Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis of Head in Laodelphax striatellus upon Rice Stripe Virus Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects
2.2. Samples Preparation
2.3. RNA Isolation and cDNA Library Construction for Sequencing
2.4. Data Quality Controlling and Mapping to Reference Genome
2.5. Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes and Enrichment
2.6. Validation of DEGs through Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
3. Results
3.1. Data Quality Evaluation and Mapping to Reference Genome
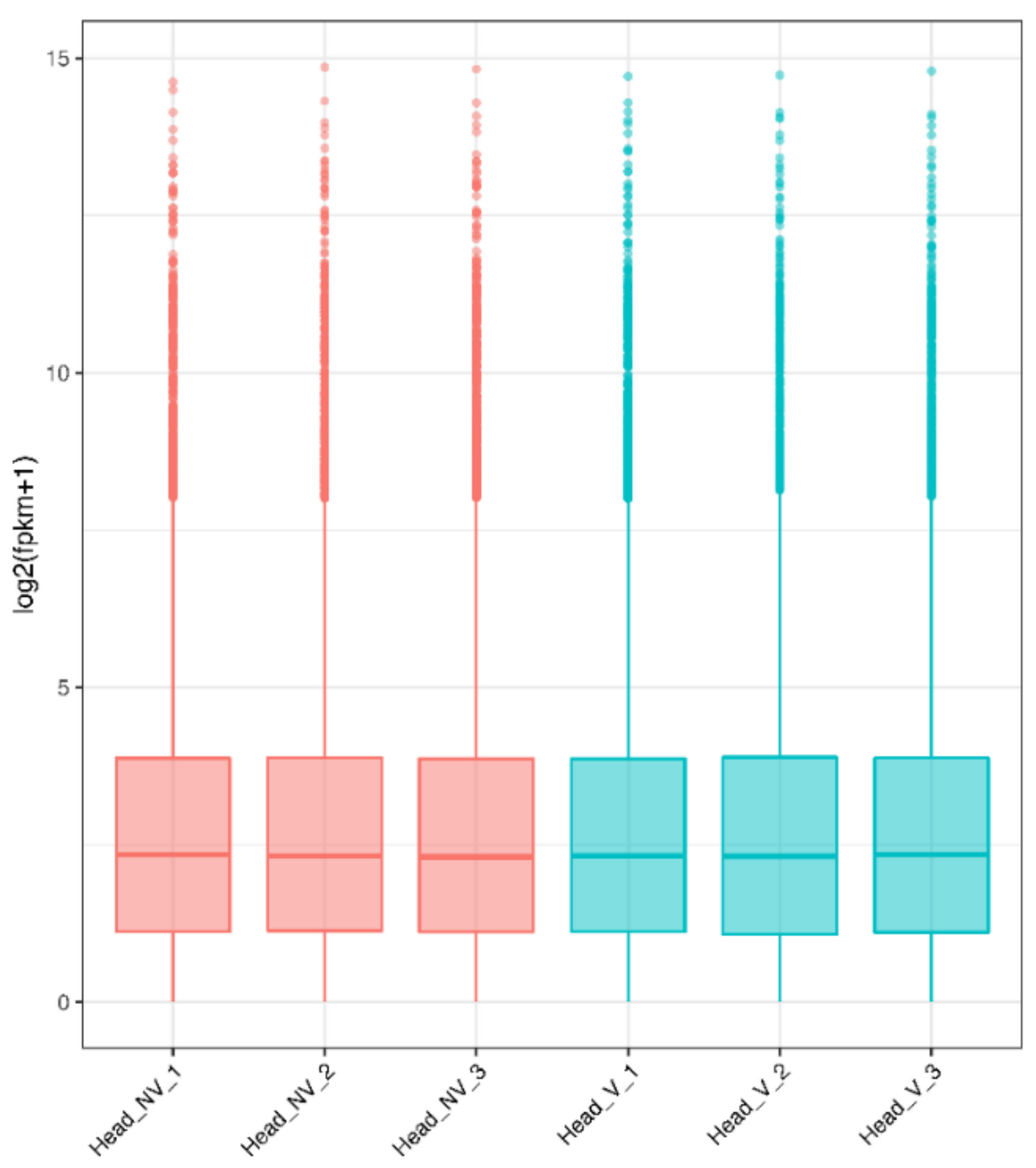
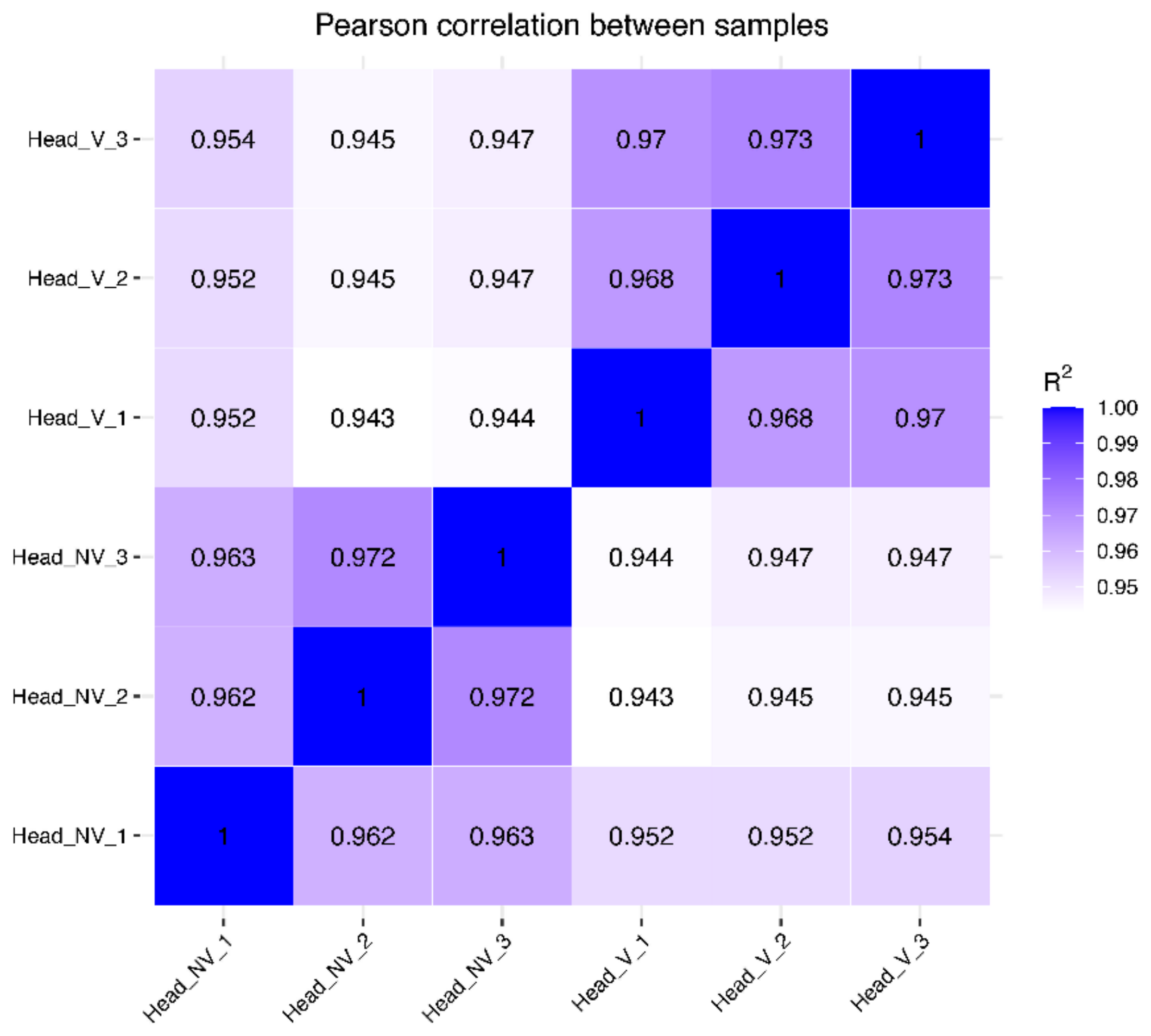
3.2. Gene Expression Distribution and Pearson Correlations between Samples
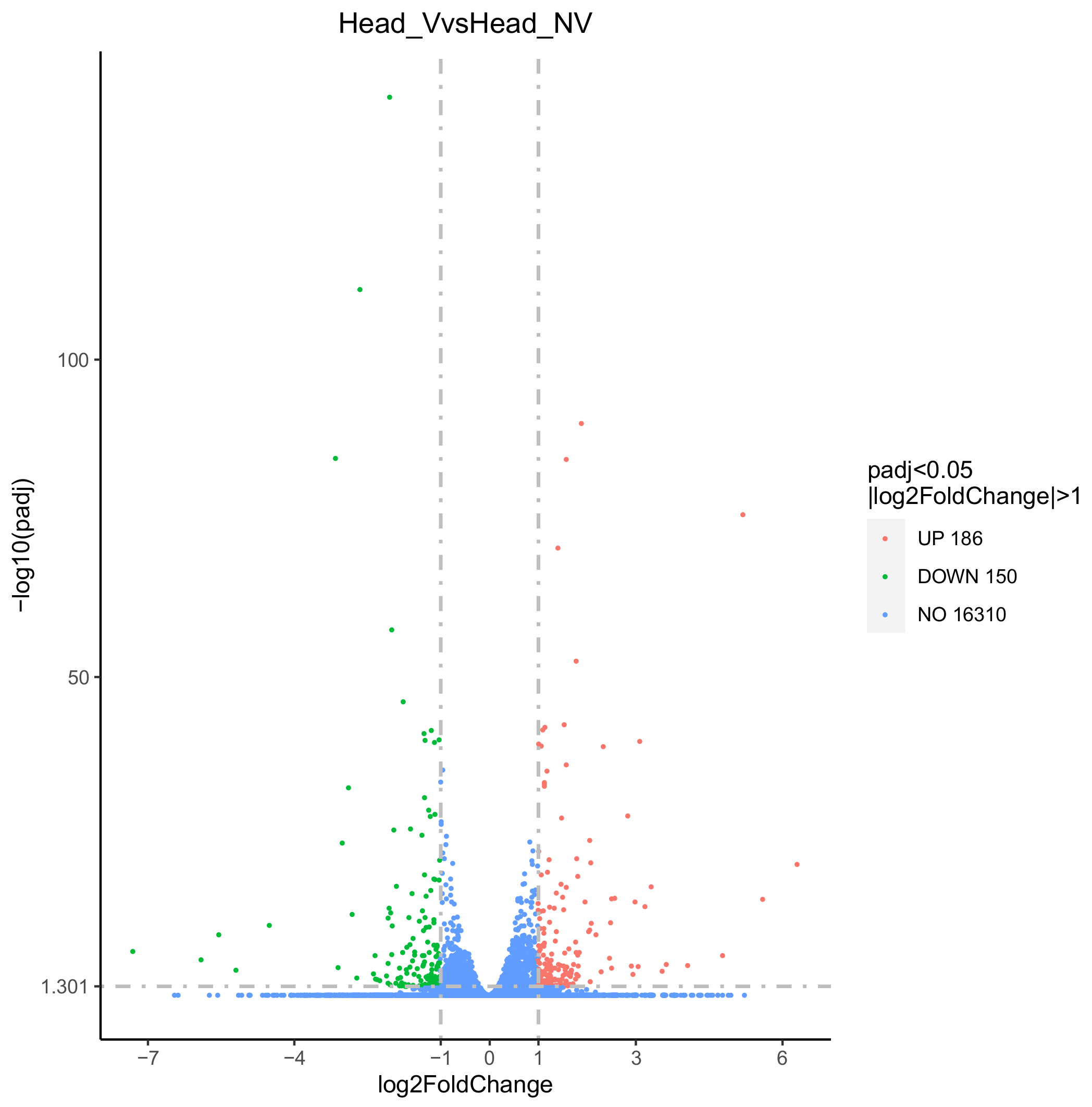
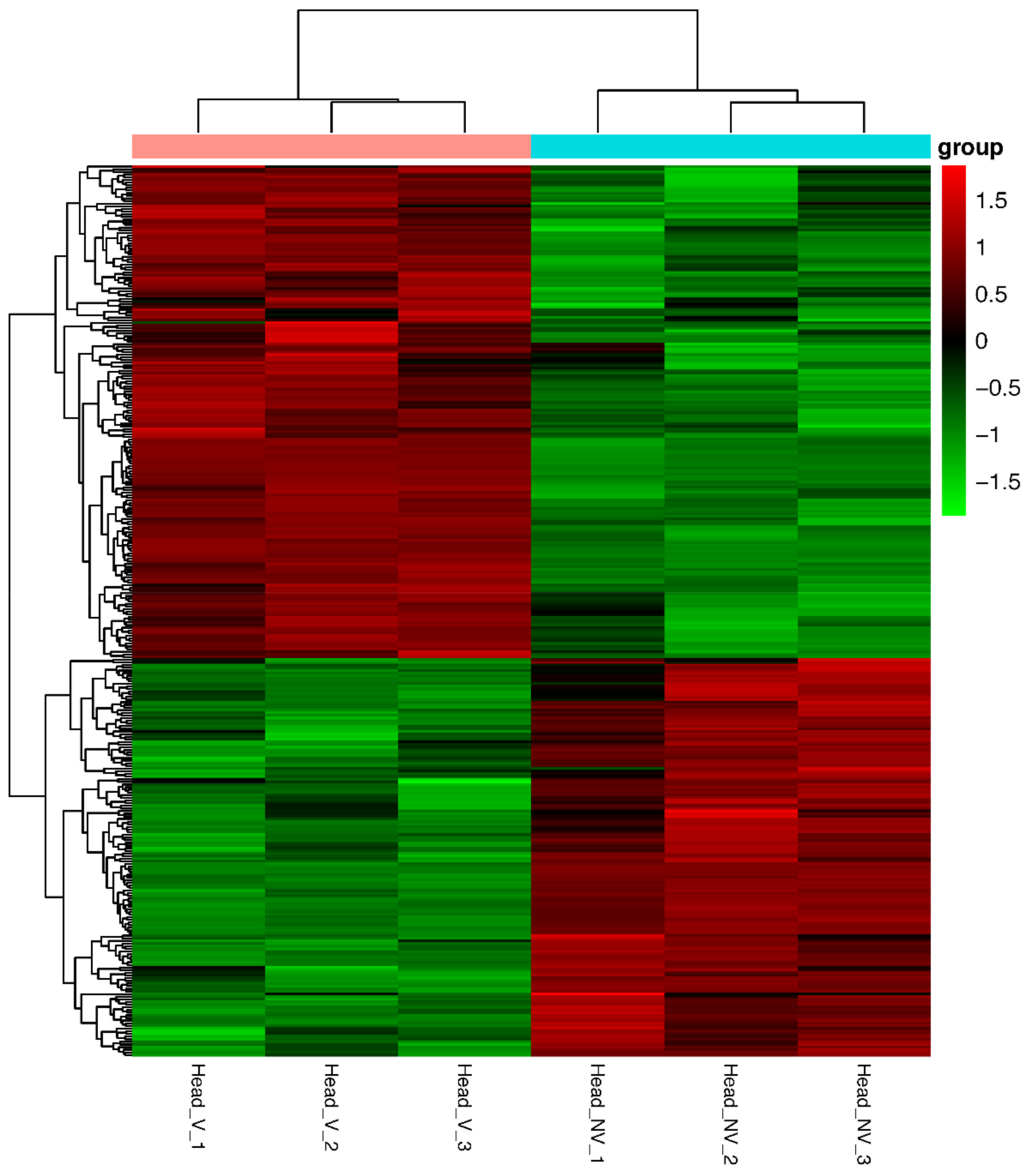
3.3. Identification and Analysis of DEGs
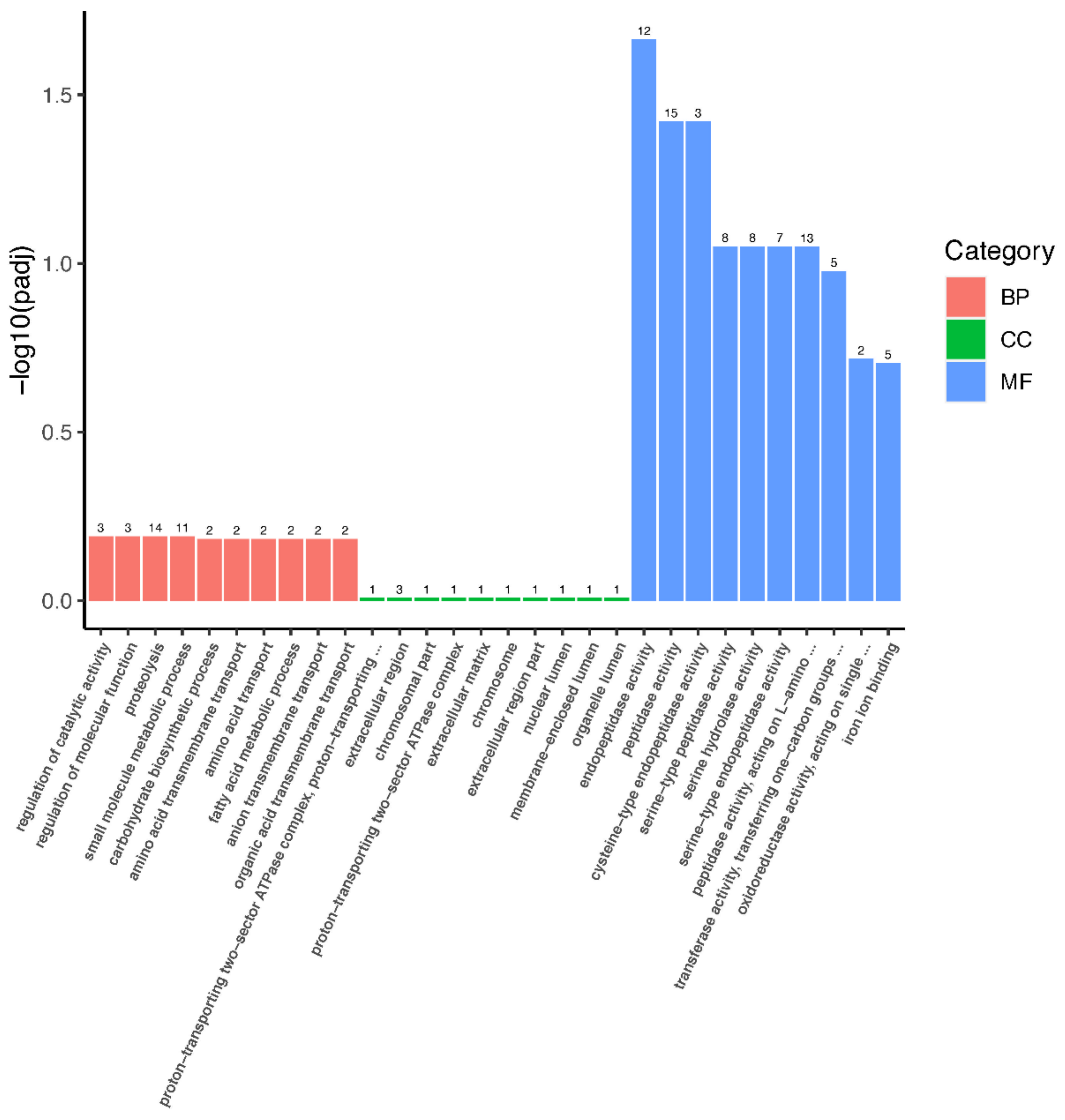
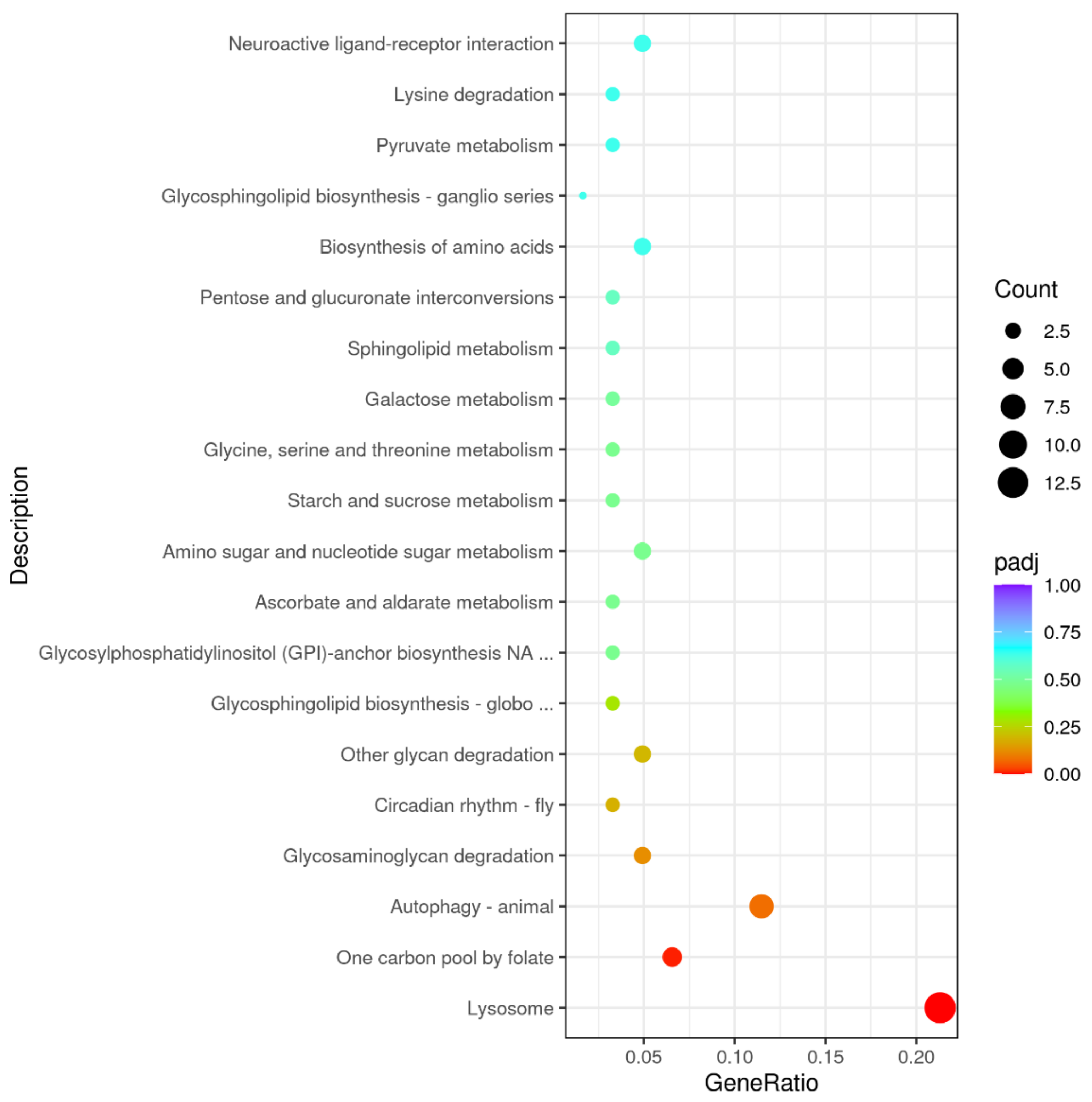
3.4. GO and KEGG Enrichments Analysis of DEGs
3.5. DEGs Potentially Associated with Virus Transmission
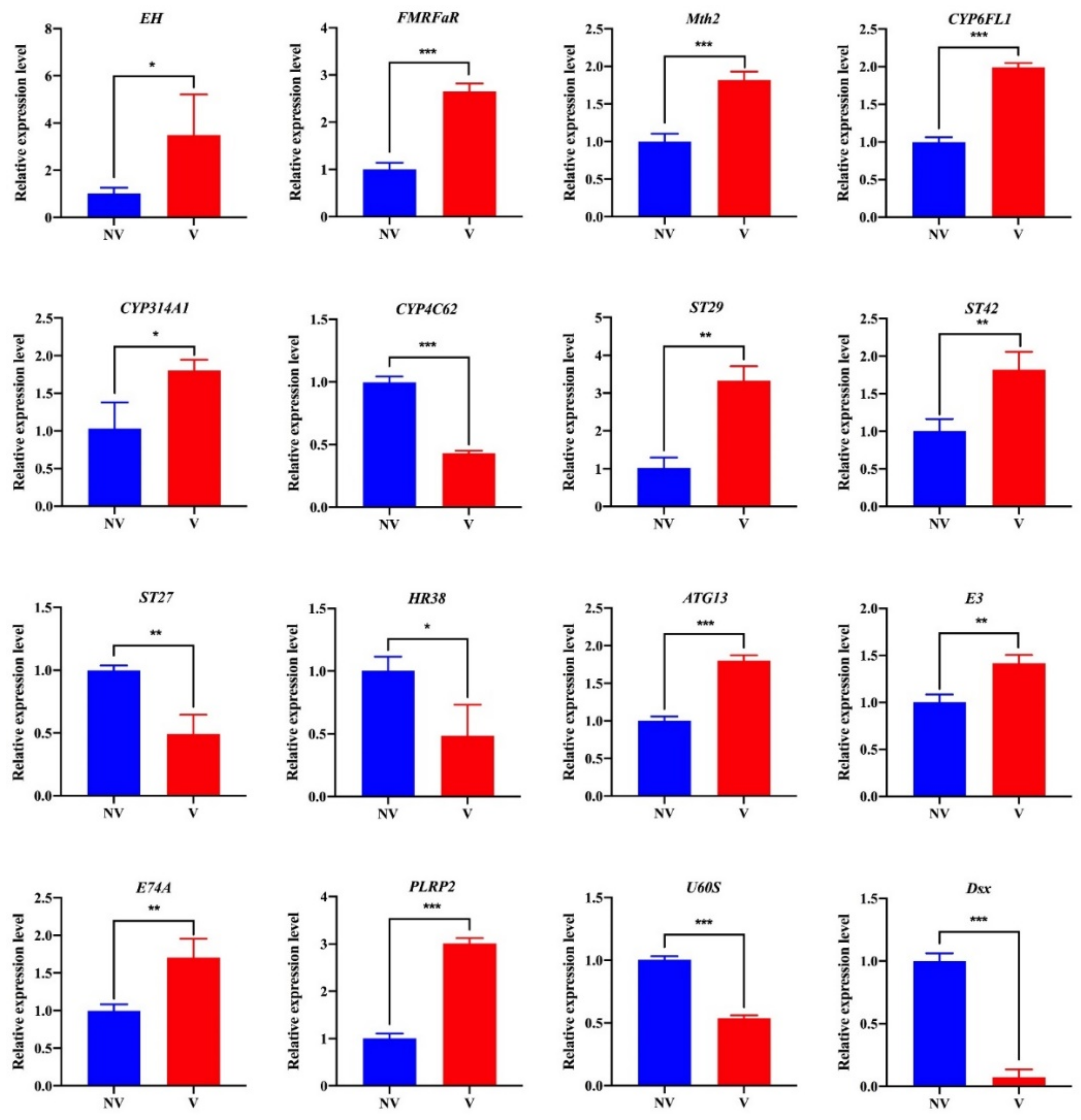
3.6. Transcriptome Validation by qRT-PCR
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eigenbrode, S.D.; Bosque-Pérez, N.A.; Davis, T.S. Insect-Borne plant pathogens and their vectors: Ecology, evolution, and complex interactions. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2018, 63, 169–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verheggen, F.; Barrès, B.; Bonafos, R.; Desneux, N.; Escobar-Gutiérrez, A.J.; Gachet, E.; Laville, J.; Siegwart, M.; Thiéry, D.; Jactel, H. Producing sugar beets without neonicotinoids: An evaluation of alternatives for the management of viruses-transmitting aphids. Entomol. Gen. 2022, 42, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, A.; Miranda, M.P.; Fereres, A. Psyllids as major vectors of plant pathogens. Entomol. Gen. 2021, 41, 419–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LoTora, A.G.; Lai, P.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Gautam, S.; Abney, M.R.; Srinivasan, R. Frankliniella fusca (Thysanoptera: Thripidae), the vector of tomato spotted wilt orthotospovirus infecting peanut in the southeastern united states. J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2022, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodino, N.; Cavalieri, V.; Pegoraro, M.; Altamura, G.; Canuto, F.; Zicca, S.; Fumarola, G.; Almeida, R.P.P.; Saponari, M.; Dongiovanni, C. Temporal dynamics of the transmission of Xylella fastidiosa subsp. pauca by Philaenus spumarius to olive plants. Entomol. Gen. 2021, 41, 463–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauck, K.E.; De Moraes, C.M.; Mescher, M.C. Deceptive chemical signals induced by a plant virus attract insect vectors to inferior hosts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 3600–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesey, I.W.; Koerte, S.; Khallaf, M.A.; Retzke, T.; Guillou, A.; Grosse-Wilde, E.; Buchon, N.; Knaden, M.; Hansson, B.S. Pathogenic bacteria enhance dispersal through alteration of Drosophila social communication. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.; Gadhave, K.R.; Buck, J.W.; Dutta, B.; Coolong, T.; Adkins, S.; Srinivasan, R. Virus-virus interactions in a plant host and in a hemipteran vector: Implications for vector fitness and virus epidemics. Virus Res. 2020, 286, 198069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.; Mugerwa, H.; Sundaraj, S.; Gadhave, K.R.; Murphy, J.F.; Dutta, B.; Srinivasan, R. Specific and spillover effects on vectors following infection of two RNA viruses in pepper plants. Insects 2020, 11, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngumbi, E.; Eigenbrode, S.D.; Bosque-Pérez, N.A.; Ding, H.; Rodriguez, A. Myzus persicae is arrested more by blends than by individual compounds elevated in headspace of plrv-infected potato. J. Chem. Ecol. 2007, 33, 1733–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Guo, H.; Ge, F.; Sun, Y. Apoptotic neurodegeneration in whitefly promotes the spread of TYLCV. eLife 2020, 9, e56168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.B.; Wang, X.Z.; Zhang, D.Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, J.; Zheng, L.M.; Zhou, X.G.; Tan, X.Q.; Liu, Y. Silencing of odorant-binding protein gene OBP3 using RNA interference reduced virus transmission of tomato chlorosis virus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Yang, H.H.; Liu, S.; He, H.L.; Ding, W.B.; Qiu, L.; Li, Y.Z. Odorant-binding protein 2 is involved in the preference of Sogatella furcifera (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) for rice plants infected with the southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus. Fla. Entomol. 2019, 102, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Choi, J.Y.; Park, D.H.; Park, M.G.; Kim, J.Y.; Wang, M.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, W.J.; Je, Y.H. Suppression of rice stripe virus replication in Laodelphax striatellus using vector insect-derived double-stranded RNAs. Plant Pathol. J. 2020, 36, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Park, M.G.; Choi, J.Y.; Park, D.H.; Wang, M.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, W.J.; Je, Y.H. Insecticidal and synergistic activity of dsRNAs targeting buprofezin-specific genes against the small brown planthopper, Laodelphax striatellus. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 105, e21739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.B.; Choi, J.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Fang, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Park, D.H.; Park, M.G.; Woo, R.M.; Kim, W.J.; Je, Y.H. Silencing of rice stripe virus in Laodelphax striatellus using virus-derived double-stranded RNAs. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2017, 20, 695–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Fu, S.; Tao, X.; Zhou, X. Rice stripe virus: Exploring molecular weapons in the arsenal of a negative-sense RNA virus. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2021, 59, 351–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Xu, G.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, C.; Yang, G.Q. Sublethal effects of imidacloprid on fecundity, apoptosis and virus transmission in the small brown planthopper Laodelphax striatellus. Insects 2021, 12, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Yu, Y.L.; Chen, L.Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, M.T.; Song, Z.Y.; Chen, X.Y.; Fang, R.X.; Zhang, L.L. Insect tissue-specific vitellogenin facilitates transmission of plant virus. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Yu, Y.L.; Liu, Q.; Liu, D.; Zhang, M.T.; Liang, J.N.; Chen, X.Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Fang, R.X. Rice stripe virus hitchhikes the vector insect vitellogenin ligand-receptor pathway for ovary entry. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2019, 374, 20180312. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chen, D.Y.; Hu, J.; Zhang, K.; Kang, L.; Chen, Y.; Huang, L.J.; Zhang, L.; Xiang, Y.; Song, Q.S.; et al. The α-tubulin of Laodelphax striatellus mediates the passage of rice stripe virus (RSV) and enhances horizontal transmission. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.H.; Lu, H.; Wang, W.; Zhu, J.M.; Zhao, W.; Cui, F. Membrane association of importin α facilitates viral entry into salivary gland cells of vector insects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2103393118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, F.L.; Liu, W.W.; Wu, N.