Toxicity of Tris(2-chloroethyl) Phosphate (TCEP) to Alfalfa’s Root System: An Insight into TCEP’s Damage to Morphology, Respiration, and Antioxidant Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Measurement Indicators and Methods
2.3.1. Root System Geometric Configuration Parameters
2.3.2. Determination of Alfalfa Root Vigor and Cellular ATP Content
2.3.3. Root Respiration Measurements
2.3.4. Superoxide Anion (O2−), Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) Content, Malondialdehyde (MDA), and Free Proline Content Determination
2.3.5. Determination of Antioxidant Enzyme Activity
2.3.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
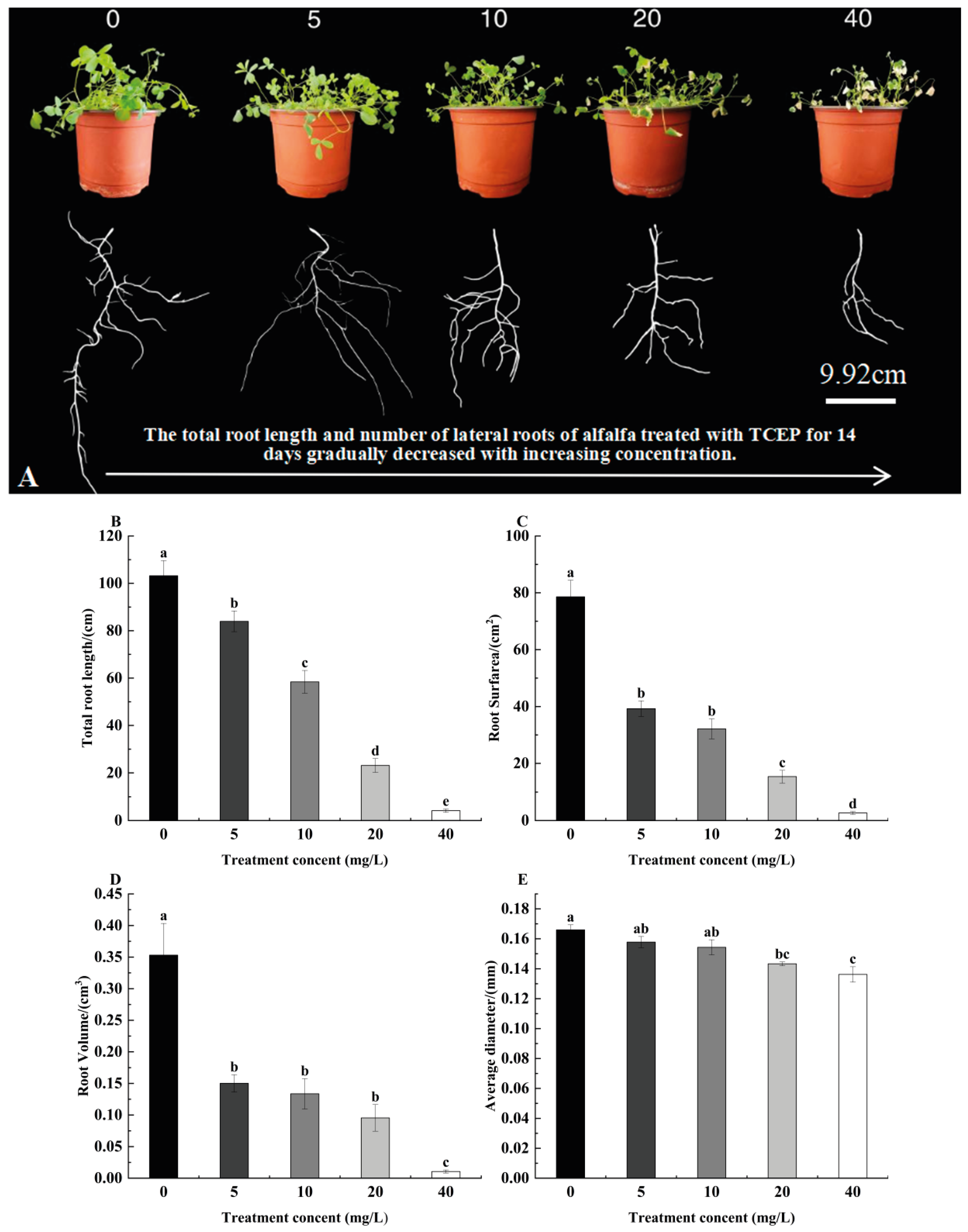
3.1. Effect of TCEP on Alfalfa Root Morphology
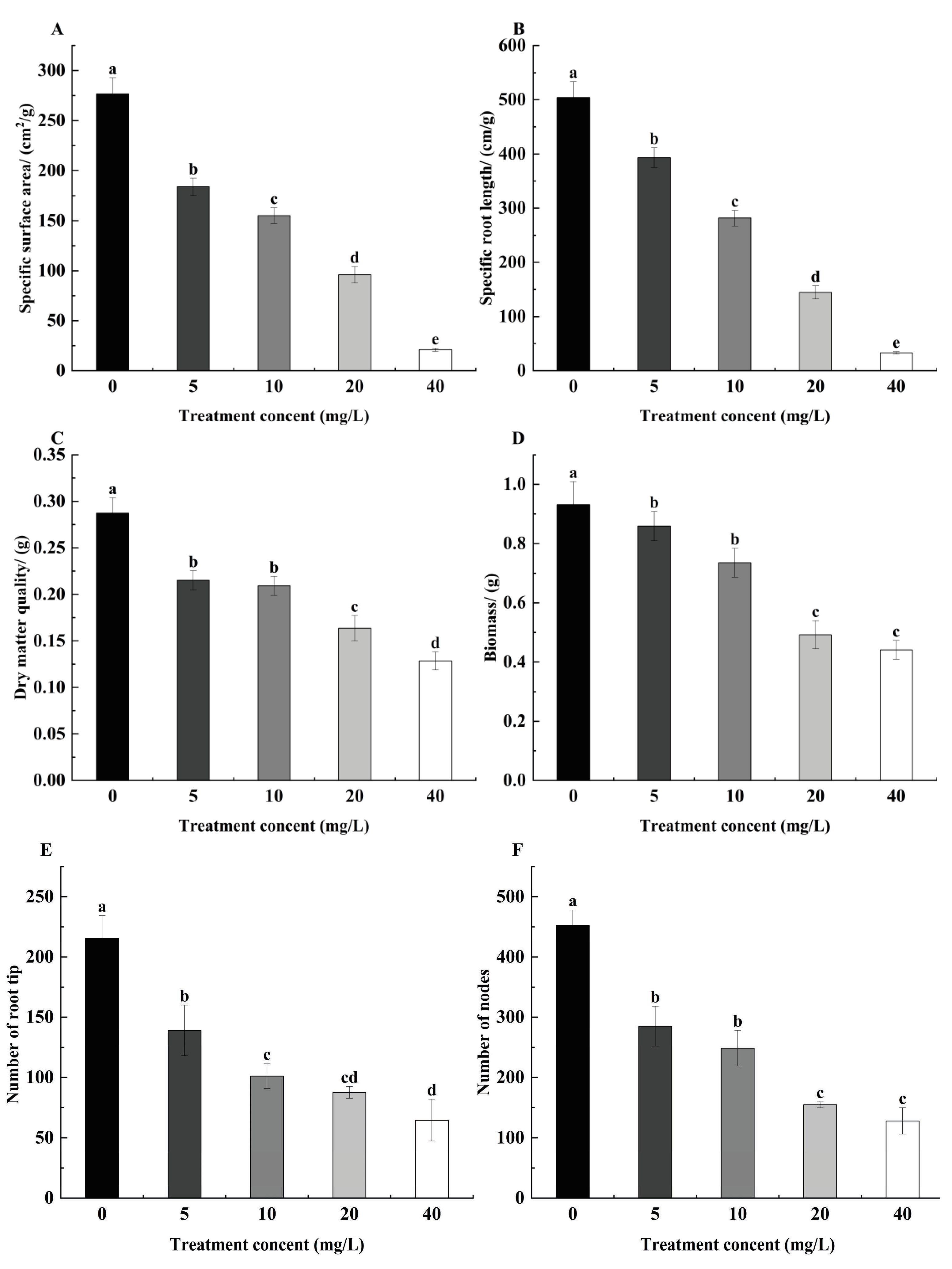
3.2. Effect of TCEP on Root Biomass, Specific Root Length, and Specific Root Surface Area of Alfalfa Roots
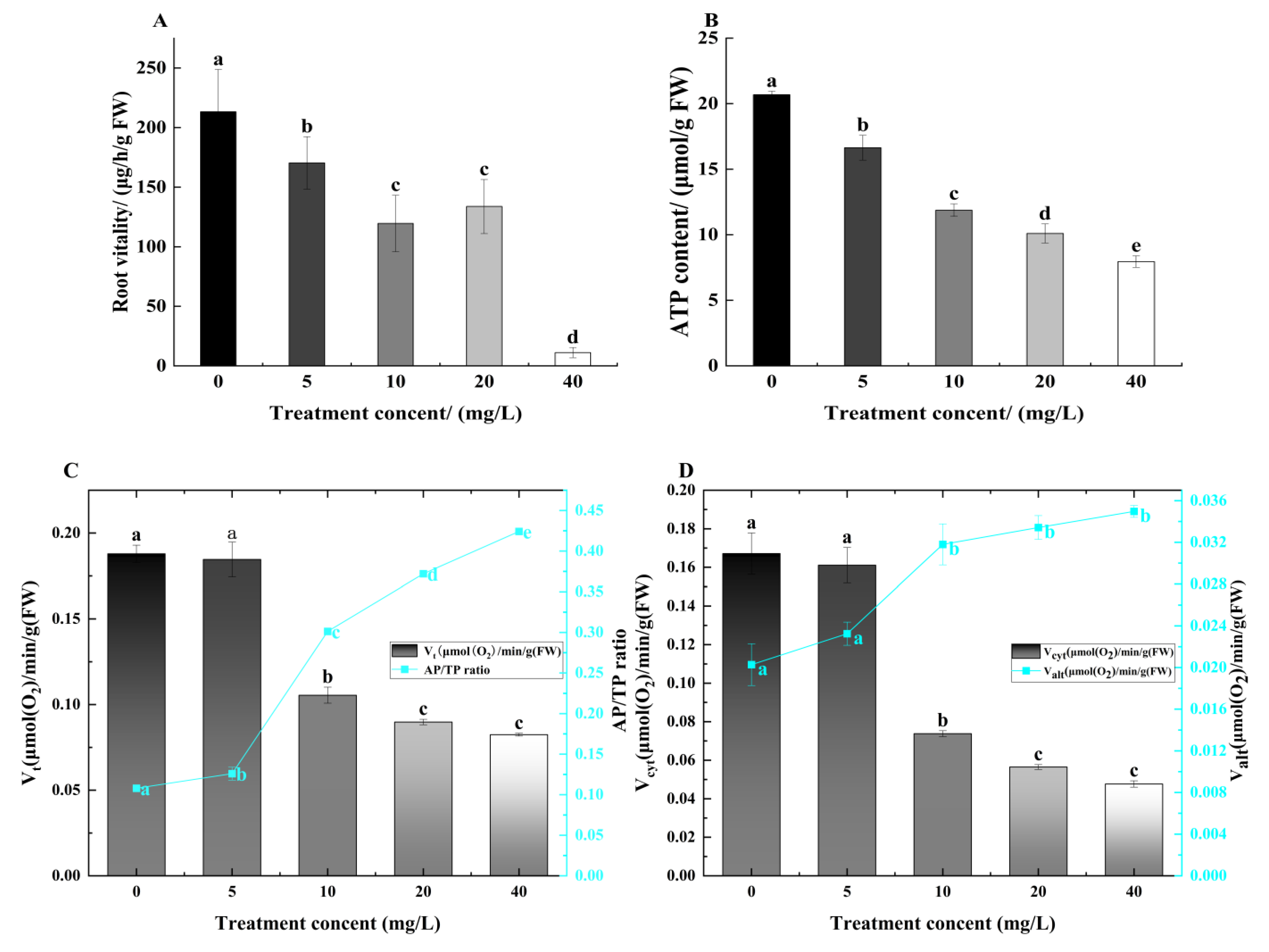
3.3. Effect of TCEP on Alfalfa Root Vigor, ATP Content, and Root Respiration
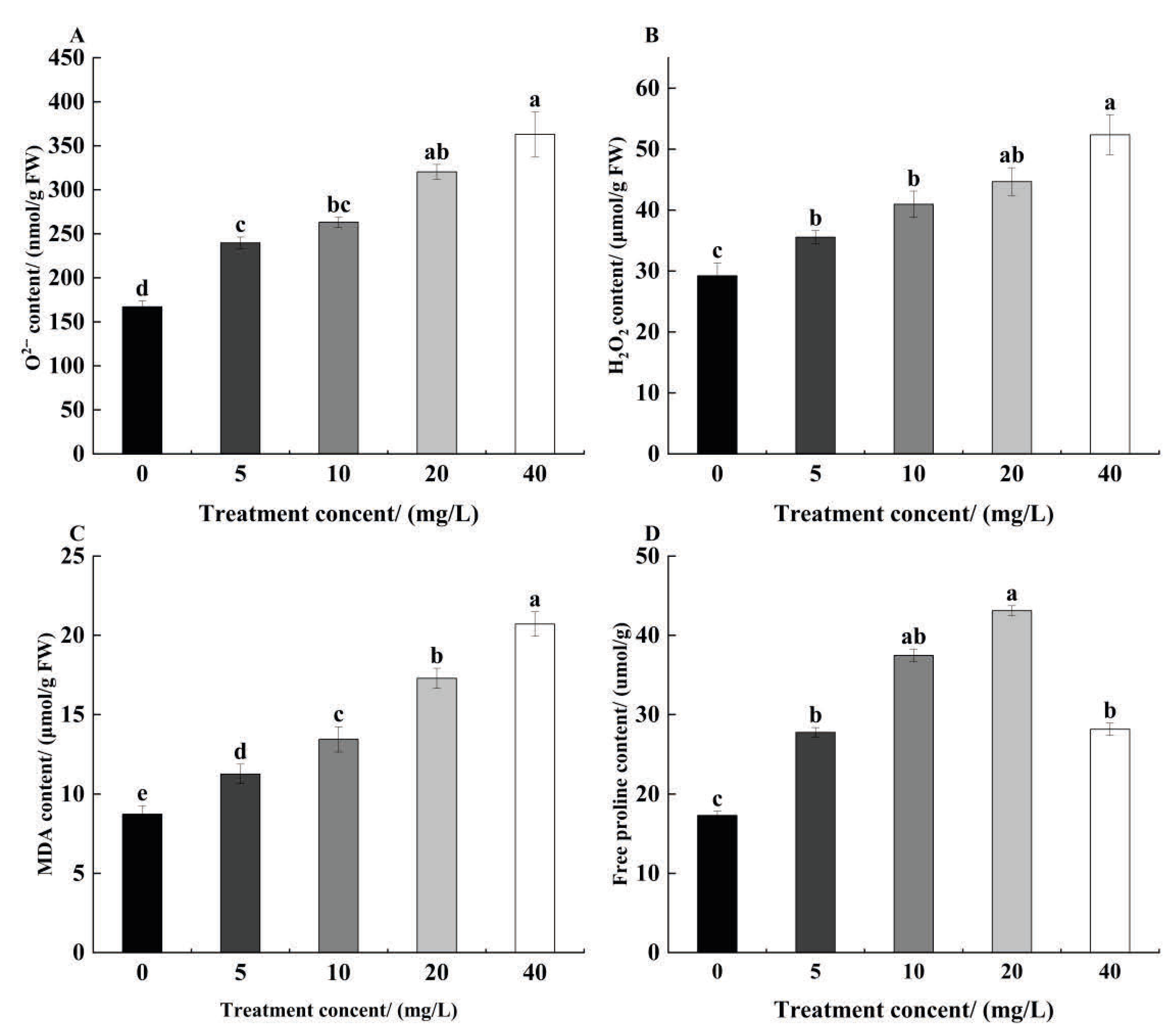
3.4. Effect of TCEP on Redox Balance in Alfalfa Roots
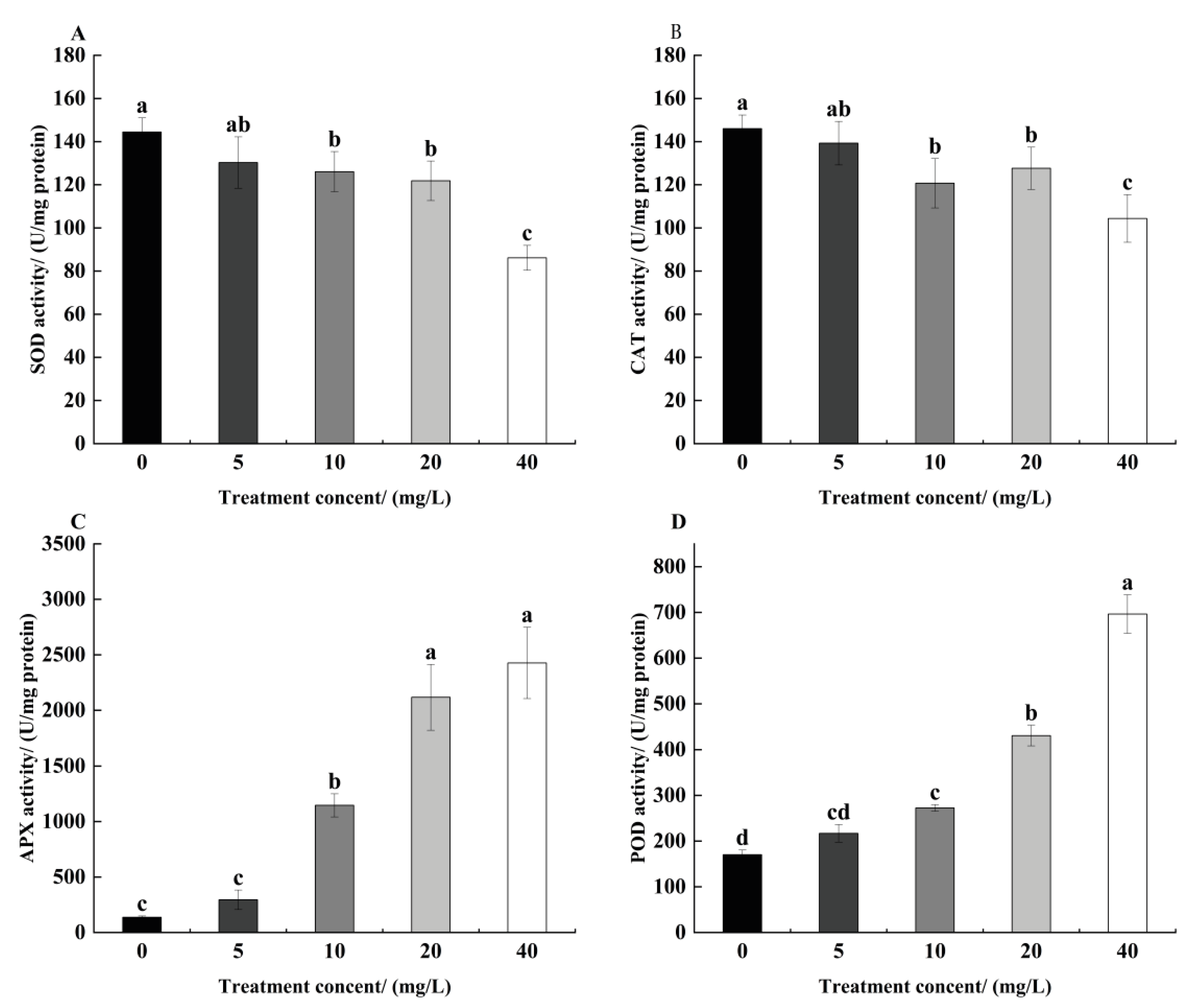
3.5. Effect of TCEP on Antioxidant Enzyme Activities of Alfalfa Roots
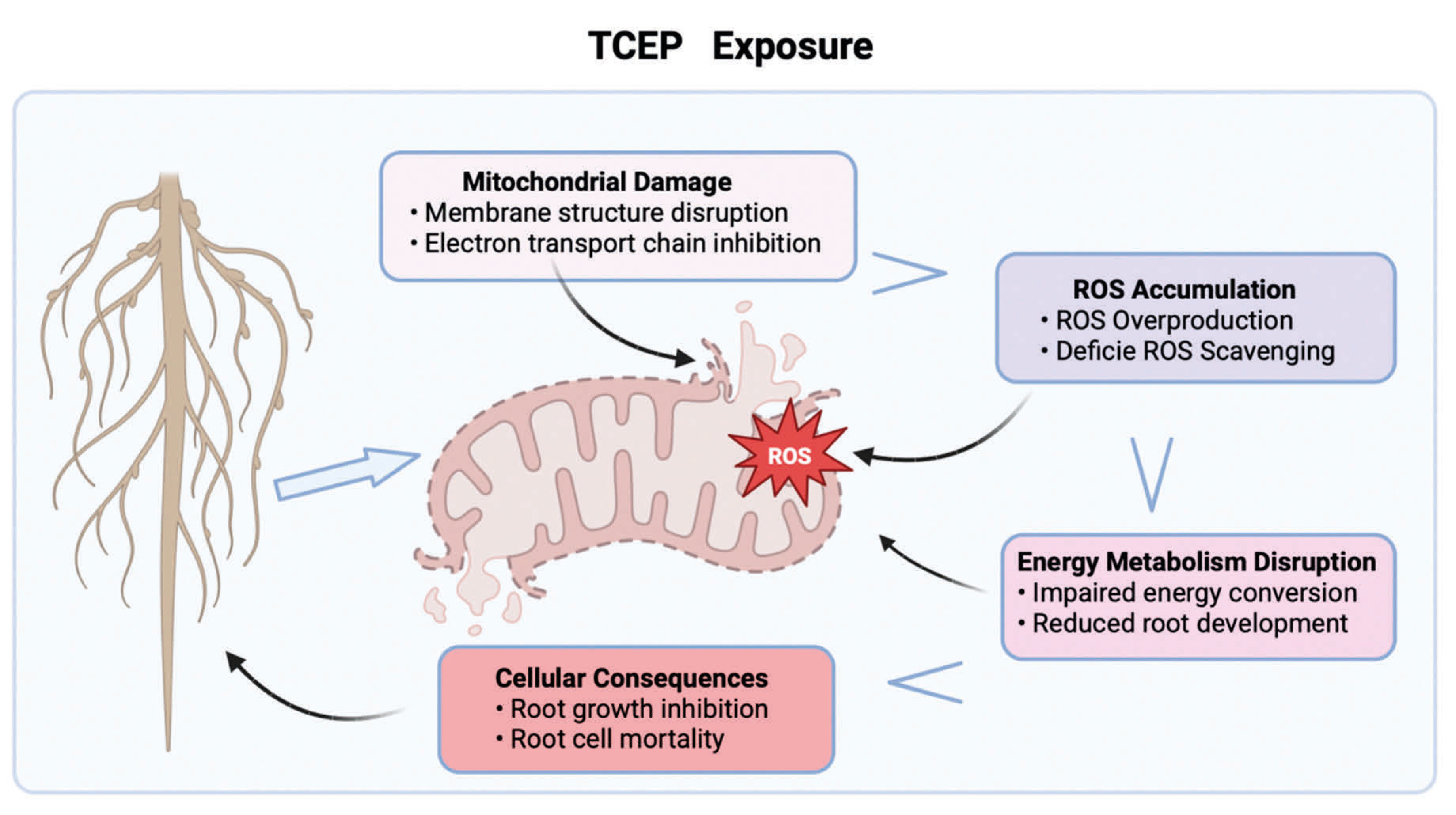
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TCEP | Tris(2-chloroethyl) phosphate |
| COX | Cytochrome C Oxidase |
| AOX | Alternative Oxidase |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| CAT | Catalase |
| APX | Ascorbate peroxidase |
| POD | Peroxidase |
| mECT | Mitochondrial electron transport chain |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| OPEs | Organophosphate esters |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| RV | Total root volume |
| RSA | Root surface area |
| AD | Average root diameter |
| TRL | Total root length |
| SRL | Specific root length |
| SRS | Specific surface area |
| TTC | Triphenyltetrazolium chloride |
| Superoxide anion | |
