Effect of Irrigation on Intercropping Systems of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) with Pea (Pisum sativum L.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Genotypes Used in the Study
2.3. Crop Management and Experimental Design
2.4. Grain Yield Determination
2.5. Seed Yield Components
2.6. Chlorophyll Fluorescence and Chlorophyll Content
2.7. Water Use Efficiency
2.8. Land Equivalent Ratio (LER)
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
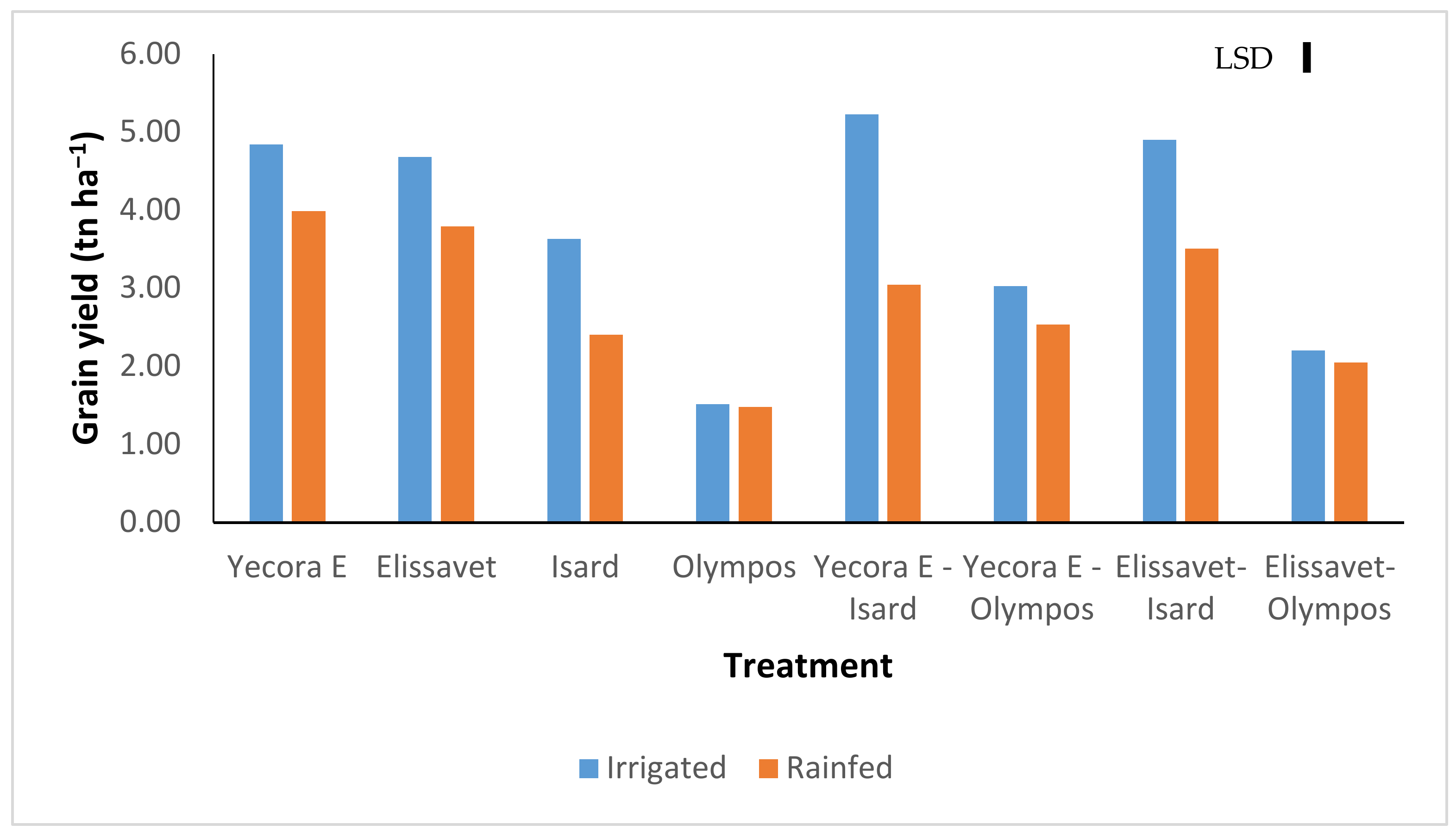
3.1. Grain Yield
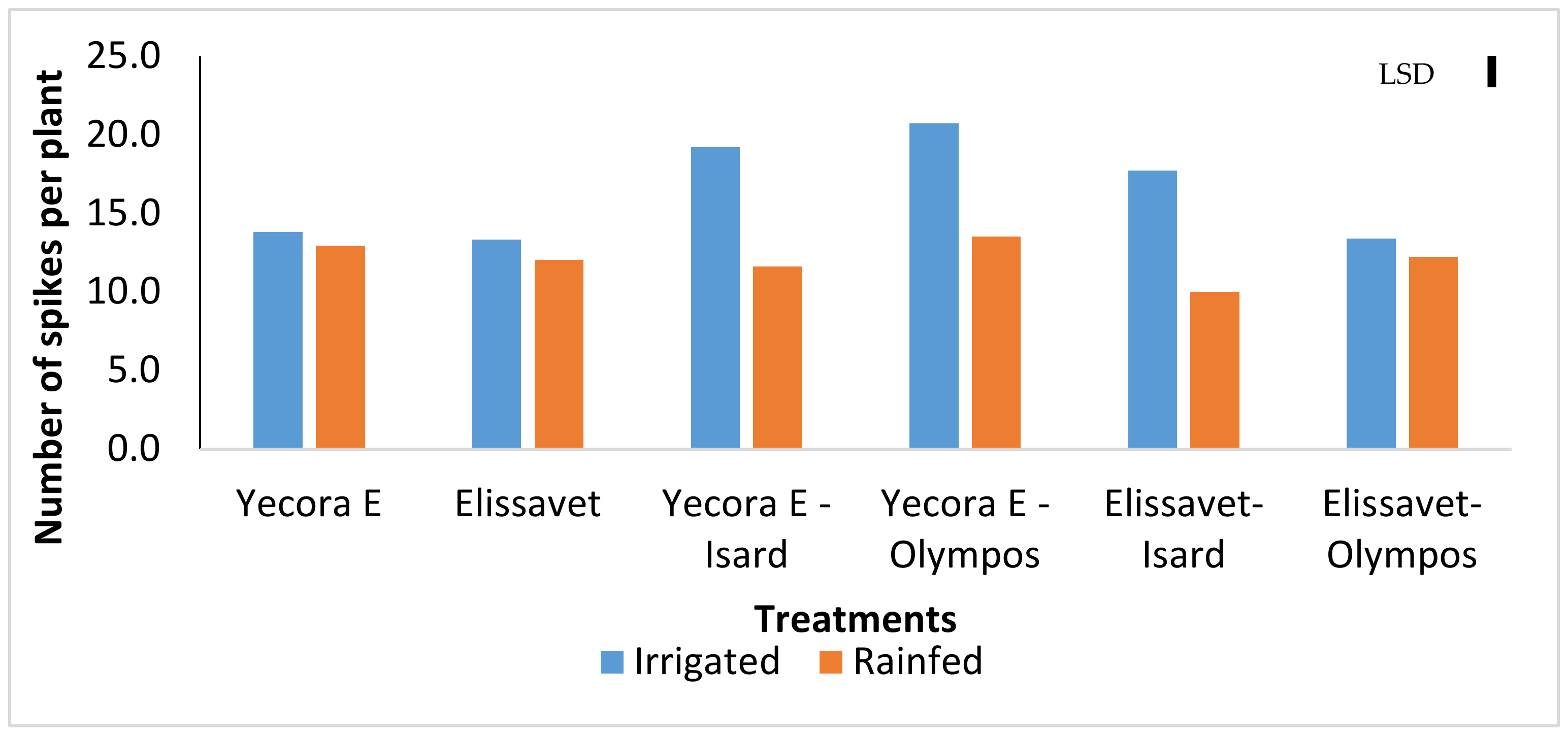
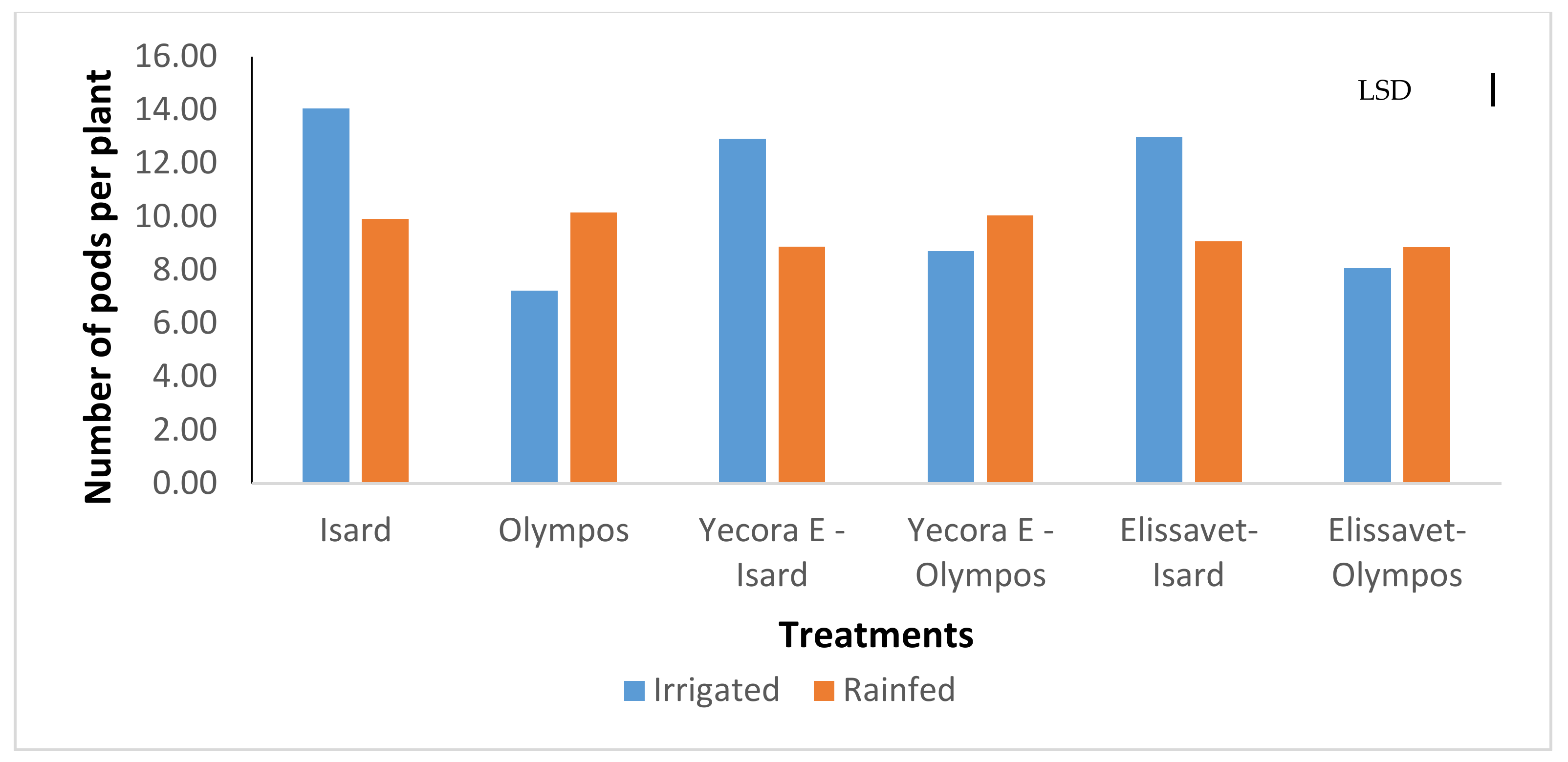
3.2. Yield Components
3.3. Chlorophyll Content and Chlorophyll Fluorescence
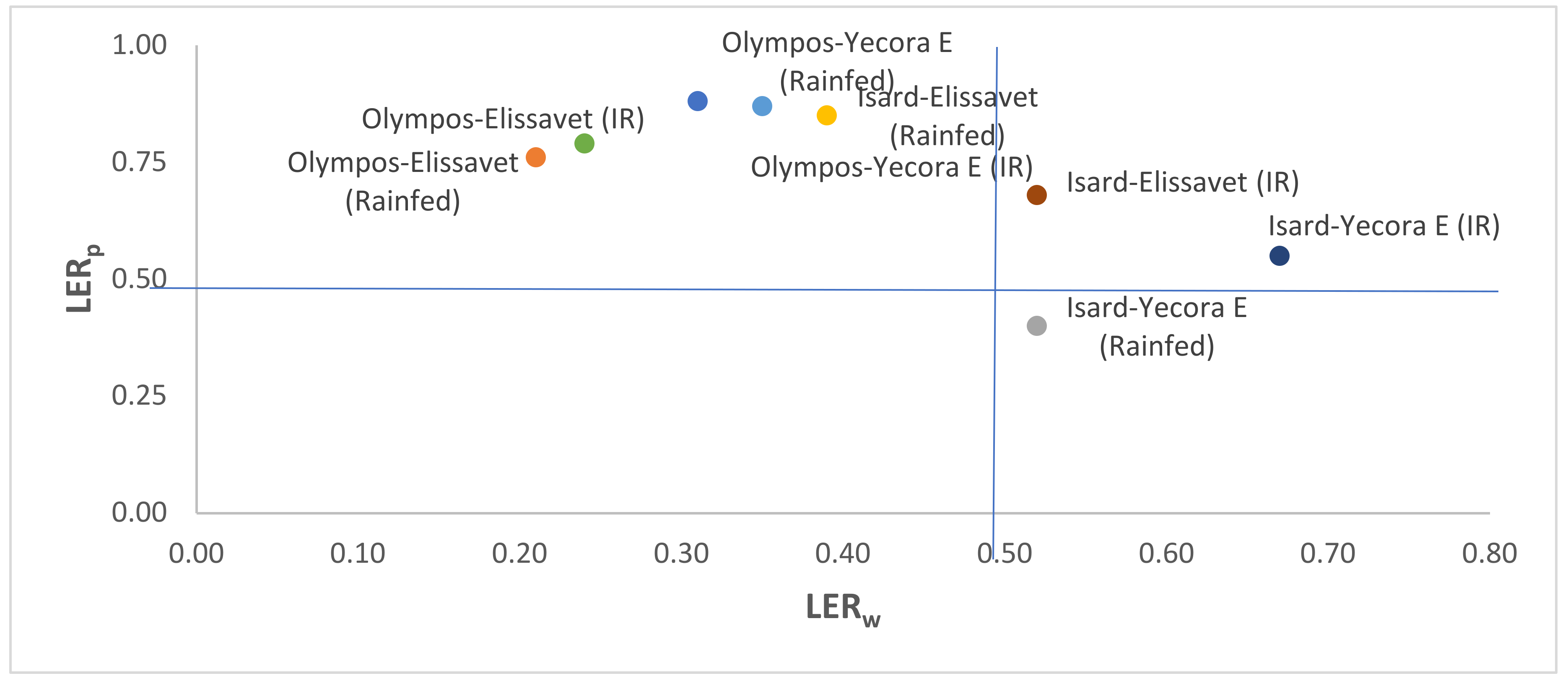
3.4. Land Equivalent Ratio (LER)
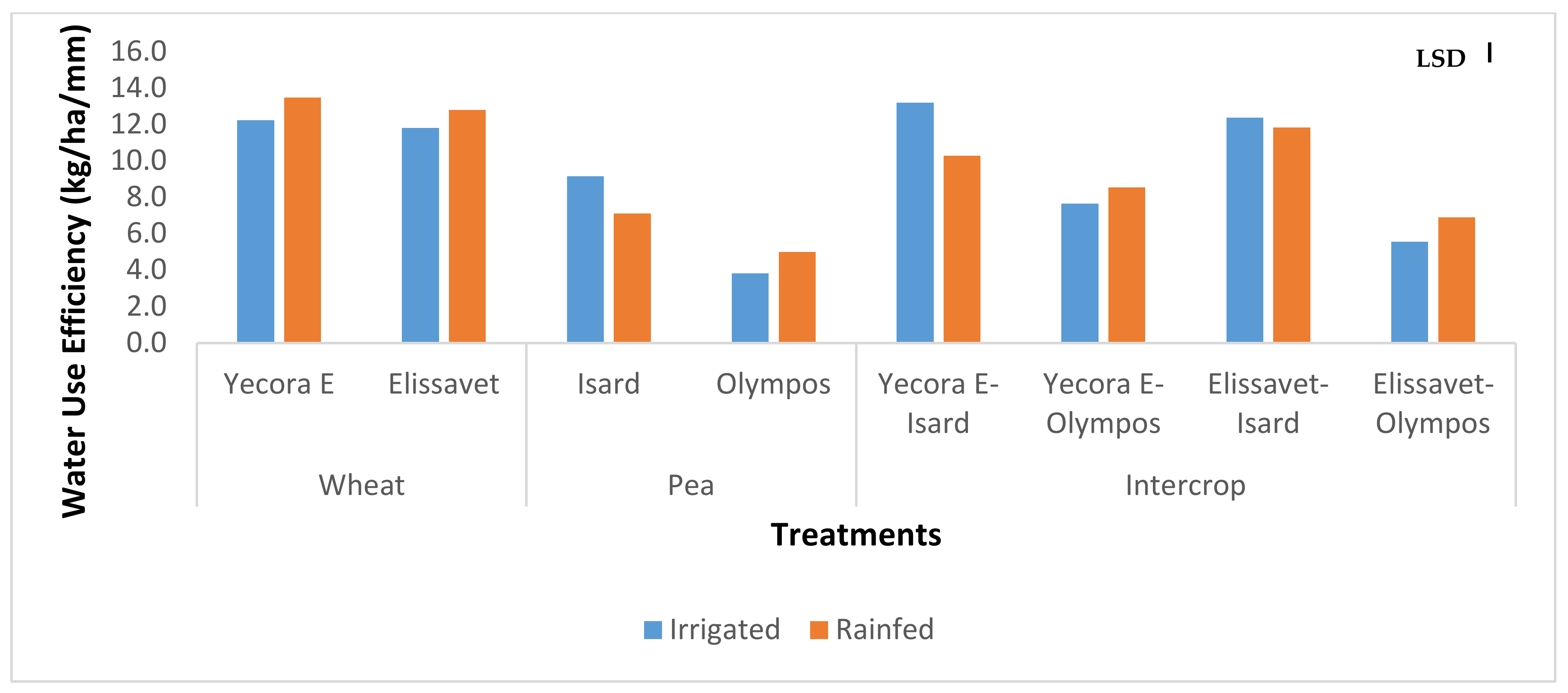
3.5. Water Use Efficiency
4. Discussion
4.1. Grain Yield
4.2. Yield Components
4.3. Chlorophyll Content and Chlorophyll Fluorescence
4.4. Land Equivalent Ratio (LER)
4.5. Water Use Efficiency
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Altieri, M.A. The ecological role of biodiversity in agroecosystems. Agron. Ecosyst. Environ. 1999, 74, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malézieux, E.; Crozat, Y.; Dupraz, C.; Laurans, M.; Makowski, D.; Ozier-Lafontaine, H.; Rapidel, B.; de Tourdonnet, S.; Valantin-Morison, M. Mixing plant species in cropping systems: Concepts, tools and models. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2009, 29, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stomph, T.; Dordas, C.; Baranger, A.; Bedoussac, L.; de Rijk, J.; Dong, B.; Evers, J.; Gu, C.; Li, L.; Simon, J.; et al. Designing intercrops for high yield, yield stability and efficient use of resources: Are there principles? Adv. Agron. 2020, 160, 1–50. [Google Scholar]
