Multifunctional High-Concentration Polyepoxysuccinic Acid for Water-Based Drilling Fluids: Achieving Ultra-Low Friction and Filtration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Materials
2.2. Extreme Pressure Lubricity Test
2.3. Four-Ball Tribotest
2.4. Bentonite Inhibition Test
2.5. Preparation of the SP-WBDFs
2.6. Rheological Measurement
2.7. Filtration Measurement
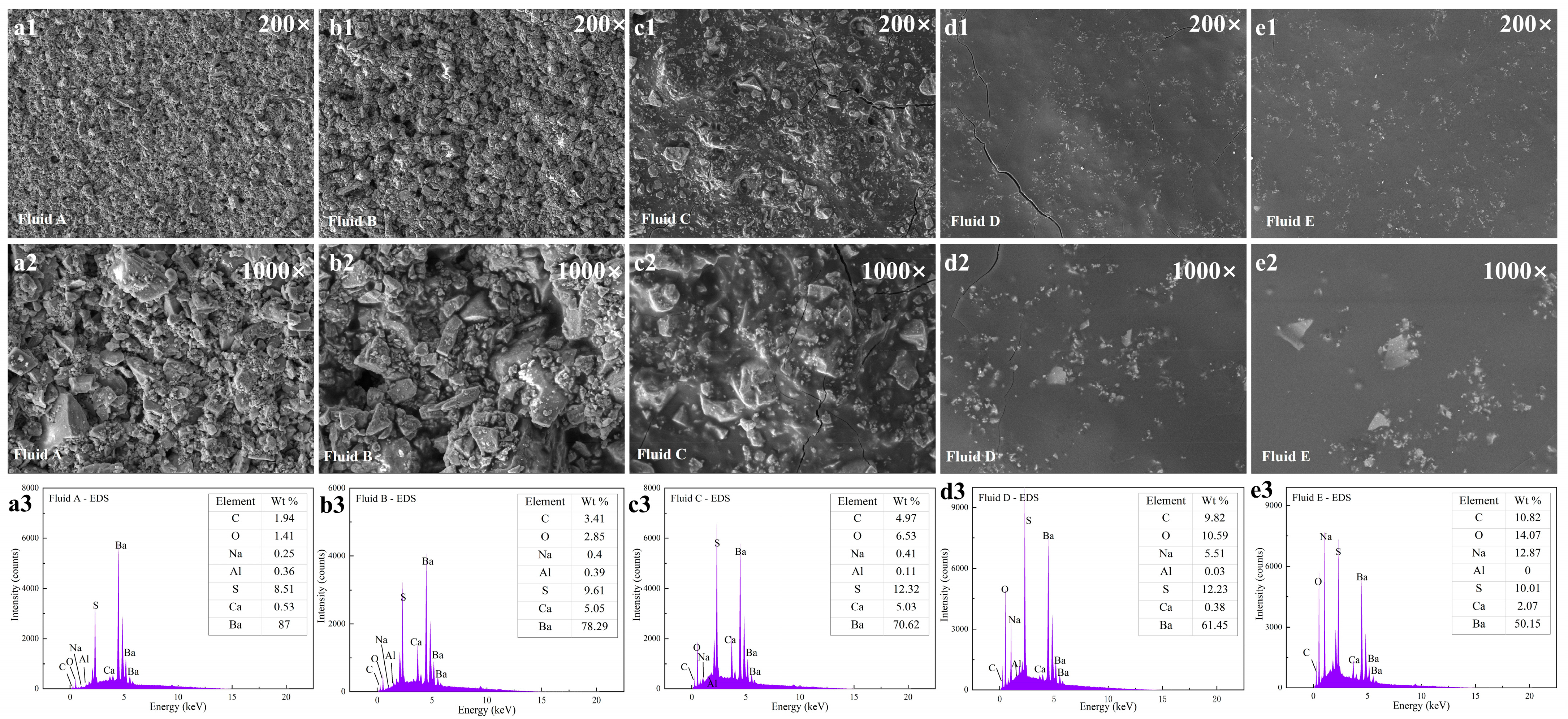
2.8. SEM and EDS Analysis
2.9. XPS Analysis
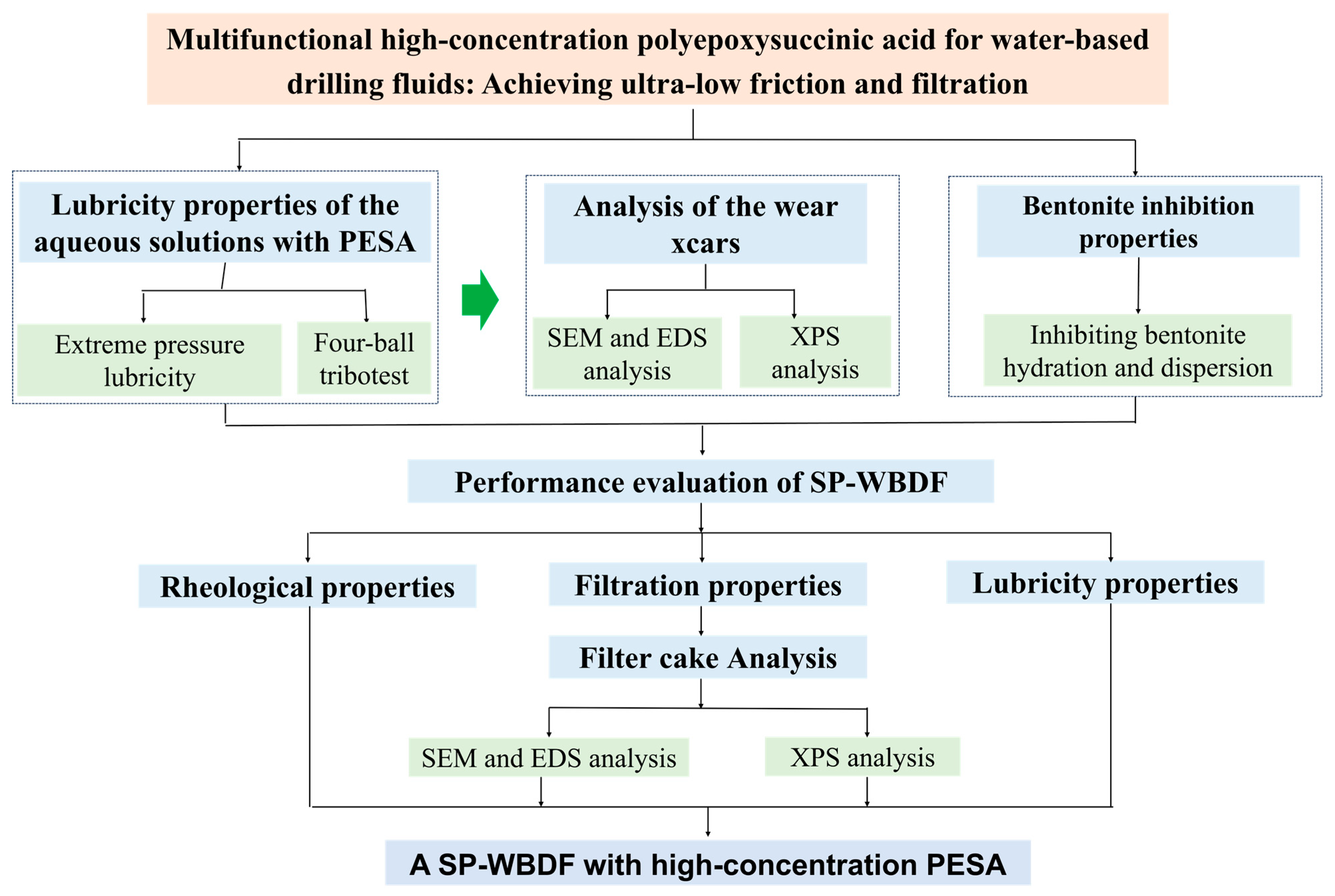
3. Results and Discussion
