Agronomic Practices vs. Climate Factors: A Meta-Analysis of Influences on Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Corn and Soybean Fields
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Literature Review
Research Materials
2.2. Data Analysis
2.2.1. Effect of Land Management
2.2.2. Effect of Climate–Soil Factors
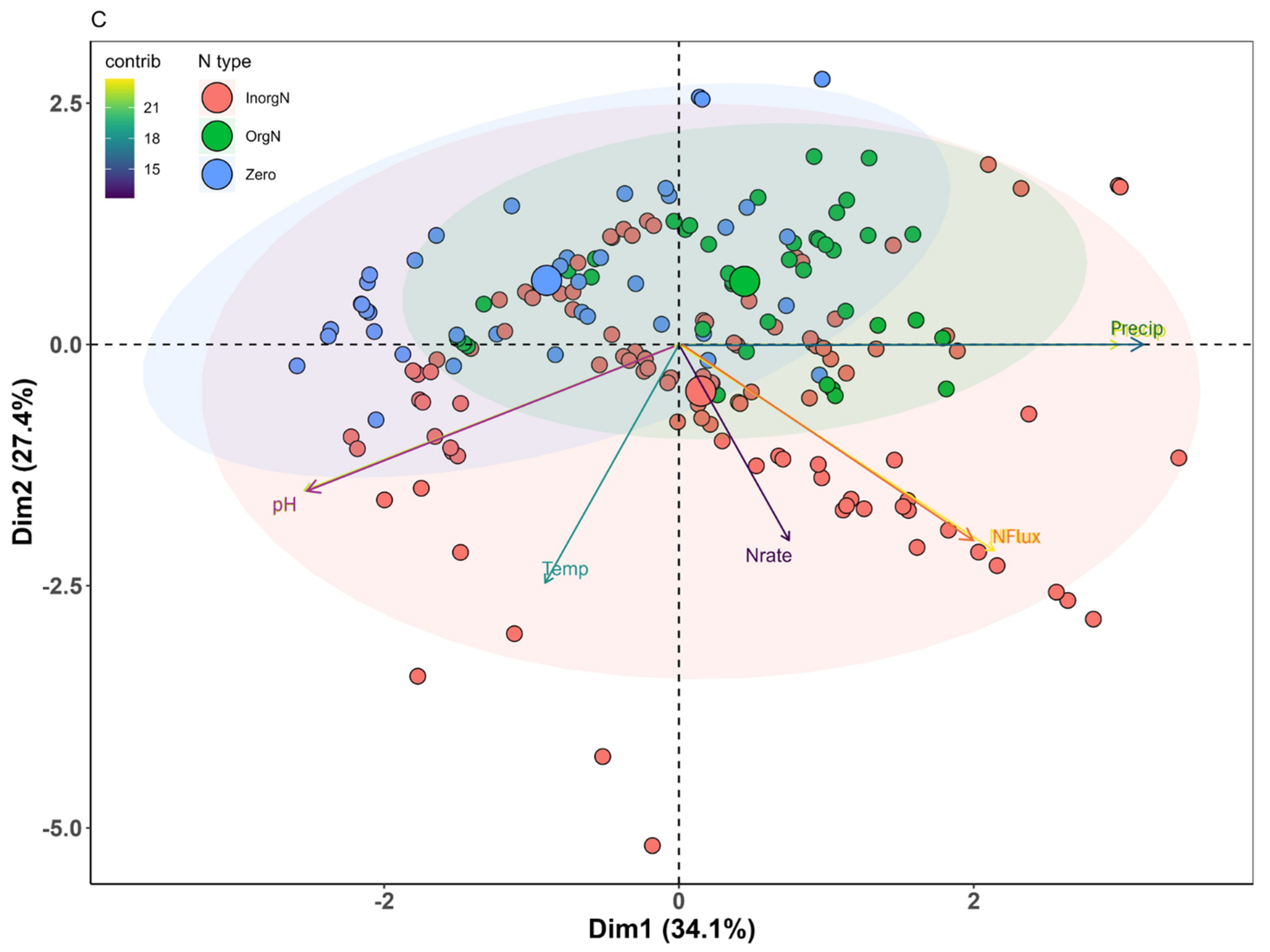
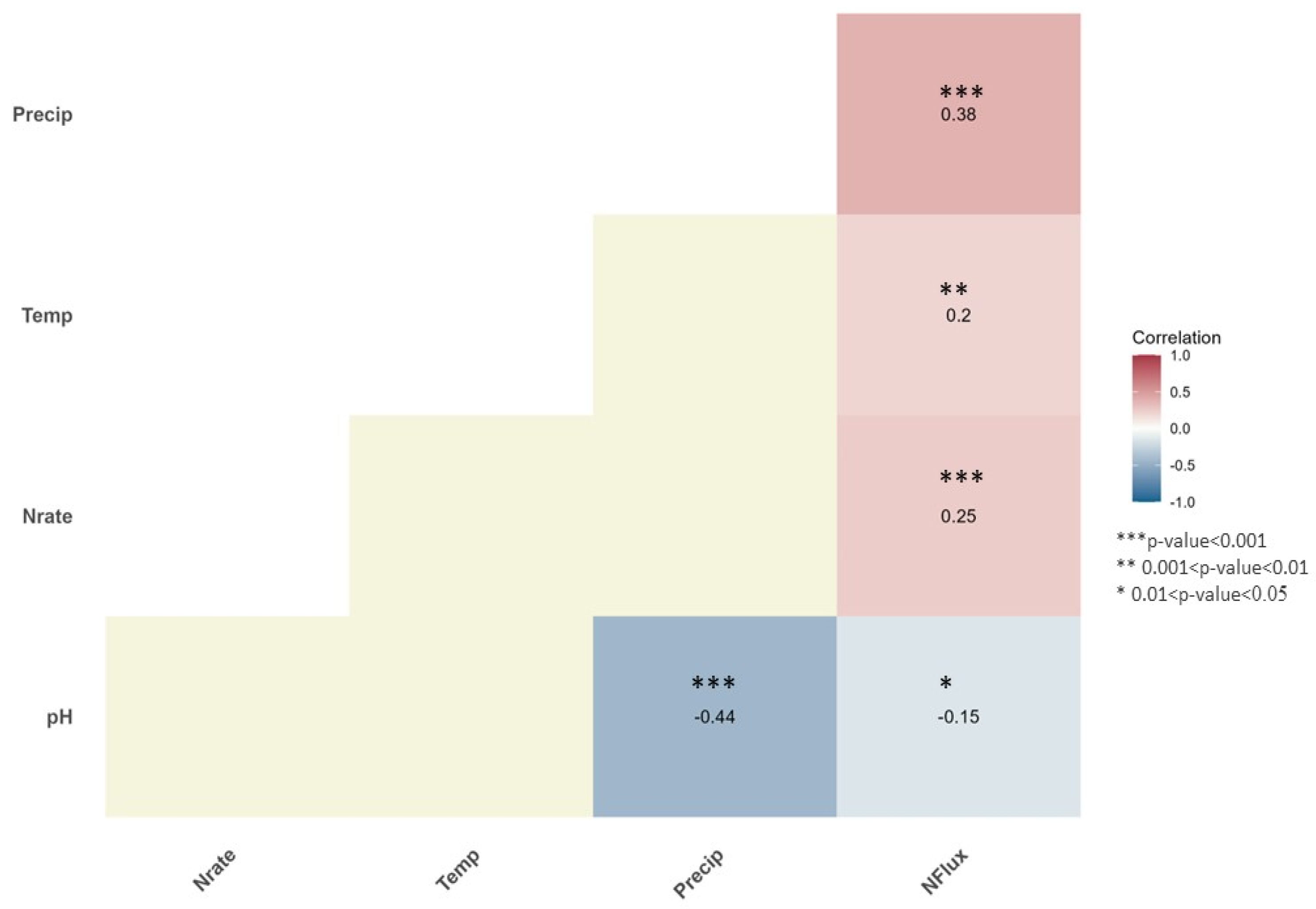
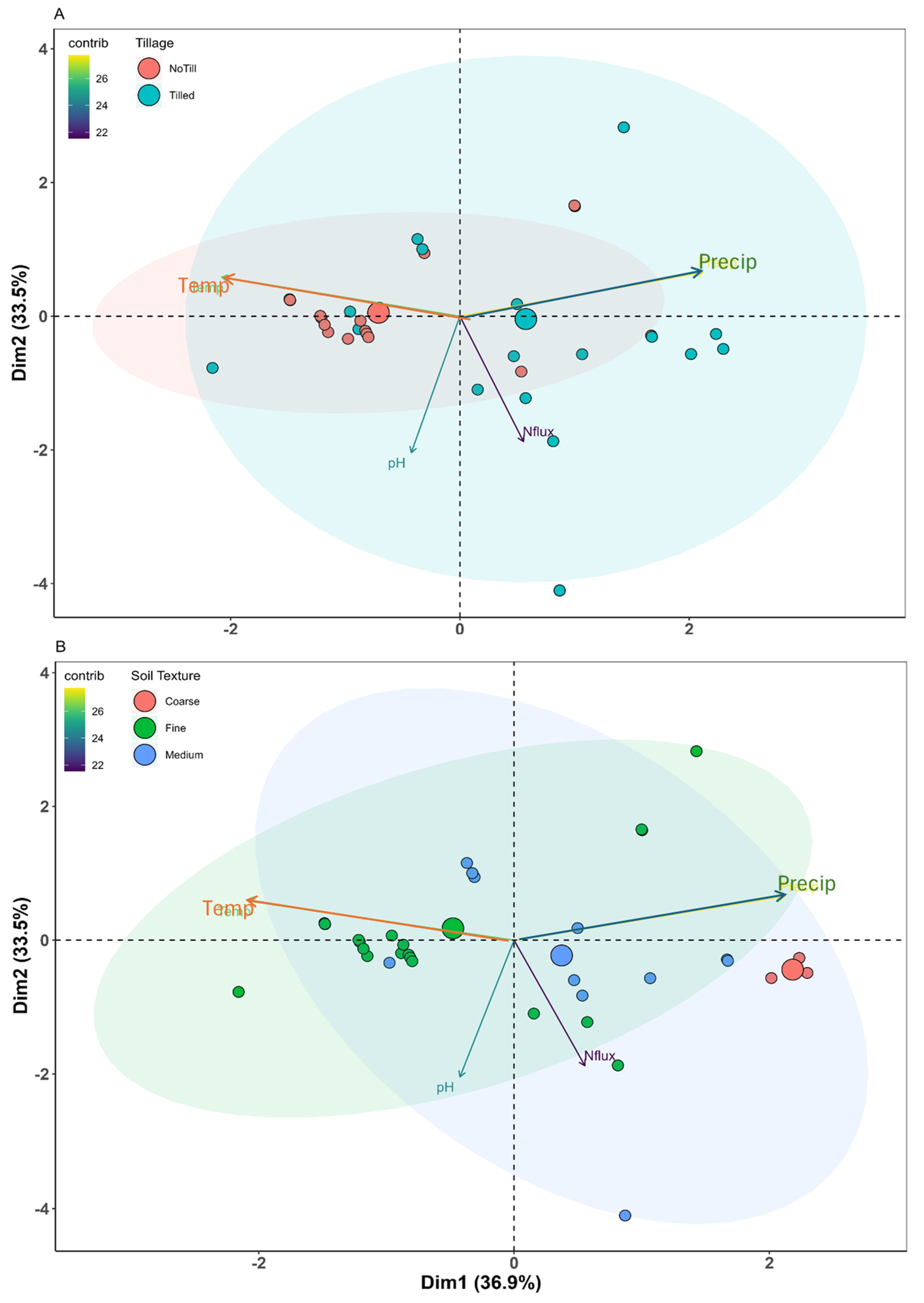
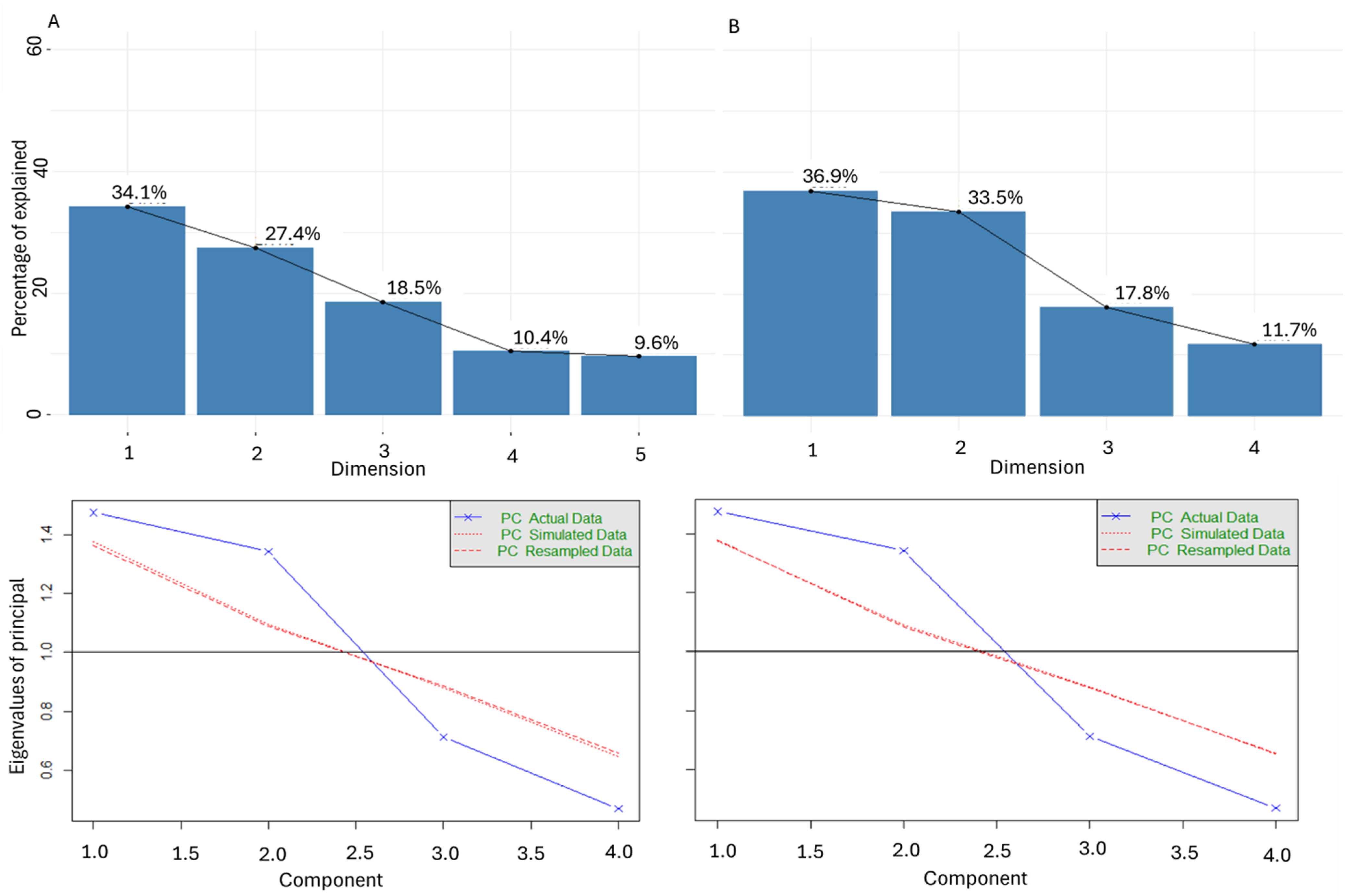
2.2.3. Principal Component Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
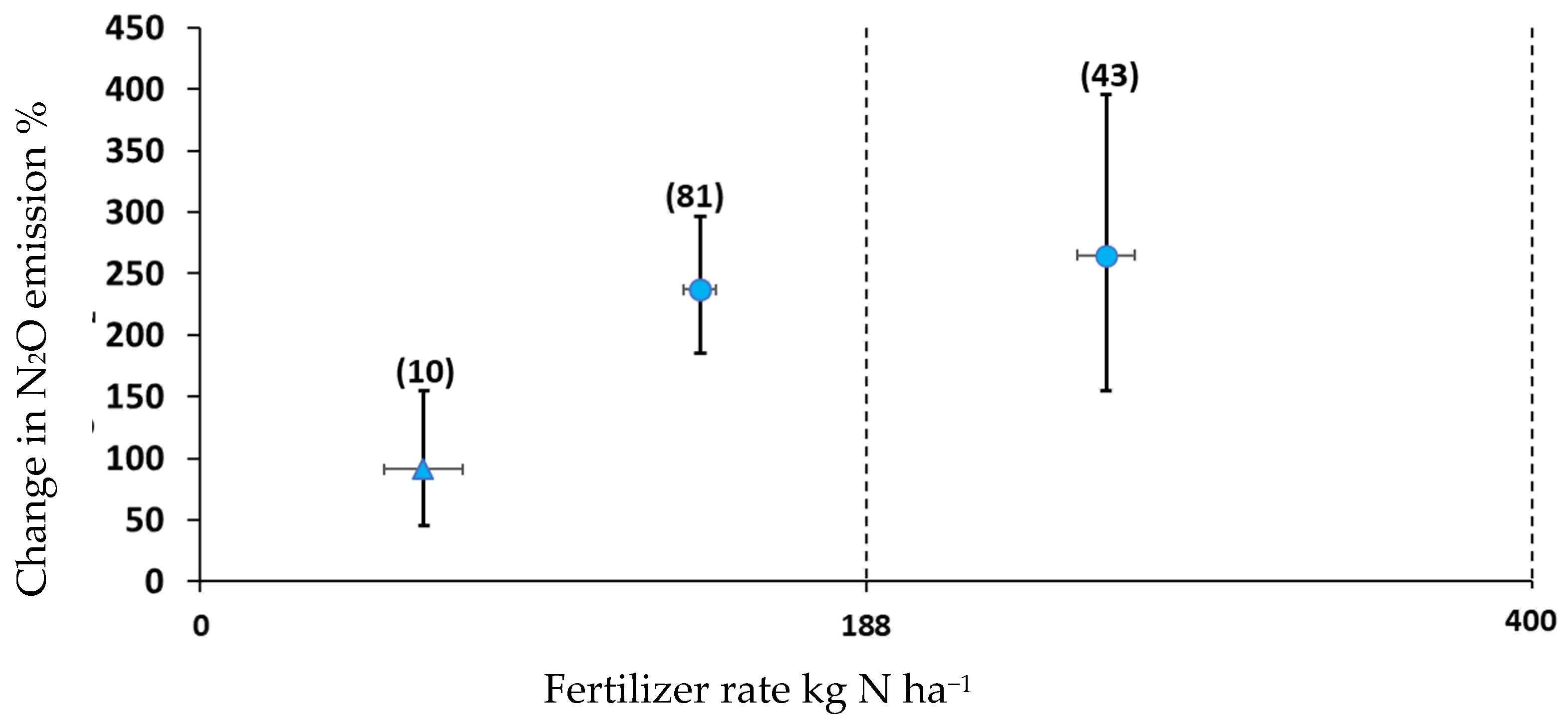
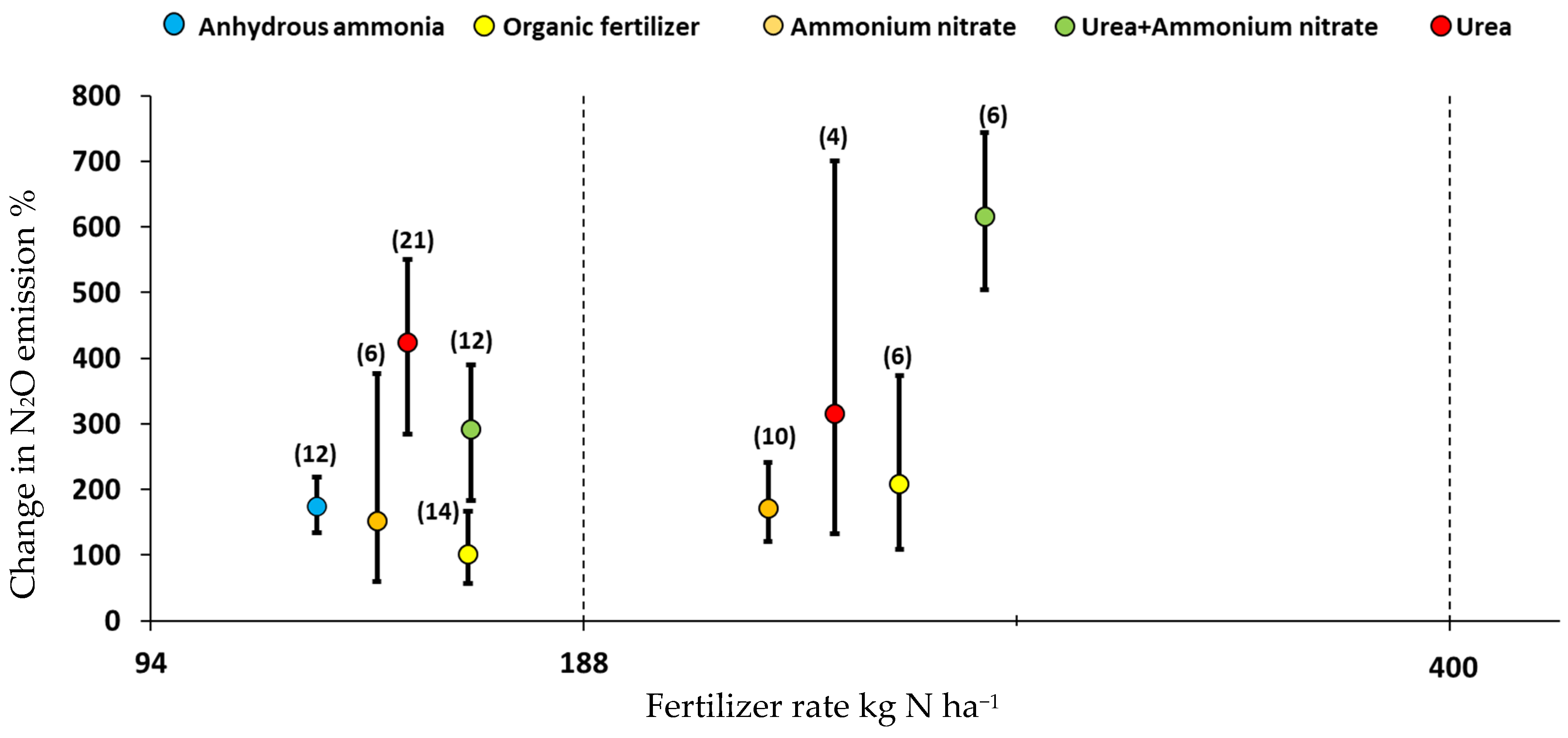
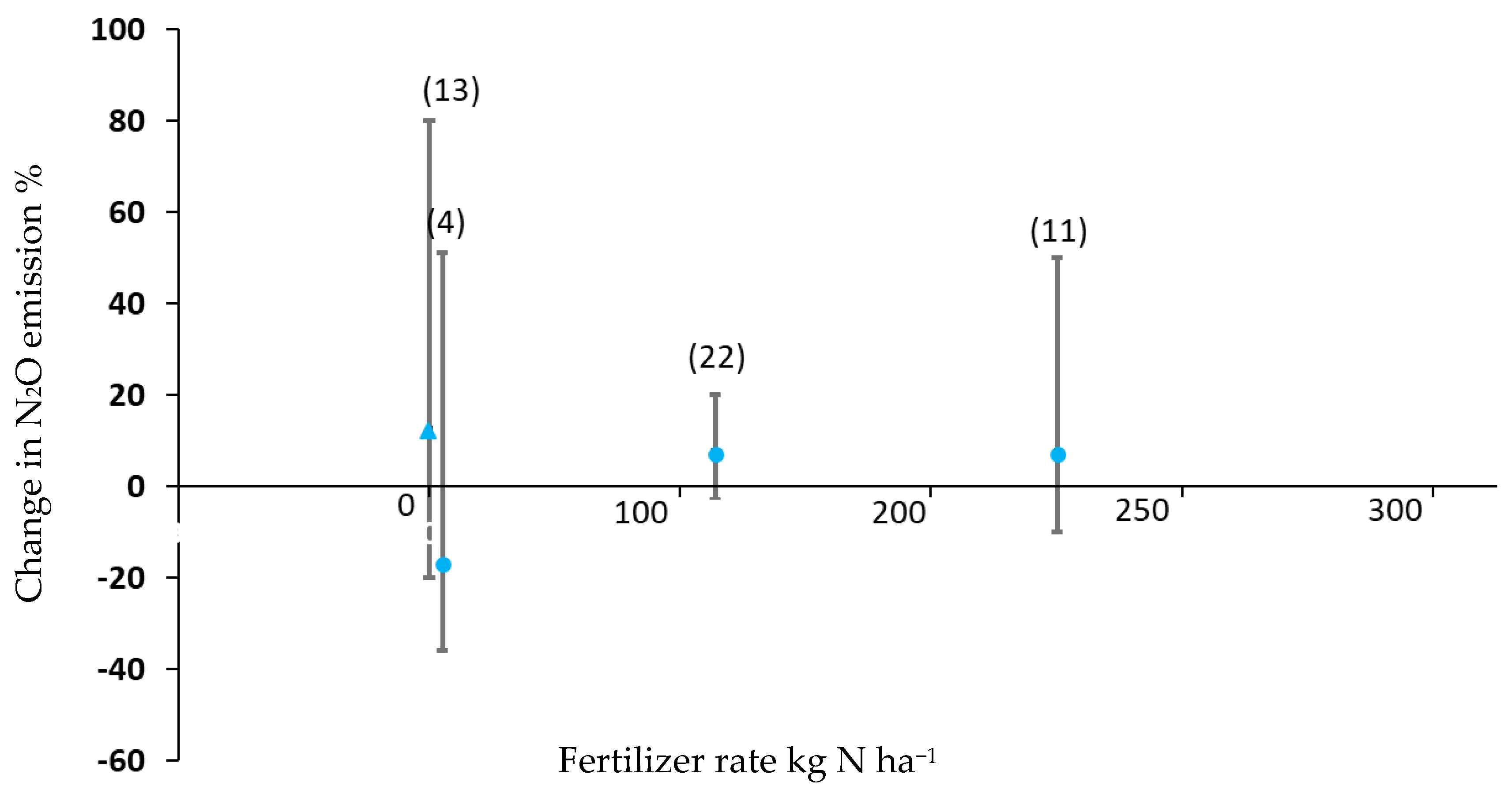
3.1. Nitrogen Fertilizer
| Land Use | N Rate | Mean N Rate | Obs 1 | N2O Emissions | 95% CI | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kg N ha−1 | kg N2O-N ha−1 Season−1 | |||||
| Corn 2 | 0 | 0.0 | 47 | 0.91 a | 0.56 to 1.39 | <0.0001 |
| <188 | 142.6 | 165 | 2.34 b | 1.82 to 2.93 | ||
| 188–400 | 243.9 | 95 | 2.45 b | 2.02 to 2.96 | ||
| Soybean 3 | 0 | 0.0 | 36 | 0.74 a | 0.41 to 1.30 | 0.028 |
| <188 | 55.8 | 14 | 1.87 b | 1.41 to 2.65 | ||
| Land Use | Fertilizer | Obs 1 | <188 kg ha−1 | 95% CI | 188–400 kg ha−1 | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <188 | 188–400 | ||||||
| Corn | Organic fertilizer 2 | 14 | 6 | 0.69 a | 0.45–0.96 | 1.12 a | 0.73–1.55 |
| Urea 3 | 21 | 4 | 1.65 b | 1.36–1.87 | 1.42 ab | 0.84–2.08 | |
| Urea + Ammonium nitrate 4 | 6 | 6 | 1.18 ab | 0.82–1.55 | 1.96 b | 1.80–2.13 | |
| Ammonium nitrate 5 | 6 | 10 | 1.3 ab | 0.84–1.63 | 1.0 a | 0.80–1.23 | |
| Anhydrous Ammonia 6 | 12 | - | 1.03 a | 0.84–1.16 | - | - | |
