Demographic Characteristics of Novius penicillioides (Coleoptera, Coccinellidae) in Relation to Icerya jacobsoni (Hemiptera, Monophlebidae) Reared on Different Host Plants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Host Plants
2.2. Insects
2.3. Growth and Survival of I. jacobsoni
2.4. Longevity and Reproduction of I. jacobsoni
2.5. Growth and Survival of N. penicillioides Immatures
2.6. Longevity and Fecundity of N. penicillioides Adults
2.7. Life Table Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Host Plants on Growth and Survival
3.2. Effect of Host Plants on Longevity and Reproduction
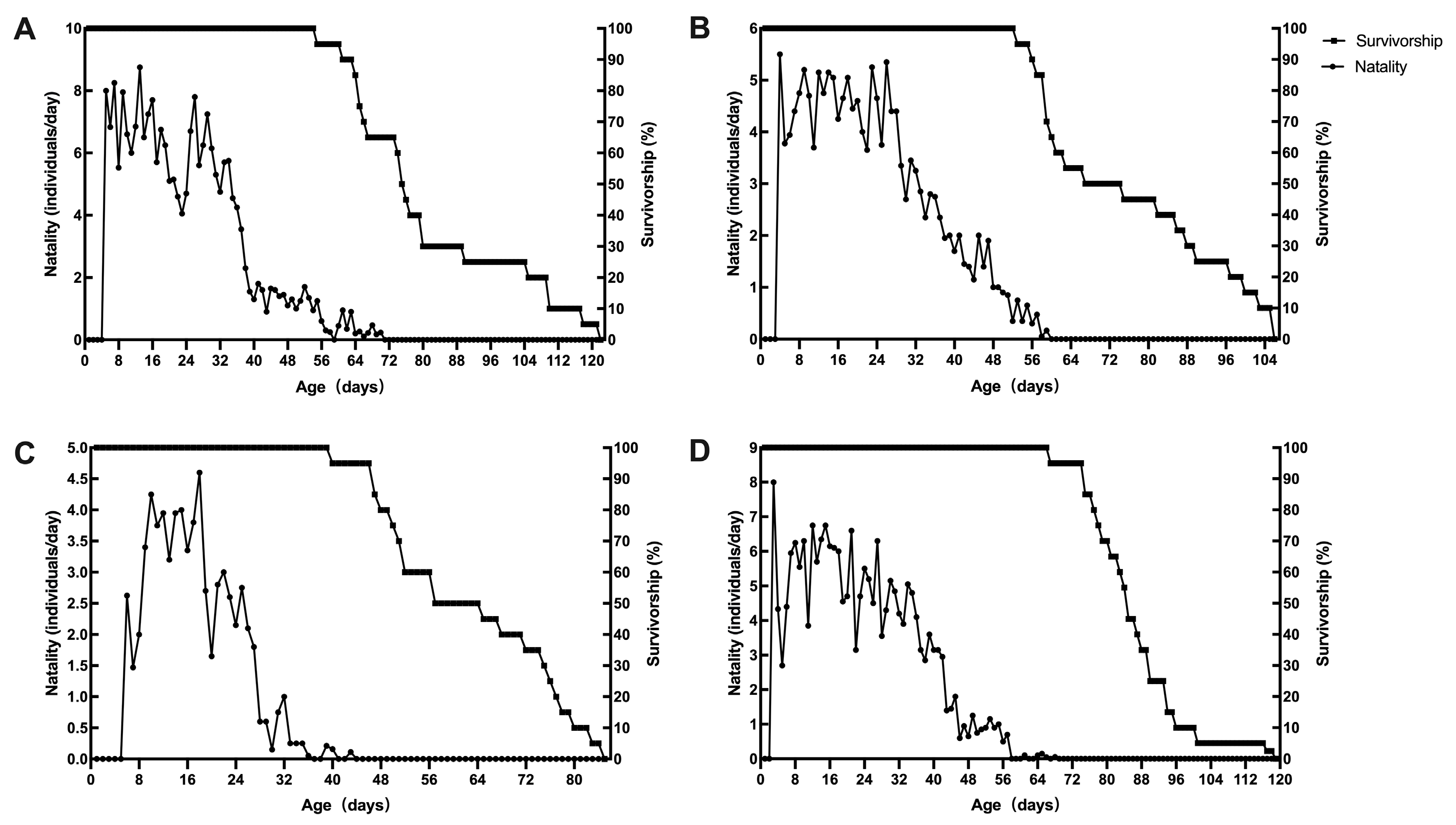
3.3. Life Table Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hodek, I.; Hone, A. Scale insects, mealybugs, whiteflies and psyllids (Hemiptera, Sternorrhyncha) as prey of ladybirds. Biol. Control 2009, 51, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, M.E. Adaptation of Rodolia cardinalis (Mulsant) (Col., Coccinellidae) to lcerya aegyptiaca (Douglas) (horn., Margrodidae) as compared with lcerya purchasi mask. J. Appl. Entomol. 1995, 119, 621–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beshr, S.M. Scanning electron microscopy of Icerya aegyptiaca (Douglas, 1890) (Hemiptera: Monophlebidae). Alexandria Sci. Exch. J. 2015, 36, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dong, W.X.; Han, B.Y. Research progress on the chemical ecology of scale insects. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2005, 23, 878–884. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Akintola, A.J.; Oyegoke, O.O.; Ikusebiala, I. Morphometry and preffered feeding site of egyptian mealybug (Icerya aegyptiaca Douglas) on croton Codiaeum variegatum plant. Int. J. Appl. Agric. Apic. Res. 2013, 9, 189–195. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Fornazier, M.J.; Martins, D.S.; Willink, D.E.; Pirovani, V.D.; Ferreira, P.; Zanuncio, J.C. Scale insects (Hemiptera: Coccoidea) associated with arabica coffee and geographical distribution in the neotropical region. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2017, 89, 3083–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, J.Y.Z.; Lin, S.K.; He, J.L.; Deng, Y.Y.; He, J.C.; Cheng, D.M. The synergistic effects of rosehip oil and matrine against Icerya aegyptiaca (Douglas) (Hemiptera: Coccoidea) and the underlying mechanisms. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 3424–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uesato, T.; Kondo, T.; Unruh, C.; Williams, D.J. Establishment and host records of Icerya aegyptiaca (Douglas) (Hemiptera: Coccoidea: Monophlebidae) in the Sakishima Islands of the Ryukyu archipelago, Japan, with notes on its worldwide distribution. Entomol. Sci. 2011, 14, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.C.C. List of Coccoidea (Homoptera) of China; Special Publication (Taiwan Agricultura Research Institute): Taichung City, Taiwan, 1999; pp. 1–176. [Google Scholar]
