Variations of Rice Yield and Quality in Response to Different Establishment Methods at Farmers’ Field
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Experiments Design
2.2. Survey Study Design
2.3. Determination of Rice Yield and Quality
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Differences in Rice Grain Yields among Different Establishment Methods
3.2. Differences of Grain Yields among Different Rice Types
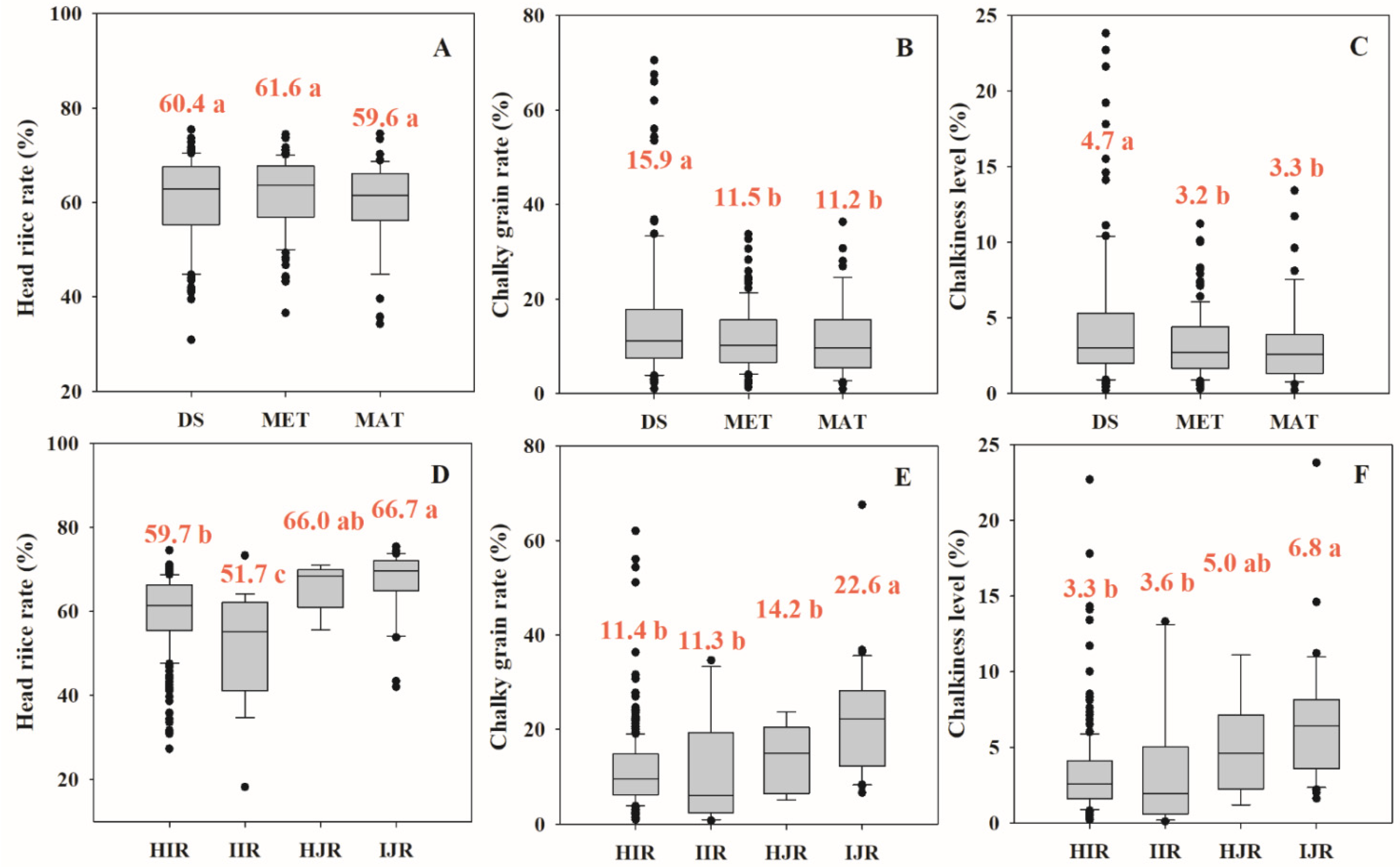
3.3. Difference in Grain Quality among Different Establishment Methods and Rice Types
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Establishment Methods on Rice Grain
4.2. Differences in Rice Quality in Response to Establishment Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tu, D.; Wu, W.; Xi, M.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, Y.; Chen, J.; Shao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Q. Effect of temperature and radiation on indica rice yield and quality in middle rice cropping system. Plants 2022, 11, 2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Zou, Y. Integrating mechanization with agronomy and breeding to ensure food security in china. Field Crops Res. 2018, 224, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.; Li, Y.; Qian, Q. Recent progress on molecular breeding of rice in china. Plant Cell Rep. 2014, 33, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, G.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Yu, X.; Wu, Y.; Xiong, F. Effects of high temperature during two growth stages on caryopsis development and physicochemical properties of starch in rice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Zhan, X.; Yu, T.; Nie, L.; Huang, J.; Cui, K.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Peng, S. Yield performance of direct-seeded, double-season rice using varieties with short growth durations in central china. Field Crops Res. 2018, 227, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Tang, Q.; Zou, Y. Current status and challenges of rice production in China. Plant Prod. Sci. 2009, 12, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, E.V. Development of a mechanism for transplanting rice seedlings. Mech. Mach. Theory 2002, 37, 395–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Chen, H. The development of machine-transplanted rice and food security. China Rice 2009, 15, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.C.; Gong, J.L. Research status and development discussion on high-yielding agronomy of mechanized planting rice in china. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2014, 47, 1273–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharawat, Y.S.; Singh, B.; Malik, R.K.; Ladha, J.K.; Gathala, M.K.; Jat, M.L.; Kumar, V. Evaluation of alternative tillage and crop establishment methods in a rice–wheat rotation in North Western IGP. Field Crop Res. 2010, 116, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hussain, S.; Zheng, M.; Peng, S.; Huang, J.; Cui, K.; Nie, L. Dry direct-seeded rice as an alternative to transplanted-flooded rice in central china. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devkota, K.P.; Sudhir-Yadav Khanda, C.M.; Beebout, S.J.; Mohapatra, B.K.; Singleton, G.R.; Puskur, R. Assessing alternative crop establishment methods with a sustainability lens in rice production systems of Eastern India. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhir-Yadav Kumar, V.; Singh, S.; Kumar, R.M.; Sharma, S.; Tripathi, R.; Nayak, A.K.; Ladha, J.K. Growing Rice in Eastern India: New Paradigms of Risk Reduction and Improving Productivity. In The Future Rice Strategy for India; Mohanty, S., Chengappa, P.G., Mruthyunjaya, Ladha, J.K., Baruah, S., Kannan, E., Manjunatha, A.V., Eds.; Academic Press: Massachusetts, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 221–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Tan, X.; Zeng, Y.; Xie, X.; Pan, X.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, J. Changes in the rice grain quality of different high-quality rice varieties released in southern china from 2007 to 2017. J. Cereal Sci. 2019, 87, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Tao, F.; Xiao, D.; Liu, F.; Zhang, H. Attribution of yield change for rice-wheat rotation system in china to climate change, cultivars and agronomic management in the past three decades. Clim. Change 2016, 135, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Zhang, J. Shanyou 63: An elite mega rice hybrid in china. Rice 2018, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, F.; Yang, F.; Fan, T.; Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Long, X. Analysis of Rice Variety Approval Data from 1977 to 2018 in China. China Seed Ind. 2019, 2, 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, C.; Xu, Q.; Xu, Z.; Chen, W. Effect of rice breeding process on improvement of yield and quality in china. Rice Sci. 2020, 27, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hu, Y.; Yang, J.; Dai, Q.; Huo, Z.; Xu, K.; Wei, H.; Gao, H.; Guo, B.; Xing, Z.; et al. Development and Prospect of Rice Cultivation in China. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2021, 54, 1301–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, N.; Ling, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, C.; Fahad, S.; Peng, S.; Cui, K.; Nie, L.; Huang, J. Influence of temperature and solar radiation on grain yield and quality in irrigated rice system. Eur. J. Agron. 2015, 64, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Ren, W.; Teng, Y.; Chen, W.; Wenting, M.A.; Huang, Y. Basic physico-chemical properties and fertility comprehensive evaluation of main paddy soils in Anhui province. Soils 2018, 50, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; van Groenigen, K.J.; Yang, H.; Huangate, B.A.; Yang, B.; Tian, Y.; Chen, J.; Dong, W.; Huang, S.; Deng, A.; et al. Global warming and shifts in cropping systems together reduce china’s rice production. Glob. Food Secur. 2020, 24, 100359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, I.; Mishra, A.; Behera, B.; Khanda, C.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, A. Productivity trade-off with different water regimes and genotypes of rice under non-puddled conditions in Eastern India. Field Crops Res. 2018, 222, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Ge, Q.; Chu, G.; Xu, C.; Yan, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D. Seasonal differences in the rice grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency response to seedling establishment methods in the Middle and Lower reaches of the Yangtze River in China. Field Crops Res. 2017, 205, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, M.; Roy, R. Effect of nursery seeding density and fertilizer on seedling growth and yield of rice (Oryza sativa). Indian J. Agron. 