| H2O2 | Hydrogen peroxide |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| CP | Cytochrome respiration pathway |
| AP | Alternate respiration pathway |
References
- Wang, X.; Song, F. The neurotoxicity of organophosphorus flame retardant tris (1,3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate (TDCPP): Main effects and its underlying mechanisms. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 346, 123569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wan, Y.; Wang, Y.; He, Z.; Xu, S.; Xia, W. Occurrence, spatial variation, seasonal difference, and ecological risk assessment of organophosphate esters in the Yangtze River, China: From the upper to lower reaches. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851 Pt 1, 158021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Yuan, R.Y.; Wei, S.Q.; He, M.J. Occurrence, correlation, and partitioning of organophosphate esters in soil and tree bark from a megacity, Western China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 4359–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Peng, M.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Fu, D. Prepubertal Exposure to Tris(2-chloroethyl) Phosphate Disrupts Blood-Testis Barrier Integrity via Ferritinophagy-Mediated Ferroptosis. Toxics 2025, 13, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paun, I.; Pirvu, F.; Chiriac, F.L.; Iancu, V.I.; Pascu, L.F. Organophosphate flame retardants in Romania coastline: Occurrence, faith and environmental risk. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 208, 116982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, L.; Ding, H.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Y.; Na, G.; Cai, Y. Occurrence, distribution, sources, and risk assessment of organophosphate esters in typical coastal aquaculture waters of China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astuti, M.P.; Notodarmojo, S.; Priadi, C.R.; Padhye, L.P. Contaminants of emerging concerns (CECs) in a municipal wastewater treatment plant in Indonesia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 21512–21532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, F.; Wang, J.; Fu, X.; Zhou, T. Fate of organophosphate flame retardants (OPFRs) in the "Cambi® TH + AAD" of sludge in a WWTP in Beijing, China. Waste Manag. 