Determination of Gingerols and Shogaols Content from Ginger (Zingiber officinale Rosc.) through Microwave-Assisted Extraction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Natural Matrix and Reagents Used
2.2. Microwave-Assisted Extraction
2.3. Gingerols and Shogaols Analyzed and Quantified via UHPLC-Q-ToF-MS
2.4. Experimental Design: BBD
3. Results and Discussion
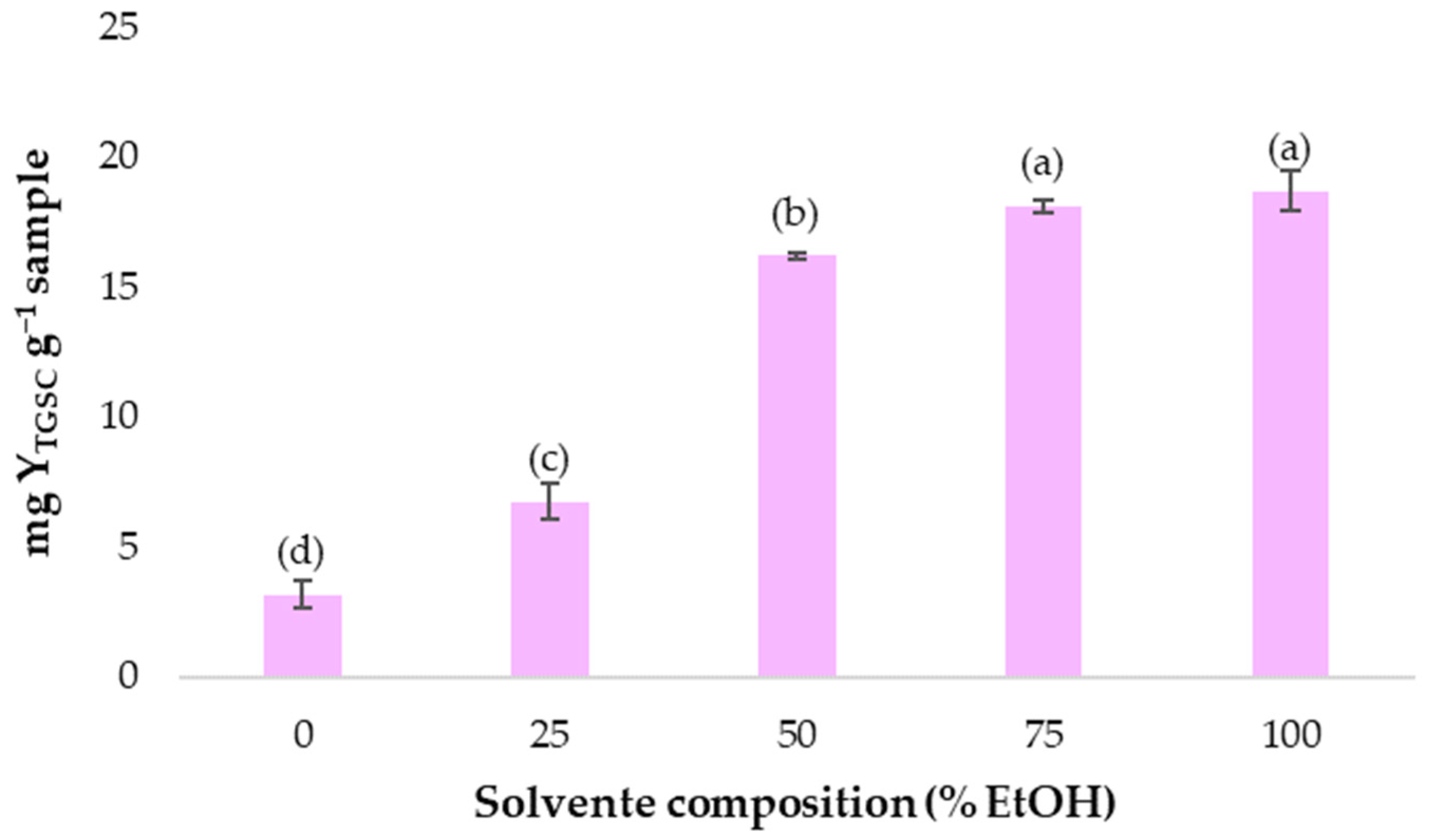
3.1. Establishing the Optimal Range of Ethanol Percentage in Water to Be Used as a Solvent
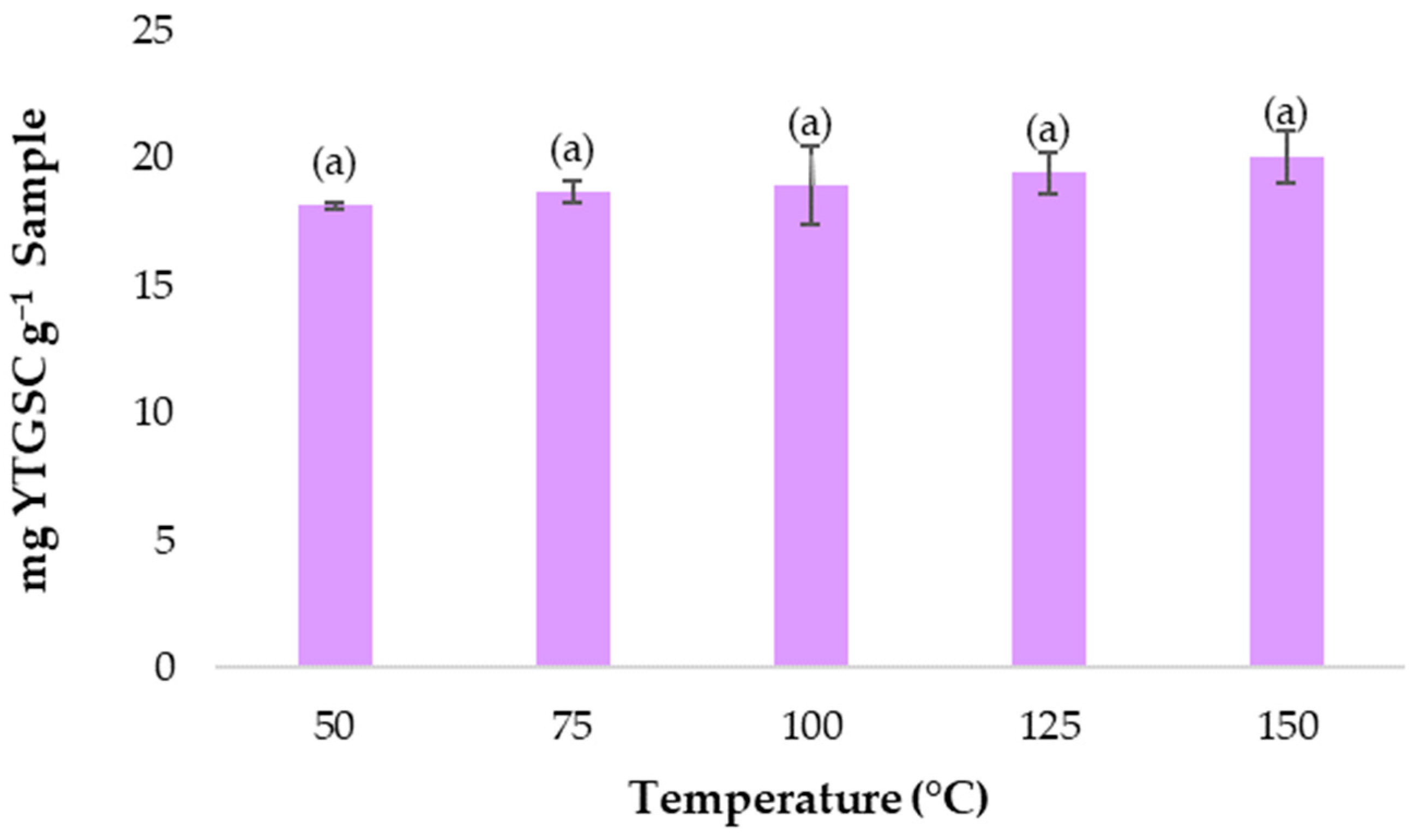
3.2. Establishing the Extraction Temperature Range
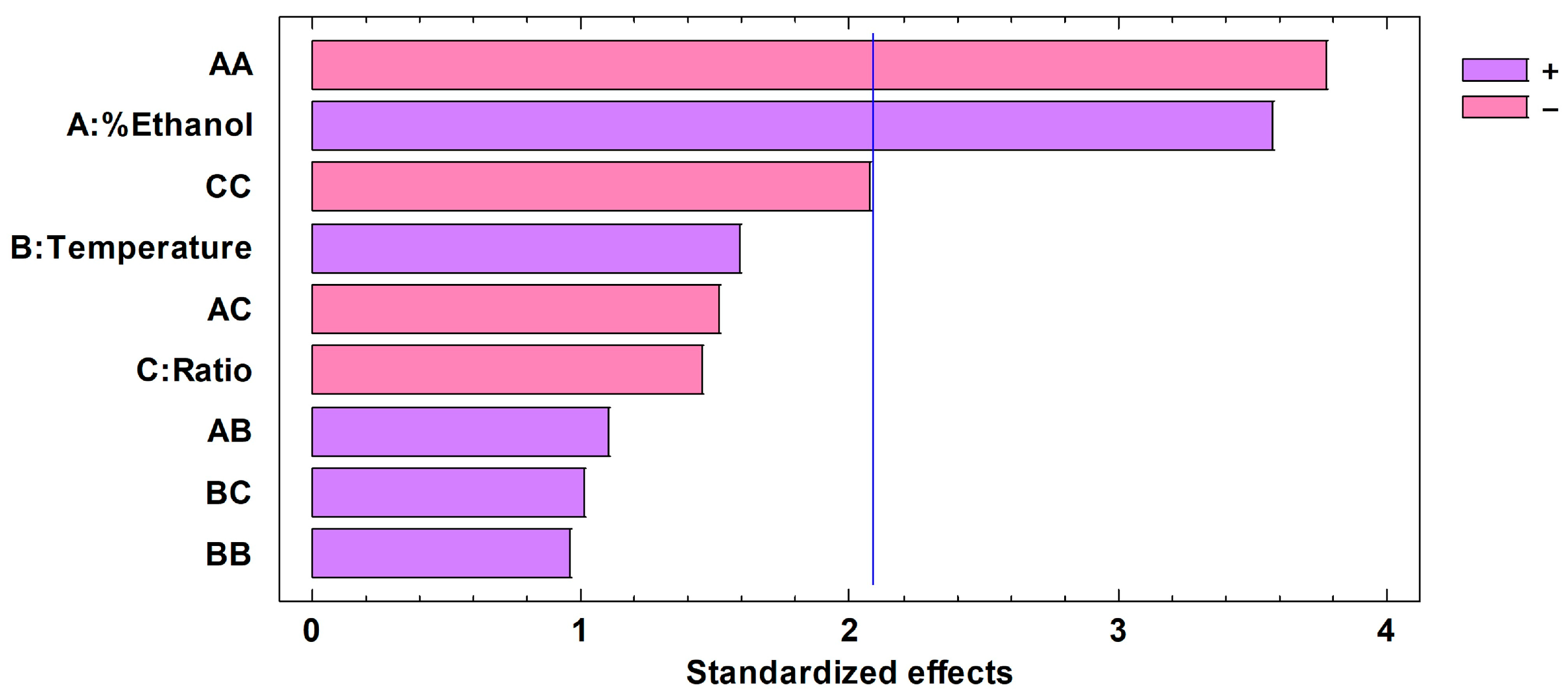
3.3. Optimizing the Conditions for Microwave-Assisted Extractions
3.4. Optimal Extraction Conditions
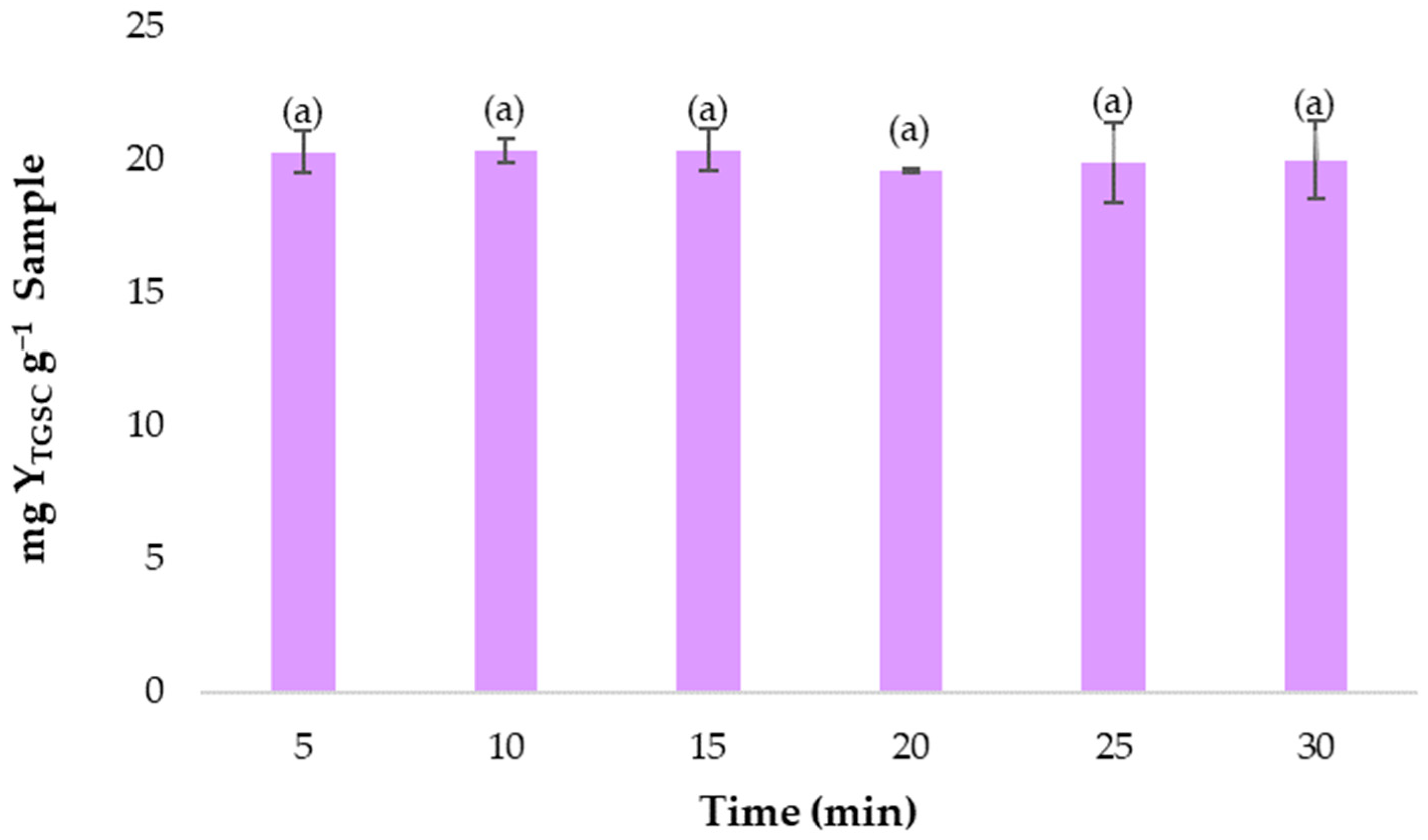
3.5. Optimization of Extraction Time for Maximum Recoveries
3.6. Precision Evaluation of the Optimized MAE Method
3.7. Applying the Optimum MAE Method to Various Commercial Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stoilova, I.; Krastanov, A.; Stoyanova, A.; Denev, P.; Gargova, S. Antioxidant Activity of a Ginger Extract (Zingiber officinale). Food Chem. 2007, 102, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semwal, R.B.; Semwal, D.K.; Combrinck, S.; Viljoen, A.M. Gingerols and Shogaols: Important Nutraceutical Principles from Ginger. Phytochemistry 2015, 117, 554–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Laviada, I. Effect of Capsaicin on Prostate Cancer Cells. Future Oncol. 2010, 6, 1545–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, M.G.; Sánchez, A.M.; Collado, B.; Malagarie-Cazenave, S.; Olea, N.; Carmena, M.J.; Prieto, J.C.; Díaz-Laviada, I. Expression of the Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) in LNCaP and PC-3 Prostate Cancer Cells and in Human Prostate Tissue. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 515, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, D.L.; Rafferty, M.F.; Boctor, A.M. Inhibition of Human Neutrophil 5-Lipoxygenase Activity by Gingerdione, Shogaol, Capsaicin and Related Pungent Compounds. Prostaglandins Leukot. Med. 1986, 24, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Surh, Y.J. Induction of Apoptosis in HL-60 Cells by Pungent Vanilloids, [6]-Gingerol and [6]-Paradol. Cancer Lett. 1998, 134, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, T.; Srivastava, K.C.; Jensen, K.B. Drug Development Report: 9. Pharmacology of Ginger, Zingiber officinale. J. Drug Dev. 1993, 6, 25–39. [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki, Y.; Morita, A.; Iwasawa, T.; Kobata, K.; Sekiwa, Y.; Morimitsu, Y.; Kubota, K.; Watanabe, T. A Nonpungent Component of Steamed Ginger—[10]-Shogaol—Increases Adrenaline Secretion via the Activation of TRPV1. Nutr. Neurosci. 2006, 9, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedov, V.N.; Tran, V.H.; Duke, C.C.; Connor, M.; Christie, M.J.; Mandadi, S.; Roufogalis, B.D. Gingerols: A Novel Class of Vanilloid Receptor (VR1) Agonists. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 137, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, I.; Chin, N.L.; Fakurazi, S.; Palanisamy, A. Comparison of Phytochemicals, Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Sun-, Oven- and Freeze-Dried Ginger Extracts. Foods 2019, 8, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.-L.; Li, X.-Z.; Dai, F.; Kang, Y.-F.; Li, Y.; Ma, M.-M.; Ren, X.-R.; Du, G.-W.; Jin, X.-L.; Zhou, B. Influence of Side Chain Structure Changes on Antioxidant Potency of the [6]-Gingerol Related Compounds. Food Chem. 2014, 165, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-H.; Jung, S.-J.; Choi, E.-K.; Ha, K.-C.; Baek, H.-I.; Park, Y.-K.; Han, K.-H.; Jeong, S.-Y.; Oh, J.-H.; Cha, Y.-S.; et al. The Effects of Steamed Ginger Ethanolic Extract on Weight and Body Fat Loss: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 29, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szallasi, A.; Di Marzo, V. New Perspectives on Enigmatic Vanilloid Receptors. Trends Neurosci. 