Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analysis Reveals the Role of Exogenous GA3 in Regulating Strawberry Fruit Development via Auxin Signaling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Exogenous GA3 Spraying Treatment
2.2. RNA Extraction and Transcriptome Sequencing
2.3. Screen for Differentially Expressed Genes
2.4. RNA-Seq Data Analysis and Annotation
2.5. Metabolite Profiling of Hormone Content Using UPLC-MS/MS
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Role of GA3 in Berry Growth During Fruit Development
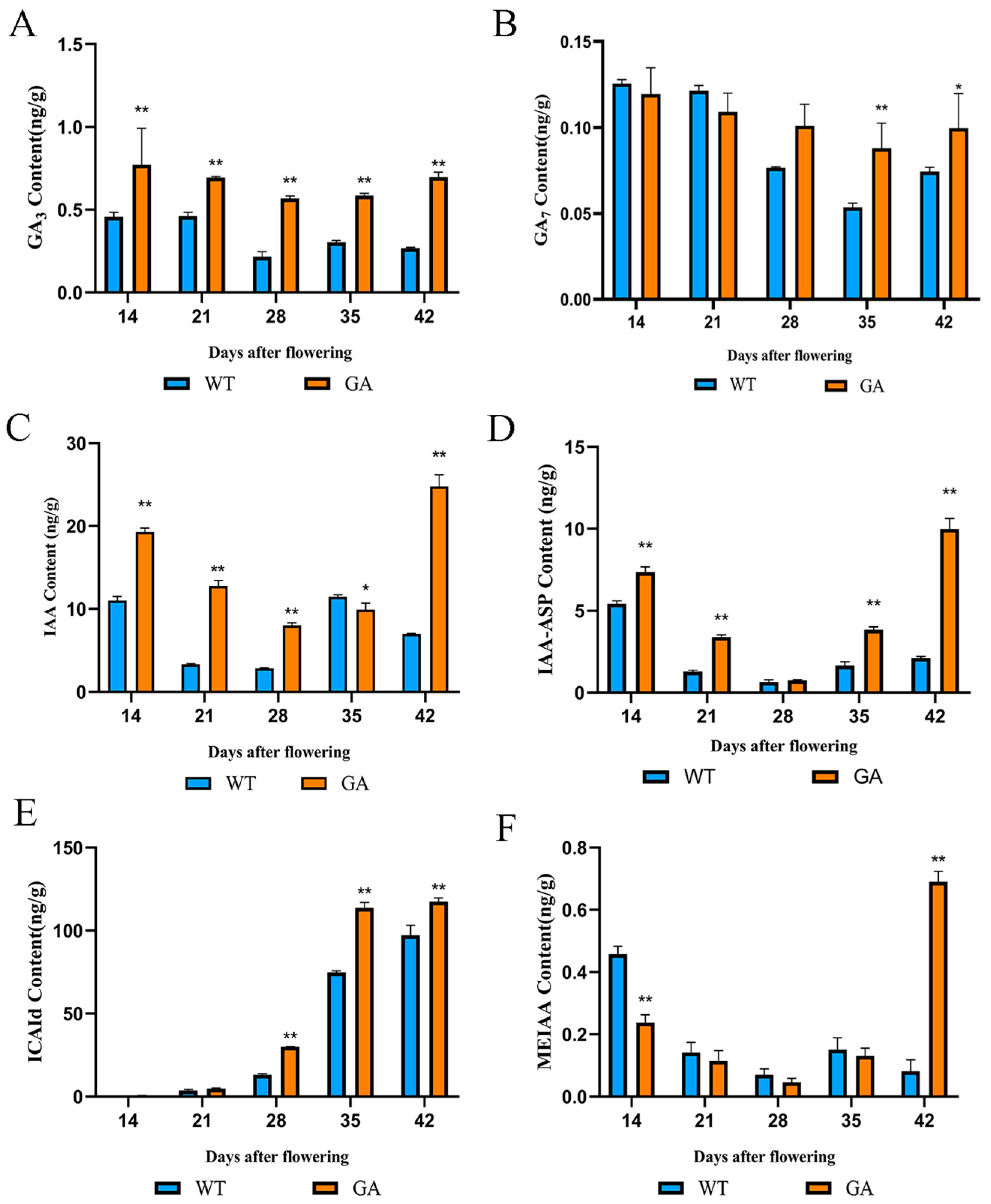
3.2. Phytohormone Content of Strawberry Fruits Under GA3
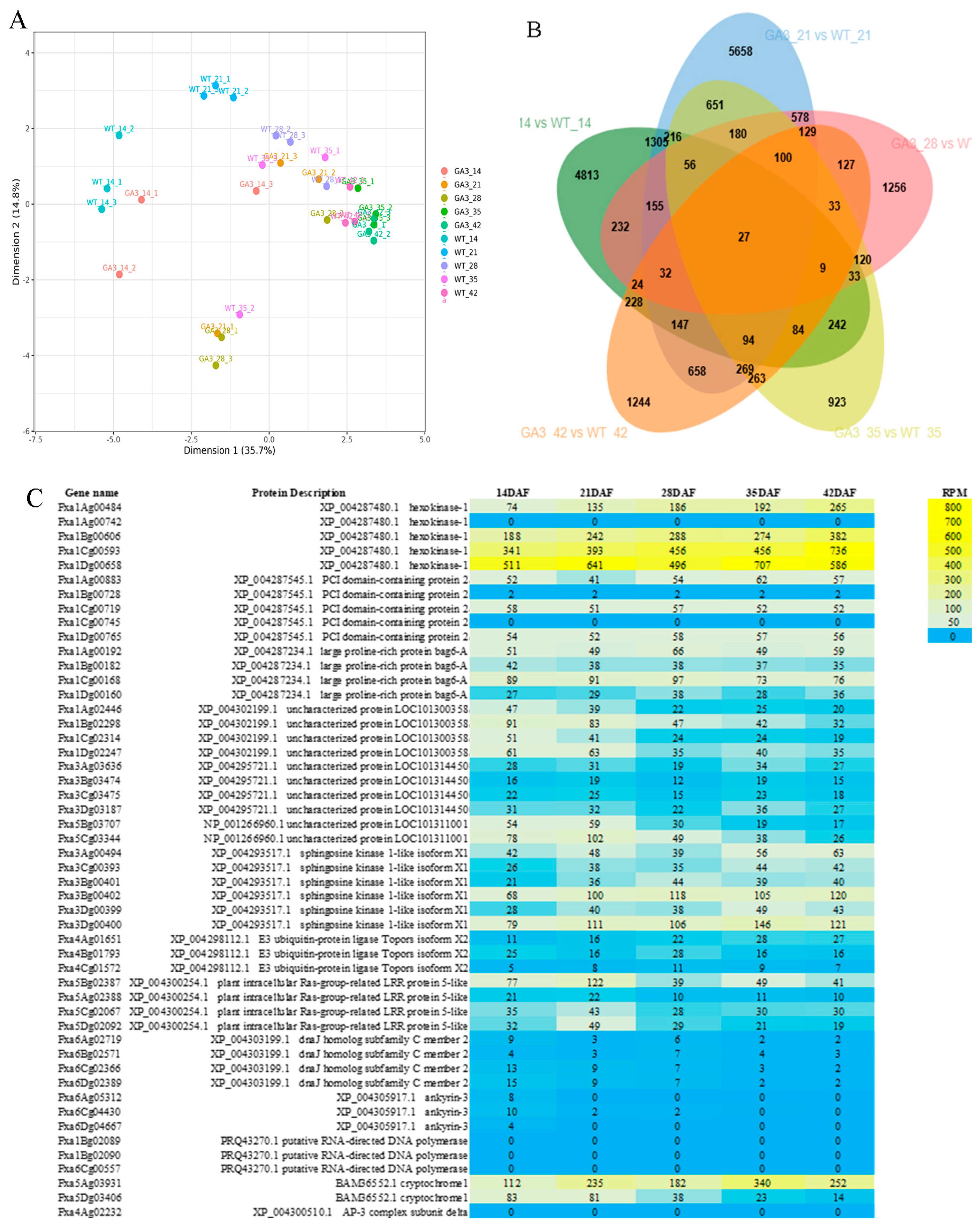
3.3. Regulatory Role of Exogenous GA3 in the Transcriptional Profile
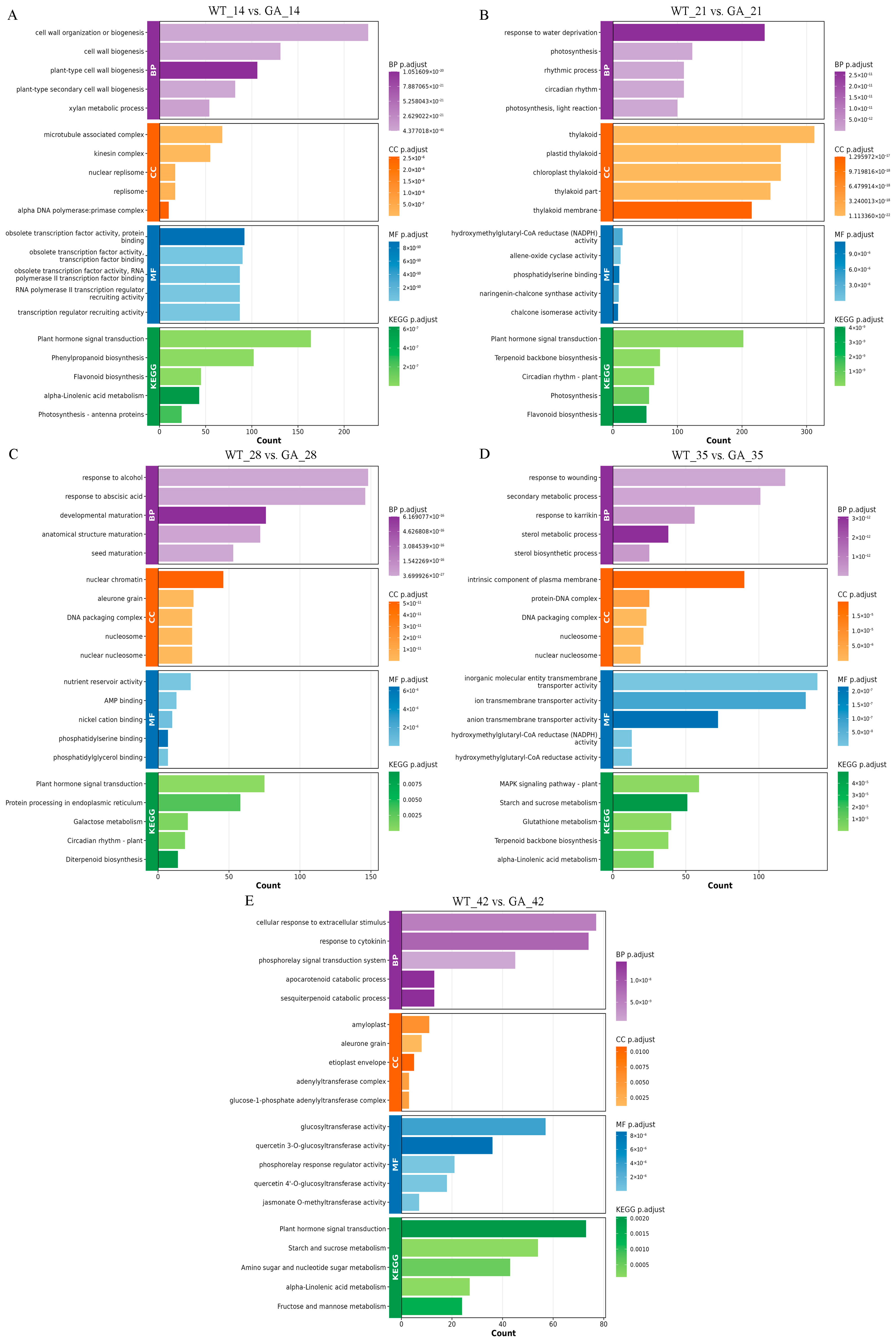
3.4. Functional Enrichment Analysis of DEGs in GO and KEGG Pathways
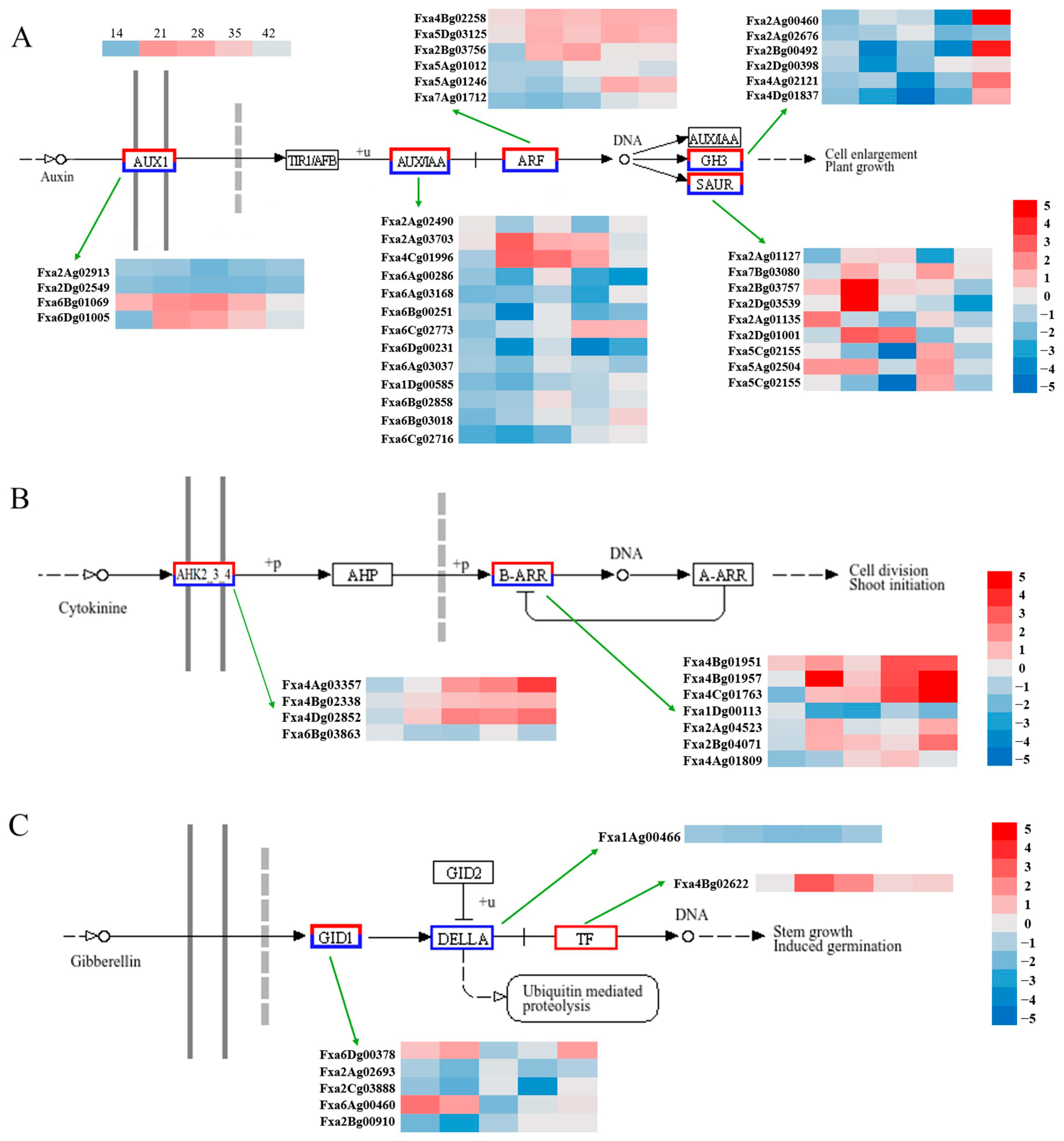
3.5. DEGs Associated with Plant Hormones in Fruit Traits
4. Discussion
4.1. Regulatory Cascade Linking GA3 and Auxin-Mediated Cell Expansion
4.2. Differential Gene Expression Analysis via Transcriptomics and Metabolomics Across Strawberry Fruit Developmental Stages
4.3. The Role of GA in Interaction with Other Hormone Pathways
4.4. The Role of DELLA Proteins in the GA Hormone Pathway
4.5. Linking GA to Agronomic Traits
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Staudt, G. Systematics and Geographic Distribution of the American Strawberry Species: Taxonomic Studies in the Genus Fragaria (Rosaceae: Potentilleae); University of California Press: Oakland, CA, USA, 1999; Volume 81. [Google Scholar]
- Mochizuki, Y.; Iwasaki, Y.; Fuke, M.; Ogiwara, I. Analysis of a high-yielding strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa Duch.) cultivar ‘Benihoppe’ with focus on root dry matter and activity. J. Jpn. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2014, 83, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulao, L.F.; Oliveira, C.M. Cell wall modifications during fruit ripening: When a fruit is not the fruit. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 19, 4–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenn, M.A.; Giovannoni, J.J. Phytohormones in fruit development and maturation. Plant J. 2021, 105, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Wani, S.H.; Razzaq, A.; Skalicky, M.; Samantara, K.; Gupta, S.; Pandita, D.; Goel, S.; Grewal, S.; Hejnak, V. Abscisic acid: Role in fruit development and ripening. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 817500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Gu, H.; Wang, L.; Shao, Y.; Li, R.; Li, W. Exogenous ethylene promotes peel color transformation by regulating the degradation of chlorophyll and synthesis of anthocyanin in postharvest mango fruit. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 911542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, Z.; Feng, C.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Peng, X.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Jiao, J.; Wang, W. Genome-wide identification of the xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase (XTH) and polygalacturonase (PG) genes and characterization of their role in fruit softening of sweet cherry. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannetta, P.P.; Van Den Berg, J.; Wheatley, R.E.; McNicol, R.J.; Davies, H.V. The role of ethylene and cell wall modifying enzymes in raspberry (Rubus idaeus) fruit ripening. Physiol. Plant. 1999, 105, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Li, M.; Wang, G.; Zhu, S. Application of ABA and GA3 alleviated browning of litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn.) via different strategies. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2021, 181, 111672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourcaud, T.; Zhang, X.; Stokes, A.; Lambers, H.; Körner, C. Plant growth modelling and applications: The increasing importance of plant architecture in growth models. Ann. Bot. 2008, 101, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebregziabher, A.A.; Supriyadi, S.; Indarti, S.; Setyowati, L. Texture profile and pectinase activity in tomato fruit (Solanum Lycopersicum, Servo F1) at different maturity