Adsorption of Pb2+ and Cd2+ in Agricultural Water by Potassium Permanganate and Nitric Acid-Modified Coconut Shell Biochar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Materials
2.2. Characterization of Biochar
2.3. Adsorption Experiment
3. Results and Discussion
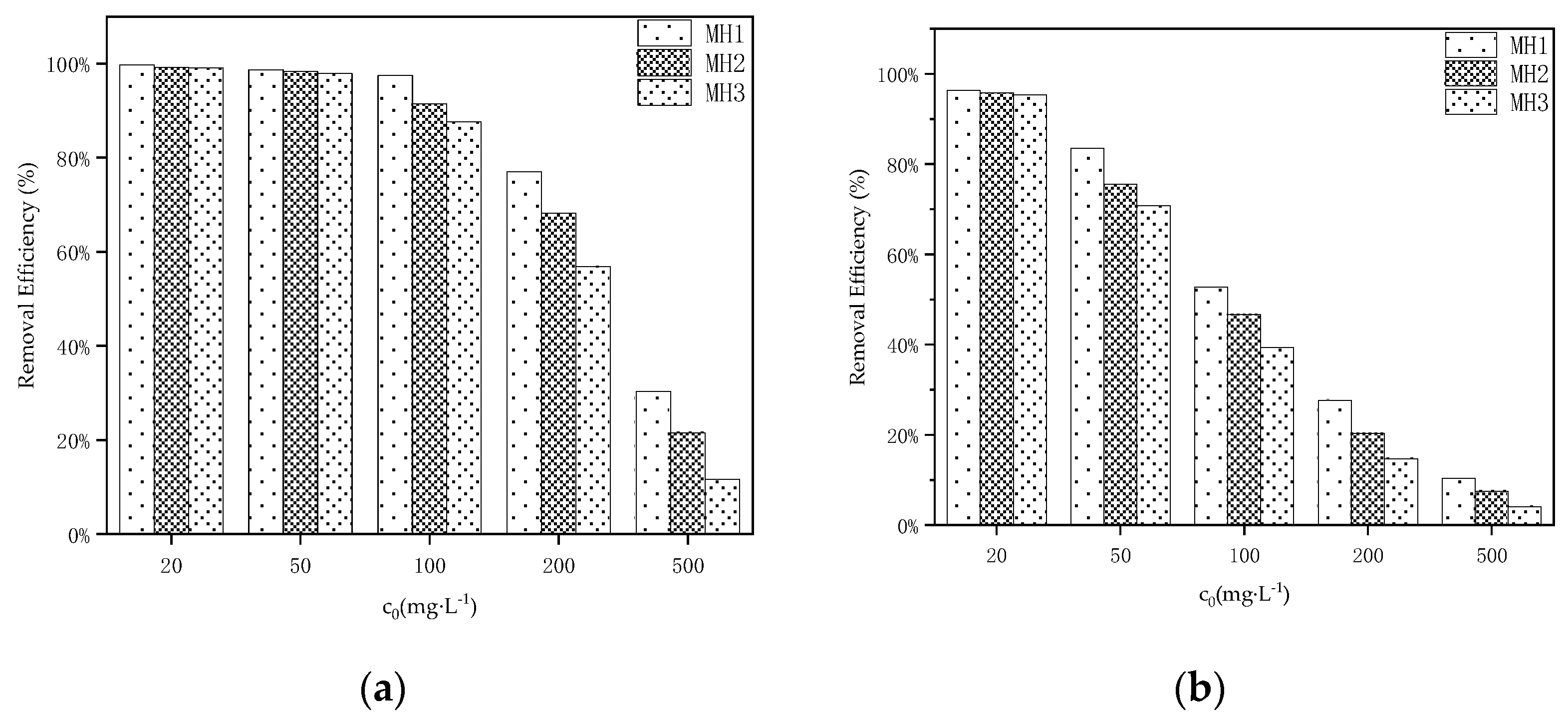
3.1. Determination of Optimal MHBC Conditions
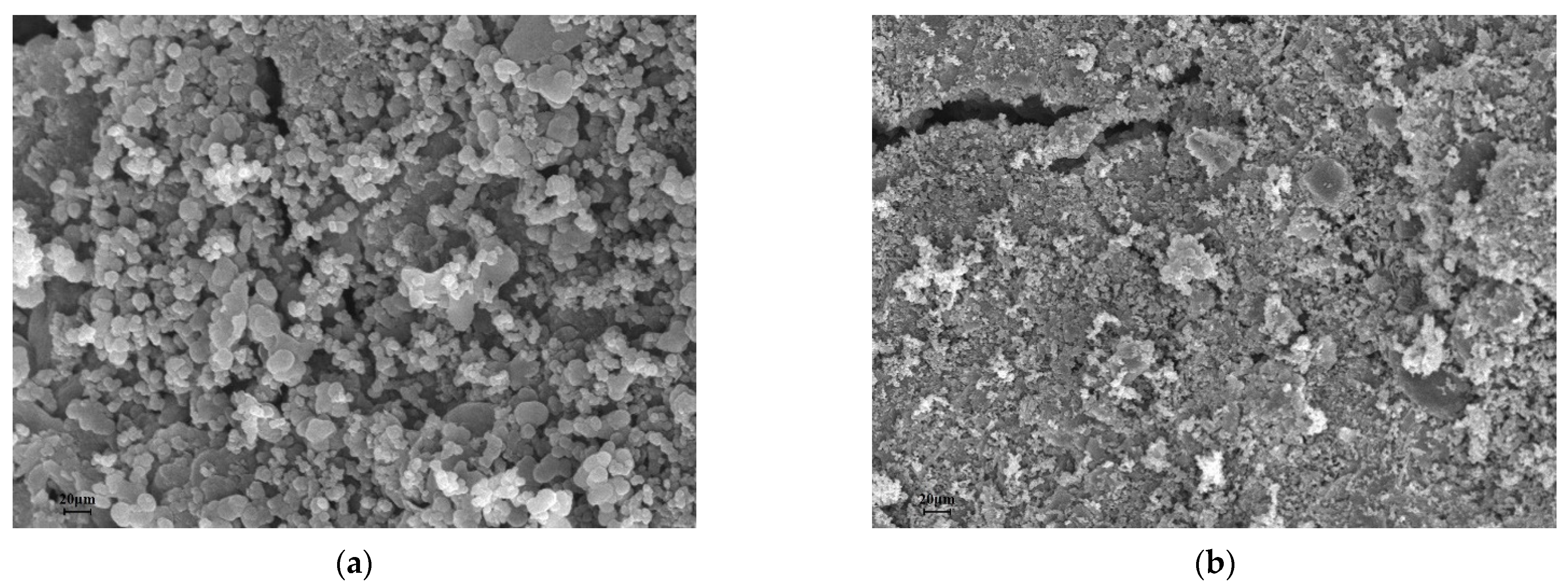
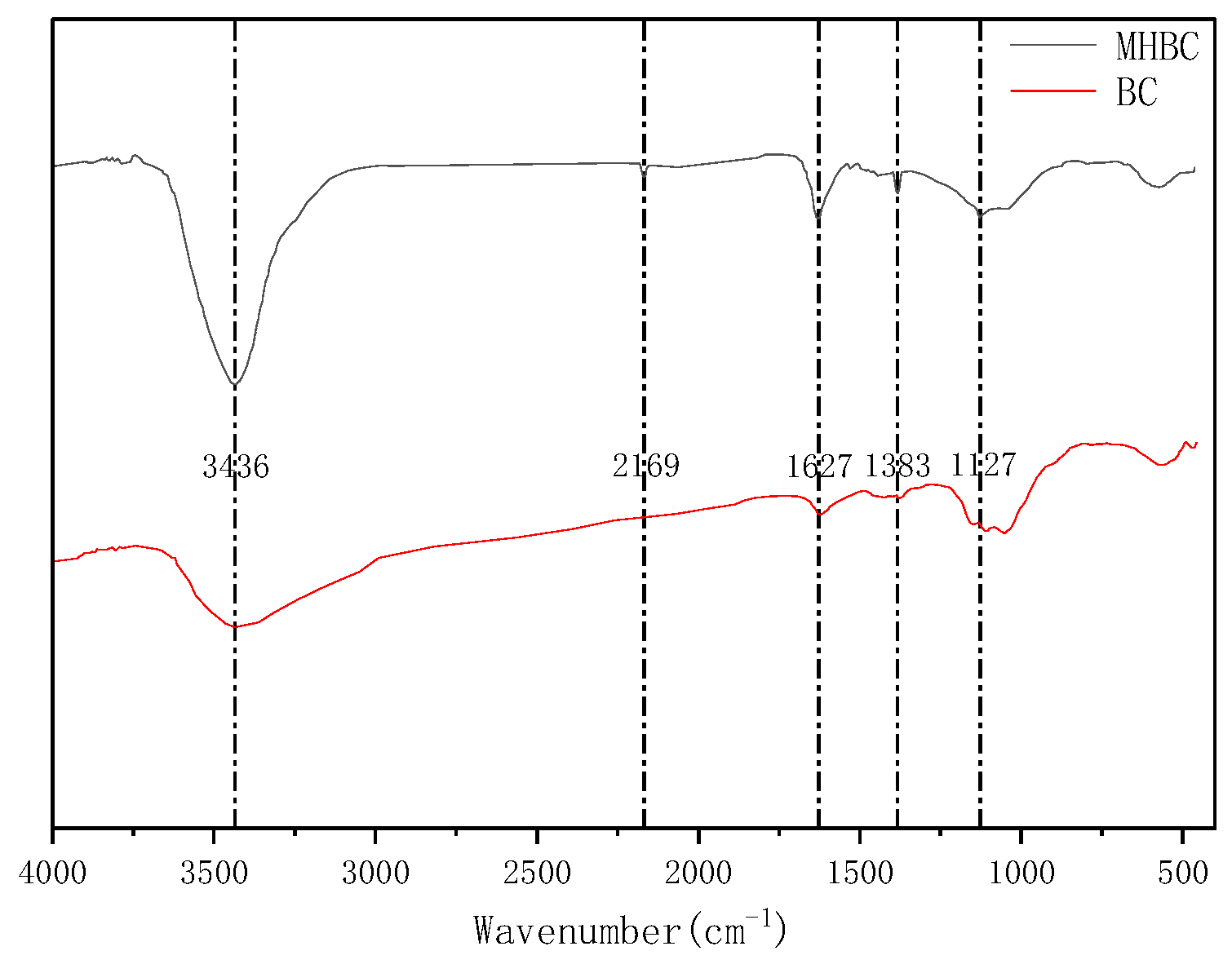
3.2. Characterization
2R-COOH + M2+ → (R-COOH) 2M + 2H2+
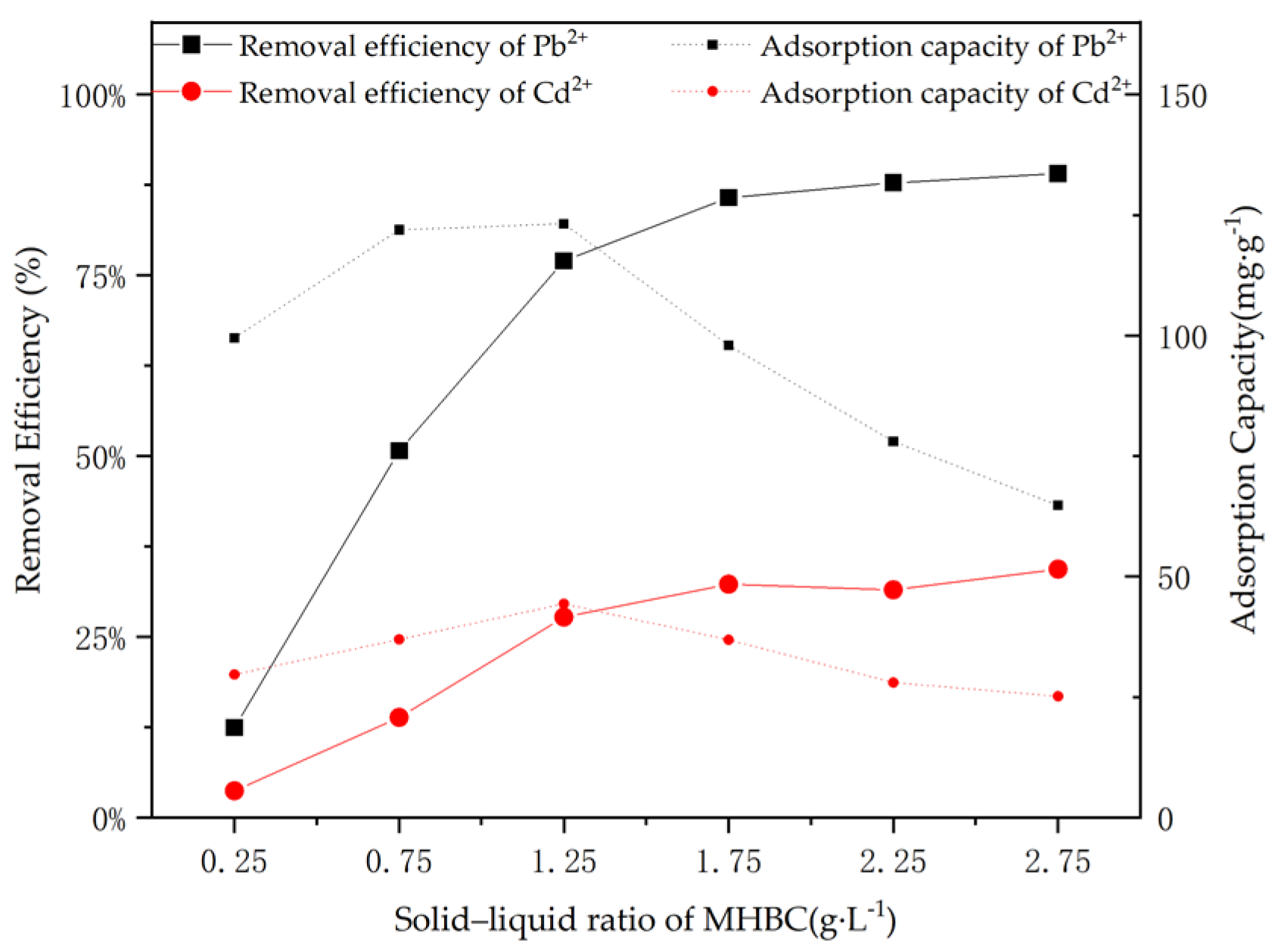
3.3. Optimization of MHBC Dose
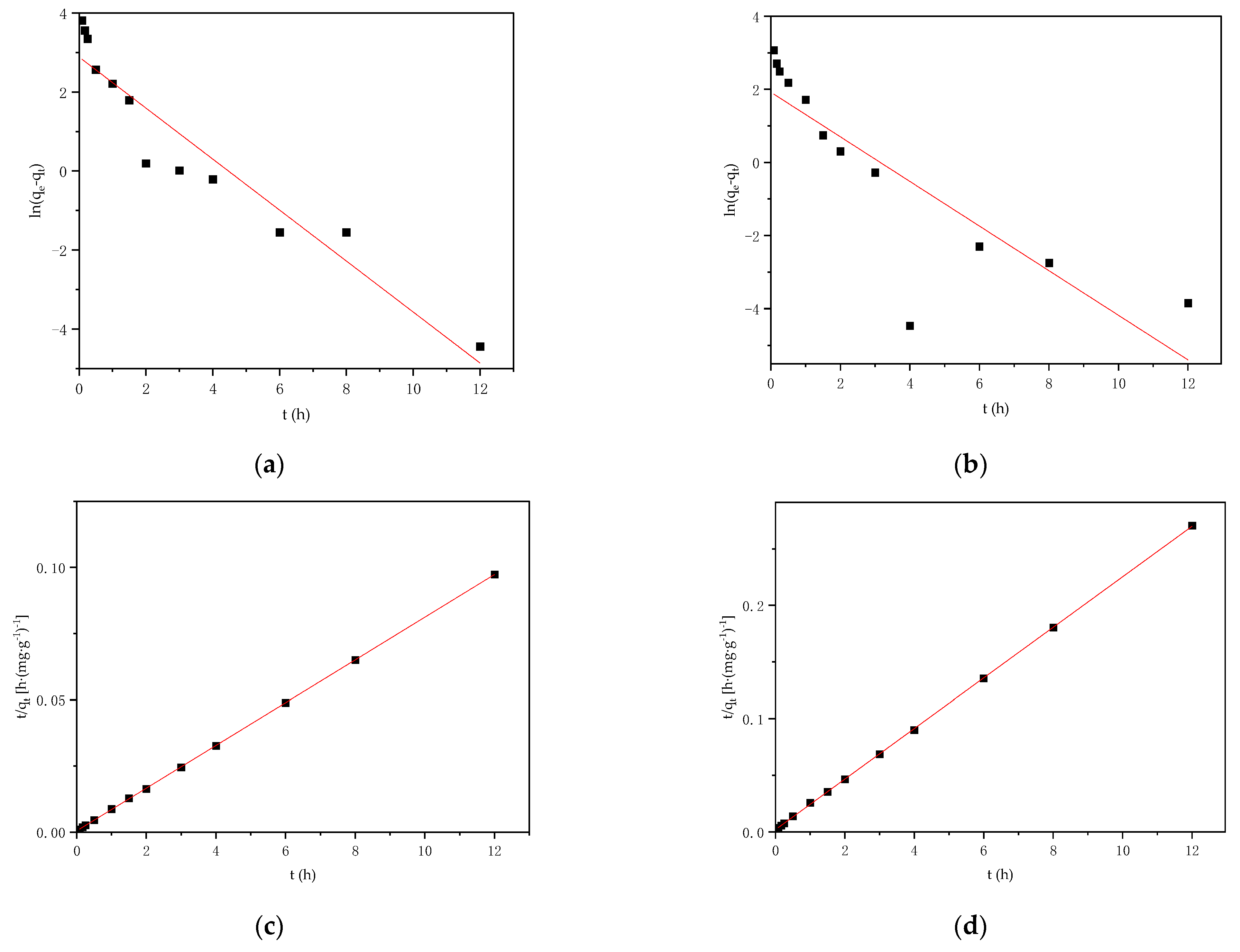
3.4. Adsorption Kinetics
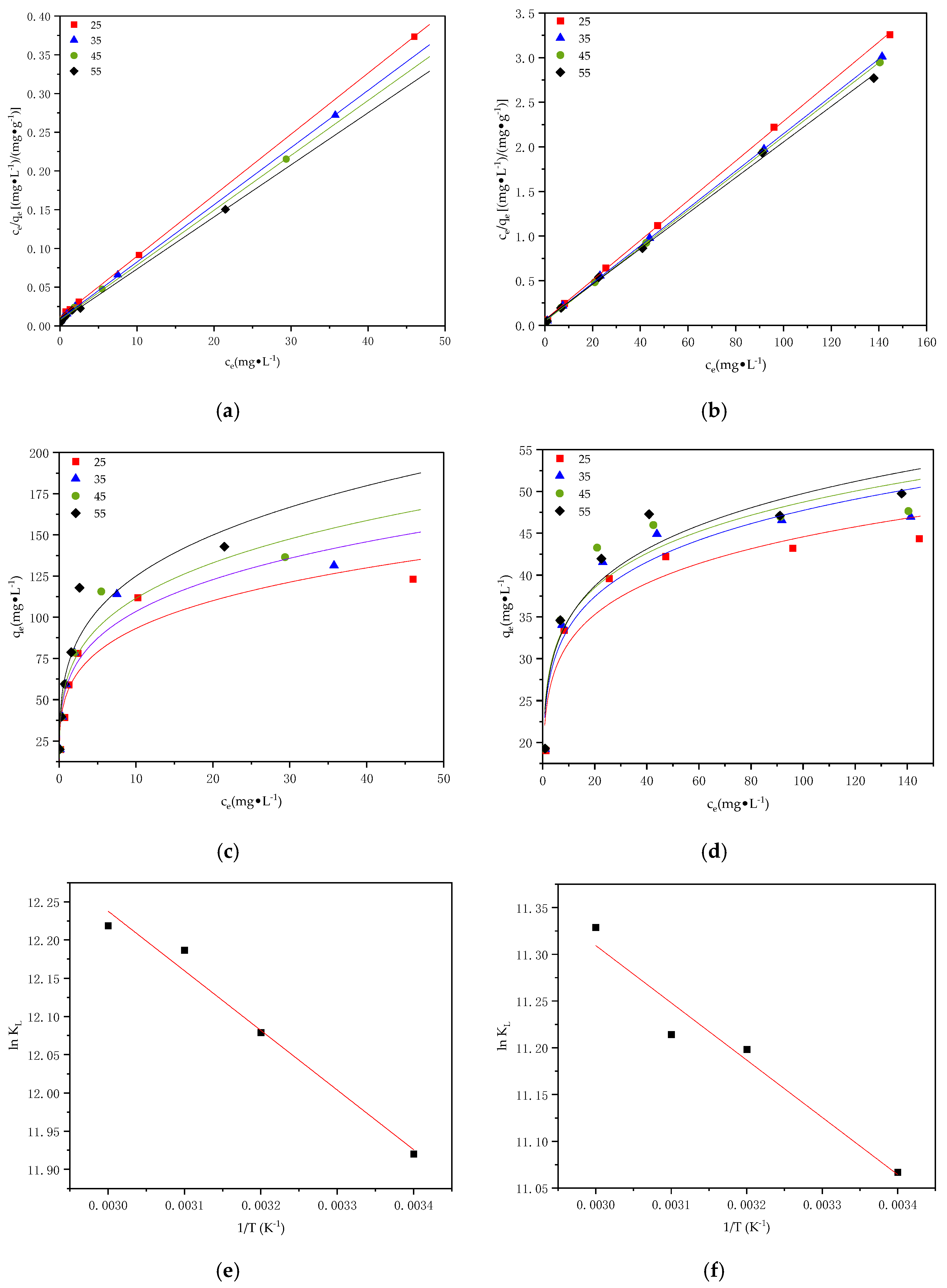
3.5. Adsorption Thermodynamics
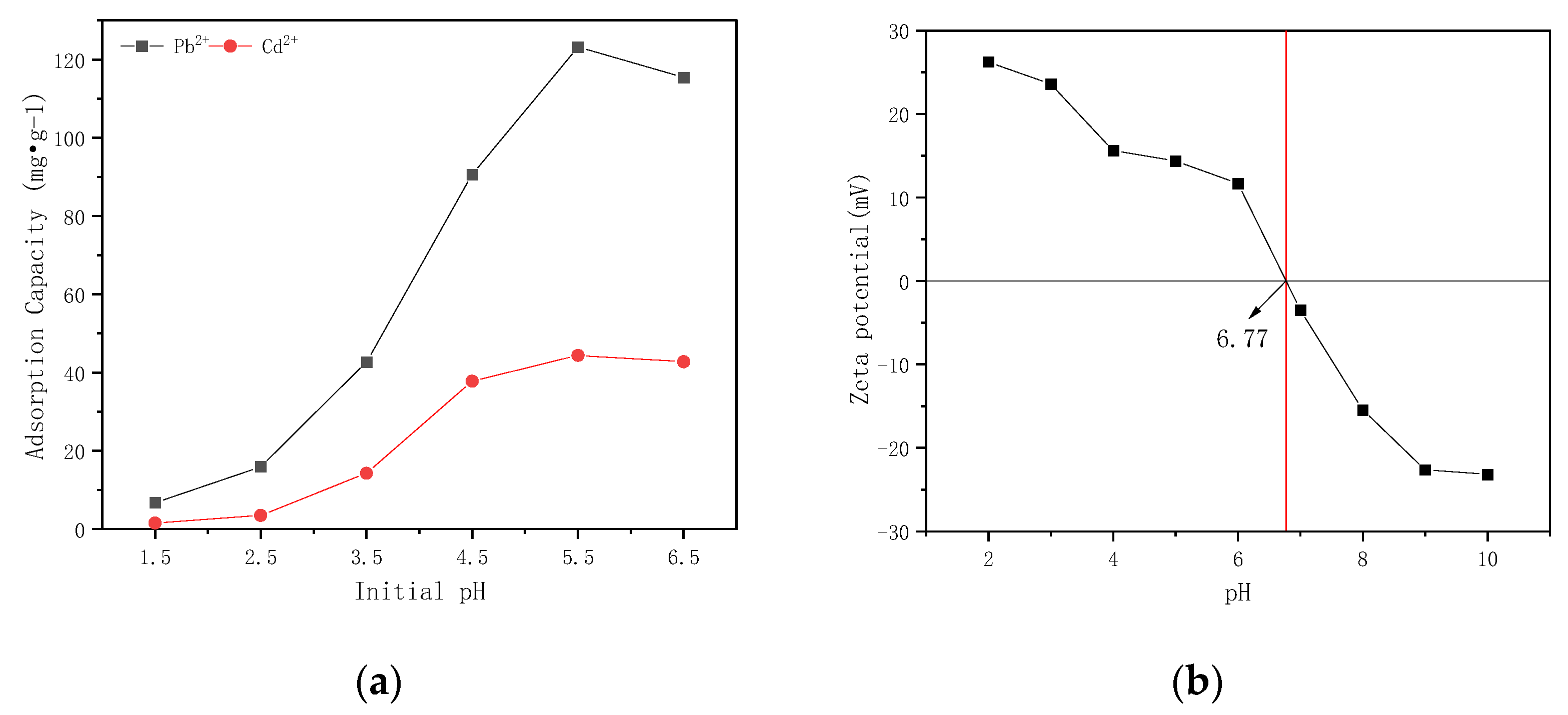
3.6. pH
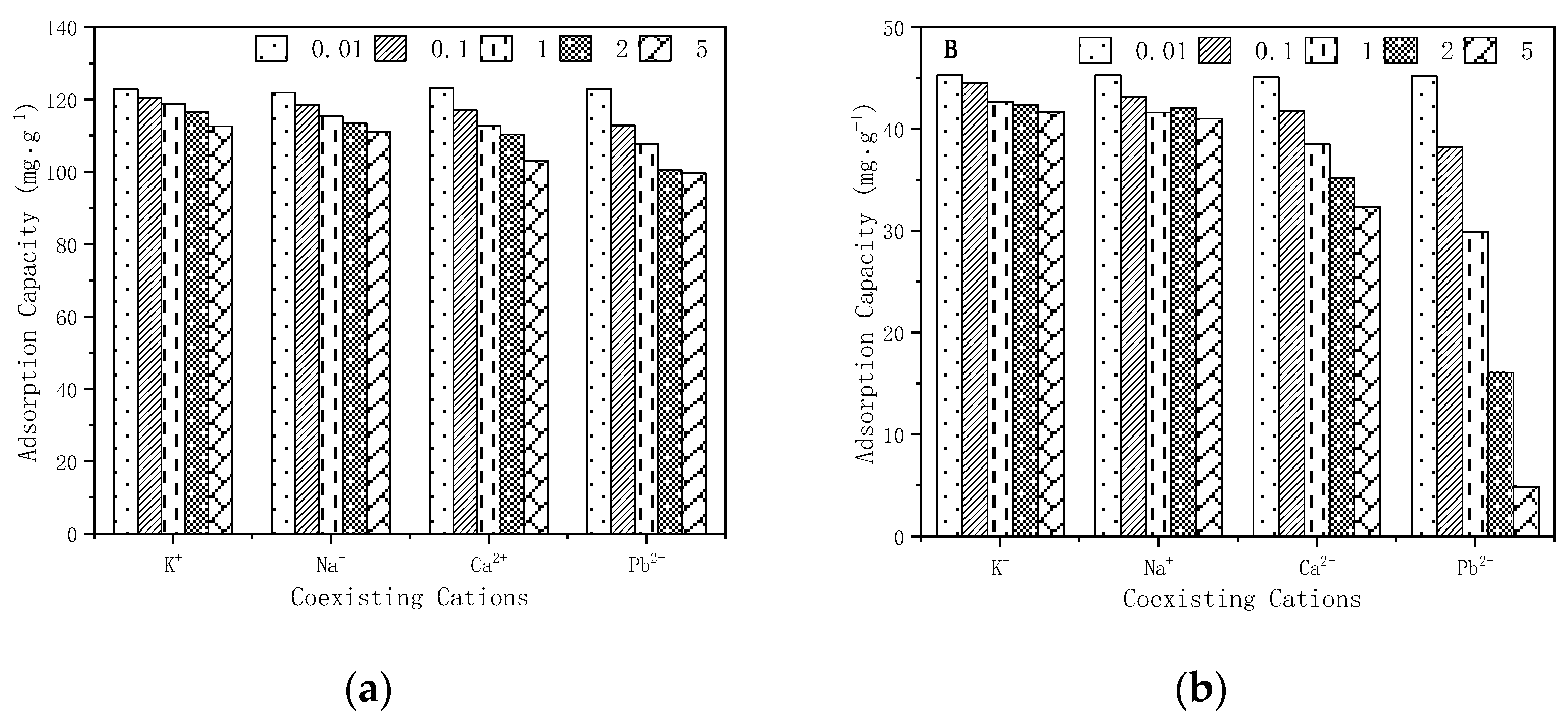
3.7. Coexisting Ion
3.8. Reuse
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.Y.; Xue, D.W.; Zhao, L.M.; Zhang, X.Y. Concentration of heavy metals in vegetables and potential health risk assessment in China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.K.; Mao, X.Y.; Hamoud, Y.A.; Zhu, N.Y.; Shao, X.H.; Wang, Q.L.; Shaghaleh, H. Nitrogen Removal for Low Concentration Ammonium Wastewater by Adsorption, Shortcut Simultaneous Nitrification and Denitrification Process in MBBR. Water 2023, 15, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.K.; Zhu, N.Y.; Shaghaleh, H.; Mao, X.Y.; Shao, X.H.; Wang, Q.L.; Hamoud, Y.A. The Effect of Functional Ceramsite in a Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor and Its Ammonium Nitrogen Adsorption Mechanism. Water 2023, 15, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Ma, Z.W.; van der Kuijp, T.J.; Yuan, Z.W.; Huang, L. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: Pollution and health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burakov, A.E.; Galunin, E.V.; Burakova, I.V.; Kucherova, A.E.; Agarwal, S.; Tkachev, A.G.; Gupta, V.K. Adsorption of heavy metals on conventional and nanostructured materials for wastewater treatment purposes: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, P.J.; Handley, H.K.; Taylor, M.P. Identification of the sources of metal (lead) contamination in drinking waters in north-eastern Tasmania using lead isotopic compositions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 12276–12288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Wang, J.; Wu, D.; Li, X.; Luo, Y.; Han, C.; Ma, W.; He, S. Investigating the Heavy Metal Adsorption of Mesoporous Silica Materials Prepared by Microwave Synthesis. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.Y.; Sun, J.J.; Shaghaleh, H.; Jiang, X.S.; Yu, H.Z.; Zhai, S.M.; Hamoud, Y.A. Environmental Assessment of Soils and Crops Based on Heavy Metal Risk Analysis in Southeastern China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinathan, R.; Bhowal, A.; Garlapati, C. Adsorption Characteristics of Activated Carbon for the Reclamation of Colored Effluents Containing Orange G and New Solid-Liquid Phase Equilibrium Model. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2017, 62, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grotzner, M.; Melchiors, E.; Schroeder, L.H.; dos Santos, A.R.; Moscon, K.G.; de Andrade, M.A.; Martinelli, S.H.S.; Xavier, C.R. Pulp and Paper Mill Effluent Treated by Combining Coagulation-Flocculation-Sedimentation and Fenton Processes. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafarzadeh, N.; Baboli, Z.; Noorimotlagh, Z.; Martinez, S.S.; Ahmadi, M.; Alavi, S.; Mirzaee, S.A. Efficient adsorption of bisphenol A from aqueous solutions using low-cost activated carbons produced from natural and synthetic carbonaceous materials. Desalination Water Treat. 2019, 154, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnib, M.; Kabbani, A.; Holail, H.; Olama, Z. Heavy Metals Removal Using Activated Carbon, Silica and Silica Activated Carbon Composite. Energy Procedia 2014, 50, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Niu, D.; Sang, W.; Verpoort, F. Investigating the sorption behavior of cadmium from aqueous solution by potassium permanganate-modified biochar: Quantify mechanism and evaluate the modification method. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 8330–8339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewage, N.B.; Fowler, R.E.; Pittman, C.U.; Mohan, D.; Mlsna, T. Lead (Pb2+) sorptive removal using chitosan-modified biochar: Batch and fixed-bed studies. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 25368–25377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.H.; Liu, W.J.; Jiang, R.F.; Wang, Z.S. Study on the adsorption mechanism of activated carbon removing low concentrations of heavy metals. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 7812–7822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.T.; Cao, X.; Ouyang, X.; Sohi, S.P.; Chen, J.W. Adsorption kinetics of magnetic biochar derived from peanut hull on removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution: Effects of production conditions and particle size. Chemosphere 2016, 145, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyk, A.; Sokolowska, Z.; Boguta, P. Biochar physicochemical properties: Pyrolysis temperature and feedstock kind effects. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio. Technol. 2020, 19, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doumer, M.E.; Rigol, A.; Vidal, M.; Mangrich, A.S. Removal of Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn from aqueous solutions by biochars. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 2684–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Ok, Y.S.; Kim, S.H.; Cho, J.S.; Heo, J.S.; Delaune, R.D.; Seo, D.C. Competitive adsorption of heavy metals onto sesame straw biochar in aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 2016, 142, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Lu, H.H.; Yang, R.Q.; Yang, S.M. Competitive adsorption of Pb(II), Cu(II), and Zn(II) ions onto hydroxyapatite-biochar nanocomposite in aqueous solutions. J. Solid State Chem. 2018, 261, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Zong, Y. Pore structure