- Bedoussac, L.; Journet, E.-P.; Hauggaard-Nielsen, H.; Naudin, C.; Corre-Hellou, G.; Jensen, E.S.; Prieur, L.; Justes, E. Ecological principles underlying the increase of productivity achieved by cereal-grain legume intercrops in organic farming. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 911–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooker, R.W.; Bennett, A.E.; Cong, W.-F.; Daniell, T.J.; George, T.S.; Hallett, P.D.; Hawes, C.; Iannetta, P.P.M.; Jones, H.G.; Karley, A.J.; et al. Improving intercropping: A synthesis of research in agronomy, plant physiology and ecology. New Phytol. 2015, 206, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lithourgidis, A.S.; Dordas, C.A.; Damalas, C.A.; Vlachostergios, D.N. Annual intercrops: An alternative pathway for sustainable agriculture. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2011, 5, 396–410. [Google Scholar]
- Bedoussac, L.; Journet, E.-P.; Hauggaard-Nielsen, H.; Naudin, C.; Corre-Hellou, G.; Jensen, E.S.; Justes, E. Grain legume–cereal intercropping systems. In Achieving Sustainable Cultivation of Grain Legumes Volume 1: Advances in Breeding and Cultivation Techniques; Sivasankar, S., Ed.; Burleigh Dodds Science Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Inal, A.; Gunes, A.; Zhang, F.; Cakmak, I. Peanut/maize intercropping induced changes in rhizosphere and nutrient concentrations in shoots. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2007, 45, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, A. Plant Breeding for Water-Limited Environment; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-1-4419-7490-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.X.; Kong, Y.; Gan, R.; Zhang, F.; Feng, A.; Yu, C.; Zhao, S.; Wan, Q. Chai Enhancing the systems productivity and water use efficiency through coordinated soil water sharing and compensation in strip intercropping. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Chai, Q.; Huang, G.; Yu, A.; Huang, P.; Yang, C.; Tao, Z.; Liu, H. Yield and water consumption characteristics of wheat/maize intercropping with reduced tillage in an Oasis region. Eur. J. Agron. 2013, 45, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Huang, G.; Chai, Q.; Luo, Z. Water use and yield of wheat/maize intercropping under alternate irrigation in the oasis field of northwest China. Field Crops Res. 2011, 124, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dordas, C.A.; Vlachostergios, D.N.; Lithourgidis, A.S. Growth dynamics and agronomic-economic benefits of pea-oat and pea-barley intercrops. Crop Pasture Sci. 2012, 63, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lithourgidis, A.S.; Vlachostergios, D.N.; Dordas, C.A.; Damalas, C.A. Dry matter yield, nitrogen content, and competition in pea-cereal intercropping systems. Eur. J. Agron. 2011, 34, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lithourgidis, A.S.; Dordas, C.A. Forage yield, growth rate, and nitrogen uptake of faba bean intercrops with wheat, barley, and rye in three seeding ratios. Crop Sci. 2010, 50, 2148–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalamartzis, I.; Dordas, C.; Georgiou, P.; Menexes, G. The Use of Appropriate Cultivar of Basil (Ocimum basilicum) Can Increase Water Use Efficiency under Water Stress. Agronomy 2020, 10, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, T.A. Enhancing water use efficiency in irrigated agriculture. Agron. J. 2001, 93, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, R.; Willey, R.W. The concept of a ‘land equivalent ratio’ and advantages in yields from intercropping. Exp. Agric. 