3.2. Tillage
3.3. Soil Texture
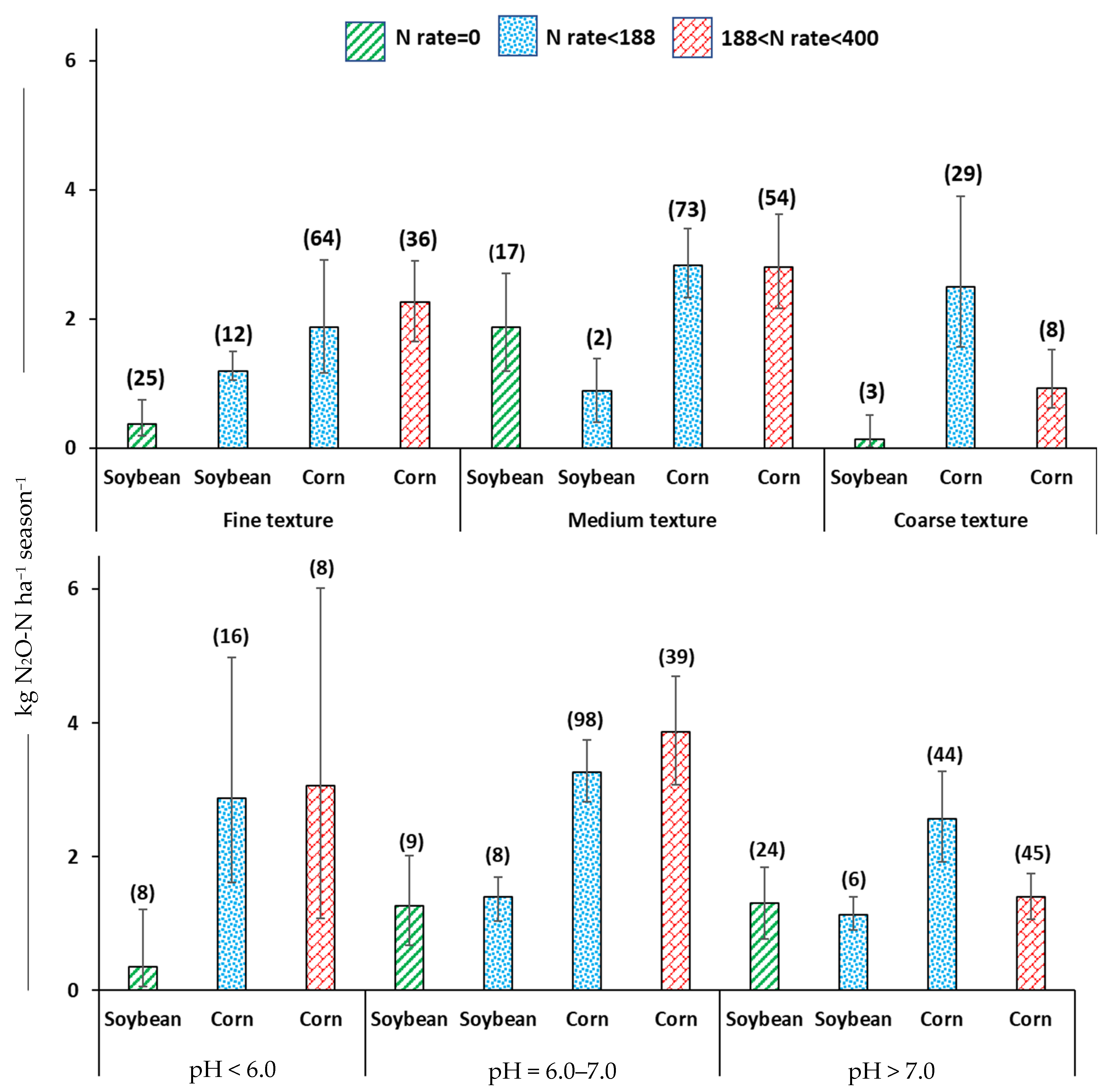
3.4. Soil pH
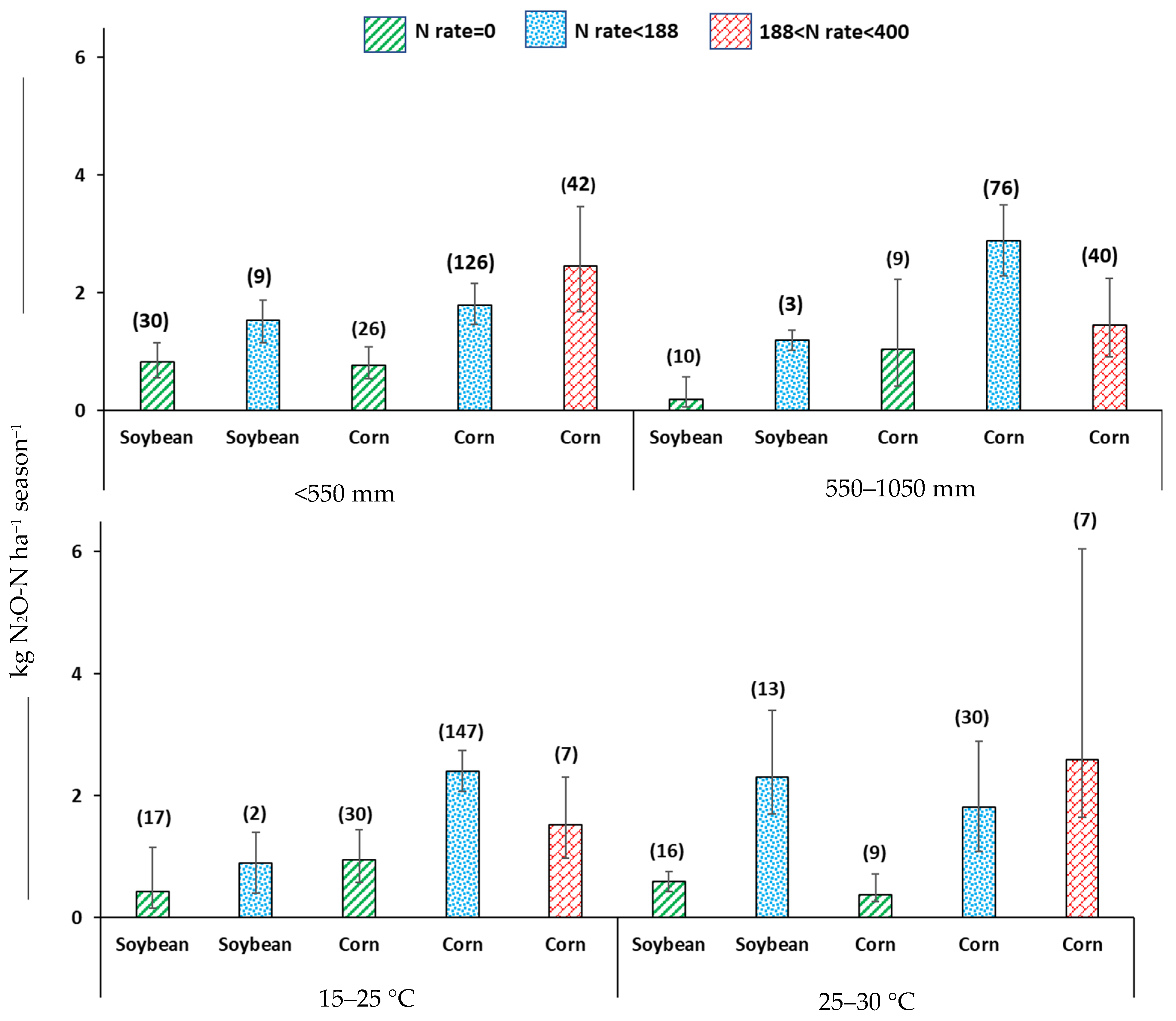
3.5. Precipitation and Temperature
3.6. Environmental Factors vs. Agronomic Activities
3.6.1. Key Drivers of N2O Emissions
3.6.2. Interactions and Implications
4. Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Summary for Policymakers. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021.
- Report of the Conference of the Parties on Its Twenty-Third Session, Held in Bonn from 6 to 18 November 2017. Addendum. Part Two: Action Taken by the Conference of the Parties at Its Twenty-Third Session; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Available online: https://unfccc.int/documents/65126 (accessed on 16 October 2022).
- Kwak, J.H.; Lim, S.S.; Baah-Acheamfour, M.; Choi, W.J.; Fatemi, F.; Carlyle, C.N.; Chang, S.X. Introducing trees to agricultural lands increases greenhouse gas emission during spring thaw in Canadian agroforestry systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baah-Acheamfour, M.; Carlyle, C.N.; Lim, S.S.; Bork, E.W.; Chang, S.X. Forest and grassland cover types reduce net greenhouse gas emissions from agricultural soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitzman, J.N.; Groffman, P.M.; Adler, P.R.; Dell, C.J.; Johnson, F.E.; Lerch, R.N.; Strickland, T.C. Drivers of hot spots and hot moments of denitrification in agricultural systems. