Traceability and Heavy Metal Contamination in Agrosystems of Two Rice-Producing Areas of the Ecuadorian Coast
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Microwave-Assisted Digestion
2.3. Elemental Analysis by ICP-OES
2.4. Bioaccumulation and Translocation Factors
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Heavy Metals Detected in Rice Agrosystems
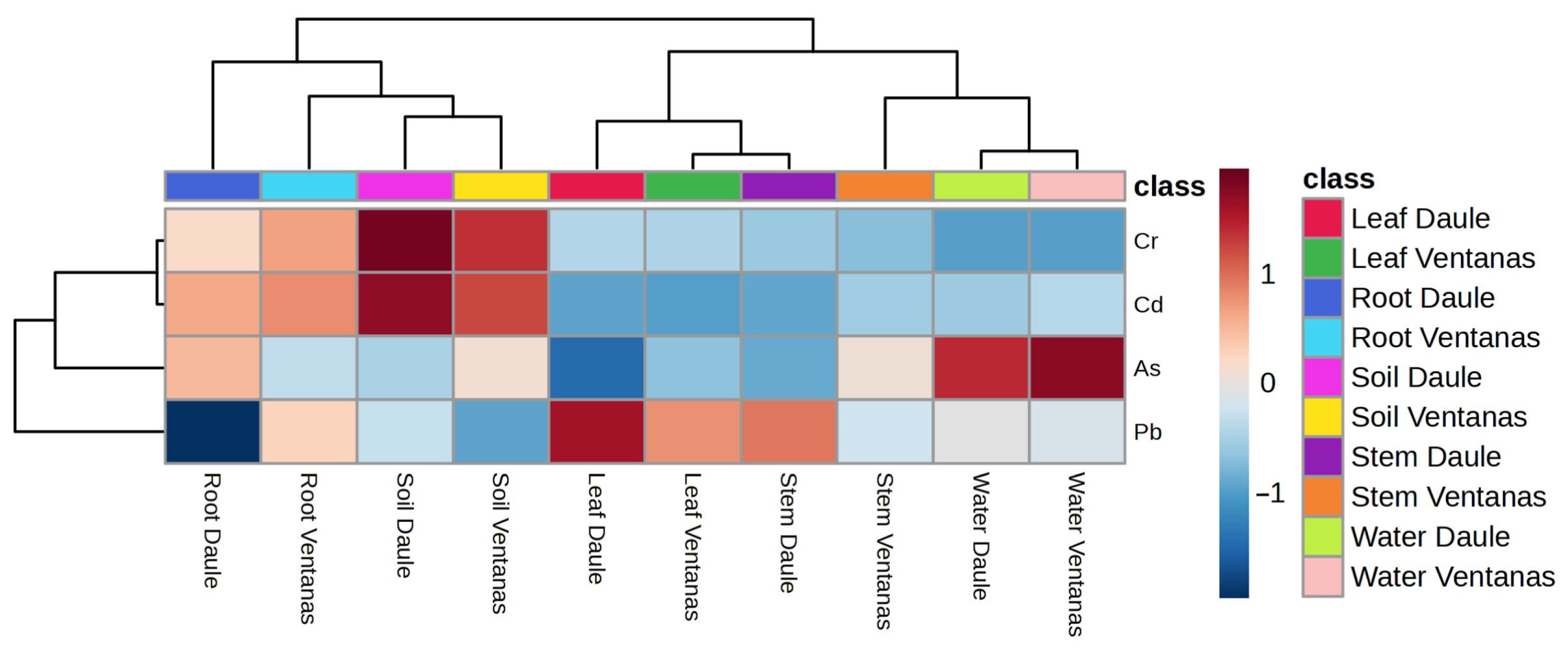
3.2. Multivariate Analysis of Heavy Metals Detected in Rice Agrosystems
3.3. Bioaccumulation and Translocation of Heavy Metals Detected in Rice Agrosystems
3.4. Heavy Metals Detected in Commercial Polished Rice Grains
4. Discussion
4.1. Trace Levels of Heavy Metals Detected in Rice Agrosystems
4.2. Comparison of Heavy Metals Levels with Regulatory Standards
4.3. Bioaccumulation and Translocation of as and Pb from Soil to Rice Plants
4.4. Trace Levels of Heavy Metals Detected in Commercial Rice
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| BAF | Bioaccumulation Factor |
| FAO | Food and Agriculture Organization |
| ICP-OS | Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy |
| NIOSH | National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health |
| OsHMA3 | Oryza sativa Heavy Metal ATPase 3 |
| PLSDA | Partial Least Squares-Discriminant Analysis |
| TF | Translocation Factor |
| TULSMA | Unified Text of the Secondary Legislation of the Ministry of Environment |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Sánchez-Sabando, C.F.; Sánchez-Urdaneta, A.B.; Sánchez-Mora, F.D.; Loor-Escobar, G.E.; Olivares, B.O. Fertilization for Growth or Feeding the Weeds? A Deep Dive into Nitrogen’s Role in Rice Dynamics in Ecuador. Life 2024, 14, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viteri, G.; Zambrano, C. Comercialización de Arroz En Ecuador: Análisis de La Evolución de Precios En El Eslabón Productor-Consumidor. Cienc. Tecnol. 2016, 9, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, Y.; Vergara, I.; Torres, O.; Díaz-Lagos, M.; González-Jimenez, E.E. Contaminación Por Metales Pesados: Implicaciones En Salud, Ambiente y Seguridad Alimentaria. Ing. Investig. Desarro. 2016, 16, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavides, Á.; Romero, B.; Pérez-Almeida, I.; Pernía, B. Evaluation of the Concentration of Heavy Metals in Vegetables from Ecuador. Bionatura 2022, 7, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves Peixoto, R.R.; Jadán-Piedra, C. Cadmium Pollution of Water, Soil, and Food: A Review of the Current Conditions and Future Research Considerations in Latin America. Environ. Rev. 2022, 30, 110–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, X.L.; Tierra, W.; Atiaga, O.; Guanoluisa, D.; Nunes, L.M.; Ferreira, T.O.; Ruales, J. Arsenic in Rice Agrosystems (Water, Soil and Rice Plants) in Guayas and Los Ríos Provinces, Ecuador. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 778–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atiaga, O.; Ruales, J.; Nunes, L.M.; Otero, X.L. Toxic Elements in Soil and Rice in Ecuador. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, M.S.; Hoy, K.S.; Schofield, J.R.M.; Uppal, J.S.; Lin, Y.; Lu, X.; Peng, H.; Le, X.C. Arsenic Speciation Analysis: A Review with an Emphasis on Chromatographic Separations. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 123, 115770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.; Anas, M.; Quraishi, U.M.; Malik, R.N. Arsenic Accumulation Pattern in Water-Soil-Rice Systems: A Study of Tolerance Mechanisms and Associated Health Risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 167916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amore, T.; Miedico, O.; Pompa, C.; Preite, C.; Iammarino, M.; Nardelli, V. Characterization and Quantification of Arsenic Species in Foodstuffs of Plant Origin by HPLC/ICP-MS. Life 2023, 13, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves Lange, C.; Revelo Monteiro, L.; Moreira Freire, B.; Fernandez Franco, D.; Oliveira de Souza, R.; Sacramento dos Reis Ferreira, C.; Centeno da Silva, J.J.; Lemos Batista, B. Mineral Profile Exploratory Analysis for Rice Grains Traceability. Food Chem. 2019, 300, 125145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, P.; Wei, X.; Peng, H.; Hu, L.; Zhu, X. Migration, Transformation of Arsenic, and Pollution Controlling Strategies in Paddy Soil-Rice System: A Comprehensive Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar Upadhyay, M.; Majumdar, A.; Suresh Kumar, J.; Srivastava, S. Arsenic in Rice Agro-Ecosystem: Solutions for Safe and Sustainable Rice Production. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2020, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, N.R.; Joardar, M.; Das, A.; Bhattacharya, P.; Roychowdhury, T. Current Opinion on the Role of Post-Harvesting and Cooking on Arsenic Mobility in Rice Grain, Its Surmounting Risk towards Human and Domestic Livestock with Sustained Management. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2024, 38, 100535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Carey, M.; Meharg, C.; Williams, P.N.; Signes-Pastor, A.J.; Triwardhani, E.A.; Pandiangan, F.I.; Campbell, K.; Elliott, C.; Marwa, E.M.; et al. Rice Grain Cadmium Concentrations in the Global Supply-Chain. Expo. Health 2020, 12, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bau, D.T.; Wang, T.S.; Chung, C.H.; Wang, A.S.S.; Jan, K.Y. Oxidative DNA Adducts and DNA-Protein Cross-Links Are the Major DNA Lesions Induced by Arsenite. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 753–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, L.M.; Otero, X. Quantification of Health Risks in Ecuadorian Population Due to Dietary Ingestion of Arsenic in Rice. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 27457–27468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). Cadmium—Overview. Available online: https://www.osha.gov/cadmium (accessed on 6 May 2025).
