Hygrothermal Treatment Improves the Dimensional Stability and Visual Appearance of Round Bamboo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Characterizing Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectra
2.4. Dimensional Stability
2.5. Visual Appearance Quantification of Round Bamboo
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
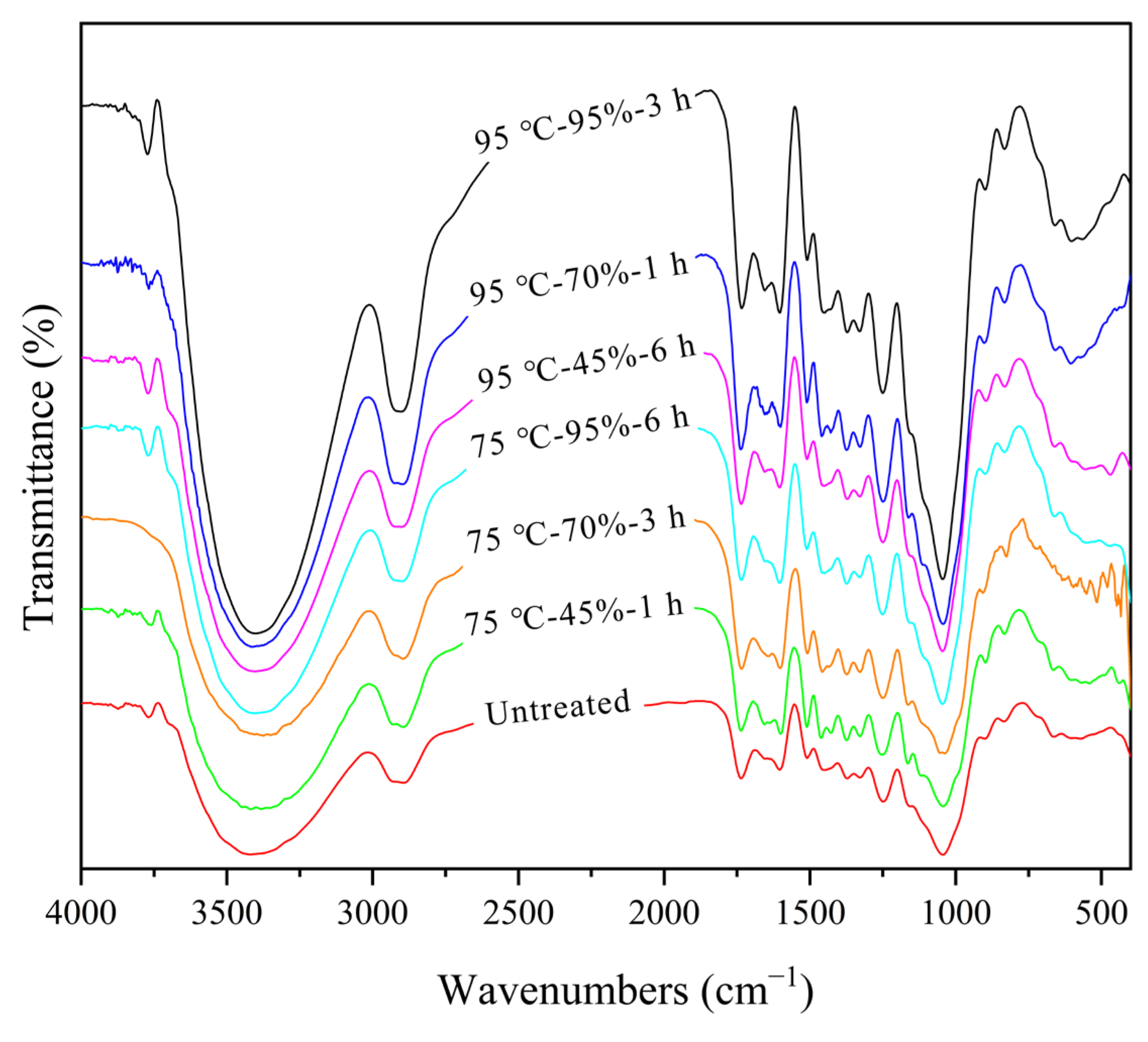
3.1. Chemical Structure of Round Bamboo
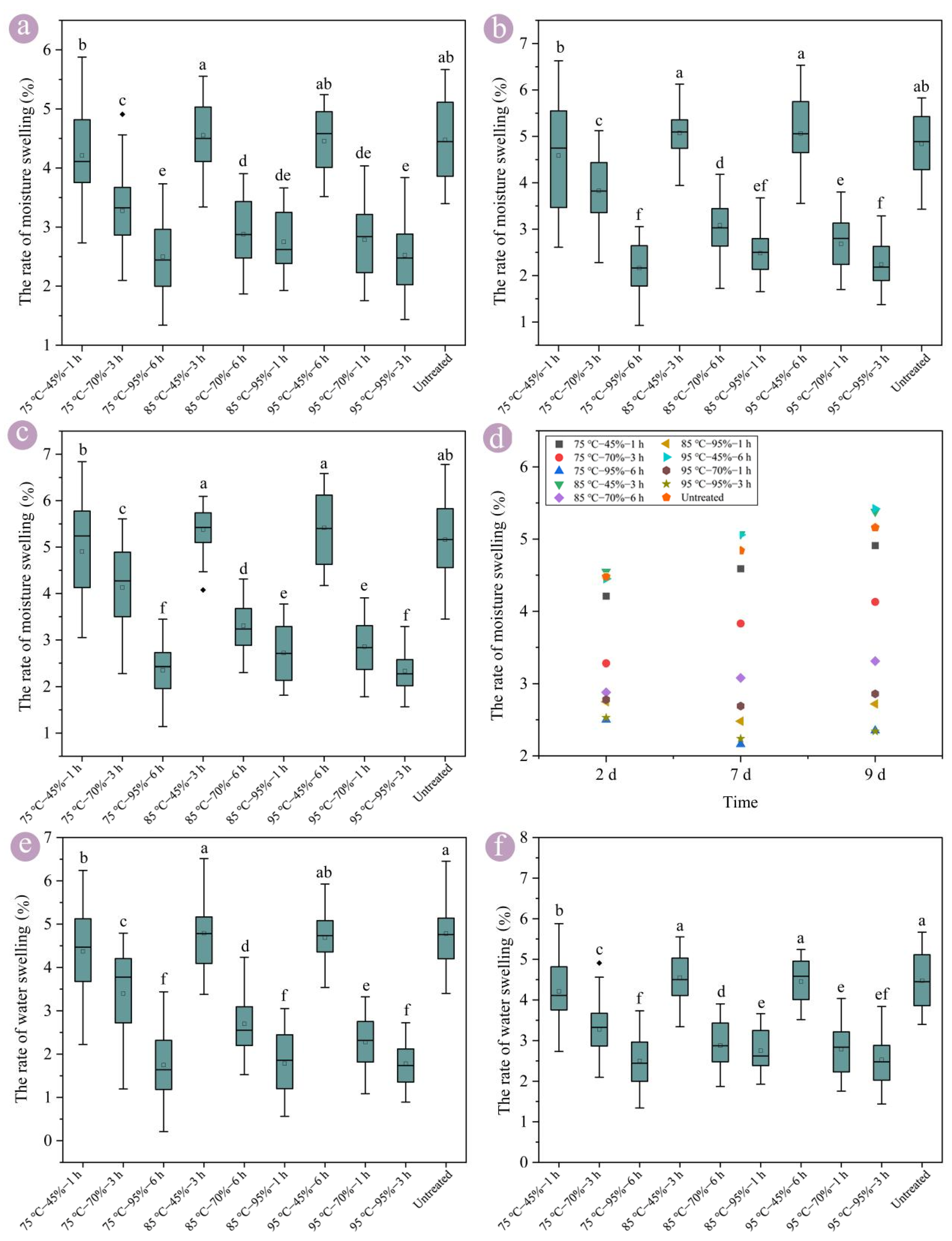
3.2. Swelling of Round Bamboo
3.3. Shrinkage of Round Bamboo
3.4. Optimization of Modification Conditions
3.5. Visual Appearance of Round Bamboo
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.J.; Du, H.Q.; Mao, F.J.; Zhou, G.M.; Xing, L.Q.; Liu, T.Y.; Han, N.; Liu, E.B.; Ge, H.L.; Liu, Y.L.; et al. Mapping spatiotemporal decisions for sustainable productivity of bamboo forest land. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 939–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Yang, K.L.; Yuan, Z.Q.; Liu, Z.M.; Li, X.Y.; Liu, S.J.; Li, C.C.; Meng, S.T.; Wu, R.M. Effect of physical treatment methods on the properties of natural bamboo materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 394, 132170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, M.J.; Li, Y.J.; Xu, X.J.; Fu, R. Anti-mold and hydrophobicity of cutinized bamboo prepared via different annealing processes. Ind. Crop Prod. 2022, 187, 115399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Y.; Ma, Y.F.; Liu, L.T.; Fei, B.H.; Fang, C.H. A novel bamboo engineering material with uniform density, high strength, and high utilization rate. Ind. Crop Prod. 2022, 184, 115045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, L.M.D.; Innocentini, M.D.D.; Kadivar, M.; Savastano, H., Jr. An exploratory study on bamboo permeability for evaluation of treatability with chemical solutions. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 40, 109719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.F.; He, L.X.; Xu, K.; Zhao, X.Y.; Gao, J.J.; He, Z.B.; Yi, S.L. Effects of different pretreatment methods on the dimensional stability of steamed bamboo units. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2023, 81, 1161–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.K.; Chen, X.H.; Huang, B.; Chen, L.; Fang, C.H.; Ma, X.X.; Fei, B.H. Gradient changes in fiber bundle content and mechanical properties lead to asymmetric bending of bamboo. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 395, 132328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Wang, X.K.; Chen, L.; Su, N.; Liu, L.T.; Luan, Y.; Ma, X.X.; Fei, B.H.; Fang, C.H. Impact of the natural structure of cortex and pith ring on water loss and deformation in bamboo processing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.K.; Zhang, S.Q.; Chen, L.; Huang, B.; Fang, C.H.; Ma, X.X.; Liu, H.R.; Sun, F.B.; Fei, B.H. Effects of pith ring on the hygroscopicity and dimensional stability of bamboo. Ind. Crop Prod. 2022, 184, 115027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; He, Y.Y.; Lai, S.Z.; Qi, J.Q.; Zhang, S.B.; Jia, S.S.; Xiao, H.; Chen, Y.Z.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Fei, B.H.; et al. 3D characterization of vascular bundle in moso bamboo node and its effect on compressive properties. Holzforschung 2023, 77, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhang, S.Q.; Semple, K.; Lian, C.P.; Chen, M.L.; Luo, J.J.; Yang, F.; Dai, C.P.; Fei, B.H. Precise microcasting revealing the connectivity of bamboo pore network. Ind. Crop Prod. 2021, 170, 113787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Fei, B.H.; Liu, S.Q. The relationship between moisture content and shrinkage strain in the process of bamboo air seasoning and cracking. Dry. Technol. 2020, 40, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.F.; Chen, X.F.; Liu, X.M.; Fang, C.H.; Liu, H.R.; Zhang, B.; Fei, B.H. The vacuum-assisted microwave drying of round bamboos: Drying kinetics, color and mechanical property. Mater. Lett. 2018, 223, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.R.; Abdullah, U.H.; Ashaari, Z.; Hamid, N.H.; Hua, L.S. Hydrothermal modification of wood: A review. Polymers 2021, 13, 2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, H.J.; Xu, C.; Li, J.; Kong, F.X.; Cai, Y.C. Effects of pretreatment with saturated wet air and steaming on the high-frequency vacuum drying characteristics of wood. Bioresources 2019, 14, 9601–9610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashti, H.; Tarmian, A.; Faezipour, M.; Hedjazi, S.; Shahverdi, M. Effect of pre-steaming on mass transfer properties of fir wood (Abies alba L.); A gymnosperm species with torus margo pit membrane. Bioresources 2012, 7, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ratnasingam, J.; Grohmann, R.; Scholz, F. Effects of pre-steaming on the drying quality of Rubberwood. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2013, 72, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Z.; Song, L.L.; Cheng, D.L.; Liang, X.Y.; Xu, B. Effects of saturated steam pretreatment on the drying quality of moso bamboo culms. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2019, 77, 949–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Chen, X.F.; Zhang, B.; Liu, X.M.; Fei, B.H. Research on the physico-mechanical properties of moso bamboo with thermal treatment in tung oil and its influencing factors. Materials 2019, 12, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.C.; Zhou, Z.Z.; Zhu, Y.D.; Dai, J.F.; Yu, Y.M.; Song, P.G. High-pressure steam: A facile strategy for the scalable fabrication of flattened bamboo biomass. Ind. Crop Prod. 2019, 129, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.Y.; Chen, J.X.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Xie, F.F.; Lu, Y. Review on wood deformation and cracking during moisture loss. Polymers 2023, 15, 3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Startsev, O.V.; Makhonkov, A.; Erofeev, V.; Gudojnikov, S. Impact of moisture content on dynamic mechanical properties and transition temperatures of wood. Wood Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 12, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vural, D.; Smith, J.C.; Petridis, L. Dynamics of the lignin glass transition. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 20504–20512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.L.; Zhao, Z.J.; He, Z.B.; Yi, S.L. Effects of steaming treatment on crystallinity and glass transition temperature of Eucalyptuses grandis × E. urophylla. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 914–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelte, W.; Clemons, C.; Holm, J.K.; Ahrenfeldt, J.; Henriksen, U.B.; Sanadi, A.R. Thermal transitions of the amorphous polymers in wheat straw. Ind. Crop Prod. 2011, 34, 1053–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Fang, C.H.; Chen, Q.; Fei, B.H. Observing bamboo dimensional change caused by humidity. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 309, 124988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Sui, Z.; Fei, B.H. The microstructure of Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys heterocycla) with tung oil thermal treatment. IAWA J. 2022, 43, 322–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Zhang, X.B.; Fei, B.H. Tung oil improves dimensional stability of flattened bamboo. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2023, 81, 1543–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolya, H.; Kang, C.W. Hygrothermal treated paulownia hardwood reveals enhanced sound absorption coefficient: An effective and facile approach. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 174, 107758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.Q.; Wang, L.H.; Liu, J.L.; Wu, J.Z. FTIR and XPS analysis of the changes in bamboo chemical structure decayed by white-rot and brown-rot fungi. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 280, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzele, S.; van Herwijnen, H.W.G.; Edler, M.; Gindl-Altmutter, W.; Konnerth, J. Cell-layer dependent adhesion differences in wood bonds. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 114, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.L.; Ansari, F.; Zhou, Q.; Berglund, L.A. Wood nanotechnology for strong, mesoporous, and hydrophobic biocomposites for selective separation of oil/water mixtures. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 2222–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stelte, W.; Clemons, C.; Holm, J.K.; Ahrenfeldt, J.; Henriksen, U.B.; Sanadi, A.R. Fuel pellets from wheat straw: The effect of lignin glass transition and surface waxes on pelletizing properties. BioEnerg Res. 2011, 5, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, M.J.; Xu, X.J.; Tang, X.Y.; Li, Y.J. Optimization of supercritical CO2 extraction by response surface methodology, composition analysis and economic evaluation of bamboo green wax. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 330, 129906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.K.; Huang, J.W.; Lin, X.Y.; Xu, K.M.; Ou, R.X.; Wang, X.J.; Zhou, J.H.; Hu, C.S.; Tu, D.Y. A clean and novel drying method for bamboo colorization and in-situ surface wax utilization. Ind. Crop Prod. 2024, 222, 119885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, S.S.; Rials, T.G.; Glasser, W.G. Relaxation behavior of the amorphous components of wood. J. Mater. Sci. 1987, 22, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, T.Y.; Jiang, J.L.; Lu, J.X.; Zhang, Y.L.; Chang, J.M. Temperature-humidity-time equivalence and relaxation in dynamic viscoelastic response of Chinese fir wood. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 227, 116637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Altgen, M.; Rautkari, L. Thermal modification of wood-a review: Chemical changes and hygroscopicity. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 6581–6614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.T.; Cao, M.D.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, J.W.; Wang, H.K.; Yu, Y. Pore structure evolution of bamboo fiber and parenchyma cell wall during sequential chemical removal. Ind. Crop Prod. 2023, 193, 16165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Yuan, J.; Wang, G.; Chen, F.M.; Chen, X.Y.; Jiang, H.; Smith, L.M.; Deng, J.C. Effect of chemical composition and cell structure on water vapor sorption behavior of parenchyma cells and fiber cells in moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). Ind. Crop Prod. 2022, 178, 114652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konopka, D.; Kaliske, M. Transient multi-Fickian hygro-mechanical analysis of wood. Comput. Struct. 2018, 197, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.K.; Chen, F.; Xu, K.M.; Xiang, J.P.; Wang, X.J.; Hu, C.S.; Zhou, Q.F.; Tu, D.Y. Moisture migration mechanism of round bamboo in the radial direction during drying. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 435, 136819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Morita, G.; Inagaki, T.; Tsuchikawa, S. Moisture transport dynamics in wood during drying studied by long-wave near-infrared hyperspectral imaging. Cellulose 2021, 29, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.S.; Luo, S.Y.; Liang, Z.X.; Yan, Q.; Yu, W.F.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, S.F.; Shen, Y.L. Revolutionizing wood permeability via microwave-initiated persulfate activation. Ind. Crop Prod. 2024, 208, 117910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; He, S.; Li, J.P.; Yu, H.; Zhao, S.Q.; Chen, Y.H.; Ma, L.F. Effect of vacuum freeze-drying on enhancing liquid permeability of Moso bamboo. Bioresources 2018, 13, 4159–4174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.F.; Xu, Y.J.; Lin, T.; Liang, Q.P.; Yang, B.; Duan, C. Further understanding of the silicon morphological fundamentals of bamboo culm. Bioresources 2016, 11, 10329–10338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Guan, M.J.; Jia, Q.D.; Wang, G.N.; Pan, L.C.; Li, Y.J. Degradation mechanism of cuticular wax composition and surface properties of bamboo culm during storage. Ind. Crop Prod. 2024, 214, 118558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Z.; Tang, K.; He, L.; Shao, H.J.; Wang, Y.M.; He, Y.Y.