Pathogenic Variability of the Jackfruit-Bronzing Bacterium Pantoea stewartii Subspecies stewartii Infection to Jackfruit Varieties and Its Pivotal Plant Hosts in Malaysia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Isolates
2.2. Pathogenicity Test
2.3. Other Hosts Tests on Sweetcorn, Cucumber and Pineapple
2.4. Disease Rating Assessment
2.5. Assessment of AUDPC and Statistical Analysis
2.6. Koch’s Postulates on Jackfruit Varieties, Sweetcorn, Cucumber and Pineapple
3. Results
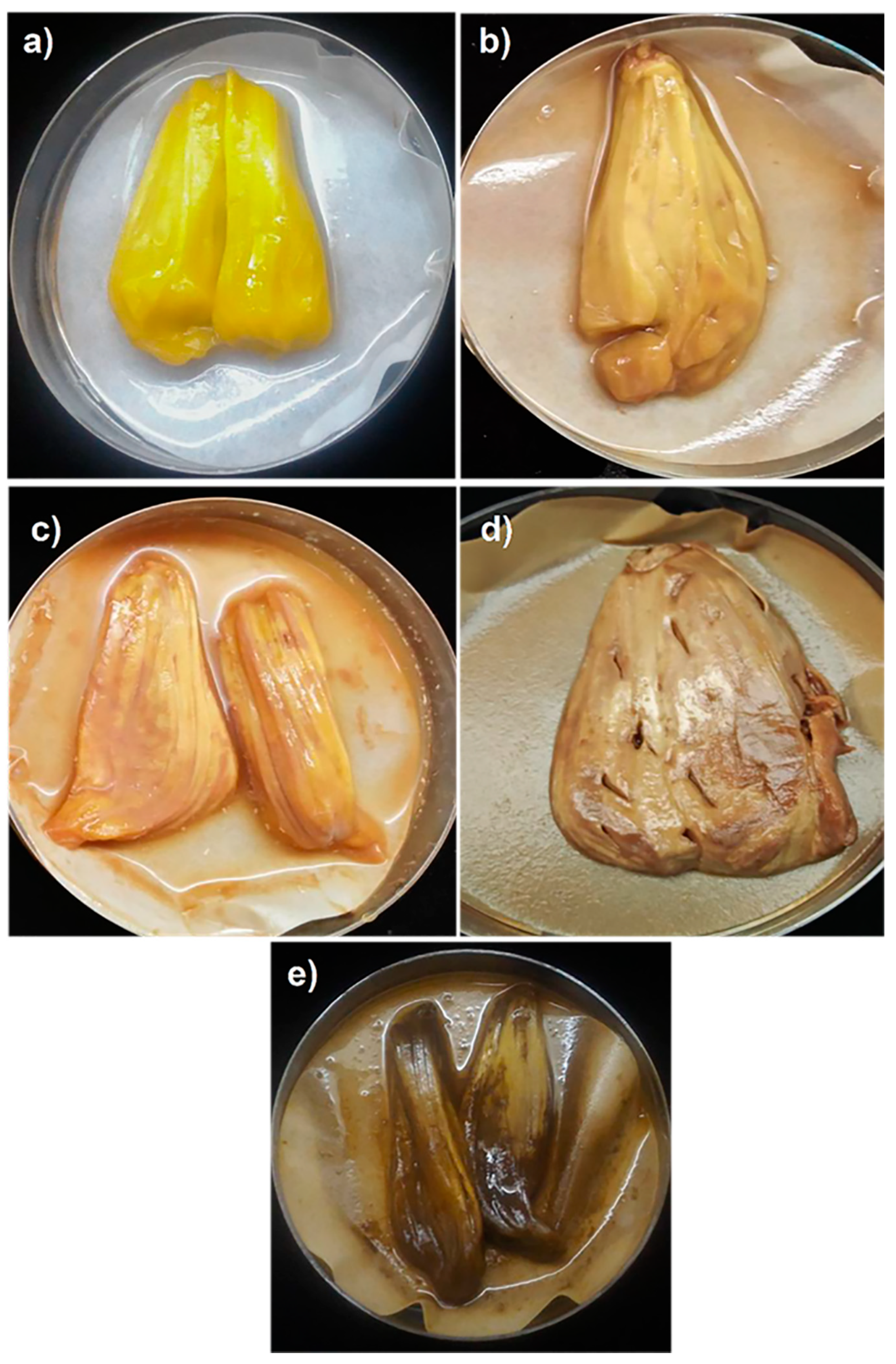
3.1. Disease Rating Assessment on Jackfruit
3.2. Disease Rating Assessment on Sweetcorn
3.3. Disease Rating Assessment on Cucumber
3.4. Disease Rating Assessment on Pineapple
3.5. Disease Rating and AUDPC Assessment of Pantoea Stewartii Subspecies Stewartii Inoculated on Jackfruit Varieties, Sweetcorn, Cucumber and Pineapple
3.6. Koch’s Postulates on Jackfruit Varieties, Sweetcorn, Cucumber and Pineapple
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balamaze, J.; Muyonga, J.H.; Byaruhanga, Y.B. Production and utilization of jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus) in Uganda. Afr. J. Food Agric. Nutr. Dev. 2019, 19, 14289–14302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Agriculture (DOA). Fruit Crops Statistics; Department of Agriculture: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Agriculture (DOA). Jackfruit (Minimally Processed) Export to Australia; Department of Agriculture: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Agriculture (DOA). Mengenali Variety Nangka Popular di Malaysia; Department of Agriculture: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Agriculture (DOA). Mengenali Varieti Nangka Popular di Malaysia; Department of Agriculture: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, N.; Kaur, B. Consumer preference for jackfruit varieties in Malaysia. J. Int. Food Agribusiness Mark. 2013, 6, 37–51. [Google Scholar]
- Zulperi, D.; Manaf, N.; Ismail, S.I.; Karam, D.S.; Yusof, M.T. First report of Pantoea stewartii subsp. stewartii causing fruit bronzing of jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus), a new emerging disease in Peninsular Malaysia. Plant Dis. 2017, 101, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidin, N.; Ismail, S.I.; Vadamalai, G.; Yusof, M.T.; Hakiman, M.; Karam, D.S.; Ismail-Suhaimy, N.W.; Ibrahim, R.; Zulperi, D. Genetic diversity of Pantoea stewartii subspecies stewartii causing jackfruit-bronzing disease in Malaysia. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, R.; Ismail-Suhaimy, N.W.; Shu-Qing, T.; Ismail, S.I.; Abidin, N.; Hakiman, M.; Karam, D.S.; Ahmad-Hamdani, M.S.; Yusof, M.T.; Zulperi, D. Molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis of Pantoea stewartii subspecies stewartii causing bronzing disease of jackfruit in Malaysia based on cps and hrp gene sequences. J. Plant Pathol. 2020, 102, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gapasin, R.M.; Garcia, R.P.; Christine, T.; De Cruz, C.S.; Borines, L.M. Fruit Bronzing: A new disease affecting jackfruit caused by Pantoea stewartii (Smith) Mergaert et al. Ann. Trop. Res. 2014, 36, 17–31. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Morales, A.; Pérez-Casillas, J.M.; Soria-Guerra, R.E.; VelázquezFernández, J.B.; Arvizu-Gómez, J.L. First report of Pantoea stewartii subsp. stewartii causing jackfruit bronzing disease in Mexico. J. Plant Pathol. 2017, 99, 807. [Google Scholar]