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.K.; Zhou, X.P.; Wang, X.F. Invasion of midgut epithelial cells by a persistently transmitted virus is mediated by sugar transporter 6 in its insect vector. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.W.; Gray, S.W.; Huo, Y.; Li, L.; Wei, T.Y.; Wang, X.F. Proteomic analysis of interaction between a plant virus and its vector insect reveals new functions of Hemipteran cuticular protein. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2015, 14, 2229–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, J.X.; Fu, S.; Li, C.Y.; Zhu, Z.R.; Zhou, X.P. Rice stripe tenuivirus nonstructural protein 3 hijacks the 26S proteasome of the small brown planthopper via direct interaction with regulatory particle non-ATPase subunit 3. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 4296–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, W.; Li, J.; Luo, L.; Kang, L.; Cui, F. The c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway of a vector insect is activated by virus capsid protein and promotes viral replication. eLife 2017, 6, e26591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Shen, M.; Ge, L.Q.; Liu, F. Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 E inhibits the accumulation of rice stripe virus in Laodelphax striatellus (Fallén). Viruses 2020, 12, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Choi, J.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Park, D.H.; Park, M.G.; Woo, R.M.; Lee, B.R.; Kim, W.J.; Li, S.; et al. RNA interference of E75 nuclear receptor gene suppresses transmission of rice stripe virus in Laodelphax striatellus. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2017, 20, 1140–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y.J. Ribosomal protein L18 is an essential factor that promote rice stripe virus accumulation in small brown planthopper. Virus Res. 2018, 247, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.J.; Yan, X.T.; Wang, X.; Qi, Y.H.; Lu, G.; Chen, J.P.; Zhang, C.X.; Li, J.M. Proteomic analysis of Laodelphax striatellus in response to rice stripe virus infection reveal a potential role of ZFP36L1 in restriction of viral proliferation. J. Proteom. 2021, 239, 104–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.L.; Zhang, M.T.; Huo, Y.; Tang, J.L.; Liu, Q.; Chen, X.Y.; Fang, R.X.; Zhang, L.L. Laodelphax striatellus Atg8 facilitates rice stripe virus infection in an autophagy-independent manner. Insect Sci. 2021, 28, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Pan, W.Y.; Zhao, S.L.; Liang, C.Y. Heat shock cognate protein 70 is required for rice stripe tenuivirus accumulation and transmission in small brown planthopper. Arch. Virol. 2022, 167, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Song, Z.Y.; Wang, H.T.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Xiao, N.; Fang, R.X.; Zhang, Y.M.; Zhang, L.L. GrpE is involved in mitochondrial function and is an effective target for RNAi-mediated pest and arbovirus control. Insect Mol. Biol. 2022, 31, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Ullah, F.; Ding, Q.; Gao, X.W.; Desneux, N.; Song, D. Comparison of full-length transcriptomes of different imidacloprid-resistant strains of Rhopalosiphum padi (L.). Entomol. Gen. 2021, 41, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Huang, F.; Yang, J.; Bei, Y.; Lu, Y. De novo transcriptome sequencing in Frankliniella occidentalis to identify genes involved in plant virus transmission and insecticide resistance. Genomics 2013, 101, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Tao, X.