Responses of the Lodging Resistance of Indica Rice Cultivars to Temperature and Solar Radiation under Field Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
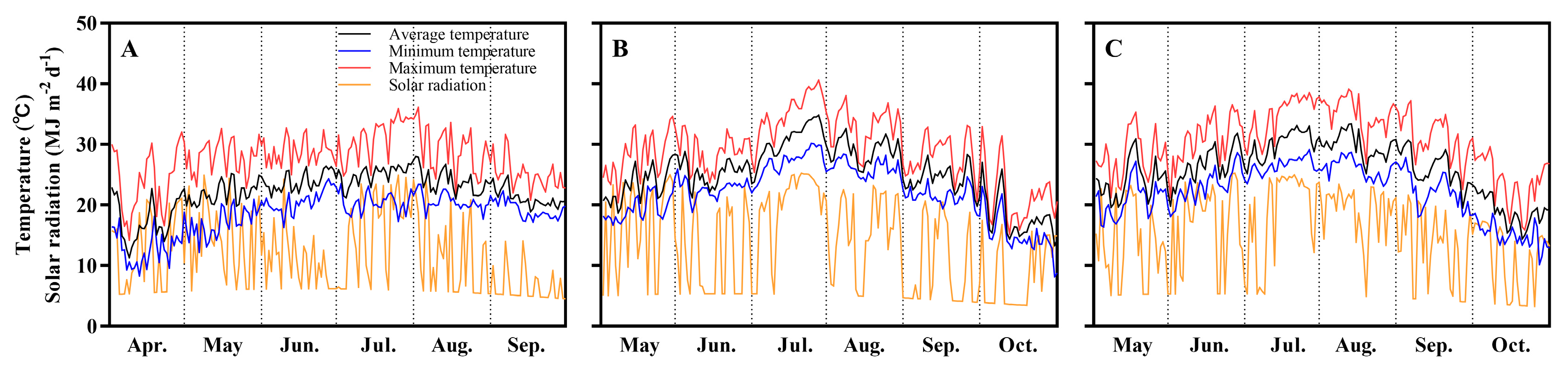
2.3. Meteorological Data Collection
2.4. Plant Sampling and Measurements
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
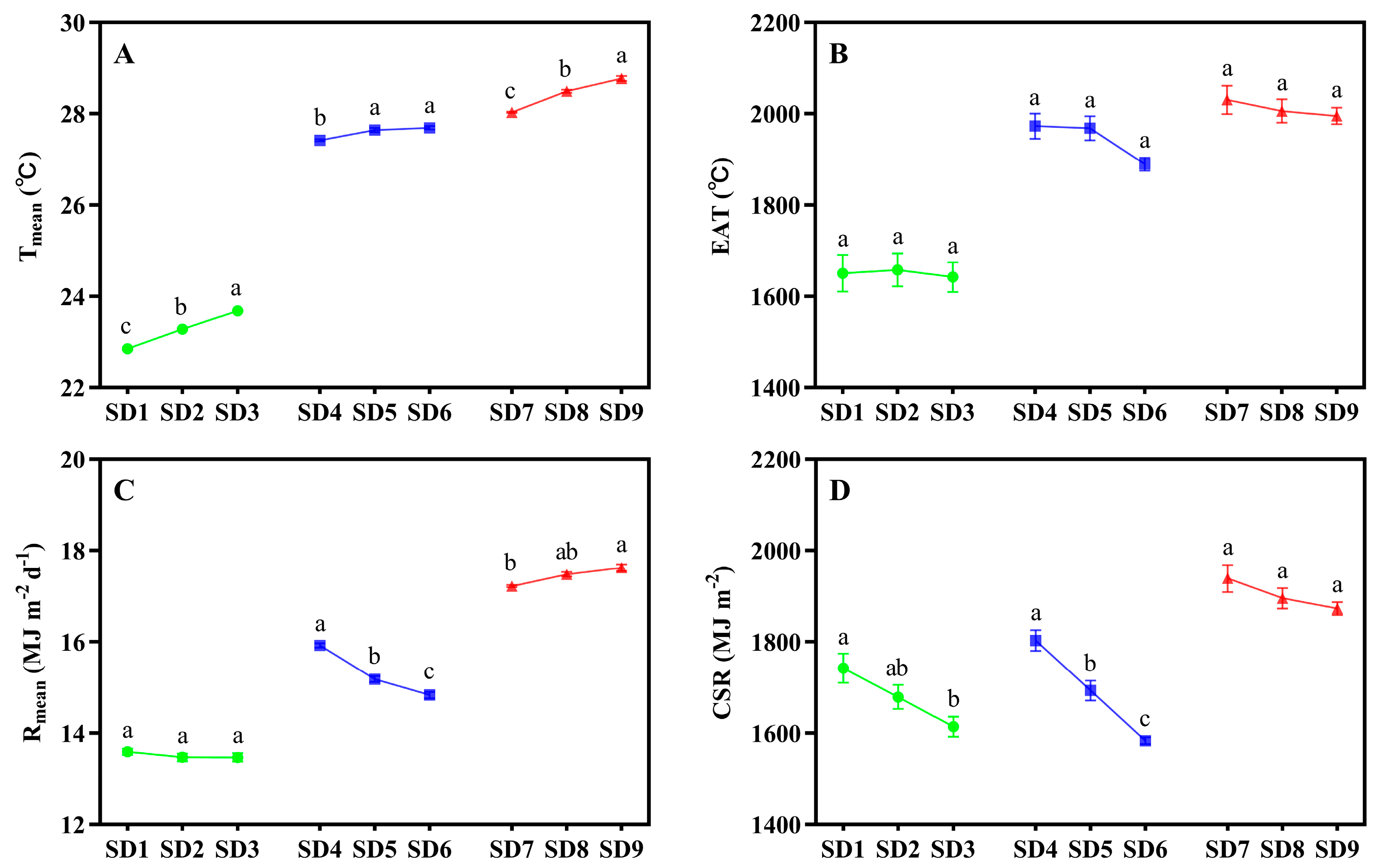
3.1. Effects of Sowing Date on Determined Growth Durations and Temperature and Solar Radiation Conditions
3.2. Effects of Sowing Date on LI and △BM
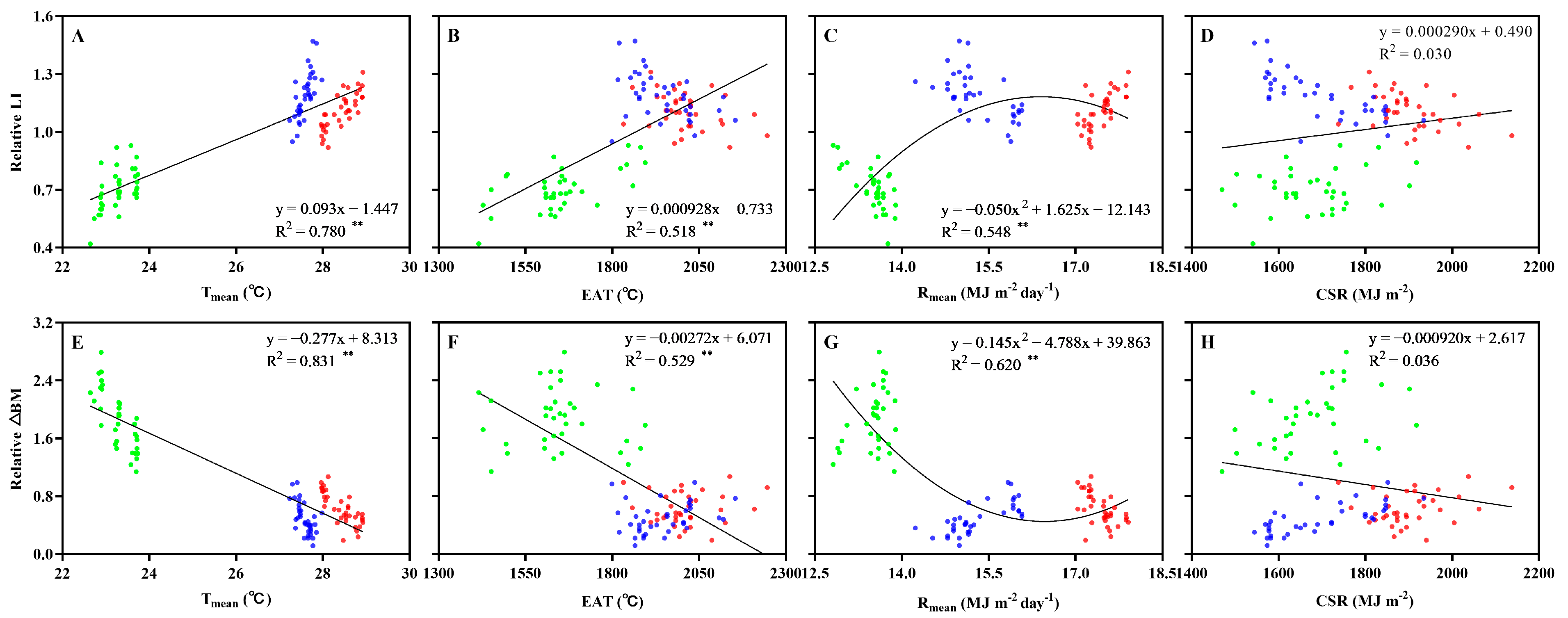
3.3. Relationship of Temperature and Solar Radiation Parameters with Relative LI and △BM
3.4. Correlation analysis of the Tmean and Relative Lodging-Related Traits
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lang, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, M.; Zhu, Q. Effects of lodging at different filling stages on rice yield and grain quality. Rice Sci. 2012, 19, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshikawa, K.; Wang, S. Studies on lodging in rice plants: I. A general observation on lodged rice culms. Jpn. J. Crop Sci. 1990, 59, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kono, M. Physiological aspects of lodging. Physiology 1995, 2, 971–982. [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima, T.; Yoshida, M.; Tomimura, K. Effect of lodging on the level of mycotoxins in wheat, barley, and rice infected with the Fusarium graminearum species complex. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2008, 74, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khush, G.S. Green revolution: Preparing for the 21st century. Genome 1999, 42, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khush, G.S. Green revolution: The way forward. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001, 2, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedden, P. The genes of the Green Revolution. Trends Genet. 2003, 19, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalrymple, D.G. The Development and Adoption of High-Yielding Varieties of Wheat and Rice in Developing Countries. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 1985, 67, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Yi, Y.; Wang, W.; Zeng, Y.; Tan, X.; Wu, Z.; Chen, X.; Pan, X.; Shi, Q.; Zeng, Y. Innovative furrow ridging fertilization under a mechanical direct seeding system improves the grain yield and lodging resistance of early indica rice in South China. Field Crops Res. 2021, 270, 108184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Du, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Tan, X.; Pan, X.; Shi, Q.; Wu, Z.; Zeng, Y. Effects of different mechanical direct seeding methods on grain yield and lodging resistance of early indica rice in South China. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 1204–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khush, G.S. Breaking the yield frontier of rice. GeoJournal 1995, 35, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, P.M.; Sterling, M.; Spink, J.H.; Baker, C.J.; Sylvester-Bradley, R.; Mooney, S.J.; Tams, A.R.; Ennos, A.R. Understanding and reducing lodging in cereals. Adv. Agron. 