Optimizing Nutrient Compensation Intervals Based on Ionic Monitoring in Drainage Water from Open and Closed Tomato Hydroponics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ionic Monitoring in Commercial Tomato Farm (Exp. 1)
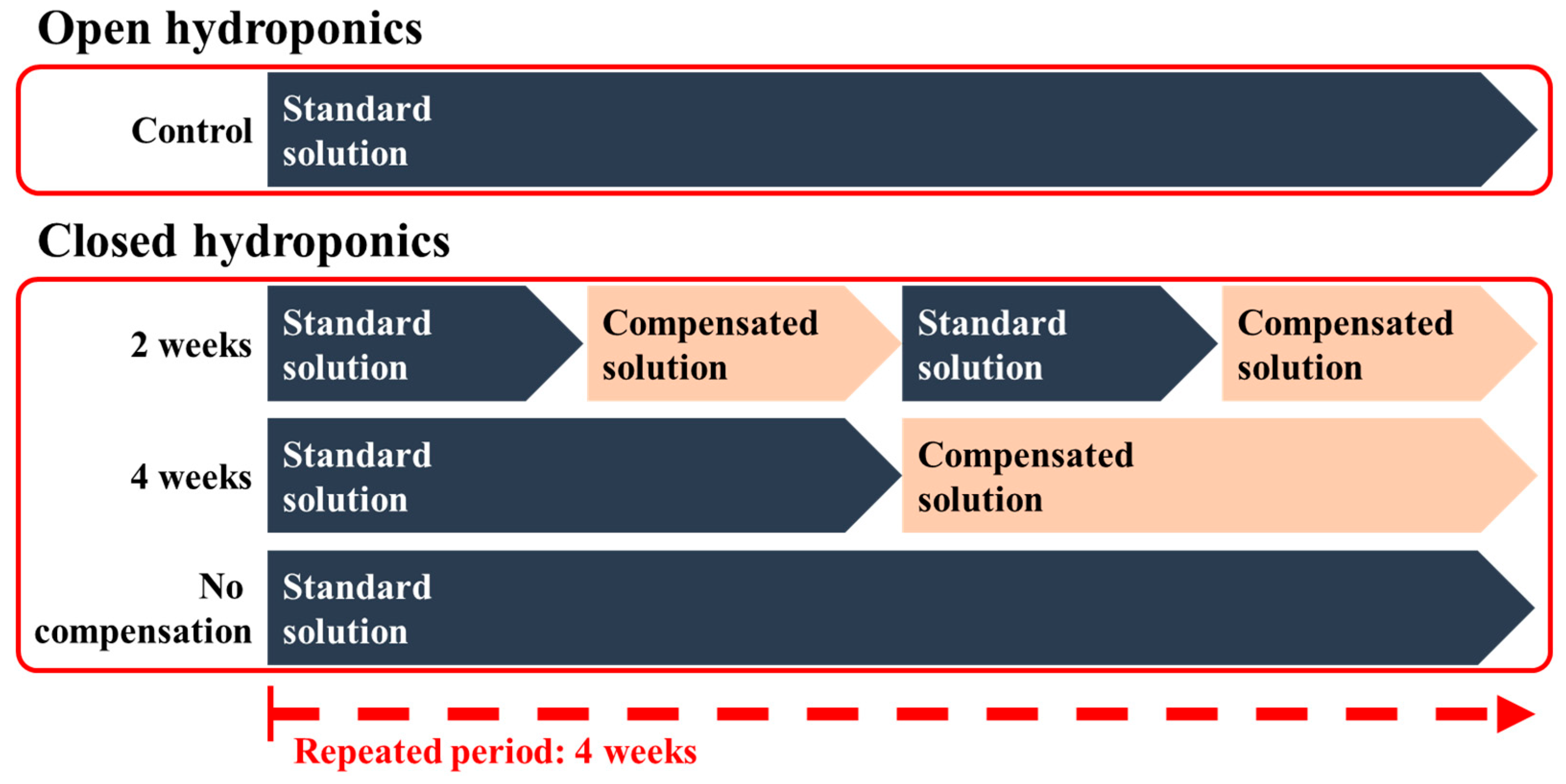
2.2. Effects of Nutrient Compensation Intervals in Closed Hydroponic Systems (Exp. 2)
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
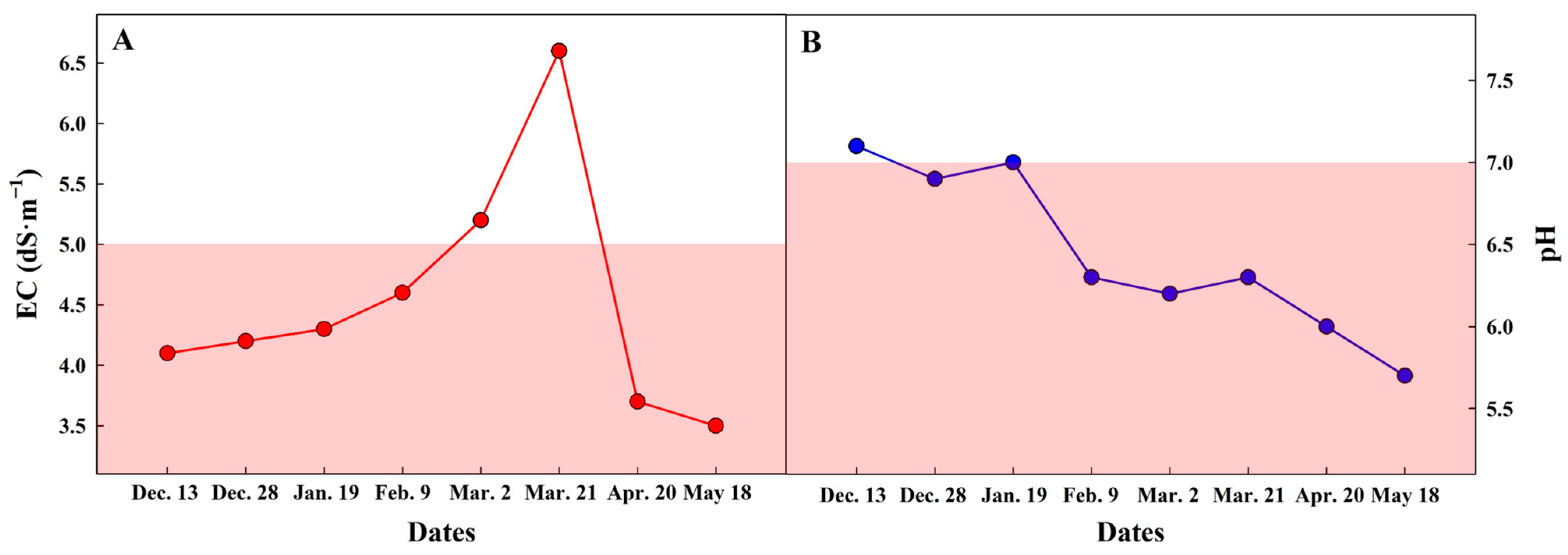
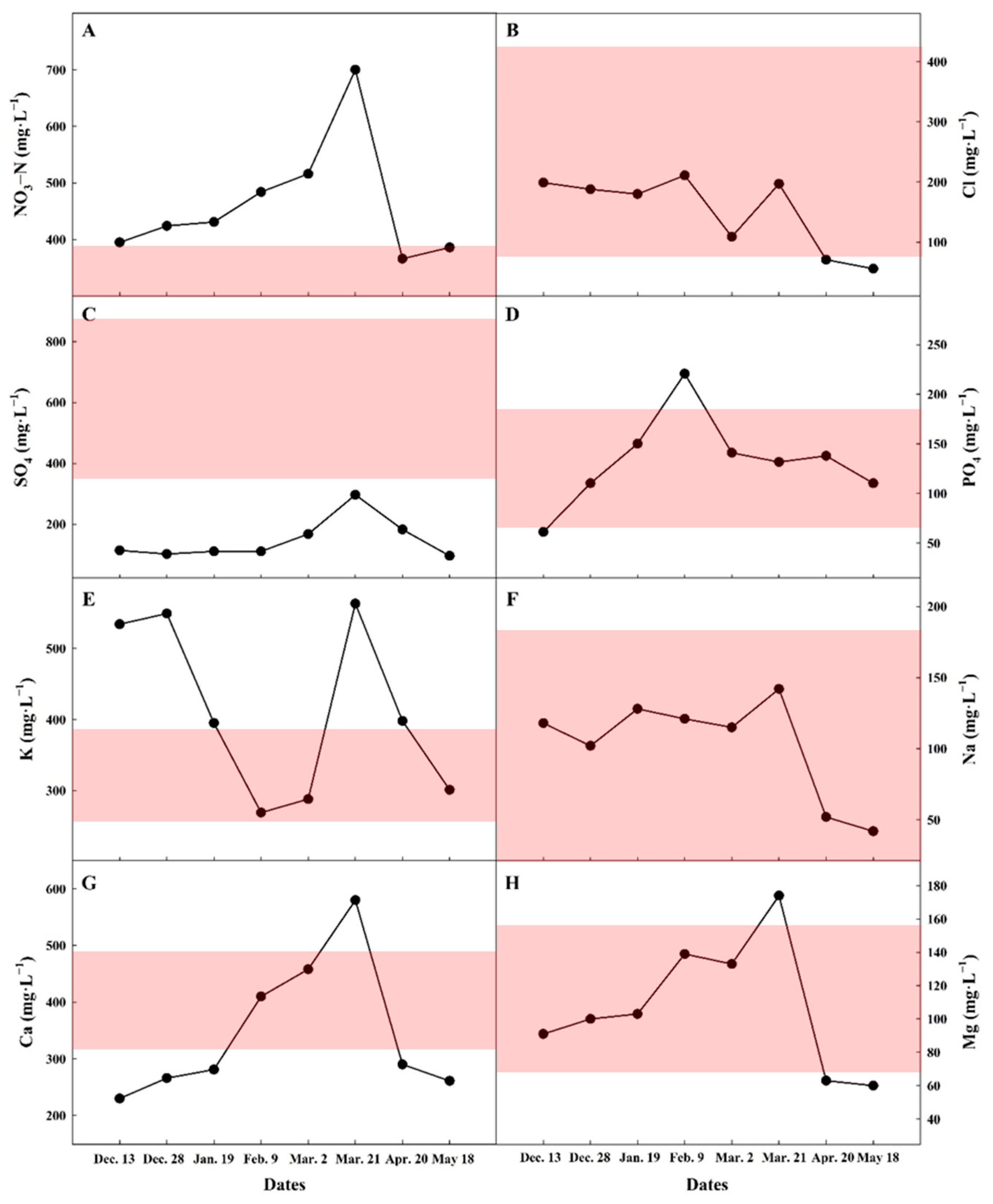
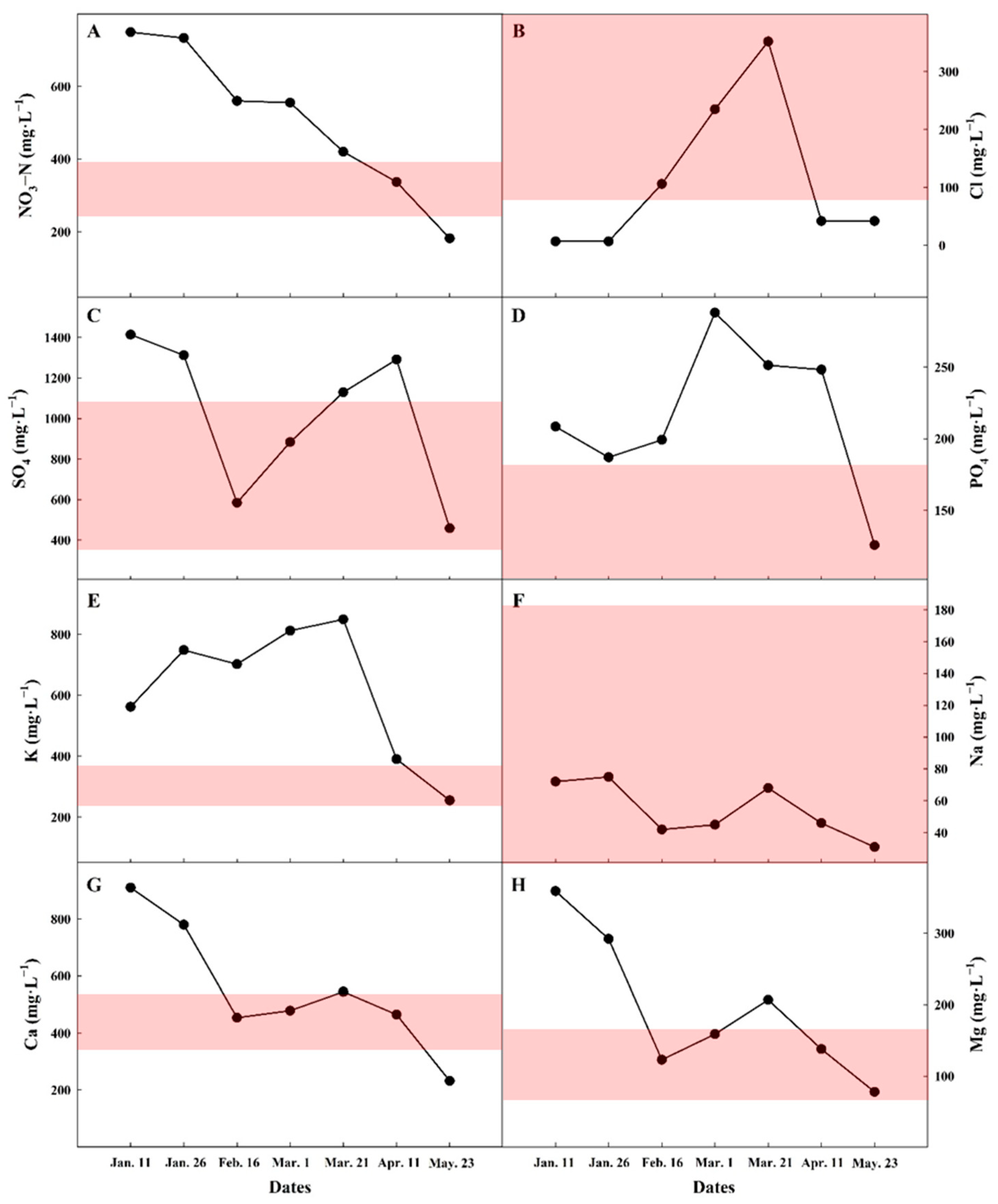
3.1. Ionic Monitoring in Commercial Tomato Farm (Exp. 1)
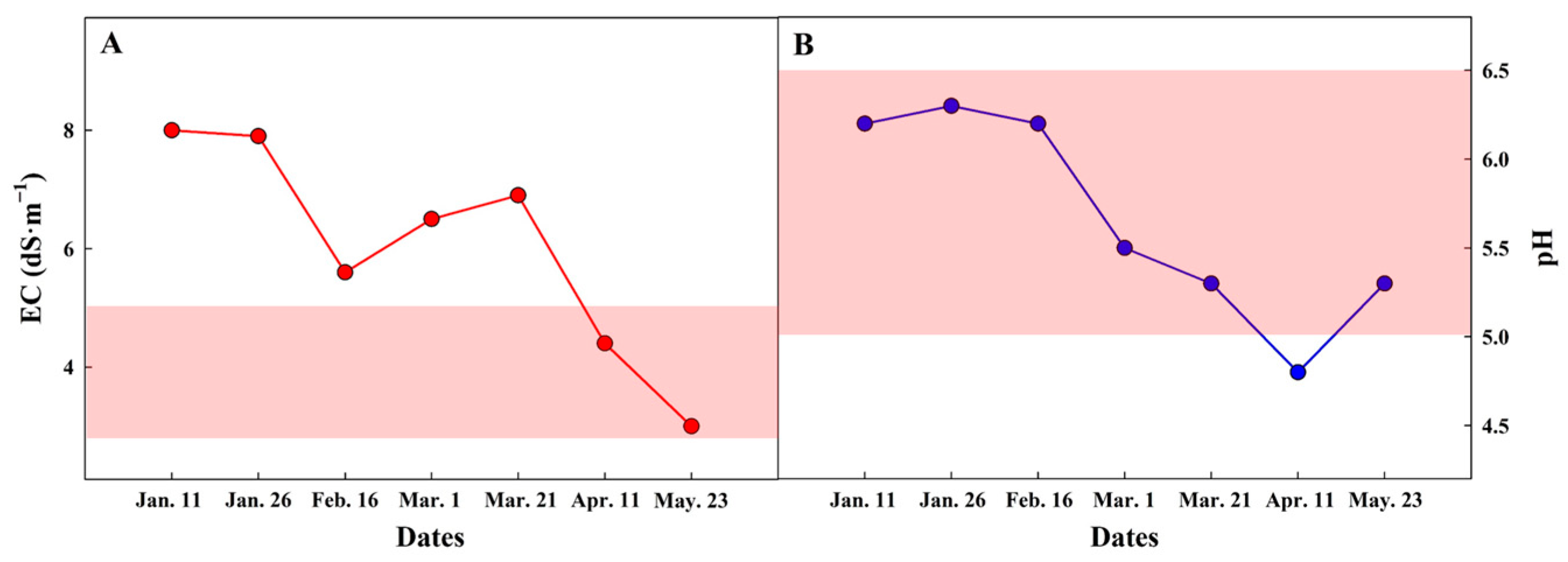
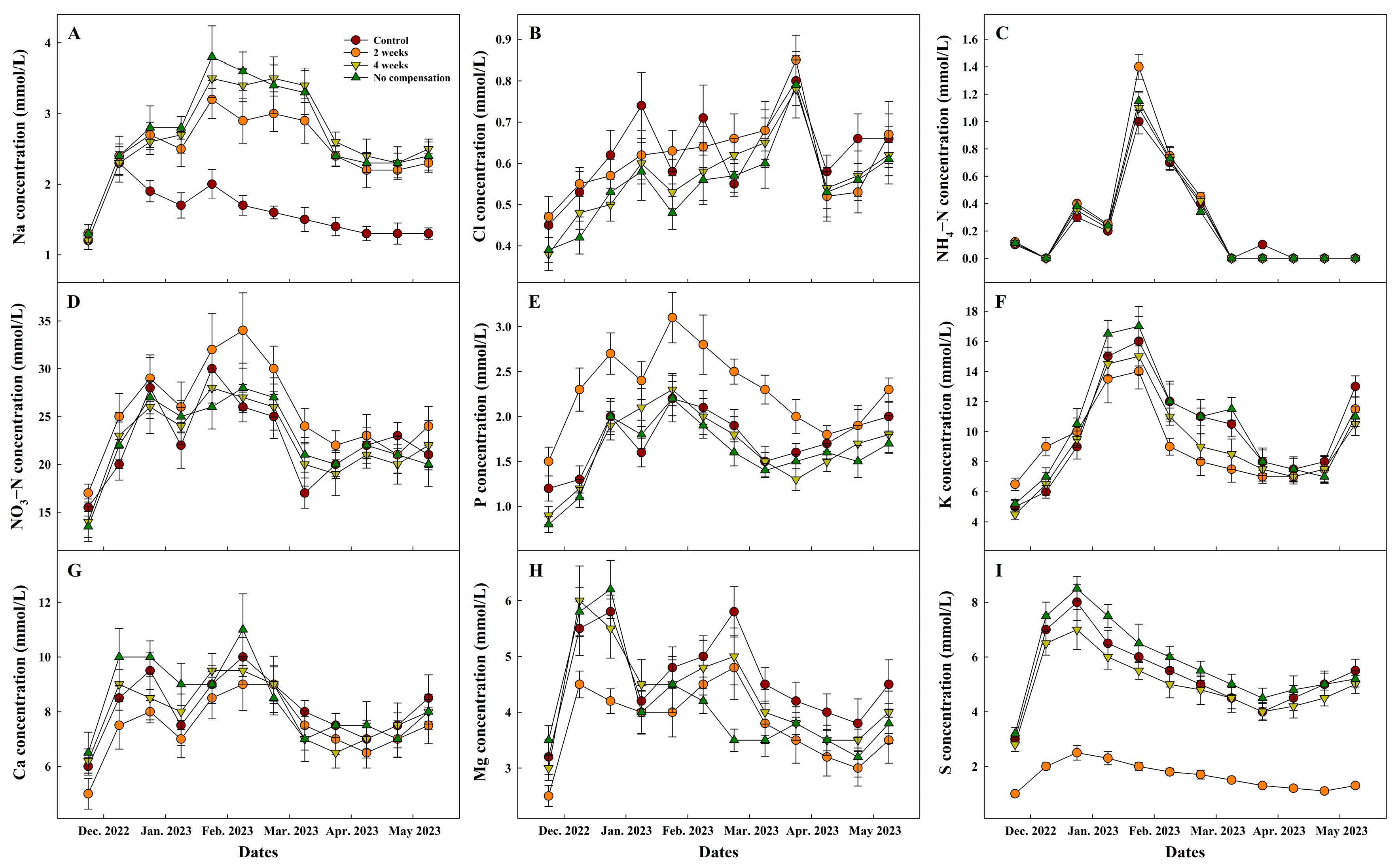
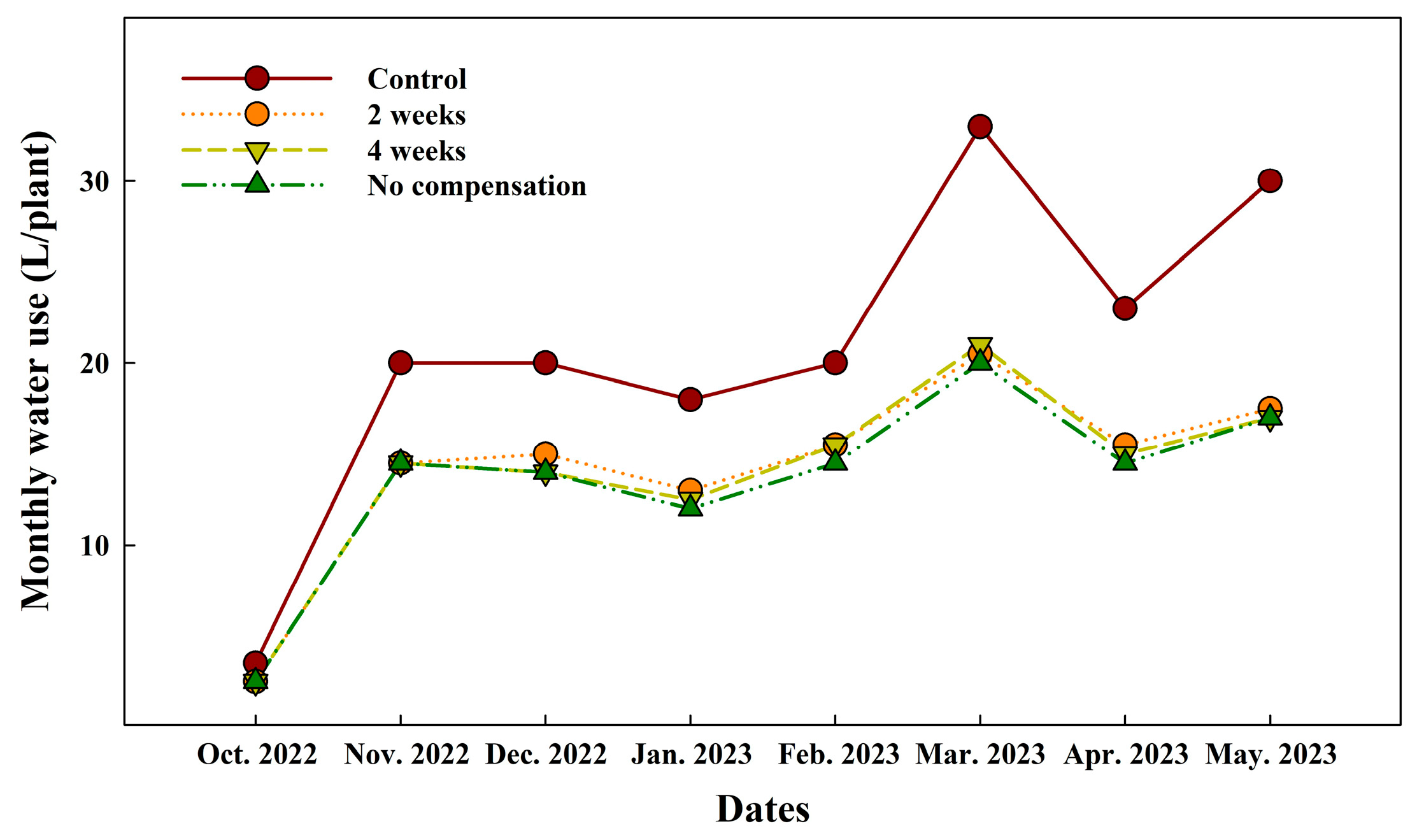
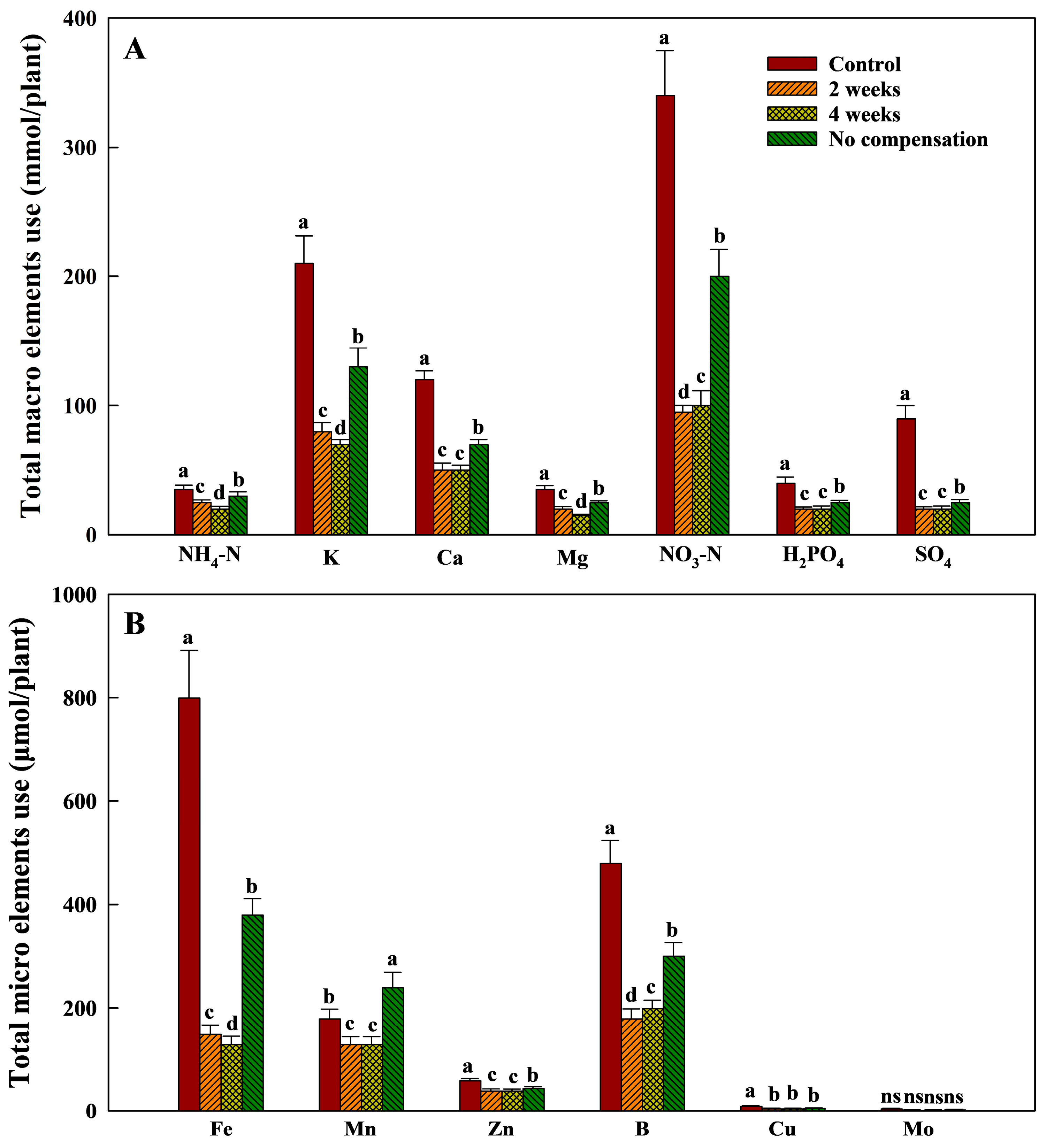
3.2. Effects of Nutrient Compensation Intervals in Closed Hydroponic Systems (Exp. 2)
3.3. Economic Comparison of Closed and Open Hydroponic Systems Based on Fertilizer Input (Exp. 2)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Potapov, P.; Turubanova, S.; Hansen, M.C.; Tyukavina, A.; Zalles, V.; Khan, A.; Song, X.P.; Pickens, A.; Shen, Q.; Cortez, J. Global maps of cropland extent and change show accelerated cropland expansion in the twenty-first century. Nat. Food. 2022, 3, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, D.; Choudhury, A.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Shaw, R. The role of data-driven agritech startups—The case of India and Japan. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Ahn, S.E. Policy suggestions to encourage the conversion of marginal farmland to forestland. Korea Spat. Plan. Rev. 2005, 46, 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Pertierra Lazo, R.; Gonzabay, J.Q. Economic analysis of hydroponic lettuce under floating root system in semi-arid climate. Granja Rev. Cienc. Vida. 2020, 31, 121–133. [Google Scholar]