1980, 16, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhima, K.V.; Lithourgidis, A.S.; Vasilakoglou, I.B.; Dordas, C.A. Competition indices of common vetch and cereal intercrops in two seeding ratio. Field Crops Res. 2007, 100, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steel, R.G.D.; Torrie, J.H.; Dickey, D.A. Principles and Procedures of Statistics: A Biometrical Approach, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Berkenkamp, B.; Meeres, J. Mixtures of annual crops for forage in central Alberta. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1987, 67, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lithourgidis, A.S.; Vasilakoglou, I.B.; Dhima, K.V.; Dordas, C.A.; Yiakoulaki, M.D. Forage yield and quality of common vetch mixtures with oat and triticale in two seeding ratios. Field Crops Res. 2006, 99, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, P.M.; Horsley, R.D.; Poland, W.W. Barley, oat, and cereal–pea mixtures as dryland forages in the northern Great Plains. Agron. J. 2004, 96, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agegnehu, G.; Ghizaw, A.; Sinebo, W. Yield potential and land-use efficiency of wheat and faba bean mixed intercropping. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2008, 28, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lithourgidis, A.S.; Dhima, K.V.; Vasilakoglou, I.B.; Dordas, C.A.; Yiakoulaki, M.D. Sustainable production of barley and wheat by intercropping common vetch. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2007, 27, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Aulakh, C.S.; Walia, S.S. Productivity and water use of organic wheat–chickpea intercropping system under limited moisture conditions in northwest India. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2019, 34, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxevanos, D.; Tsialtas, I.T.; Vlachostergios, D.