2000, 23, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, F.; Capasso, R.; Pinto, A.; Izzo, A.A. Inhibitory Effect of Ginger (Zingiber officinale) on Rat Ileal Motility in Vitro. Life Sci. 2004, 74, 2889–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delazar, A.; Nahar, L.; Hamedeyazdan, S.; Sarker, S.D. Microwave-Assisted Extraction in Natural Products Isolation. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 864, 89–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, W.; Han, L.; Shi, B. Microwave-Assisted Extraction of Flavonoids from Radix astragali. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 62, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camel, V. Microwave-Assisted Solvent Extraction of Environmental Samples. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2000, 19, 229–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubrakova, I.V.; Toropchenova, E.S. Microwave Heating for Enhancing Efficiency of Analytical Operations (Review). Inorg. Mater. 2008, 44, 1509–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhou, C.; Zhao, J.; Chen, D.; Li, Q. Optimized microwave-assited extraction of 6-gingerol from Zingiber officinale Roscoe and evaluation of antioxidant activity in vitro. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2014, 13, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.; Seuseu, K.T.; Lee, W.-Y.; Chen, L. Comparing the Effects of Microwave Radiation on 6-Gingerol and 6-Shogaol from Ginger Rhizomes (Zingiber officinale Rosc). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Weller, C. Recent Advances in Extraction of Nutraceuticals from Plants. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.; Alvis Bermúdez, A.; Acevedo Correa, D.; Castillo, P.; Tirado, D. Optimization of Vacuum Frying Conditions of Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) Slices by Response Surface Methodology. Interciencia 2017, 42, 683–691. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Gonzalez, M.; Yerena-Prieto, B.Y.; Carrera, C.; Vázquez-Espinosa, M.; González-de-Peredo, A.V.; García-Alvarado, M.A.; Palma, M.M.; Rodríguez-Jimenes, G.C.; Barbero, G.F. Optimization of an Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction Method for the Extraction of Gingerols and Shogaols from