and environmental serves of biochars derived from different feedstocks and pyrolysis conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 30401–30409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalina, M.; Sovova, S.; Svec, J.; Trudicova, M.; Hajzler, J.; Kubikova, L.; Enev, V. The Effect of Pyrolysis Temperature and the Source Biomass on the Properties of Biochar Produced for the Agronomical Applications as the Soil Conditioner. Materials 2022, 15, 8855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.B.; Gao, P.; Chu, G.; Pan, B.; Peng, J.H.; Xing, B.S. Enhanced adsorption of Cu(II) and Cd(II) by phosphoric acid-modified biochars. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicola, R.; Costisor, O.; Ciopec, M.; Negrea, A.; Lazau, R.; Ianasi, C.; Piciorus, E.M.; Len, A.; Almasy, L.; Szerb, E.I.; et al. Silica-Coated Magnetic Nanocomposites for Pb2+ Removal from Aqueous Solution. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongrod, S.; Simon, S.; Guibaud, G.; Lens, P.N.L.; Pechaud, Y.; Huguenot, D.; van Hullebusch, E.D. Lead sorption by biochar produced from digestates: Consequences of chemical modification and washing. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 219, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ianasi, C.; Piciorus, M.; Nicola, R.; Ciopec, M.; Negrea, A.; Niznansky, D.; Len, A.; Almasy, L.; Putz, A.M. Removal of cadmium from aqueous solutions using inorganic porous nanocomposites. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 688–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Yin, M.L.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Yang, S.T.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Song, G.; Wang, J. Mechanisms of U(VI) removal by biochar derived from Ficus microcarpa aerial root: A comparison between raw and modified biochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.A.; Owija, N.Y.; Kosa, S. Removal of the toxic cadmium ions from aqueous solutions by zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 2391–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Banna, M.F.; Mosa, A.; Gao, B.; Yin, X.Q.; Wang, H.Y.; Ahmad, Z. Scavenging effect of oxidized biochar against the phytotoxicity of lead ions on hydroponically grown chicory: An anatomical and ultrastructural investigation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 170, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyuan, Y.A.O.; Zhifeng, D.O.U.; Guangmin, H.; Rencheng, L.I.U. Pyrolysis and pyrolysis kinetics of coconut shell, coconut shell residue and de-ashed coconut shell residue. J. Chem. Ind. Eng. 2007, 58, 1210–1214. [Google Scholar]