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, W.; Je, Y.H. Transcriptome analysis of the small brown planthopper, Laodelphax Striatellus carrying rice stripe virus. Plant Pathol. J. 2013, 29, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Lu, L.; Yang, P.; Cui, N.; Kang, L.; Cui, F. Organ-specific transcriptome response of the small brown planthopper toward rice stripe virus. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 70, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugerwa, H.; Gautam, S.; Catto, M.A.; Dutta, B.; Brown, J.K.; Adkins, S.; Srinivasan, R. Differential transcriptional responses in two old world Bemisia tabaci cryptic species post acquisition of old and new world begomoviruses. Cells 2022, 11, 2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catto, M.A.; Mugerwa, H.; Myers, B.K.; Pandey, S.; Dutta, B.; Srinivasan, R. A review on transcriptional responses of interactions between insect vectors and plant viruses. Cells 2022, 11, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Jiang, F.; Wang, X.; Yang, P.; Bao, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wang, W.; Lu, H.; Wang, Q.; Cui, N. Genome sequence of the small brown planthopper, Laodelphax Striatellus. Gigascience 2017, 6, gix109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Chen, D.; Hu, J.; Liu, F. Comparative transcriptome analysis of chemoreception organs of Laodelphax striatellus in response to rice stripe virus infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, N.N.; Liu, F.; Yang, G.Q. Triazophos-induced vertical transmission of rice stripe virus is associated with host vitellogenin in the small brown planthopper Laodelphax striatellus. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 1949–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.Z.; Ma, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, G.; Yang, G. Decoyinine induced resistance in rice against small brown planthopper Laodelphax striatellus. Insects 2022, 13, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.Z.; Zhou, Y.J.; Chen, Z.X.; Zhou, X.P. Production of monoclonal antibodies to rice stripe virus and application in virus detection. Acta Phytopathol. Sin. 2004, 34, 302–306. [Google Scholar]
- Anders, S.; Huber, W. Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.A. The Benjamini-Hochberg method in the case of discrete test statistics. Int. J. Biostat. 2007, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Gui, W.; Zhang, Q.X.; Xu, G.; Yang, G.Q. Priming of rice seed with decoyinine enhances resistance against the brown planthopper Nilparvata lugens. Crop Prot. 2022, 157, 105970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Hasegawa, D.K.; Ling, K.S.; Wintermantel, W.M. Application of genomics for understanding plant virus-insect vector interactions and insect vector control. Phytopathology 2016, 106, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Guo, H.; Zheng, H.; Zhou, T.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.; Fang, R.; Qian, W.; Chen, X. Massively parallel pyrosequencing-based transcriptome analyses of small brown planthopper (Laodelphax striatellus), a vector insect transmitting rice stripe virus (RSV). BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, E.D.; Hogenhout, S.A. A neurotropic route for maize mosaic virus (Rhabdoviridae) in its planthopper vector Peregrinus maidis. Virus Res. 2008, 131, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, A.E.; Huot, O.B.; Martin, K.M.; Kondo, H.; Dietzgen, R.G. Plant rhabdoviruses-their origins and vector interactions. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2018, 33, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Sun, X.; Li, P.; Sun, J.; Yue, Y.; Wei, J.; Wei, T.; Jia, D. Infection characteristics of rice stripe mosaic virus in the body of the vector leafhoppers. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zeng, T.