Ν.; Hadjigeorgiou, I.; Dordas, C.; Lithourgidis, A. Cultivar competitiveness in pea-oat intercrops under Mediterranean conditions. Field Crops Res. 2017, 214, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsialtas, I.T.; Baxevanos, D.; Vlachostergios, D.N.; Dordas, C.; Lithourgidis, A. Cultivar complementarity for symbiotic nitrogen fixation and water use efficiency in pea-oat intercrops and its effect on forage yield and quality. Field Crops Res. 2018, 226, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamine, F.; Farès, M. Barriers and Levers to Developing Wheat–Pea Intercropping in Europe: A Review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dordas, C.A. Variation in dry matter and nitrogen accumulation and remobilization in barley as affected by fertilization, cultivar, and source-sink relations. Eur. J. Agron. 2012, 37, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haby, V.A.; Black, A.L.; Bergman, J.W.; Larson, R.A. Nitrogen Fertilizer Requirements of Irrigated Safflower in the Northern Great Plains 1. Agron. J. 1982, 74, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dordas, C.; Papathanasiou, F.; Lithourgidis, A.; Petrevska, J.K.; Papadopoulos, I.; Pankou, C.; Gekas, F.; Ninou, E.; Mylonas, I.; Sistanis, I.; et al. Evaluation of physiological characteristics as selection criteria for drought tolerance in maize inbred lines and their hybrids. Maydica 2018, 63, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Ciompi, S.; Gentili, E.; Guidi, L.; Soldatini, G.F. The effect of nitrogen deficiency on leaf gas exchange and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters in sunflower. Plant Sci. 1996, 118, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cechin, I.; Fumis, T.F. Effect of nitrogen supply on growth and photosynthesis of sunflower plants grown in the greenhouse. Plant Sci. 2004, 166, 1379–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Reddy, R.K.; Kakani, V.G.; Reddy, V.R. Nitrogen deficiency effects on plant growth, leaf photosynthesis, and hypespectral reflectance properties of sorghum. Eur. J. Agron. 