- Dorais, M.; Papadopoulos, A.P.; Gosselin, A. Greenhouse tomato fruit quality. Hortic. Rev. 2001, 26, 239–319. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, S.V.; Gimenes, R.M.T.; Binotto, E. Economic viability for deploying hydroponic system in emerging countries: A differentiated risk adjustment proposal. Land Use Policy 2019, 83, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.L.; Cho, H.M.; Kim, M.S. Environmental impact of hydroponic nutrient wastewater, used hydroponic growing media, and crop wastes from acyclic hydroponic farming system. J. Korea Org. Resour. Recycl. Assoc. 2021, 29, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Kleiner, Y.; Clark, S.M.; Raghavan, V.; Tartakovsky, B. Review of current hydroponic food production practices and the potential role of bioelectrochemical systems. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 23, 897–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, S.; Verheust, Y.; Bonarrigo, G.; Van Hulle, S.V. Closed hydroponic systems: Operational parameters, root exudates occurrence and related water treatment. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 16, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, P.; Chen, J.; Hamad, A.A.A.; Dai, X.; Jin, Q.; Ding, S. Tomato performance and changes in soil chemistry in response to salinity and Na/Ca ratio of irrigation water. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 285, 108363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.O.; Bae, J.H. Development of optimal nutrient solution of tomato (Lycopercicon esculentum Mill.) in a closed soilless culture system. J. Bio-Environ. Control. 2005, 14, 203–211. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.H.; Lim, M.Y.; Choi, G.L.; Kim, S.H.; Jeong, H.J. Growth and quality of two melon cultivars in hydroponics affected by mixing ratio of coir substrate and different irrigation amount on spring season. Prot. Hortic. Plant Fact. 2019, 28, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Kim, S.E.; Lee, S.D.