Spatio-Temporal Variations in Soil Organic Carbon Stocks in Different Erosion Zones of Cultivated Land in Northeast China Under Future Climate Change Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
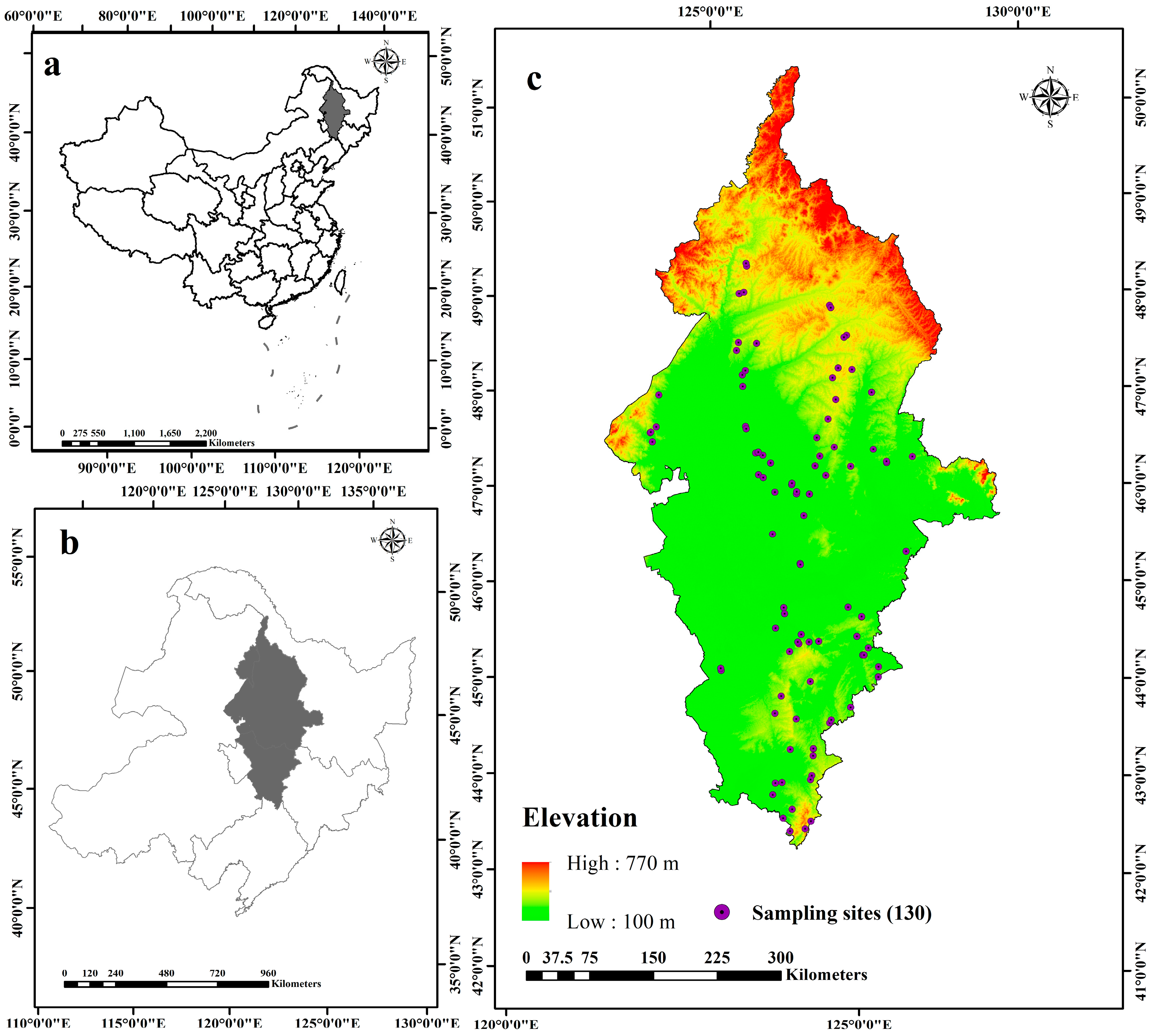
2.1. Overview of the Research Area
2.2. Collection of Soil Samples in the Field
2.3. Calculation of SOC Stocks
2.4. Environmental Variables
2.4.1. Topographic Variables
2.4.2. Climatic Variables
2.5. Prediction Models
2.5.1. Boosted Regression Trees
2.5.2. Space-for-Time Substitution Method
2.6. Model Validation
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
3.2. Model Performance and Uncertainty
3.3. Relative Importance of Environmental Variables
3.4. Spatial Distribution Variation in SOC Stocks Under Various Erosion Types
4. Discussion
4.1. Controls of SOC Stocks
4.2. Response of SOC Stocks in Different Erosion Zones Under Future Climate Change
4.3. Uncertainties in the Present Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lal, R. Soil carbon sequestration in China through agricultural intensification, and restoration of degraded and desertified ecosystems. Land Degrad. Dev. 2002, 13, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, U. Enriching Soil Organic Carbon for Sustainable Agriculture, Food Security, and Health. J. Indones. Sustain. Dev. Plan. 2024, 5, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil carbon sequestration impacts on global climate change and food security. Science 2004, 304, 1623–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchoms, S.; Wang, Z.; Vanacker, V.; Van Oost, K. Evaluating the effects of soil erosion and productivity decline on soil carbon dynamics using a model-based approach. Soil 2019, 5, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, A.; Webb, N.P.; Leys, J.F.; Waters, C.M.; Orgill, S.; Eyres, M.J. Minimising soil organic carbon erosion by wind is critical for land degradation neutrality. Environ. Sci. Policy 2019, 93, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Gao, C.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, W.; Lu, X.; Wang, G. Temporal and spatial changes in black carbon sedimentary processes in wetlands of Songnen Plain, Northeast of China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Tang, J.; Gao, Y.; Gu, Z.; Liu, G.; Ren, X. Spatial distribution of soil erosion and its impacts on soil productivity in Songnen typical black soil region. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2023, 11, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil erosion and the global carbon budget. Environ. Int. 2003, 29, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugato, E.; Paustian, K.; Panagos, P.; Jones, A.; Borrelli, P. Quantifying the erosion effect on current carbon budget of European agricultural soils at high spatial resolution. Glob. Change Biol. 2016, 22, 1976–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.; Jhariya, M.K.; Raj, A.; Banerjee, A.; Meena, R.S. Soil carbon stock and sequestration: Implications for climate change adaptation and mitigation. In Ecological Intensification of Natural Resources for Sustainable Agriculture; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 461–489. [Google Scholar]