2004, 84, 215–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, P.M.; Sterling, M.; Mooney, S.J. Development of a model of lodging for barley. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2006, 192, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, P.M.; Sylvester-Bradley, R.; Berry, S. Ideotype design for lodging-resistant wheat. Euphytica 2007, 154, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, E.G. Effect of mineral nutrition on lodging of cereals. Plant Soil 1954, 5, 246–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, K.; Ordonio, R.L.; Matsuoka, M. Engineering the lodging resistance mechanism of post-Green Revolution rice to meet future demands. Proc. Jpn. Acad. B-Phys. 2017, 93, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Islam, M.S.; Peng, S.B.; Visperas, R.M.; Ereful, N.; Bhuiya, M.S.U.; Julfiquar, A.W. Lodging-related morphological traits of hybrid rice in a tropical irrigated ecosystem. Field Crops Res. 2007, 101, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Ziska, L.H.; Sakai, H.; Zhu, J.; Hasegawa, T. Vulnerability of lodging risk to elevated CO2 and increased soil temperature differs between rice cultivars. Eur. J. Agron. 2013, 46, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, G.; Yang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Tang, S.; Ding, Y. Effects of nitrogen application rate and ratio on lodging resistance of super rice with different genotypes. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wu, L.; Ding, Y.; Weng, F.; Wu, X.; Li, G.; Liu, Z.; Tang, S.; Ding, C.; Wang, S. Top-dressing nitrogen fertilizer rate contributes to decrease culm physical strength by reducing structural carbohydrate content in japonica rice. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 992–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, B.; Yuan, X.; Xing, Y.; Liu, H.; Luo, L.; Chen, G.; Xiong, L. Genetic analyses of lodging resistance and yield provide insights into post-Green-Revolution breeding in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 814–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, K.A.; Horiuchi, T.; Miyagawa, S. Effects of powdered rice chaff application on Si and N absorption, lodging resistance and yield in rice plants (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Prod. Sci. 1999, 2, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duy, P.Q.; Abe, A.; Hirano, M.; Sagawa, S.; Kuroda, E. Analysis of lodging-resistant characteristics of different rice genotypes grown under the standard and nitrogen-free basal dressing accompanied with sparse planting density practices. Plant Prod. Sci. 2004, 7, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobasser, H.R.; Yadi, R.; Azizi, M.; Ghanbari, A.M.; Samdaliri, M. Effect of density on morphological characteristics related-lodging on yield and yield components in varieties rice (Oryza sativa L.) In Iran. Am.-Eurasian J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2009, 5, 745–754. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.Y.; Wu, Z.F.; Fu, L.; Dan, Z.W.; Yuan, Z.Q.; Liang, T.; Zhu, R.S.; Hu, Z.L.; Wu, X.T. Evaluation of lodging resistance in rice based on an optimized parameter from lodging index. Crop Sci. 2022, 62, 1318–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, T.; Kawahara, H.; Chonan, N. Histological studies on breaking resistance of lower internodes in rice culm: IV. The roles of each tissue of internode and leaf sheath in breaking resistance. Jpn. J. Crop Sci. 1983, 52, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, T. Studies on breeding for culm stifness in rice: 1. Varietal differences in culm stiffness and its related traits. Jpn. J. Breed. 1983, 33, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichii, M.; Hada, K. Application of ratoon to a test of agronomic characters in rice breeding. II. The relationship between ratoon ability and lodging resistance. Jpn. J. Breed. 1983, 33, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ookawa, T.; Ishihara, K. Varietal difference of physical characteristics of the culm related to lodging resistance in paddy rice. Jpn. J. Crop Sci. 1992, 61, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kashiwagi, T.; Togawa, E.; Hirotsu, N.; Ishimaru, K. Improvement of lodging resistance with QTLs for stem diameter in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2008, 117, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Xu, Z.; Xu, H. Lodging resistance in japonica rice varieties with different panicle types. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2009, 23, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ookawa, T.; Yasuda, K.; Kato, H.; Sakai, M.; Seto, M.; Sunaga, K.; Motobayashi, T.; Tojo, S.; Hirasawa, T. Biomass production and lodging resistance in ‘Leaf Star’, a new long-culm rice forage cultivar. Plant Prod. Sci. 2010, 13, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, G.; Song, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yang, C.; Tang, S.; Zheng, C.; Wang, S.; Ding, Y. Lodging resistance characteristics of high-yielding rice populations. Field Crops Res. 2014, 161, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Li, Y.; Hu, Z.; Hu, H.; Wang, G.; Li, A.; Wang, Y.; Tu, Y.; Xia, T.; Peng, L.; et al. Ectopic expression of a novel OsExtensin-like gene consistently enhances plant lodging resistance by regulating cell elongation and cell wall thickening in rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hirano, K.; Okuno, A.; Hobo, T.; Ordonio, R.; Shinozaki, Y.; Asano, K.; Kitano, H.; Matsuoka, M. Utilization of stiff culm trait of rice smos1 mutant for increased lodging resistance. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Murata, K.; Yamazaki, M.; Onosato, K.; Miyao, A.; Hirochika, H. Three distinct rice cellulose synthase catalytic subunit genes required for cellulose synthesis in the secondary wall. Plant Physiol. 2003, 133, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Fu, C.; Liang, C.; Ni, X.; Zhao, X.; Chen, M.; Ou, L. Crop Lodging and The Roles of Lignin, Cellulose, and Hemicellulose in Lodging Resistance. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimaru, K.; Togawa, E.; Ookawa, T.; Kashiwagi, T.; Madoka, Y.; Hirotsu, N. New target for rice lodging resistance and its effect in a typhoon. Planta 2008, 227, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.J.; Yang, Y.; Yao, J.L.; Chen, G.X.; Li, X.H.; Zhang, Q.F.; Wu, C.Y. FLEXIBLE CULM 1 encoding a cinnamyl-alcohol dehydrogenase controls culm mechanical strength in rice. Plant Mol. Biol. 2009, 69, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, F.; Jin, Z.; Ma, G.; Shang, W.; Liu, H.; Xu, M.; Liu, Y. Relationship between lodging resistance and chemical contents in culms and sheaths of japonica rice during grain filling. Rice Sci. 2010, 17, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, G.; Huang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Ding, C.; Tang, S.; Chen, L.; Wang, S.