- Newlands, N.K. Model-Based Forecasting of Agricultural Crop Disease Risk at the Regional Scale, Integrating Airborne Inoculum, Environmental, and Satellite-Based Monitoring Data. Front. Environ. Sci. 2018, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ayodele, V.O.; Olowe, O.M.; Afolabi, C.G.; Kehinde, I.A. Identification, assessment of diseases and agronomic parameters of Curcuma amada Roxb (Mango ginger). Curr. Plant Biol. 2018, 15, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Agriculture (DOA). Phytosanitary Requirement for Exportation of Horticultural Produce from Malaysia 2021; Department of Agriculture: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, R.; Chen, Q.; Robleh Djama, Z.; Tambong, J.T. Miniprimer PCR assay targeting multiple genes: A new rapid and reliable tool for genotyping Pantoea stewartii subsp. stewartii. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 50, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehring, I.; Wensing, A.; Gernold, M.; Wiedemann, W.; Coplin, D.L.; Geider, K. Molecular differentiation of Pantoea stewartii subsp. indologenes from subspecies stewartii and identification of new isolates from maize seeds. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 116, 1553–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, V.R.; Majerczak, D.R.; Ammar, E.-D.; Merighi, M.; Pratt, R.C.; Hogenhout, S.A.; Redinbaugh, M.G. The bacterium Pantoea stewartii uses two different type III secretion systems to colonize its plant host and insect vector. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 6327–6336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahma, H.; Sinaga, M.S.; Surahman, M. First report of Stewart’s Wilt of maize caused by Pantoea stewartii subsp. stewartii in Bogor district, Indonesia. J. Int. Soc. Southeast Asian Agric. Sci. 2014, 20, 131–141. [Google Scholar]
- Orio, A.G.A.; Brücher, E.; Plazas, M.C.; Sayago, P.; Guerra, F.; De Rossi, R.; Ducasse, D.A.; Guerra, G.D. First report of Stewart’s wilt of maize in Argentina caused by Pantoea stewartii. Plant Dis. 2012, 96, 1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, D.; Huang, M.-T.; Hu, C.-Y.; Su, J.-B.; Lin, L.-H.; Javed, T.; Deng, Z.-H.; Gao, S.-J. First report of Pantoea stewartii subsp. stewartii causing bacterial leaf wilt of sugarcane in China. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeger, M.; Bragard, C.; Candresse, T.; Chatzivassiliou, E.; Dehnen-Schmutz, K.; Gilioli, G.; Grégoire, J.; Jaques Miret, J.A.; MacLeod, A.; Navajas Navarro, M.; et al. Pest categorisation of Pantoea stewartii subsp. stewartii. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05356. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Coplin, D.L.; Majerczak, D.R.; Zhang, Y.; Kim, W.