- Samsudin, M.H.; Hassan, M.A.; Idris, J.; Ramli, N.; Mohd Yusoff, M.Z.; Ibrahim, I.; Othman, M.R.; Mohd Ali, A.A.; Shirai, Y. A one-step self-sustained low temperature carbonization of coconut shell biomass produced a high specific surface area biochar-derived nano-adsorbent. Waste Manag. Res. 2019, 37, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamran, U.; Park, S.J. MnO2-decorated biochar composites of coconut shell and rice husk: An efficient lithium ions adsorption-desorption performance in aqueous media. Chemosphere 2020, 260, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.K.; Xu, F.; Xie, Y.L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, A.K.; Li, L.L.; Xu, H. Effect of modified coconut shell biochar on availability of heavy metals and biochemical characteristics of soil in multiple heavy metals contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.D.; Li, J.H.; Lan, T.; Muller, K.; Niazi, N.K.; Chen, X.; Xu, S.; Zheng, L.R.; Chu, Y.C.; Li, J.W.; et al. Unraveling sorption of lead in aqueous solutions by chemically modified biochar derived from coconut fiber: A microscopic and spectroscopic investigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 576, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.R.; Zhang, Z.M.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Hu, S.; Xiang, J.; Hu, X. Steam reforming of acetic acid over Ni/biochar catalyst treated with HNO3: Impacts of the treatment on surface properties and catalytic behaviors. Fuel 2020, 278, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhang, C.; Liu, B.; Liu, G.; Xing, B. A New Paradigm for Environmental Chemistry and Toxicology; Jiang, G.B., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 153–196. [Google Scholar]
- Ajeng, A.A.; Abdullah, R.; Ling, T.C.; Ismail, S.; Lau, B.F.; Ong, H.C.; Chew, K.W.; Show, P.L.; Chang, J.S. Bioformulation of biochar as a potential inoculant carrier for sustainable agriculture. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 20, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanhaei, B.; Ayati, A.; Lahtinen, M.; Sillanpaa, M. Preparation and characterization of a novel chitosan/Al2O3/magnetite nanoparticles composite adsorbent for kinetic, thermodynamic and isotherm studies of Methyl Orange adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.J.; Li, X.D.; Xu, S.X.; Zhao, X.Y.; Ni, M.J.; Cen, K.F. Comparison of adsorption behavior of PCDD/Fs on carbon nanotubes and activated carbons in a bench-scale dioxin generating system. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 10463–10470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Q.; Li, K.X.; Sun, G.H.; Wang, J.L. Synthesis and characterization of activated carbon with a high mesoporosity. New Carbon Mater. 2011, 26, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.L.; Zhou, D.D.; Zhu, L.Z. Transitional adsorption and partition of nonpolar and polar aromatic contaminants by biochars of pine needles with different pyrolytic temperatures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5137–5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantrell, K.B.; Hunt, P.G.; Uchimiya, M.; Novak, J.M.; Ro, K.S. Impact of pyrolysis temperature and manure source on physicochemical characteristics of biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 107, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiluweit, M.; Nico, P.S.; Johnson, M.G.; Kleber, M. Dynamic Molecular Structure of Plant Biomass-Derived Black Carbon (Biochar). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.L.; Johnson, E.J.; Chefetz, B.; Zhu, L.Z.; Xing, B.S. Sorption of polar and nonpolar aromatic organic contaminants by plant cuticular materials: Role of polarity and accessibility. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 6138–6146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Pan, B.C.; Li, H.Y.; Zhang, W.M.; Lv, L.; Wu, J. Selective Removal of Cu(II) Ions by Using Cation-exchange Resin-Supported Polyethyleneimine (PEI) Nanoclusters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3508–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, I.A.; Jafarzadeh, M.; Sipaut, C.S. Synthesis of organo-functionalized nanosilica via a co-condensation modification using gamma-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES). Ceram. Int. 2009, 35, 1883–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yang, L.; Wang, C.Q.; Zhang, Q.P.; Liu, Q.C.; Li, Y.D.; Xiao, R. Adsorption of Cd(II) from aqueous solutions by rape straw biochar derived from different modification processes. Chemosphere 2017, 175, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, D.; Pittman, C.U.; Bricka, M.; Smith, F.; Yancey, B.; Mohammad, J.; Steele, P.H.; Alexandre-Franco, M.F.; Gomez-Serrano, V.; Gong, H. Sorption of arsenic, cadmium, and lead by chars produced from fast pyrolysis of wood and bark during bio-oil production. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 310, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.Y.; Jiang, J.; Xu, R.K.; Li, Z. Adsorption of Pb(II) on variable charge soils amended with rice-straw derived biochar. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trakal, L.; Veselska, V.; Safarik, I.; Vitkova, M.; Cihalova, S.; Komarek, M. Lead and cadmium sorption mechanisms on magnetically modified biochars. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 203, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.H.; Tang, J.C.; Huang, Y.; Gai, L.S.; Zeng, E.Y.; Liber, K.; Gong, Y.Y. Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solutions by a novel biochar supported nanoscale iron sulfide composite. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 322, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Kinetic models for the sorption of dye from aqueous solution by wood. Process Saf. Environ. Protect. 1998, 76, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.Q.; Fang, S.Y.; Yao, Y.Q.; Li, T.Q.; Ni, Q.J.; Yang, X.E.; He, Z.L. Potential mechanisms of cadmium removal from aqueous solution by Canna indica derived biochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 562, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapica, J.; Pelech, R.; Przepiorski, J.; Morawski, A.W. Kinetics of the adsorption of copper and lead ions from aqueous solution on to WD-ekstra activated carbon. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2002, 20, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumi, A.; Ghaemy, M.; Bakht, A.N. Removal of Metal Ions from Water Using Poly(MMA-co-MA)/Modified-Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanocomposite: Isotherm and Kinetic Study. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 8188–8197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, P.; Shim, W.G.; Sounthararajah, D.P.; Kalaruban, M.; Nur, T.; Vigneswaran, S. Modelling equilibrium adsorption of single, binary, and ternary combinations of Cu, Pb, and Zn onto granular activated carbon. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 16664–16675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Zhang, Y.S.; Fu, J.G.; Yuan, L.X.; Li, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhao, D.; Wang, X.B. A novel magnetic biochar/MgFe-layered double hydroxides composite removing Pb2+ from aqueous solution: Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics. Colloid Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 567, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, M.; Seipenbusch, M. Highly controlled structuring of Pt nanoparticles on TiO2 and on ZrO2 by a modified MOCVD process. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 259, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthy, M.; Saravanakumar, M.P. Isotherm modeling, kinetic study and optimization of batch parameters for effective removal of Acid Blue 45 using tannery waste. J. Mol. Liq. 2013, 187, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zama, E.F.; Zhu, Y.G.; Reid, B.J.; Sun, G.X. The role of biochar properties in influencing the sorption and desorption of Pb(II), Cd(II) and As(III) in aqueous solution. J. Clean Prod. 2017, 148, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantu, Y.; Remes, A.; Reyna, A.; Martinez, D.; Villarreal, J.; Ramos, H.; Trevino, S.; Tamez, C.; Martinez, A.; Eubanks, T.; et al. Thermodynamics, kinetics, and activation energy studies of the sorption of chromium(III) and chromium(VI) to a Mn3O4 nanomaterial. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 254, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Gao, B.; Wang, S.S.; Fang, J.; Xue, Y.W.; Yang, K. Removal of Pb(II), Cu(II), and Cd(II) from aqueous solutions by biochar derived from KMnO4 treated hickory wood. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 197, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.N.; Qiu, W.W.; Wang, D.; Huang, Q.; Song, Z.G.; Chau, H.W. Arsenic removal in aqueous solution by a novel Fe-Mn modified biochar composite: Characterization and mechanism. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 144, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argun, M.E.; Dursun, S.; Ozdemir, C.; Karatas, M. Heavy metal adsorption by modified oak sawdust: Thermodynamics and kinetics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 141, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benzaoui, T.; Selatnia, A.; Djabali, D. Adsorption of copper (II) ions from aqueous solution using bottom ash of expired drugs incineration. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2018, 36, 114–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mall, I.D.; Srivastava, V.C.; Agarwal, N.K. Removal of Orange-G and Methyl Violet dyes by adsorption onto bagasse fly ash—Kinetic study and equilibrium isotherm analyses. Dyes. Pigment. 2006, 69, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferson, W.A.; Hu, C.Z.; Liu, H.J.; Qu, J.H. Reaction of aqueous Cu-Citrate with MnO2 birnessite: Characterization of Mn dissolution, oxidation products and surface interactions. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.B.; Cao, X.H.; Liang, P.; Liu, Y.H. Adsorption of uranium from aqueous solution using biochar produced by hydrothermal carbonization. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2013, 295, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Li, S.W.; Peng, X.Q.; Liu, W.; Zhang, C.L.; Yang, Y.; Han, L.F.; Du, Z.W.; Sun, K.; Wang, X.K. HNO3 modified biochars for uranium (VI) removal from aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 256, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, D.; Laldanwngliana, C.; Choi, C.H.; Lee, S.M. Manganese-modified natural sand in the remediation of aquatic environment contaminated with heavy metal toxic ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.G.; Zhang, F.S. Removal of lead from water using biochars prepared from hydrothermal liquefaction of biomass. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, A.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Harris, W. Surface chemistry variations among a series of laboratory-produced biochars. Geoderma 2011, 163, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.L.; Ma, L.N.Q.; Li, Y.C. Characteristics and mechanisms of hexavalent chromium removal by biochar from sugar beet tailing. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Yang, H.; Wang, B.; Xie, J. Effects of coexisting ions on adsorption of Pb~(2+)onto Bentonite/LS-g-AM-co-MAH. Acta Mater. Compos. Sin. 2016, 33, 2181–2186. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.D.; Ma, L.N.; Gao, B.; Harris, W. Dairy-Manure Derived Biochar Effectively Sorbs Lead and Atrazine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3285–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Liu, Y.G.; Liu, S.B.; Li, Z.W.; Tan, X.F.; Huang, X.X.; Zeng, G.M.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Zheng, B.H.; Cai, X.X. Competitive removal of Cd(II) and Pb(II) by biochars produced from water hyacinths: Performance and mechanism. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 5223–5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shan, B.Q.; Tang, W.Z.; Zhu, Y.Y. Comparison of cadmium and lead sorption by Phyllostachys pubescens biochar produced under a low-oxygen pyrolysis atmosphere. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sample | Pb | Cd | SBET | Vtot | Pore Width | C | H | O | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg·kg−1 | mg·kg−1 | m2·g−1 | cm3·g−1 | nm | |||||
| BC | 12.37 | 0.19 | 157.46 | 0.21 | 3.80 | 77.62 | 3.91 | 9.15 | 0.33 |
| MHBC | 12.38 | 0.18 | 475.36 | 0.38 | 1.65 | 71.58 | 3.22 | 13.37 | 0.52 |