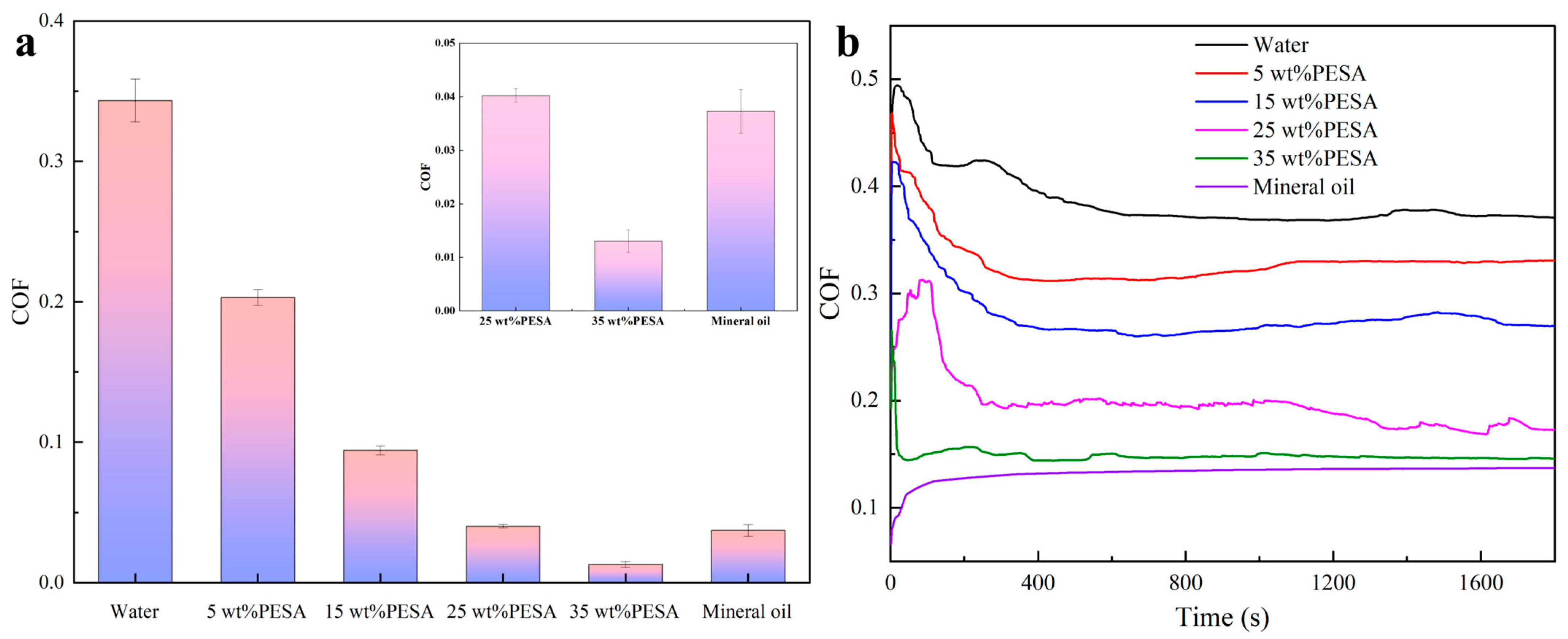
3.1. Lubricity Properties of the Aqueous Solutions with PESA
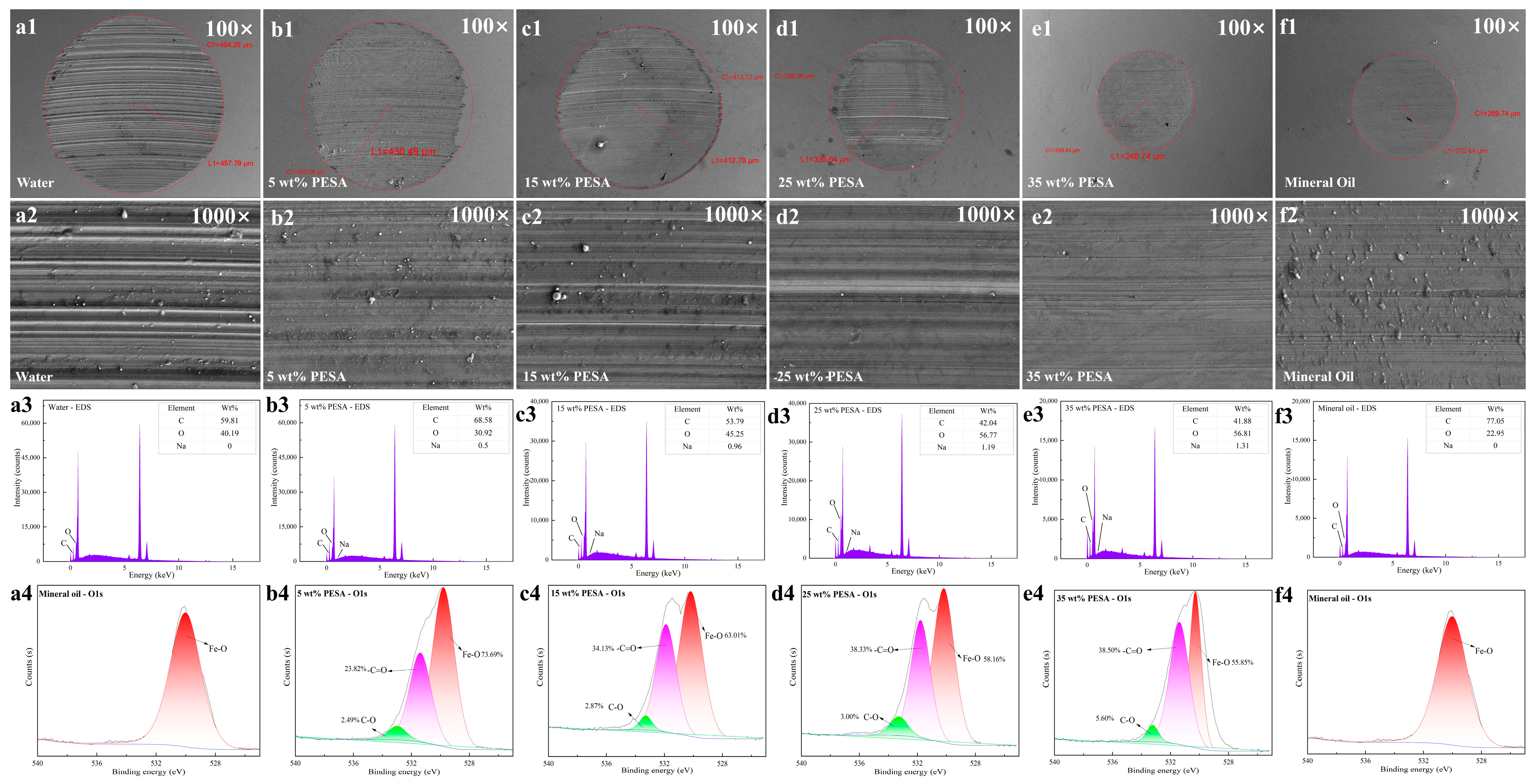
3.2. Analysis of the Wear Scars
3.3. Inhibition Properties of the Aqueous Solutions with PESA
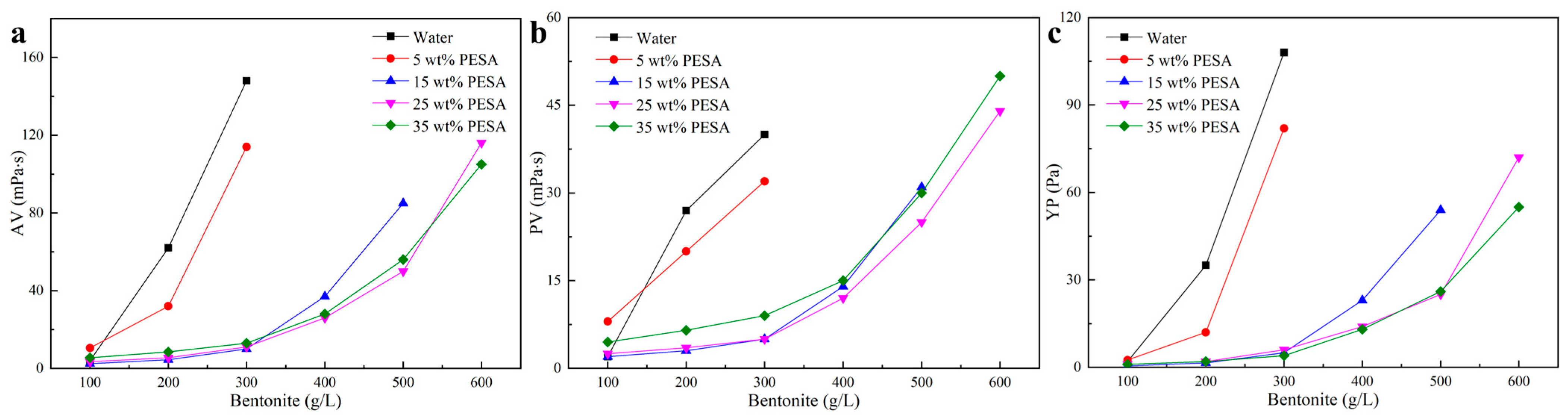