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2021, 126, e2020JG006234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraha, M.; Gelfand, I.; Hamilton, S.K.; Chen, J.; Robertson, G.P. Legacy effects of land use on soil nitrous oxide emissions in annual crop and perennial grassland ecosystems. Ecol. Appl. 2018, 28, 1362–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, B.D.; Kaur, G.; Motavalli, P.P.; Zurweller, B.A.; Svoma, B.M. Soil greenhouse gas emissions from agroforestry and other land uses under different moisture regimes in lower Missouri River Floodplain soils: A laboratory approach. Agrofor. Syst. 2018, 92, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, J.; Udawatta, R.P.; Anderson, S.H. Soil Nitrous Oxide Emission from Agroforestry, Rowcrop, Grassland and Forests in North America: A Review. Agrofor. Syst. 2023, 97, 1465–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendis, S.S.; Udawatta, R.; Anderson, S.H.; Ansari, J.; Salceda, M. Effects of cover crops on soil thermal properties of a corn cropping system. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2022, 86, 1194–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Tao, B.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Yang, X.; Grove, J.H.; Ren, W. Simulating no-tillage effects on crop yield and green-house gas emissions in Kentucky corn and soybean cropping systems: 1980–2018. Agric. Syst. 2022, 197, 103355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, J.; Davis, M.P.; Anderson, S.H.; Eivazi, F.; Bardhan, S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Row Crop, Agroforestry, and Forested Land Use Systems in Floodplain Soils. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heil, J.; Vereecken, H.; Brüggemann, N. A review of chemical reactions of nitrification intermediates and their role in nitrogen cycling and nitrogen trace gas formation in soil. