Effects of Salinity-Stress on Seed Germination and Growth Physiology of Quinclorac-Resistant Echinochloa crus-galli (L.) Beauv
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Detection of Quinclorac-Resistance Level of All Selected E. crus-galli Populations
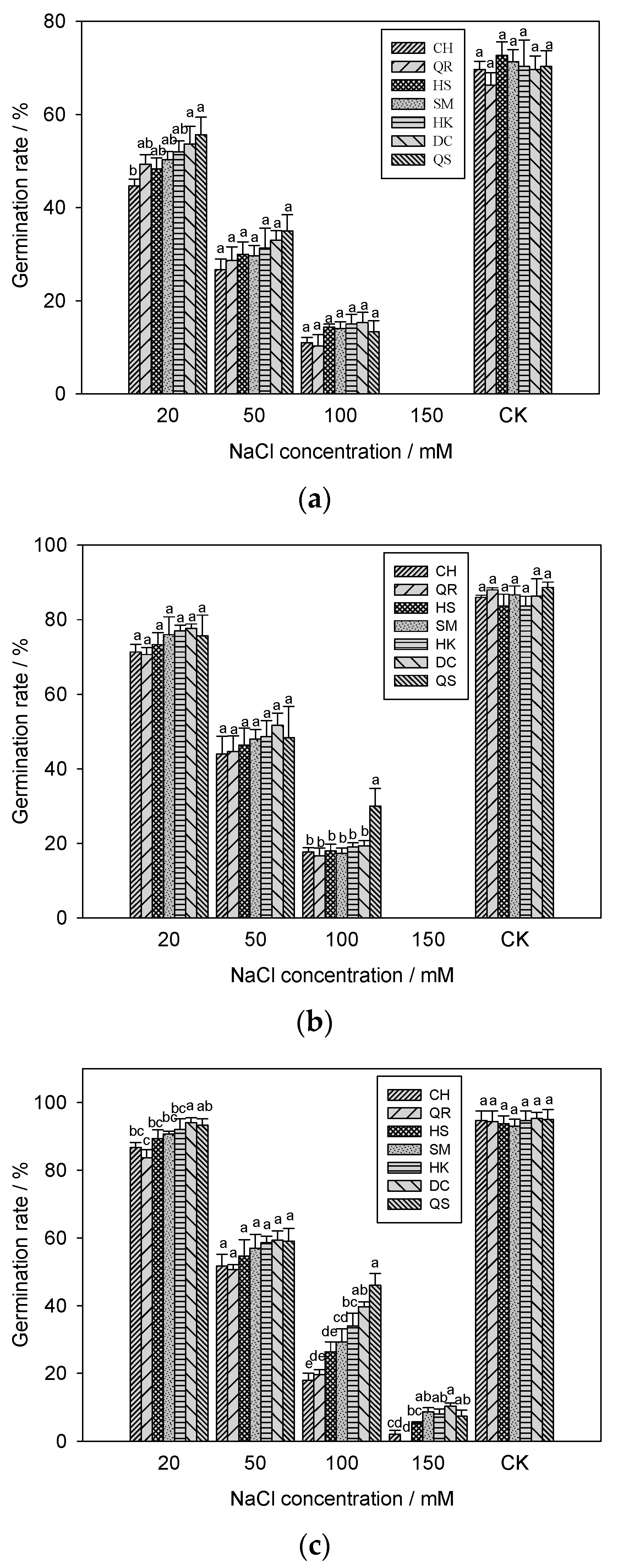
2.3. Effects of Salinity Stress on the Seed Germination of E. crus-galli
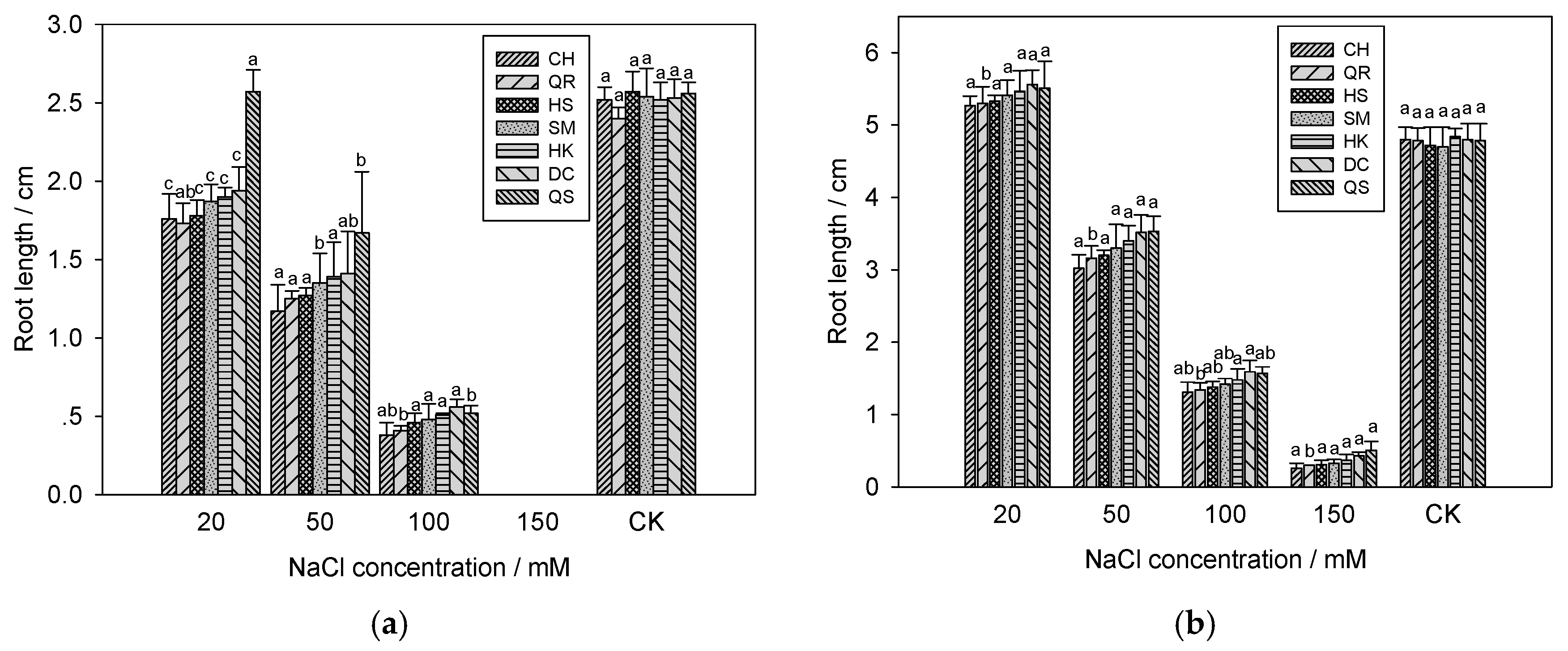
2.4. Effects of Salinity Stress on the Young Shoots and Roots Growth of E. crus-galli
2.5. Effects of Salinity Stress on the Fresh Weight of E. crus-galli
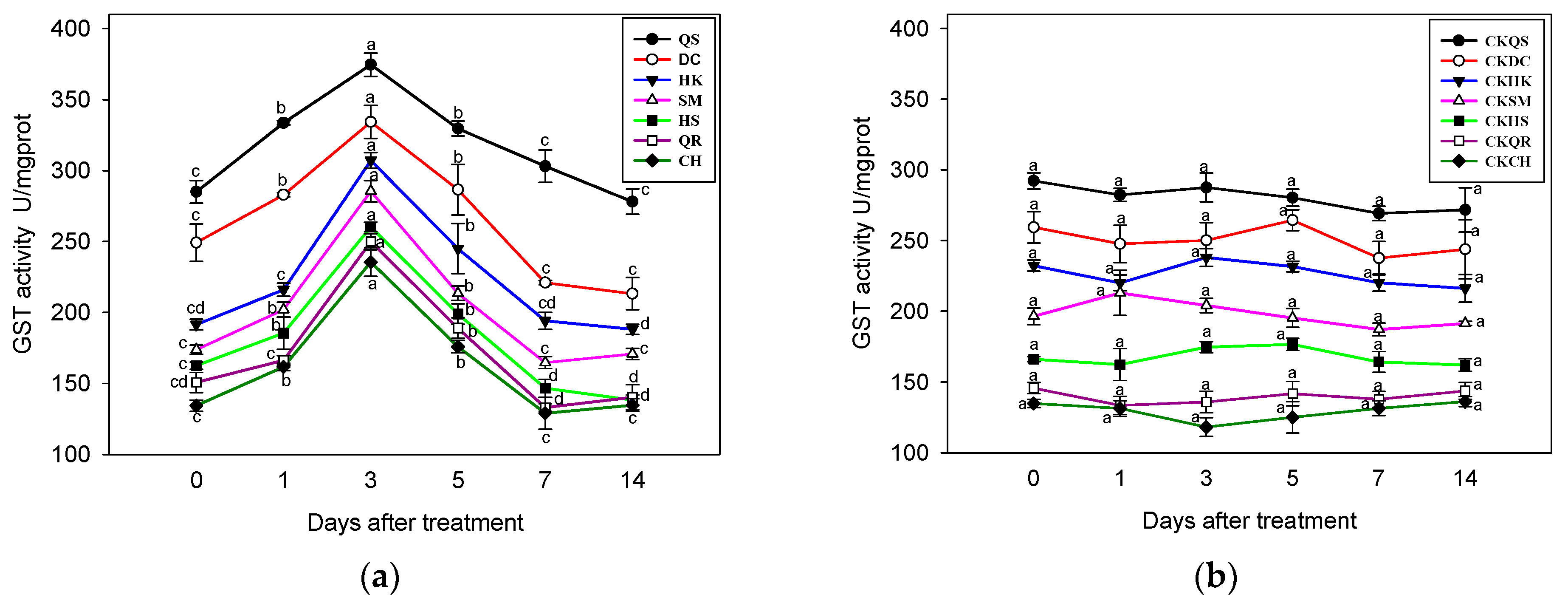
2.6. Effects of Salinity Stress on the GST Activity of E. crus-galli
2.7. Transcriptomics of Quinclorac-Resistant and Sensitive E. crus-galli under Salt Stress
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Susceptibility of E. crus-galli to Quinclorac
3.2. Seed Germination of Seven E. crus-galli Populations under Salinity Stress
3.3. Shoots and Roots Growth of Seven E. crus-galli Populations under Salinity Stress
3.4. Fresh Weight of Seven E. crus-galli Populations under Salinity Stress
3.5. GST Activity Analysis
3.6. Transcription and Functional Analysis of E. crus-galli Induced by Salinity Stress
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mumtaz, M.Z.; Saqib, M.; Abbas, G.; Akhtar, J.; Qamar, Z. Genotypic variation in rice for grain yield and quality as affected by salt-affected field conditions. J. Plant Nutr. 2018, 41, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R.; Tester, M. Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2018, 59, 651–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amador, B.; López-Aguilar, R.; Kaya, C.; Larrinaga-Mayoral, J.; Flores-Hernández, A. Comparative effects of NaCl andpolyethylene glycol on germination, emergence and seedling growth of cowpea. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2002, 188, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnusamy, V.; Jagendorf, A.; Zhu, J. Understanding and improving salt tolerance in plants. Crop Sci. 2005, 45, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richard, L.A. Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soil. Soil Sci. 1954, 78, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maun, M.A.; Barrett, S.C.H. Biology of Canadian weeds: 77. Echinochloa crus-galli (L.) Beauv. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1986, 66, 739–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.Y.; Lin, Z.X.; Li, G.M.; Wang, Y.Y.; Qiu, J.; Fu, F. Echinochloa chloroplast genomes: Insights into the evolution andtaxonomic identification of two weedy species. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113657. [Google Scholar]
