Biodegradation in Freshwater: Comparison Between Compostable Plastics and Their Biopolymer Matrices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Design and Field Activity
2.3. Sample Cleaning Procedures
2.4. Spectroscopic Characterization
2.5. Water Contact Angle Measurements
2.6. Thermal Characterization
2.7. Morphological Characterization
2.8. Characterization of Mechanical Properties
2.9. Catalysed Reporter Deposition Fluorescence in Situ Hybridisation (CARD-FISH) and Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM)
2.10. DNA Extraction from Surface-Attached Communities
2.11. Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
3. Results
3.1. Cleaning Procedure Test
3.2. Sample Characterization
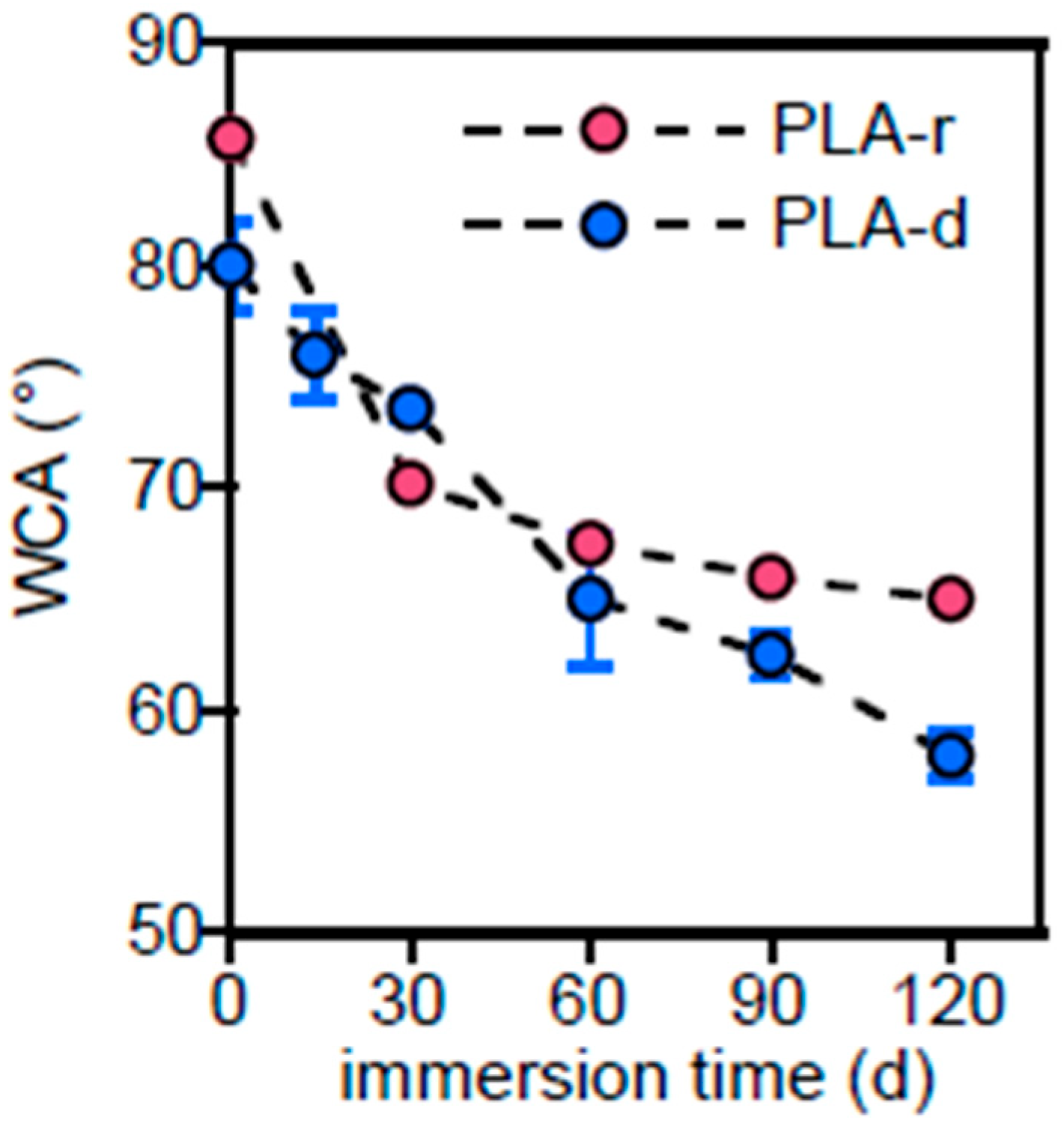
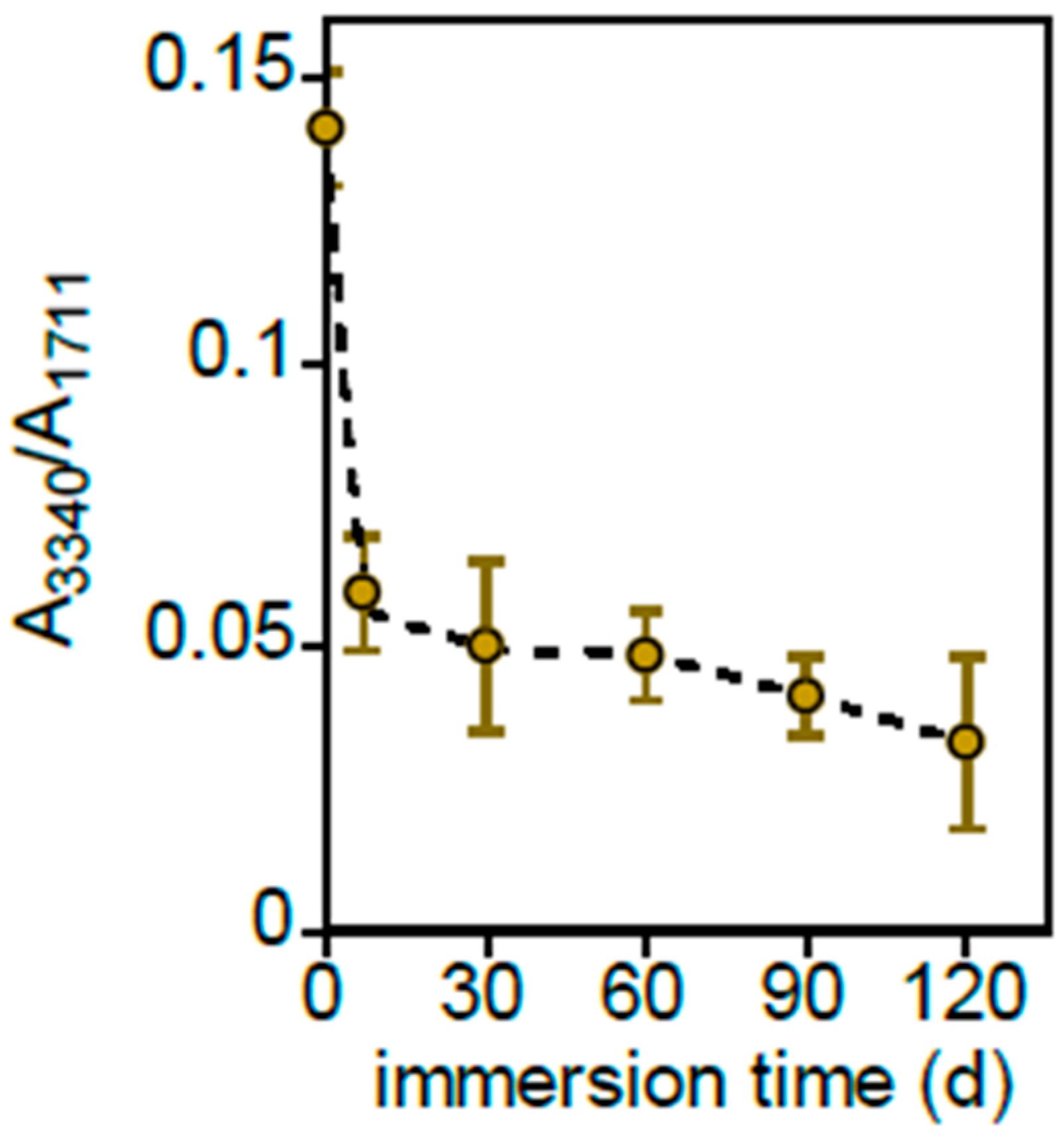
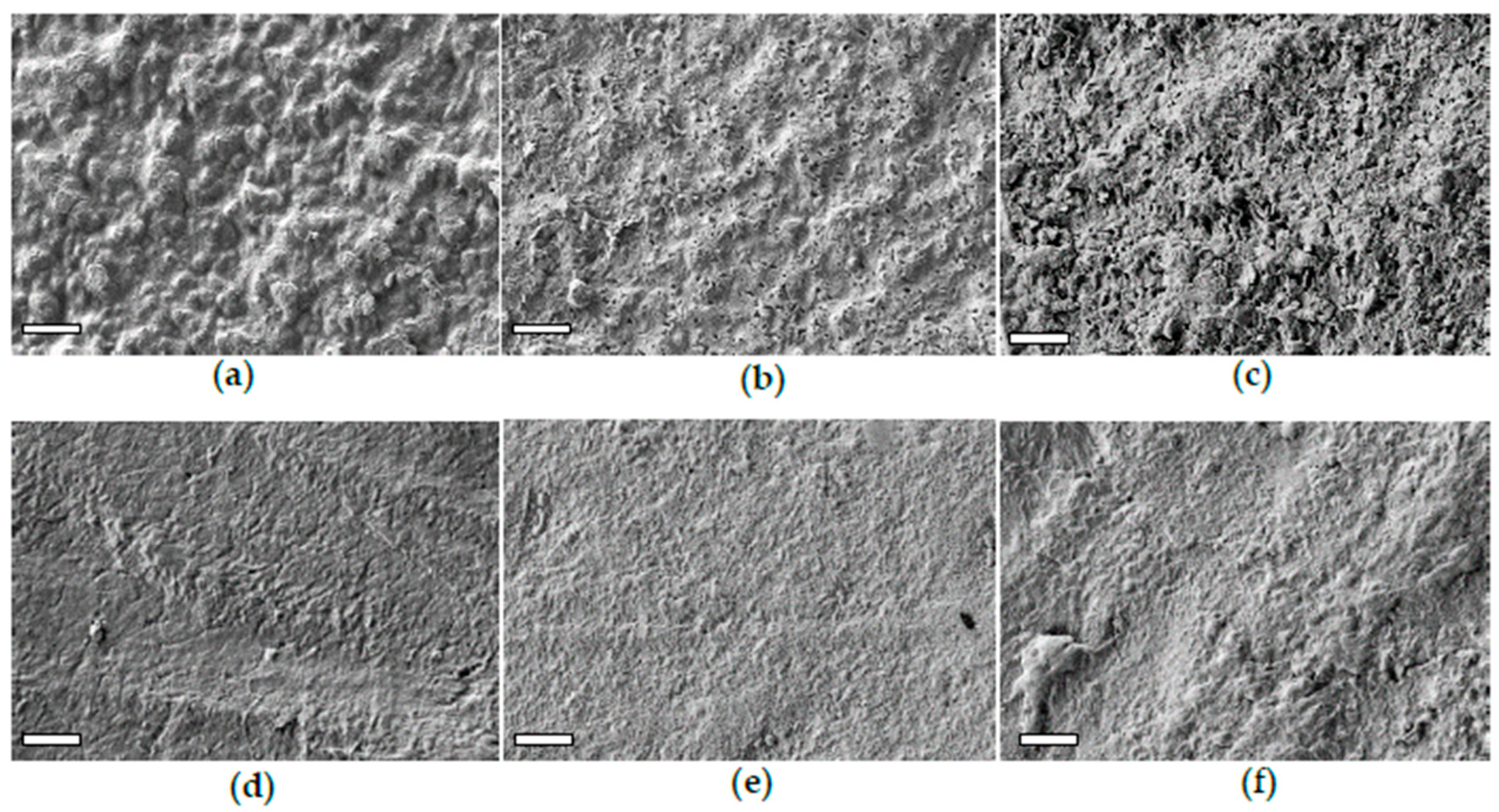
3.2.1. PLA-d and PLA-r Surface Characterization
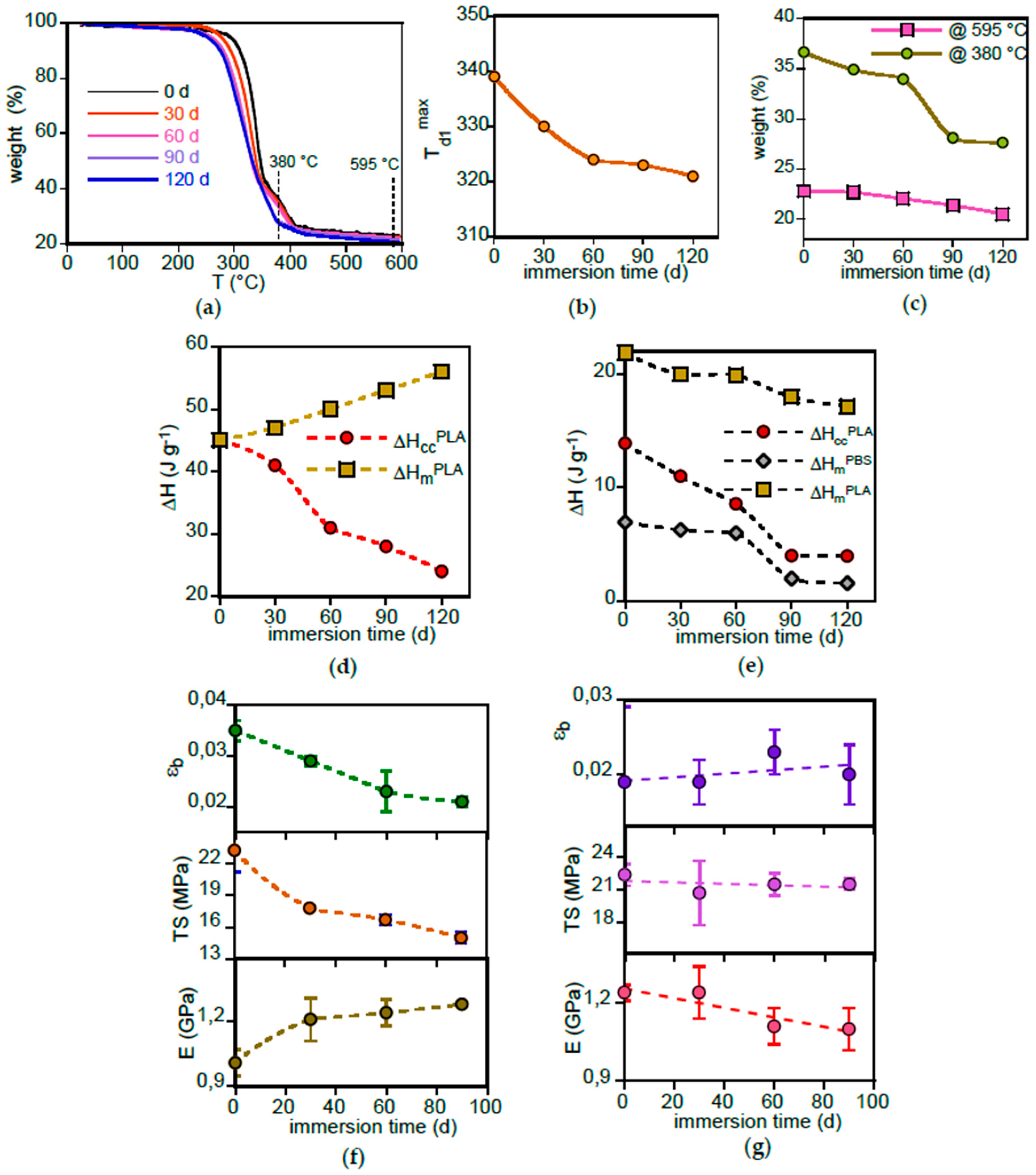
3.2.2. PLA-d and PLA-r Bulk Characterization