2023, 169, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.P.; Zhang, Z.F.; Guo, C.S.; Lü, J.P.; Deng, Y.H.; Zhang, H.; Xu, J. Pollution Characteristics and Risk Assessment of Organophosphate Esters in Rivers and Water Body Around Taihu Lake. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2021, 42, 1801–1810. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.X.; Jiang, X.X.; Xu, H.Z.; Luo, Y.Q.; Long, T.T.; Li, J.; Xing, L. Spatial occurrence and composition profile of organophosphate esters (OPEs) in farmland soils from different regions of China: Implications for human exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 276, 116729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Ma, X.; Yu, Y. Occurrence of organophosphate esters (OPEs) in tobacco leaves across China: Spatial distribution, sources and exposure risk assessment. Environ. Res. 2025, 279 Pt 2, 121855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, H.; Huang, C.; Ben, Y.; Zhou, H.; Guo, H.; Han, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tong, P. Occurrence and potential risks of organophosphate esters in agricultural soils: A case study of Fuzhou City. Southeast China J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 150, 571–581. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Tan, F. Kinetics of uptake, translocation, and metabolism of organophosphate esters in japonica rice (Oryza sativa L.): Hydroponic experiment combined with model. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, Z.L.; Wu, D.; Li, H.R.; Liu, Y.S.; Zhang, L.W.; Feng, Y.F.; Jiang, X.Y.; Wu, D.W.; Hu, J.J.; Ying, G.G. Uptake mechanism, translocation, and transformation of organophosphate esters in water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes): A hydroponic study. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 341, 122933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, M.; Wu, S.; Xiao, B.; Wang, X.; Sun, B.; Zhu, L. Metabolomics Reveals Antioxidant Stress Responses of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Exposed to Chlorinated Organophosphate Esters. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 6520–6529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wang, G.; Xing, Z.; Xue, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Dong, X.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y. Stable Isotope and Multiomics Reveal Uptake, Translocation, and Transformation Mechanisms of Tris(2-chloroethyl) Phosphate in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 27797–27807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta-Videa, J.; de la Rosa, G.; Gonzalez, J.; Gardea-Torresdey, J. Effects of the growth stage on the heavy metal tolerance of alfalfa plants. Adv. Environ. Res. 2004, 8, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Dou, H.; Zhang, W.; He, Z.; Li, S.; Xiang, D.; Zhang, Y. The root system dominates the growth balance between the aboveground and belowground parts of cotton. Crop Environ. 2023, 2, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wan, L.; Nie, Z.; Li, X. Fractal and Topological Analyses and Antioxidant Defense Systems of Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Root System under Drought and Rehydration Regimes. Agronomy 2020, 10, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Shi, J.Y.; Song, H.F.; Li, J.C. Effects of salt stress on growth, photosynthetic and fluorescence characteristics, and root architecture of Corylus heterophylla × C. avellan seedlings. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 3376–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.L.; Zhang, M.M.; Li, C.S.; Li, B.Y.; Zhuo, S.L.; Yang, Y.S.; Chen, Y.D.; Zhong, A.N.; Liu, H.Y.; Lai, W.F.; et al. Response mechanism of water status and photosynthetic characteristics of Cotoneaster multiflorus under drought stress and rehydrated conditions. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 15, 1457955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanlerberghe, G.C.; Martyn, G.D.; Dahal, K. Alternative oxidase: A respiratory electron transport chain pathway essential for maintaining photosynthetic performance during drought stress. Physiol. Plant 2016, 157, 322–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghavendra, A.S.; Padmasree, K. Beneficial interactions of mitochondrial metabolism with photosynthetic carbon assimilation. Trends Plant Sci. 2003, 8, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.W.; Shi, K.; Fu, L.J.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Dong, D.K.; Jiang, Y.P.; Zhou, Y.H.; Xia, X.J.; Liang, W.S.; et al. The reduction of reactive oxygen species formation by mitochondrial alternative respiration in tomato basal defense against TMV infection. Planta 2012, 235, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora, K.S.; Sharma, A. Phytochemical and pharmacological potential of Medicago sativa: A review. Pharm. Biol. 2011, 49, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.Z.; Liu, X.J.; Ouyang, J.H.; Tu, X.J.; Song, W.Z.; Cao, W.; Tao, Q.B.; Sun, J. Effects of biochar and phosphorus fertilizer combination on the physiological growth characteristics of alfalfa in saline-alkali soil of the Yellow River Delta. Chin. J. Grassl. 2024, 46, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsenault, J.-L.; Poulcur, S.; Messier, C.; Guay, R. WinRHlZO™, a Root-measuring System with a Unique Overlap Correction Method. HortScience 2019, 30, 906D. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erktan, A.; Roumet, C.; Bouchet, D.; Stokes, A.; Pailler, F.; Munoz, F. Two dimensions define the variation of fine root traits across plant communities under the joint influence of ecological succession and annual mowing. J. Ecol. 2018, 106, 2031–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, F.P. Tetrazolium salts and formazans. Prog. Histochem. Cytochem. 