Impact of Fungicide Application and Host Genotype on Susceptibility of Brassica napus to Sclerotinia Stem Rot across the South-Western Australian Grain Belt: A Genotype × Environment × Management Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
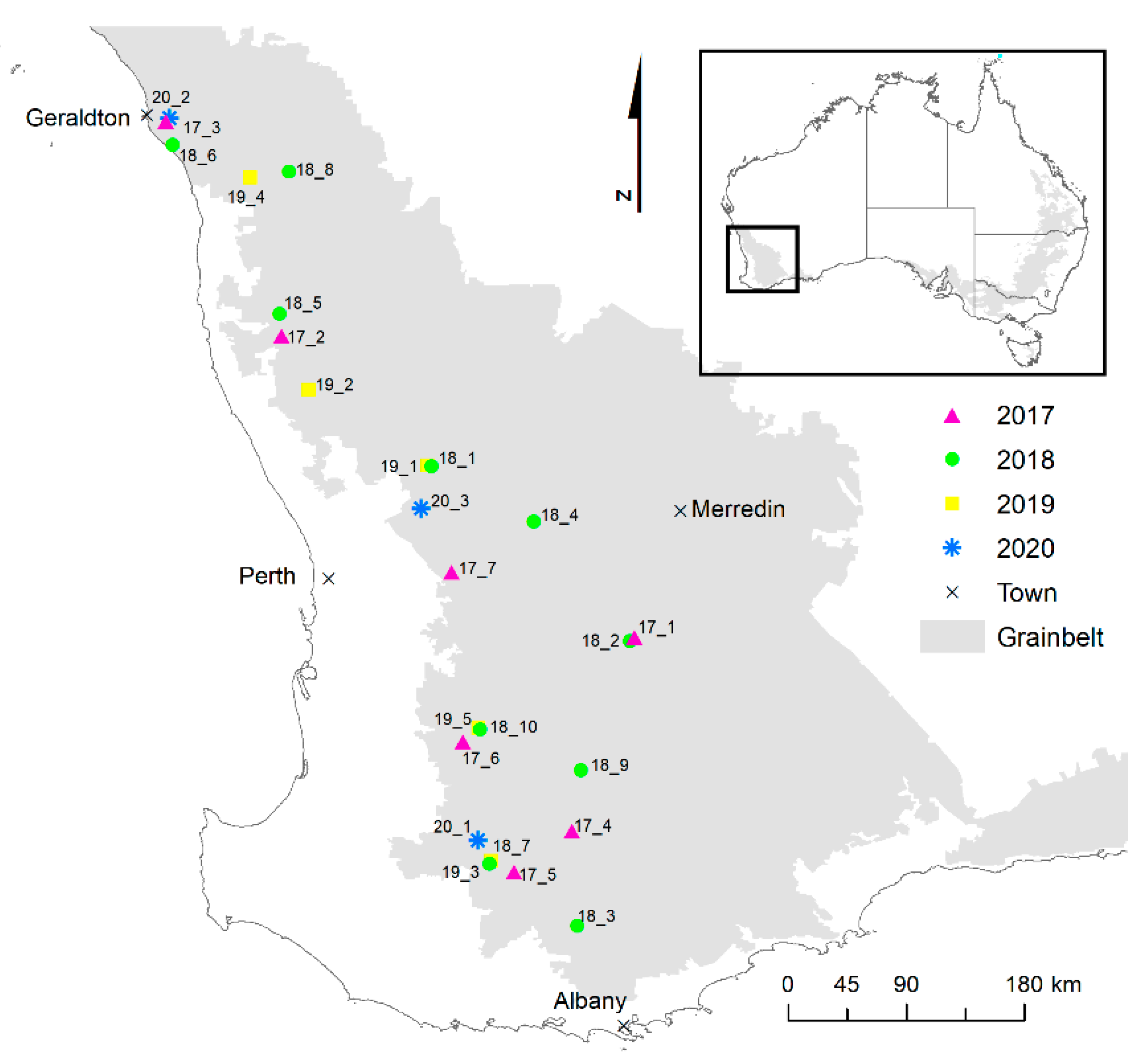
2.1. Sites and Experimental Design
2.2. Field Measurements
2.3. Statistical Analysis and GIS Methods
3. Results
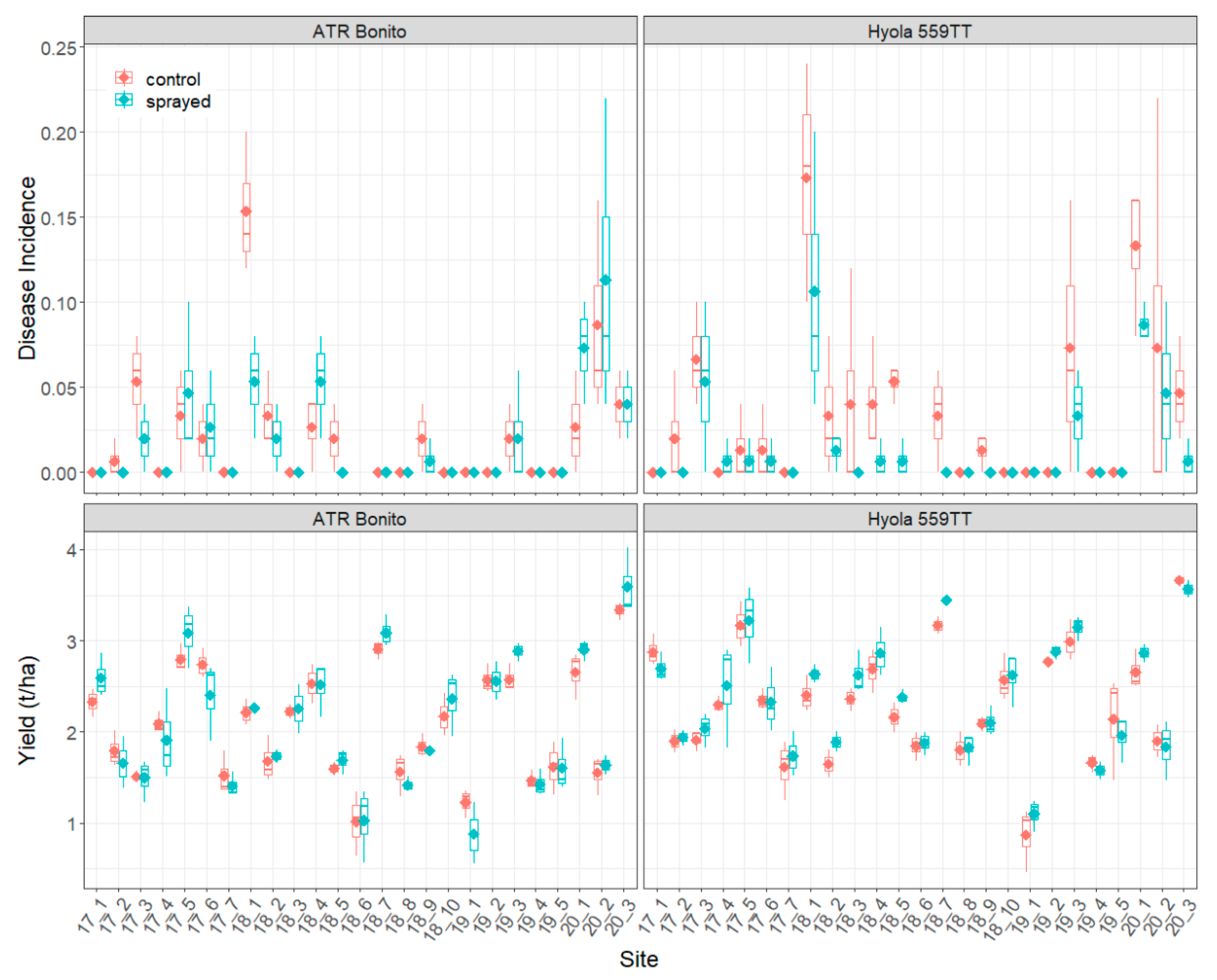
3.1. Disease Incidence and Yield
3.2. Pre-Season Soil Sclerotia
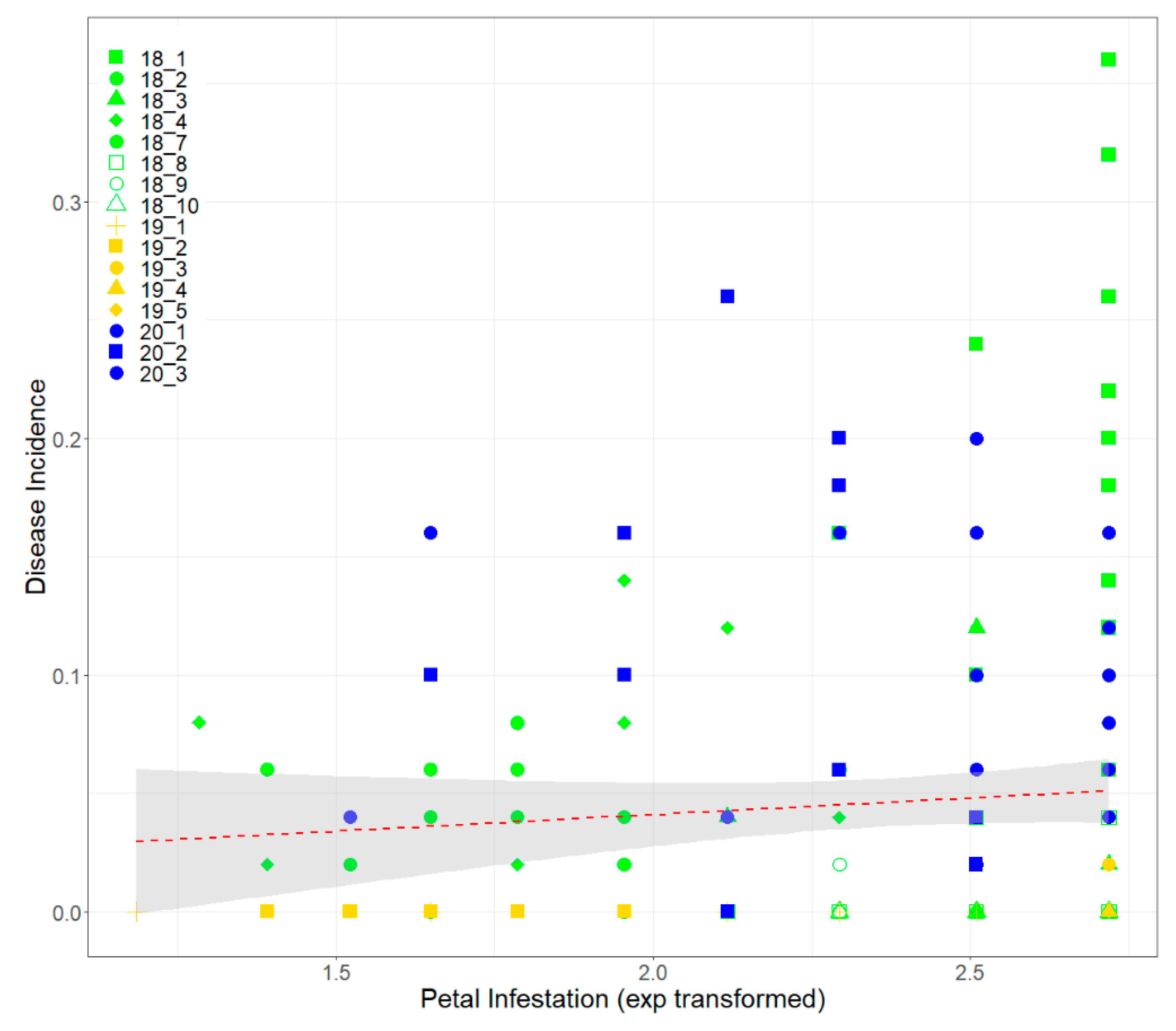
3.3. Petal Test Assay
3.4. Diseased Stem Variables
3.5. AMMI Analysis
3.6. Principal Components Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, X.; Koopmann, B.; Ulber, B.; von Tiedemann, A. A global survey on diseases and pests in oilseed rape—Current challenges and innovative strategies of control. Front. Agron. 2020, 2, 590908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkegaard, J.; Lilley, J.M.; Morrison, M.J. Drivers of trends in Australian canola productivity and future prospects. Crop Pasture Sci. 2016, 67, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derbyshire, M.C.; Denton-Giles, M. The control of Sclerotinia stem rot on oilseed rape (Brassica napus): Current practices and future opportunities. Plant Pathol. 2016, 65, 859–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkegaard, J.A.; Robertson, M.J.; Hamblin, P.; Sprague, S.J. Effect of blackleg and sclerotinia stem rot on canola yield in the high rainfall zone of southern New South Wales, Australia. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2006, 57, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twengström, E.; Sigvald, R.; Svensson, C.; Yuen, J. Forecasting Sclerotinia stem rot in spring sown oilseed rape. Crop Protect. 1998, 17, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boland, G.J.; Hall, R. Index of plant hosts of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 1994, 16, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, M.D.; Thomma, B.; Nelson, B.D. Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (Lib.) de Bary: Biology and molecular traits of a cosmopolitan pathogen. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2006, 7, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harries, M.; Anderson, G.C.; Hüberli, D. Crop sequences in Western Australia: What are they and are they sustainable? Findings of a four-year survey. Crop Pasture Sci. 2015, 66, 634–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Van de Wouw, A.P.; Idnurm, A.; Davidson, J.A.; Sprague, S.J.; Khangura, R.K.; Ware, A.H.; Lindbeck, K.D.; Marcroft, S.J. Fungal diseases of canola in Australia: Identification of trends, threats and potential therapies. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2016, 45, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, K.D.; Bennett, S.J.; Hodgson, L.M.; Ashworth, M.B. Narrow windrow burning canola (Brassica napus L.) residue for Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (Lib.) de Bary sclerotia destruction. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 2594–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrall, R.A.A.; Thomson, J.R. Petal Test Manual for Sclerotinia in Canola; University of Saskatchewan: Saskatoon, SK, Canada, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- GRDC. Canola. Western Region. GRDC GrowNotes; Grains Research and Development Corporation: Canberra, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Carson, M.L.; Goodman, M.M.; Williamson, S.M. Variation in aggressiveness among isolates of Cercospora from maize as a potential cause of genotype-environment interaction in gray leaf spot trials. Plant Dis. 2002, 86, 1089–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Shackley, B.; Paynter, B.; Bucat, J.; Troup, G.; Seymour, M. Western Australian Crop Sowing Guide Bulletin 4917; State of Western Australia: Perth, Australia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. SILO Patched Point Data. Available online: data.qld.gov.au (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- R Core Team. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- de Mendiburu, F. Agricolae: Statistical Procedures for Agricultural Research; R Package Version 1.3-3; 2020; Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=agricolae (accessed on 1 February 2021).