-S.; Jock, S.; Geider, K. Identification of Pantoea stewartii subsp. stewartii by PCR and strain differentiation by PFGE. Plant Dis. 2002, 86, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- EPPO. PM 7/60 (2) Pantoea stewartii subsp. stewartii. EPPO Bull. 2016, 46, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Maayer, P.; Aliyu, H.; Vikram, S.; Blom, J.; Duffy, B.; Cowan, D.A.; Coutinho, T.A. Phylogenomic, pan-genomic, pathogenomic and evolutionary genomic insights into the agronomically relevant enterobacteria Pantoea ananatis and Pantoea stewartii. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1755–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ITFN. Rust-Like Symptoms and Rot on Jackfruit: A Combination of Disease and Abiotic Factors? ITFN Tropical Fruit Network: Serdang, Malaysia, 2012; pp. 16–17. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Morales, A.; Soria-Guerra, R.E.; Isiordia-Aquino, N.; Campos-Guillén, J.; Pacheco-Aguilar, J.R.; Martínez-Rizo, A.B.; Arvizu-Gómez, J.L. Association of Pantoea stewartii subsp. stewartii with ChrysSA genus flea beetles in jackfruit crops. J. Plant Pathol. 2021, 103, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kini, K.; Agnimonhan, R.; Dossa, R.; Silué, D.; Koebnik, R. A diagnostic multiplex PCR scheme for identification of plant-associated bacteria of the genus Pantoea. bioRxiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, R.F.; Spósito, M.B.; Ayres, M.R.; Sosnowski, M.R. Phylogeny, morphology and pathogenicity of Elsinoë ampelina, the causal agent of grapevine anthracnose in Brazil and Australia. J. Phytopathol. 2018, 166, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Cheon, W.; Lee, Y.; Kwon, H.T.; Seo, S.T.; Balaraju, K.; Jeon, Y. Identification and characterization of Xanthomonas arboricola pv. juglandis causing bacterial blight of walnuts in Korea. Plant Pathol. J. 2021, 37, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumin, W.; Park, M.J.; Park, J.H.; Yang, C.Y.; Back, C.G. First report of black spot disease caused by Xanthomonas arboricola pv. pruni on plumcot in South Korea. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filiz Doksöz, S.; Bozkurt, İ.A. A new and simple pathogenicity test using carrot slices for Pseudomonas savastanoi pv. savastanoi, causal disease agent of olive knot. J. Plant Pathol. 2020, 102, 1173–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredricks, D.N.; Relman, D.A. Sequence-based identification of microbial pathogens: A reconsideration of Koch’s postulates. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1996, 9, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, M.B.; Williamson, M.R.; Maloy, O. Plant disease diagnosis. Plant Health Instr. 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichhane, J.R.; Venturi, V. Synergisms between microbial pathogens in plant disease complexes: A growing trend. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pariaud, B.; Ravigné, V.; Halkett, F.; Goyeau, H.; Carlier, J.; Lannou, C. Aggressiveness and its role in the adaptation of plant pathogens. Plant Pathol. 2009, 58, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, J.; Smetham, G.; Russ, M.H.; McMurray, L.; Rodda, M.; Krysinska-Kaczmarek, M.; Ford, R. Changes in aggressiveness of the Ascochyta lentis population in Southern Australia. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, A.; Coventry, E.; Jones, J.E.; Clarkson, J.P. Resistance to a highly aggressive isolate of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in a Brassica napus diversity set. Plant Pathol. 2015, 64, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, L.M.R.; Almeida, I.M.G.; Patrício, F.R.A.; Beriam, L.O.S.; Maciel, K.W.; Braghini, M.T.; Filho, O.G. Aggressiveness of strains and inoculation methods for resistance assessment to bacterial halo blight on coffee seedlings. J. Phytopathol. 2017, 165, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantinel, V.S.; Muniz, M.F.B.; Poletto, T.; Harakava, R.; Ciotta, M.N.; Savian, L.G.; Favaretto, R.F.; Krahn, J.R.T. Pathogenicity and susceptibility/resistance reaction of feijoa (Feijoa sellowiana) cultivars to anthracnose. Rev. Bras. Ciências Agrári 2020, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahma, H.; Sinaga, M.S.; Surahman, M. Tingkat Keterjadian Penyakit Layu Stewart pada Benih dan Respon beberapa Varietas Jagung terhadap Infeksi Pantoea stewartii subsp. stewartii. Jurnal Hama dan Penyakit Tumbuhan Tropika 2013, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goszczynska, T.; Botha, W.J.; Venter, S.N.; Coutinho, T.A. Isolation and identification of the causal agent of brown stalk rot, a new disease of maize in South Africa. Plant Dis. 2007, 91, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- RAL Deutsches Institut für Güte sicherung und Kennzeichnung. RAL K1 (RAL Classic Colour); RAL gemeinnützige GmbH: Sankt Augustin, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, N.D.; Pataky, J.K. Levels of Stewart’s wilt resistance necessary to prevent reductions in yield of sweet corn hybrids. Plant Dis. 2001, 85, 278–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campbell, L.; Madden, L.V. The Epidemiology of Plant Diseases; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R; RStudio IDE: Boston, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H.; Bryan, J. Readxl: Read Excel Files. In R Package Version 1.3.1. 2019. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/readxl/index.html (accessed on 18 July 2021).
- Henry, L.; Wickham, H. Purrr: Functional Programming Tools. In R Package Version 0.3.4. 2020. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/purrr/index.html (accessed on 18 July 2021).
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.D.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuwirth, E. RColorBrewer: ColorBrewer Palettes. In R Package Version 1.1-2. 2014. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/RColorBrewer/index.html (accessed on 18 July 2021).
- Ogle, D.; Doll, J.; Wheeler, P.; Dinno, A. FSA: Fisheries Stock Analysis. In R Package Version 0.9.0. 2021. Available online: https://github.com/droglenc/FSA (accessed on 18 July 2021).
- Mangiafico, S. Rcompanion: Functions to support Extension Education Program Evaluation. In R Package Version 2.4.1. 2020. Available online: http://rcompanion.org/ (accessed on 18 July 2021).
- Pedersen, T.L. Patchwork: The Composer of Plots. In R Package Version 1.1.1. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=patchwork (accessed on 18 July 2021).