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Qi, J.Q.; Chen, Q.; Xie, J.L. Effect of sand blasting treatment on green colour preservation and surface characteristics of Moso bamboo culms. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2022, 80, 1413–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.F.; Ma, X.X.; Zhang, B.; Chen, X.F.; Liu, X.M.; Fang, C.H.; Fei, B.H. Microwave-vacuum drying of round bamboo: A study of the physical properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 211, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Fei, B.H.; Song, W.; Su, N.; Sun, F.B. Tung oil thermal treatment improves the visual effects of moso bamboo materials. Polymers 2022, 14, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, U.P.; Ralph, S.A.; Padmakshan, D.; Liu, S.; Foster, C.E. Estimation of syringyl units in wood lignins by FT-Raman spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 4367–4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.N.; Lee, K.Y.; Rahman, M.S.; Kim, H.J.; Kerr, W.L.; Choi, S.G. Thermal treatment of apple puree under oxygen-free condition: Effect on phenolic compounds, ascorbic acid, antioxidant activities, color, and enzyme activities. Food Biosci. 2021, 39, 100802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.X.; Wang, M.J.; Zhang, P.; Chen, Y.; Gao, J.M.; Fan, Y. The role of phenolic extractives in color changes of locust wood (Robinia pseudoacacia) during heat treatment. Bioresources 2017, 12, 7041–7055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, H.; Hatakeyama, T. Lignin Structure, Properties, and Applications. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2010, 232, 1–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bregado, J.L.; Souto, F.; Secchi, A.R.; Tavares, F.W.; Calado, V. Molecular dynamics study of thermophysical and mechanical properties in hydrated lignin with compositions close to softwood. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2022, 11, 238–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guigo, N.; Mija, A.; Vincent, L.; Sbirrazzuoli, N. Molecular mobility and relaxation process of isolated lignin studied by multifrequency calorimetric experiments. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
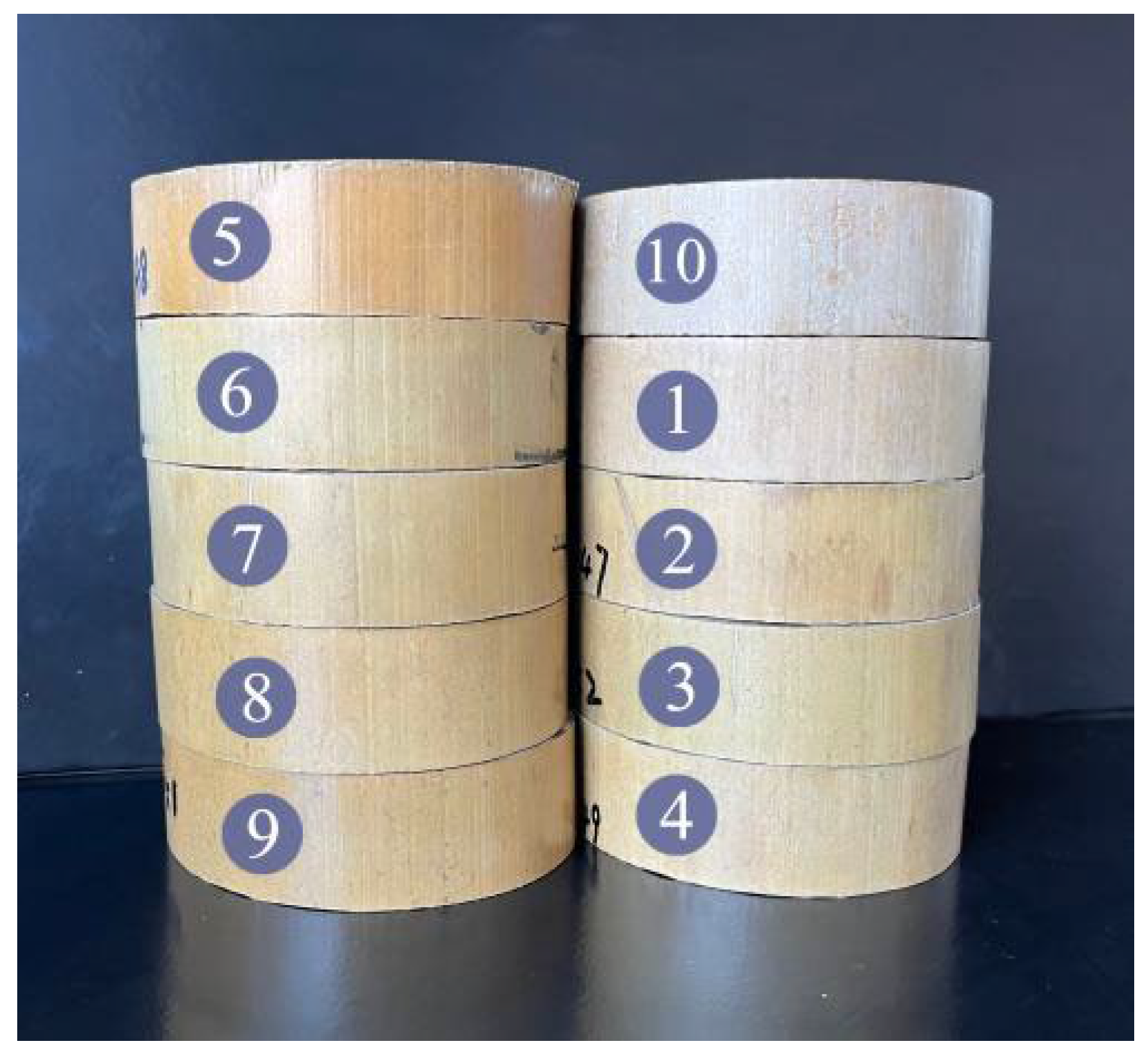
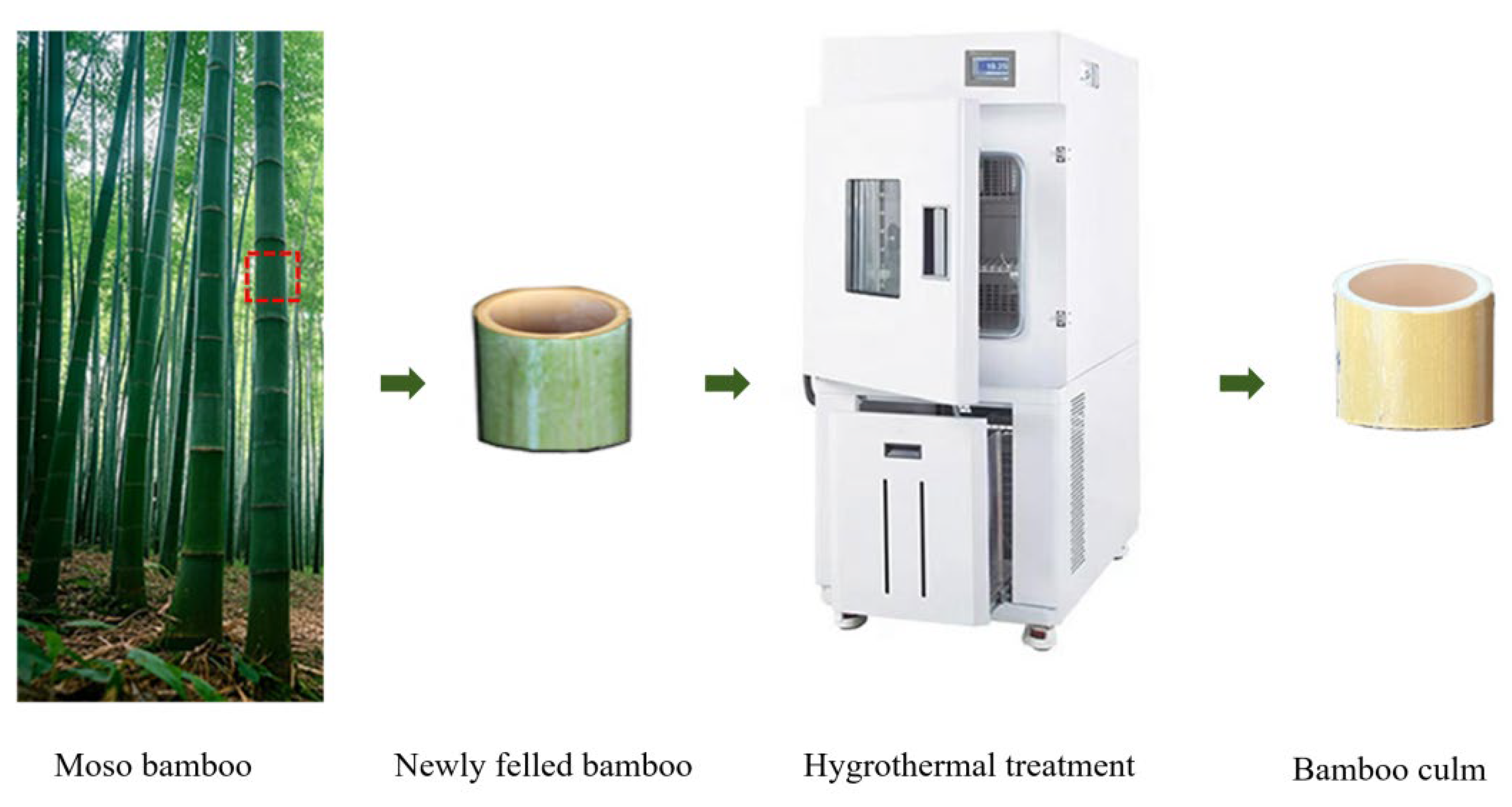


| Experiment No. | Definition | Temperature (°C) | Relative Humidity (%) | Duration (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 75 °C–45%–1 h | 75 | 45 | 1 |
| 2 | 75 °C–70%–3 h | 75 | 70 | 3 |
