Simulating the Impact of Long-Term Fertilization on Basic Soil Productivity in a Rainfed Winter Wheat System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description and Experimental Design
2.2. Brief Description of the DSSAT Model
2.2.1. DSSAT-CERES-Wheat Model
2.2.2. Meteorological Data
2.2.3. Soil Data
2.2.4. Crop Variety and Field Management Data
2.3. Model Building and Simulation
2.4. Model Calibration and Evaluation
2.5. Simulation Method of BSP
2.6. Contribution Percentage of BSP
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
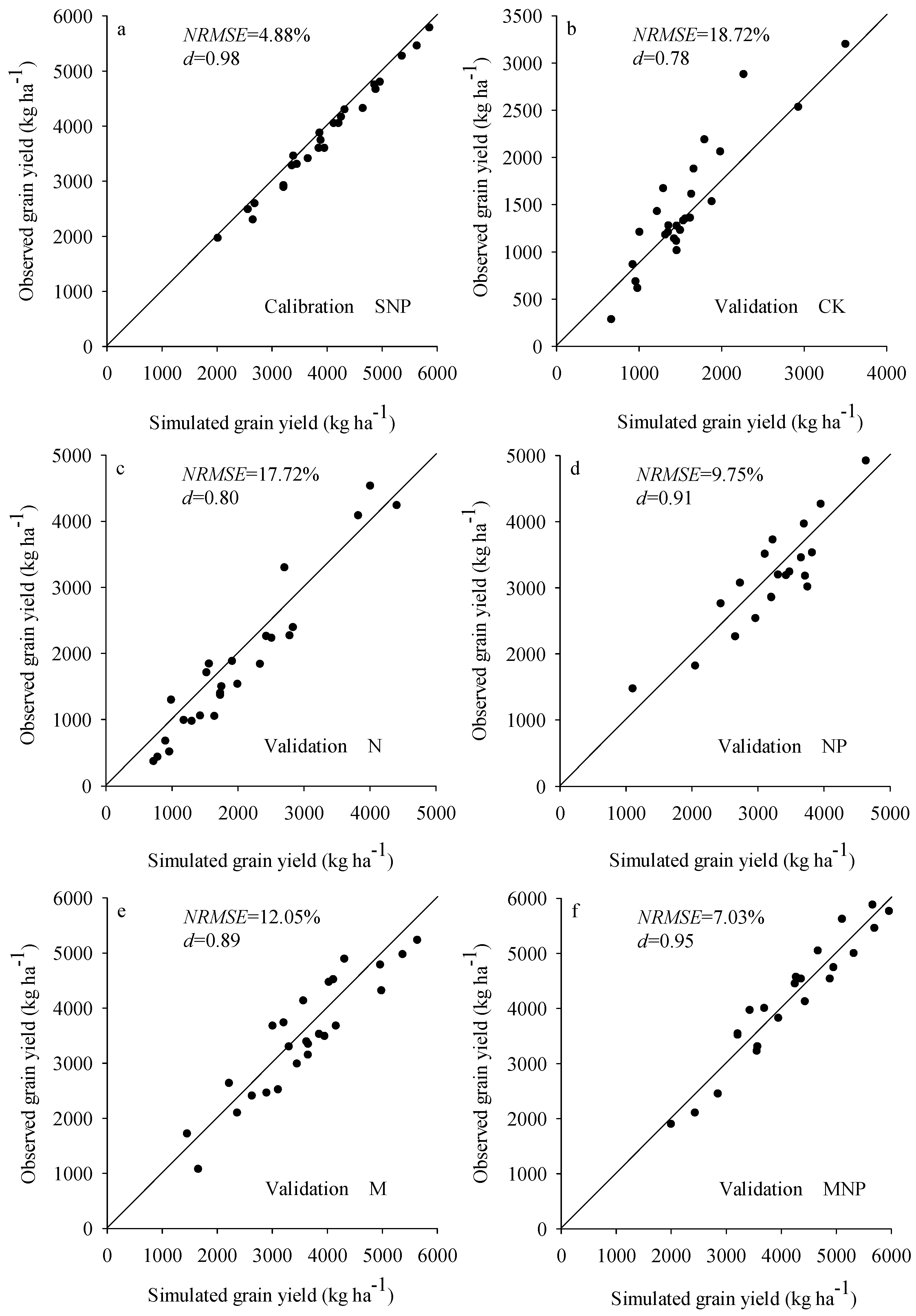
3.1. Calibration and Validation of Crop Genetic Parameters
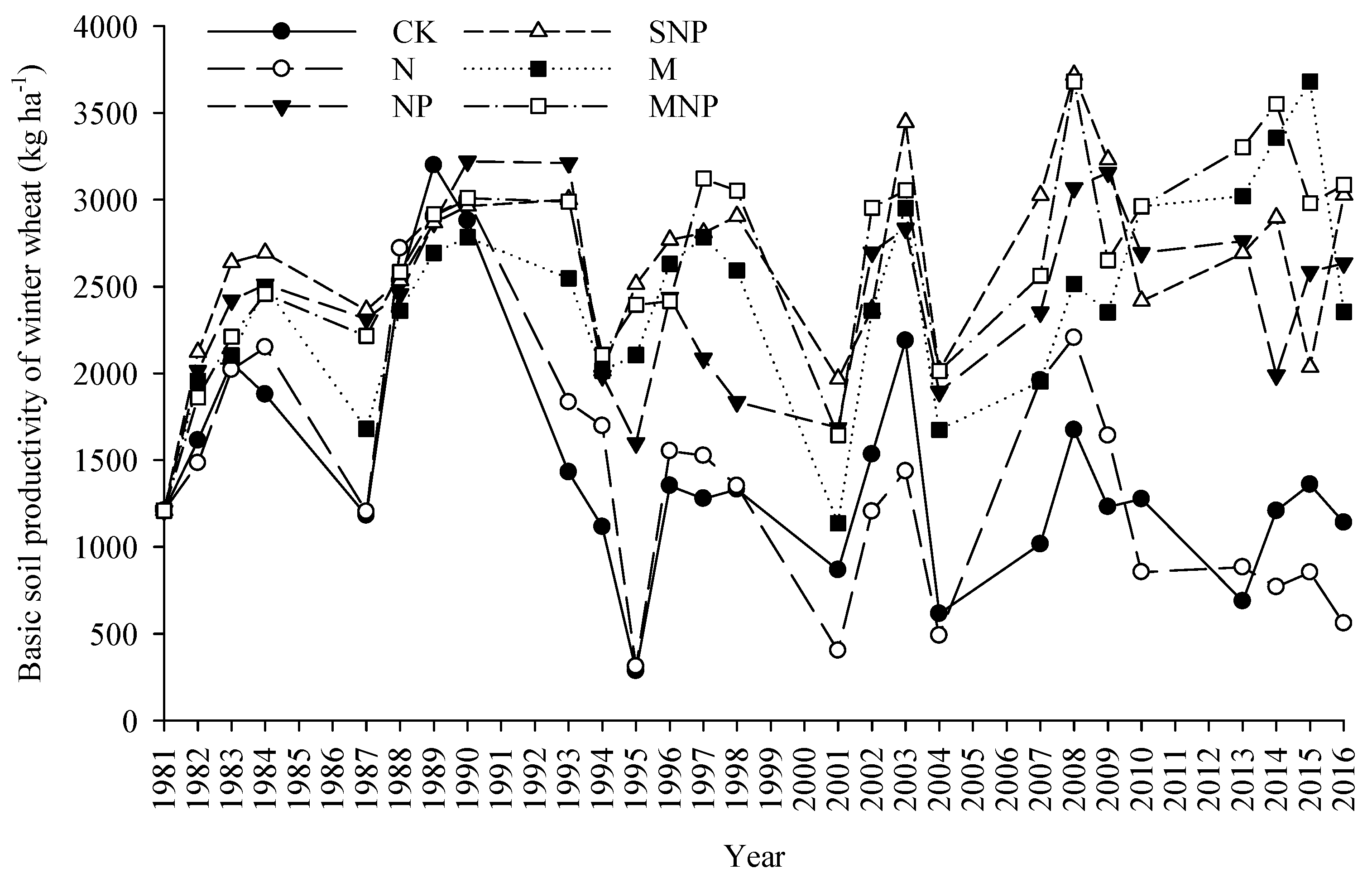
3.2. Basic Soil Productivity
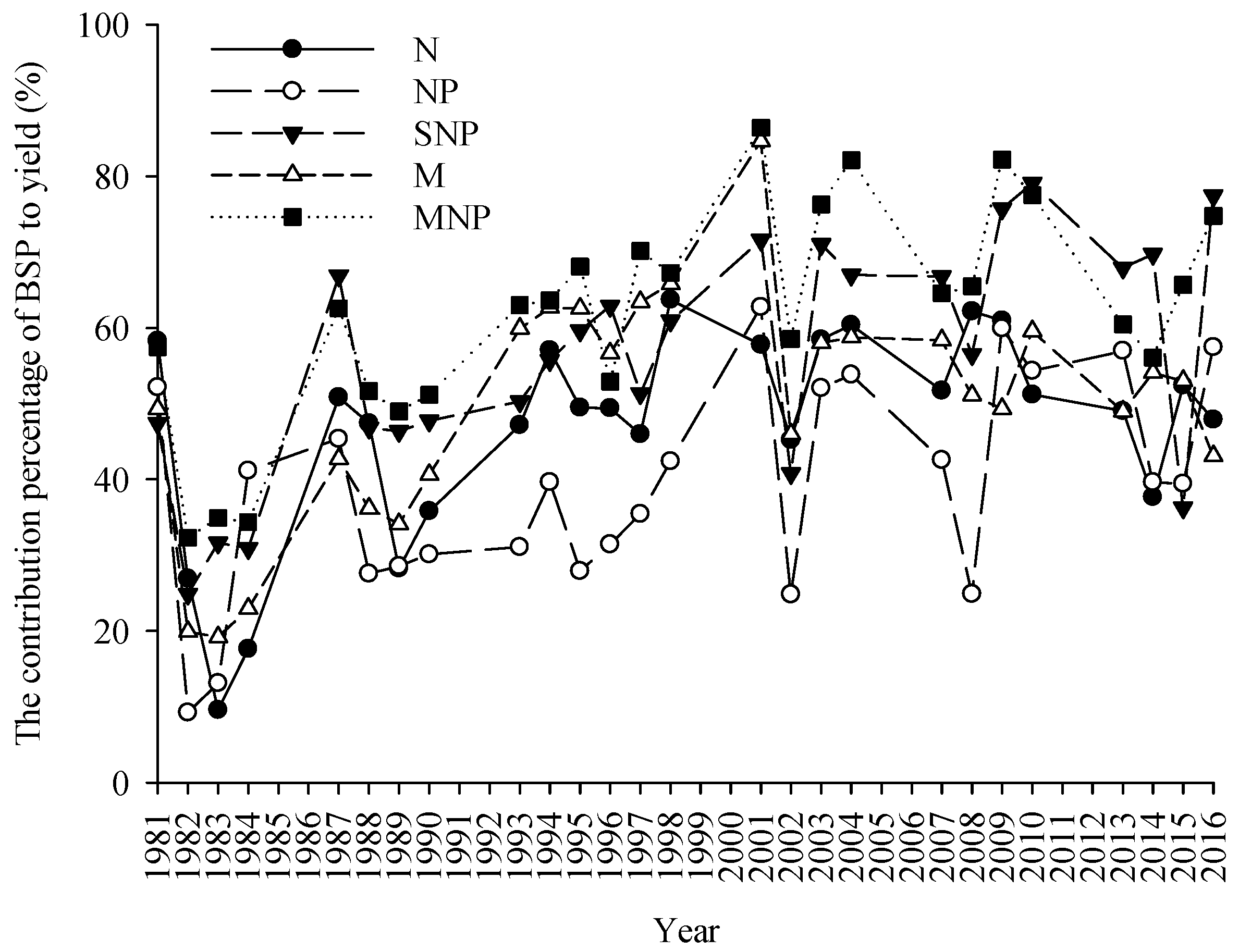
3.3. The Contribution Percentage of BSP
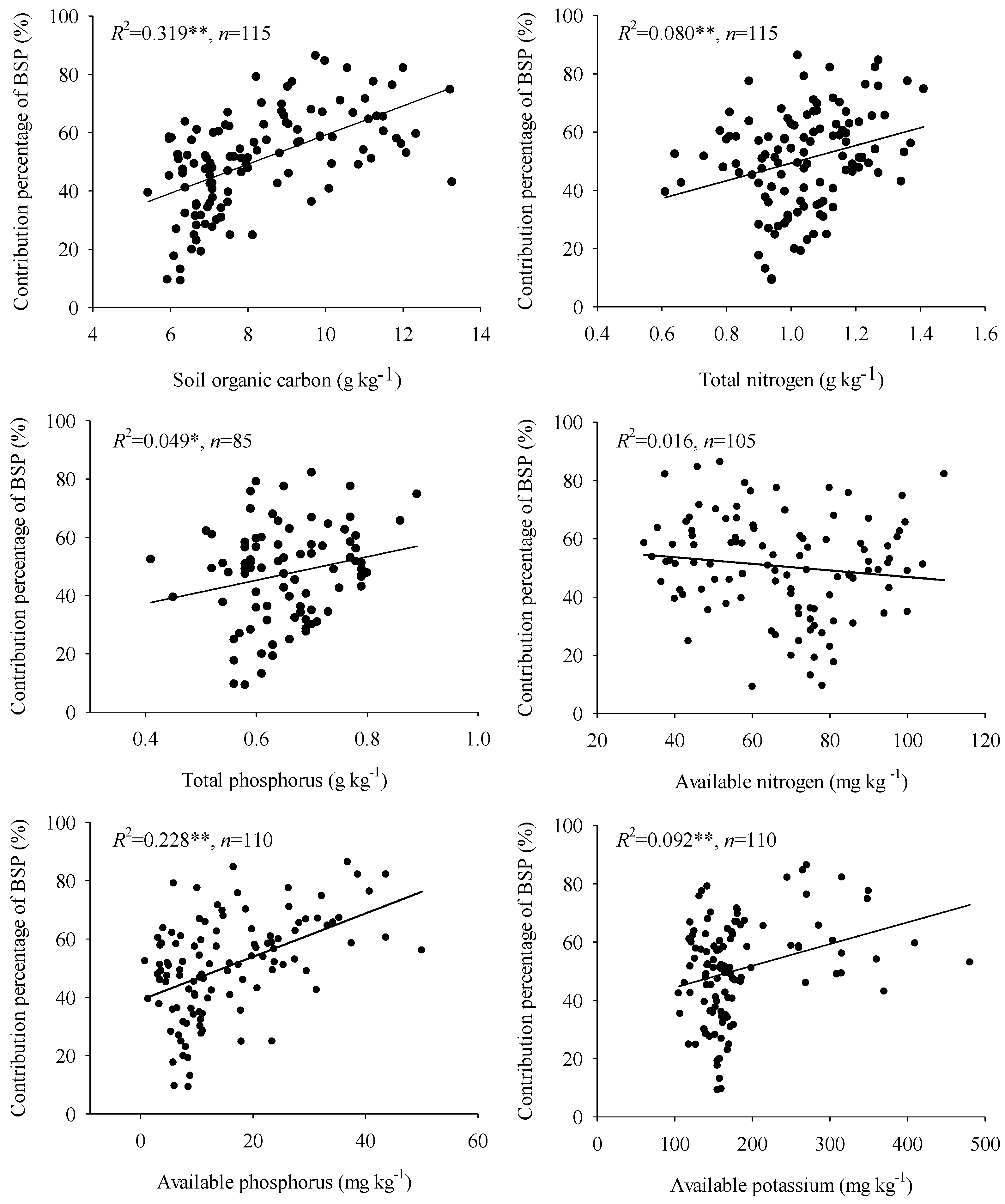
3.4. The Relationship between the Contribution Percentage of BSP and Soil Nutrients
4. Discussion
4.1. Accuracy of Simulated BSP by DSSAT
4.2. The Effect of Long-Term Fertilization on Basic Soil Productivity
4.3. The Effect of Soil Nutrients on the Contribution Percentage of BSP
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- van der Bom, F.; Magid, J.; Jensen, L.S. Long-term P and K fertilisation strategies and balances affect soil availability indices, crop yield depression risk and N use. Eur. J. Agron. 2017, 86, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-H.; Li, S.-X.; Malhi, S. Effects of fertilization and other agronomic measures on nutritional quality of crops. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2008, 88, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erisman, J.W.; Sutton, M.A.; Galloway, J.; Klimont, Z.; Winiwarter, W. How a century of ammonia synthesis changed the world. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 636–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Q.; Ling, N.; Feng, X.; Yang, X.; Wu, P.; Zou, J.; Shen, Q.; Guo, S. Soil fertility and its significance to crop productivity and sustainability in typical agroecosystem: A summary of long-term fertilizer experiments in China. Plant Soil 2014, 381, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisseler, D.; Scow, K.M. Long-term effects of mineral fertilizers on soil microorganisms—A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 75, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, A.; Xu, H.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ashraf, M.N.; Zhang, W.; Xu, M. Changes in mineral-associated carbon and nitrogen by long-term fertilization and sequestration potential with various cropping across China dry croplands. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 205, 104725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmeades, D.C. The long-term effects of manures and fertilisers on soil productivity and quality: A review. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2003, 66, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Han, X.; Chen, X.; Lu, X.; Chen, W.; Wang, E.; Zou, W.; Zhang, Z. Effects of Long-Term Fertilization Strategies on Soil Productivity and Soybean Rhizobial Diversity in a Chinese Mollisol. Pedosphere 2019, 29, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachter, J.M.; Painter, K.M.; Carpenter-Boggs, L.A.; Huggins, D.R.; Reganold, J.P. Productivity, economic performance, and soil quality of conventional, mixed, and organic dryland farming systems in eastern Washington State. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 286, 106665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albornoz, F. Crop responses to nitrogen overfertilization: A review. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 205, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norse, D.; Ju, X. Environmental costs of China’s food security. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 209, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.H.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.L.; Han, W.X.; Zhang, W.F.; Christie, P.; Goulding, K.W.T.; Vitousek, P.M.; Zhang, F.S. Significant Acidification in Major Chinese Croplands. Science 2010, 327, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fan, T.; Stewart, B.A.; Yong, W.; Junjie, L.; Guangye, Z. Long-term fertilization effects on grain yield, water-use efficiency and soil fertility in the dryland of Loess Plateau in China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 106, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, J.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Li, X. Effects of different covering planting patterns on soil moisture, temperature characteristics and Maize yield in semi-arid region of the Loess Plateau. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2020, 53, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ni, S.; Wang, L. Relationship between rainfall variation with yield and growth of winter wheat in Loess Plateau of east Gansu Province. Agric. Res. Arid Areas 2013, 31, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.; Zhu, H.; Dang, T.; Wu, J.; Liu, W.; Hao, M.; Li, Y.; Syers, J.K. Winter wheat grain yield associated with precipitation distribution under long-term nitrogen fertilization in the semiarid Loess Plateau in China. Geoderma 2012, 189, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Wang, S.; Xiaoming, T.; Luo, J.; Stewart, B.A.; Gao, Y. Grain yield and water use in a long-term fertilization trial in Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 76, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E, S.; Ding, N.; Li, L.; Yuan, J.; Che, Z.; Zhou, H.; Shang, L. Contribution of fertilization to accumulative crop yield and soil fertility in Heilu Soil region of the Loess Plateau. ACTA Pedol. Sin. 2019, 56, 195–206. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.; Wu, J.; Dang, T.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Wei, W.; Keith Syers, J. Impacts of fertilizer practices on environmental risk of nitrate in semiarid farmlands in the Loess Plateau of China. Plant Soil 2010, 330, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Li, J. Soil water use and crop yield increase under different long-term fertilization practices incorporated with two-year tillage rotations. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 221, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Ding, N.; Li, L.; Zhou, H.; Shang, L. Combining chemical fertilizer with organic manure or straw increase the yield stability and sustainability of maize and wheat in Loess Plateau of east Gansu Province. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2019, 25, 1817–1826. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, A.E.; Poulton, P.R. The importance of long-term experiments in agriculture: Their management to ensure continued crop production and soil fertility; the Rothamsted experience. Eur. J. Soil. Sci. 2018, 69, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gong, F.; Zha, Y.; Wu, X.; Huang, S.; Xu, M.; Zhang, H.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, X.; Cai, D. Analysis on basic soil productivity change of winter wheat in fluvo-aquic soil under long-term fertilization. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2013, 29, 120–129. [Google Scholar]
- Zha, Y.; Wu, X.; He, X.; Zhang, H.; Gong, F.; Cai, D.; Zhu, P.; Gao, H. Basic Soil Productivity of Spring Maize in Black Soil Under Long-Term Fertilization Based on DSSAT Model. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-Y.; Yan, X.-Y.; Gong, W. Effect of Long-Term Fertilization on Soil Productivity on the North China Plain. Pedosphere 2015, 25, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Han, T.; Huang, J.; Zhang, S.; Gao, H.; Zhang, L.; Shah, A.; Huang, S.; Zhu, P.; Gao, S.; et al. Change of soil productivity in three different soils after long-term field fertilization treatments. J. Integr. Agric. 2020, 19, 848–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhang, S.; Lu, C. Assessment of the contribution percentage of inherent soil productivity of cultivated land in China. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 2619–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.W.; Hoogenboom, G.; Porter, C.H.; Boote, K.J.; Batchelor, W.D.; Hunt, L.A.; Wilkens, P.W.; Singh, U.; Gijsman, A.J.; Ritchie, J.T. The DSSAT cropping system model. Eur. J. Agron. 