- García Morales, M.; Denno, B.D.; Miller, D.R.; Miller, G.L.; Ben-Dov, Y.; Hardy, N.B. ScaleNet: A literature-based model of scale insect biology and systematics. Database 2016, 2016, bav118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Bi, K.K.; Wu, C.; Huo, L.Z.; Deng, J.R.; Sun, L.H. Research on occurrence trends of plant disease and insect pests of ficus in Guangzhou. Garden 2020, 9, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Guo, J.N.; Yang, T.T.; Huang, S.B. Comparison of morphological characteristics of Icerya aegyptiaca (Douglas) and I. iacobsoni Green (Hemiptera, Coccomorpha, Monophlebidae). J. Environ. Entomol. 2023, 45, 828–832. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.L.; Wen, Y.J. A Preliminary Study on the Biology of the Icerya jacobsoni. For. Environ. Sci. 2024, 40, 114–118. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.H.; He, J.C.; Liang, C.P.; Cheng, D.M. Isolation, identification, biological characteristics, and pathogenicity of an entomogenous fungus against the Egyptian mealybug, Icerya aegyptiaca (J.) (Hemiptera: Monophlebidae). Egypt. J. Biol. Pest. Control 2024, 34, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.H.; Lü, L.L.; Lin, L.; Zhou, J.H.; Wei, X.Y.; Wang, X.M. Review of the genus Novius Mulsant (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) from China with description of four new species. Zootaxa 2024, 5528, 668–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiling, P.; Moon, D.C. Quality or quantity: The direct and indirect effects of host plants on herbivores and their natural enemies. Oecologia 2005, 142, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boavida, C.; Neuenschwander, P. Influence of host plant on the mango mealybug, Rastrococcus invadens. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1995, 76, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.Q.; Wu, J.H.; Qiu, B.L.; Ren, S.X.; Ali, S. Effect of host plant on the development, survivorship and reproduction of Dysmicoccus neobrevipes Beardsley (Hemiptera: Pseudoccocidae). Biol. Control 2011, 30, 1124–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, L.C. The Intrinsic rate of natural increase in an insect population. J. Anim. Ecol. 1948, 17, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, F.; Gharekhani, G.; Shirazi, J.; Vaez, N. Effect of host plant cultivar and nitrogen fertilization on life history of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Plant. Prot. Res. 2020, 60, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EI-Refaie, R.M.; Shaurub, E.S.; Abd-Allah, G.E.; Ebeid, A.A.; Abouelnaga, Z.S. Effect of four host plants on the life history and nutritional indices of Spodoptera littoralis. Int. J. Trop. Insect. Sci. 2024, 44, 1091–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.H.; Wang, J.J. Effects of host plants on biology and life table parameters of Aphid spiraecola (Homoptera: Aphididae). Environ. Entomol. 2001, 30, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.D.; Li, D.M.; Gong, P.Y.; Wu, K.J. Life Table Studies of the Cotton Bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), on Different Host Plants. Environ. Entomol. 2024, 33, 1570–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanga, C.M.; Mohamed, S.A.; Govender, P.; Ekesi, S. Effect of host plant on bionomic and life history parameters of Anagyrus pseudococci (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae), a parasitoid of the mango mealybug Rastrococcus iceryoides (Homoptera: Pseudococcidae). Biol. Control 2013, 65, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EI Aalaoui, M.; Sbaghi, M. Life cycle and population growth parameter analysis of the mealybug Phenacoccus solenopsis on three new host plants. Arthropod-Plant Interact. 