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, X.F.; Wei, T. Rice yellow stunt nucleorhabdovirus matrix protein mediates viral axonal transport in the central nervous system of its insect vector. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Mo, L.; Huo, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhong, P.; Jia, D.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Q.; Chen, H.; et al. A neuron-specific antiviral mechanism modulates the persistent infection of rice rhabdoviruses in leafhopper vectors. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llopis-Giménez, A.; Parenti, S.; Han, Y.; Ros, V.I.D.; Herrero, S. A proctolin-like peptide is regulated after baculovirus infection and mediates in caterpillar locomotion and digestion. Insect Sci. 2021, 29, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ja, W.W.; West, A.P., Jr.; Delker, S.L.; Bjorkman, P.J.; Benzer, S.; Roberts, R.W. Extension of Drosophila melanogaster life span with a GPCR peptide inhibitor. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2007, 3, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Sadamoto, H.; Aonuma, H. Identification and expression analysis of the genes involved in serotonin biosynthesis and transduction in the field cricket Gryllus bimaculatus. Insect Mol. Biol. 2011, 20, 619–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.D.; Liao, H.J.; Li, L.Y.; Wu, M.M.; Xie, W.; Wu, Q.J.; Zhang, Y.J.; Zhou, X.M.; Wang, S.L. The CYP392D8 gene is not directly associated with abamectin resistance, a case study in two highly resistant Tetranychus urticae strains. Entomol. Gen. 2022. published online. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Feng, Z.J.; Chen, Z.S.; Wang, X.X.; Cong, H.S.; Fan, Y.L.; Liu, T.X. Connection between cuticular hydrocarbons and melanization in Harmonia axyridis revealed by RNAi-mediated silencing of the CYP4G79. Entomol. Gen. 2021, 41, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Sun, H.; Liu, Z. Metabolic imidacloprid resistance in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens, relies on multiple P450 enzymes. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 79, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, Y.; Liu, B.; Yang, Q.; Guo, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Fang, J. Resistance monitoring and cross-resistance role of CYP6CW1 between buprofezin and pymetrozine in field populations of Laodelphax striatellus (Fallén). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Cang, X.; Liu, Z. Expression induction of P450 genes by imidacloprid in Nilaparvata lugens: A genome-scale analysis. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2016, 132, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Wu, M.; Han, Z. Overexpression of multiple detoxification genes in deltamethrin resistant Laodelphax striatellus (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) in China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niwa, R.; Niwa, Y.S. Enzymes for ecdysteroid biosynthesis: Their biological functions in insects and beyond. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 1283–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iga, M.; Kataoka, H. Recent studies on insect hormone metabolic pathways mediated by cytochrome P450 enzymes. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 35, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Zhao, M.; Zhou, Y.J.; Xu, Q.F.; Yang, Y.X. Cytochrome P450 Monooxygenases CYP6AY3 and CYP6CW1 regulate rice black-streaked dwarf virus replication in Laodelphax striatellus (Fallén). Viruses 2021, 13, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikawada, T.; Saito, A.; Kanamori, Y.; Nakahara, Y.; Iwata, K.; Tanaka, D.; Watanabe, M.; Okuda, T. Trehalose transporter 1, a facilitated and high-capacity trehalose transporter, allows exogenous trehalose uptake into cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11585–11590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagisaka, A.; Fujita, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Ishibashi, J.; Noda, H.; Imanishi, S.; Mita, K.; Yamakawa, M.; Tanaka, H. Genome-wide analysis of host gene expression in the silkworm cells infected with Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus. Virus Res. 2010, 147, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajano, J.; Raza, A.; Zhang, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, X. Ribavirin targets sugar transporter 6 to suppress acquisition and transmission of rice stripe tenuivirus by its vector Laodelphax striatellus. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 4086–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, S.W. Odorant reception in insects: Roles of receptors, binding proteins, and degrading enzymes. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 373–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosi, P.; Iovinella, I.; Zhu, J.; Wang, G.; Dani, F.R. Beyond chemoreception: Diverse tasks of soluble olfactory proteins in insects. Biol. Rev. 2018, 93, 184–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grapputo, A.; Thrimawithana, A.H.; Steinwender, B.; Newcomb, R.D. Differential gene expression in the evolution of sex pheromone communication in New Zealand’s endemic leafroller moths of the genera Ctenopseustis and Planotortrix. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, Y. Olfactory co-receptor Orco stimulated by Rice stripe virus is essential for host seeking behavior in small brown planthopper. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 75, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futahashi, R.; Okamoto, S.; Kawasaki, H.; Zhong, Y.S.; Iwanaga, M.; Mita, K.; Fujiwara, H. Genome-wide identification of cuticular protein genes in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 38, 1138–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombrovsky, A.; Gollop, N.; Chen, S.; Chejanovsky, N.; Raccah, B. In vitro association between the helper component-proteinase of zucchini yellow mosaic virus and cuticle proteins of Myzus persicae. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 1602–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilia, M.; Tamborindeguy, C.; Fish, T.; Howe, K.; Thannhauser, T.W.; Gray, S. Genetics coupled to quantitative intact proteomics links heritable aphid and endosymbiont protein expression to circulative polerovirus transmission. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 2148–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzest, M.; Gargani, D.; Drucker, M.; Hébrard, E.; Garzo, E.; Candresse, T.; Fereres, A.; Blanc, S. A protein key to plant virus transmission at the tip of the insect vector stylet. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 17959–17964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, F.; Chen, X.; Li, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, T.; Fang, R.; Wang, X. Transovarial transmission of a plant virus is mediated by vitellogenin of its insect vector. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Lin, K.; Ding, S.; Wang, G.; Li, F. The vitellogenin receptor has an essential role in vertical transmission of rice stripe virus during oogenesis in the small brown plant hopper. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 75, 1370–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stilwell, G.E.; Nelson, C.A.; Weller, J.; Cui, H.; Hiruma, K.; Truman, J.W.; Riddiford, L.M. E74 exhibits stage-specific hormonal regulation in the epidermis of the tobacco hornworm, Manduca Sexta. Dev. Biol. 2003, 258, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Shi, Q.; Xu, C.; Wang, R.; Wang, H.; Song, Y.; Zeng, R. Regulation of NlE74A on vitellogenin may be mediated by angiotensin converting enzyme through a fecundity-related SNP in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2018, 225, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelly, S.; Lukinova, N.; Bambina, S.; Berman, A.; Cherry, S. Autophagy is an essential component of Drosophila immunity against vesicular stomatitis virus. Immunity 2009, 30, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Li, Z.; Hou, M. Silencing the autophagy-related genes ATG3 and ATG9 promotes SRBSDV propagation and transmission in Sogatella furcifera. Insects 2022, 13, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swatek, K.N.; Komander, D. Ubiquitin modifications. Cell Res. 2016, 26, 399–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, C. Search and destroy: The role of protein quality control in maintaining cardiac function. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2006, 40, 438–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Samples | Raw Reads (Raw Bases) | Clean Reads (Clean Bases) | Q20 (%) | Q30 (%) | GC Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Head_NV_1 | 46331750 (6.95G) | 45130720 (6.77G) | 96.38 | 90.85 | 38.29 |
| Head_NV_2 | 45655372 (6.85G) | 44961050 (6.74G) | 97.94 | 93.95 | 39.93 |
| Head_NV_3 | 45314050 (6.80G) | 44820814 (6.72G) | 98.03 | 94.11 | 39.27 |
| Head_V_1 | 43979590 (6.60G) | 42331612 (6.35G) | 96.5 | 91.03 | 39.49 |
| Head_V_2 | 46100826 (6.92G) | 44752470 (6.71G) | 96.52 | 91.04 | 38.26 |
| Head_V_3 | 46261636 (6.94G) | 44899720 (6.73G) | 96.49 | 91.03 | 38.78 |
| Sample | Total Map | Unique Map | Positive Map | Negative Map |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Head_NV_1 | 27538563 (61.02%) | 25858563 (57.3%) | 12855357 (28.48%) | 13003206 (28.81%) |
| Head_NV_2 | 29477643 (65.56%) | 27663936 (61.53%) | 13792682 (30.68%) | 13871254 (30.85%) |
| Head_NV_3 | 28886428 (64.45%) | 27130248 (60.53%) | 13533887 (30.2%) | 13596361 (30.33%) |
| Head_V_1 | 26801186 (63.31%) | 25281577 (59.72%) | 12598477 (29.76%) | 12683100 (29.96%) |
| Head_V_2 | 27767897 (62.05%) | 26191345 (58.52%) | 13049235 (29.16%) | 13142110 (29.37%) |
| Head_V_3 | 28265984 (62.95%) | 26661723 (59.38%) | 13278992 (29.57%) | 13382731 (29.81%) |
| Gene ID | Gene Name | Annotation | Length (bp) | p-Value | log2 Fold Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neural-associated gene | |||||
| LSTR_LSTR006557 | EH | eclosion hormone (Nilaparvata lugens) | 2139 | 5.91 × 10−18 | 5.61 |
| LSTR_LSTR004655 | CCH1R | CCHamide-1 receptor (Nilaparvata lugens) | 1083 | 0.0015 | 1.12 |
| LSTR_LSTR005567 | FMRFaR | FMRFamide receptor (Nilaparvata lugens) | 1511 | 2.73 × 10−10 | 1.02 |
| LSTR_LSTR007145 | Mth2 | G-protein coupled receptor Mth2 (Nilaparvata lugens) | 1290 | 1.14 × 10−6 | 3.06 |
| LSTR_LSTR012676 | 5HT1B | 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor (Homalodisca vitripennis) | 1562 | 0.0024 | 1.03 |
| LSTR_LSTR017186 | SK | sulfakinin (Nilaparvata lugens) | 322 | 1.03 × 10−13 | −4.50 |
| Cytochrome P450 | |||||
| LSTR_LSTR014118 | CYP6FL1 | cytochrome P450 CYP6FL1 (Sogatella furcifera) | 1677 | 6.00 × 10−6 | 1.28 |
| LSTR_LSTR011334 | CBR1 | cytochrome b reductase 1 (Schistocerca gregaria) | 986 | 2.86 × 10−5 | 1.56 |
| LSTR_LSTR004091 | CYP314A1 | cytochrome P450 CYP314A1, partial (Laodelphax striatellus) | 3730 | 4.08 × 10−7 | 1.15 |
| LSTR_LSTR000771 | CYP4C62 | cytochrome P450 CYP4C62 (Laodelphax striatellus) | 2026 | 1.17 × 10−115 | −2.64 |
| Sugar-associated gene | |||||
| LSTR_LSTR002783 | ST4 | sugar transporter 4 (Nilaparvata lugens) | 1998 | 1.55 × 10−17 | 1.97 |
| LSTR_LSTR012604 | ST29 | sugar transporter 29 (Nilaparvata lugens) | 3063 | 1.91 × 10−5 | 1.65 |