stages and storage temperatures. Planta Trop. 2021, 9, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Jia, S.; Huang, X.; Wang, L.; Fu, W.; Huo, G.; Gan, L.; Ding, J.; Li, Y. Transcriptome and hormone analyses provide insights into hormonal regulation in strawberry ripening. Planta 2019, 250, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Wu, Q.; Fu, X.; Zhu, B.; Chen, F.; Liu, B.; Mao, L.; Luo, Z.; Li, L.; Ying, T. Understanding of exogenous auxin in regulating sucrose metabolism during postharvest tomato fruit ripening. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2022, 189, 111913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, Y.; Savaldi-Goldstein, S. Brassinosteroids in growth control: How, when and where. Plant Sci. 2013, 209, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieber, J.J.; Schaller, G.E. Cytokinins. Arab. Book/Am. Soc. Plant Biol. 2014, 12, e0168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, M.; Yan, J.; Khurshid, M.; Weng, W.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, K. Jasmonic acid signaling pathway in plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, S. Gibberellin metabolism and its regulation. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 225–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, W.; Raab, T. Developmental changes during strawberry fruit ripening and physico-chemical changes during postharvest storage. In Production Practices and Quality Assessment of Food Crops: Quality Handling and Evaluation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 341–369. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Meng, Y.; Zeng, J.; Luo, Y.; Feng, Z.; Bian, L.; Gao, S. Coordination between GROWTH-REGULATING FACTOR1 and GRF-INTERACTING FACTOR1 plays a key role in regulating leaf growth in rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, S.K.; Steber, C.M. Transcriptional mechanisms associated with seed dormancy and dormancy loss in the gibberellin-insensitive sly1-2 mutant of Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-W. Regulation of flowering time by the miR156-mediated age pathway. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 4723–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Iqbal, A.; Yang, M.; Yang, Y. Research Progress on Gene Regulation of Plant Floral Organogenesis. Genes 2025, 16, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csukasi, F.; Osorio, S.; Gutierrez, J.R.; Kitamura, J.; Giavalisco, P.; Nakajima, M.; Fernie, A.R.; Rathjen, J.P.; Botella, M.A.; Valpuesta, V. Gibberellin biosynthesis and signalling during development of the strawberry receptacle. New Phytol. 2011, 191, 376–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabagh, A.E.; Mbarki, S.; Hossain, A.; Iqbal, M.A.; Islam, M.S.; Raza, A.; Llanes, A.; Reginato, M.; Rahman, M.A.; Mahboob, W. Potential role of plant growth regulators in administering crucial processes against abiotic stresses. Front. Agron. 2021, 3, 648694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virág, E.; Hegedűs, G.; Nagy, Á.; Pallos, J.P.; Kutasy, B. Temporal Shifts in Hormone Signaling Networks Orchestrate Soybean Floral Development Under Field Conditions: An RNA-Seq Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, V.; Lucchetti, S.; Ciolfi, A.; Felici, B.; Possenti, M.; D’Orso, F.; Morelli, G.; Baima, S. ATHB1 Interacts with Hormone-Related Gene Regulatory Networks Involved in Biotic and Abiotic Stress Responses in Arabidopsis. Cells 2025, 14, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribarska, T.; Bjørnstad, P.M.; Sundaram, A.Y.; Gilfillan, G.D. Optimization of enzymatic fragmentation is crucial to maximize genome coverage: A comparison of library preparation methods for Illumina sequencing. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.; Jin, Z.; Ge, Y.; Nadeem, H.; Cheng, Z.; Azeem, F.; Zhan, R. Comprehensive ESI-Q TRAP-MS/MS based characterization of metabolome of two mango (Mangifera indica L.) cultivars from China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashikari, M.; Sasaki, A.; Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; Itoh, H.; Nishimura, A.; Datta, S.; Ishiyama, K.; Saito, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Khush, G.S. Loss-of-function of a rice gibberellin biosynthetic gene, GA20 oxidase (GA20ox-2), led to the rice ‘green revolution’. Breed. Sci. 2002, 52, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Ravindran, P.; Kumar, P.P. Plant hormone-mediated regulation of stress responses. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Guo, Y.; Hu, H.; Fang, C.; Wang, L.; Hu, L.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, D.; Yang, Z.; Wu, Y. Regulation of Cell Metabolism and Changes in Berry Shape of Shine Muscat Grapevines Under the Influence of Different Treatments with the Plant Growth Regulators Gibberellin A3 and N-(2-Chloro-4-Pyridyl)-N′-Phenylurea. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, G.B.; Østergaard, L.; Chapman, N.H.; Knapp, S.; Martin, C. Fruit development and ripening. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2013, 64, 219–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Shi, Z.; Zhao, S.; Wang, F.T.; Zhou, T.T.; Liu, B.; Bao, J.K. Programmed cell death pathways in cancer: A review of apoptosis, autophagy and programmed necrosis. Cell Prolif. 2012, 45, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauxion, J.-P.; Chevalier, C.; Gonzalez, N. Complex cellular and molecular events determining fruit size. Trends Plant Sci. 2021, 26, 1023–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.-S.; Li, H.-L.; Grierson, D.; Fu, D.-Q. NAC transcription factor family regulation of fruit ripening and quality: A review. Cells 2022, 11, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.; Anwar, R.; Malik, A.U.; Khan, A.S.; Ahmad, S.; Hussain, Z.; Hasan, M.U.; Nasir, M.; Chen, F. Plant growth and fruit quality response of strawberry is improved after exogenous application of 24-epibrassinolide. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2022, 41, 1786–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, F.; Klingmüller, U.; Müller-Decker, K. Cellular Signal Processing: An Introduction to the Molecular Mechanisms of Signal Transduction; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Phukan, U.J.; Jeena, G.S.; Shukla, R.K. WRKY transcription factors: Molecular regulation and stress responses in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasinski, S.; Piazza, P.; Craft, J.; Hay, A.; Woolley, L.; Rieu, I.; Phillips, A.; Hedden, P.; Tsiantis, M. KNOX action in Arabidopsis is mediated by coordinate regulation of cytokinin and gibberellin activities. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 1560–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, J.P.; Xu, R.R.; Wang, X.N.; Zhang, X.W.; You, C.X.; Han, Y. MdbHLH162 connects the gibberellin and jasmonic acid signals to regulate anthocyanin biosynthesis in apple. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2024, 66, 265–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmberg, R.L.; Watson, M.B.; Galloway, G.L.; Yu, W. Molecular genetic analyses of plant polyamines. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 1998, 17, 199–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, R.; Zhu, K.M.; Jiang, T.; Ding, P.; Gao, Y.; Tan, X.L. DELLAs directed gibberellins responses orchestrate crop development: A brief review. Crop Sci. 2023, 63, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.-p. The molecular mechanism and evolution of the GA–GID1–DELLA signaling module in plants. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, R338–R345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Song, Y.; Kang, D.; Zhang, L. Effect of Prohexadione-calcium on the Shoot Growth, Fruits, Endogenous Hormones and Expression of GA-related Genes in ‘Fuji’ Apple (Malus Domestica Borkh.). Res. Sq. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanksley, S.D. The genetic, developmental, and molecular bases of fruit size and shape variation in tomato. Plant Cell 2004, 16, S181–S189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naor, A.; Klein, I.; Hupert, H.; Grinblat, Y.; Peres, M.; Kaufman, A. Water stress and crop level interactions in relation to nectarine yield, fruit size distribution, and water potentials. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1999, 124, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Yuan, Y.; Xu, M.