Untargeted UHPLC-MS Metabolomics Reveals the Metabolic Perturbations of Helicoverpa armigera under the Stress of Novel Insect Growth Regulator ZQ-8
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Test Insects
2.3. Sample Preparation for the Epidermis and Viscera of H. armigera
2.4. Extraction of Metabolites
2.5. UHPLC-MS/MS Conditions
2.6. Data Preprocessing and Metabolite Identification
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. UHPLC-MS/MS Identification Results and Data Quality Control
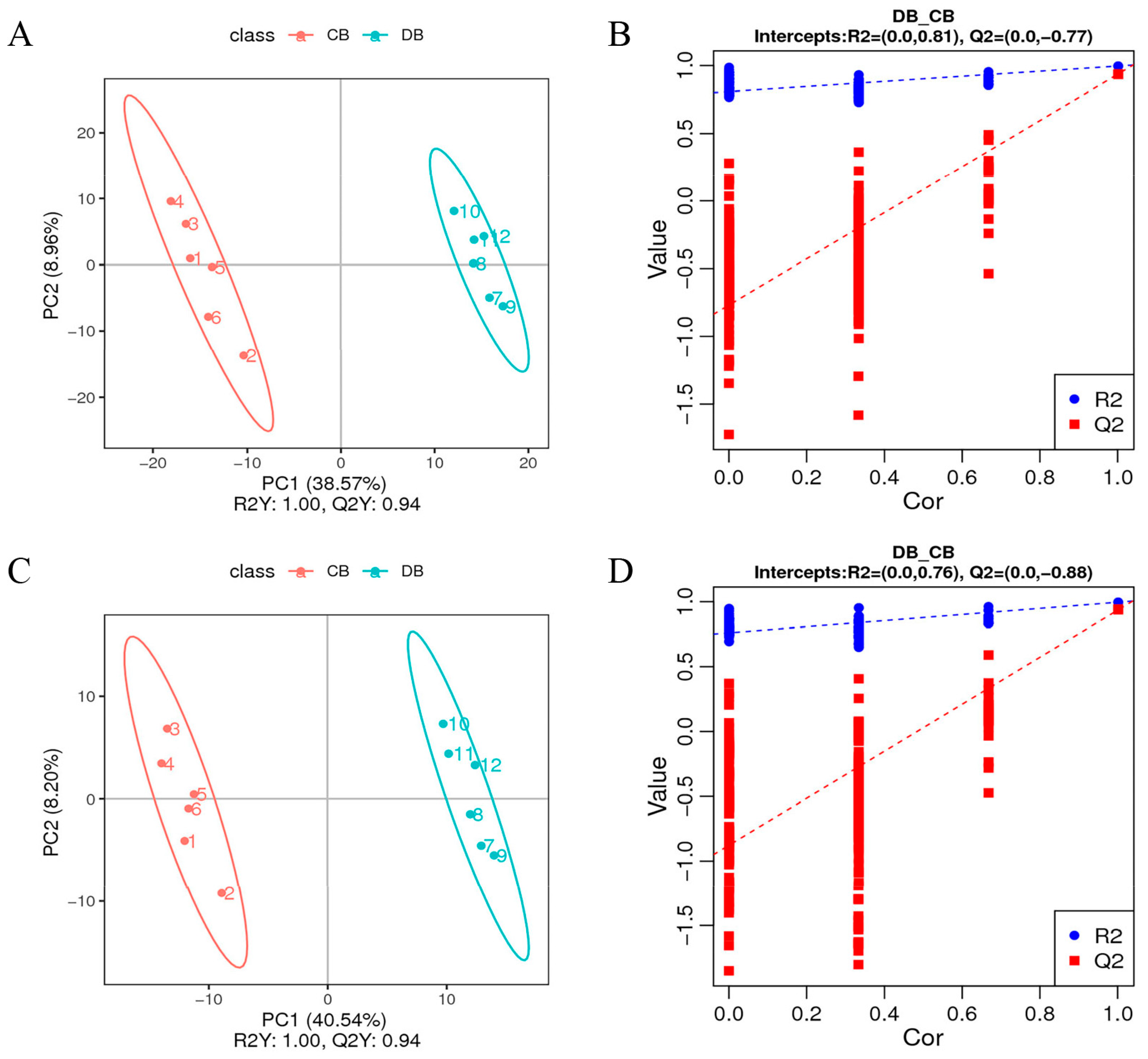
3.2. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
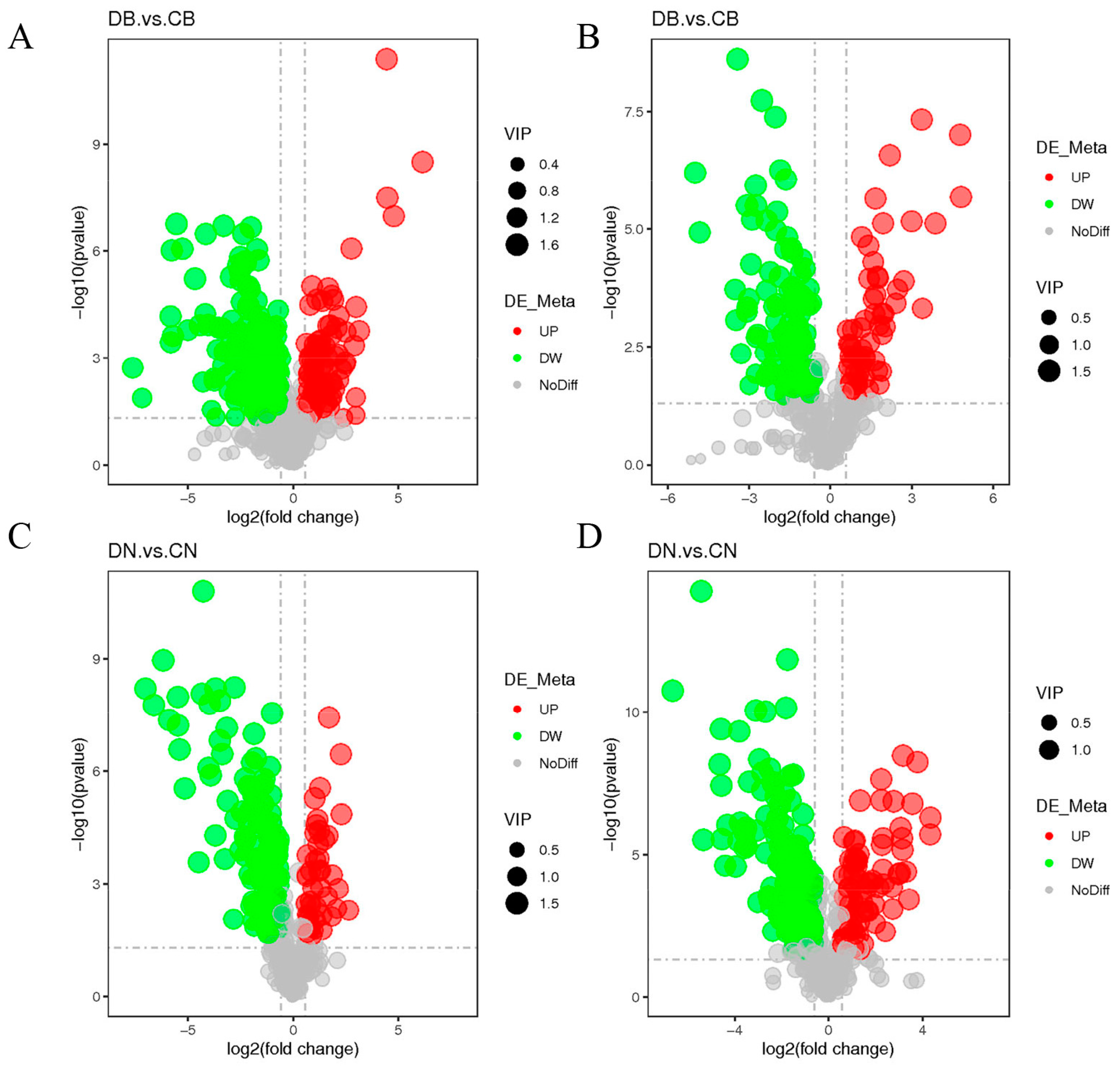
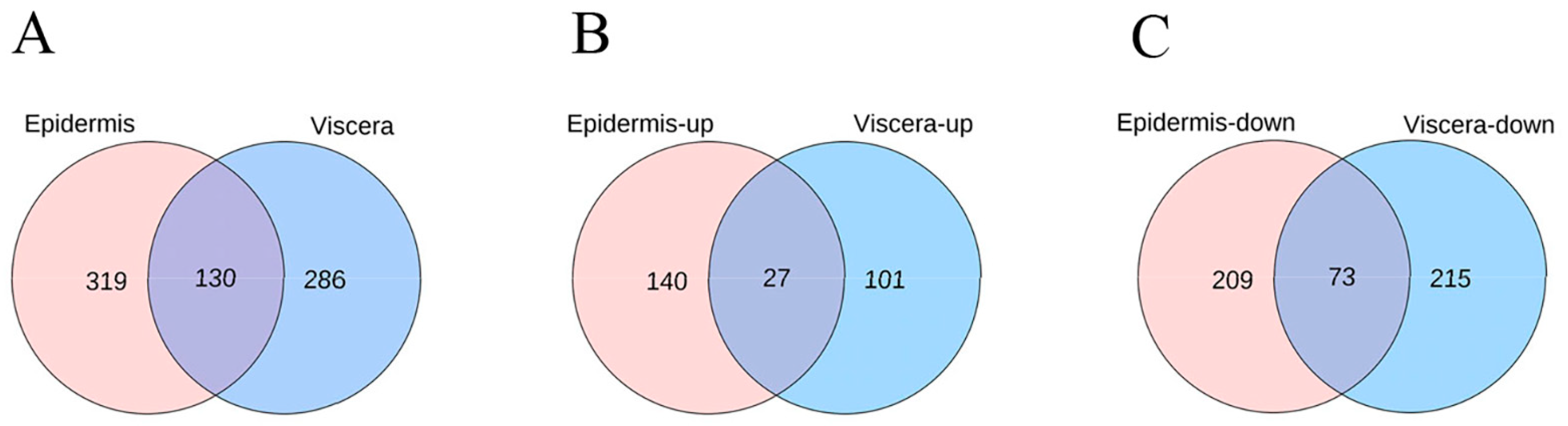
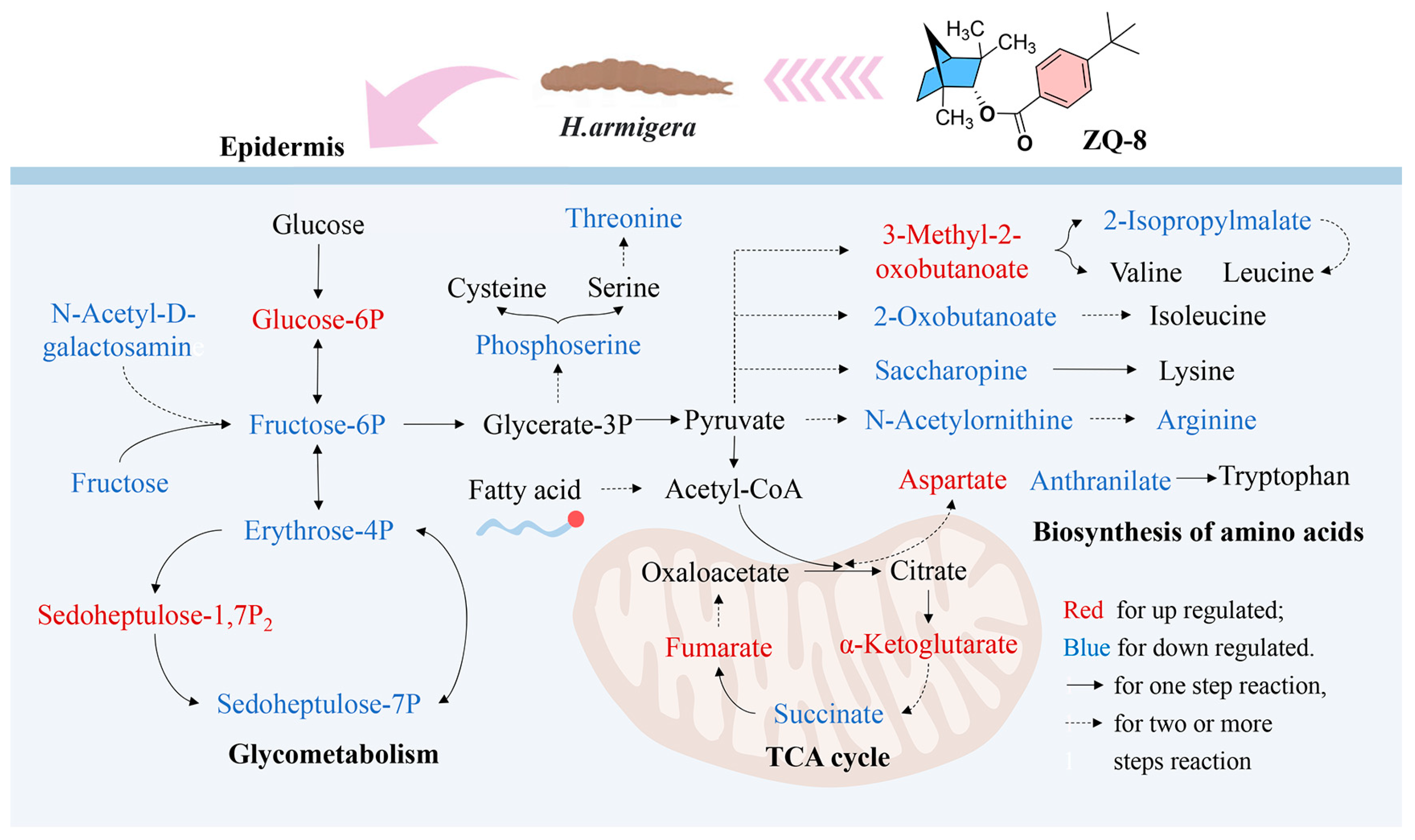
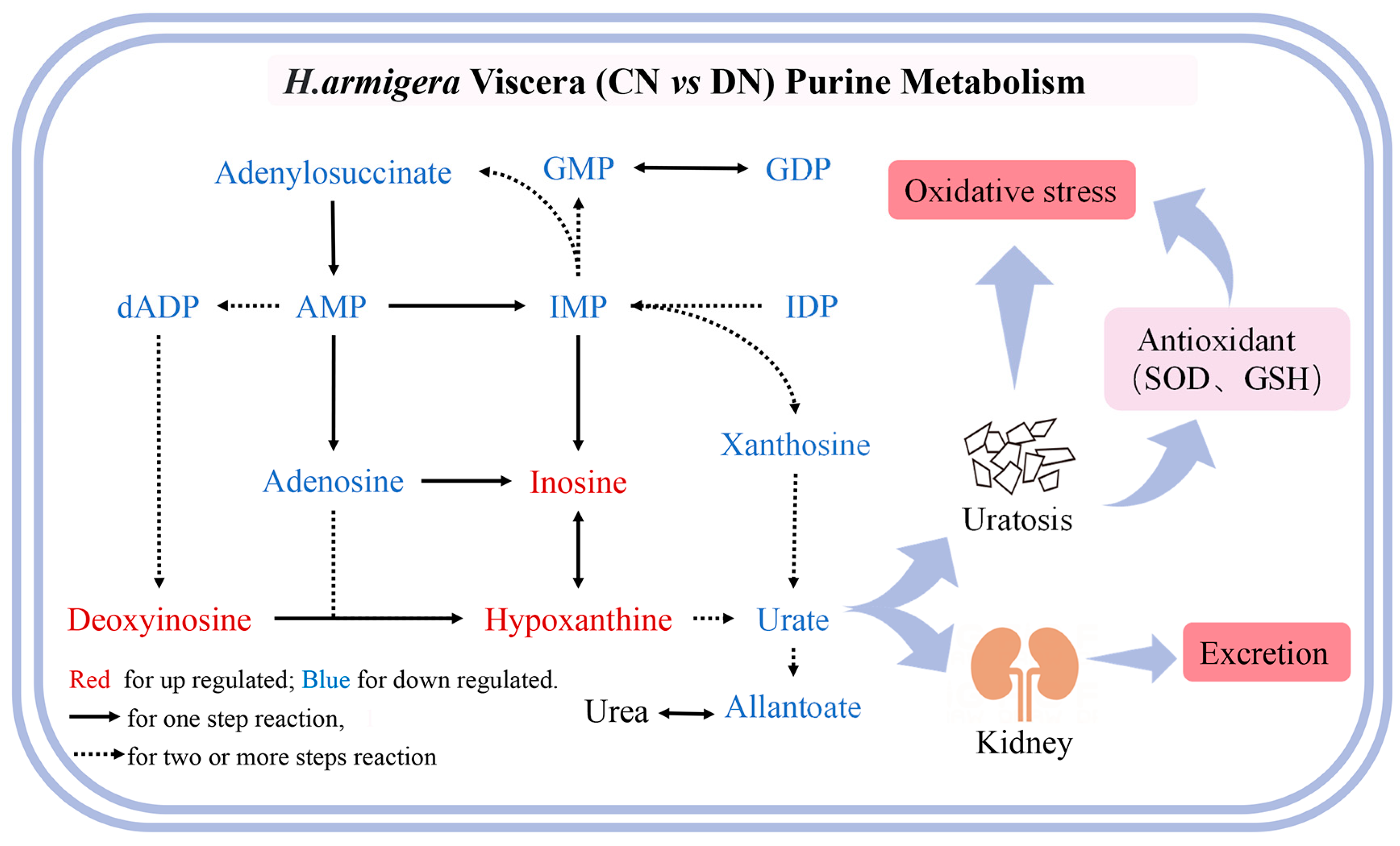
3.3. Effect of ZQ-8 on Metabolite Levels in Epidermis and Viscera of H. armigera
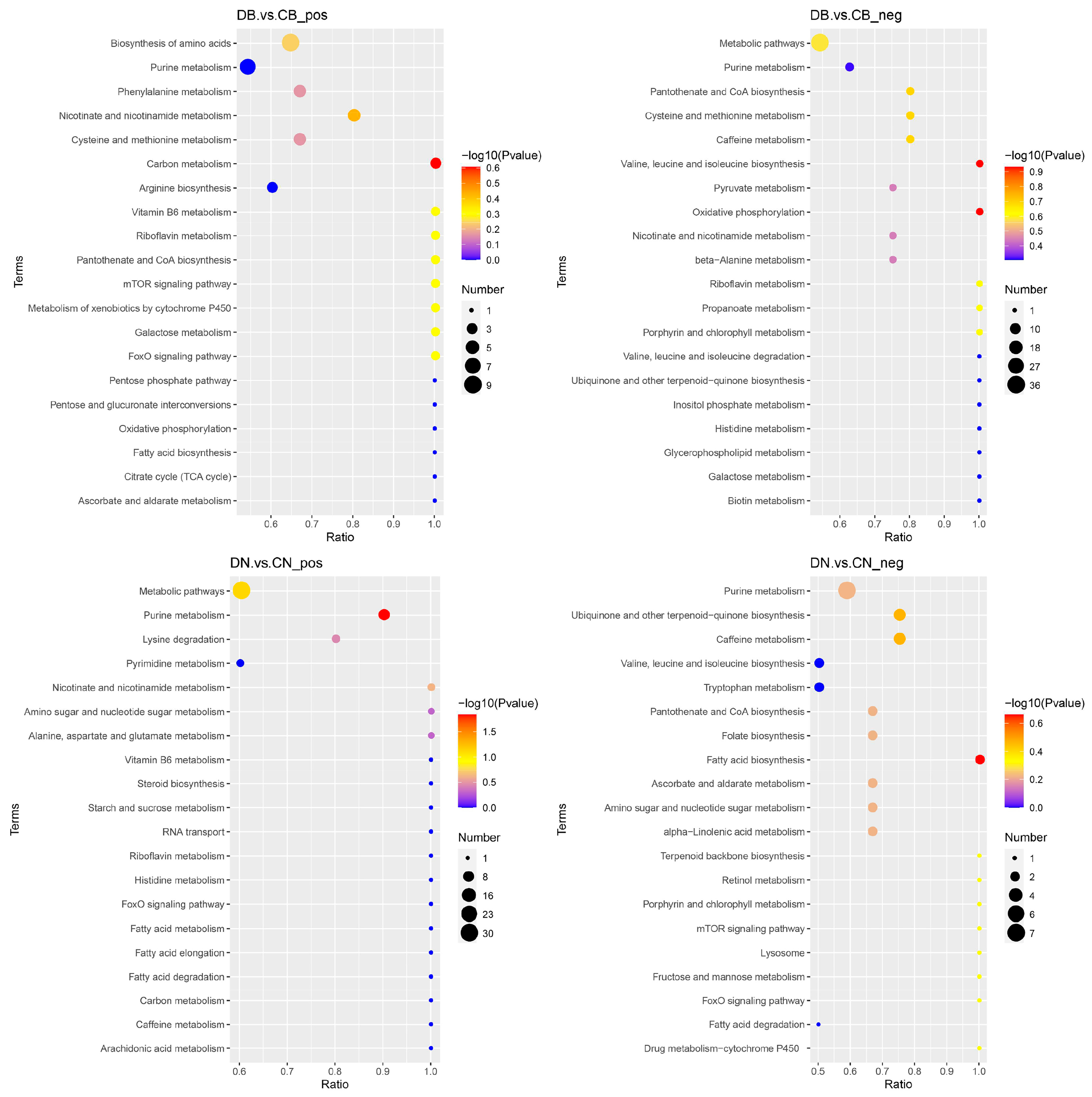
3.4. Effect of ZQ-8 on Metabolic Pathways of Epidermis and Viscera of H. armigera
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Du, L.; Ge, F.; Ding, Y.Q.; Wu, K.J. Using population energetics to evaluate potential damage to cotton by the cotton bollworm Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in North China. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2003, 38, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, W.T.; Walsh, T.K.; Downes, S.; Anderson, C.; Jermiin, L.S.; Wong, T.K.F.; Piper, M.C.; Chang, E.S.; Macedo, I.B.; Czepak, C.; et al. Mitochondrial DNA and trade data support multiple origins of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera, Noctuidae) in Brazil. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nibouche, S.; Gozé, E.; Babin, R.; Beyo, J.; Brévaultet, T. Modeling Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) Damages on Cotton. Environ. Entomol. 2007, 36, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, W.T.; Soria, M.F.; Walsh, T.; Thomazoni, D.; Silvie, P.; Behere, G.T.; Anderson, C.; Downes, S. A brave new world for an old world pest: Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in Brazil. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vatanparast, M.; Kazzazi, M.; Sajjadian, S.M.; Park, Y. Knockdown of Helicoverpa armigera protease genes affects its growth and mortality via RNA interference. Arch. Insect Biochem. Phys. 2021, 108, e21840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnsworth, C.A.; Teese, M.G.; Yuan, G.R.; Li, Y.Q.; Scott, C.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.D.; Russell, R.J.; Oakeshott, J.G.; CSIRO, E.; et al. Esterase-based metabolic resistance to insecticides in heliothine and spodopteran pests. J. Pestic. Sci. 2010, 35, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horoiwa, S.; Yokoi, T.; Masumoto, S.; Minami, S.; Ishizuka, C.; Kishikawa, H.; Ozaki, S.; Kitsuda, S.; Nakagawa, Y.; Miyagawa, H. Structure-based virtual screening for insect ecdysone receptor ligands using MM/PBSA. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 1065–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harðardóttir, H.M.; Male, R.; Nilsen, F.; Eichner, C.; Dondrup, M.; Dalvin, S. Chitin synthesis and degradation in Lepeophtheirus salmonis: Molecular characterization and gene expression profile during synthesis of a new exoskeleton. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Phys. 2019, 227, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelkenberg, M.; Odman-Naresh, J.; Muthukrishnan, S.; Merzendorfer, H. Chitin is a necessary component to maintain the barrier function of the peritrophic matrix in the insect midgut. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 56, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, F. Studies on the action mechanism of benzoylurea insecticides to inhibit the process of chitin synthesis in insects: A review on the status of research activities in the past, the present and the future prospects. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2010, 97, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douris, V.; Steinbach, D.; Panteleri, R.; Livadaras, I.; Pickett, J.A.; Van Leeuwen, T.; Nauen, R.; Vontas, J. Resistance mutation conserved between insects and mites unravels the benzoylurea insecticide mode of action on chitin biosynthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 14692–14697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wang, K.; Ji, W.N.; Xu, H.; Liu, Y.B.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Gao, F.C.; Lin, Z.G.; Ji, T. Metabolomic analysis of honey bees (Apis mellifera) response to carbendazim based on UPLC-MS. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2021, 179, 104975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Tian, Y.Q.; Du, M.Y.; Xie, Q.R.; Chen, Y.Y.; Ma, L.L.; Huang, Y.D.; Yin, Z.B.; Xu, H.H.; Wu, X.Z. Mechanism of rotenone toxicity against Plutella xylostella: New perspective from a spatial metabolomics and lipidomics study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhao, Z.H. Metabonomics reveals that entomopathogenic nematodes mediate tryptophan metabolites that kill host insects. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1042145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, S.T.; Du, W.X.; Bai, S.M.; Chen, G. Insecticidal effect of juglone and its disturbance analysis in metabolic profiles of Aphis gossypii glover using 1H NMR-based metabonomics approach. Phytoparasitica 2018, 46, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.T.; Wang, C.J.; Xin, F.; Han, X.Q.; Zhang, J.; Sun, K. Synthesis, Insecticidal, Fungicidal Activities and Structure-Activity Relationships of Tschimganin Analogs. Molecules 2018, 23, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chen, M.H.; Han, X.Q.; Liu, C.Y.; Wang, C.J.; Zhang, G.Q.; Yang, D.S.; Zhao, S.F. Discovery of ZQ-8, a Novel Starting Point to Develop Inhibitors against the Potent Molecular Target Chitinase. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 11314–11323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Want, E.J.; Masson, P.; Michopoulos, F.; Wilson, I.D.; Theodoridis, G.; Plumb, R.S.; Shockcor, J.; Loftus, N.; Holmes, E.; Nicholson, J.K. Global metabolic profiling of animal and human tissues via UPLC-MS. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, B.; Mei, Z.L.; Zeng, C.W.; Liu, S.Q. metaX: A flexible and comprehensive software for processing metabolomics data. BMC Bioinf. 2017, 18, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelgaffar, H.; Tague, E.D.; Castro Gonzalez, H.F.; Campagna, S.R.; Jurat-Fuentes, J.L. Midgut metabolomic profiling of fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) with field-evolved resistance to Cry1F corn. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 106, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batz, Z.A.; Armbruster, P.A. Diapause-associated changes in the lipid and metabolite profile of the Asian tiger mosquito, Aedes albopictus. J. Exp. Biol. 2018, 221, 189480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gika, H.G.; Theodoridis, G.A.; Plumb, R.S.; Wilson, I.D. Current practice of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry in metabolomics and metabonomics. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. 2014, 87, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, T.F.; Burton, S.; Wang, Y.F.; Xu, S.Y.; Zhang, W.X.; Yu, L.S. Metabolomic analysis of honey bee, Apis mellifera L. response to thiacloprid. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2018, 152, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, L.S.; Tian, H.F.; Hang, Y.; Wen, C.W.; Huang, Y.H.; Wang, B.F.; Hu, J.W.; Xu, J.P.; Deng, M.J. 1HNMR-based metabonomic evaluation of the pesticides camptothecin and matrine against larvae of Spodoptera litura. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.F.; Long, Z.X.; Zhang, Y.J.; Luo, C.Y.; Yan, L.T.; Gao, W.Y.; Li, H. The chemical mechanisms of the enzymes in the branched-chain amino acids biosynthetic pathway and their applications. Biochimie 2021, 184, 72–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.J.; Lin, X.D.; Wen, C.W.; Dong, M.J.; Lin, Q.T.; Zhang, S.Z.; Xu, J.P. Metabolic changes in the midgut of Eri silkworm after Oral administration of 1-deoxynojirimycin: A 1H-NMR-based metabonomic study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e173213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weihrauch, D.; Donnell, M.J.O. Mechanisms of nitrogen excretion in insects. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2021, 47, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patetsini, E.; Dimitriadis, V.K.; Kaloyianni, M. Biomarkers in marine mussels, Mytilus galloprovincialis, exposed to environmentally relevant levels of the pesticides, chlorpyrifos and penoxsulam. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 126, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, R.D.; Vionette-Amaral, R.J.; Lowenberger, C.; Rivera-Pomar, R.; Monteiro, F.A.; Minx, P.; Spieth, J.; Carvalho, A.B.; Panzera, F.; Lawson, D.; et al. Genome of Rhodnius prolixus, an insect vector of Chagas