- Holm, L.G.; Plucknett, D.L.; Pancho, J.V.; Herberger, J.P.; East-West, C. The World’s Worst Weeds: Their Distribution and Biology; The University Press of Hawaii: Hawaii, HI, USA, 1997; Illus. maps; pp. 565–586. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.Y.; Lv, B.; Wang, Q. A resistance mechanism dependent upon the inhibition of ethylene biosynthesis. Pest Manag. Sci. 2013, 69, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Martinez, N.; Marshall, G.; Prado, R. Resistance of barnyardgrass (Echinochloa crus-galli) to atrazine and quinclorac. Pest Manag. Sci. 1997, 51, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovelace, M.L.; Talbert, R.E.; Hoagland, R.E.; Scherder, E. Quinclorac absorption and translocation characteristics in quinclorac- and propanil-resistant and -susceptible barnyardgrass (Echinochloa crus-galli) biotypes. Weed Technol. 2007, 21, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.L.; Bai, L.Y.; Liu, D.C.; Liu, X.Y.; Yu, L.Q. Resistance of Echinochloa crus-galli (L.) Beauv. to quinclorac in the Rice Growing region of the middle andlower reaches of Yangtze River in China. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2013, 27, 184–190. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.H.; Ie, S.S.; Katsuichiro, K.; Usui, K. Relationship between Na content or K/Na ratio in shoots and salt tolerance in several gramineous plants. J. Weed Sci. Technol. 1999, 44, 293–299. [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan, B.; Abugho, S.; Amas, R.A.; Gregorio, G. Effect of Salinity on Growth of Barnyardgrass (Echinochloa crus-galli), Horse Purslane (Trianthema portulacastrum), Junglerice (Echinochloa colona), and Rice. Weed Sci. 2013, 61, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abogadallah, G.M.; Serag, M.M.; El-Katony, T.; Quick, W.P. Salt tolerance at germination and vegetative growth involves different mechanisms in barnyard grass (Echinochloa crus-galli L.) mutants. Plant Growth Regul. 2010, 60, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roxas, V.P.; Smith, R.K.J.; Allen, E.R.; Allen, R.D. Overexpression of glutathione S-transferase/glutathione peroxidase enhances the growth of transgenic tobacco seedlings during stress. Nat. Biotechnol. 1997, 15, 988–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.M.; Fang, Y.; Yang, H.N.; Bai, L.Y. Effects of drought-stress on seed germination and growth physiology of quinclorac-resistant Echinochloa crus-galli. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214480. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.F.; Jin, S.; Wu, L.M.; Zhou, X.M.; Liu, X.Y.; Bai, L.Y. Influence of environmental factors on seed germination and emergence of Asia minor bluegrass (Polypogon fugax). Weed Technol. 2016, 30, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Williams, B.A.; Pertea, G.; Mortazavi, A.; Kwan, G.; Baren, M.J.V.; Salzberg, S.L.; Wold, B.J.; Pachrer, L. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Öztetik, E.A. A Tale of Plant Glutathione S-Transferases: Since 1970. Bot. Rev. 2008, 74, 419–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.M.; Lee, H.J.; Song, Y.H.; Kim, H.J. Effect of salt stress on the growth, mineral contents, and metabolite profiles of spinach. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 101, 3787–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasanpour, Z.; Karimi, H.R.; Mirdehghan, S.H. Effects of salinity and water stress on echophysiological parameters and micronutrients concentration of pomegranate (Punica granatum L.). J. Plant Nutr. 2015, 38, 795–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, H.R.; Sadeghi-Seresht, E. Effects of salinity stress on growth indices, physiological parameters and element concentration in Banebaghi (Pistacia sp.) as rootstock for pistachio. J. Plant Nutr. 2018, 41, 1094–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, F.; Xie, Y.; Farooq, M.A.; Wang, J.; Yang, C.; Gill, R.A.; Zhu, J.W.; Zhou, W.J. Salinity reduces 2,4-D efficacy in Echinochloa crus-galli by affecting redox balance, nutrient acquisition, and hormonal regulation. Protoplasma 2017, 255, 785–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lv, M.T.; Islam, F.; Gill, R.A.; Chong, Y.; Ali, B.; Yan, G.J.; Zhou, W.J. Salicylic acid mediates antioxidant defense system and ABA pathway related gene expression in Oryza sativa against quinclorac toxicity. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 133, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Islam, F.; Li, L.; Long, M.J.; Yang, C.; Jin, X.L.; Ali, B.; Mao, B.Z.; Zhou, W.J. Complementary RNA-sequencing based transcriptomics and iTRAQ proteomics reveal the mechanism of the alleviation of quinclorac qtress by salicylic acid in Oryza sativa ssp. japonica. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zöerb, C.; Geilfus, C.M.; Dietz, K.J. Salinity and crop yield. Plant Biol. 2019, 21 (Suppl. S1), 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, M.; Binoy, S.; Hanuman, S.J.; Parbodh, C.S.; Nanthi, S.B. Soil salinity under climate change: Challenges for sustainable agriculture and food security. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 280, 111736. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Zhai, D.P.; Zhang, C.P.; Ma, J.J. Influence of saline water irrigation on root distribution, wheat yield, and soil salinity. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2021, 147, 04021005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, B.S.; Johnson, D.E. Seed germination ecology of Junglerice (Echinochloa colona): A major weed of rice. Weed Sci. 2009, 57, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, F.; Fogliatto, S.; Vidotto, F. Effect of salinity on Echinochloa crus-galli germination as affected by herbicide resistance. Ital. J. Agron. 2018, 13, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.B.; Huang, H.Z.; Huang, B.Q.; Zhao, J.B. Studies on resistance of Echinochloa crus-glli to quinclorac in the rice plantation in south and middle China. J. S. China Agric. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2002, 23, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.B.; Wang, X.L.; Xia, Y.; Huang, H.Z. Studies on the resistance of Echinochloa crus-galli to quinclorac in rice planting areas in Hunan province. Plant Protect. 2004, 30, 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.B.; Wu, Z.H.; Chen, X.; Liu, H.B.; Huang, B.Q. Determination of resistance of Echinochloa crus-galli to quinclorac in the rice planting areas of south China. Chin. J. Pest Sci. 2003, 4, 88–92. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamurthy, S.L.; Gautam, R.K.; Sharma, P.C.; Sharma, D.K. Effect of different salt stresses on agro-morphological traits and utilisation of salt stress indices for reproductive stage salt tolerance in rice. Field Crop Res. 2016, 190, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, V.S.; Alencar, N.L.M.; Lacerda, C.F.; Prisco, J.T.; Gomes-Filho, E. Changes in physiological Changes in physiological and biochemical indicators associated with salt tolerance in cotton, sorghum and cowpea. Afr. J. Biochem. Res. 2011, 5, 264–271. [Google Scholar]
- Noreen, F.; Muhammad, S.; Ghulam, A.; Mubshar, H.; Muhammad, N.; Allah, W. Germination, growth and ions uptake of moringa (Moringa oleifera L.) grown under saline condition. J. Plant Nutr. 2018, 12, 1555–1565. [Google Scholar]
- Kukorelli, G.; Reisinger, P.; Pinke, G. ACCase inhibitor herbicides—Selectivity, weed resistance and fitness cost: A review. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2013, 59, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnhoff, E.; Keith, B.; Dyer, W.K.; Peterson, R.; Menalled, F. Multiple herbicide resistance in wild oat and impacts on physiology, germinability, and seed production. Agron. J. 2013, 105, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menchari, Y.; Chauvel, B.; Darmency, H.; Délye, C. Fitness