Impact of Subsurface Application of Compound Mineral Fertilizer on Soil Enzymatic Activity under Reduced Tillage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Field Experiment
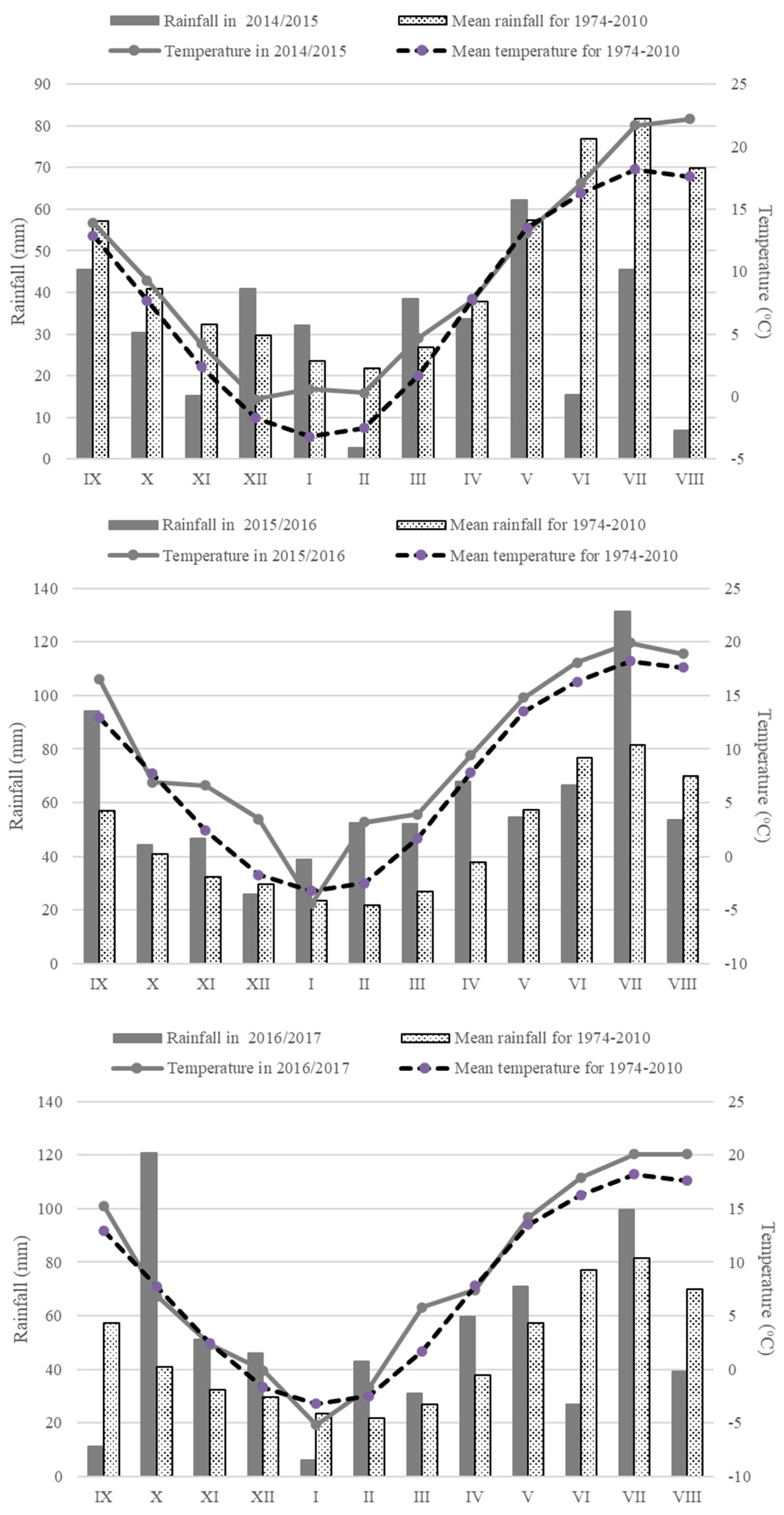
2.2. Weather Conditions
2.3. Sampling and Analyses
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Properties and Soil Enzymatic Activity of Soybean Growing Plots
3.2. Chemical Properties and Enzymatic Activity of the Soil on Winter Wheat Plots
3.3. Chemical Properties and Enzymatic Activity of the Soil on Maize Plots
3.4. Effect of Method of Fertilizer Application and the Fertilizer Dose on Soil Biochemical Properties of Plant Plots
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. Transforming our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. 2015. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/2030agenda (accessed on 15 September 2021).
