Regional Variation of Water Extractable Carbon and Relationships with Climate Conditions and Land Use Types
Abstract
1. Introduction
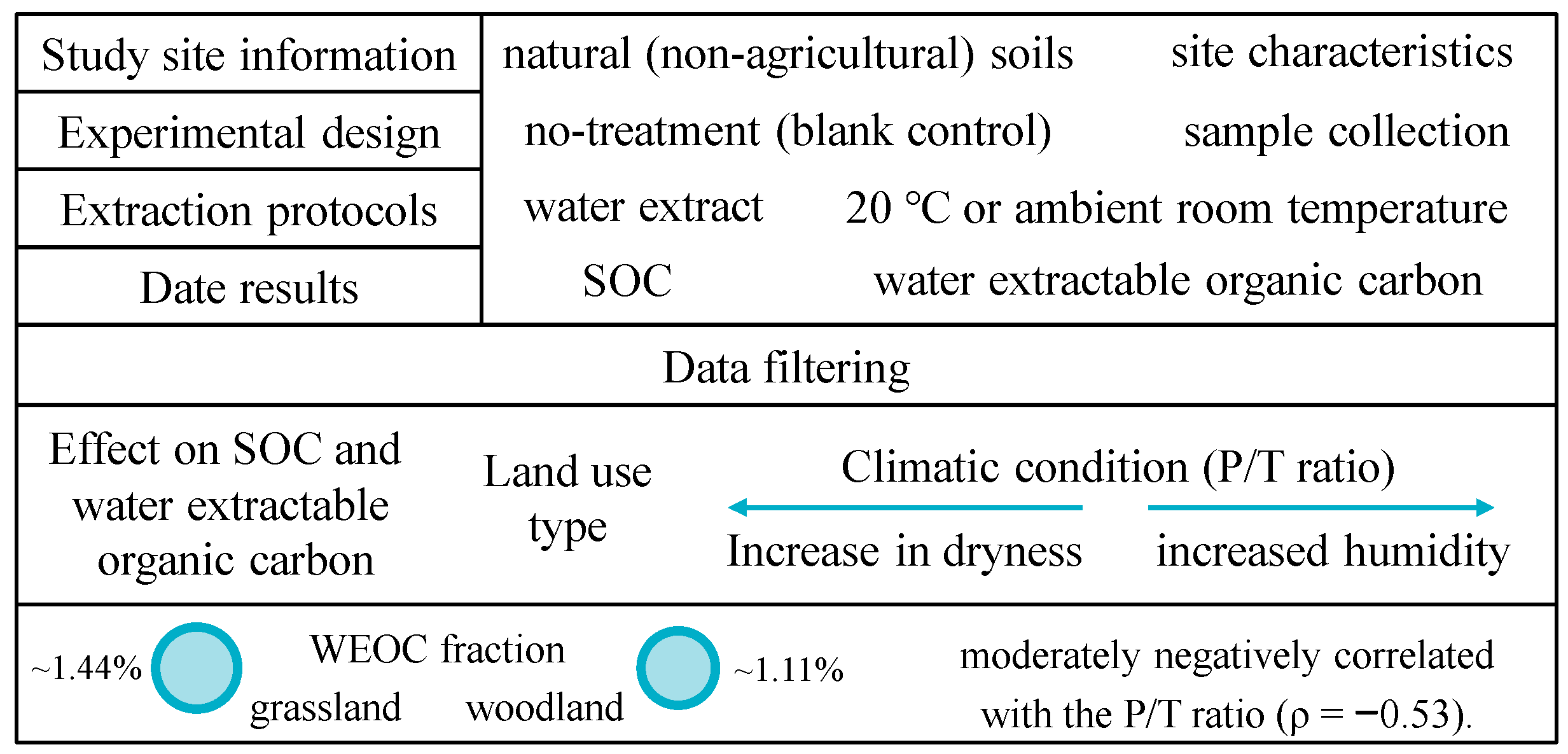
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Databases
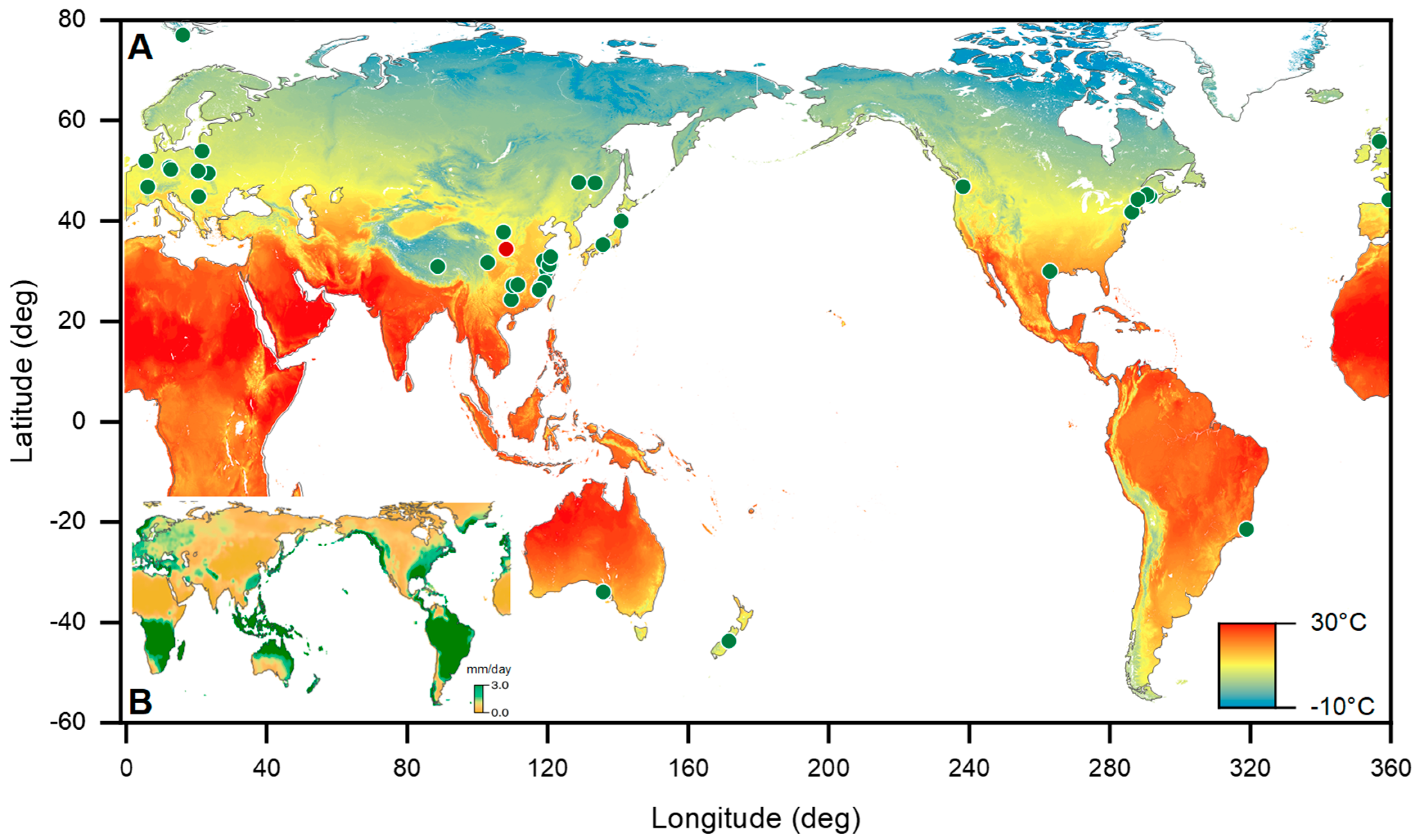
2.2. Sites and Soil Collection
2.3. Soil Processing
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
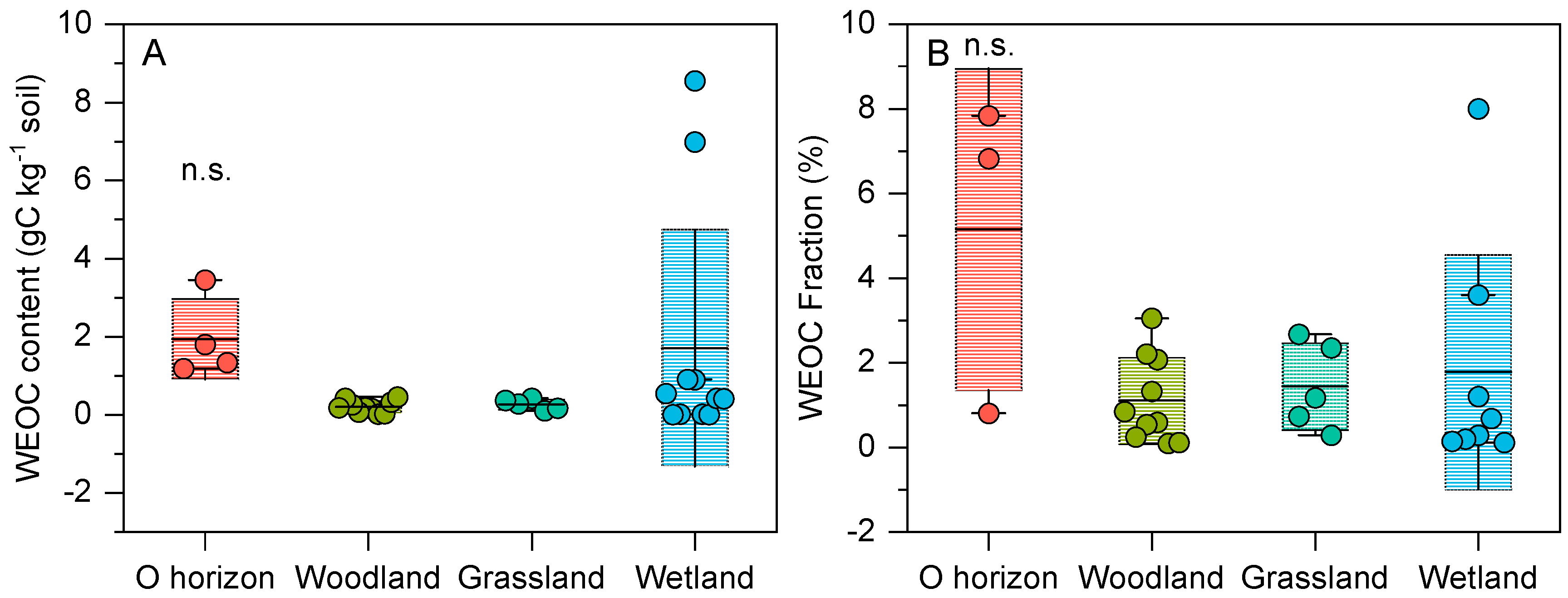
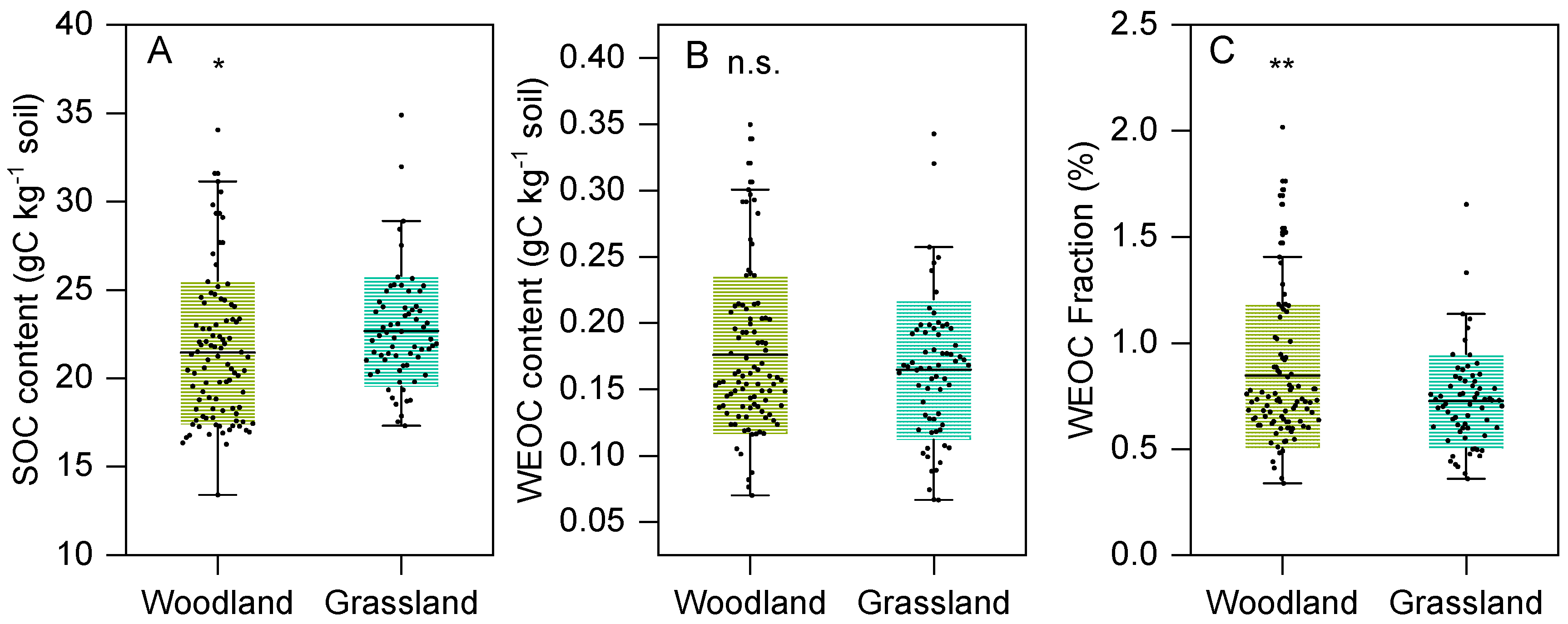
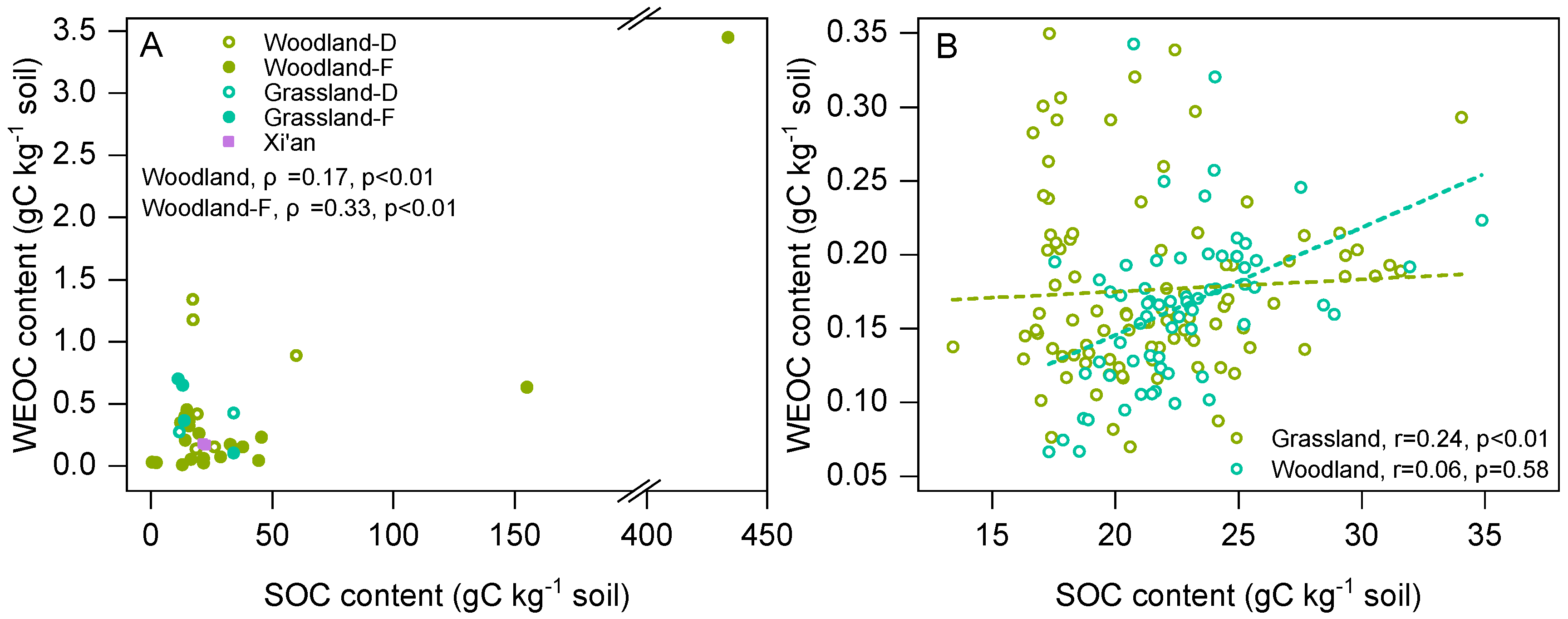
3.1. Differences in WEOC Between Woodland and Grassland Land Use Types
3.2. WEOC of Xi’an Nature Park
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of Climatic Conditions on WEOC
4.2. Influence of Land Use Type on WEOC
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poeplau, C.; Don, A.; Six, J.; Kaiser, M.; Benbi, D.; Chenu, C.; Cotrufo, M.F.; Derrien, D.; Gioacchini, P.; Grand, S.; et al. Isolating organic carbon fractions with varying turnover areas in temperature agricultural soils—A comprehensive method comparison. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 125, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelleher, B.P.; Simpson, A.J. Humic substances in soils: Are they really chemically distinct? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 4605–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fissore, C.; Giardina, C.P.; Kolka, R.K. Reduced substrate supply limits the temperature response of soil organic carbon decomposition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 67, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkhot, D.V.; Grunwald, S.; Ge, Y.; Morgan, C.L.S. Comparison and detection of total and available soil carbon fractions using visible/near infrared diffuse relfectance spectroscopy. Geoderma 2011, 164, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.W.I.; Torn, M.S.; Abiven, S.; Dittmar, T.; Guggenberger, G.; Janssens, I.A.; Kleber, M.