- Duong, D.A.; Jensen, R.V.; Stevens, A.M. Discovery of Pantoea stewartii ssp. stewartii genes important for survival in corn xylem through a Tn-Seq analysis. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 19, 1929–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asselin, J.E.; Lin, J.; Perez-Quintero, A.L.; Gentzel, I.; Majerczak, D.; Opiyo, S.O.; Zhao, W.; Paek, S.M.; Kim, M.G.; Coplin, D.L.; et al. Perturbation of maize phenylpropanoid metabolism by an AvrE family type III effector from Pantoea stewartii. Plant Physiol. 2015, 167, 1117–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ham, J.H.; Majerczak, D.; Ewert, S.; Sreerekha, M.-V.; Mackey, D.; Coplin, D. WtsE, an AvrE-family type III effector protein of Pantoea stewartii subsp. stewartii, causes cell death in non-host plants. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2008, 9, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pinto, M.C.; Lavermicocca, P.; Evidente, A.; Corsaro, M.M.; Lazzaroni, S.; De Gara, L. Exopolysaccharides produced by plant pathogenic bacteria affect ascorbate metabolism in Nicotiana tabacum. Plant Cell Physiol. 2003, 44, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roper, M.C. Pantoea stewartii subsp. stewartii: Lessons learned from a xylem-dwelling pathogen of sweet corn. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2011, 12, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, U.; Senthil-Kumar, M. Plant and pathogen nutrient acquisition strategies. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KADA. Varieties Registered For National Crop List; Kemubu Agricultural Development Authority: Kota Bharu, Kelantan, Malaysia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski, M. Angular Leaf Spot. Available online: https://extension.umn.edu/diseases/angular-leaf-spot (accessed on 22 June 2020).
- Meng, X.; Chai, A.; Shi, Y.; Xie, X.; Ma, Z.; Li, B. Emergence of Bacterial Soft Rot in Cucumber Caused by Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. brasiliense in China. Plant Dis. 2017, 101, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frenkel, O.; Brewer, M.T.; Milgroom, M.G. Variation in pathogenicity and aggressiveness of Erysiphe necator from different Vitis spp. and geographic origins in the eastern United States. Phytopathology 2010, 100, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartoli, C.; Roux, F.; Lamichhane, J.R. Molecular mechanisms underlying the emergence of bacterial pathogens: An ecological perspective. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2015, 17, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| NS 1 | Isolate Name | Host | Jackfruit Variety | Collection Area | State | Year Collected | Symptom | GenBank Accession | HR 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | JEN-3 | AH 3 | J33 4 | Jenderam | Selangor | 2017 | RD 5 | MK802515 | + 7 |
| 2 | JEN-5 | AH | J33 | Jenderam | Selangor | 2017 | RD | MK802516 | + |
| 3 | JEN-8 | AH | J33 | Jenderam | Selangor | 2017 | RD | MK802517 | + |
| 4 | JEN-13 | AH | J33 | Jenderam | Selangor | 2017 | BSYD 6 | MK802518 | + |
| 5 | JEN-14 | AH | J33 | Jenderam | Selangor | 2017 | BSYD | MK802519 | + |
| 6 | JEN-16 | AH | J33 | Jenderam | Selangor | 2017 | BSYD | MK802520 | + |
| 7 | JEN-20 | AH | J33 | Jenderam | Selangor | 2017 | RD | MK802521 | + |
| 8 | MAR-A | AH | J33 | Maran | Pahang | 2017 | BSYD | MK802522 | + |
| 9 | MAR-D | AH | J33 | Maran | Pahang | 2017 | RD | MK802523 | + |
| 10 | MAR-E | AH | J33 | Maran | Pahang | 2017 | BSYD | MK802524 | + |
| 11 | MAR-F | AH | J33 | Maran | Pahang | 2017 | BSYD | MK802525 | + |
| 12 | MAR-H | AH | J33 | Maran | Pahang | 2017 | RD | MK802526 | + |
| 13 | MAR-M | AH | J33 | Maran | Pahang | 2017 | BSYD | MK802527 | + |