- Lahmar, R. Adoption of conservation agriculture in Europe: Lessons of the KASSA project. Land Use Policy 2010, 27, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wauters, E.; Bielders, C.; Poesen, J.; Govers, G.; Mathijs, E. Adoption of soil conservation practices in Belgium: An examination of the theory of planned behaviour in the agri-environmental domain. Land Use Policy 2010, 27, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Enhancing ecosystem services with no-till. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2013, 28, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonteyne, S.; Martinez Gamiño, M.A.; Saldivia Tejeda, A.; Verhulst, N. Conservation Agriculture Improves Long-term Yield and Soil Quality in Irrigated Maize-oats Rotation. Agronomy 2019, 9, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kraska, P.; Andruszczak, S.; Gierasimiuk, P.; Rusecki, H. The Effect of Subsurface Placement of Mineral Fertilizer on Some Soil Properties under Reduced Tillage Soybean Cultivation. Agronomy 2021, 11, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, A.; Lee, J.; Yin, X.; Tyler, D.D.; Jagadamma, S.; Arelli, P. Soil physical properties and soybean yield as influenced by long-term tillage systems and cover cropping in the Midsouth USA. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harasim, E.; Antonkiewicz, J.; Kwiatkowski, C.A. The effects of catch crops and tillage systems on selected physical properties and enzymatic activity of loess soil in a spring wheat monoculture. Agronomy 2020, 10, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- González-Sánchez, E.; Ordóñez-Fernández, R.; Carbonell-Bojollo, R.; Veroz-González, O.; Gil-Ribes, J. Meta-analysis on atmospheric carbon capture in Spain through the use of conservation agriculture. Soil Tillage Res. 2012, 122, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddaway, N.R.; Hedlund, K.; Jackson, L.E.; Kätterer, T.; Lugato, E.; Thomsen, I.K.; Jørgensen, H.B.; Isberg, P.E. How does tillage intensity affect soil organic carbon? A systematic review. Environ. Evid. 2017, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van den Putte, A.; Govers, G.; Diels, J.; Langhans, C.; Clymans, W.; Vanuytrecht, E.; Merckx, R.; Raes, D. Soil functioning and conservation tillage in the Belgian Loam Belt. Soil Tillage Res. 2012, 103, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messiga, A.J.; Ziadi, N.; Grant, C.; Morel, C.; Tremblay, G.; Lamarre, G.; Parent, L.E. Long term impact of tillage practices and biennial P and N fertilization on maize and soybean yields and soil P status. Field Crops Res. 2012, 133, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, D.; Jia, G.; Cai, L.; Ma, Z.; Eneji, A.E.; Cui, Y. Effects of tillage practices on root characteristics and root lodging resistance of maize. Field Crops Res. 2016, 185, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.K.; Bell, R.W.; Salahin, N.; Pathan, S.; Mondol, A.T.M.A.I.; Alam, M.J.; Rashid, M.H.; Paul, P.L.C.; Hossain, M.I.; Shil, N.C. Banding of Fertilizer Improves Phosphorus Acquisition and Yield of Zero Tillage Maize by Concentrating Phosphorus in Surface Soil. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fageria, N.K. The Role of Plant Roots in Crop Production, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, K.W.; Sweeney, D.W. Placement of preplant liquid nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer and nitrogen rate affects no-till wheat following different summer crops. Agron. J. 2007, 99, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkebiwe, P.M.; Weinmann, M.; Bar-Tal, A.; Muller, T. Fertilizer placement to improve crop nutrient acquisition and yield: A review and meta-analysis. Field Crops Res. 2016, 196, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, F.G.; Schaefer, D. Assessment of Soil Phosphorus and Potassium following Real Time Kinematic-Guided Broadcast and Deep-Band Placement in Strip-Till and No-Till. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 76, 1090–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parry, M.L.; Rosenzweig, C.; Iglesias, A.; Livermore, M.; Fischer, G. Effects of climate change on global food production under SRES emissions and socio-economic scenarios. Glob. Environ. Change 2004, 14, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, H.R.; Norton, J.B.; van Diepen, L.T.A. Effects of Semiarid Wheat Agriculture Management Practices on Soil Microbial Properties: A Review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannipieri, P.; Giagnoni, L.; Landi, L.; Renella, G. Role of phosphatase enzymes in soil. Soil Biol. 2011, 26, 215–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielińska, E.J.; Mocek-Płóciniak, A. Impact of the tillage system on the soil enzymatic activity. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2012, 38, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowski, C.A.; Harasim, E.; Feledyn-Szewczyk, B.; Antonkiewicz, J. Enzymatic Activity of Loess Soil in Organic and Conventional Farming Systems. Agriculture 2020, 10, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shukla, G.; Varma, A. (Eds.) Soil Enzymology. In Soil Biology; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2011; Volume 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianfreda, L.; Rao, M.A. (Eds.) Enzymes in Agricultural Sciences; OMICS International: Hyderabad, India, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dick, W.A.; Cheng, L.; Wang, P. Soil acid alkaline phosphatase activity as pH adjustment indicators. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 1915–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melero, S.; Panettieri, M.; Madejón, E.; Gómez Macpherson, H.; Moreno, F.; Murillo, J.M. Implementation of chiseling and mouldboard ploughing in soil after 8 years of no-till management in SW, Spain: Effect on soil quality. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 112, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; He, X.; Hu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, W. Response of soil chemical and microbial indicators to conservational tillage versus traditional tillage in the North China Plain. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2010, 46, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ferreiro, J.; Gascó, G.; Gutiérrez, B.; Méndez, A. Soil biochemical activities and the geometric mean of enzyme activities after application of sewage sludge and sewage sludge biochar to soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2012, 48, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majchrzak, L.; Sawinska, Z.; Natywa, M.; Skrzypczak, G.; Głowicka-Wołoszyn, R. Impact of different tillage systems on soil dehydrogenase activity and spring wheat infection. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2016, 18, 1871–1881. [Google Scholar]
- Adetunji, A.T.; Lewu, F.B.; Mulidzi, R.; Ncube, B. The biological activities of β-glucosidase, phosphatase and urease as soil quality indicators: A review. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2017, 17, 794–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps. In World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014, Update 2015; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015; Volume 106. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Common Catalogue of Varieties of Agricultural Plant Species, 28th ed.; European Commission: Luxembourg, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Descriptive List of Agricultural Plant Varieties 2020, Maize; Central Research Centre for Cultivar Testing: Słupia Wielka, Poland, 2020; p. 58. ISSN 1641-7003.
- Stachowski, P. Assessment of meteorological droughts on the postmining areas in the Konin Region. Środkowo-Pomorskie Towarzystwo Naukowe Ochrony Środowiska. Rocz. Ochr. Środowiska 2010, 12, 587–606. [Google Scholar]