1996, 41, 642–644. [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan, B.S.; Abeysekera, A.S.K.; Wickramarathe, M.S.; Kulatunga, S.D.; Wickrama, U.B. Effect of rice establishment methods on weedy rice (Oryza sativa L.) infestation and grain yield of cultivated rice (O. sativa L.) in Sri Lanka. Crop Prot. 2014, 55, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhou, X.F.; Cao, F.B.; Xia, B.; Zou, Y.B. No-tillage effect on rice yield In China: A meta-analysis. Field Crops Res. 2015, 183, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Brueck, H.; Dittert, K.; Kreye, C.; Lin, S.; Sattelmacher, B. Growth and yield formation of ricez (Oryza sativa L.) in the water-saving ground cover rice production system (GCRPS). Field Crop Res. 2006, 95, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Khush, G.S.; Virk, P.; Tang, Q.; Zou, Y. Progress in ideotype breeding to increase rice yield potential. Field Crops Res. 2008, 108, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafarge, T.; Bueno, C.S. Higher crop performance of rice hybrids than elite inbreds in the tropics: 2. Does sink regulation, rather than sink size play a major role? Field Crops Res. 2009, 114, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Xie, X.; Huang, M.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, R.; Chen, J.; Wu, D.; Xia, B.; Xiong, H.; Xu, F.; et al. Potential yield increase of hybrid rice at five locations in southern China. Rice 2016, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Gong, J.; Chang, Y.; Li, M.; Gao, H.; Dai, Q.; Huo, Z.; Xu, K.; Wei, H. The productive advantages and formation mechanisms of “indica rice to japonica rice”. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2013, 46, 686–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, T.; Wei, H.; Li, X.; Dai, Q.; Huo, Z. A better root morpho-physiology after heading contributing to yield superiority of japonica/indica hybrid rice. Field Crops Res. 2018, 228, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, G.; Chen, S.; Xu, C.; Wang, D.; Zhang, X. Agronomic and physiological performance of indica/japonica hybrid rice cultivar under low nitrogen conditions. Field Crops Res. 2019, 243, 107625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyman, N.B.; Jagadish, K.S.V.; Nalley, L.L.; Dixon, B.L.; Siebenmorgen, T. Neglecting Rice Milling Yield and Quality Underestimates Economic Losses from High-Temperature Stress. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, D.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cai, M.; Li, C.; Cao, C. Effect of various combinations of temperature during different phenological periods on indica rice yield and quality in Yangtze River Basin in China. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 2900–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.A.; Iqbal, N.; Saleem, M.U.; Akhtar, M. Effect of different planting methods on economic yield and grain quality of rice. Int. J. Agric. Appl. Sci. 2012, 4, 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- Sudhir-Yadav Evangelista, G.; Faronilo, J.; Humphreys, E.; Henry, A.; Fernandez, L. Establishment method effects on crop performance and water productivity of irrigated rice in the tropics. Field Crop Res. 2014, 166, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Siddique, K.; Rehman, H.; Aziz, T.; Lee, D.J.; Wahid, A. Rice direct seeding: Experiences, challenges and opportunities. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 111, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.P.; Zhu, M.; Wu, P.; Qian, H.J.; Cao, W.W.; Hu, Y.J.; Guo, B.W.; Wei, H.Y.; Xu, K.; Huo, Z.Y.; et al. Effect of mechanical transplanting with pothole seedlings on grain quality of different types of rice in rice-wheat rotation system. Acta Agron. Sin. 2017, 43, 581–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, Z.; Lu, H.; Zhou, X.; Qian, Y.; Li, Q.; Lu, Y.; Gu, M.; Liu, Q. Characterization of grain quality and starch fine structure of two japonica rice (Oryza sativa) cultivars with good sensory properties at different temperatures during the filling stage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 4048–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Khan, M.; Dixit, S.; Cruz, P.; Septiningsih, E.; Ismail, A.M. Growth, productivity and grain quality of AG1 and AG2 QTLs introgression lines under flooding in direct-seeded rice system. Field Crops Res. 2020, 248, 107713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Li, Y.; Qin, X.; Liao, Y.; Siddique, K. Changes in rice grain quality of indica and japonica type varieties released in china from 2000 to 2014. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, J. Grain-filling problem in ‘super’ rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Lin, G.; Yu, X.; Wu, Y.; Chen, G.; Xiong, F. Endosperm enrichment and physicochemical properties of superior and inferior grain starch in super hybrid rice. Plant Biol. 2020, 22, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, G.; Yao, H.; Xu, H. Variation in rice quality of different cultivars and grain positions as affected by water management. Field Crops Res. 2003, 80, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Years | Variety | Treatment | Sowing Date | Heading Date | Harvest Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | YY4949 | MET | 12 May | 15 August | 6 October |
| MAT | 12 May | 13 August | 5 October | ||
| YY4149 | MET | 12 May | 18 August | 9 October | |
| MAT | 12 May | 14 August | 7 October | ||
| YY1540 | MET | 12 May | 5 September | 17 October | |
| MAT | 12 May | 4 September | 17 October | ||
| CLYHZ | MET | 12 May | 20 August | 2 October | |
| MAT | 12 May | 18 August | 2 October | ||
| 2017 | HLY858 | MET | 21 May | 17 August | 29 September |
| MAT | 21 May | 17 August | 29 September | ||
| DS | 21 May | 12 August | 21 September | ||
| HLY898 | MET | 21 May | 16 August | 27 September | |
| MAT | 21 May | 15 August | 27 September | ||
| DS | 21 May | 9 August | 18 September |
| Region | Number of MAT | Number of MET | Number of DS | Total Number of Sampled Paddy Plot |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anqing | 6 | 5 | 21 | 32 |
| Chizhou | 2 | 7 | 14 | 23 |
| Chuzhou | 2 | 16 | 10 | 28 |
| Fuyang | 4 | 7 | 2 | 13 |
| Hefei | 10 | 17 | 6 | 33 |
| Huainan | 7 | 17 | 5 | 29 |
| Huangshan | 3 | 6 | 3 | 12 |
| Lu’an | 4 | 14 | 9 | 27 |
| Maanshan | 2 | 18 | 6 | 26 |
| Wuhu | 6 | 7 | 9 | 22 |