- Adhikari, K.; Owens, P.R.; Libohova, Z.; Miller, D.M.; Wills, S.A.; Nemecek, J. Assessing soil organic carbon stock of Wisconsin, USA and its fate under future land use and climate change. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 667, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Xu, L.; Zhuang, Q.; He, N. Investigating the spatio-temporal variability of soil organic carbon stocks in different ecosystems of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldock, J.A.; Wheeler, I.; McKenzie, N.; McBrateny, A. Soils and climate change: Potential impacts on carbon stocks and greenhouse gas emissions, and future research for Australian agriculture. Crop Pasture Sci. 2012, 63, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes Rojas, L.A.; Adhikari, K.; Ventura, S.J. Projecting soil organic carbon distribution in central Chile under future climate scenarios. J. Environ. Qual. 2018, 47, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lal, R.; Kimble, J.; Follett, R.F. Pedospheric processes and the carbon cycle. In Soil Processes and the Carbon Cycle; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- McBratney, A.B.; Santos, M.M.; Minasny, B. On digital soil mapping. Geoderma 2003, 117, 3–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Minasny, B.; Malone, B.P.; Mcbratney, A.B. Pedology and digital soil mapping (DSM). Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2019, 70, 216–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elith, J.; Leathwick, J.R.; Hastie, T. A working guide to boosted regression trees. J. Anim. Ecol. 2008, 77, 802–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Zhang, G.; Liu, F.; Lu, Y.; Yang, F.; Yang, F.; Yang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Li, D. Comparison of boosted regression tree and random forest models for mapping topsoilorganic carbon concentration in an alpine ecosystem. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.; Davies, C.A.; Ogle, S.; Zanchi, G.; Bellarby, J.; Bird, N.; Braimoh, A.K. Towards an integrated global framework to assess the impacts of land use and management change on soil carbon: Current capability and future vision. Glob. Change Biol. 2012, 18, 2089–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, K.W.; Libohova, Z.; Adhikari, K.; Kome, C.; Maness, X.; Silman, M.R. Influence of land use and topographic factors on soil organic carbon stocks and their spatial and vertical distribution. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Xie, Y.; Ren, X.; Cheng, C.; Wei, X. Spatial variation of soil organic carbon density in the black soil region of Northeast China under the influence of erosion and deposition. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 475, 143616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Li, X.; Mao, D.; Wang, Z.; Jia, M.; Chen, L. Investigating spatial and vertical patterns of wetland soil organic carbon concentrations in China’s Western Songnen plain by comparing different algorithms. Sustainability 2020, 12, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Luo, C.; Kong, D.; Yu, Y.; Zang, D.; Wang, F. Spatial and Temporal Variations in Soil Organic Matter and Their Influencing Factors in the Songnen and Sanjiang Plains of China (1984–2021). Land 2024, 13, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Nong, H.; He, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Yu, M. Opportunities and implementation pathway for China’s forestry development under the “Dual Carbon” strategy. Carbon Res. 2024, 3, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Feng, Q.; Qin, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhang, M.; Liu, W.; Li, B. The role of topography in shaping the spatial patterns of soil organic carbon. Catena 2019, 176, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batjes, N.H. Total carbon and nitrogen in the soils of the world. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1996, 47, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013; Available online: https://www.rproject.org/ (accessed on 26 July 2025).