2003, 18, 235–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogenboom, G.; Porter, C.H.; Shelia, V.; Boote, K.J.; Singh, U.; White, J.W.; Hunt, L.A.; Ogoshi, R.; Lizaso, J.I.; Koo, J.; et al. Decision Support System for Agrotechnology Transfer (DSSAT) Version 4.7 (www.DSSAT.net); DSSAT Foundation: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hoogenboom, G.; Porter, C.H.; Boote, K.J.; Shelia, V.; Wilkens, P.W.; Singh, U.; White, J.W.; Asseng, S.; Lizaso, J.I.; Moreno, L.P.; et al. The DSSAT crop modeling ecosystem. In Advances in Crop Modeling for a Sustainable Agriculture; Boote, K.J., Ed.; Burleigh Dodds Science Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.; Liu, J.; Gao, Y.; Sun, Z.; Chen, S.; Yao, N.; Ma, H.; Feng, H.; Yu, Q.; He, J. Simulation of plant height of winter wheat under soil Water stress using modified growth functions. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 232, 106066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Dou, Z.; Liu, J.; Gao, Y.; Malone, R.W.; Chen, S.; Feng, H.; Yu, Q.; Xue, G.; He, J. Simulating the Influences of Soil Water Stress on Leaf Expansion and Senescence of Winter Wheat. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 291, 108061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wallach, D.; Liu, B.; Dingkuhn, M.; Boote, K.J.; Singh, U.; Asseng, S.; Kahveci, T.; He, J.; Zhang, R.; et al. Comparison of three calibration methods for modeling rice phenology. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 280, 107785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Feng, H.; He, J.; Chen, H.; Ding, D.; Luo, X.; Dong, Q. Modeling wheat nutritional quality with a modified CERES-wheat model. Eur. J. Agron. 2019, 109, 125901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddique, Q.; Cai, H.; Ishaque, W.; Chen, H.; Chau, H.; Chattha, M.; Hassan, M.; Khan, M.; He, J. Optimizing the Sowing Date and Irrigation Strategy to Improve Maize Yield by Using CERES (Crop Estimation through Resource and Environment Synthesis)-Maize Model. Agronomy 2019, 9, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Jiang, T.; Ma, H.; He, C.; Xu, F.; Malone, R.W.; Feng, H.; Yu, Q.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Dong, Q.; et al. Dynamic within-season irrigation scheduling for maize production in Northwest China: A Method Based on Weather Data Fusion and yield prediction by DSSAT. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 285–286, 107928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobell, D.B.; Ortiz-Monasterio, J.I. Evaluating strategies for improved water use in spring wheat with CERES. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 84, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Jin, X.; Liu, H.; Xu, X.; Wang, J. Global sensitivity analysis of wheat grain yield and quality and the related process variables from the DSSAT-CERES model based on the extended Fourier Amplitude Sensitivity Test method. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 1547–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boote, K.J.; Prasad, V.; Allen, L.H.; Singh, P.; Jones, J.W. Modeling sensitivity of grain yield to elevated temperature in the DSSAT crop models for peanut, soybean, dry bean, chickpea, sorghum, and millet. Eur. J. Agron. 2018, 100, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timsina, J.; Humphreys, E. Performance of CERES-Rice and CERES-Wheat models in rice–wheat systems: A review. Agric. Syst. 2006, 90, 5–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Li, X.; Ju, H.; Liu, Q. The impacts of climate change on wheat yield in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain of China using DSSAT-CERES-Wheat model under different climate scenarios. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 1379–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, W.; Dechmi, F. DSSAT modelling for best irrigation management practices assessment under Mediterranean conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 216, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhao, W.; He, J.; Flerchinger, G.N.; Feng, H. Simulating soil surface temperature under plastic film mulching during seedling emergence of spring maize with the RZ–SHAW and DNDC models. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 197, 104517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Y.; Wu, X.; Gong, F.; Xu, M.; Zhang, H.; Chen, L.; Huang, S.; Cai, D. Long-term organic and inorganic fertilizations enhanced basic soil productivity in a fluvo-aquic soil. J. Integr. Agric. 2015, 14, 2477–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; He, J.; Xu, X.; Jin, X.; Huang, W.; Clark, B.; Yang, G.; Li, Z. Estimating genetic parameters of DSSAT-CERES model with the GLUE method for winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) production. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 154, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- E, S.; Ding, N.; Li, L.; Yuan, J.; Che, Z.; Zhou, H.; Shang, L. Relationship of crop yield and soil organic carbon and nitrogen under long-term fertilization in black loessial soil region on the Loess Plateau in China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 29, 4047–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angstrom, A. Solar and terrestrial radiation. Report to the international commission for solar research on actinometric investigations of solar and atmospheric radiation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1924, 50, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Dukes, M.D.; Jones, J.W.; Graham, W.D.; Judge, J. Applying GLUE