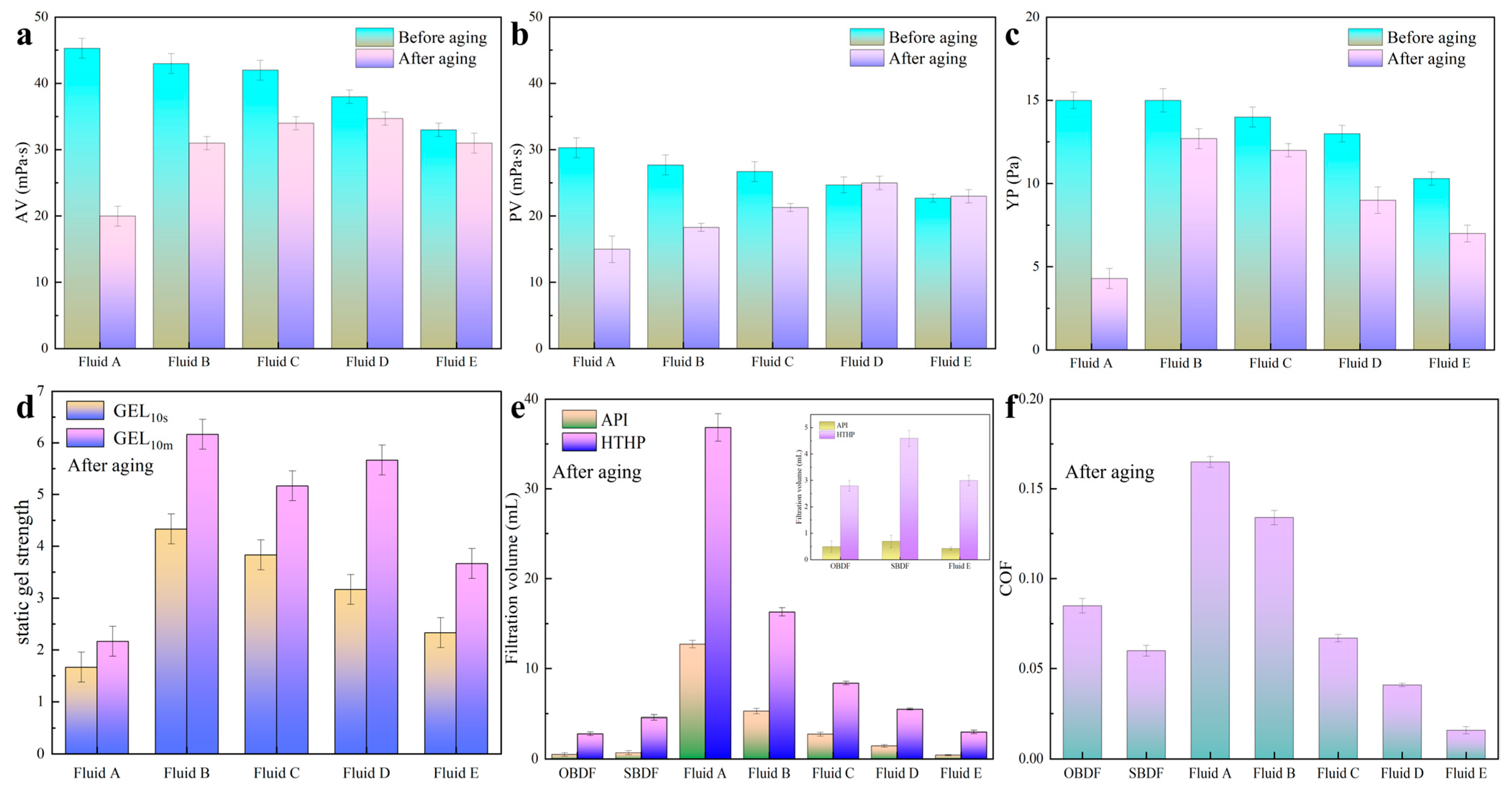
3.4. Performance Evaluation of SP-WBDFs
3.5. Analysis of the Filter Cake of SP-WBDFs
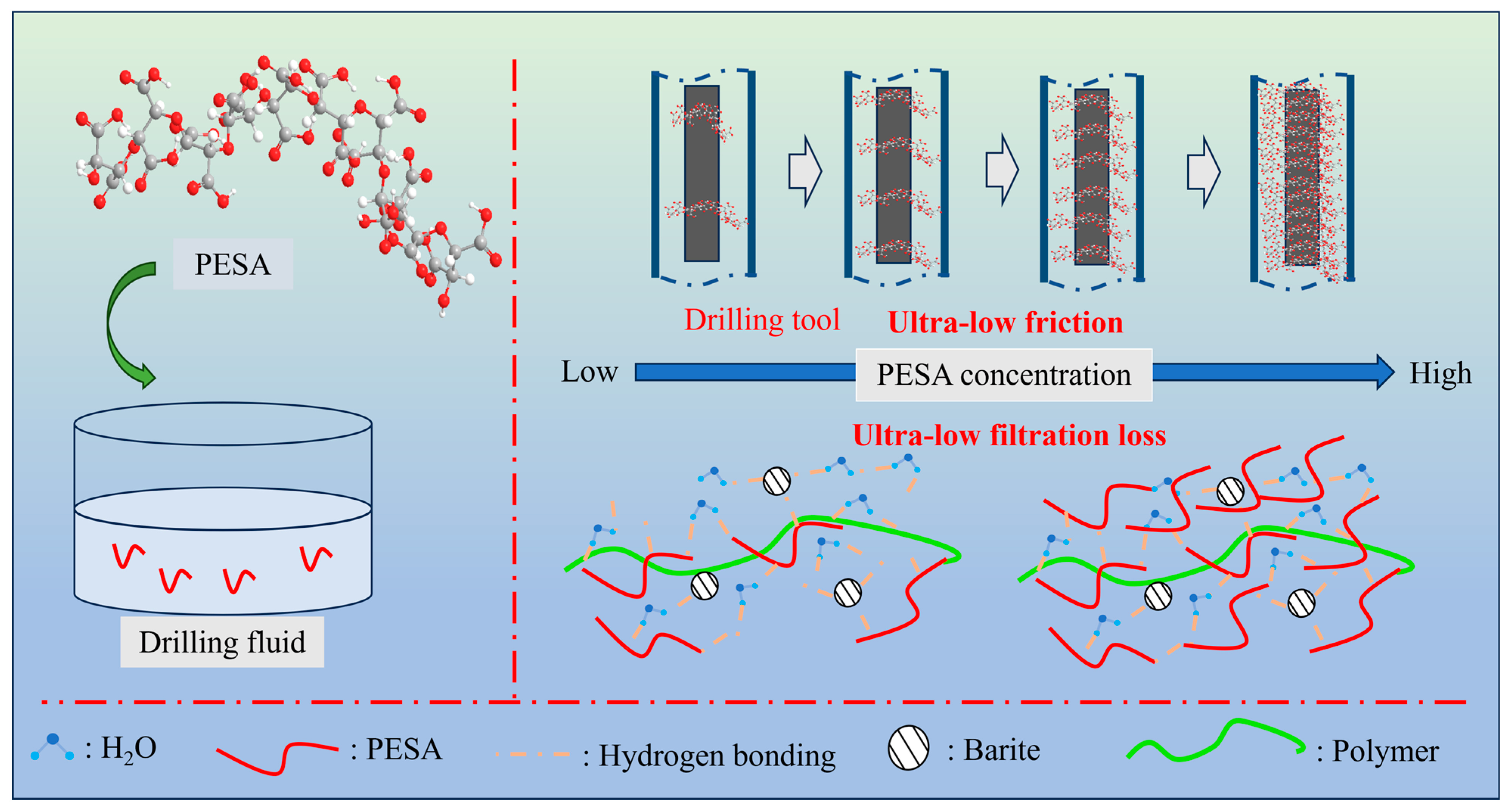
3.6. Discussion Mechanism of Lubricity and Filtration Control
3.7. Environmental Sustainability and Economic Viability
4. Conclusions
- The COF of the aqueous solution with 25 wt% PESA was close to that of the mineral oi, while the COF of the aqueous solution with 35 wt% PESA was 0.013, significantly lower than the 0.037 observed for mineral oil.