- Offor, J.I.; Madu, C.N.; Ugochukwu, U.C.; Anyanwu, D.C.; C.P., P.-M.; E.C, N. Lead Uptake and Bioconcentration in Selected Vegetables: Implications for Phytoremediation of Heavy Metals. Int. J. Res. Sci. Innov. 2024, 10, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikas, M.R.; Kumar, R.; Lathwal, M.; Kamboj, A. Effect and Responses of Lead Toxicity in Plants. In Lead Toxicity Mitigation: Sustainable Nexus Approaches; Kumar, N., Jha, A.K., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 211–241. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Mateos, S.; Pérez, L.V.; Córdova Suárez, M.A.; Cabrera-Riofrio, D.A. Heavy Metal Contamination in the Cotopaxi and Tungurahua Rivers: A Health Risk. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atiaga-Franco, O.L.; Otero, X.L.; Gallego-Picó, A.; Escobar-Castañeda, L.A.; Bravo-Yagüe, J.C.; Carrera-Villacrés, D. Analysis of Total Arsenic Content in Purchased Rice from Ecuador. Czech J. Food Sci. 2019, 37, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez, A.I.; Villamar, J.M.; Moncada, B.C.; Cajas, M.P.; Flores, L.R. Analysis of the Rice Agri-Food Chain in Ecuador [Análisis de La Cadena Agroalimentaria de Arroz En Ecuador]. Polo Conoc. 2023, 8, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedé, J.L.; Pena-Pereira, F. On the Greenness of Recent Microwave-Assisted Digestion Methods: An Evaluation with AGREEprep. Adv. Sample Prep. 2025, 14, 100177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.R.; Sharma, B.; Chawla, P.A.; Bhatia, R. Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES): A Powerful Analytical Technique for Elemental Analysis. Food Anal. Methods 2022, 15, 666–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, Y. Translocation and Accumulation of Heavy Metals from the Rhizoshphere Soil to the Medicinal Plant (Paeonia lactiflora Pall.) Grown in Bozhou, Anhui Province, China. Environ. Pollut. Bioavailab. 2023, 35, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Wishart, D.S. Web-Based Inference of Biological Patterns, Functions and Pathways from Metabolomic Data Using MetaboAnalyst. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 743–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mng’ong’o, M.E. Potentially Toxic Metals Partitioning in Paddy Rice in Usangu Agro-Ecosystem, Tanzania. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2023, 8, 100379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, L.; Han, J.; Katuwal, H.B.; Jiao, S.; Qiu, G. Human Dietary Exposure to Heavy Metals via Rice in Nepal. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Crespo, P.; Jiménez-Oyola, S.; Salgado-Almeida, B.; Zambrano-Anchundia, J.; Goyburo-Chávez, C.; González-Valoys, A.; Higueras, P. Trace Elements in Farmland Soils and Crops, and Probabilistic Health Risk Assessment in Areas Influenced by Mining Activity in Ecuador. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 4549–4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Maiti, S.K. Assessment of Potentially Toxic Heavy Metal Contamination in Agricultural Fields, Sediment, and Water from an Abandoned Chromite-Asbestos Mine Waste of Roro Hill, Chaibasa, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 2617–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, M.; Tierra, W.; Tupuna-Yerovi, D.S.; Guanoluisa, D.; Otero, X.L.; Ruales, J. Assessment of Cadmium and Lead Contamination in Rice Farming Soils and Rice (Oryza sativa L.) from Guayas Province in Ecuador. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, X.L.; Atiaga, O.; Estrella, R.; Tierra, W.; Ruales, J.; Zayas, L.; Souza, V.; Ferreira, T.O.; Nóbrega, G.N.; Oliveira, D.P.; et al. Geographical Variations in Arsenic Contents in Rice Plants from Latin America and the Iberian Peninsula in Relation to Soil Conditions. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 3351–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, D.L.; Bundschuh, J.; Birkle, P.; Armienta, M.A.; Cumbal, L.; Sracek, O.; Cornejo, L.; Ormachea, M. Arsenic in Volcanic Geothermal Fluids of Latin America. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 429, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, Y.; Lu, H.; Li, Z.; Zhuang, P.; Zou, B.; Xia, H.; Wang, F.; Wang, G.; Duan, J.; Zhang, J. Purification of Contaminated Paddy Fields by Clean Water Irrigation over Two Decades. Environ. Geochem. Health 2013, 35, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Wang, Z.; Williams, G.D.Z.; Dwyer, G.S.; Gatiboni, L.; Duckworth, O.W.; Vengosh, A. Evidence for the Accumulation of Toxic Metal(Loid)s in Agricultural Soils Impacted from Long-Term Application of Phosphate Fertilizer. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 167863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Huqail, A.A.; Kumar, P.; Eid, E.M.; Singh, J.; Arya, A.K.; Goala, M.; Adelodun, B.; Abou Fayssal, S.; Kumar, V.; Širić, I. Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals Contamination in Soil and Two Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Varieties Irrigated with Paper Mill Effluent. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawia, A.M.; Hui, S.; Zhou, L.; Li, H.; Tabassum, J.; Lai, C.; Wang, J.; Shao, G.; Wei, X.; Tang, S.; et al. Inorganic Arsenic Toxicity and Alleviation Strategies in Rice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipriani-Avila, I.; Molinero, J.; Jara-Negrete, E.; Barrado, M.; Arcos, C.; Mafla, S.; Custode, F.; Vilaña, G.; Carpintero, N.; Ochoa-Herrera, V. Heavy Metal Assessment in Drinking Waters of Ecuador: Quito, Ibarra and Guayaquil. J. Water Health 2020, 18, 1050–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environment of Ecuador. BooK VI, Annex 1: Water Environmental Quality Standard. In Unified Text of the Secondary Legislation of the Ministry of Environment (TULSMA); Official Registry No. 316; Ministry of Environment of Ecuador: Quito, Ecuador, 2017; pp. 286–339. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Environment of Ecuador. BooK VI, Annex 2: Soil Environmental Quality Standard. In Unified Text of the Secondary Legislation of the Ministry of Environment (TULSMA); Official Registry No. 316; Ministry of Environment of Ecuador: Quito, Ecuador, 2017; pp. 341–370. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, Z.; Imran, M.; Natasha, N.; Murtaza, B.; Amjad, M.; Shah, N.S.; Khan, Z.U.H.; Ahmad, I.; Ahmad, S. Distribution and Health Risk Assessment of Trace Elements in Ground/Surface Water of Kot Addu, Punjab, Pakistan: A Multivariate Analysis. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preonty, N.E.J.; Hassan, M.N.; Reza, A.H.M.S.; Rasel, M.I.A.; Mahim, M.M.A.; Jannat, M.F.T. Pollution and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Surface Water of the Industrial Region in Gazipur, Bangladesh. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2025, 7, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO/WHO Codex Alimentariu. General Standard for Contaminants and Toxins in Food and Feed (CODEX STAN 193-1995, Rev 2014); FAO: Rome, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Marrugo-Negrete, J.; Pinedo-Hernández, J.; Díez, S. Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution, Spatial Distribution and Origin in Agricultural Soils along the Sinú River Basin, Colombia. Environ. Res. 2017, 154, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alloway, B.J. (Ed.) Heavy Metals in Soils: Trace Metals and Metalloids in Soils and Their Bioavailability; Environmental Pollution; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 22, ISBN 978-94-007-4469-1. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; Kaur, I.; Nagpal, A.K. Contamination of Rice Crop with Potentially Toxic Elements and Associated Human Health Risks-a Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 12282–12299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Pan, J.; Yang, Y.; Cao, Z.; Xu, P.; Chen, M.; Guan, M. Water Management Affects Arsenic Uptake and Translocation by Regulating Arsenic Bioavailability, Transporter Expression and Thiol Metabolism in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 206, 111208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimi, G.; Kolahchi, Z.; Charkhabi, A. Uptake and Translocation of Some Heavy Metals by Rice Crop (Oryza sativa) in Paddy Soils. Agriculture (Pol’nohospodarstvo) 2017, 63, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.B.V.; Nascimento, C.W.A.; Alvarez, A.M.; Araújo, P.R.M. Inputs of Rare Earth Elements in Brazilian Agricultural Soils via P-Containing Fertilizers and Soil Correctives. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 232, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.C.; Zhang, Q.C.; Yan, C.A.; Tang, G.Y.; Zhang, M.Y.; Ma, L.Q.; Gu, R.H.; Xiang, P. Heavy Metal(Loid)s in Agriculture Soils, Rice, and Wheat across China: Status Assessment and Spatiotemporal Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 882, 163361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Deng, S.; Tan, D.; Long, J.; Lei, M. Heavy Metal Distribution, Translocation, and Human Health Risk Assessment in the Soil-Rice System around Dongting Lake Area, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 17655–17665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukusamude, C.; Sricharoen, P.; Limchoowong, N.; Kongsri, S. Heavy Metals and Probabilistic Risk Assessment via Rice Consumption in Thailand. Food Chem. 2021, 334, 127402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bascuñán, K.A.; Orosteguí, C.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Roncoroni, L.; Doneda, L.; Elli, L.; Araya, M. Heavy Metal and Rice in Gluten-Free Diets: Are They a Risk? Nutrients 2023, 15, 2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, R.; Bashir, K.; Ishimaru, Y.; Nishizawa, N.K.; Nakanishi, H. The Role of Heavy-Metal ATPases, HMAs, in Zinc and Cadmium Transport in Rice. Plant Signal Behav. 2012, 7, 1605–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, Z.; Zulkafflee, N.S.; Mohd Redzuan, N.A.; Selamat, J.; Ismail, M.R.; Praveena, S.M.; Tóth, G.; Abdull Razis, A.F. Understanding Potential Heavy Metal Contamination, Absorption, Translocation and Accumulation in Rice and Human Health Risks. Plants 2021, 10, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Liu, H.; Wu, J.; Gao, X.; Nyasha, N.K.; Cai, G.; Zhang, W. Bi-Directional Pollution Characteristics and Ecological Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soil and Crops in Wanjiang Economic Zone, Anhui Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Origin | Sample | As | Cd | Pb | Cr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daule | Water | 1.12 ± 0.20 c (0.80–1.30) | ND | 0.38 ± 0.09 e (0.30–0.50) | 0.53 ± 0.14 d (0.40–0.70) |
| Soil | 1.50 ± 0.31 c (1.10–2.00) | 1.45 ± 0.23 a (1.20–1.80) | 1.23 ± 0.42 bcd (0.80–1.80) | 26.12 ± 3.81 a (21.30–30.40) | |
| Root | 4.53 ± 1.12 a (2.20–5.60) | 0.88 ± 0.31 c (0.30–1.30) | 1.03 ± 0.33 d (0.50–1.50) | 13.20 ± 4.35 c (5.20–19.80) | |