for Estimating CERES-Maize Genetic and Soil Parameters for Sweet Corn Production. Trans. ASABE 2009, 52, 1907–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.W.; He, J.; Boote, K.J.; Wilkens, P.; Porter, C.H.; Hu, Z. Estimating DSSAT croping system cultivar-Specific Parameters Using Bayesian Techniques. In Methods of Introducing System Models into Agricultural Research; Ahuja, L.R., Ma, L., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Paris, France, 2011; pp. 365–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Niwas, R.; Khichar, M.L.; Singh, A.; Badal, P.; Kumar, Y.; Chauthan, A.S. Genetic Coefficient and Validation of DSSAT Model for Cotton under Different Growing Environments. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2017, 6, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar]
- Janssen, P.H.M.; Heuberger, P.S.C. Calibration of process-oriented models. Ecol. Model. 1995, 83, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.J.; Ackleson, S.G.; Davis, R.E.; Feddema, J.J.; Klink, K.M.; Legates, D.R.; O’Donnell, J.; Rowe, C.M. Statistics for the evaluation and comparison of models. J. Geophys. Res. 1985, 90, 8995–9005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loague, K.; Green, R.E. Statistical and graphical methods for evaluating solute transport models: Overview and application. J. Contam. Hydrol. 1991, 7, 51–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadiyala, M.D.M.; Jones, J.W.; Mylavarapu, R.S.; Li, Y.C.; Reddy, M.D. Identifying irrigation and nitrogen best management practices for aerobic rice–maize cropping system for semi-arid tropics using CERES-rice and maize models. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 149, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, N.; Zhou, Y.; Song, L.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, S.; Feng, H.; He, J. Parameter estimation and verification of DSSAT-CERES-Wheat model for simulation of growth and development of winter wheat under water stresses at different growth stages. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 138–150. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Chen, G.; Liu, E.; Ju, H.; Liu, Q. The variations in winter wheat potential yields in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River under the RCP scenarios. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 3219–3229. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, N.; Li, Y.; Xu, F.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Ma, H.; Wai Chau, H.; Liu, D.L.; Li, M.; Feng, H.; et al. Permanent wilting point plays an important role in simulating winter wheat growth under water deficit conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 229, 105954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouna, B.B.; Katerji, N.; Mastrorilli, M. Using the CERES-Maize model in a semi-arid Mediterranean environment. New modelling of leaf area and water stress functions. Eur. J. Agron. 