1976, 9, III-51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Yu, P.; Fu, W.; Li, G.; Feng, B.; Chen, T.; Li, H.; Tao, L.; Fu, G. Acid invertase confers heat tolerance in rice plants by maintaining energy homoeostasis of spikelets. Plant Cell Environ. 2020, 43, 1273–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Jin, N.; Jin, L.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Sun, M.; Huang, S.; Xie, Y.; Meng, X.; Xu, Z.; et al. Use of silicon to protect tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) seedlings from low-calcium stress-derived oxidative damage. Sci. Hortic. 2025, 349, 114231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulou, M.; Spyrou, A.; Giova, L.; Varela-Athanasatou, M.; Mouaimi, M.; Christodoulou, N.; Dailianis, S.; Vlastos, D. Flame-retardant Tris(2-chloroethyl) phosphate: Assessing the effects on microalgae, mussel hemocytes and human peripheral blood cells. Environ. Res. 2025, 276, 121512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, M.; Li, H.; Shen, C. Distribution Characteristics and Ecological Risk Assessment of Organophosphate Esters in Surface Soils of China. Toxics 2024, 12, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Gao, H.; Yi, X.; Tian, S.; Liu, X. Root Uptake Pathways and Cell Wall Accumulation Mechanisms of Organophosphate Esters in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 11892–11900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Liu, L.Y.; Stubbings, W.A.; Wang, S. Analysis and subcellular distribution of organophosphate esters (OPEs) in rice tissues. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 74021–74030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.; Wang, Y.; Pu, J.; Zhang, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, L. The environment behavior of organophosphate esters (OPEs) and di-esters in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.): Uptake