Ginger (Zingiber officinale). Agronomy 2023, 13, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez Espinosa, M.; Velasco González de Peredo, A.; Espada-Bellido, E.; Ferreiro-González, M.; Barbero, G.; Palma, M. Simultaneous Determination by UHPLC-PDA of Major Capsaicinoids and Capsinoids Contents in Peppers. Food Chem. 2021, 356, 129688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza-Cadena, C.; Ortega-Rivera, D.M.; Machorro-García, G.; Gonzalez-Zermeño, E.M.; Homma-Dueñas, D.; Plata-Gryl, M.; Castro-Muñoz, R. A comprehensive review on Ginger (Zingiber officinale) as a potential source of nutraceuticals for food formulations: Towards the polishing of gingerol and other present biomolecules. Food Chem. 2023, 413, 135629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-Espinosa, M.; González de Peredo, A.V.; Ferreiro-González, M.; Barroso, C.G.; Palma, M.; Barbero, G.F.; Espada-Bellido, E. Optimizing and comparing ultrasound- And microwave-assisted extraction methods applied to the extraction of antioxidant capsinoids in peppers. Agronomy 2019, 9, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbero, G.F.; Palma, M.; Barroso, C.G. Determination of capsaicinoids in peppers by microwave-assisted extraction-high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 578, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Guo, Z.; Glasius, M.; Kristensen, K.; Xiao, L.; Xu, X. Pressurized liquid extraction of ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) with bioethanol: An efficient and sustainable approach. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 5765–5773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endy Yulianto, M.; Paramita, V.; Amalia, R.; Wahyuningsih, N.; Dwi Nyamiati, R. Production of bioactive compounds from ginger (Zingiber officianale) dregs through subcritical water extraction. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 63, S185–S194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso, T.L.C.T.; Castro, L.E.N.; Barbero, G.F.; Palma, M.; Carrera, C.; Rostagno, M.A.; Forster-Carneiro, T. Optimization of a Microwave-Assisted Extraction Method for the Recovery of the Anthocyanins from Jabuticaba By-Products. Agronomy 2023, 13, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-de-Peredo, A.V.; Vázquez-Espinosa, M.; Espada-Bellido, E.; Ferreiro-González, M.; Barbero, G.F.; Palma, M.; Carrera, C. Optimization of a Microwave Assisted Extraction Method for Maximum Flavonols and Antioxidant Activity of Onion Extracts. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo-Castellano, C.; Álvarez, J.Á.; Palma, M.; Barbero, G.F.; Ayuso, J.; Ferreiro-González, M. Optimization through a Box–Behnken Experimental Design of the Microwave-Assisted Extraction of the Psychoactive Compounds in Hallucinogenic Fungi (Psylocibe cubensis). J. Fungi 2022, 8, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalsasso, R.R.; Valencia, G.A.; Monteiro, A.R. Impact of drying and extractions processes on the recovery of gingerols and shogaols, the main bioactive compounds of ginger. Food Res. Int. 2022, 154, 111043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamaruddin, M.S.H.; Chong, G.H.; Mohd Daud, N.; Putra, N.R.; Md Salleh, L.; Suleiman, N. Bioactivities and green advanced extraction technologies of ginger oleoresin extracts: A review. Food Res. Int. 2023, 164, 112283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbero, G.F.; Ferreiro-González, M.; Freitas, V.C.M.; Carrera, C.; Espada-Bellido, E.; Ruiz-Rodríguez, A.; Liazid, A.; Rostagno, M.A.; Prado, J.M.; Palma, M. Extraction of Natural Products: Principles and Fundamental Aspects. In Natural Product Extraction Principles and Applications, 2nd ed.; RSC Green Chemistry; Rostagno, M.A., Prado, J.M., Eds.; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2022; Chapter 2; pp. 66–116. ISBN 9781839162640. [Google Scholar]