2003, 19, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeJonge, K.C.; Ascough, J.C.; Andales, A.A.; Hansen, N.C.; Garcia, L.A.; Arabi, M. Improving evapotranspiration simulations in the CERES-Maize model under limited irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 115, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, Z.; Xie, Y.; Gao, Y.; Ren, X.; Cheng, C.; Wang, S. Quantitative assessment of soil productivity and predicted impacts of water erosion in the black soil region of northeastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637–638, 706–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Huang, Y. Statistical Analysis of the Percentage of Soil Fertility Contribution to Grain Crop Yield and Driving Factors in Mainland China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2008, 27, 1283–1289. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Jia, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, K. Analysis on soil nutrient influencing factors of winter wheat yield gaps of basic soil productivity by boundary line method in central and southern Hebei Province. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z. Research on nitrogen in China. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2008, 45, 778–783. [Google Scholar]

| Soil Depth (cm) | Bulk Density (g cm−3) | Organic Carbon (%) | Total Nitrogen (g kg−1) | pH | Sand (%) | Silt (%) | Clay (%) | Saturated Water Conductivity (cm h−1) | Saturated Water Content (%) | Root Growth Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1979 | ||||||||||
| 20 | 1.30 | 0.56 | 0.95 | 8.2 | 23.1 | 43.2 | 33.6 | 1.32 | 31.5 | 1 |
| 40 | 1.47 | 0.45 | 0.8 | 8.2 | 21.6 | 44.2 | 34.2 | 1.32 | 27.4 | 0.549 |
| 60 | 1.36 | 0.55 | 0.8 | 8.3 | 11.8 | 43.5 | 44.2 | 1.32 | 31.5 | 0.368 |
| 80 | 1.34 | 0.40 | 0.6 | 8.4 | 19.7 | 42.8 | 37.5 | 1.32 | 31.9 | 0.247 |
| 100 | 1.30 | 0.18 | 0.5 | 8.3 | 24.3 | 41 | 34.2 | 2.59 | 31.9 | 0.165 |
| 2000 | ||||||||||
| 20 | 1.21 | 0.90 | 0.98 | 8.2 | 19.9 | 47.4 | 32.7 | 1.32 | 31.5 | 1 |
| 40 | 1.40 | 0.51 | 0.56 | 8.2 | 13.8 | 49.4 | 36.8 | 1.32 | 27.4 | 0.549 |
| 60 | 1.38 | 0.53 | 0.60 | 8.3 | 11.7 | 45.2 | 43.1 | 1.32 | 31.5 | 0.368 |
| 80 | 1.35 | 0.33 | 0.42 | 8.5 | 15.8 | 46.3 | 37.9 | 1.32 | 31.9 | 0.247 |
| 100 | 1.33 | 0.27 | 0.31 | 8.4 | 17.9 | 45.3 | 36.8 | 2.59 | 31.9 | 0.165 |
| Cultivars | P1V 1 | P1D 2 | P5 3 | G1 4 | G2 5 | G3 6 | PHINT 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat 80Ping8 | 73.34 | 90.24 | 598.7 | 18.78 | 45.67 | 1.865 | 95 |
| Wheat 15-0-36 | 42.87 | 98.45 | 678.9 | 16.67 | 38.77 | 1.765 | 88 |