| Xuanchen | 4 | 7 | 17 | 28 |
| Treatment | Panicles per m−2 | Spikelets per Panicle | Percentage of Filled Grains | 1000-Grain Weight | Grain Yield | Total Dry Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variety (V) | ** | ** | ns | ** | ** | ** |
| Establishment method (E) | ** | ns | ns | ns | ** | ** |
| E × V | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
| Rice Establishment Methods | Panicle Size (Grains Panicle−1) | Rice Yield (t hm−2) | Cv (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Minimum | Mean | |||
| DS | ≥190 | 10.2 | 7.5 | 8.6 | 9.4 |
| 155–190 | 9.8 | 6.0 | 8.3 | 10.6 | |
| ≤155 | 10.1 | 5.3 | 8.4 | 17.2 | |
| MET | ≥190 | 10.5 | 6.3 | 8.7 | 9.2 |
| 155–190 | 12.3 | 6.0 | 8.9 | 14.3 | |
| ≤155 | 9.8 | 5.6 | 8.5 | 10.7 | |
| MAT | ≥190 | 9.8 | 5.3 | 8.1 | 20.0 |
| 155–190 | 10.5 | 6.8 | 8.7 | 12.3 | |
| ≤155 | 9.8 | 5.7 | 7.7 | 19.5 | |
| Rice Establishment Methods | Panicle Size (Grains Panicle−1) | Head Rice Rate (%) | Chalky Grain Rate (%) | Chalkiness Level (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | Min | Mean | Cv (%) | Max | Min | Mean | Cv (%) | Max | Min | Mean | Cv (%) | ||
| DS | ≥190 | 70.7 | 50.0 | 63.4 | 8.7 | 27.7 | 4.1 | 12.0 | 46.3 | 8.5 | 0.9 | 3.4 | 55.2 |
| 155–190 | 71.0 | 30.9 | 58.2 | 16.8 | 62.0 | 2.2 | 14.2 | 104.8 | 22.7 | 0.4 | 4.1 | 120.9 | |
| ≤155 | 70.7 | 45.8 | 61.5 | 13.6 | 24.6 | 3.0 | 9.5 | 64.2 | 8.5 | 0.6 | 2.7 | 73.0 | |
| MET | ≥190 | 70.2 | 47.9 | 62.5 | 9.6 | 23.5 | 3.6 | 10.9 | 44.7 | 10.0 | 0.7 | 3.2 | 55.9 |
| 155–190 | 68.4 | 44.0 | 60.3 | 12.0 | 24.1 | 2.1 | 9.2 | 65.8 | 8.3 | 0.6 | 2.5 | 80.9 | |
| ≤155 | 71.1 | 43.2 | 58.0 | 12.8 | 22.3 | 1.3 | 9.4 | 64.9 | 5.5 | 0.3 | 2.4 | 67.2 | |
| MAT | ≥190 | 70.2 | 35.8 | 60.1 | 14.1 | 36.3 | 2.1 | 13.9 | 72.3 | 13.4 | 0.6 | 4.2 | 88.6 |
| 155–190 | 68.5 | 34.3 | 59.1 | 15.4 | 22.0 | 4.4 | 10.0 | 56.5 | 7.3 | 1.1 | 2.8 | 77.9 | |
| ≤155 | 74.5 | 35.7 | 56.6 | 20.9 | 15.8 | 0.9 | 8.5 | 62.4 | 5.0 | 0.2 | 2.3 | 64.4 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, W.; Tu, D.; Xi, M.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Z.; Ji, Y.; Sun, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, F. Variations of Rice Yield and Quality in Response to Different Establishment Methods at Farmers’ Field. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3174. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123174
Wu W, Tu D, Xi M, Xu Y, Zhou Y, Li Z, Ji Y, Sun X, Yang Y, Li F. Variations of Rice Yield and Quality in Response to Different Establishment Methods at Farmers’ Field. Agronomy. 2022; 12(12):3174. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123174
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Wenge, Debao Tu, Min Xi, Youzun Xu, Yongjin Zhou, Zhong Li, Yalan Ji, Xueyuan Sun, Yachun Yang, and Feiyue Li. 2022. "Variations of Rice Yield and Quality in Response to Different Establishment Methods at Farmers’ Field" Agronomy 12, no. 12: 3174. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123174
APA StyleWu, W., Tu, D., Xi, M., Xu, Y., Zhou, Y., Li, Z., Ji, Y., Sun, X., Yang, Y., & Li, F. (2022). Variations of Rice Yield and Quality in Response to Different Establishment Methods at Farmers’ Field. Agronomy, 12(12), 3174. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12123174