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, H.S.; Cho, S.K.; Sim, S.Y.; Kim, Y.S. Development of drainage water disinfection system by electric shock in recirculating soilless culture. J. Bio-Environ. Congr. 2016, 25, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaduzzaman, M.; Niu, G.; Asao, T. Editorial: Nutrients recycling in hydroponics: Opportunities and challenges toward sustainable crop production under controlled environment agriculture. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 845472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vought, K.; Bayabil, H.K.; Pompeo, J.; Crawford, D.; Zhang, Y.; Correll, M.; Martin-Ryals, A. Dynamics of micro and macronutrients in a hydroponic nutrient film technique system under lettuce cultivation. Heliyon 2024, 10, e32316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neocleous, D.; Savvas, D. NaCl accumulation and macronutrient uptake by a melon crop in a closed hydroponic system in relation to water uptake. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 165, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.M.; Liu, S.Y.; Shi, B.Y.; Peng, J.Y.; Kao, Z.W.; Chen, Y.Y.; Hsieh, T.Y.; Chung, H.Y.; Lin, C.Y.; Fang, W.; et al. IoT-interfaced solid-contact ion-selective electrodes for cyber-monitoring of element- specific nutrient information in hydroponics. Comput. Electr. Agric. 2023, 214, 108266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awal, M.D.; Pio, A.S.; Mim, M.J.; Partha, P.K.P.; Kafi, M.A.A.; Farha, S. A smart IoT-based hydroponics system for small-scale household in Bangladesh. Smart Agric. Technol. 2025, 12, 101163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Lee, J.; Park, S.; Kim, J.; Jang, K.J. Next-generation nitrate, ammonium, phosphate, and potassium ion monitoring system in closed hydroponics: Review on state-of-the-art sensors and their applications. AgriEngineering 2024, 6, 