mechanism, in vivo hydrolysis and subcellular distribution. Environ. Int. 2020, 135, 105405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Q.; Zhao, X.Y.; Xuan, W.; Wang, P.; Zhao, F.J. Rice roots avoid asymmetric heavy metal and salinity stress via an RBOH-ROS-auxin signaling cascade. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1678–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauhus, J.; Khanna, P.R.; Menden, N. Aboveground and belowground interactions in mixed plantations of Eucalyptus globulus and Acacia mearnsii. Can. J. For. Res. 2000, 30, 1886–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, A.H.; Whelan, J.; Soole, K.L.; Day, D.A. Organization and regulation of mitochondrial respiration in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2011, 62, 79–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, E.; Kato, N.; Lawton, M. Programmed cell death, mi- tochondria and the plant hypersensitive response. Nature 2001, 411, 848–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, S.; Jin, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, L.; Qian, H.; Fu, Z. TPP and TCEP induce oxidative stress and alter steroidogenesis in TM3 Leydig cells. Reprod. Toxicol. 2015, 57, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Aken, O.; Van Breusegem, F. Licensed to Kill: Mitochondria, Chloroplasts, and Cell Death. Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 754–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del-Saz, N.F.; Florez-Sarasa, I.; Clemente-Moreno, M.J.; Mhadhbi, H.; Flexas, J.; Fernie, A.R.; Ribas-Carbó, M. Salinity tolerance is related to cyanide-resistant alternative respiration in Medicago truncatula under sudden severe stress. Plant Cell Environ. 2016, 39, 2361–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxwell, D.P.; Wang, Y.; McIntosh, L. The alternative oxidase lowers mitochondrial reactive oxygen production in plant cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 8271–8276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Aken, O.; Giraud, E.; Clifton, R.; Whelan, J. Alternative oxidase: A target and regulator of stress responses. Physiol. Plant. 