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, W. Effects of culm carbohydrate partitioning on basal stem strength in a high-yielding rice population. Crop J. 2017, 5, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Xie, L.; Zheng, S.; Li, J.; Yuan, J. Effects of nitrogen rate and transplanting density on physical and chemical characteristics and lodging resistance of culms in hybrid rice. Acta Agron. Sin. 2009, 35, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Huang, J.; Cui, K.; Nie, L.; Wang, Q.; Yang, F.; Shah, F.; Yao, F.; Peng, S. Sheath blight reduces stem breaking resistance and increases lodging susceptibility of rice plants. Field Crops Res. 2012, 128, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.; Zhang, X.; Yao, J.; Dai, G.; Yu, G.; Zhu, Q.; Gao, Q.; Zheng, W. Synergistic effects of bast fiber seedling film and nano-silicon fertilizer to increase the lodging resistance and yield of rice. Sci. Rep.-UK 2021, 11, 12788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Chen, Y.; Huang, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tang, X.; Pan, S.; Tian, H.; Mo, Z. Optimization of nitrogen–silicon (N-Si) fertilization for grain yield and lodging resistance of early-season indica fragrant rice under different planting methods. Eur. J. Agron. 2022, 136, 126508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohe, M.; Tamura, A.; Mimoto, H. Effects of deep water treatment on the growth of culms and the lodging resistance in Japonica type paddy rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars. Jpn. J. Crop Sci. 1996, 65, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niu, L.; Feng, S.; Ding, W.; Li, G. Influence of speed and rainfall on large-scale wheat lodging from 2007 to 2014 in China. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimono, H.; Okada, M.; Yamakawa, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Hasegawa, T. Lodging in rice can be alleviated by atmospheric CO2 enrichment. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 118, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revilla-Molina, I.M.; Bastiaans, L.; Van Keulen, H.; Kropff, M.J.; Hui, F.; Castilla, N.P.; Mew, T.W.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Leung, H. Does resource complementarity or prevention of lodging contribute to the increased productivity of rice varietal mixtures in Yunnan, China? Field Crops Res. 2009, 111, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olagunju, S.O.; Atayese, M.O.; Sakariyawo, O.S.; Dare, E.O.; Tang, C. Effects of multi-growth stage water deficit and orthosilicic acid fertiliser on lodging resistance of rice cultivars. Crop Pasture Sci. 2022, 73, 370–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.H. What is ’dangerous’ climate change? Nature 2001, 411, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuan, M.; Leirvik, T.; Wild, M. Global trends in downward surface solar radiation from spatial interpolated ground observations during 1961–2019. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 9501–9521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, V.; Feng, Y. Air pollution, greenhouse gases and climate change: Global and regional perspectives. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakun, J.D.; Clark, P.U.; He, F.; Marcott, S.A.; Mix, A.C.; Liu, Z.Y.; Otto-Bliesner, B.; Schmittner, A.; Bard, E. Global warming preceded by increasing carbon dioxide concentrations during the last deglaciation. Nature 2012, 484, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change). Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Stanhill, G.; Cohen, S. Global dimming: A review of the evidence for a widespread and significant reduction in global radiation with discussion of its probable causes and possible agricultural consequences. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2001, 107, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambezidis, H.D.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Kharol, S.K.; Moorthy, K.K.; Satheesh, S.K.; Kalapureddy, M.C.R.; Badarinath, K.V.S.; Sharma, A.R.; Wild, M. Multi-decadal variation of the net downward shortwave radiation over south Asia: The solar dimming effect. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 50, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.-B.; Zhang, J.; Fang, S.-L.; Wei, H.-Y.; Zhang, H.-C. Effects of temperature and solar radiation on yield of good eating-quality rice in the lower reaches of the Huai River Basin, China. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 1762–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; Zhang, C.; He, L.; Liao, S.; Li, Q.; Li, B.; Zhu, S.; Gao, Y.; Tao, Y.; Zhou, W.; et al. Delayed sowing date improves the quality of mechanically transplanted rice by optimizing temperature conditions during growth season. Field Crops Res. 2022, 281, 108493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsura, K.; Maeda, S.; Lubis, I.; Horie, T.; Cao, W.; Shiraiwa, T. The high yield of irrigated rice in Yunnan, China. Field Crops Res. 2008, 107, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, W.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, M.; Liu, F. Single rice growth period was prolonged by cultivars shifts, but yield was damaged by climate change during 1981-2009 in China, and late rice was just opposite. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 3200–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, F.; Zhang, W.; Wu, X.; Xu, X.; Ding, Y.; Li, G.; Liu, Z.; Wang, S. Impact of low-temperature, overcast and rainy weather during the reproductive growth stage on lodging resistance of rice. Sci. Rep.-UK 2017, 7, 46596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agrama, H.A.; Yan, W.G.; Lee, F.; Fjellstrom, R.; Chen, M.H.; Jia, M.; McClung, A. Genetic Assessment of a Mini-Core Subset Developed from the USDA Rice Genebank. Crop Sci. 2009, 49, 1336–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Meteorological Data Service Centre. Available online: http://data.cma.cn/en (accessed on 18 December 2019).