- Zia, S.; Khan, M.R.; Shabbir, M.A.; Aslam Maan, A.; Khan, M.K.I.; Nadeem, M.; Khalil, A.A.; Din, A.; Aadil, R.M. An Inclusive Overview of Advanced Thermal and Nonthermal Extraction Techniques for Bioactive Compounds in Food and Food-Related Matrices. Food Rev. Int. 2022, 38, 1166–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro, M.J.; Bélanger, J.M.R.; Padilla, F.C.; Jocelyn Paré, J.R. Influence of Solvent, Matrix Dielectric Properties, and Applied Power on the Liquid-Phase Microwave-Assisted Processes (MAPTM) Extraction of Ginger (Zingiber officinale). Food Res. Int. 2003, 36, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keosaeng, K.; Songoen, W.; Yooboon, T.; Bullangpoti, V.; Pluempanupat, W. Insecticidal activity of isolated gingerols and shogaols from Zingiber officinale Roscoe rhizomes against Spodoptera spp. (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Nat. Prod. Res. 2023, 37, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, A.; Naik, S.N.; Goud, V.V.; Das, C. Supercritical CO2 extraction and online fractionation of dry ginger for production of high-quality volatile oil and gingerols enriched oleoresin. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 130, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, R.; Gani, A.; Masarat Dar, M.; Bhat, N.A. Bioactive characterization of ultrasonicated ginger (Zingiber officinale) and licorice (Glycyrrhiza glabra) freeze dried extracts. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 88, 106048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destandau, E.; Michel, T. Microwave-assisted Extraction. In Natural Product Extraction Principles and Applications, 2nd ed.; RSC Green Chemistry; Rostagno, M.A., Prado, J.M., Eds.; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2022; Chapter 4; pp. 144–201. ISBN 9781839162640. [Google Scholar]
- Arshanitsa, A.; Ponomarenko, J.; Lauberte, L.; Jurkjane, V.; Pals, M.; Akishin, Y.; Lauberts, M.; Jashina, L.; Bikovens, O.; Telysheva, G. Advantages of MW-assisted water extraction, combined with steam explosion, of black alder bark in terms of isolating valuable compounds and energy efficiency. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 181, 114831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Official Methods of Analysis, 22nd Edition. 2023. Available online: https://www.aoac.org/official-methods-of-analysis/ (accessed on 26 June 2023).