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Lehmann, J.; Manning, D.A.C.; et al. Persistence of soil organic matter as an ecosystem property. Nature 2011, 478, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conant, R.T.; Drijber, R.A.; Haddix, M.L.; Parton, W.J.; Paul, E.A.; Plante, A.F.; Six, J.; Steinweg, J.M. Sensitivity of organic matter decomposition to warming varies with its quality. Glob. Chang Biol. 2008, 14, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witzgall, K.; Vidal, A.; Schubert, D.I.; Höschen, C.; Schweizer, S.A.; Buegger, F.; Pouteau, V.; Chenu, C.; Mueller, C.W. Particulate organic matter as a functional soil component for persistent soil organic carbon. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Martínez, P.; Maestre, F.T.; Moreno-Jiménez, E.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Eldridge, D.J.; Saiz, H.; Gross, N.; Le Bagousse-Pinguet, Y.; Gozalo, B.; Ochoa, V.; et al. Vulnerability of mineral-associated soil organic carbon to climate across global drylands. Nat. Clim. Change 2024, 14, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jílková, V.; Jandová, K.; Kukla, J.; Cajthaml, T. Soil organic carbon content decreases in both surface and subsoil mineral horizons by simulated future increases in labile carbon inputs in a temperate Coniferous forest. Ecosystems 2021, 24, 2028–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, C.W.; Rethemeyer, J.; Kao-Kniffin, J.; Löppmann, S.; Hinkel, K.M.; Bockheim, J. Large amounts of labile organic carbon in permafrost soils of northern Alaska. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 2804–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Numa, K.B.; Robinson, J.M.; Arcus, V.I.; Schipper, L.A. Separating the temperature response of soil respiration derived from soil organic matter and added labile carbon compounds. Geodrema 2021, 400, 115128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsolnay, A. Dissolved humus in soil waters. In Humic Substances in Terrestrial Ecosystems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 171–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guigue, J.; Mathieu, O.; Lévêque, J.; Mounier, S.; Laffont, R.; Maron, P.A. A comparison of extraction procedures for water-extractable organic matter in soils. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2014, 65, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison-Kirk, T.; Beare, M.H.; Meenken, E.D.; Condron, L.M. Soil organic matter and texture affect responses to dry/wet cycles: Changes in soil organic matter fractions and relationships with C and N mineralisation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 74, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.F.; Spaccini, R.; Mazzei, P.; Rezende, C.E.; Canellas, L.P. Changes in water-extractable organic matter in tropical forest and agricultural soils as detected by the DRIFT spectroscopy technique. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 4755–4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Peng, C.; Xue, W.; Yang, B.; Yang, Z.; Niu, S.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, M. Dynamics of soil water extractable organic carbon and inorganic nitrogen and their environmental controls in mountain forest and meadow ecosystems in China. Catena 2020, 187, 104338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartos, A.; Szymański, W.; Klimek, M. Impact of conventional agriculture on the concentration and quality of water-extractable organic matter (WEOM) in the surface horizons of Retisols―A case study from the Carpathian Foothills in Poland. Soil Till. Res. 2020, 204, 104750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halvorson, J.J.; Hansen, A.M.; Stewart, C.E. Patterns of water-extractable soil organic matter in the US Great Plains: Insights from the Haas Soil Archive. Agrosys. Geosci. Env. 2025, 8, e70060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landgraf, D.; Leinweber, P.; Makeschin, F. Cold and hot water-extractable organic matter as indicators of litter decomposition in forest soils. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2006, 169, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.P.; Martínez, C.E. The influence of tillage on dissolved organic matter dynamics in a Mid-Atlantic agroecosystem. Geoderma 2019, 344, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canarini, A.; Schmidt, H.; Fuchslueger, L.; Martin, V.; Herbold, C.W.; Zezula, D.; Gündler, P.; Hasibeder, R.; Jecmenica, M.; Bahn, M.; et al. Ecological memory of recurrent drought modifies soil processes via changes in soil microbial community. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Mayes, M.A.; Shekoofa, A.; Kivlin, S.N.; Bansal, S.; Jagadamma, S. Soil organic carbon cycling in response to simulated soil moisture variation under field conditions. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.Y.; Koal, P.; Gerl, G.; Schroll, R.; Joergensen, R.G.; Munch, J.C. Response of water extractable organic matter and its fluorescence fractions to organic farming and tree species in poplar and robinia-based alley cropping agroforestry systems. Geoderma 2017, 290, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Hansel, C.M.; Kaiser, C.; Kleber, M.; Maher, K.; Manzoni, S.; Nunan, N.; Reichstein, M.; Schimel, J.P.; Torn, M.S.; et al. Persistence of soil organic carbon caused by functional complexity. Nat. Geosci. 2020, 13, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebig, M.A.; Calderon, F.J.; Clemensen, A.K.; Durso, L.; Duttenhefner, J.L.; Eberly, J.O.; Halvorson, J.J.; Jin, V.L.; Mankin, K.; Margenot, A.J.; et al. Long-term soil change in the US Great Plains: An evaluation of the Haas Soil Archive. Agrosys. Geosci. Environ. 2024, 7, e20502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantigny, M.H. Dissolved and water-extractable organic matter in soils: A review on the influence of land use and management practices. Geoderma 2003, 113, 357–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymański, W. Quantity and chemistry of water-extractable organic matter in surface horizons of Arctic soils under different types of tundra vegetation—A case study from the Fuglebergsletta coastal plain (SW Spitsbergen). Geoderma 2017, 305, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chittleborough, D.J.; Smettem, K.R.J.; Cotsaris, E.; Leaney, F.W. Seasonal changes in pathways of dissolved organic carbon through a hillslope soil (Xeralf) with contrasting texture. Soil Res. 1992, 30, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiedung, H.; Bornemann, L.; Welp, G. Seasonal variability of soil organic carbon fractions under arable land. Pedosphere 2017, 27, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsolnay, A.; Görlitz, H. Water extractable organic matter in arable soils: Effects of drought and long-term fertilization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1994, 