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2016, 67, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaufler, G.; Kitzler, B.; Schindlbacher, A.; Skiba, U.; Sutton, M.A.; Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S. Greenhouse gas emissions from European soils under different land use: Effects of soil moisture and temperature. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2010, 61, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinen, M. Simplified denitrification models: Overview and properties. Geoderma 2006, 133, 444–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggs, E.M.; Smales, C.L.; Bateman, E.J. Changing pH shifts the microbial sourceas well as the magnitude of N2O emission from soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2010, 46, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y.; Rousseau, A.N.; Wang, L.; Yan, B.; Gumiere, T.; Zhu, H. Identification of the alteration of riparian wetland on soil properties, enzyme activities and microbial communities following extreme flooding. Geoderma 2019, 337, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liang, Z.; He, X.; Wang, X.; Shi, X.; Zou, C.; Chen, X. The effects of controlled release urea on maize productivity and reactive nitrogen losses: A meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Moher, D. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2020, 372, n71. [Google Scholar]
- Soil Survey Staff, Natural Resources Conservation Service, United States Department of Agriculture. Web Soil Survey. Available online: https://websoilsurvey.nrcs.usda.gov/ (accessed on 12 February 2023).
- Schmidt, J.P.; Hong, N.; Dellinger, A.; Beegle, D.B.; Lin, H. Hillslope variability in corn response to nitrogen linked to in-season soil moisture redistribution. Agron. J. 2007, 99, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, L.V.; Gurevitch, J.; Curtis, P.S. The meta-analysis of response ratios in experimental ecology. Ecology 1999, 80, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linquist, B.; Van Groenigen, K.J.; Adviento-Borbe, M.A.; Pittelkow, C.; Van Kessel, C. An agronomic assessment of greenhouse gas emissions from major cereal crops. Glob. Change Biol. 2012, 18, 194–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Han, X.; Bol, R.; Smith, P.; Wu, W.; Meng, F. Impacts of natural factors and farming practices on greenhouse gas emissions in the North China Plain: A meta-analysis. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 6702–6715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drury, C.F.; Yang, X.M.; Reynolds, W.D.; McLaughlin, N.B. Nitrous oxide and carbon dioxide emissions from monoculture and rotational cropping of corn, soybean and winter wheat. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2008, 88, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Xu, R.; Canadell, J.G.; Thompson, R.L.; Winiwarter, W.; Suntharalingam, P.; Yao, Y. A comprehensive quantification of global nitrous oxide sources and sinks. Nature 2020, 586, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAOSTAT Database-Resources. Food Agriculture Organization of United Nations. Available online: https://www.fao.org/sustainability (accessed on 4 August 2023).