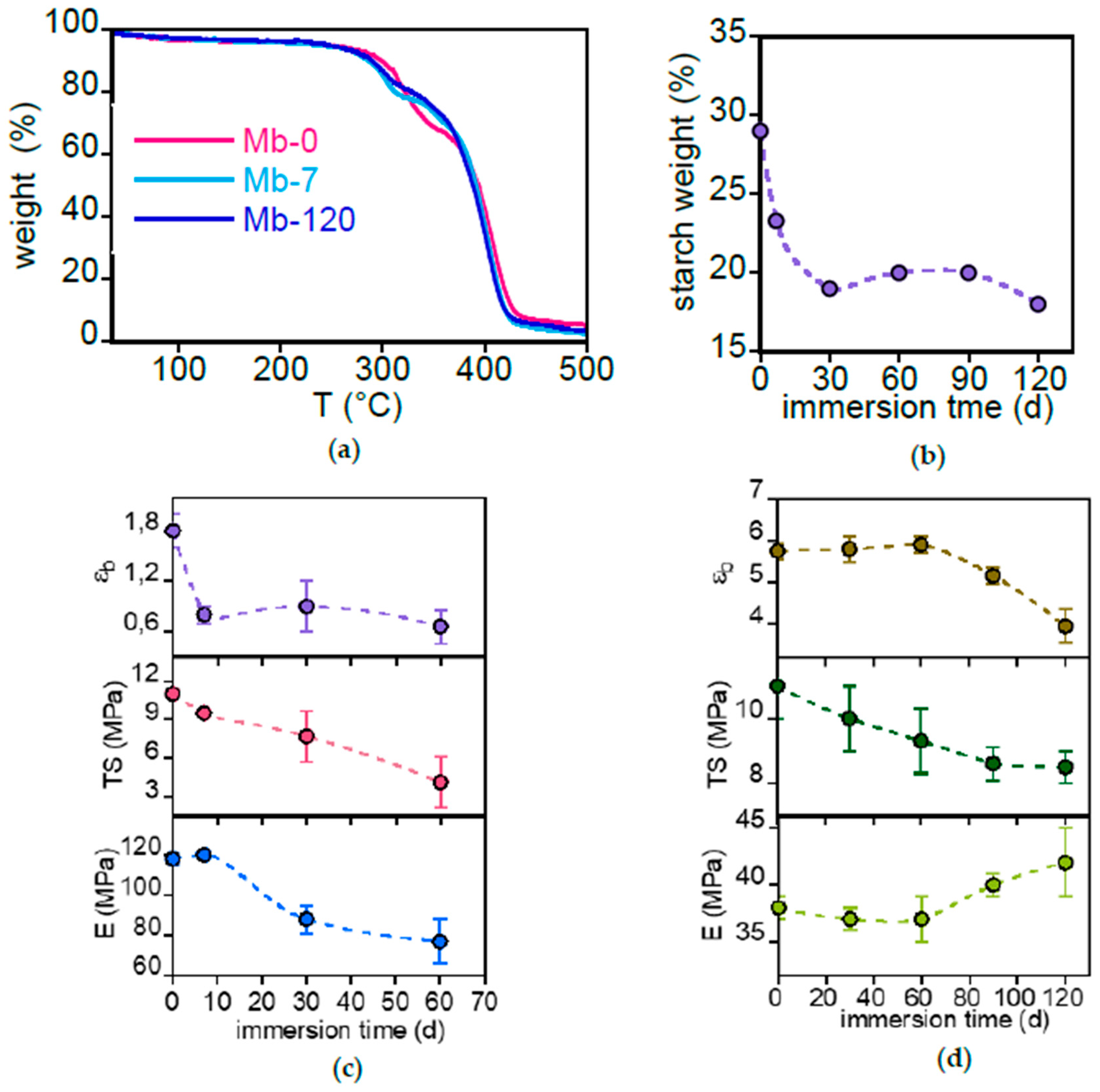
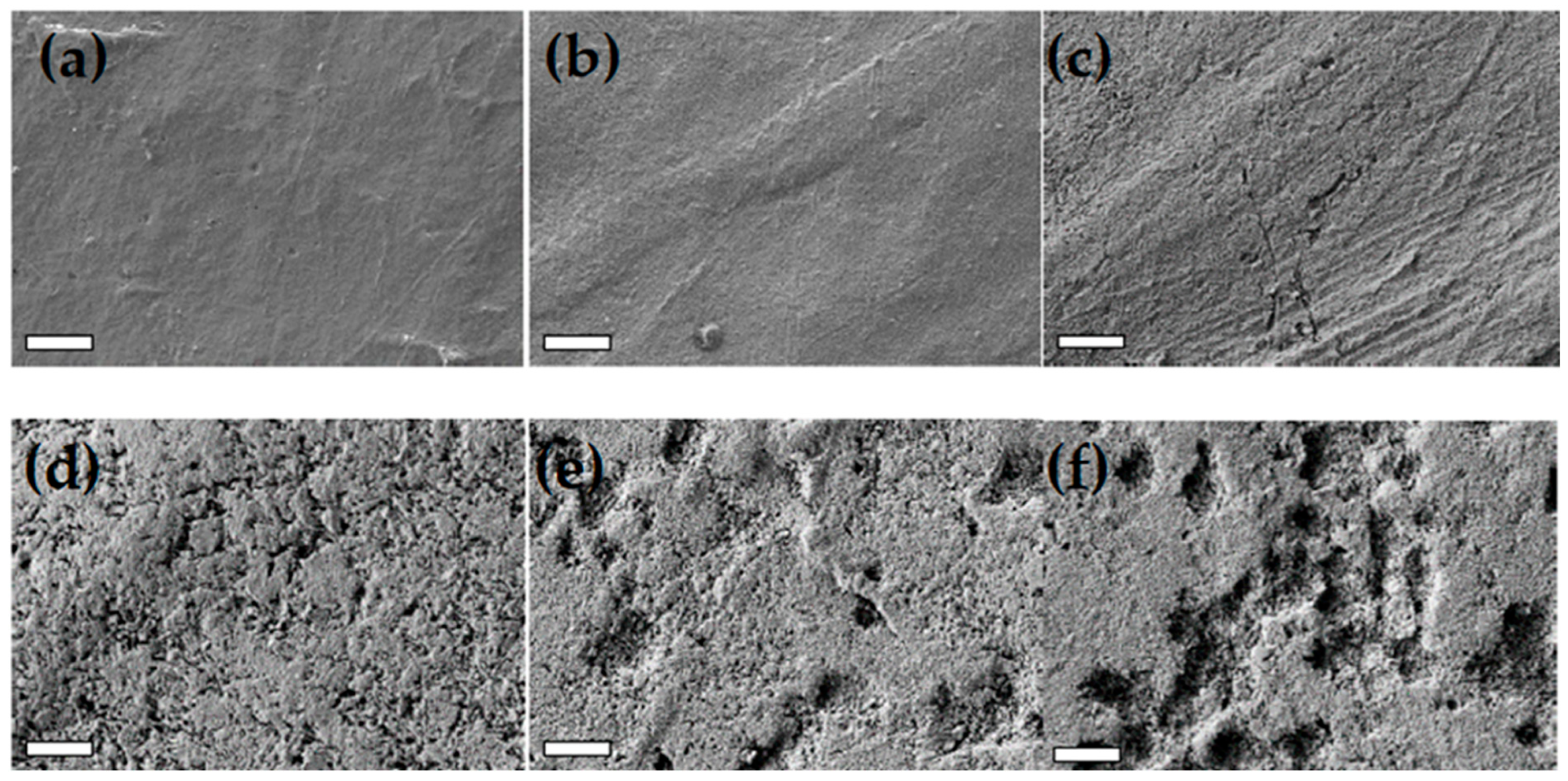
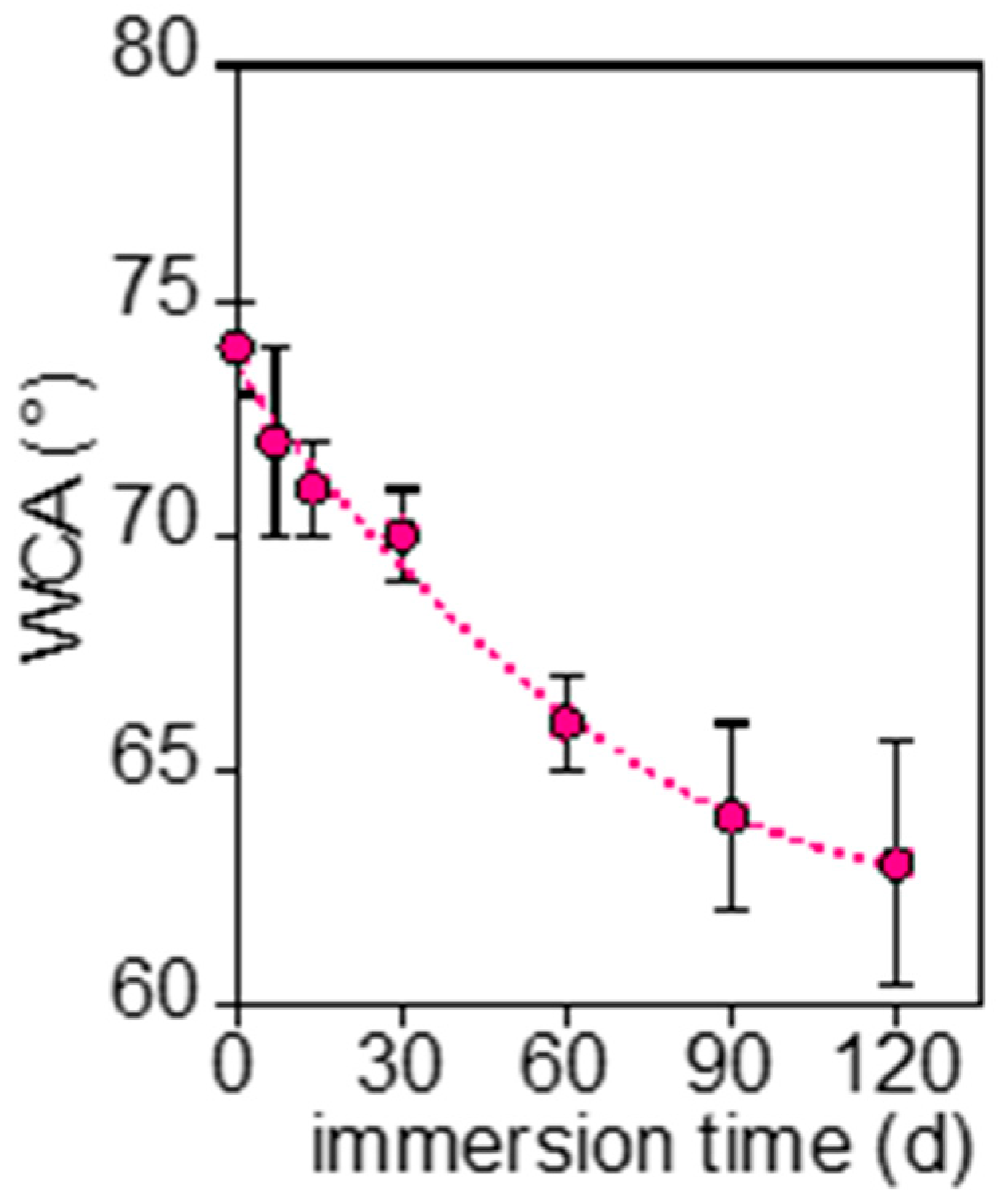
3.2.3. Mb and PBAT Surface Characterization
3.2.4. Mb and PBAT Bulk Characterization
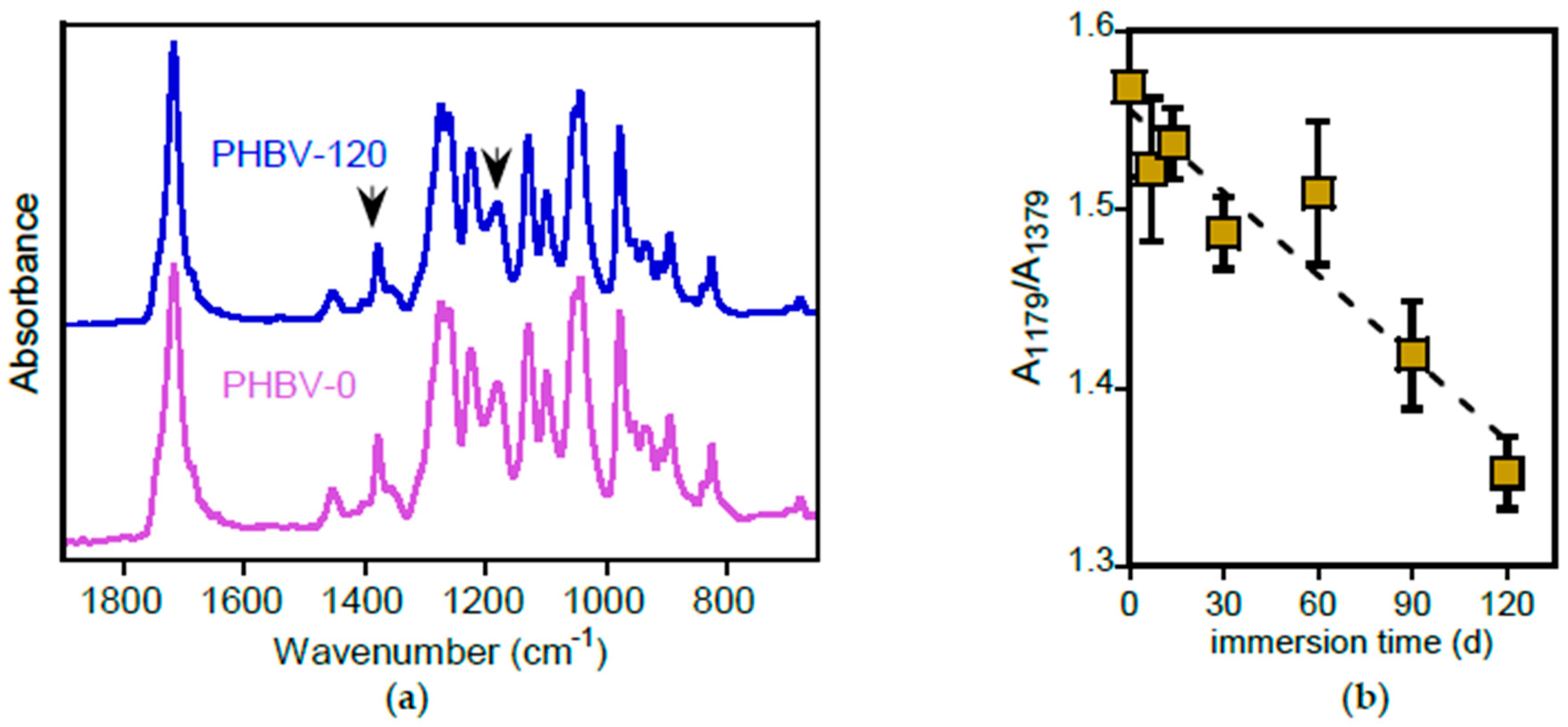
3.2.5. PHA Surface Characterization
3.2.6. PHA Bulk Characterization
3.2.7. PP Characterization
3.3. Quantitative and Imaging-Based Analysis of Microbial Colonization on Polymers
4. Discussion
- ATR-FTIR analysis revealed no direct evidence of biodegradation or degradation in pure polymers or the polymer matrices of commercial plastics, presumably due to the removal of low molecular weight degradation products during the immersion;
- degradation or biodegradation processes primarily occurred at the sample surface at the expense of the amorphous polymer phase;
- so-called compostable materials exhibited leaching of organic (starch in Mater-Bi®) and inorganic (calcium carbonate and talc in PLA-based dishes) fillers, with negligible or limited degradation of the polymer matrix;