- Wickham, H. Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Das, A.; Parihar, A.K.; Saxena, D.; Singh, D.; Singha, K.D.; Kushwaha, K.P.S.; Chand, R.; Bal, R.S.; Chandra, S.; Gupta, S. Deciphering genotype-by- environment interaction for targeting test environments and rust resistant genotypes in field pea (Pisum sativum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beres, B.L.; Brûlé-Babel, A.L.; Ye, Z.; Graf, R.J.; Turkington, T.K.; Harding, M.W.; Kutcher, H.R.; Hooker, D.C. Exploring Genotype × Environment × Management synergies to manage fusarium head blight in wheat. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2018, 40, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekalign, A.; Sibiya, J.; Derera, J.; Fikre, A. Analysis of genotype × environment interaction and stability for grain yield and chocolate spot (Botrytis fabae) disease resistance in faba bean (Vicia faba). Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2017, 11, 1228–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derbyshire, M.; Denton-Giles, M.; Hane, J.; Chang, S.; Mousavi-Derazmahalleh, M.; Raffaele, S.; Buchwaldt, L.; Kamphuis, L. Selective sweeps in populations of the broad host range plant pathogenic fungus Sclerotinia Sclerotiorum. bioRxiv 2018, 352930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, P.; Lui, K.Y.; Thomson, L.L.; Lamichhane, A.R.; Bennett, S.J. Impact of preconditioning temperatures and duration period on carpogenic germination of diverse Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (Lib.) de Bary populations. Plant Dis. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, P.J.; Lui, K.Y.; Thomson, L.L.; Stefanova, K.; Bennett, S.J. Carpogenic germinability of diverse Sclerotinia sclerotiorum populations within the southwestern Australian grain belt. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 2891–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denton-Giles, M.; Derbyshire, M.C.; Khentry, Y.; Buchwaldt, L.; Kamphuis, L.G. Partial stem resistance in Brassica napus to highly aggressive and genetically diverse Sclerotinia sclerotiorum isolates from Australia. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2018, 40, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Río, L.E.; Bradley, C.A.; Henson, R.A.; Endres, G.J.; Hanson, B.K.; McKay, K.; Halvorson, M.; Porter, P.M.; Le Gare, D.G.; Lamey, H.A. Impact of Sclerotinia stem rot on yield of canola. Plant Dis. 2007, 91, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, R.; Werezuk, R. Sclerotinia Stem Rot Field Nursery for Evaluation of Resistance and Fungicide Efficacy. Canola Agronomic Research Program. AG#2006-07 Final Project Report; Alberta Research Council: Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Turkington, T.K.; Morrall, R.A.A.; Gugel, R.K. Use of petal infestation to forecast sclerotinia stem rot of canola: Evaluation of early bloom sampling, 1985–1990. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 1991, 13, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkington, T.K.; Morrall, R.A.A.; Rude, S.V. Use of petal infestation to forecast sclerotinia stem rot of canola: The impact of diurnal and weather-related inoculum fluctuations. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 1991, 13, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bečka, D.; Prokinová, E.; Šimka, J.; Cihlář, P.; Bečková, L.; Bokor, P.; Vašák, J. Use of petal test in early-flowering varieties of oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) for predicting the infection pressure of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (Lib.) de Bary. Crop Protect. 