| LSTR_LSTR010413 | ST42 | sugar transporter 42 (Nilaparvata lugens) | 2363 | 3.22 × 10−10 | 1.13 |
| LSTR_LSTR013190 | ST27 | sugar transporter 27 (Nilaparvata lugens) | 916 | 0.0001 | −1.81 |
| LSTR_LSTR005915 | TPS2 | trehalose-6-phosphate synthase 2 (Nilaparvata lugens) | 3078 | 2.30 × 10−10 | −1.05 |
| Olfaction-related gene | |||||
| LSTR_LSTR001830 | SNMP2 | sensory neuron membrane protein 2 (Nilaparvata lugens) | 942 | 0.0039 | 1.13 |
| LSTR_LSTR001538 | OR104 | odorant receptor 104 (Halyomorpha halys) | 2015 | 4.88 × 10−6 | 1.57 |
| LSTR_LSTR001409 | OR23a | odorant receptor 23a-like (Nilaparvata lugens) | 1571 | 0.0022 | 1.66 |
| LSTR_LSTR007970 | OR23a | odorant receptor 23a-like (Nilaparvata lugens) | 1658 | 0.0055 | 1.04 |
| Cuticular-related gene | |||||
| LSTR_LSTR005116 | CPR61 | cuticular protein (Nilaparvata lugens) | 1713 | 0.0033 | 1.40 |
| LSTR_LSTR009161 | CPR96 | cuticular protein (Nilaparvata lugens) | 1795 | 1.23 × 10−9 | 1.06 |
| Other virus-transmission-related gene | |||||
| LSTR_LSTR011186 | ATG13 | autophagy-related protein 13 (Nilaparvata lugens) | 5805 | 3.49 × 10−31 | 1.49 |
| LSTR_LSTR015356 | HR38 | nuclear hormone receptor HR38 (Nilaparvata lugens) | 1419 | 0.0013 | −2.07 |
| LSTR_LSTR001348 | E3 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF139 (Nilaparvata lugens) | 2405 | 1.10 × 10−16 | 1.25 |
| LSTR_LSTR002356 | E74A | E74A (Nilaparvata lugens) | 1203 | 3.29 × 10−7 | 1.05 |
| LSTR_LSTR012920 | bicaudal C | protein bicaudal C homolog 1 (Nilaparvata lugens) | 2890 | 3.83 × 10−6 | 1.23 |
| LSTR_LSTR010541 | PLRP2 | Pancreatic lipase-related protein 2 (Nilaparvata lugens) | 3627 | 7.18 × 10−26 | 1.02 |
| LSTR_LSTR011577 | VgR | vitellogenin receptor (Laodelphax striatellus) | 7648 | 3.40 × 10−14 | 1.24 |
| LSTR_LSTR014469 | SHP | salivary sheath protein (Nilaparvata lugens) | 738 | 4.89 × 10−43 | 1.02 |
| LSTR_LSTR003055 | HSGC | head-specific guanylate cyclase (Nilaparvata lugens) | 1894 | 0.0038 | 1.01 |
| LSTR_LSTR001253 | ApD | apolipoprotein D (Nilaparvata lugens) | 994 | 4.60 × 10−9 | 1.78 |
| LSTR_LSTR008185 | UAP | UDP-N-acetylglucosamine pyrophosphorylase (Sogatella furcifera) | 4828 | 3.81 × 10−11 | 1.36 |
| LSTR_LSTR008501 | period | period (Laodelphax striatellus) | 4424 | 1.06 × 10−43 | −1.30 |
| LSTR_LSTR016981 | U60S | ubiquitin-60S ribosomal protein L40 (Nilaparvata lugens) | 184 | 5.15 × 10−6 | −5.18 |
| LSTR_LSTR001934 | Dsx | doublesex- and mab-3-related transcription factor 3 (Nilaparvata lugens) | 2205 | 1.74 × 10−6 | −1.03 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, M.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, G.; Xu, G. Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis of Head in Laodelphax striatellus upon Rice Stripe Virus Infection. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3202. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123202
Yu Y, Zhang Y, Qian M, Zhang Q, Yang G, Xu G. Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis of Head in Laodelphax striatellus upon Rice Stripe Virus Infection. Agronomy. 2022; 12(12):3202. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123202
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Youxin, Yuanyuan Zhang, Mingshi Qian, Qiuxin Zhang, Guoqing Yang, and Gang Xu. 2022. "Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis of Head in Laodelphax striatellus upon Rice Stripe Virus Infection" Agronomy 12, no. 12: 3202. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123202
APA StyleYu, Y., Zhang, Y., Qian, M., Zhang, Q., Yang, G., & Xu, G. (2022). Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis of Head in Laodelphax striatellus upon Rice Stripe Virus Infection. Agronomy, 12(12), 3202. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123202