| Sample | Acidic Functional Groups | Carboxyl | Lactone | Phenol |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mmol·g−1 | mmol·g−1 | mmol·g−1 | mmol·g−1 | |
| BC | 0.43 | 0.11 | 0.13 | 0.17 |
| MHBC | 1.14 | 0.36 | 0.44 | 0.25 |
| Adsorbate | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe,cal (mg·g−1) | k1 (h−1) | R2 | qe,cal (mg·g−1) | k2 (g·mg−1·h−1) | R2 | |
| Pb2+ | 17.90 | 0.65 | 0.904 | 123.92 | 0.13 | 0.999 |
| Cd2+ | 9.13 | 0.59 | 0.906 | 44.80 | 0.24 | 0.999 |
| Adsorbate | Weber–Morris | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First-Stage | Second-Stage | Third-Stage | |||||||
| C | k | R2 | C | k | R2 | C | k | R2 | |
| Pb2+ | 56.27 | 76.54 | 0.998 | 103.17 | 11.68 | 0.840 | 121.57 | 0.49 | 0.775 |
| Cd2+ | 16.25 | 28.94 | 0.898 | 33.68 | 6.14 | 0.778 | 44.21 | 0.01 | 0.006 |
| T | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe,cal (mg·g−1) | kL (L·mg−1) | R2 | kF | n | R2 | |
| 25 | 124.31 | 0.73 | 0.993 | 53.63 | 4.17 | 0.855 |
| 35 | 131.54 | 0.85 | 0.990 | 59.06 | 4.49 | 0.833 |
| 45 | 144.29 | 0.95 | 0.976 | 62.06 | 3.93 | 0.896 |
| 55 | 160.41 | 0.98 | 0.958 | 68.25 | 3.81 | 0.848 |
| Table | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe,cal (mg·g−1) | kL (L·mg−1) | R2 | kF | n | R2 | |
| 25 | 44.37 | 0.57 | 0.968 | 22.82 | 6.88 | 0.872 |
| 35 | 45.82 | 0.65 | 0.956 | 23.69 | 6.88 | 0.883 |
| 45 | 47.16 | 0.66 | 0.953 | 24.20 | 6.79 | 0.886 |
| 55 | 47.46 | 0.78 | 0.941 | 24.39 | 6.54 | 0.876 |
| Temp k | kJ·mol−1 | kJ·mol−1 | kJ·mol−1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb2+ | 298 | 150,273.72 | −29.53 | 6.485 | 121.20 |
| 308 | 176,132.16 | −30.93 | |||
| 318 | 196,169.76 | −32.22 | |||
| 328 | 202,551.57 | −33.32 | |||
| Cd2+ | 298 | 64,027.04 | −27.42 | 5.092 | 109.30 |
| 308 | 73,009.44 | −28.68 | |||
| 318 | 74,180.96 | −29.65 | |||
| 328 | 83,195.84 | −30.89 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, H.; Shao, X.; Shaghaleh, H.; Gao, W.; Hamoud, Y.A. Adsorption of Pb2+ and Cd2+ in Agricultural Water by Potassium Permanganate and Nitric Acid-Modified Coconut Shell Biochar. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1813. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13071813
Qin H, Shao X, Shaghaleh H, Gao W, Hamoud YA. Adsorption of Pb2+ and Cd2+ in Agricultural Water by Potassium Permanganate and Nitric Acid-Modified Coconut Shell Biochar. Agronomy. 2023; 13(7):1813. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13071813
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Hengji, Xiaohou Shao, Hiba Shaghaleh, Wei Gao, and Yousef Alhaj Hamoud. 2023. "Adsorption of Pb2+ and Cd2+ in Agricultural Water by Potassium Permanganate and Nitric Acid-Modified Coconut Shell Biochar" Agronomy 13, no. 7: 1813. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13071813
APA StyleQin, H., Shao, X., Shaghaleh, H., Gao, W., & Hamoud, Y. A. (2023). Adsorption of Pb2+ and Cd2+ in Agricultural Water by Potassium Permanganate and Nitric Acid-Modified Coconut Shell Biochar. Agronomy, 13(7), 1813. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13071813