2005, 22, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghzawi, A.L.A.; Khalaf, Y.B.; Al-Ajlouni, Z.I.; AL-Quraan, N.A.; Musallam, I.; Hani, N.B. The Effect of Supplemental Irrigation on Canopy Temperature Depression, Chlorophyll Content, and Water Use Efficiency in Three Wheat (Triticum aestivum L. and T. durum Desf.) Varieties Grown in Dry Regions of Jordan. Agriculture 2018, 8, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botyanszka, L.; Zivcak, M.; Chovancek, E.; Sytar, O.; Barek, V.; Hauptvogel, P.; Halabuk, A.; Brestic, M. Chlorophyll Fluorescence Kinetics May Be Useful to Identify Early Drought and Irrigation Effects on Photosynthetic Apparatus in Field-Grown Wheat. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedoussac, L.; Justes, E. A comparison of commonly used indices for evaluating species interactions and intercrop efficiency: Application to durum wheat–winter pea intercrops. Field Crops Res. 2011, 124, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helenius, J.; Jokinen, K. Yield advantage and competition in intercropped oats (Avena sativa L.) and faba bean (Vicia faba L.): Application of the hyperbolic yield-density model. Field Crops Res. 1994, 37, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agegnehu, G.; Ghizaw, A.; Sinebo, W. Yield performance and land-use efficiency of barley and faba bean mixed cropping in Ethiopian highlands. Eur. J. Agron. 2006, 25, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Month | Rainfall (mm) | Temperature (°C) | ETo (mm/Month) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 2018 | 30 Years | 2017 | 2018 | 30 Years | 2017 | 2018 | 30 Years | |
| December | 26.0 | 36.0 | 50.8 | 9.3 | 6.4 | 6.5 | 44.6 | 23.7 | 28.1 |
| January | 14.2 | 44.8 | 29.3 | 7.1 | 6.1 | 5.2 | 34.1 | 18.7 | 20.3 |