4786–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, H.; Yusof, A.A.; Nor, M.K.M. Automated hydroponic nutrient dosing system: A scoping review of pH and electrical conductivity dosing frameworks. AgriEngineering 2025, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.Y.; Jeong, E.S.; Roh, M.Y.; Choi, G.L.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, C.K. Changes of plant growth and nutrient concentrations of the drainage according to drainage reuse and substrate type in sweet pepper hydroponics. J. Bio-Environ. Congr. 2022, 4, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, M.Y.; Choi, G.L.; Rhee, H.C.; Seo, T.C.; Kim, W.S.; Lee, Y.B. Changes in nutrient element concentrations and growth of cucumber plants (Cucumis sativus L. cv. Joeun Baegdadagi) as affected by nutrient solution composition in recirculating hydroponic systems. J. Bio-Environ. Congr. 2009, 18, 363–369. [Google Scholar]
- Christie, E.C. Water and Nutrient Reuse Within Closed Hydroponic Systems. Master’s Thesis, Georgia Southern University, Statesboro, GA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, T.I.; Son, J.E. Changes in ion balance and individual ionic contributions to EC reading at different renewal intervals of nutrient solution under EC-based nutrient control in closed-loop soilless culture for sweet peppers (Capsicum annum L. ‘Fiesta’). Korea J. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 2011, 29, 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- Katsoulas, N.; Savvas, D.; Kitta, E.; Bartzanas, T.; Kittas, C. Extension and evaluation of a model for automatic drainage solution management in tomato crops grown in semi-closed hydroponic systems. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 113, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Kim, Y.C. Water treatment for closed hydroponic systems. J. Korea Soc. Environ. Eng. 2019, 41, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halbert-Howard, A.; Häfner, F.; Karlowsky, S.; Schwarz, D.; Krause, A. Evaluating recycling fertilizers for tomato cultivation in hydroponics, and their impact on greenhouse gas emissions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 28, 59284–59303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayezizadeh, M.R.; Ansari, N.A.Z.A.; Albaji, M.; Khaleghi, E. Effects of hydroponic systems on yield, water productivity and stomatal gas exchange of greenhouse tomato cultivars. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 258, 107171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kreij, C.; Voogt, W.; Van den Bos, A.L.; Baas, R. Bemestings Adviesbasis Substraten; Proefstation voor Bloemisterij & Glasgroente (PBG): Aalsmeer, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 7–42. [Google Scholar]
- Sonneveld, W.; Voogt, W. Plant Nutrition of Greenhouse Crops; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Banach, J.L.; Hoffmans, Y.; Appelman, W.A.J.; van Bokhorst-van de Veen, H.; Van Asselt, E.D. Application of water disinfection technologies for agricultural waters. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 244, 106527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambo, P.; Nicoletto, C.; Giro, A.; Pii, Y.; Valentinuzzi, F.; Mimmo, T.; Lugli, P.; Orzes, G.; Mazzetto, F.; Astolfi, S.; et al. Hydroponic solutions for soilless production systems: Issues and opportunities in a smart agriculture perspective. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Zhang, R.; Fu, B.; Chen, H.; Song, X.; Lv, G.; Zhang, R. Effects of potassium supply in nutrient solution on water and nutrient absorption of substrate-grown tomato plants. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathidarehnijeh, E.; Nadeem, M.; Cheema, M.; Thomas, R.; Krishnapillai, M.; Galagedara, L. Current perspective on nutrient solution management strategies to improve the nutrient and water use efficiency in hydroponic system. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2023, 104, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.J.; Kang, T.G.; Lim, R.G.; Kim, H.W.; Kang, D.H.; Park, M.J.; Son, J.K. A study on drainage characteristics and load amount evaluation by crop type in a hydroponic cultivation facility of horticultural complex. J. Wetl. Res. 2021, 23, 352–363. [Google Scholar]
- Sanjuan-Delmás, D.; Josa, A.; Muñoz, P.; Gassó, S.; Rieradevall, J.; Gabarrell, X. Applying nutrient dynamics to adjust the nutrient-water balance in hydroponic crops. A case study with open hydroponic tomato crops from Barcelona. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 261, 108908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, Y.B. Mineral elements control of the nutrient solution in perlite culture of cucumber. J. Korea Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2001, 42, 497–500. [Google Scholar]
- Bando, K. Recirculating rockwool culture of tomato (2). Agric. Hortic. 1991, 66, 61–72. [Google Scholar]
- Gowda, P.H.; Mulla, D.J.; Jaynes, D.B. Simulated long-term nitrogen losses for a Midwestern agricultural watershed in the United States. Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 95, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trejo-Tellez, L.I.; Gomez-Merino, F.C. Nutrient Solutions for Hydroponic Systems. In Hydroponics—A Standard Methodology for Plant Biological Researches; Asao, T., Ed.; BoD-Books on Demand: Nordstedt, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Meric, M.K.; Tuzel, I.H.; Tuzel, Y.; Oztekin, G.B. Effects of nutrition systems and irrigation programs on tomato in soilless culture. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 99, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nederhoff, E.; Stanghellini, C. Water use efficiency of tomatoes in greenhouses and hydroponics. Pract. Hydroponics Greenh. 2010, 115, 52–59. [Google Scholar]