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, X.; Li, X.; Li, R.; Cui, X. TKN3 affects cell expansion to regulate fruit development in tomato. Hortic. Plant J. 2025, 11, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, F.; Li, Q.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, H.; Li, J. Mechanism of abscisic acid in promoting softening of postharvest ‘Docteur Jules Guyot’pear (Pyrus communis L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1502623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Qian, M.; Song, C.; Li, J.; Zhao, C.; Li, G.; Wang, A.; Han, M. Down-regulation of PpBGAL10 and PpBGAL16 delays fruit softening in peach by reducing polygalacturonase and pectin methylesterase activity. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, H.; Chen, S.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, W.; Chen, Q.; Gao, H. Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analysis Reveals the Role of Exogenous GA3 in Regulating Strawberry Fruit Development via Auxin Signaling. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2645. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112645
Gao H, Chen S, Cheng Y, Wu W, Chen Q, Gao H. Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analysis Reveals the Role of Exogenous GA3 in Regulating Strawberry Fruit Development via Auxin Signaling. Agronomy. 2025; 15(11):2645. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112645
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Han, Shen Chen, Yu Cheng, Weiwen Wu, Qijia Chen, and Hongsheng Gao. 2025. "Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analysis Reveals the Role of Exogenous GA3 in Regulating Strawberry Fruit Development via Auxin Signaling" Agronomy 15, no. 11: 2645. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112645
APA StyleGao, H., Chen, S., Cheng, Y., Wu, W., Chen, Q., & Gao, H. (2025). Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analysis Reveals the Role of Exogenous GA3 in Regulating Strawberry Fruit Development via Auxin Signaling. Agronomy, 15(11), 2645. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112645