| February | 69.6 | 8.4 | 31.5 | 9.1 | 7.9 | 6.4 | 50.0 | 23.7 | 35.8 |
| March | 49.8 | 14.6 | 31.5 | 13.0 | 12.0 | 9.6 | 72.4 | 62.1 | 65.4 |
| April | 70.0 | 71.4 | 38.2 | 18.9 | 14.5 | 13.9 | 102.3 | 95.2 | 98.3 |
| May | 25.2 | 23.0 | 44.4 | 23.3 | 19.5 | 19.3 | 177.3 | 139.5 | 152.4 |
| June | 87.0 | 52.0 | 32.4 | 24.6 | 26.7 | 24.5 | 209.7 | 148.9 | 181.7 |
| Treatments | Number of Grains per Spike | Number of Grains per Pod | Length of Spike | Length of Pod | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat | Pea | Wheat | Pea | |||||
| Irrigated | Rainfed | Irrigated | Rainfed | Irrigated | Rainfed | Irrigated | Rainfed | |
| Yecora E | 36.3 | 30.3 | - | - | 10.35 | 9.83 | - | - |
| Elissavet | 46.9 | 45.5 | - | - | 9.75 | 10.17 | - | - |
| Isard | - | - | 5.43 | 4.53 | - | - | 5.68 | 4.87 |
| Olympos | - | - | 4.85 | 5.00 | - | - | 4.65 | 4.72 |
| Yecora E-Isard | 43.9 | 30.5 | 4.77 | 4.57 | 11.98 | 12.00 | 5.47 | 4.75 |
| Yecora E-Olympos | 38.9 | 31.3 | 4.92 | 5.05 | 11.58 | 11.55 | 4.42 | 4.92 |
| Elissavet-Isard | 53.4 | 42.6 | 5.08 | 4.30 | 10.27 | 10.20 | 5.37 | 4.75 |
| Elissavet-Olympos | 45.8 | 43.1 | 4.65 | 5.55 | 9.83 | 10.27 | 4.45 | 4.82 |
| LSD | 10.05 | 0.95 | 1.01 | 0.55 | ||||
| Treatments | Chlorophyll Content | Quantum Yield (Chlorophyll Fluorescence) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat | Pea | Wheat | Pea | |||||
| Irrigated | Rainfed | Irrigated | Rainfed | Irrigated | Rainfed | Irrigated | Rainfed | |
| Yecora E | 46.4 | 48.4 | - | - | 0.66 | 0.65 | - | - |
| Elissavet | 48.6 | 50.0 | - | - | 0.67 | 0.65 | - | - |
| Isard | - | - | 43.9 | 45.7 | - | - | 0.64 | 0.66 |
| Olympos | - | - | 43.1 | 43.7 | - | - | 0.67 | 0.66 |
| Yecora E-Isard | 48.9 | 50.4 | 44.9 | 47.2 | 0.65 | 0.67 | 0.61 | 0.65 |
| Yecora E-Olympos | 49.0 | 49.9 | 42.5 | 44.1 | 0.65 | 0.63 | 0.66 | 0.63 |
| Elissavet-Isard | 49.6 | 51.3 | 43.6 | 45.6 | 0.62 | 0.63 | 0.64 | 0.63 |