- Angstrom, A. Solar and terrestrial radiation. Quart. J. Roy. Met. Soc. 1924, 50, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Rahman, L.; Rahman, M.M. Techniques to obtain improved predictions of global radiation from sunshine duration. Renew. Energy 1999, 18, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Ersi, K.; Yang, J.; Lu, S.; Zhao, W. Validation of five global radiation models with measured daily data in China. Energy Convers. Manag. 2004, 45, 1759–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I—A discussion of principles. J. Contam. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, N.; Ling, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, C.; Fahad, S.; Peng, S.; Cui, K.; Nie, L.; Huang, J. Influence of temperature and solar radiation on grain yield and quality in irrigated rice system. Eur. J. Agron. 2015, 64, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seko, H. Studies on lodging in rice plants. Bull. Kyusyu Agric. Exp. Sta. 1962, 7, 419–499. [Google Scholar]
- Ookawa, T.; Ishihara, K. Varietal difference of the cell wall components affecting the bending stress of the culm in relation to the lodging resistance in paddy rice. Jpn. J. Crop Sci. 1993, 62, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ookawa, T.; Hobo, T.; Yano, M.; Murata, K.; Ando, T.; Miura, H.; Asano, K.; Ochiai, Y.; Ikeda, M.; Nishitani, R.; et al. New approach for rice improvement using a pleiotropic QTL gene for lodging resistance and yield. Nat. Commun. 2010, 1, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Updegraff, D.M. Semimicro determination of cellulose inbiological materials. Anal. Biochem. 1969, 32, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, R.S.; Hatfield, R.D. Comparison of the acetyl bromide spectrophotometric method with other analytical lignin methods for determining lignin concentration in forage samples. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 3713–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.B.; Moore, W.E.; Zank, L.C. The spectrophotometric determination of lignin in small wood samples. Tappi 1961, 44, 793–798. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.; Liu, X. Comparison and optimization of various non-dimensionalized methods based on comprehensive evaluation method–a case study of land development in Yongdeng county of Lanzhou city. Hunan Agric. Sci. 2010, 17, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.F.; Zhang, J.Y.; Jia, W.J.; Ji, F.M.; Yan, Q.; Xu, Q.; Ke, S.; Ke, J.S. Analyzing the role of soil and rice cadmium pollution on human renal dysfunction by correlation and path analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 2047–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Huang, Y.; Yang, X. Climate warming over the past three decades has shortened rice growth duration in China and cultivar shifts have further accelerated the process for late rice. Global Change Biol. 2013, 19, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wu, W.; Du, M.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Bryant, C.R. Modeling Climate Change Impacts on Rice Growth and Yield under Global Warming of 1.5 and 2.0 °C in the Pearl River Delta, China. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, X.; Wang, Y.; Dong, X.; Qian, T.; Yin, L.; Dong, S.; Chu, J.; He, M. Delayed sowing can increase lodging resistance while maintaining grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency in winter wheat. Crop J. 2017, 5, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Ma, B.L. Assessment of canola crop lodging under elevated temperatures for adaptation to climate change. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 248, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiji, Y.; Hayashi, S.; Horie, T. Influences of nitrogen nutrient and solar radiation in the canopy on length of lower internodes of rice. Jpn. J. Crop Sci. 1993, 62, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ookawa, T.; Todokoro, Y.; Ishihara, K. Changes in physical and chemical characteristics of culm associated with lodging resistance in paddy rice under different growth conditions and varietal difference of their changes. Jpn. J. Crop Sci. 1993, 62, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Yang, C.; Li, L. Shade-induced stem elongation in rice seedlings: Implication of tissue-specific phytohormone regulation. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2016, 58, 614–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, W.