- Futa, B.; Oleszczuk, P.; Andruszczak, S.; Kwiecińska-Poppe, E.; Kraska, P. Effect of natural aging of biochar on soil enzymatic activity and physicochemical properties in long-term field experiment. Agronomy 2020, 10, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- International Organization for Standardization. Soil Quality. Sampling; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- International Organization for Standardization. Soil Quality. Determination of pH; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- International Organization for Standardization. Soil Quality. Determination of Organic Carbon by Sulfochromic Oxidation; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- International Organization for Standardization. Soil Quality. Determination of Total Nitrogen Content by Dry Combustion; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Polish Committee for Standardization. Polish Standard: The Chemical and Agricultural Analysis of the Soil—Determination of the Content of Assailable Phosphorus in Mineral Soils; Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Schinner, F.; Ohlinger, R.; Kandeler, E.; Margesin, R. Methods in Soil Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Dick, R.P. Methods of Soil Enzymology. In SSSA Book Series 9; Soil Science Society of America Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Stavi, I.; Bel, G.; Zaady, E. Soil functions and ecosystem services in conventional, conservation, and integrated agricultural systems. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 36, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gajda, A.; Czyż, E.; Ukalska-Jaruga, A. Comparison of the Effects of Different Crop Production Systems on Soil Physico-Chemical Properties and Microbial Activity under Winter Wheat. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallarino, A.P.; Borges, R. Phosphorus and Potassium Distribution in Soil Following Long-Term Deep-Band Fertilization in Different Tillage Systems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Shen, J.; Yuan, L.; Jiang, R.; Chen, X.; Davies, W.J.; Zhang, F. Improving crop productivity and resource use efficiency to ensure food security and environmental quality in China. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Vyn, T.J. Residual effects of potassium placement and tillage systems for corn on subsequent no-till soybean. Agron. J. 2002, 94, 1112–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rychel, K.; Meurer, K.H.E.; Börjesson, G.; Strömgren, M.; Getahun, G.T.; Kirchmann, H.; Kätterer, T. Deep N fertilizer placement mitigated N2O emissions in a Swedish field trial with cereals. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2020, 118, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.L.; Islam, M.R.; Sumon, M.H.; Huda, A. Deep placement of N fertilizers influences N use efficiency and yield of BRRI dhan29 under flooded condition. Asian J. Med. Biol. Res. 2016, 2, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, P.A.; Sainz Rozas, H.R.; Covacevich, F.; Echeverría, H.E. Phosphorus placement effects on phosphorous recovery efficiency and grain yield of wheat under no-tillage in the humid pampas of Argentina. Int. J. Agron. 2014, 2014, 507105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansel, F.D.; Amado, T.J.C.; Ruiz Diaz, D.A.; Rosso, L.H.M.; Nicoloso, F.T.; Schorr, M. Phosphorus Fertilizer Placement and Tillage Affect Soybean Root Growth and Drought Tolerance. Agron. J. 2017, 109, 2936–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Limousin, G.; Tessier, D. Effect of no-tillage on chemical gradients and topsoil acidification. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 92, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilienfein, J.; Wilcke, W.; Vilela, L.; Lima, S.D.; Thomas, R.; Zech, W. Effect of no-tillage and conventional tillage systems on the chemical composition of soil. J. Plant. Nutr. Soil Sci. 2000, 163, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.Y.; Stewart, B.A.; Zhang, F.S. Long-term experiments for sustainable nutrient management in China. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 31, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hinsinger, P.; Plassard, C.; Tang, C.; Jaillard, B. Origins of root-mediated pH changes in the rhizosphere and their responses to environmental constraints: A review. Plant Soil 2003, 248, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, R.G.; De Forest, J.L.; Marxsen, J.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Stromberger, M.E.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Weintraubg, M.N.; Zoppinih, A. Soil enzymes in a changing environment: Current knowledge and future directions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 58, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Martínez, V.; Bell, C.W.; Morris, B.E.L.; Zak, J.; Allen, V.G. Long-term soil microbial community and enzyme activity responses to an integrated cropping-livestock system in a semi-arid region. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 137, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajda, A.M.; Przewłoka, B.; Gawryjołek, K. Changes in soil quality associated with tillage system applied. Int. Agrophys. 2013, 27, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, R.; Sharma, S. Soil enzyme activity as affected by tillage and residue management. Practices under diverse cropping systems. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2017, 6, 1211–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawicka, B.; Krochmal-Marczak, B.; Pszczółkowski, P.; Bielińska, E.J.; Wójcikowska-Kapusta, A.; Barbaś, P.; Skiba, D. Effect of Differentiated Nitrogen Fertilization on the Enzymatic Activity of the Soil for Sweet Potato (Ipomoea batatas L. [Lam.]) Cultivation. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futa, B.; Tajchman, K.; Steiner-Bogdaszewska, Ż.; Drozd, L.; Gruszecki, T.M. Preliminary Results of Effect of Rotational Grazing of Farmed Red Deer (Cervus elaphus) on the Biochemical Status of Soil. Agronomy 2021, 11, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csitari, G.; Hoffmann, S. Comparative study on soil biological parameters at a long-term field experiment. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2005, 51, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielińska, E.J.; Mocek, A.; Paul-Lis, M. Impact of tillage system cultivation on enzymatic activity of typologically diverse soils. J. Res. Appl. Agric. Eng. 2008, 53, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Dahm, H. Generic composition and physiological and cultural properties of heterotrophic bacteria isolated from soil, rhizosphere and mycorrhizosphere of pine (Pinus silvestris L.). Acta Microbiol. Pol. 1984, 33, 147–156. [Google Scholar]
- Bielińska, E.J.; Futa, B.; Chmielewski, S.; Patkowski, K.; Gruszecki, T. Quantification of biodiversity related to the active protection of grassland habitats in the eastern Lublin region of Poland based on the activity of soil enzymes. Pol. J. Soil Sci. 2017, 50, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Błońska, E.; Lasota, J.; Zwydak, M. The relationship between soil properties, enzyme activity and land use. Leśne Prace Badaw. For. Res. Pap. 2017, 78, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gałązka, A.; Gawryjołek, K.; Perzyński, A.; Gałązka, R.; Księżak, J. Changes in Enzymatic Activities and Microbial Communities in Soil under Long-Term Maize Monoculture and Crop Rotation. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2017, 26, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Włodarczyk, T.; Stępniewski, W.; Brzezińska, M. Dehydrogenase activity, redox potential, and emissions of carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide from Cambisols under flooding conditions. Biol. Fert. Soils 2002, 36, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazza, G.; Pellegrino, E.; Moscatelli, M.C.; Ercoli, L. Long-term conservation tillage and nitrogen fertilization effects on soil aggregate distribution, nutrient stocks and enzymatic activities in bulk soil and occluded microaggregates. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 196, 104482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajda, A.M.; Czyż, E.A.; Dexter, A.R.; Furtak, K.M.; Grządziel, J.; Stanek-Tarkowska, J. Effects of different soil management practices on soil properties and microbial diversity. Int. Agrophys. 