disease, reveals unique adaptations to hematophagy and parasite infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 14936–14941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruegenberg, S.; Mayr, F.A.M.C.; Atanassov, I.; Baumann, U.; Denzel, M.S. Protein kinase A controls the hexosamine pathway by tuning the feedback inhibition of GFAT-1. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruegenberg, S.; Horn, M.; Pichlo, C.; Allmeroth, K.; Baumann, U.; Denzel, M.S. Loss of GFAT-1 feedback regulation activates the hexosamine pathway that modulates protein homeostasis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, E. Chitin synthesis and inhibition: A revisit. Pest Manag. Sci. 2001, 57, 946–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolognesi, R.; Arakane, Y.; Muthukrishnan, S.; Kramer, K.J.; Terra, W.R.; Ferreira, C. Sequences of cDNAs and expression of genes encoding chitin synthase and chitinase in the midgut of Spodoptera frugiperda. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005, 35, 1249–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, Y.X.; Ren, H.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J.H.; Fan, X.J. Advances in study and application on chitinase. Life Sci. Res. 2015, 19, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Wang, S.S.; Zhong, F.; Zhou, M.; Jiang, X.Y.; Cheng, Y.S.; Dan, Y.H.; Hu, G.; Li, C.; Tang, B.; et al. Chitinase (CHI) of Spodoptera frugiperda affects molting development by regulating the metabolism of chitin and trehalose. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 1034926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Yang, L.; Jin, F.; Yin, Y.; Xie, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, G.; Yang, D.; Han, X. Untargeted UHPLC-MS Metabolomics Reveals the Metabolic Perturbations of Helicoverpa armigera under the Stress of Novel Insect Growth Regulator ZQ-8. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13051315
Liu C, Yang L, Jin F, Yin Y, Xie Z, Yang L, Zhao S, Zhang G, Yang D, Han X. Untargeted UHPLC-MS Metabolomics Reveals the Metabolic Perturbations of Helicoverpa armigera under the Stress of Novel Insect Growth Regulator ZQ-8. Agronomy. 2023; 13(5):1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13051315
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Caiyue, Lin Yang, Fuqiang Jin, Yuelan Yin, Zizheng Xie, Longfei Yang, Sifeng Zhao, Guoqiang Zhang, Desong Yang, and Xiaoqiang Han. 2023. "Untargeted UHPLC-MS Metabolomics Reveals the Metabolic Perturbations of Helicoverpa armigera under the Stress of Novel Insect Growth Regulator ZQ-8" Agronomy 13, no. 5: 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13051315
APA StyleLiu, C., Yang, L., Jin, F., Yin, Y., Xie, Z., Yang, L., Zhao, S., Zhang, G., Yang, D., & Han, X. (2023). Untargeted UHPLC-MS Metabolomics Reveals the Metabolic Perturbations of Helicoverpa armigera under the Stress of Novel Insect Growth Regulator ZQ-8. Agronomy, 13(5), 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13051315