- in PLA-based dishes, the leaching of fillers promoted the formation of voids, increasing the surface area available for subsequent degradation processes;
- immersion in water led to an increase in the crystallinity of pure PLA and PHBV films. This increased crystallinity, which may slow down the degradation process, embrittles the samples, thereby facilitating their fragmentation and dispersion in the environment;
- morphological analysis indicated that PHBV appears to degrade at a faster rate compared to the other polyesters investigated;
- the polypropylene (PP) film exhibited surface corrugation, likely attributable to deformation of the outermost layer composed of a compliant propylene-ethylene copolymer. However, its bulk properties remained largely unchanged;
- temporal variations in microbial colonization appeared closely linked to differences in polymer structure and environmental degradability.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thompson, R.C.; Courtene-Jones, W.; Boucher, J.; Pahl, S.; Raubenheimer, K.; Koelmans, A.A. Twenty years of microplastic pollution research—What have we learned? Science 2024, 386, eadl2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, S.; Wagner, M. Microplastics Are Contaminants of Emerging Concern in Freshwater Environments: An Overview in Freshwater Microplastics; Wagner, M., Lambert, S., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 58, pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binelli, A.; Pietrelli, L.; Di Vito, S.; Coscia, L.; Sighicelli, M.; Della Torre, C.; Parenti, C.C.; Magni, S. Hazard evaluation of plastic mixtures from four Italian subalpine great lakes on the basis of laboratory exposures of zebra mussels. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 699, 134366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallitelli, L.; Cera, A.; Cesarini, G.; Pietrelli, L.; Scalici, M. Preliminary indoor evidences of microplastic effects on freshwater benthic macroinvertebrates. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Ma, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, T.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, F. Microbial degradation and other environmental aspects of microplastics/plastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, T.; Gillie, H.; Thomson, A. European Union’s plastic strategy and an impact assessment of the proposed directive on tackling single-use plastics items. In Plastic Waste and Recycling; Letcher, T.M., Ed.; Elsevier: Essex, UK, 2020; pp. 601–633. [Google Scholar]
- Emadian, S.M.; Onay, T.T.; Demirel, B. Biodegradation of bioplastics in natural environments. Waste Manag. 2017, 59, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, J.P.; Boardman, C.; O’Callaghan, K.; Delort, A.M.; Song, J. Biodegradability standards for carrier bags and plastic films in aquatic environments: A critical review. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 171792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasinkova, D.; Serbruyns, L.; Julinova, M.; Bakhsh, A.F.; De Wilde, B.; Koutny, M. Evaluation of the biodegradation of polymeric materials in the freshwater environment—An attempt to prolong and accelerate the biodegradation experiment. Polym. Degr. Stab. 2022, 203, 110085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zettler, E.R.; Mincer, T.J.; Amaral-Zettler, L.A. Life in the “Plastisphere”: Microbial Communities on Plastic Marine Debris. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7137–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amobonye, A.; Bhagwat, P.; Singh, S.; Pillai, S. Plastic biodegradation: Frontline microbes and their enzymes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierzwa-Hersztek, M.; Gondek, K.; Kopeć, M. Degradation of Polyethylene and Biocomponent-Derived Polymer Materials: An Overview. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 600–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.-L.; Xiang, H.; Xiong, H.-Q.; Fang, Y.C.; Wang, Y. Bioremediation of microplastics in freshwater environments: A systematic review of biofilm culture, degradation mechanisms, and analytical methods. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 863, 160953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosiorowska, K.E.; Biniarz, P.; Dobrowolski, A.; Leluk, K.; Mironczuk, A.M. Metabolic engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica for poly(ethylene terephthalate) degradation. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission: Directorate-General for Research and Innovation, Biodegradability of Plastics in the Open Environment; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2021; pp. 1–38.