2018, 32, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niewiadomska, A.; Majchrzak, L.; Borowiak, K.; Wolna-Maruwka, A.; Waraczewska, Z.; Budka, A.; Gaj, R. The influence of tillage and cover cropping on soil microbial parameters and spring wheat physiology. Agronomy 2020, 10, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woźniak, A. Chemical Properties and Enzyme Activity of Soil as Affected by Tillage System and Previous Crop. Agriculture 2019, 9, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nannipieri, P.; Ascher, J.; Ceccherini, M.T.; Landi, L.; Pietramellara, G.; Renella, G. Microbial diversity and soil functions. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2003, 54, 655–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahas, E. Microrganismos do solo produtores de fosfatases em diferentes sistemas agrícolas. Bragantia 2002, 61, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Martinez, V.; Cano, A.; Johnson, J. Simultaneous determination of the activity of many soil enzymes for biogeochemical indicators of soil health. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 126, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natywa, M.; Sawicka, A.; Wolna-Murawka, A. Microbial and enzymatic activity in the soil under maize crop in relation to differentiated nitrogen fertilisation. Water Environ. Rural Areas 2010, 10, 111–120. [Google Scholar]
- Carbrera, M.L.; Kissel, D.L.; Bock, B.R. Urea hydrolysis in soil. Effect of urea concentration and soil pH. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1994, 23, 1121–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, B.A. Enzyme activities as a component of soil biodiversity: A review. Pedobiologia 2005, 49, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, R.P.; Feng, Y.; Githinji, L.; Ankumah, R.; Balkcom, K.S. Impact of No-Tillage and Conventional Tillage Systems on Soil Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2012, 2012, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vetanovetz, R.; Peterson, J. Effect of carbon source and nitrogen on urease activity in a sphagnum peat medium. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1992, 23, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Rengel, Z.; Rose, T. The effectiveness of deep placement of fertilisers is determined by crop species and edaphic conditions in Mediterranean-type environments: A review. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2009, 47, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Fernández, F.G.; Pittelkow, C.M.; Greer, K.D.; Schaefer, D. Soil and crop response to phosphorus and potassium management under conservation tillage. Agron. J. 2020, 112, 2302–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| MFA | Machinery and Tools Used | |
|---|---|---|
| S | After harvesting the pre-crop: | TERRADISC 6001 T (6 m) (Pöttinger, Austria) + John Deere 8230 (USA) |
| Pre-winter cultivation (does not apply winter wheat): | TERRADISC 6001 T (6 m) + John Deere 8230 | |
| Preparing the field for sowing (does not apply to maize): | tiller SYNKRO 5030 K (5 m) (Pöttinger, Austria) + Case Magnum 280 (Case IH, USA) | |
| Mineral fertilization: | ZA TS 4200 (Amazone, Germany) + John Deere 8230 | |
| Sowing (does not apply to maize): | tillage and sowing unit TERRASEM C6 (6 m) (Pöttinger, Austria) + John Deere 8230 | |
| Pre-sowing and sowing (does not apply to soybean and winter wheat): | generator of our own design STRIPTILL + seeder Gaspardo Manta (Maschio Gaspardo, Italy) + Case Magnum 280 | |
| Sub-S | After harvesting the pre-crop: | TERRADISC 6001 T (6 m) + John Deere 8230 |
| Pre-winter cultivation (does not apply winter wheat): | TERRADISC 6001 T (6 m)+ John Deere 8230 | |
| Pre-sowing and sowing (does not apply to soybean and winter wheat): | tiller Pöttinger SYNKRO 5030 K (5 m)+ Case Magnum 280 | |
| Sowing (does not apply to maize): | tillage and sowing unit TERRASEM C6 (6 m) + John Deere 8230 | |