- Water contaminated with over 300 g/L of bentonite experienced significant thickening, making it impossible to measure AV of the resulting mixture. In contrast, the aqueous solutions with over 15 wt% PESA exhibited excellent performance in inhibiting bentonite hydration and dispersion. The AV of the aqueous solutions with over 25 wt% PESA can still be measured, even after contamination with 600 g/L of bentonite.
- The SP-WBDF with 35 wt% PESA exhibited excellent rheological properties that meet drilling requirements, achieving ultra-low friction and minimal filtration loss; the COF, API filtration loss, and HTHP filtration loss were 0.016, 0.4 mL, and 3.0 mL, respectively.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chomphosy, W.H.; Varriano, S.; Lefler, L.H.; Nallur, V.; McClung, M.R.; Moran, M.D. Ecosystem services benefits from the restoration of non-producing US oil and gas lands. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 4, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Partridge, T.; Harthorn, B.H.; Pidgeon, N. Deliberating the perceived risks, benefits, and societal implications of shale gas and oil extraction by hydraulic fracturing in the US and UK. Nat. Energy 2017, 2, 17054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sena, M.F.M.; Rosa, L.P.; Szklo, A. Will Venezuelan extra-heavy oil be a significant source of petroleum in the next decades? Energy Policy 2013, 61, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubrecht, M.D. Horizontal directional drilling: A green and sustainable technology for site remediation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 2484–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidic, R.D.; Brantley, S.L.; Vandenbossche, J.M.; Yoxtheimer, D.; Abad, J.D. Impact of shale gas development on regional water quality. Science 2013, 340, 1235009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, J.K.; Lai, C.W.; Johan, M.R.; Gan, S.S.; Chua, W.W. Recent advances of modified polyacrylamide in drilling technology. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 215, 110566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoodi, S.; SA, A.R.; Soleimanian, A.; Jahromi, A.F. Application of a novel acrylamide copolymer containing highly hydrophobic comonomer as filtration control and rheology modifier additive in water-based drilling mud. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 180, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stout, S.A.; Payne, J.R. Footprint, weathering, and persistence of synthetic-base drilling mud olefins in deep-sea sediments following the Deepwater Horizon disaster. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 118, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayfield, E.N.; Cohon, J.L.; Muller, N.Z.; Azevedo, I.M.L.; Robinson, A.L. Cumulative environmental and employment impacts of the shale gas boom. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 1122–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheisari, R.; Polycarpou, A.A. Synergistic physical and chemical interactions of selected additives and base oil used in extended reach drilling applications. Wear 2021, 478–479, 203889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konate, N.; Salehi, S. Experimental investigation of inhibitive drilling fluids performance: Case studies from United States shale basins. Energies 2020, 13, 5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aftab, A.; Ali, M.; Sahito, M.F.; Mohanty, U.S.; Jha, N.K.; Akhondzadeh, H.; Azhar, M.R.; Ismail, A.R.; Keshavarz, A.; Iglauer, S. Environmental friendliness and high performance of multifunctional tween 80/ZnO-nanoparticles-added water-based drilling fluid: An experimental approach. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 11224–11243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwally, M.; Nguyen, T.; Wiggins, H.; Saasen, A.; Gipson, M. Experimental lab approach for water based drilling fluid using polyacrylamide friction reducers to drill extended horizontal wells. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 212, 110132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Du, H.; Zheng, T.; Liu, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, R.; Li, H.; Xie, H.; Zhang, X.; Ma, M.; et al. Recent advances in cellulose and its derivatives for oilfield applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 259, 117740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aftab, A.; Ismail, A.; Ibupoto, Z.; Akeiber, H.; Malghani, M. Nanoparticles based drilling muds a solution to drill elevated temperature wells: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 76, 1301–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumalsamy, J.; Gupta, P.; Sangwai, J.S. Performance evaluation of esters and graphene nanoparticles as an additives on the rheological and lubrication properties of water-based drilling mud. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 204, 108680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricky, E.; Mpelwa, M.; Wang, C.; Hamad, B.; Xu, X. Modified corn starch as an environmentally friendly rheology enhancer and fluid loss reducer for water-based drilling mud. SPE J. 2022, 27, 1064–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beg, M.; Sharma, S.; Ojha, U. Effect of cationic copolyelectrolyte additives on drilling fluids for shales. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 161, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoveidavianpoor, M.; Samsuri, A. The use of nano-sized Tapioca starch as a natural water-soluble polymer for filtration control in water-based drilling muds. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 34, 832–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboori, R.; Sabbaghi, S.; Kalantariasl, A. Improvement of rheological, filtration and thermal conductivity of bentonite drilling fluid using copper oxide/polyacrylamide nanocomposite. Powder Technol. 2019, 353, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morenov, V.; Leusheva, E.; Liu, T. Development of a weighted barite-free formate drilling mud for well construction under complicated conditions. Polymers 2021, 13, 4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadl, A.; Abdou, M.; Ahmed, H.E.