| 3 | 75 °C–95%–6 h | 75 | 95 | 6 |
| 4 | 85 °C–45%–3 h | 85 | 45 | 3 |
| 5 | 85 °C–70%–6 h | 85 | 70 | 6 |
| 6 | 85 °C–95%–1 h | 85 | 95 | 1 |
| 7 | 95 °C–45%–6 h | 95 | 45 | 6 |
| 8 | 95 °C–70%–1 h | 95 | 70 | 1 |
| 9 | 95 °C–95%–3 h | 95 | 95 | 3 |
| 10 | Untreated | Untreated round bamboo served as the control group | ||
| Dimensional Stability | Index | Factors | K1 | K2 | K3 | R-Value | Primary and Secondary Order | Optimal Combination |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The rate of moisture swelling | 2 d | Temperature (A) | 3.33 | 3.39 | 3.26 | 0.13 | B > C > A | A3B3C1 |
| Relative humidity (B) | 4.41 | 2.98 | 2.59 | 1.82 | ||||
| Time (C) | 3.25 | 3.45 | 3.28 | 0.20 | ||||
| 7 d | Temperature (A) | 3.53 | 3.55 | 3.33 | 0.22 | B > C > A | A3B3C1 | |
| Relative humidity (B) | 4.91 | 3.20 | 2.29 | 2.62 | ||||
| Time (C) | 3.25 | 3.71 | 3.43 | 0.46 | ||||
| 9 d | Temperature (A) | 3.80 | 3.80 | 3.54 | 0.26 | B > C > A | A3B3C1 | |
| Relative humidity (B) | 5.23 | 3.43 | 2.47 | 2.76 | ||||
| Time (C) | 3.49 | 3.95 | 3.69 | 0.46 | ||||
| The rate of water swelling | 7 d | Temperature (A) | 3.17 | 3.09 | 2.91 | 0.26 | B > C > A | A3B3C1 |
| Relative humidity (B) | 4.62 | 2.79 | 1.77 | 2.85 | ||||
| Time (C) | 2.81 | 3.32 | 3.04 | 0.51 | ||||
| 60 d | Temperature (A) | 3.69 | 3.71 | 3.40 | 0.31 | B > C > A | A3B3C1 | |
| Relative humidity (B) | 5.21 | 3.41 | 2.19 | 3.02 | ||||
| Time (C) | 3.27 | 3.92 | 3.61 | 0.65 | ||||
| The rate of shrinkage | 7 d | Temperature (A) | 1.666 | 1.811 | 1.988 | 0.32 | C > A > B | A1B3C1 |
| Relative humidity (B) | 1.888 | 1.899 | 1.677 | 0.22 | ||||
| Time (C) | 1.644 | 1.755 | 2.066 | 0.42 |
| Dimensional Stability | Index | Factors | f | Sum of Square | Mean Square | F | P | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The rate of moisture swelling | 2 d | Temperature (A) | 2 | 1.035 | 0.518 | 1.308 | 0.272 | |
| Relative humidity (B) | 2 | 197.006 | 98.503 | 249.051 | 0.000 | * | ||
| Time (C) | 2 | 2.610 | 1.305 | 3.299 | 0.038 | * | ||
| 7 d | Temperature (A) | 2 | 3.106 | 1.553 | 2.958 | 0.053 | ||
| Relative humidity (B) | 2 | 380.292 | 190.146 | 362.168 | 0.000 | * | ||
| Time (C) | 2 | 11.730 | 5.865 | 11.171 | 0.000 | * | ||
| 9 d | Temperature (A) | 2 | 4.969 | 2.485 | 4.589 | 0.011 | * | |
| Relative humidity (B) | 2 | 425.166 | 212.583 | 392.581 | 0.000 | * | ||
| Time (C) | 2 | 11.189 | 5.595 | 10.332 | 0.000 | * | ||
| The rate of water swelling | 7 d | Temperature (A) | 2 | 3.769 | 1.884 | 3.109 | 0.046 | * |