| Pre-sowing and sowing (does not apply to soybean and winter wheat): | generator of our own design STRIPTILL + seeder Gaspardo Manta + Case Magnum 280 | |
| III | IV | V | VI | VII | VIII | IX | X | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | k = 2.73 very humid | k = 1.47 optimal | k= 4.75 extremely humid | k = 0.30 extremely dry | k = 0.70 very dry | k = 0.10 extremely dry | k = 1.90 rather humid | k = 2.14 Humid |
| 2016 | k = 4.49 extremely humid | k = 2.40 humid | k = 1.23 rather dry | k = 1.23 rather dry | k = 2.20 humid | k = 0.94 dry | k = 0.24 extremely dry | k = 5.89 extremely humid |
| 2017 | k = 1.79 rather humid | k = 2.66 very humid | k = 1.67 rather humid | k = 0.50 very dry | k = 1.66 rather humid | k = 0.65 very dry | k = 2.50 very humid | k = 3.97 extremely humid |
| Enzymes | EC | Acronym | Substrate Name | Product Name | Unit Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dehydrogenses | EC 1.1 | ADh | 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) | triphenyl formazane (TPF) | mg TPF kg−1 DM 24 h−1 |
| Urease | EC 3.5.1.5 | AU | urea | N-NH4+ | mg N-NH4+ kg−1 DM h−1 |
| Alkaline Phosphatase | EC 3.1.3.1 | APhal | p-nitrophenyl phosphate disodium | p-nitrophenol (PNP) | mmol PNP kg−1 DM h−1 |
| Acid Phosphatase | EC 3.1.3.2 | APhac |
| Treatmet | Fertilizer Dose (FD) | pHKCl | TOC | TN | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | F85 | 5.34 a | 14.42 a | 1.30 a | 17.88 a |
| F170 | 5.40 b | 14.36 a | 1.28 a | 19.47 b | |
| Sub-S | F85 | 5.27 c | 14.57 a | 1.39 a | 19.26 c |
| F170 | 5.37 d | 15.73 a | 1.43 a | 20.83 d | |
| LSD0.05 | 0.005 | n.s | n.s | 0.399 | |
| Mean for MFA | S | 5.37 a | 14.39 a | 1.29 a | 18.68 a |
| Sub-S | 5.32 b | 15.15 a | 1.41 a | 20.05 b | |
| LSD0.05 | 0.004 | n.s | n.s | 0.728 | |
| Mean for FD | F85 | 5.31 a | 14.50 a | 1.35 a | 18.57 a |
| F170 | 5.39 b | 15.05 a | 1.36 a | 20.15 b | |
| LSD0.05 | 0.004 | n.s | n.s | 0.728 | |
| Years (Y) * | 2015 | 5.27 a | 11.83 a | 1.21 a | 17.76 a |
| 2016 | 5.42 b | 13.65 b | 1.25 b | 19.31 b | |
| 2017 | 5.31 c | 18.71 c | 1.58 c | 21.03 c | |
| LSD0.05 | 0.011 | 2.978 | 0.049 | 0.407 |
| Treatmet | Fertilizer Dose (FD) | ADh | AU | APhal | APhac |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | F85 | 11.45 a | 14.11 a | 50.96 a | 70.67 a |
| F170 | 7.51 b | 13.83 b | 69.89 b | 98.50 b | |
| Sub-S | F85 | 11.60 c | 14.17 c | 55.27 c | 128.74 c |
| F170 | 9.19 d | 12.54 d | 65.57 d | 138.89 d | |
| LSD0.05 | 2.016 | 0.239 | 2.202 | 4.237 | |
| Mean for MFA | S | 9.48 a | 13.97 a | 60.43 a | 86.84 a |
| Sub-S | 10.40 a | 13.36 b | 60.42 a | 133.82 b | |
| LSD0.05 | n.s | 0.261 | n.s | 6.734 | |
| Mean for FD | F85 | 11.53 a | 14.14 a | 53.12 a | 99.71 a |
| F170 | 8.35 b | 13.19 b | 67.73 b | 118.70 b | |
| LSD0.05 | 1.482 | 0.261 | 4.252 | 6.734 | |
| Years (Y) * | 2015 | 12.15 a | 13.85 a | 82.58 a | 94.80 a |
| 2016 | 6.55 b | 15.06 b | 32.38 b | 98.23 b | |
| 2017 | 11.11 c | 12.08 c | 66.31 c | 134.57 c | |
| LSD0.05 | 1.580 | 0.188 | 1.726 | 3.321 |
| Treatmet | Fertilizer Dose (FD) | pHKCl | TOC | TN | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | F85 | 5.47 a | 12.22 a | 1.02 a | 22.04 a |
| F170 | 5.32 b | 12.71 a | 1.04 a | 26.12 b | |
| Sub-S | F85 | 5.40 c | 13.08 a | 1.14 a | 30.23 c |
| F170 | 5.29 d | 12.60 a | 1.09 a | 33.95 d | |
| LSD0.05 | 0.009 | n.s | n.s | 1.047 | |
| Mean for MFA | S | 5.40 a | 12.47 a | 1.03 a | 24.08 a |
| Sub-S | 5.35 b | 12.84 a | 1.12 a | 32.09 b | |
| LSD0.05 | 0.018 | n.s | n.s | 2.536 | |
| Mean for FD | F85 | 5.44 a | 12.65 a | 1.08 a | 26.14 a |
| F170 | 5.31 b | 12.66 a | 1.07 a | 30.04 b | |
| LSD0.05 | 0.018 | n.s | n.s | 2.536 | |
| Years (Y) * | 2015 | 5.28 a | 11.22 a | 0.98 a | 21.54 a |
| 2016 | 5.35 b | 12.48 b | 1.05 b | 27.82 b | |
| 2017 | 5.47 c | 14.36 c | 1.19 c | 34.91 c | |
| LSD0.05 | 0.006 | 1.66 | 0.009 | 0.723 |
| Treatmet | Fertilizer Dose (FD) | ADh | AU | APhal | APhac |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | F85 | 3.08 a | 15.62 a | 57.14 a | 105.74 a |