| Wheat 85108 | 63.33 | 92.45 | 584.5 | 15.34 | 39.37 | 1.431 | 94 |
| Wheat PL44 | 55.61 | 94.91 | 610.9 | 15.34 | 47.54 | 1.929 | 99 |
| Wheat Chang6387 | 61.19 | 93.8 | 756.4 | 15.01 | 40.83 | 1.426 | 85 |
| Mean | 59.27 | 93.97 | 645.88 | 16.23 | 42.44 | 1.68 | 92.20 |
| Standard deviation | 11.19 | 3.05 | 71.63 | 1.56 | 3.93 | 0.24 | 5.63 |
| Coefficient of variation, % | 18.87 | 3.25 | 11.09 | 9.63 | 9.27 | 14.24 | 6.11 |
| Fertilization Treatments | Regression Equation | Annual Increasing Yield, kg hm−2 | Annual Increasing Rate, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | Y = −24.9x − 51291.6, R2 = 0.168, p < 0.05 1 | −24.9 | −0.23 |
| N | Y = −32.8x − 67093.4, R2 = 0.234, p < 0.05 | −32.8 | −3.03 |
| NP | Y = 12.3x − 22080.1, R2 = 0.065, p > 0.05 | 12.3 | 3.17 |
| SNP | Y = 16.3x − 29877.4, R2 = 0.113, p > 0.05 | 16.3 | 3.74 |
| M | Y = 25.7x − 48964.1, R2 = 0.224, p < 0.05 | 25.7 | 2.70 |
| MNP | Y = 31.6x − 60491.4, R2 = 0.349, p < 0.01 | 31.6 | 3.82 |
| Treatment | Contribution Rate of Basic Soil Productivity, % | Average Contribution Rate of Basic Soil Productivity, % |
|---|---|---|
| N | 26.92~63.73 | 47.02 ± 10.28 c 1 |
| NP | 9.23~62.76 | 39.37 ± 16.31 d |
| SNP | 24.88~77.46 | 56.30 ± 16.84 b |
| M | 19.19~62.71 | 50.04 ± 12.71 c |
| MNP | 32.31~77.48 | 61.88 ± 14.36 a |
| Treatment | SOC | TN | TP | AN | AP | AK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 0.244 | −0.068 | −0.166 | −0.484 * | −0.331 | −0.460 * 1 |
| NP | 0.469 * | −0.098 | 0.260 | −0.136 | 0.379 | −0.075 |
| SNP | 0.560 ** | −0.147 | −0.340 | −0.263 | 0.430 * | −0.342 |
| M | 0.539 ** | 0.243 | 0.085 | −0.439 * | 0.471 * | 0.363 |
| MNP | 0.693 ** | 0.351 | 0.279 | −0.390 | 0.647 ** | 0.594 ** |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, T.; Ding, N.; Li, L.; Lyu, X.; Chai, Q.; Dou, X. Simulating the Impact of Long-Term Fertilization on Basic Soil Productivity in a Rainfed Winter Wheat System. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10101544
Wang T, Ding N, Li L, Lyu X, Chai Q, Dou X. Simulating the Impact of Long-Term Fertilization on Basic Soil Productivity in a Rainfed Winter Wheat System. Agronomy. 2020; 10(10):1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10101544
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ting, Ningping Ding, Lili Li, Xiaodong Lyu, Qiang Chai, and Xuecheng Dou. 2020. "Simulating the Impact of Long-Term Fertilization on Basic Soil Productivity in a Rainfed Winter Wheat System" Agronomy 10, no. 10: 1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10101544
APA StyleWang, T., Ding, N., Li, L., Lyu, X., Chai, Q., & Dou, X. (2020). Simulating the Impact of Long-Term Fertilization on Basic Soil Productivity in a Rainfed Winter Wheat System. Agronomy, 10(10), 1544. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10101544