costs associated with three mutant acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase alleles endowing herbicide resistance in black-grass Alopecurus myosuroides. J. Appl. Ecol. 2008, 45, 939–947.41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulmasov, T.; Ohmiya, A.; Hagen, G.; Guilfoyle, T. The soybean GH2/4 gene that encodes a glutathione S-transferase has a promoter that is activated by a wide range of chemical agents. Plant Physiol. 1995, 108, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hatzios, K.K.; Hoagland, R.E. Crop Safeners for Herbicides: Development, Uses and Mechanisms of Action; Academic Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 65–101. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, M.C.; Ko, K.; Chang, W.L.; Kuo, W.C.; Chen, G.H.; Lin, T.P. Increased glutathione contributes to stress tolerance and global translational changes in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2015, 83, 926–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.L.; Zhao, P.Y.; Zhou, X.M.; Bai, L.Y. Excellent sustained-release efficacy of herbicide quinclorac with cationic covalent organic frameworks. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 126979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| E. crus-galli Populations | GR50 (g a.i./ha) | Resistant Index |
|---|---|---|
| CH | 4417.91 | 159.78 |
| QR | 3855.01 | 139.42 |
| HS | 141.64 | 5.12 |
| SM | 86.64 | 3.13 |
| HK | 64.12 | 2.32 |
| DC | 31.46 | 1.14 |
| QS | 27.65 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, L.; Yang, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Peng, Q. Effects of Salinity-Stress on Seed Germination and Growth Physiology of Quinclorac-Resistant Echinochloa crus-galli (L.) Beauv. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12051193
Wu L, Yang H, Li Z, Wang L, Peng Q. Effects of Salinity-Stress on Seed Germination and Growth Physiology of Quinclorac-Resistant Echinochloa crus-galli (L.) Beauv. Agronomy. 2022; 12(5):1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12051193
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Lamei, Haona Yang, Zuren Li, Lifeng Wang, and Qiong Peng. 2022. "Effects of Salinity-Stress on Seed Germination and Growth Physiology of Quinclorac-Resistant Echinochloa crus-galli (L.) Beauv" Agronomy 12, no. 5: 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12051193
APA StyleWu, L., Yang, H., Li, Z., Wang, L., & Peng, Q. (2022). Effects of Salinity-Stress on Seed Germination and Growth Physiology of Quinclorac-Resistant Echinochloa crus-galli (L.) Beauv. Agronomy, 12(5), 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12051193