- Cecchin, A.; Pourhashem, G.; Gesch, R.W.; Lenssen, A.W.; Mohammed, Y.A.; Patel, S.; Berti, M.T. Environmental trade-offs of relay-cropping winter cover crops with soybean in a maize-soybean cropping system. Agric. Syst. 2021, 189, 103062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhady, A.; Hallmann, J.; Heuer, H. Symbiosis of soybean with nitrogen fixing bacteria affected by root lesion nematodes in a density-dependent manner. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyanage, A.; Grace, P.R.; Scheer, C.; de Rosa, D.; Ranwala, S.; Rowlings, D.W. Carbon limits non-linear response of nitrous oxide (N2O) to increasing N inputs in a highly-weathered tropical soil in Sri Lanka. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 292, 106808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, C.; Ming, H.; Oenema, O.; Schaefer, D.A.; Dong, W.; Li, X. Methane, carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide fluxes in soil profile under a winter wheat-summer maize rotation in the North China Plain. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvaro-Fuentes, J.; Arrúe, J.L.; Cantero-Martínez, C.; Isla, R.; Plaza-Bonilla, D.; Quílez, D. Fertilization scenarios in sprinkler-irrigated corn under mediterranean conditions: Effects on greenhouse gas emissions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2016, 80, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dungan, R.S.; Leytem, A.B.; Tarkalson, D.D. Greenhouse gas emissions from an irrigated cropping rotation with dairy manure utilization in a semiarid climate. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 1222–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, R.L.; Tanaka, D.L.; Archer, D.W.; Hanson, J.D. Fertilizer application timing influences greenhouse gas fluxes over a growing season. J. Environ. Qual. 2009, 38, 1569–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, K.; Zheng, X. Responses of N2O and CH4 fluxes to fertilizer nitrogen addition rates in an irrigated wheat-maize cropping system in northern China. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantigny, M.H.; Rochette, P.; Angers, D.A.; Bittman, S.; Buckley, K.; Massé, D.; Gasser, M.O. Soil nitrous oxide emissions following band-incorporation of fertilizer nitrogen and swine manure. J. Environ. Qual. 2010, 39, 1545–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardia, G.; Cangani, M.T.; Sanz-Cobena, A.; Junior, J.L.; Vallejo, A. Management of pig manure to mitigate NO and yield-scaled N2O emissions in an irrigated Mediterranean crop. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 238, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessard, R.; Rochette, P.; Gregorich, E.G.; Pattey, E.; Desjardins, R.L. Nitrous oxide fluxes from manure-amended soil under maize. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1996, 25, 1371–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosier, A.R.; Guenzi, W.D.; Schweizer, E.E. Soil losses of dinitrogen and nitrous oxide from irrigated crops in northeastern Colorado. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1986, 50, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelster, D.E.; Chantigny, M.H.; Rochette, P.; Angers, D.A.; Rieux, C.; Vanasse, A. Nitrous oxide emissions respond differently to mineral and organic nitrogen sources in contrasting soil types. J. Environ. Qual. 2012, 41, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almaraz, J.J.; Mabood, F.; Zhou, X.; Madramootoo, C.; Rochette, P.; Ma, B.L.; Smith, D.L. Carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide fluxes in corn grown under two tillage systems in southwestern Quebec. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2009, 73, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, M.; Guardia, G.; Recio, J.; Castellano-Hinojosa, A.; Ginés, C.; Bedmar, E.J.; Vallejo, A. Zinc-nitrogen co-fertilization influences N2O emissions and microbial communities in an irrigated maize field. Geoderma 2021, 383, 114735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abagandura, G.O.; Şentürklü, S.; Singh, N.; Kumar, S.; Landblom, D.G.; Ringwall, K. Impacts of crop rotational diversity and grazing under integrated crop-livestock system on soil surface greenhouse gas fluxes. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.B.; Sun, N. Soil CO2 and N2O emissions in maize growing season under different fertilizer regimes in an upland red soil region of South China. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bah, H.; Ren, X.; Wang, Y.; Tang, J.; Zhu, B. Characterizing greenhouse gas emissions and global warming potential of wheat-maize cropping systems in response to organic amendments in eutric regosols, China. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horák, J.; Aydin, E.; Igaz, D.; Šimanský, V.; Buchkina, N.; Balashov, E. Effects of biochar combined with n-fertilization on soil CO2 emissions, crop yields and relationships with soil properties. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 3597–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burzaco, J.P.; Smith, D.R.; Vyn, T.J. Nitrous oxide emissions in Midwest US maize production vary widely with band-injected N fertilizer rates, timing and nitrapyrin presence. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 035031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fangueiro, D.; Pereira, J.L.; Fraga, I.; Surgy, S.; Vasconcelos, E.; Coutinho, J. Band application of acidified slurry as an alternative to slurry injection in a Mediterranean double cropping system: Agronomic effect and gaseous emissions. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 267, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos, L.M.; Rice, C.W.; Tomlinson, P.J.; Mengel, D. Untangling soil-weather drivers of daily N2O emissions and fertilizer management mitigation strategies in no-till corn. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2021, 85, 1437–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkin, T.B.; Hatfield, J.L. Enhanced efficiency fertilizers: Effect on nitrous oxide emissions in Iowa. Agron. J. 2014, 106, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Mu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, P. Effect of nitrification inhibitors on mitigating N2O and NO emissions from an agricultural field under drip fertigation in the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, D.; Mu, Y. The influence of straw returning on N2O emissions from a maize-wheat field in the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijide, A.; Díez, J.A.; Sánchez-Martín, L.; López-Fernández, S.; Vallejo, A. Nitrogen oxide emissions from an irrigated maize crop amended with treated pig slurries and composts in a Mediterranean climate. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 121, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, L.; Qiu, J.J.; Liu, H.Y. Impacts of fertilization alternatives and crop straw incorporation on N2O emissions from a spring maize field in Northeastern China. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recio, J.; Vallejo, A.; Le-Noe, J.; Garnier, J.; García-Marco, S.; Álvarez, J.M.; Sanz-Cobena, A. The effect of nitrification inhibitors on NH3 and N2O emissions in highly N fertilized irrigated Mediterranean cropping systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, D.; Mu, Y. Impact of dicyandiamide on emissions of nitrous oxide, nitric oxide and ammonia from agricultural field in the North China Plain. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 40, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recio, J.; Montoya, M.; Ginés, C.; Sanz-Cobena, A.; Vallejo, A.; Alvarez, J.M. Joint mitigation of NH3 and N2O emissions by using two synthetic inhibitors in an irrigated cropping soil. Geoderma 2020, 373, 114423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Men, M.; Zheng, Y.; Noulas, C. Response of soil N2O emission and nitrogen utilization to organic matter in the wheat and maize rotation system. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, J.; Al-Kaisi, M.; Parkin, T. Greenhouse gas emissions dynamics as influenced by corn residue removal in continuous corn system. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2015, 79, 612–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilen, S.; Jacinthe, P.A.; Shrestha, R.; Jagadamma, S.; Nakajima, T.; Kendall, J.R.; Dick, W. Greenhouse gas fluxes in a no-tillage chronosequence in Central Ohio. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 218, 105313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oates, L.G.; Duncan, D.S.; Gelfand, I.; Millar, N.; Robertson, G.P.; Jackson, R.D. Nitrous oxide emissions during establishment of eight alternative cellulosic bioenergy cropping systems in the North Central United States. GCB Bioenergy 2016, 8, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlamini, J.C.; Cardenas, L.M.; Tesfamariam, E.H.; Dunn, R.M.; Evans, J.; Hawkins, J.M.B.; Collins, A.L. Soil N2O and CH4 emissions from fodder maize production with and without riparian buffer strips of differing vegetation. Plant Soil 2022, 477, 297–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Luesma, S.; Álvaro-Fuentes, J.; Plaza-Bonilla, D.; Arrúe, J.L.; Cantero-Martínez, C.; Cavero, J. Influence of irrigation time and frequency on greenhouse gas emissions in a solid-set sprinkler-irrigated maize under Mediterranean conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 221, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumadi, O.; Hala, Y.; Muis, A.B.D.; Ali, A.; Palennari, M.; Yagi, K.; Inubushi, K. Influences of chemical fertilizers and a nitrification inhibitor on greenhouse gas fluxes in a corn (Zea mays L.) field in Indonesia. Microbes Environ. 2008, 23, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, J.; Young, E.; Jokela, W.; Kieke, B. Manure application timing and Incorporation effects on ammonia and green-house gas emissions in corn. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehman, R.M.; Osborne, S.L. Greenhouse gas fluxes from no-till rotated corn in the upper midwest. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 170, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosongo, P.S.; Pelster, D.E.; Li, X.; Gaudel, G.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Hu, C. Greenhouse gas emissions response to fertilizer application and soil moisture in dry agricultural uplands of Central Kenya. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitombo, L.M.; Carmo, J.B.D.; Maria, I.C.D.; Andrade, C.A.D. Carbon sequestration and greenhouse gases emissions in soil under sewage sludge residual effects. Sci. Agric. 2015, 72, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duxbury, J.M.; McConnaughey, P.K. Effect of fertilizer source on denitrification and nitrous oxide emissions in a maize-field. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1986, 50, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duxbury, J.M.; Bouldin, D.R.; Terry, R.E.; Tate, R.L., III. Emissions of nitrous oxide from soils. Nature 1982, 298, 462–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochette, P.; Angers, D.A.; Chantigny, M.H.; Gagnon, B.; Bertrand, N. N2O fluxes in soils of contrasting textures fertilized with liquid and solid dairy cattle manures. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2008, 88, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner-Riddle, C.; Thurtell, G.W.; Kidd, G.K.; Beauchamp, E.G.; Sweetman, R. Estimates of nitrous oxide emissions from agricultural fields over 28 months. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1997, 77, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebarth, B.J.; Rochette, P.; Burton, D.L.; Price, M. Effect of fertilizer nitrogen management on N2O emissions in commercial corn fields. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2008, 88, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Nakajima, T.; Kadono, A.; Lal, R.; Fausey, N. Long-term tillage and drainage influences on greenhouse gas fluxes from a poorly drained soil of central Ohio. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2014, 69, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drury, C.F.; Woodley, A.L.; Reynolds, W.D.; Yang, X.M.; Phillips, L.A.; Rehmann, L.; Calder, W. Impacts of corn stover removal on carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide emissions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2021, 85, 1334–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosulski, T.; Stępień, W.; Wąs, A.; Szymańska, M. N2O and CO2 emissions from bare soil: Effect of fertilizer management. Agriculture 2020, 10, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.; Woo, S.H.; Park, K.D.; Chung, K.Y. Effect of no-tillage and conventional tillage practices on the nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions in an upland soil: Soil N2O emission as affected by the fertilizer applications. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2016, 59, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, M.; Gorji Anari, M.; Taghizadeh-Toosi, A.; Zaman, M.; Saronjic, N.; Mohammed, S.; Caballero-Calvo, A. Soil nitrous oxide emissions following crop residues management in corn-wheat rotation under conventional and no-tillage systems. Air Soil Water Res. 2022, 15, 11786221221128789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.S.; Amin, A.S.; Hamani, A.K.M.; Wang, G.S.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Liu, K.; Gao, Y. Effects of maize (Zea mays L.) inter-cropping with legumes on nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2021, 19, 1589–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omonode, R.A.; Vyn, T.J. Tillage and nitrogen source impacts on relationships between nitrous oxide emission and nitrogen recovery efficiency in corn. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snowdon, E.; Zebarth, B.J.; Burton, D.L.; Goyer, C.; Rochette, P. Growing season N2O emissions from two-year potato rotations in a humid environment in New Brunswick, Canada. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2013, 93, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterholz, W.R.; Kucharik, C.J.; Hedtcke, J.L.; Posner, J.L. Seasonal nitrous oxide and methane fluxes from grain-and forage-based production systems in Wisconsin, USA. J. Environ. Qual. 2014, 43, 1833–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnke, G.D.; Zuber, S.M.; Pittelkow, C.M.; Nafziger, E.D.; Villamil, M.B. Long-term crop rotation and tillage effects on soil greenhouse gas emissions and crop production in Illinois, USA. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 261, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Hopmans, J.W.; van Kessel, C.; King, A.P.; Evatt, K.J.; Louie, D.; Six, J. Tillage and seasonal emissions of CO2, N2O and NO across a seed bed and at the field scale in a Mediterranean climate. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 129, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ussiri, D.A.; Lal, R.; Jarecki, M.K. Nitrous oxide and methane emissions from long-term tillage under a continuous corn cropping system in Ohio. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 104, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo-Marín, N.; Quilez, D.; Guillen, M.; Isla, R. Feasibility of stabilised nitrogen fertilisers decreasing greenhouse gas emissions under optimal management in sprinkler irrigated conditions. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 290, 106725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruis, S.J.; Blanco-Canqui, H.; Jasa, P.J.; Jin, V.L. No-till farming and greenhouse gas fluxes: Insights from literature and experimental data. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 220, 105359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Yan, G.; Zhou, Z.; Zheng, X.; Deng, J. Annual emissions of nitrous oxide and nitric oxide from a wheat–maize cropping system on a silt loam calcareous soil in the North China Plain. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 48, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Cobena, A.; García-Marco, S.; Quemada, M.; Gabriel, J.L.; Almendros, P.; Vallejo, A. Do cover crops enhance N2O, CO2 or CH4 emissions from soil in Mediterranean arable systems? Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 466, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amours, J.; Pelster, D.E.; Gagné, G.; Wilkinson, J.A.; Chantigny, M.H.; Angers, D.A.; Halde, C. Combining reduced tillage and green manures minimized N2O emissions from organic cropping systems in a cool humid climate. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 341, 108205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodroad, L.L.; Keeney, D.R.; Peterson, L.A. Nitrous oxide emissions from agricultural soils in Wisconsin. J. Environ. Qual. 1984, 13, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Han, J.; Wen, X.; Liao, Y. Plastic-film mulching and urea types affect soil CO2 emissions and grain yield in spring maize on the Loess Plateau, China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhu, L.; Cheng, H.; Yue, S.; Li, S. Effects of biochar application on CO2 emissions from a cultivated soil under semiarid climate conditions in Northwest China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.U.; Lee, H.H.; Moon, S.M.; Han, H.R.; Hong, C.O. Nitrous oxide emissions and maize yield as influenced by nitrogen fertilization and tillage operations in upland soil. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2021, 64, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Greer, K.D.; Nafziger, E.D.; Villamil, M.B.; Pittelkow, C.M. Soil N2O emissions as affected by long-term residue removal and no-till practices in continuous corn. GCB Bioenergy 2018, 10, 972–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A. Nitrogen dynamics under corn fields in the Red River Valley of North Dakota. Agrosyst. Geosci. Environ. 2021, 4, e20178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce de Leon, M.A.; Dell, C.J.; Karsten, H.D. Nitrous oxide emissions from manured, no-till corn systems. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2021, 119, 405–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.L.; Yu, L.L.; Guan, A.M.; Zhou, X.Y.; Wang, Z.G.; Gou, Y.G.; Wang, J.W. Soil mineral nitrogen and yield-scaled soil N2O emissions lowered by reducing nitrogen application and intercropping with soybean for sweet maize production in southern China. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 2586–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmett, B.D.; O’Brien, P.L.; Malone, R.W.; Rogovska, N.; Kovar, J.L.; Kohler, K.; Parkin, T.B. Nitrate losses in subsurface drainage and nitrous oxide emissions from a winter camelina relay cropping system reveal challenges to sustainable intensification. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 339, 108136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkin, T.B.; Kaspar, T.C.; Jaynes, D.B.; Moorman, T.B. Rye cover crop effects on direct and indirect nitrous oxide emissions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2016, 80, 1551–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenka, S.; Lenka, N.K.; Singh, A.B.; Singh, B.; Raghuwanshi, J. Global warming potential and greenhouse gas emission under different soil nutrient management practices in soybean–wheat system of central India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 4603–4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Arora, P.; Tomer, R.; Mishra, S.V.; Bhatia, A.; Pathak, H.; Singh, J.P. Greenhouse gases emission from soils under major crops in Northwest India. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Qiao, Y.; Han, X.; Brancher Franco, R.; Burger, M. Frozen cropland soil in northeast China as source of N2O and CO2 emissions. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langeroodi, A.S.; Osipitan, O.A.; Radicetti, E. Benefits of sustainable management practices on mitigating greenhouse gas emissions in soybean crop (Glycine max). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 1593–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavin, T.K.; Griffis, T.J.; Baker, J.M.; Venterea, R.T. Impact of reduced tillage and cover cropping on the greenhouse gas budget of a maize/soybean rotation ecosystem. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 134, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphal, M.; Tenuta, M.; Entz, M.H. Nitrous oxide emissions with organic crop production depends on fall soil moisture. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 254, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, B.R.; Chalise, K.S.; Singh, S.; Lai, L.; Abagandura, G.O.; Kumar, S.; Jagadamma, S. Response of soil surface greenhouse gas fluxes to crop residue removal and cover crops under a corn–soybean rotation. J. Environ. Qual. 2018, 47, 1146–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorich, E.G.; McLaughlin, N.B.; Lapen, D.R.; Ma, B.L.; Rochette, P. Soil compaction, both an environmental and agronomic culprit: Increased nitrous oxide emissions and reduced plant nitrogen uptake. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 1913–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Xing, G.; Tsuruta, H.; Shen, G.; Shi, S.; Du, L. Field study on nitrous oxide emissions from upland cropping systems in China. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2002, 48, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelfand, I.; Shcherbak, I.; Millar, N.; Kravchenko, A.N.; Robertson, G.P. Long-term nitrous oxide fluxes in annual and perennial agricultural and unmanaged ecosystems in the upper Midwest USA. Glob. Change Biol. 2016, 22, 3594–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Z.; Huang, A.; Kimura, S.D.; Jin, T.; Wei, S.; Hatano, R. Linking N2O emission to soil mineral N as estimated by CO2 emission and soil C/N ratio. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 2593–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Baggs, E.M.; Dannenmann, M.; Kiese, R.; Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S. Nitrous oxide emissions from soils: How well do we understand the processes and their controls? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2013, 368, 20130122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorich, E.; Janzen, H.H.; Helgason, B.; Ellert, B. Nitrogenous gas emissions from soils and greenhouse gas effects. Adv. Agron. 2015, 132, 39–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehfest, E.; Bouwman, L. N2O and NO emission from agricultural fields and soils under natural vegetation: Summarizing available measurement data and modeling of global annual emissions. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2006, 74, 207–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, V.L.; Schmer, M.R.; Stewart, C.E.; Sindelar, A.J.; Varvel, G.E.; Wienhold, B.J. Long-term no-till and stover retention each decrease the global warming potential of irrigated continuous corn. Glob. Change Biol. 2017, 23, 2848–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortoletto-Santos, R.; Cavigelli, M.A.; Montes, S.E.; Schomberg, H.H.; Le, A.; Thompson, A.I.; Ribeiro, C. Oil-based polyurethane-coated urea reduces nitrous oxide emissions in a corn field in a Maryland loamy sand soil. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 249, 119329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiske, A.; Benckiser, G.; Ottow, J.C. Effect of the new nitrification inhibitor DMPP in comparison to DCD on nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions and methane (CH4) oxidation during 3 years of repeated applications in field experiments. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2001, 60, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Li, Z.J.; Wang, Y.; Ning, T.Y.; Zheng, Y.H.; Shi, Z.Q. Effects of soil tillage and returning straw to soil on wheat growth status and yield. Trans. CSAE 2007, 23, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Venterea, R.T.; Maharjan, B.; Dolan, M.S. Fertilizer source and tillage effects on yield-scaled nitrous oxide emissions in a corn cropping system. J. Environ. Qual. 2011, 40, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govaerts, B.; Fuentes, M.; Mezzalama, M.; Nicol, J.M.; Deckers, J.; Etchevers, J.D.; Sayre, K.D. Infiltration, soil moisture, root rot and nematode populations after 12 years of different tillage, residue and crop rotation managements. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 94, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaraz, J.J.; Zhou, X.; Mabood, F.; Madramootoo, C.; Rochette, P.; Ma, B.L.; Smith, D.L. Greenhouse gas fluxes associated with soybean production under two tillage systems in southwestern Quebec. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 104, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihara, J.; Martius, C.; Bationo, A.; Vlek, P.L. Effects of tillage and crop residue application on soybean nitrogen fixation in a tropical ferralsol. Agriculture 2011, 1, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Cai, Y.; Cai, Z.; Yagi, K.; Zheng, X. Nitrous oxide emissions from an intensively cultivated maize-wheat rotation soil in the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 373, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, J.; Kaya, B.; Soutoura, M.; Skiba, U.; Smith, R.; Niang, A.; Tabo, R. The contribution of agricultural practices to nitrous oxide emissions in semi-arid Mali. Soil Use Manag. 2008, 24, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosier, A.R.; Hutchinson, G.L. Nitrous oxide emissions from cropped fields. J. Environ. Qual. 1981, 10, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beare, M.H.; Gregorich, E.G.; St-Georges, P. Compaction effects on CO2 and N2O production during drying and rewetting of soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillard, R.; Duval, B.D.; Osterholz, W.R.; Kucharik, C.J. Simulated effects of soil texture on nitrous oxide emission factors from corn and soybean agroecosystems in Wisconsin. J. Environ. Qual. 2016, 45, 1540–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelster, D.E.; Chantigny, M.H.; Royer, I.; Angers, D.A.; Vanasse, A. Reduced tillage increased growing season N2O emissions from a fine but not a coarse textured soil under the cool, humid climate of eastern Canada. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 206, 104833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, P.R.; Baker, K.L.; Graceson, A.; Bonnett, S.A.F.; Ball, B.C.; Cloy, J.M. Use of a nitrification inhibitor reduces nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions from compacted grassland with different soil textures and climatic conditions. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 310, 107307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.J.; Spoor, G.; Thomasson, A.J. Vulnerability of subsoils in Europe to compaction: A preliminary analysis. Soil Tillage Res. 2003, 73, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yan, Z.; Ju, X.; Song, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Zhu-Barker, X. Quantifying nitrous oxide production rates from nitrification and denitrification under various moisture conditions in agricultural soils: Laboratory study and literature synthesis. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1110151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifah, S.; Foltz, M.E. The ratio of denitrification end-products were influenced by soil pH and clay content across different texture classes in Oklahoma soils. Front. Soil Sci. 2024, 4, 1342986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oishy, M.N.; Shemonty, N.A.; Fatema, S.I.; Mahbub, S.; Mim, E.L.; Raisa, M.B.H.; Anik, A.H. Unravelling the effects of climate change on the soil-plant-atmosphere interactions: A critical review. Soil Environ. Health 2025, 2, 100130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Land Use | Treatment | Obs 1 | No Fertilizer | 95% CI | <188 | 95% CI | 188–400 | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corn 2 | Tilled | 4, 23, 15 | 1.74 a | 0.83–2.19 | 1.53 a | 0.68–3.39 | 4.07 a | 2.96–5.54 |
| No-tilled | 4, 12, 11 | 2.49 a | 0.66–3.50 | 2.11 a | 0.78–4.45 | 4.67 a | 2.96–6.31 | |
| Soybean 3 | Tilled | 24 | 0.71 a | 0.33–1.49 | - | - | - | - |
| No-tilled | 15 | 0.73 a | 0.30–1.50 | - | - | - | - |
| Variable/Principle Component | PC1 | PC2 |
|---|---|---|
| pH | −0.55 | 0.37 |
| N-rate | 0.16 | 0.49 |
| Air-Temp (seasonal) | −0.20 | 0.60 |
| Precipitation (seasonal) | 0.65 | 0.00 |
| N-Flux | 0.46 | 0.52 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ansari, J.; Davis, M.P.; Li, C.; Bansal, S. Agronomic Practices vs. Climate Factors: A Meta-Analysis of Influences on Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Corn and Soybean Fields. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102358
Ansari J, Davis MP, Li C, Bansal S. Agronomic Practices vs. Climate Factors: A Meta-Analysis of Influences on Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Corn and Soybean Fields. Agronomy. 2025; 15(10):2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102358
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnsari, Jamshid, Morgan P. Davis, Chenhui Li, and Sheel Bansal. 2025. "Agronomic Practices vs. Climate Factors: A Meta-Analysis of Influences on Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Corn and Soybean Fields" Agronomy 15, no. 10: 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102358
APA StyleAnsari, J., Davis, M. P., Li, C., & Bansal, S. (2025). Agronomic Practices vs. Climate Factors: A Meta-Analysis of Influences on Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Corn and Soybean Fields. Agronomy, 15(10), 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102358