| Stem | 0.95 ± 0.49 c (0.30–1.80) | ND | 1.33 ± 0.20 bcd (1.10–1.70) | 2.27 ± 0.80 d (1.50–3.90) | |
| Leaf | 0.67 ± 0.26 c (0.30–1.00) | ND | 1.85 ± 0.23 b (1.60–2.20) | 3.17 ± 1.32 d (1.90–5.10) | |
| Ventanas | Water | 0.85 ± 0.08 c (0.80–1.00) | ND | 0.25 ± 0.08 e (0.20–0.40) | 0.37 ± 0.14 d (0.20–0.60) |
| Soil | 2.82 ± 0.87 b (2.10–4.60) | 1.22 ± 0.07 ab (1.10–1.30) | 1.20 ± 0.25 cd (0.90–1.60) | 24.28 ± 1.81 ab (21.90–27.40) | |
| Root | 3.30 ± 0.80 b (2.20–4.40) | 1.17 ± 0.07 b (1.10–1.30) | 2.90 ± 0.32 a (2.40–3.40) | 21.30 ± 0.97 b (20.20–22.50) | |
| Stem | 1.42 ± 0.40 c (1.00–2.10) | 0.05 ± 0.05 d (ND–0.10) | 0.87 ± 0.33 de (0.70–1.60) | 1.92 ± 0.79 d (1.30–3.60) | |
| Leaf | 1.28 ± 0.39 c (0.80–1.70) | ND | 1.70 ± 0.47 bc (0.80–2.20) | 3.53 ± 1.28 d (1.40–5.10) |
| Origin | Metal | Bioaccumulation Factor (BAF) | Translocation Factor (TF) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Root | Stem | Leaf | Plant | Stem | Leaf | Aerial Parts | ||
| Daule | As | 3.02 | 0.63 | 0.44 | 4.10 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 0.36 |
| Cd | 0.61 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.61 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Pb | 0.84 | 1.08 | 1.50 | 3.42 | 1.29 | 1.79 | 3.08 | |
| Cr | 0.51 | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0.71 | 0.17 | 0.24 | 0.41 | |
| Ventanas | As | 1.17 | 0.50 | 0.46 | 2.13 | 0.43 | 0.39 | 0.82 |
| Cd | 0.96 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.04 | |
| Pb | 2.42 | 0.72 | 1.42 | 4.56 | 0.30 | 0.59 | 0.89 | |
| Cr | 0.88 | 0.08 | 0.15 | 1.10 | 0.08 | 0.17 | 0.26 | |
| Origin | Sample | As | Cd | Pb | Cr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daule | rice grains | 0.92 ± 0.94 (ND–2.50) | 0.02 ± 0.04 (ND–0.10) | 0.17 ± 0.09 (ND–0.30) | 0.08 ± 0.04 (ND–0.10) |
| Ventanas | rice grains | 0.68 ± 1.04 (ND–2.70) | ND | 0.10 ± 0.08 (ND–0.20) | 0.27 ± 0.29 (0.10–0.90) |
| Heavy Metal | FAO/WHO | TULSMA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil (mg/kg) | Water (mg/L) | Soil 1 (mg/kg) | Water 2 (mg/L) | |
| As | 1.00 | 0.01 | 5.00 | 0.10 |
| Cd | 0.34 | 0.03 | 0.50 | 0.01 |
| Pb | 81.00 | 0.05 | 20.00 | 0.05 |
| Cr | 31.00 | 0.05 | 25.00 | 0.10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaime-Carvajal, J.; Naranjo-Morán, J.; Vinces, K.C.; Ballesteros, J.; Espinoza-Lozano, F.; Chóez-Guaranda, I.; Pérez-Martinez, S. Traceability and Heavy Metal Contamination in Agrosystems of Two Rice-Producing Areas of the Ecuadorian Coast. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2359. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102359
Jaime-Carvajal J, Naranjo-Morán J, Vinces KC, Ballesteros J, Espinoza-Lozano F, Chóez-Guaranda I, Pérez-Martinez S. Traceability and Heavy Metal Contamination in Agrosystems of Two Rice-Producing Areas of the Ecuadorian Coast. Agronomy. 2025; 15(10):2359. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102359
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaime-Carvajal, Jairo, Jaime Naranjo-Morán, Kevin Cedeño Vinces, José Ballesteros, Fernando Espinoza-Lozano, Ivan Chóez-Guaranda, and Simón Pérez-Martinez. 2025. "Traceability and Heavy Metal Contamination in Agrosystems of Two Rice-Producing Areas of the Ecuadorian Coast" Agronomy 15, no. 10: 2359. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102359
APA StyleJaime-Carvajal, J., Naranjo-Morán, J., Vinces, K. C., Ballesteros, J., Espinoza-Lozano, F., Chóez-Guaranda, I., & Pérez-Martinez, S. (2025). Traceability and Heavy Metal Contamination in Agrosystems of Two Rice-Producing Areas of the Ecuadorian Coast. Agronomy, 15(10), 2359. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102359