| Elissavet-Olympos | 48.9 | 51.1 | 44.6 | 44.2 | 0.65 | 0.65 | 0.62 | 0.63 |
| LSD | 2.06 | 2.48 | 0.037 | 0.052 | ||||
| Treatments | Partial Land Equivalent Ratio | Land Equivalent Ratio (LER) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat (LERw) | Pea (LERp) | Total | ||||
| Irrigated | Rainfed | Irrigated | Rainfed | Irrigated | Rainfed | |
| Yecora E-Isard | 0.67 | 0.52 | 0.55 | 0.43 | 1.22 | 0.95 |
| Yecora E-Olympos | 0.35 | 0.31 | 0.87 | 0.88 | 1.22 | 1.19 |
| Elissavet-Isard | 0.52 | 0.39 | 0.68 | 0.85 | 1.20 | 1.24 |
| Elissavet-Olympos | 0.21 | 0.24 | 0.79 | 0.76 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Mean | 0.44 | 0.37 | 0.72 | 0.73 | 1.16 | 1.10 |
| LSD | 0.06 | 0.11 | 0.15 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pankou, C.; Lithourgidis, A.; Dordas, C. Effect of Irrigation on Intercropping Systems of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) with Pea (Pisum sativum L.). Agronomy 2021, 11, 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11020283
Pankou C, Lithourgidis A, Dordas C. Effect of Irrigation on Intercropping Systems of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) with Pea (Pisum sativum L.). Agronomy. 2021; 11(2):283. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11020283
Chicago/Turabian StylePankou, Chrysanthi, Anastasios Lithourgidis, and Christos Dordas. 2021. "Effect of Irrigation on Intercropping Systems of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) with Pea (Pisum sativum L.)" Agronomy 11, no. 2: 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11020283
APA StylePankou, C., Lithourgidis, A., & Dordas, C. (2021). Effect of Irrigation on Intercropping Systems of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) with Pea (Pisum sativum L.). Agronomy, 11(2), 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11020283