-S.; Gaber, M.W. Delaminated iron ore (hematite-barite) as alternative weighting agent to barite in petroleum drilling fluids engineering operations and mechanism study. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2020, 11, 1317–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Chen, S.; Lee, H.; Mei, D.; Engelhard, M.H.; Burton, S.D.; Zhao, W.; Zheng, J.; Li, Q.; Ding, M.S.; et al. Localized high-concentration sulfone electrolytes for high-efficiency lithium-metal batteries. Chem 2018, 4, 1877–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Zou, L.; Gao, P.; Cao, X.; Zhao, W.; He, Y.; Engelhard, M.H.; Burton, S.D.; Wang, H.; Ren, X.; et al. High-performance silicon anodes enabled by nonflammable localized high-concentration electrolytes. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, S.; Helmers, H.; Tiwari, M.K.; Paredes, S.; Michel, B.; Wiesenfarth, M.; Bett, A.W.; Poulikakos, D. A high-efficiency hybrid high-concentration photovoltaic system. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 89, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Wei, Q.; Jiao, F.; Qin, W. Utilization of polyepoxysuccinic acid as the green selective depressant for the clean flotation of phosphate ores. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 282, 124532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Q.; Qiu, T.; Yan, H.; Li, Y. Flotation separation of bastnaesite from fluorite with an eco-friendly depressant polyepoxysuccinic acid and its depression mechanism. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 590, 152941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yao, Q.; Jiao, Q.; Liu, B.; Chen, H. Polyepoxysuccinic acid with hyper-branched structure as an environmentally friendly scale inhibitor and its scale inhibition mechanism. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2019, 23, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magadia, P.; Abdulla, S.; Elbashier, E.; Hussein, I.A.; Khaled, M.; Saad, M. Geometrical and electronic analysis of polyepoxysuccinic acid (PESA) for iron sulfide scale inhibition in oil wells. Polymers 2022, 14, 5433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- API RP 13B-1; Recommended Practice for Field Testing Water- Based Drilling Fluids, 4th ed. American Petroleum Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2009.
- ISO 10414-1:2008; Petroleum and Natural Gas Industries—Field Testing of Drilling Fluids—Part 1: Water- Based Fluids. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- Humood, M.; Ghamary, M.H.; Lan, P.; Iaccino, L.L.; Bao, X.; Polycarpou, A.A. Influence of additives on the friction and wear reduction of oil-based drilling fluid. Wear 2019, 422–423, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villabona-Estupiñán, S.; Rodrigues, J.d.A.; Nascimento, R.S.V. Understanding the clay-PEG (and hydrophobic derivatives) interactions and their effect on clay hydration and dispersion: A comparative study. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 143, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 16783.1-2014; Petroleum and Natural Gas Industries- Field Testing of Drilling Fluids—Part 1: Water- Based Fluids. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2014. Available online: https://www.renrendoc.com/paper/239697926.html (accessed on 11 January 2024).
- González, R.; Bartolomé, M.; Blanco, D.; Viesca, J.L.; Fernández-González, A.; Battez, A.E.H. Effectiveness of phosphonium cation-based ionic liquids as lubricant additive. Tribol. Int. 2016, 98, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshio, T.; Minfray, C.; Dassenoy, F.; Galipaud, J.; Yagishita, K. Dialkyl phosphonate with carboxylic acid as antiwear additives for ester-base lubricants. Wear 2023, 530–531, 205042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Røn, T.; Lee, S. Reduction in friction and wear of alumina surfaces as assisted with surface-adsorbing polymers in aqueous solutions. Wear 2016, 368–369, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, D.; Limbert, G.; Burdett, B.; Wood, R. Interpreting the effects of interfacial chemistry on the tribology of diamond-like carbon coatings against steel in distilled water. Wear 2013, 302, 918–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, Y.; Rahim, E.A.; Singh, N.K.; Sharma, A.; Singla, A.; Palamanit, A. Friction and wear characteristics of chemically modified mahua (madhuca indica) oil based lubricant with SiO2 nanoparticles as additives. Wear 2022, 508–509, 204463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Chen, F.; Han, J.; Tian, T.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, J. Evaluation of Arginine-Modified Polyepoxysuccinic Acid as Anti-scaling and Anti-corrosion Agent. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2021, 44, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, F.; Peng, C.; Liu, L. Investigation on hydration layers of fine clay mineral particles in different electrolyte aqueous solutions. Powder Technol. 2015, 283, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DU, W.; Wang, X.; Bi, T.; Liu, M.; Zhang, J.; Chen, G. Synthesis and Inhibitive mechanism of a novel clay hydration inhibitor for water-based drilling fluids. Mater. Sci. 2021, 27, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barati, P.; Keshtkar, S.; Aghajafari, A.; Shahbazi, K.; Momeni, A. Inhibition performance and mechanism of Horsetail extract as shale stabilizer. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2016, 43, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Qiu, Z.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, D.; Huang, W. Minimization shale hydration with the combination of hydroxyl-terminated PAMAM dendrimers and KCl. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 8484–8501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Elella, M.H.; Goda, E.S.; Gab-Allah, M.A.; Hong, S.E.; Pandit, B.; Lee, S.; Gamal, H.; Rehman, A.U.; Yoon, K.R. Xanthan gum-derived materials for applications in environment and eco-friendly materials: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Fan, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Yuan, J.; Yu, Y. Partially gelatinized corn starch as a potential environmentally friendly warp-sizing agent. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 3195–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Li, M.-C.; Lv, K.; Sun, J.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Shen, H.; Dai, L.; Lalji, S.M. Cellulose derivatives as environmentally-friendly additives in water-based drilling fluids: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 342, 122355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, Q.; Nan, Q.; Zhang, M.; Sun, W. Inhibition, dispersion and corrosion performance of a novel modified polyepoxysuccinic acid. Desalination Water Treat. 2020, 173, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y. Inhibition and dispersion of polyepoxysuccinate as a scale inhibitor. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, S159–S161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Shu, Z.; Chen, L.; Yan, P.; Li, B.; Yuan, C.; Jian, L. Low temperature green nano-composite vegetable-gum drilling fluid. Appl. Nanosci. 2019, 9, 1579–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deville, J.P.; Fritz, B.; Jarrett, M. Development of water-based drilling fluids customized for shale reservoirs. SPE Drill. Complet. 2011, 26, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katende, A.; Boyou, N.V.; Ismail, I.; Chung, D.Z.; Sagala, F.; Hussein, N.; Ismail, M.S. Improving the performance of oil based mud and water based mud in a high temperature hole using nanosilica nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 577, 645–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Lin, Y.; Xue, Y. Effect of ester based lubricant SMJH-1 on the lubricity properties of water based drilling fluid. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2015, 135, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwally, M.; Nguyen, T.; Wiggins, H.; Saasen, A.; Gipson, M.; Yoo, H. Evaluations of polyacrylamide water-based drilling fluids for horizontal drilling in the Shaly Wolfcamp formation. SPE J. 2023, 28, 1744–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, D.G.; Silva, A.d.P.d.; Cajaiba, J.; Pérez-Gramatges, A.; Lachter, E.R.; Nascimento, R.S.V. Influence of glycerides–xanthan gum synergy on their performance as lubricants for water-based drilling fluids. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 41085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosimbescu, L.; Vellore, A.; Ramasamy, U.S.; Burgess, S.A.; Martini, A. Low molecular weight polymethacrylates as multi-functional lubricant additives. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 104, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, J.R.; Macakova, L.; Chojnicka-Paszun, A.; de Kruif, C.G.; de Jongh, H.H.J. Lubrication, adsorption, and rheology of aqueous polysaccharide solutions. Langmuir 2011, 27, 3474–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Guo, D.; Xie, G. Nanoscale lubricating film formation by linear polymer in aqueous solution. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112, 4765674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-L.; Zhang, S.-S.; Liu, T.-L.; Wu, S.-H.; Yang, Z.-C.; Chen, W.-T.; Chen, R. Improved open-circuit voltage and ambient stability of CsPbI2Br perovskite solar cells by incorporating CH3NH3Cl. Rare Met. 2019, 39, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Peng, N.; Chen, P. Filter cake formation process by involving the influence of solid particle size distribution in drilling fluids. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2020, 79, 103350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Kong, X.; Chen, S.; Grady, B.P.; Qiu, Z. Preparation, characterization and filtration control properties of crosslinked starch nanospheres in water-based drilling fluids. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 325, 115221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Huang, X.-B.; Sun, J.-S.; Lv, K.-H.; Meng, X.; Zhang, Z. Improving the anti-collapse performance of water-based drilling fluids of Xinjiang Oilfield using hydrophobically modified silica nanoparticles with cationic surfactants. Pet. Sci. 2022, 20, 1768–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, R.; Qu, Y. Treatment of drilling fluid waste during oil and gas drilling: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 19662–19682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Fluid Compositions | Unit | Fluid A | Fluid B | Fluid C | Fluid D | Fluid E | Function | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base fluid * | Fresh water | g | 100 | 98.3 | 96.2 | 88.0 | 84.5 | Continuous phase |
| PESA ** | g | 0 | 5.2 | 17.0 | 29.4 | 45.5 | ||
| NaOH | g | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | Alkalinity regulator | |
| PAC-LV | g | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | Filtration reducer | |
| PHPA | g | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | Shale inhibitor | |
| Xanthan gum | g | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | Flow pattern regulator | |
| Starch | g | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | Filtration reducer | |
| Barite | g | 25.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | Weighting agent | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
You, F.; Wu, Y.; Gong, X.; Zheng, Y. Multifunctional High-Concentration Polyepoxysuccinic Acid for Water-Based Drilling Fluids: Achieving Ultra-Low Friction and Filtration. Polymers 2025, 17, 751. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060751
You F, Wu Y, Gong X, Zheng Y. Multifunctional High-Concentration Polyepoxysuccinic Acid for Water-Based Drilling Fluids: Achieving Ultra-Low Friction and Filtration. Polymers. 2025; 17(6):751. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060751
Chicago/Turabian StyleYou, Fuchang, Yu Wu, Xingguang Gong, and Yancheng Zheng. 2025. "Multifunctional High-Concentration Polyepoxysuccinic Acid for Water-Based Drilling Fluids: Achieving Ultra-Low Friction and Filtration" Polymers 17, no. 6: 751. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060751
APA StyleYou, F., Wu, Y., Gong, X., & Zheng, Y. (2025). Multifunctional High-Concentration Polyepoxysuccinic Acid for Water-Based Drilling Fluids: Achieving Ultra-Low Friction and Filtration. Polymers, 17(6), 751. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060751