- Conrad, O.; Bechtel, B.; Bock, M.; Dietrich, H.; Fischer, E.; Gerlitz, L.; Böhner, J. System for automated geoscientific analyses (SAGA) v. 2.1. 4. Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 1991–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L. A concordance correlation coefficient to evaluate reproducibility. Biometrics 1989, 45, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.; McConnell, C.; Coleman, K.; Cox, P.; Falloon, P.; Jenkinson, D.; Powlson, D. Global climate change and soil carbon stocks; predictions from two contrasting models for the turnover of organic carbon in soil. Glob. Change Biol. 2005, 11, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zheng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Yu, D.; Shi, X.; Xing, S.; Chen, H.; Fan, X. Combined effects of temperature and precipitation on soil organic carbon changes in the uplands of eastern China. Geoderma 2019, 337, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, U.; Hugelius, G.; Shelef, E.; Yang, Y.; Strauss, J.; Lupachev, A.; Harden, J.W.; Jastrow, J.D.; Ping, C.L.; Riley, W.J.; et al. Spatial heterogeneity and environmental predictors of permafrost region soil organic carbon stocks. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eaaz5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Huang, L.; Qiu, C.; Ciais, P. Evaluation of effects of heat released from SOC decomposition on soil carbon stock and temperature. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geremew, B.; Tadesse, T.; Bedadi, B.; Gollany, H.T.; Tesfaye, K.; Aschalew, A. Impact of land use/cover change and slope gradient on soil organic carbon stock in Anjeni watershed, Northwest Ethiopia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Liang, Y.; Yan, J.; Liu, J.; Yuan, J.; Wang, L.; Ren, J.; Cai, H. Creation and application of a full soil layer fertilization technology model for continuous maize cultivation with straw return in black soil of northeast china. Mosc. Univ. Soil Sci. Bull. 2024, 79, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Shen, Q.; Zhai, X.; Du, S.; Zhang, X. Impact of environmental factors on the spatiotemporal variability of soil organic matter: A case study in a typical small Mollisol watershed of Northeast China. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 736–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Fang, H.; Shi, R.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Tan, L.; Guo, Z. Erosion and deposition regulate soil carbon by mediating Fe-Carbon fixation mode in a typical catchment in the black soil region of Northeastern China. Catena 2024, 235, 107704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Fang, H.; Gao, L.; Zhang, W. Soil organic carbon budget and fertility variation of black soils in Northeast China. Ecol. Res. 2006, 21, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.H.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.N.; Wang, Z.Q. Advances and prospects of soil erosion research in the black soil region of Northeast China. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Foereid, B.; Lehmann, J.; Major, J. Modeling black carbon degradation and movement in soil. Plant Soil 2011, 345, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sui, Y.; Yu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Chu, H.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, G. Soil carbon content drives the biogeographical distribution of fungal communities in the black soil zone of northeast China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 83, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhao, W.; Pan, C.; Qiu, G.; Xu, S.; Liu, S. Study on the influencing factors of farmers’ adoption of conservation tillage technology in black soil region in China: A logistic-ISM model approach. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Jia, Z.; Wen, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, H.; Zeng, Y.; Li, L.; Cui, M.; Li, H.; Zhang, J. Safeguarding the “Black Soil Granary”: Innovations in Soil Conservation and Sustainable Agriculture. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2024, 38, 2024018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.; Deng, Y.; Yi, C. Effects of Conservation Tillage on Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity in Black Soil Region: Evidence from Heilongjiang Province, China. Land 2024, 13, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Luo, X.; Li, H.; Zang, Y.; Ou, Y. Progress and suggestions of conservation tillage in China. Strateg. Study Chin. Acad. Eng. 2024, 26, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Property | SOC Stocks | ELE | SG | SA | PC | CA | TWI | MAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ELE | 0.42 ** | |||||||
| SG | 0.11 | 0.42 ** | ||||||
| SA | 0.06 | −0.08 | −0.16 | |||||
| PC | −0.10 | 0.01 | −0.10 | −0.20 * | ||||
| CA | 0.09 | −0.51 ** | −0.49 ** | 0.21 * | −0.05 | |||
| TWI | −0.04 | −0.62 ** | −0.80 ** | 0.21 * | 0.06 | 0.79 ** | ||
| MAP | −0.62 ** | 0.35 ** | −0.02 | −0.28 ** | 0.07 | −0.18 * | −0.59 ** | |
| MAT | 0.42 ** | −0.43 ** | −0.16 | −0.20 * | −0.05 | 0.79 ** | −0.04 | 0.51 ** |
| Index | MAE | RESE | R2 | LCCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min. | 1.40 | 1.98 | 0.43 | 0.61 |
| 1stQu. | 1.42 | 2.00 | 0.49 | 0.64 |
| Median | 1.43 | 2.01 | 0.52 | 0.66 |
| Mean | 1.45 | 2.03 | 0.52 | 0.65 |
| 3rdQu. | 1.47 | 2.07 | 0.54 | 0.67 |
| Max. | 1.50 | 2.10 | 0.59 | 0.68 |
| Erosion Type | Level | Area (km2) | 2023 (Tg) | 2050s (Tg) | 2090s (Tg) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSP245 | SSP585 | SSP245 | SSP585 | ||||
| Water erosion | Slight | 62,660.00 | 496.18 | 389.09 | 381.92 | 377.12 | 376.77 |
| Light | 18,618.00 | 159.88 | 116.24 | 115.05 | 113.23 | 112.99 | |
| Moderate | 7665.00 | 74.75 | 48.27 | 47.84 | 47.49 | 47.36 | |
| Severe | 155.00 | 1.24 | 0.82 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.83 | |
| Wind erosion | Slight | 21.00 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.11 |
| Light | 5.00 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | |
| Moderate | 7.00 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | |
| Severe | 2.00 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| Total | 89,133.00 | 732.27 | 554.61 | 545.83 | 538.86 | 538.14 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhuang, Q.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, C.; Jin, X. Spatio-Temporal Variations in Soil Organic Carbon Stocks in Different Erosion Zones of Cultivated Land in Northeast China Under Future Climate Change Conditions. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112459
Wang S, Zhang X, Zhuang Q, Yang Z, Wang Z, Li C, Jin X. Spatio-Temporal Variations in Soil Organic Carbon Stocks in Different Erosion Zones of Cultivated Land in Northeast China Under Future Climate Change Conditions. Agronomy. 2025; 15(11):2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112459
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shuai, Xinyu Zhang, Qianlai Zhuang, Zijiao Yang, Zicheng Wang, Chen Li, and Xinxin Jin. 2025. "Spatio-Temporal Variations in Soil Organic Carbon Stocks in Different Erosion Zones of Cultivated Land in Northeast China Under Future Climate Change Conditions" Agronomy 15, no. 11: 2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112459
APA StyleWang, S., Zhang, X., Zhuang, Q., Yang, Z., Wang, Z., Li, C., & Jin, X. (2025). Spatio-Temporal Variations in Soil Organic Carbon Stocks in Different Erosion Zones of Cultivated Land in Northeast China Under Future Climate Change Conditions. Agronomy, 15(11), 2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112459