2016, 80, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer CropScience. Getting the Best Possible Sclerotinia Control from Prosaro® 420 SC in Canola; Bayer Group: Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, S.; Dunker, S.; Kleinhenz, B.; Röhrig, M.; Tiedemann, A.V. A crop loss-related forecasting model for Sclerotinia stem rot in winter oilseed rape. Phytopathology 2007, 97, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothmann, L.A.; McLaren, N.W. Sclerotinia sclerotiorum disease prediction: A review and potential applications in South Africa. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Year (Number of Sites) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variety | Herbicide Tolerance | Breeding Type | Harvest Maturity # | 2017 (7) | 2018 (10) | 2019 (5) | 2020 (3) |
| ATR Bonito | Triazine tolerant | Open pollinated | early-mid | + | + | + | + |
| Hyola 559TT | Triazine tolerant | Hybrid | mid | + | + | + | + |
| ATR Mako | Triazine tolerant | Open pollinated | early-mid | + | + | + | |
| InVigor T4510 | Triazine tolerant | Hybrid | early-mid | + | + | + | |
| DG 408RR | Glyphosate tolerant | Hybrid | early-mid | + | + | ||
| Pioneer 43Y23 RR | Glyphosate tolerant | Hybrid | early | + | + | ||
| Pioneer 44Y27 RR | Glyphosate tolerant | Hybrid | early-mid | + | + | ||
| Hyola 350TT | Triazine tolerant | Hybrid | early | + | |||
| Hyola 530XT | Triazine tolerant + Glyphosate tolerant | Hybrid | mid | + | |||
| HyTTec Trophy | Triazine tolerant | Hybrid | early-mid | + | |||
| HyTTec Trident | Triazine tolerant | Hybrid | early | + | |||
| InVigor R4022P | Glyphosate tolerant | Hybrid | early-mid | + | |||
| Xseed Raptor | Glyphosate tolerant | Hybrid | early-mid | + | |||
| 1950–2020 Growing Season Data (May–October) * | Year of Study Growing Season Data (May–October) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Site | Nearest Town | Total Rainfall (mm) | Maximum Daily Temperature (°C) | Minimum Daily Temperature (°C) | Total Rainfall (mm) | Maximum Daily Temperature (°C) | Minimum Daily Temperature (°C) |
| 2017 | 17_1 | Corrigin | 236 | 18.6 | 6.4 | 224 | 19.5 | 6.6 |
| 2017 | 17_2 | Dandaragan | 413 | 20.5 | 8.9 | 321 | 21.3 | 9.2 |
| 2017 | 17_3 | Greenough | 373 | 22.0 | 10.3 | 258 | 23.0 | 10.3 |
| 2017 | 17_4 | Katanning | 347 | 17.0 | 6.5 | 261 | 17.4 | 7 |
| 2017 | 17_5 | Kojonup | 393 | 16.6 | 6.6 | 352 | 17.0 | 6.9 |
| 2017 | 17_6 | Williams | 385 | 17.7 | 6.1 | 371 | 18.2 | 6.3 |
| 2017 | 17_7 | York | 378 | 18.7 | 6.2 | 282 | 19.5 | 6.2 |
| 2018 | 18_1 | Bolgart | 305 | 19.6 | 7.7 | 316 | 20.3 | 7.7 |
| 2018 | 18_2 | Corrigin | 245 | 18.4 | 6.3 | 228 | 19.2 | 6.3 |
| 2018 | 18_3 | Cranbrook | 362 | 16.7 | 7.2 | 294 | 17.2 | 7.3 |
| 2018 | 18_4 | Cunderdin | 242 | 19.7 | 7.0 | 227 | 20.2 | 6.5 |
| 2018 | 18_5 | Dandaragan | 417 | 20.5 | 8.9 | 415 | 20.8 | 9 |
| 2018 | 18_6 | Greenough | 373 | 22.2 | 10.3 | 267 | 22.8 | 10.4 |
| 2018 | 18_7 | Kojonup | 400 | 16.7 | 6.4 | 356 | 17.2 | 6.3 |
| 2018 | 18_8 | Mingenew | 275 | 22.3 | 9.3 | 243 | 22.7 | 9.3 |
| 2018 | 18_9 | Wagin | 261 | 17.7 | 6.6 | 267 | 18.2 | 6.7 |
| 2018 | 18_10 | Williams | 383 | 17.7 | 6.1 | 310 | 18.3 | 5.8 |
| 2019 | 19_1 | Bolgart | 306 | 19.5 | 7.7 | 246 | 21.3 | 7.4 |
| 2019 | 19_2 | Dandaragan | 438 | 20.1 | 8.9 | 300 | 21.6 | 8.9 |
| 2019 | 19_3 | Kojonup | 399 | 16.8 | 6.5 | 293 | 17.9 | 6.3 |
| 2019 | 19_4 | Mingenew | 333 | 22.2 | 9.7 | 262 | 23.8 | 9.6 |