2022, 16, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narai, Y.; Murai, T. Individual rearing of the Japanese mealybug, Planococcus kraunhiae (Kuwana) (Homoptera: Pseudococcidae) on germinated broad bean seeds. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2002, 37, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, M.S.; Lapointe, S.L. Evaluation of host plants and a meridic diet for rearing Maconellicoccus hirsutus (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) and its parasitoid Anagyrus kamali (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae). Fla. Entomol. 2002, 85, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Sadof, C.S. Variegation in Coleus blumei and the life history of citrus mealybug (Homoptera: Pseudococcidae). Environ. Entomol. 1995, 24, 1650–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marohasy, J. Acceptability and suitability of seven plant species for the mealybug Phenacoccus parvus. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1997, 84, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soroushmehr, Z.; Sahragard, A.; Salehi, L. Comparative life table statistics for the ladybeetle, Scymnus syriacus reared on the green citrus aphid, Aphis spiraecola, fed on two host plants. Entomol. Sci. 2008, 11, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotukkiaii, S.M.; Sahragard, A.; Halajisani, M.F. Comparing demographic parameters of Serangium montazerii (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) on citrus whitefly, Dialeurodes citri (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) fed on two host plants. J. Crop Prot. 2013, 2, 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- Ohgushi, T. Indirect interaction webs: Herbivore-induced effects through trait change in plants. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2005, 36, 81–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utsumi, S.; Ohgushi, T. Host plant variation in plant-mediated indirect effects: Moth boring-induced susceptibility of willows to a specialist leaf beetle. Ecol. Entomol. 2008, 33, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, K.L.; Madden, R.D.; Payton, M.E.; Dilwith, J.W. Host plants affect predator fitness via the nutritional value of herbivore prey: Investigation of a plantaphid-ladybeetle system. BioControl 2002, 47, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukunaga, Y.; Akimoto, S. Toxicity of the aphid Aulacorthum magnoliae to the predator Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) and genetic variance in the assimilation of the toxic aphids in H. axyridis larvae. Entomol. Sci. 2007, 10, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.H. Studies on the bisexual race of Dysmicoccus brevipes (Ckll), its bionomics and economic importance. J. Malaysian Agri. 1973, 49, 254–267. [Google Scholar]
- Farooq, M.; Zhu, X.; Shakeel, M.; Iftikhar, A.; Shahid, M.R.; Saeed, N.; Arain, M.S. Comparative analysis of the demographic parameters of seven spotted ladybird beetle (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) reared on various host aphid species. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqueza, M.T.A.; Casas, G.G.; Rondina, M.E.; Catubis, K.M.L. Comparative growth and development of zigzag ladybird beetle (Cheilomenes sexmaculata) fed with black bean aphids (Aphis fabae) and green peach aphids (Myzus persicae). Thai J. Agri. Sci. 2024, 57, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ramzan, Z.; Khursheed, S.; Manto, M.A.; Itoo, H.; Naseem, N.; Bhat, F.A.; Rather, G.H.; Bhat, Z.A.; Mir, M.A.; Wani, F.J.; et al. Life table and reproductive parameters of ladybird beetle, Coccinella undecimpunctata (Linnaeus) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) on aphids, Myzus persicae (Sulzer) and Brevicoryne brassicae (Linnaeus) (Hemiptera: Aphididae). J. Entomol. Res. Soc. 2023, 25, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southwood, T.R.E.; Handerson, P.A. Ecological Methods, 3rd ed.; With Particular Reference to the Study of Insect Populations; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 2000; p. 575. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, J. Predicting the potential global geographical distribution of two Icerya species under climate change. Forests 2020, 11, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, M.L.; Oetting, R.D.; Chong, J.H. Management of the mealybug Phenacoccus madeirensis. Proc. South. Nurs. Assoc. Res. Conf. 2000, 45, 162–166. [Google Scholar]

| Host Plants | 1st Instar Nymph | 2nd Instar Nymph | Female 3rd Instar Nymph | Male | Nymph to Adult | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Pupa | Pupa | Female | Male | ||||
| M. tanarius | 18.1 ± 2.0 b | 17.4 ± 2.0 b | 17.6 ± 2.4 b | 10.3 ± 0.6 c | 7.3 ± 0.5 b | 53.0 ± 2.3 b | 52.8 ± 1.9 b |
| M. denudata | 18.3 ± 2.1 b | 17.5 ± 2.0 b | 18.1 ± 2.1 b | 11.0 ± 0.8 b | 7.0 ± 0.8 b | 53.9 ± 4.3 b | 53.8 ± 3.4 b |
| F. microcarpa | 25.4 ± 4.0 a | 19.0 ± 3.3 a | 21.4 ± 4.0 a | 11.6 ± 2.1 a | 9.0 ± 1.9 a | 65.8 ± 7.8 a | 65.0 ± 6.9 a |
| P. guajava | 18.3 ± 2.2 b | 17.6 ± 2.2 b | 17.9 ± 1.0 b | 11.0 ± 1.0 b | 7.1 ± 0.9 b | 53.8 ± 1.1 b | 54.0 ± 0.7 b |
| Host Plants | 1st Instar Nymph | 2nd Instar Nymph | Female 3rd Instar Nymph | Male | Nymph to Adult | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Pupa | Pupa | Female | Male | ||||
| M. tanarius | 99.0 ± 1.0 a | 99.0 ± 1.0 a | 100.0 ± 0.0 a | 100.0 ± 0.0 a | 100.0 ± 0.0 a | 98.0 ± 1.5 a | 98.0 ± 1.5 a |
| M. denudata | 99.0 ± 1.0 a | 98.0 ± 0.0 a | 100.0 ± 2.0 a | 98.0 ± 1.0 a | 100.0 ± 0.0 a | 97.0 ± 1.5 a | 97.0 ± 1.0 a |
| F. microcarpa | 78.0 ± 5.3 b | 68.0 ± 7.6 b | 79.9 ± 9.4 b | 100.0 ± 0.0 a | 100.0 ± 0.0 a | 41.9 ± 10.4 b | 53.0 ± 8.6 b |
| P. guajava | 92.0 ± 3.6 a | 94.0 ± 6.8 a | 100.0 ± 0.0 a | 100.0 ± 0.0 a | 100.0 ± 0.0 a | 86.5 ± 8.6 a | 86.5 ± 8.6 a |
| Host Plants | Egg | Larval Instars | Pupa | Egg-Adult | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Instar | 2nd Instar | 3rd Instar | 4th Instar | ||||
| M. tanarius | 5.1 ± 0.0 a | 2.1 ± 0.1 a | 2.2 ± 0.1 a | 2.1 ± 0.0 a | 8.8 ± 0.2 a | 8.6 ± 0.2 a | 28.8 ± 0.3 a |
| M. denudata | 5.1 ± 0.1 a | 2.1 ± 0.0 a | 2.2 ± 0.1 a | 2.1 ± 0.1 a | 8.8 ± 0.2 a | 7.8 ± 0.3 b | 28.0 ± 0.3 b |
| F. microcarpa | 5.2 ± 0.1 a | 2.1 ± 0.1 a | 2.1 ± 0.1 a | 2.1 ± 0.1 a | 8.2 ± 0.3 a | 7.5 ± 0.2 b | 27.3 ± 0.3 b |
| P. guajava | 5.2 ± 0.1 a | 2.1 ± 0.3 a | 2.2 ± 0.1 a | 2.1 ± 0.1 a | 8.8 ± 0.2a | 8.6 ± 0.2 a | 28.8 ± 0.3 a |
| Host Plants | Egg | Larval Instars | Pupa | Egg-Adult | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Instar | 2nd Instar | 3rd Instar | 4th Instar | ||||
| M. tanarius | 96.0 ± 3.0 a | 92.0 ± 4.0 a | 99.0 ± 2.0 a | 98.0 ± 1.0 a | 100.0 ± 0.0 a | 100.0 ± 1.0 a | 85.7 ± 3.0 a |