| 14 | MAR-Q | AH | J33 | Maran | Pahang | 2017 | BSYD | MK802528 | + |
| 15 | MS-3 | AH | J33 | Muadzam Shah | Pahang | 2017 | RD | MK802529 | + |
| 16 | MS-4 | AH | J33 | Muadzam Shah | Pahang | 2017 | BSYD | MK802530 | + |
| 17 | MS-8 | AH | J33 | Muadzam Shah | Pahang | 2017 | BSYD | MK802531 | + |
| 18 | MS-B | AH | J33 | Muadzam Shah | Pahang | 2017 | RD | MK802532 | + |
| 19 | MS-C | AH | J33 | Muadzam Shah | Pahang | 2017 | BSYD | MK802533 | + |
| 20 | MS-F | AH | J33 | Muadzam Shah | Pahang | 2017 | BSYD | MK802534 | + |
| 21 | MS-H | AH | J33 | Muadzam Shah | Pahang | 2017 | BSYD | MK802535 | + |
| 22 | IPOH-5 | AH | J33 | Ipoh | Perak | 2017 | BSYD | MK531591 | + |
| 23 | IPOH-B | AH | J33 | Ipoh | Perak | 2017 | RD | MK802536 | + |
| 24 | IPOH-I | AH | J33 | Ipoh | Perak | 2017 | BSYD | MK802537 | + |
| 25 | IPOH-M | AH | J33 | Ipoh | Perak | 2017 | BSYD | MK802538 | + |
| 26 | IPOH-S | AH | J33 | Ipoh | Perak | 2017 | BSYD | MK802539 | + |
| 27 | IPOH-V | AH | J33 | Ipoh | Perak | 2017 | RD | MK802540 | + |
| 28 | IPOH-Z | AH | J33 | Ipoh | Perak | 2017 | RD | MK802541 | + |
| Disease Rating | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | No symptom |
| 1 | 3012 Beige Red |
| 2 | 3022 Dark Salmon Red |
| 3 | 3009 Oxide Red |
| 4 | 3007 Black Red |
| Disease Rating | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | No symptom |
| 1 | Rusty or bronzing specks with yellowish discoloration covered 1–24% of the jackfruit |
| 2 | Rusty or bronzing specks with yellowish discoloration covered 25–49% of the jackfruit |
| 3 | Rusty or bronzing specks with yellowish discoloration covered 50–74% of the jackfruit |
| 4 | Rusty or bronzing specks with yellowish discoloration covered > 75% of the jackfruit |
| Disease Rating | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | No symptom |
| 1 | 2012 Salmon Orange |
| 2 | 3012 Beige Red |
| 3 | 3022 Dark Salmon Red |
| 4 | 3011 Tomato Red |
| Disease Rating | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | No symptom |
| 1 | Localized lesion area covered 1–24% of the pineapple |
| 2 | Localized lesion area covered 25–49% of the pineapple |
| 3 | Localized lesion area covered 50–74% of the pineapple |
| 4 | Localized lesion area covered >75% of the pineapple |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abidin, N.; Ismail, S.I.; Vadamalai, G.; Yusof, M.T.; Hakiman, M.; Karam, D.S.; Zulperi, D. Pathogenic Variability of the Jackfruit-Bronzing Bacterium Pantoea stewartii Subspecies stewartii Infection to Jackfruit Varieties and Its Pivotal Plant Hosts in Malaysia. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112113
Abidin N, Ismail SI, Vadamalai G, Yusof MT, Hakiman M, Karam DS, Zulperi D. Pathogenic Variability of the Jackfruit-Bronzing Bacterium Pantoea stewartii Subspecies stewartii Infection to Jackfruit Varieties and Its Pivotal Plant Hosts in Malaysia. Agronomy. 2021; 11(11):2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112113
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbidin, Nuraizat, Siti Izera Ismail, Ganesan Vadamalai, Mohd Termizi Yusof, Mansor Hakiman, Daljit Singh Karam, and Dzarifah Zulperi. 2021. "Pathogenic Variability of the Jackfruit-Bronzing Bacterium Pantoea stewartii Subspecies stewartii Infection to Jackfruit Varieties and Its Pivotal Plant Hosts in Malaysia" Agronomy 11, no. 11: 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112113
APA StyleAbidin, N., Ismail, S. I., Vadamalai, G., Yusof, M. T., Hakiman, M., Karam, D. S., & Zulperi, D. (2021). Pathogenic Variability of the Jackfruit-Bronzing Bacterium Pantoea stewartii Subspecies stewartii Infection to Jackfruit Varieties and Its Pivotal Plant Hosts in Malaysia. Agronomy, 11(11), 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11112113