| F170 | 10.91 b | 18.47 b | 101.83 b | 86.48 b | |
| Sub-S | F85 | 6.98 c | 16.19 c | 67.60 c | 103.23 c |
| F170 | 10.16 d | 16.49 d | 69.59 d | 103.04 d | |
| LSD0.05 | 1.027 | 0.313 | 1.730 | 5.249 | |
| Mean for MFA | S | 7.00 a | 17.05 a | 79.49 a | 96.11 a |
| Sub-S | 8.95 b | 16.34 b | 68.60 b | 103.14 b | |
| LSD0.05 | 1.004 | 1.529 | 4.378 | 3.244 | |
| Mean for FD | F85 | 5.03 a | 15.91 a | 62.37 a | 104.49 a |
| F170 | 10.54 b | 17.48 b | 85.71 b | 94.76 b | |
| LSD0.05 | 1.004 | 1.529 | 4.378 | 3.244 | |
| Years (Y) * | 2015 | 6.97 a | 13.69 a | 65.71 a | 59.09 a |
| 2016 | 5.66 b | 15.47 b | 45.69 b | 101.29 b | |
| 2017 | 10.72 c | 20.92 c | 110.73 c | 138.49 c | |
| LSD0.05 | 0.805 | 0.246 | 1.356 | 4.114 |
| Treatmet | Fertilizer Dose (FD) | pHKCl | TOC | TN | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | F85 | 5.51 a | 11.80 a | 1.09 a | 17.91 a |
| F170 | 5.45 b | 11.71 a | 1.10 a | 18.83 b | |
| Sub-S | F85 | 5.40 c | 12.02 a | 1.18 a | 17.32 c |
| F170 | 5.32 d | 11.91 a | 1.18 a | 18.08 c | |
| LSD0.05 | 0.006 | n.s | n.s | 0.146 | |
| Mean for MFA | S | 5.48 a | 11.76 a | 1.10 a | 18.37 a |
| Sub-S | 5.43 b | 11.97 a | 1.18 a | 18.08 b | |
| LSD0.05 | 0.008 | n.s | n.s | 0.063 | |
| Mean for FD | F85 | 5.46 a | 11.91 a | 1.14 a | 17.62 a |
| F170 | 5.39 b | 11.81 a | 1.14 a | 18.46 b | |
| LSD0.05 | 0.008 | ns | ns | 0.063 | |
| Years (Y) * | 2015 | 5.27 a | 10.14 a | 0.97 a | 17.60 a |
| 2016 | 5.38 b | 12.12 b | 1.18 b | 17.48 b | |
| 2017 | 5.62 c | 13.47 c | 1.26 c | 19.03 c | |
| LSD0.05 | 0.004 | 1.086 | 0.072 | 0.215 |
| Treatmet | Fertilizer Dose (FD) | ADh | AU | APhal | APhac |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | F85 | 9.36 a | 15.82 a | 70.89 a | 102.30 a |
| F170 | 13.42 b | 19.64 b | 100.01 b | 77.79 b | |
| Sub-S | F85 | 10.01 c | 17.05 c | 67.68 c | 145.96 c |
| F170 | 10.59 d | 16.56 d | 70.17 d | 134.11 d | |
| LSD0.05 | 0.621 | 0.342 | 1.899 | 4.769 | |
| Mean for MFA | S | 11.39 a | 17.73 a | 85.45 a | 90.05 a |
| Sub-S | 10.30 b | 16.81 b | 68.93 b | 140.04 b | |
| LSD0.05 | 0.073 | 0.482 | 0.972 | 3.670 | |
| Mean for FD | F85 | 9.69 a | 16.44 a | 69.29 a | 124.13 a |
| F170 | 12.01 b | 18.10 b | 85.09 b | 105.95 b | |
| LSD0.05 | 0.073 | 0.482 | 0.972 | 3.670 | |
| Years (Y) * | 2015 | 8.68 a | 14.70 a | 57.58 a | 106.98 a |
| 2016 | 4.18 b | 17.48 b | 36.45 b | 101.95 b | |
| 2017 | 19.68 c | 19.63 c | 137.57 c | 136.19 c | |
| LSD0.05 | 0.487 | 0.268 | 1.488 | 3.738 |
| Enzymes | pHKCl | TOC | TN | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dehydrogenases | n.s. | 0.649 * | 0.691 * | 0.571 * |
| Urease | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| Alkaline phosphatases | n.s. | 0.734 ** | 0.696 ** | 0.685 * |
| Acid phosphatases | 0.751 * | 0.718 ** | 0.729 ** | 0.597 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Futa, B.; Kraska, P.; Andruszczak, S.; Gierasimiuk, P.; Jaroszuk-Sierocińska, M. Impact of Subsurface Application of Compound Mineral Fertilizer on Soil Enzymatic Activity under Reduced Tillage. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2213. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112213
Futa B, Kraska P, Andruszczak S, Gierasimiuk P, Jaroszuk-Sierocińska M. Impact of Subsurface Application of Compound Mineral Fertilizer on Soil Enzymatic Activity under Reduced Tillage. Agronomy. 2021; 11(11):2213. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112213
Chicago/Turabian StyleFuta, Barbara, Piotr Kraska, Sylwia Andruszczak, Paweł Gierasimiuk, and Monika Jaroszuk-Sierocińska. 2021. "Impact of Subsurface Application of Compound Mineral Fertilizer on Soil Enzymatic Activity under Reduced Tillage" Agronomy 11, no. 11: 2213. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112213
APA StyleFuta, B., Kraska, P., Andruszczak, S., Gierasimiuk, P., & Jaroszuk-Sierocińska, M. (2021). Impact of Subsurface Application of Compound Mineral Fertilizer on Soil Enzymatic Activity under Reduced Tillage. Agronomy, 11(11), 2213. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112213