| M. denudata | 94.0 ± 3.1 a | 93.5 ± 5.2 a | 98.8 ± 1.0 a | 100.0 ± 0.0 a | 100.0 ± 0.0 a | 100.0 ± 2.1 a | 86.8 ± 6.0 a |
| F. microcarpa | 88.0 ± 3.0 b | 90.0 ± 4.0 a | 85.0 ± 3.0 b | 83.0 ± 4.0 b | 100.0 ± 0.0 a | 96.0 ± 3.0 a | 53.6 ± 4.0 b |
| P. guajava | 92.0 ± 3.0 a | 91.0 ± 2.0 a | 95.0 ± 2.0 a | 95.0 ± 2.0 a | 100.0 ± 0.0 a | 100.0 ± 0.0 a | 75.6 ± 5.0 a |
| Host Plants | Sex Ratio | Pre-Lay Period (d) | Fecundity (Nymphs/Female) | Adult Longevity (d) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | ||||
| M. tanarius | 0.6 ± 0.1 a | 15.6 ± 0.5 c | 162.7 ± 21.5 a | 6.5 ±1.1 b | 40.3 ± 1.1 c |
| M. denudata | 0.6 ± 0.1 a | 15.3 ± 0.3 c | 134.4 ± 12.3 b | 7.5 ± 0.5 a | 54.3 ± 1.7 a |
| F. microcarpa | 0.4 ± 0.1 c | 25.5 ± 0.2 a | 81.6 ± 10.8 c | 5.1 ± 0.5 b | 52.7 ± 2.5 a |
| P. guajava | 0.5 ± 0.1 b | 18.4 ± 0.4 b | 93.7 ± 10.0 c | 3.2 ± 0.2 c | 45.6 ± 3.9 c |
| Host Plants | Sex Ratio | Pre-Oviposition Period (d) | Fecundity (Eggs/Female) | Adult Longevity (d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. tanarius | 0.5 ± 0.2 a | 4.9 ± 0.1 c | 199.9 ± 5.9 a | 75.0 ± 0.9 a |
| M. denudata | 0.6 ± 0.1 a | 7.2 ± 0.2 a | 216.8 ± 10.5 a | 73.4 ± 0.5 a |
| F. microcarpa | 0.3 ± 0.2 b | 6.9 ± 0.2 a | 68.1 ± 2.4 c | 48.6 ± 1.0 c |
| P. guajava | 0.4 ± 0.1 b | 5.8 ± 0.2 b | 150.7 ± 3.9 b | 57.6 ± 0.6 b |
| Host Plants | ) | Generation Time (T) | ) | Finite Rate of Increase (λ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. tanarius | 111.48 | 73.5 | 0.0642 | 1.0663 |
| M. denudata | 85.74 | 81.3 | 0.0548 | 1.0563 |
| F. microcarpa | 20.92 | 99.5 | 0.0306 | 1.0310 |
| P. guajava | 46.96 | 81.2 | 0.0474 | 1.0485 |
| Host Plants | ) | Generation Time (T) | ) | Finite Rate of Increase (λ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. tanarius | 86.53 | 51.9 | 0.0860 | 1.0898 |
| M. denudata | 65.49 | 51.5 | 0.0813 | 1.0847 |
| F. microcarpa | 4.36 | 50.0 | 0.0294 | 1.0299 |
| P. guajava | 24.15 | 53.8 | 0.0592 | 1.0610 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, J.; Liang, J.; Zheng, S.; Bashir, M.H.; Ali, S.; Wang, X. Demographic Characteristics of Novius penicillioides (Coleoptera, Coccinellidae) in Relation to Icerya jacobsoni (Hemiptera, Monophlebidae) Reared on Different Host Plants. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2457. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112457
Peng J, Liang J, Zheng S, Bashir MH, Ali S, Wang X. Demographic Characteristics of Novius penicillioides (Coleoptera, Coccinellidae) in Relation to Icerya jacobsoni (Hemiptera, Monophlebidae) Reared on Different Host Plants. Agronomy. 2025; 15(11):2457. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112457
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Jing, Jianfeng Liang, Siqin Zheng, Muhammad Hamid Bashir, Shaukat Ali, and Xingmin Wang. 2025. "Demographic Characteristics of Novius penicillioides (Coleoptera, Coccinellidae) in Relation to Icerya jacobsoni (Hemiptera, Monophlebidae) Reared on Different Host Plants" Agronomy 15, no. 11: 2457. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112457
APA StylePeng, J., Liang, J., Zheng, S., Bashir, M. H., Ali, S., & Wang, X. (2025). Demographic Characteristics of Novius penicillioides (Coleoptera, Coccinellidae) in Relation to Icerya jacobsoni (Hemiptera, Monophlebidae) Reared on Different Host Plants. Agronomy, 15(11), 2457. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112457