26, 1257–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasset, C.; Rodriguez, C.; Delolme, C.; Marmonier, P.; Bornette, G. Can soil organic carbon fractions be used as functional indicators of wetlands? Wetlands 2017, 37, 1195–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doetterl, S.; Stevens, A.; Six, J.; Merckx, R.; Oost, K.V.; Pinto, M.C.; Casanova-Katny, A.; Muñoz, C.; Boudin, M.; Venegas, E.Z.; et al. Soil carbon storage controlled by interactions between geochemistry and climate. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 31, 780–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobbágy, E.G.; Jackson, R.B. The vertical distribution of soil organic carbon and its relation to climate and vegetation. Ecol. Appl. 2000, 10, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, K.E.; Repasch, M.N.; Finstad, K.M.; Kerr, J.D.; Marple, M.; Larson, C.J.; Broek, T.A.B.; Pett-Ridge, J.; McFarlane, K.J. Diverse organic carbon dynamics captured by radiocarbon analysis of distinct compound classes in a grassland soil. Biogeosciences 2024, 21, 4395–4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craine, J.M.; Fierer, N.; McLauchlan, K.K. Widespread coupling between the rate and temperature sensitivity of organic matter decay. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 854–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd-Brown, K.E.O.; Randerson, J.T.; Post, W.M.; Hoffman, F.M.; Tarnocai, C.; Schuur, E.A.G.; Allison, S.D. Causes of variation in soil carbon simulation from CMIP5 Earth system models and comparison with observations. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 1717–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delarue, F.; Laggoun-Défarge, F.; Buttler, A.; Gogo, S.; Jassey, V.E.J.; Disnar, J. Effects of short-term ecosystem experimental warming on water-extractable organic matter in an ombrotrophic Sphagnum peatland (Le Forbonnet, France). Org. Geochem. 2011, 42, 1016–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, G.J.; Lefroy, R.D.B.; Lisle, L. Soil carbon fractions based on their degree of oxidation, and the development of a carbon management index for agricultural systems. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1995, 46, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laura, Z.; Pierre, K.; Felix, W.; Lars, B. ClimateCharts.net—An interactive climate analysis web platform. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2020, 14, 338–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lembrechts, J.J.; Hoogen, J.; Aalto, J.; Ashcroft, M.B.; De Frenne, P.; Kemppinen, J.; Kopecký, M.; Luoto, M.; Maclean, I.M.D.; Crowther, T.W.; et al. Global maps of soil temperature. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 3110–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dottmann, U.; Kraft, N.N.; Rech, R.; Heidkamp, A.; Tiemeyer, B. Analysis of peat soil organic carbon, total nitrogen, soil water content and basal respiration: Is there a ‘best’ drying temperature? Geoderma 2021, 403, 115231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Even, R.J.; Machmuller, M.B.; Lavallee, J.M.; Zelikova, T.J.; Cotrufo, M.F. Large errors in soil carbon measurements attributed to inconsistent sample processing. Soil 2025, 11, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, A.; Dexter, M.; Perrott, K.W. Hot-water extractable carbon in soils: A sensitive measurement for determining impacts of fertilisation, grazing and cultivation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 1231–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Feng, Y.; Wang, L.; Lu, H.; She, X.; Ruan, H. Variations characteristics of soil active organic carbon along a soil moisture gradient in a riparian zone of Taihu Lake. Chin. J. Ecol. 2011, 30, 1119–1124. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Lin, B. Water soluble organic carbon and its measurement in soil and sediment. Water Res. 2000, 34, 1751–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronan, C.S.; Lakshman, S.; Patterson, H.H. Effects of disturbance and soil amendments on dissolved organic carbon and organic acidity in red pine forest floors. J. Environ. Qual. 1992, 21, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Fan, J.; Yan, Y.; Wang, X. Soil water soluble organic carbon under three alpine grassland types in Northern Tibet, China. Afr. J. Agr. Res. 2011, 6, 2066–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalisz, B.; Lachacz, A.; Glazewski, R. Effects of peat drainage on labile organic carbon and water repellency in NE Poland. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2015, 39, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cincotta, M.M.; Perdrial, J.N.; Shavitz, A.; Libenson, A.; Landsman-Gerjoi, M.; Perdrial, N.; Armfield, J.; Adler, T.; Shanley, J.B. Soil aggregates as a source of dissolved organic carbon to streams: An experimental study on the effect of solution chemistry on water extractable carbon. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehler, R.; Li, J.; Reager, J.T.; Ye, H. Investigating relationship between soil moisture and precipitation globally using remote sensing observations. J. Contemp. Wat. Res. Ed. 2019, 168, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchslueger, L.; Bahn, M.; Fritz, K.; Hasibeder, R.; Richter, A. Experimental drought reduces the transfer of recently fixed plant carbon to soil microbes and alters the bacterial community composition in a mountain meadow. New Phytol. 2014, 201, 916–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preece, C.; Farré-Armengol, G.; Llusià, J.; Peñuelas, J. Thirsty tree roots exude more carbon. Tree Physiol. 2018, 38, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camenzind, T.; Mason-Jones, K.; Mansour, I.; Rillig, M.C.; Lehmann, J. Formation of necromass-derived soil organic carbon determined by microbial death pathways. Nat. Geosci. 2023, 16, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, A.Y.Y.; Six, J. Tracing root vs. residue carbon into soils from conventional and alternative cropping systems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2010, 74, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Domanski, G. Carbon input by plants into the soil. Rev. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2000, 163, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pausch, J.; Kuzyakov, Y. Carbon input by roots into the soils: Quantification of rhizodeposition from root to ecosystem scale. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadori, M.; Chen, C.; Lewis, S.; Lewis, S.; Boyd, S.; Rashti, M.R.; Esfandbod, M.; Garzon-Garcia, A.; Zwieten, L.V.; Kuzyakov, Y. Soil organic matter formation is controlled by the chemistry and bioavailability of organic carbon inputs across different land uses. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 770, 145307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiau, Y.; Chen, J.; Chung, T.; Tian, G.; Chiu, C. 13C NMR spectroscopy characterization of particle-size fractionated soil organic carbon in subalpine forest and grassland ecosystems. Bot. Stud. 2017, 58, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, J.R.; Meinzer, F.C.; Coulombe, R.; Gregg, J. Hydraulic redistribution of soil water during summer drought in two contrasting Pacific Northwest coniferous forests. Tree Physiol. 2002, 22, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Liu, D.; Yang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Darboux, F.; Jiao, J.; An, S. Effects of forest floor characteristics on soil labile carbon as varied by topography and vegetation type in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Catena 2021, 196, 104825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Gui, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z. Regional Variation of Water Extractable Carbon and Relationships with Climate Conditions and Land Use Types. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2623. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112623
Zhang F, Zhang Y, Gui C, Zhang X, Wang Z. Regional Variation of Water Extractable Carbon and Relationships with Climate Conditions and Land Use Types. Agronomy. 2025; 15(11):2623. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112623
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Fan, Yilin Zhang, Congwen Gui, Xinpei Zhang, and Zheng Wang. 2025. "Regional Variation of Water Extractable Carbon and Relationships with Climate Conditions and Land Use Types" Agronomy 15, no. 11: 2623. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112623
APA StyleZhang, F., Zhang, Y., Gui, C., Zhang, X., & Wang, Z. (2025). Regional Variation of Water Extractable Carbon and Relationships with Climate Conditions and Land Use Types. Agronomy, 15(11), 2623. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112623