- Ruijs, M.N.A. Economic evaluation of closed production systems in glasshouse horticulture. Acta Hortic. 1995, 340, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, B.A. Hydroponics: Key to sustain agriculture in water stressed and urban environment. Pak. J. Agric. Agrol. Eng. Vet. Sci. 2006, 22, 53–57. [Google Scholar]
- Chiranjeevi, P.; Yeruva, D.K.; Kumar, A.K.; Mohan, S.V.; Varjani, S. Microbial Electrochemical Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]

| Hydroponic Systems | Region | Area (m2) | Cultivar | Substrate | Water Sterilization Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Open hydroponic systems | Haman | 6611 | Dafnis | Rockwool | H2O2 |
| Closed hydroponic systems | Gimje | 10,909 | Dokia | Coir | UV |
| Value | EC | pH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Open Hydroponics | Closed Hydroponics | Open Hydroponics | Closed Hydroponics | |
| Minimum | 2.5 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 5.0 |
| Maximum | 5.0 | 5.0 | 6.5 | 7.0 |
| Concentration | NO3-N (mg·L−1) | SO4 (mg·L−1) | Cl (mg·L−1) | PO4 (mg·L−1) | K (mg·L−1) | Ca (mg·L−1) | Na (mg·L−1) | Mg (mg·L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum. | 238.2 | 384.2 | 88.6 | 66.5 | 254.2 | 320.6 | 0.0 | 65.6 |
| Maximum | 392.3 | 864.5 | 425.4 | 189.9 | 391.0 | 481.0 | 183.9 | 158.0 |
| Fertilizer Type | Unit Price (USD/25 kg) | Control (T/ha) | 2 Weeks (T/ha) | 4 Weeks (T/ha) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KH2PO4 | 43.08 | 5.69 | 1.97 | 1.88 |
| KNO3 | 41.92 | 13.90 | 4.71 | 4.32 |
| K2SO4 | 20.38 | 7.69 | 3.10 | 2.88 |
| Ca(NO3)2·10H2O | 12.69 | 30.30 | 7.17 | 6.91 |
| MgSO4·7H2O | 7.23 | 15.60 | 2.72 | 2.69 |
| NH4NO3 | 29.23 | 0.66 | 1.15 | 1.08 |
| Summary of price (USD) | - | 59,985 | 19,585 | 18,392 |
| Benefit Factor (A) | Loss Factor (B) |
|---|---|
| (1) Fertilizer costs: USD 59,985/ha/year − USD 19,585/ha/year = USD 40,400/ha/year | (1) Closed hydroponic system installation cost and depreciation: USD 57,692/10 years = USD 5769.2/year |