| 2019 | 19_5 | Williams | 375 | 17.6 | 6.1 | 274 | 19.0 | 5.7 |
| 2020 | 20_1 | Kojonup | 361 | 17.3 | 6.5 | 298 | 18.3 | 6.7 |
| 2020 | 20_2 | Moonyanooka | 385 | 21.7 | 10.0 | 262 | 23.2 | 10.9 |
| 2020 | 20_3 | Toodyay | 357 | 19.4 | 7.4 | 219 | 21.0 | 7.7 |
| Response | Variety | Site | Management | Site × Management |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disease incidence | ATR Bonito | 8.76 (23) *** | 0.46 (1) ns | 1.66 (23) * |
| Hyola 559TT | 6.62 (23) *** | 10.47 (1) ** | 0.52 (23) ns | |
| ATR Mako | 16.43 (16) *** | 18.40 (1) ** | 2.11 (16) * | |
| InVigor T4510 | 8.98 (16) *** | 20.31 (1) *** | 3.11 (16) *** | |
| Yield | ATR Bonito | 47.80 (24) *** | 0.57 (1) ns | 0.93 (24) ns |
| Hyola 559TT | 44.41 (24) *** | 5.56 (1) * | 0.56 (24) ns | |
| ATR Mako | 53.36 (17) *** | 1.87 (1) ns | 0.67 (17) ns | |
| InVigor T4510 | 58.20 (17) *** | 3.50 (1) ns | 0.30 (17) ns |
| Source | d.f. | s.s. | m.s. | v.r. | F pr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 431 | 229.05 | 0.531 | ||
| Treatments | 143 | 214.82 | 1.502 | 58.06 | <0.001 *** |
| Genotypes | 7 | 16.50 | 2.357 | 91.12 | <0.001 *** |
| Environments | 17 | 191.50 | 11.265 | 52.58 | <0.001 *** |
| Block | 36 | 7.71 | 0.214 | 8.28 | <0.001 *** |
| Interactions | 119 | 6.81 | 0.057 | 2.21 | <0.001 *** |
| IPCA 1 | 23 | 3.04 | 0.132 | 5.10 | <0.001 *** |
| IPCA 2 | 21 | 1.67 | 0.079 | 3.07 | <0.001 *** |
| Residuals | 75 | 2.11 | 0.028 | 1.09 | 0.3129 ns |
| Error | 252 | 6.52 | 0.026 |
| Component | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard deviation | 1.1074 | 1.0293 | 0.9790 | |
| Proportion of Variance | 0.3066 | 0.2648 | 0.2396 | |
| Cumulative Proportion | 0.3066 | 0.5714 | 0.8111 | |
| Loadings | ||||
| Yield | 0.4147 | −0.6996 | −0.2695 | |
| Disease Incidence | −0.7172 | 0.0849 | −0.0004 | |
| Lesion length | −0.5064 | −0.4249 | −0.5822 | |
| Number of sclerotia | −0.2391 | −0.5683 | 0.7670 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bennett, S.J.; Lamichhane, A.R.; Thomson, L.L.; Lui, K.Y.; Michael, P.J. Impact of Fungicide Application and Host Genotype on Susceptibility of Brassica napus to Sclerotinia Stem Rot across the South-Western Australian Grain Belt: A Genotype × Environment × Management Study. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1170. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11061170
Bennett SJ, Lamichhane AR, Thomson LL, Lui KY, Michael PJ. Impact of Fungicide Application and Host Genotype on Susceptibility of Brassica napus to Sclerotinia Stem Rot across the South-Western Australian Grain Belt: A Genotype × Environment × Management Study. Agronomy. 2021; 11(6):1170. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11061170
Chicago/Turabian StyleBennett, Sarita Jane, Ashmita Rijal Lamichhane, Linda L. Thomson, King Yin Lui, and Pippa J. Michael. 2021. "Impact of Fungicide Application and Host Genotype on Susceptibility of Brassica napus to Sclerotinia Stem Rot across the South-Western Australian Grain Belt: A Genotype × Environment × Management Study" Agronomy 11, no. 6: 1170. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11061170
APA StyleBennett, S. J., Lamichhane, A. R., Thomson, L. L., Lui, K. Y., & Michael, P. J. (2021). Impact of Fungicide Application and Host Genotype on Susceptibility of Brassica napus to Sclerotinia Stem Rot across the South-Western Australian Grain Belt: A Genotype × Environment × Management Study. Agronomy, 11(6), 1170. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11061170






