Gupta, H.S. Coinoculation of rhizobium leguminosarum-pr1 with a cold tolerant Pseudomonas sp. improves iron acquisition, nutrient uptake and growth of field pea (Pisum sativum L.). J. Plant Nutr. 2012, 35, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Indicator | I (Extremely Rich) | II (Rich) | III (Relatively Rich) | IV (Moderate) | V (Poor) | VI (Extremely Poor) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organic matter (g/kg) | >40 | 30~40 | 20~30 | 10~20 | 6~10 | <6 |
| Total N (g/kg) | >2 | 1.5~2 | 1~1.5 | 0.75~1 | 0.5~0.75 | <0.5 |
| Total P (g/kg) | >1 | 0.8~1 | 0.6~0.8 | 0.4~0.6 | 0.2~0.4 | <0.2 |
| Total K (g/kg) | >25 | 20~25 | 15~20 | 10~15 | 5~10 | <5 |
| Available N (mg/kg) | >150 | 120~150 | 90~120 | 60–90 | 30~60 | <30 |
| Available P (mg/kg) | >40 | 20~40 | 10~20 | 5~10 | 3–5 | <3 |
| Available K (mg/kg) | >200 | 150~200 | 100~150 | 50~100 | 30–50 | <30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, L.; Leng, P.; Jin, F.; Lu, J.; Hu, Q.; Liang, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, C.; Xu, Z.; et al. Evaluation of the Symbiotic Effects of Bradyrhizobium elkanii Y63-1 Inoculation on Soybean Zhongdou 63. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2649. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112649
Lu L, Leng P, Jin F, Lu J, Hu Q, Liang W, Huang Y, Zhang C, Li C, Xu Z, et al. Evaluation of the Symbiotic Effects of Bradyrhizobium elkanii Y63-1 Inoculation on Soybean Zhongdou 63. Agronomy. 2025; 15(11):2649. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112649
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Lu, Piao Leng, Fuxiao Jin, Jiayu Lu, Qianqian Hu, Wanwan Liang, Yi Huang, Chanjuan Zhang, Chao Li, Zhuang Xu, and et al. 2025. "Evaluation of the Symbiotic Effects of Bradyrhizobium elkanii Y63-1 Inoculation on Soybean Zhongdou 63" Agronomy 15, no. 11: 2649. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112649
APA StyleLu, L., Leng, P., Jin, F., Lu, J., Hu, Q., Liang, W., Huang, Y., Zhang, C., Li, C., Xu, Z., Yang, Z., Chen, S., Yuan, S., & Chen, H. (2025). Evaluation of the Symbiotic Effects of Bradyrhizobium elkanii Y63-1 Inoculation on Soybean Zhongdou 63. Agronomy, 15(11), 2649. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112649