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cambula, E.D.; Weng, F.; Liu, Z.; Ding, C.; Tang, S.; Chen, L.; et al. Shading contributes to the reduction of stem mechanical strength by decreasing cell wall synthesis in japonica rice (Oryza sativa L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hussain, S.; Iqbal, N.; Pang, T.; Khan, M.N.; Liu, W.G.; Yang, W.Y. Weak stem under shade reveals the lignin reduction behavior. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Duan, X.; Yao, X.; Liu, Q.; Xiao, R.; Zhang, X.; Tang, Y.; Wen, M.; Li, J. Effects of shading on stem morphological traits and lodging resistance in heavy type panicle of indica rice. Chin. Rice 2020, 26, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Shah, F.; Duncan, R.W.; Ma, B.L. Grain yield, root growth habit and lodging of eight oilseed rape genotypes in response to a short period of heat stress during flowering. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 287, 107954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zheng, S.; Gui, J.; Fu, C.; Yu, H.; Song, D.; Shen, J.; Qin, P.; Liu, X.; Han, B.; et al. Shortened basal internodes encodes a gibberellin 2-oxidase and contributes to lodging resistance in rice. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okawa, S.; Makino, A.; Mae, T. Effect of irradiance on the partitioning of assimilated carbon during the early phase of grain filling in rice. Ann. Bot. 2003, 92, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slewinski, T.L. Non-structural carbohydrate partitioning in grass stems: A target to increase yield stability, stress tolerance, and biofuel production. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 4647–4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Qian, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, M.; Sun, L.; Zhang, M.; Fu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Han, B.; Pang, X.; et al. BRITTLE CULM1, which encodes a COBRA-like protein, affects the mechanical properties of rice plants. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 2020–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhai, W.; Tong, Z.; Shen, T.; Li, Y.C.; Zhang, M.; Sigua, G.C.; Chen, J.; Ding, F. Controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer improved lodging resistance and potassium and silicon uptake of direct-seeded rice. Crop Sci. 2019, 59, 2733–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Cultivars | Growth Duration (d) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xindu/2015 | Ezhou/2017 | Ezhou/2018 | |||||||
| SD1 a | SD2 | SD3 | SD4 | SD5 | SD6 | SD7 | SD8 | SD9 | |
| Chuan 106B | 112 | 108 | 106 | 104 | 101 | 102 | 102 | 100 | 101 |
| 345B | 114 | 113 | 109 | 106 | 105 | 104 | 106 | 105 | 102 |
| Huanghuazhan | 126 | 123 | 119 | 109 | 107 | 105 | 110 | 105 | 105 |
| Jinlongsimiao | 126 | 121 | 117 | 115 | 112 | 107 | 111 | 108 | 102 |
| Chuanxiang 29B | 124 | 126 | 119 | 112 | 109 | 107 | 112 | 107 | 106 |
| Chenghui 3203 | 136 | 129 | 122 | 116 | 114 | 105 | 113 | 107 | 108 |
| Guichao 2 | 126 | 121 | 117 | 111 | 108 | 106 | 111 | 106 | 103 |
| II-32B | 128 | 127 | 121 | 116 | 121 | 111 | 117 | 116 | 113 |
| Teqing | 128 | 125 | 119 | 116 | 114 | 106 | 114 | 107 | 107 |
| R379 | 144 | 139 | 134 | 125 | 122 | 116 | 125 | 121 | 115 |
| 9311 | 129 | 124 | 121 | 112 | 111 | 106 | 112 | 110 | 108 |
| Jiangan | 147 | 142 | 136 | 117 | 115 | 107 | 118 | 110 | 106 |
| Cultivars | Lodging Index (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xindu/2015 | Ezhou/2017 | Ezhou/2018 | |||||||
| SD1 | SD2 | SD3 | SD4 | SD5 | SD6 | SD7 | SD8 | SD9 | |
| Chuan 106B | 47.11 b a | 69.62 a | 78.72 a | 107.73 c | 143.22 b | 164.70 a | 117.37 b | 139.24 a | 147.66 a |
| 345B | 63.46 b | 88.30 a | 89.25 a | 123.65 b | 138.31 ab | 147.49 a | 117.79 b | 122.94 b | 142.64 a |
| Huanghuazhan | 70.98 b | 69.87 b | 84.58 a | 136.87 b | 165.57 a | 181.87 a | 116.95 b | 137.56 a | 150.58 a |
| Jinlongsimiao | 78.09 b | 86.15 ab | 93.18 a | 145.71 b | 161.86 ab | 178.79 a | 125.62 b | 152.64 a | 154.23 a |
| Chuanxiang 29B | 80.84 b | 99.29 a | 94.52 a | 163.60 a | 169.84 a | 178.62 a | 155.36 b | 165.75 ab | 179.44 a |
| Chenghui 3203 | 83.25 a | 92.10 a | 91.25 a | 151.27 b | 159.50 ab | 176.02 a | 145.68 a | 153.73 a | 152.95 a |
| Guichao 2 | 83.72 a | 86.04 a | 93.91 a | 131.29 b | 161.73 a | 163.69 a | 127.07 b | 139.46 a | 148.41 a |
| II-32B | 89.32 b | 109.54 a | 114.86 a | 162.52 a | 166.74 a | 184.31 a | 155.90 b | 178.68 a | 186.06 a |