2009, 137, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espenes, A.; Press, C.M.; Dannevig, B.H.; Landsverk, T. Immune-complex trapping in the splenic ellipsoids of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Cell Tissue Res. 1995, 282, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Miao, Y.; Kong, J.; Lindsey, K.; Zhang, X.; Min, L. ROS signaling and its involvement in abiotic stress with emphasis on heat stress-driven anther sterility in plants. Crop Environ. 2024, 3, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, M.; Gong, L.; Yan, A.; Liu, W.; Li, H.; Guo, P. Toxicity of Tris(2-chloroethyl) Phosphate (TCEP) to Alfalfa’s Root System: An Insight into TCEP’s Damage to Morphology, Respiration, and Antioxidant Systems. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2483. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112483
Liu M, Gong L, Yan A, Liu W, Li H, Guo P. Toxicity of Tris(2-chloroethyl) Phosphate (TCEP) to Alfalfa’s Root System: An Insight into TCEP’s Damage to Morphology, Respiration, and Antioxidant Systems. Agronomy. 2025; 15(11):2483. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112483
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Meijun, Liangzhu Gong, An Yan, Wenjing Liu, Haojie Li, and Peiyi Guo. 2025. "Toxicity of Tris(2-chloroethyl) Phosphate (TCEP) to Alfalfa’s Root System: An Insight into TCEP’s Damage to Morphology, Respiration, and Antioxidant Systems" Agronomy 15, no. 11: 2483. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112483
APA StyleLiu, M., Gong, L., Yan, A., Liu, W., Li, H., & Guo, P. (2025). Toxicity of Tris(2-chloroethyl) Phosphate (TCEP) to Alfalfa’s Root System: An Insight into TCEP’s Damage to Morphology, Respiration, and Antioxidant Systems. Agronomy, 15(11), 2483. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112483