- An, K.; Zhao, D.; Wang, Z.; Wu, J.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, G. Comparison of Different Drying Methods on Chinese Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe): Changes in Volatiles, Chemical Profile, Antioxidant Properties, and Microstructure. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 1292–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olguín-Rojas, J.; Fayos, O.; Vázquez León, L.A.; Ferreiro-González, M.; Rodriguez-Jimenes, G.; Palma, M.; Garcés-Claver, A.; Barbero, G. Progression of the Total and Individual Capsaicinoids Content in the Fruits of Three Different Cultivars of Capsicum chinense Jacq. Agronomy 2019, 9, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Udenigwe, C.C.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, Y. Preparation, Pungency and Bioactivity of Gingerols from Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe): A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 22, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Compound | Abbreviation | m/z | Retention Time (min) | Calibration Curve | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6-gingerol | 6-G | 294.4 | 1.88 | y = 3335.6x − 2574.5 | 0.9986 |
| 6-shogaol | 6-S | 276.4 | 3.69 | y = 1839x − 2241.5 | 0.9973 |
| 8-gingerol | 8-G | 322.4 | 3.79 | y = 3335.6x − 2574.5 | 0.9986 |
| 8-shogaol | 8-S | 304.4 | 4.78 | y = 1839x − 2241.5 | 0.9973 |
| 10-gingerol | 10-G | 350.5 | 4.80 | y = 3335.6x − 2574.5 | 0.9986 |
| 10-shogaol | 10-S | 332.5 | 5.52 | y = 1839x − 2241.5 | 0.9973 |
| Factor | −1 | 0 | +1 | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1: % Ethanol in water | 50 | 75 | 100 | % |
| X2: Temperature | 50 | 75 | 100 | °C |
| X3: Sample-to-solvent ratio | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | g:20 mL |
| Experiment | Factors | Responses | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | X2 | X3 | YTGSC (mg g−1) | ||
| Experimental | Predicted | ||||
| 1 | −1 | −1 | 0 | 17.574 | 16.212 |
| 2 | −1 | 1 | 0 | 15.479 | 14.695 |
| 3 | 1 | −1 | 0 | 15.869 | 16.653 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 19.664 | 21.026 |
| 5 | −1 | 0 | −1 | 9.886 | 11.965 |
| 6 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 13.599 | 13.666 |
| 7 | 1 | 0 | −1 | 17.993 | 17.926 |
| 8 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 16.556 | 14.477 |
| 9 | 0 | −1 | −1 | 20.109 | 19.392 |
| 10 | 0 | −1 | 1 | 16.939 | 18.234 |
| 11 | 0 | 1 | −1 | 21.830 | 20.535 |
| 12 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 19.229 | 19.946 |
| 13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20.225 | 19.575 |
| 14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 19.384 | 19.575 |
| 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 19.115 | 19.575 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | Degrees of Freedom | Coefficients | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1: %EtOH | 22.928 | 1 | 19.5753 | 22.928 | 6.15 | 0.055 |
| X2: Temperature | 4.074 | 1 | 1.69294 | 4.074 | 1.09 | 0.343 |
| X3: Ratio | 1.526 | 1 | 0.713704 | 1.526 | 0.41 | 0.550 |
| X1X1 | 51.185 | 1 | −0.436851 | 51.185 | 13.73 | 0.013 |
| X1X2 | 8.671 | 1 | −3.72328 | 8.6710 | 2.33 | 0.187 |
| X1X3 | 6.630 | 1 | 1.47233 | 6.630 | 1.78 | 0.239 |