| (2) Agricultural water (tap water) use costs: 4030 T/ha/year × USD 0.55/T = USD 2216.5/ha/year | (2) Closed hydroponic system management costs: (2–1) Analysis costs USD 76.9 × 2/month × 12 months = USD 1845.6/year (2–2) UV sterilization operating costs: EUR 0.09/m3/10 years × USD 1.1/EUR × 10,000 m2 = USD 990/10 years = USD 99.0/year |
| Total (A): USD 42,616.5 (Calculated as USD 40,400 + USD 2216.5) | Total (B): USD 7713.8 (Calculated as USD 5769.2 + USD 1845.6 + USD 99.0) |
| Estimated annual cost saving profit (A − B): 42,616.5 − 7713.8 = USD 34,902.7 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, M.Y.; Kim, D.; Kim, S.J.; Choi, G.L.; Rho, M.Y.; Hwang, H.S. Optimizing Nutrient Compensation Intervals Based on Ionic Monitoring in Drainage Water from Open and Closed Tomato Hydroponics. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2438. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102438
Lim MY, Kim D, Kim SJ, Choi GL, Rho MY, Hwang HS. Optimizing Nutrient Compensation Intervals Based on Ionic Monitoring in Drainage Water from Open and Closed Tomato Hydroponics. Agronomy. 2025; 15(10):2438. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102438
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Mi Young, Dongpil Kim, Se Jin Kim, Gyeong Lee Choi, Mi Young Rho, and Hee Sung Hwang. 2025. "Optimizing Nutrient Compensation Intervals Based on Ionic Monitoring in Drainage Water from Open and Closed Tomato Hydroponics" Agronomy 15, no. 10: 2438. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102438
APA StyleLim, M. Y., Kim, D., Kim, S. J., Choi, G. L., Rho, M. Y., & Hwang, H. S. (2025). Optimizing Nutrient Compensation Intervals Based on Ionic Monitoring in Drainage Water from Open and Closed Tomato Hydroponics. Agronomy, 15(10), 2438. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102438