| Teqing | 99.70 b | 110.16 b | 127.81 a | 155.11 a | 172.41 a | 172.32 a | 147.48 c | 162.21 b | 177.00 a |
| R379 | 86.56 a | 100.41 a | 98.20 a | 127.60 b | 142.23 a | 152.40 a | 118.40 b | 131.65 a | 127.62 ab |
| 9311 | 91.19 b | 106.94 a | 117.20 a | 160.74 a | 173.83 a | 170.69 a | 149.48 b | 162.77 a | 167.92 a |
| Jiangan | 94.39 b | 103.09 a | 104.54 a | 110.10 b | 118.95 b | 137.43 a | 103.25 b | 115.53 a | 123.70 a |
| Cultivars | △BM (g cm) | CV a (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xindu/2015 | Ezhou/2017 | Ezhou/2018 | ||||||||
| SD1 | SD2 | SD3 | SD4 | SD5 | SD6 | SD7 | SD8 | SD9 | ||
| Chuan 106B | 2644.12 a b | 2039.94 b | 1346.41 c | 1150.50 a | 671.60 b | 349.58 c | 1177.42 a | 758.29 b | 517.23 b | 63.19 |
| 345B | 2501.73 a | 1790.85 b | 1642.24 b | 922.84 a | 617.56 b | 477.06 b | 1078.02 a | 926.45 a | 642.13 b | 56.76 |
| Huanghuazhan | 3149.41 a | 2629.95 ab | 2036.62 b | 736.20 a | 341.49 b | 146.86 c | 1082.53 a | 660.49 b | 473.25 b | 86.74 |
| Jinlongsimiao | 3123.09 a | 2740.98 a | 2137.34 b | 811.33 a | 550.77 ab | 292.45 b | 1176.19 a | 733.90 b | 635.89 b | 76.76 |
| Chuanxiang 29B | 2600.97 a | 2163.80 b | 1957.99 b | 540.39 a | 416.68 ab | 264.07 b | 684.26 a | 481.05 ab | 250.41 b | 88.95 |
| Chenghui 3203 | 3174.04 a | 2443.57 b | 2444.77 b | 850.97 a | 591.92 ab | 300.71 b | 1003.42 a | 696.71 b | 695.78 b | 76.57 |
| Guichao 2 | 2213.49 a | 2108.17 a | 1613.65 b | 897.83 a | 420.38 b | 353.33 b | 1046.41 a | 725.54 b | 551.51 b | 64.28 |
| II-32B | 1793.73 a | 1436.09 ab | 1176.57 b | 480.55 a | 354.43 ab | 159.34 b | 559.40 a | 302.48 ab | 133.49 b | 85.05 |
| Teqing | 1891.21 a | 1511.49 b | 1039.69 c | 586.78 a | 329.64 b | 312.78 b | 703.07 a | 451.53 b | 252.74 c | 73.69 |
| R379 | 5442.30 a | 3728.34 b | 3329.22 b | 1836.23 a | 1144.77 b | 847.96 c | 2181.02 a | 1483.45 b | 1454.91 b | 62.88 |
| 9311 | 3678.55 a | 2560.75 b | 1839.95 c | 727.80 a | 407.82 b | 461.61 ab | 1043.13 a | 663.80 b | 488.15 b | 86.82 |
| Jiangan | 5089.65 a | 4192.39 ab | 3563.15 b | 2838.87 a | 2033.76 b | 1280.59 c | 3062.08 a | 2090.83 b | 1609.43 c | 43.87 |
| Dependent Variable | Independent Variable | Correlation Coefficient | Direct Effect | Indirect Effect | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tmeana | Rmeana | ||||
| Relative LI | Tmean | 0.883 ** b | 1.556 | - | −0.673 |
| Rmean | 0.621 ** | −0.759 | 1.380 | - | |
| Relative △BM | Tmean | −0.912 ** | −1.473 | - | 0.561 |
| Rmean | −0.674 ** | 0.633 | −1.307 | - | |
| Year/Location | CL a | SL | PL | BR | FW | BM | M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015/Xindu | 0.424 ** b | 0.708 ** | −0.645 ** | −0.912 ** | −0.365 * | −0.207 | −0.912 ** |
| 2017/Ezhou | 0.024 | 0.456 ** | −0.547 ** | −0.603 ** | −0.202 | −0.148 | −0.603 ** |
| 2018/Ezhou | −0.303 | 0.782 ** | −0.795 ** | −0.882 ** | −0.638 ** | −0.627 ** | −0.882 ** |
| All | 0.794 ** | 0.789 ** | −0.014 | −0.864 ** | −0.273 ** | 0.195 * | −0.864 ** |
| Year/Location | CD a | CT | SM | LC | CC | TC | BS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018/Ezhou | −0.851 ** b | −0.754 ** | −0.837 ** | 0.685 ** | −0.551 ** | 0.332 * | 0.437 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, X.; Wu, Z.; Fu, L.; Dan, Z.; Long, W.; Yuan, Z.; Liang, T.; Zhu, R.; Hu, Z.; Wu, X. Responses of the Lodging Resistance of Indica Rice Cultivars to Temperature and Solar Radiation under Field Conditions. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2603. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112603
Luo X, Wu Z, Fu L, Dan Z, Long W, Yuan Z, Liang T, Zhu R, Hu Z, Wu X. Responses of the Lodging Resistance of Indica Rice Cultivars to Temperature and Solar Radiation under Field Conditions. Agronomy. 2022; 12(11):2603. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112603
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Xiaoyun, Zefang Wu, Lu Fu, Zhiwu Dan, Weixiong Long, Zhengqing Yuan, Ting Liang, Renshan Zhu, Zhongli Hu, and Xianting Wu. 2022. "Responses of the Lodging Resistance of Indica Rice Cultivars to Temperature and Solar Radiation under Field Conditions" Agronomy 12, no. 11: 2603. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112603
APA StyleLuo, X., Wu, Z., Fu, L., Dan, Z., Long, W., Yuan, Z., Liang, T., Zhu, R., Hu, Z., & Wu, X. (2022). Responses of the Lodging Resistance of Indica Rice Cultivars to Temperature and Solar Radiation under Field Conditions. Agronomy, 12(11), 2603. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112603