| X2X2 | 6.191 | 1 | −1.28753 | 6.191 | 1.66 | 0.253 |
| X2X3 | 0.080 | 1 | 1.29497 | 0.080 | 0.02 | 0.888 |
| X3X3 | 6.65916 | 1 | 0.14215 | 6.65916 | 1.79 | 0.239 |
| Error total | 18.6437 | 5 | −1.34295 | 3.72873 | ||
| Total (corr.) | 128.137 | 14 |
| Factor | Optimum Extraction Conditions |
|---|---|
| Ethanol in water (%) | 87 |
| Temperature (°C) | 100 |
| Sample-to-solvent ratio (g:20 mL) | 0.431 |
| Commercial Samples | 6-G | 6-S | 8-G | 8-S | 10-G | 10-S | YTGSC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 | 4.36 ± 0.30 a | 1.34 ± 0.09 a | 1.75 ± 0.15 a | 0.88 ± 0.29 a | 0.47 ± 0.32 a | 0.65 ± 0.05 a | 9.48 ± 0.89 a |
| Sample 2 | 2.65 ± 0. 51 b | 0.88 ± 0.12 b | 3.00 ± 0.65 b | 0.54 ± 0.19 b | 0.31 ± 0.22 a | 0.17 ± 0.02 b | 7.58 ± 1.52 b |
| Sample 3 | 4.95 ± 0.54 c | 1.55 ± 0.15 c | 2.69 ± 0.21 b | 1.20 ± 0.12 c | 0.45 ± 0.16 a | 3.46 ± 0.29 c | 14.31 ± 1.33 c |
| Sample 4 | 4.72 ± 0.07 c | 1.59 ± 0.33 c | 1.51 ± 0.07 c | 1.04 ± 0.35 c | 0.62 ± 0.37 a | 0.92 ± 0.72 a | 10.43 ± 1.41 d |
| Sample 5 | 4.79 ± 1.10 c | 1.64 ± 0.19 c | 1.69 ± 0.68 ac | 1.18 ± 0.06 c | 0.47 ± 0.12 a | 2.20 ± 1.26 d | 12.00 ± 3.3 d |
| Sample 6 | 6.24 ± 0.10 d | 2.10 ± 0.10 d | 1.98 ± 0.61 ac | 1.23 ± 0.04 c | 0.72 ± 0.045 ab | 3.39 ± 0.06 c | 15.67 ± 0.58 c |
| Sample 7 | 3.33 ± 0.05 e | 6.52 ± 0.13 e | 0.96 ± 0.01 d | 0.66 ± 0.00 b | 0.55 ± 0.09 a | 0.32 ± 0.13 a | 12.37 ± 0.06 d |
| Sample 8 | 6.28 ± 0.03 d | 2.01 ± 0.21 d | 1.53 ± 0.06 c | 1.38 ± 0.10 d | 0.84 ± 0.18 ab | 3.78 ± 0.03 c | 15.84 ± 0.23 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gonzalez-Gonzalez, M.; Yerena-Prieto, B.J.; Carrera, C.; Vázquez-Espinosa, M.; González-de-Peredo, A.V.; García-Alvarado, M.Á.; Palma, M.; Rodríguez-Jimenes, G.d.C.; Barbero, G.F. Determination of Gingerols and Shogaols Content from Ginger (Zingiber officinale Rosc.) through Microwave-Assisted Extraction. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2288. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13092288
Gonzalez-Gonzalez M, Yerena-Prieto BJ, Carrera C, Vázquez-Espinosa M, González-de-Peredo AV, García-Alvarado MÁ, Palma M, Rodríguez-Jimenes GdC, Barbero GF. Determination of Gingerols and Shogaols Content from Ginger (Zingiber officinale Rosc.) through Microwave-Assisted Extraction. Agronomy. 2023; 13(9):2288. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13092288
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzalez-Gonzalez, Monserrat, Beatriz Juliana Yerena-Prieto, Ceferino Carrera, Mercedes Vázquez-Espinosa, Ana V. González-de-Peredo, Miguel Ángel García-Alvarado, Miguel Palma, Guadalupe del Carmen Rodríguez-Jimenes, and Gerardo Fernández Barbero. 2023. "Determination of Gingerols and Shogaols Content from Ginger (Zingiber officinale Rosc.) through Microwave-Assisted Extraction" Agronomy 13, no. 9: 2288. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13092288
APA StyleGonzalez-Gonzalez, M., Yerena-Prieto, B. J., Carrera, C., Vázquez-Espinosa, M., González-de-Peredo, A. V., García-Alvarado, M. Á., Palma, M., Rodríguez-Jimenes, G. d. C., & Barbero, G. F. (2023). Determination of Gingerols and Shogaols Content from Ginger (Zingiber officinale Rosc.) through Microwave-Assisted Extraction. Agronomy, 13(9), 2288. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13092288