| Relative humidity (B) | 2 | 449.101 | 224.551 | 370.515 | 0.000 | * | ||
| Time (C) | 2 | 14.246 | 7.123 | 11.753 | 0.000 | * | ||
| 60 d | Temperature (A) | 2 | 6.608 | 3.304 | 4.518 | 0.012 | * | |
| Relative humidity (B) | 2 | 498.144 | 249.072 | 340.567 | 0.000 | * | ||
| Time (C) | 2 | 22.590 | 11.295 | 15.444 | 0.000 | * | ||
| The rate of shrinkage | 7 d | Temperature (A) | 2 | 5.565 | 2.783 | 8.113 | 0.000 | * |
| Relative humidity (B) | 2 | 3.504 | 1.752 | 5.109 | 0.007 | * | ||
| Time (C) | 2 | 10.137 | 5.069 | 14.778 | 0.000 | * |
| Experiment No. | L* | a* | b* | C* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (75 °C–45%–1 h) | 58.14 (2.85) | 4.80 (1.57) | 22.92 (2.89) | 23.46 (2.94) |
| 2 (75 °C–70%–3 h) | 56.95 (2.18) | 7.88 (1.25) | 25.08 (1.94) | 26.30 (2.06) |
| 3 (75 °C–95%–6 h) | 56.06 (1.53) | 7.60 (0.73) | 26.60 (2.70) | 27.67 (2.74) |
| 4 (85 °C–45%–3 h) | 59.28 (1.64) | 7.28 (1.28) | 25.69 (2.11) | 26.73 (2.19) |
| 5 (85 °C–70%–6 h) | 56.58 (1.56) | 9.63 (1.69) | 26.55 (1.69) | 28.28 (1.90) |
| 6 (85 °C–95%–1 h) | 56.30 (1.21) | 7.65 (0.92) | 25.98 (1.86) | 27.75 (2.30) |
| 7 (95 °C–45%–6 h) | 57.13 (1.38) | 7.73 (1.14) | 26.42 (1.97) | 27.69 (2.13) |
| 8 (95 °C–70%–1 h) | 57.80 (1.94) | 7.69 (1.13) | 26.68 (2.79) | 27.79 (2.78) |
| 9 (95 °C–95%–3 h) | 54.39 (1.29) | 9.77 (1.18) | 26.19 (2.46) | 27.96 (2.64) |
| 10 (Untreated) | 63.22 (2.37) | 2.00 (0.81) | 18.36 (2.56) | 18.48 (2.55) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, T.; Fang, C.; Sui, Z.; Fu, C.; Li, X. Hygrothermal Treatment Improves the Dimensional Stability and Visual Appearance of Round Bamboo. Polymers 2025, 17, 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060747
Tang T, Fang C, Sui Z, Fu C, Li X. Hygrothermal Treatment Improves the Dimensional Stability and Visual Appearance of Round Bamboo. Polymers. 2025; 17(6):747. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060747
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Tong, Changhua Fang, Zhen Sui, Chuanle Fu, and Xuelin Li. 2025. "Hygrothermal Treatment Improves the Dimensional Stability and Visual Appearance of Round Bamboo" Polymers 17, no. 6: 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060747
APA StyleTang, T., Fang, C., Sui, Z., Fu, C., & Li, X. (2025). Hygrothermal Treatment Improves the Dimensional Stability and Visual Appearance of Round Bamboo. Polymers, 17(6), 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060747