- Syranidou, E.; Karkanorachaki, K.; Amorotti, F.; Avgeropoulos, A.; Kolvenbach, B.; Zhou, N.Y.; Fava, F.; Corvini, P.F.; Kalogerakis, N. Biodegradation of mixture of plastic films by tailored marine consortia. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 375, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pippo, F.; Bocci, V.; Amalfitano, S.; Crognale., S.; Levantesi, C.; Pietrelli, L.; Di Lisio, V.; Martinelli, A.; Rossetti, S. Microbial colonization patterns and biodegradation of petrochemical and biodegradable plastics in lake waters: Insights from a field experiment. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1290441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pippo, F.; Venezia, C.; Sighicelli, M.; Pietrelli, L.; Di Vito, S.; Nuglio, S.; Rossetti, S. Microplastic-associated biofilms in lentic Italian ecosystems. Water Res. 2020, 187, 116429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, D.; Gupta, K.K.; Chandra, H.; Sharma, K.H.; Sagar, K.; Mori, E.; De Farias, P.A.; Coutinho, H.D.M.; Mishra, A.P. Biodegradation of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) through application of indigenous strain Alcaligenes faecalis ISJ128. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 9391–9409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualandi, C.; Govoni, M.; Foroni, L.; Valente, S.; Bianchi, M.; Giordano, E.; Pasquinelli, G.; Biscarini, F.; Focarete, M.L. Ethanol disinfection affects physical properties and cell response of electrospun poly(l-lactic acid) scaffolds. Eur. Polym. J. 2012, 48, 2008–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.T.; Taylor, L.T.; DeLong, E.F. Quantitative Analysis of Small-Subunit rRNA Genes in Mixed Microbial Populations via 5′-Nuclease Assays. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 4605–4614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czekalski, N.; Berthold, T.; Caucci, S.; Egli, A.; Burmann, H. Increased Levels of Multiresistant Bacteria and Resistance Genes after Wastewater Treatment and Their Dissemination into Lake Geneva, Switzerland. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Kopitzky, R.; Tolga, S.; Kabasci, S. Polylactide (PLA) and Its Blends with Poly(butylene succinate) (PBS): A Brief Review. Polymers 2019, 11, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyavahare, O.; Ng, D.; Hsu, S.L. Analysis of Structural Rearrangements of Poly(lactic acid) in the Presence of Water. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 4185–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Yu, J.; Zhang, X. Thermal, crystallization, and mechanical properties of polylactic acid (PLA)/poly(butylene succinate) (PBS) blends. Polym. Bull. 2024, 81, 2481–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koca, N.; Aversa, C.; Barletta, M. Recycling of poly(lactic acid)/poly(butylene succinate) (PLA/PBS) blends with high amounts of secondary raw material. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2023, 140, e54659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, K.; Cuiffi, J.D.; Mathers, R.T. Ranking environmental degradation trends of plastic marine debris based on physical properties and molecular structure. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min Soo, K.; Hochan, C.; Lei, Z.; Qiang, Y.; Pfleger, B.F.; Klier, J.; Nelson, K.; Majumder, E.; Huber, G.W. A Review of Biodegradable Plastics: Chemistry, Applications, Properties, and Future Research Needs. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 9915–9939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; He, L.; Cai, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, G.; Zhang, D.; Pan, X.; Wang, Y.Z. Deterioration of single-use biodegradable plastics in high-humidity air and freshwaters over one year: Significant disparities in surface physicochemical characteristics and degradation rates. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delacuvellerie, A.; Benali, S.; Cyriaque, V.; Moins, S.; Raquez, J.M.; Gobert, S.; Wattiez, R. Microbial biofilm composition and polymer degradation of compostable and non-compostable plastics immersed in the marine environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artru, M.; Lecerf, A. Slow degradation of compostable plastic carrier bags in a stream and its riparian area. Ann. De Limnol. -Int. J. Limnol. 2019, 55, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.R.; Laforsch, C.; Greiner, A.; Agarwal, S. Fate of So-Called Biodegradable Polymers in Seawater and Freshwater. Glob. Chall. 2017, 1, 1700048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, S.; Wagner, M. Formation of microscopic particles during the degradation of different polymers. Chemosphere 2016, 161, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldas, M.; Rayón, E.; López-Martínez, J.; Arrieta, M.P. A Deeper Microscopic Study of the Interaction between Gum Rosin Derivatives and a Mater-Bi Type Bioplastic. Polymers 2020, 12, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, R.; Alagumalai, K.; Jebapriya, M.; Thulasidhas, D.; Almutairi, T.M. Enhancing PBAT nanocomposite films: The impact of AgVO3 nanorods on mechanical, hydrophobicity, and antibacterial properties. Polym. Compos. 2024, 45, 15340–15355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessini, V.; Arrieta, M.P.; Raquez, J.-M.; Dubois, P.; Kenny, J.M.; Peponi, L. Thermal and composting degradation of EVA/Thermoplastic starch blends and their nanocomposites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2019, 159, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Seligra, P.; Eloy Moura, L.; Famá, L.; Druzian, J.I.; Goyanes, S. Influence of incorporation of starch nanoparticles in PBAT/TPS composite films. Polym. Int. 2016, 65, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatino, R.; Zullo, R.; Di Cesare, A.; Piscia, R.; Musazzi, S.; Corno, G.; Volta, P.; Galafassi, S. Traditional and biodegradable plastics host distinct and potentially more hazardous microbes when compared to both natural materials and planktonic community. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, A.; Zhang, M.; Sharaf, F.; Chengtao, L. Screening and characterization of novel lipase producing Bacillus species from agricultural soil with high hydrolytic activity against PBAT poly (butylene adipate co terephthalate) co-polyesters. Polym. Bull. 2022, 79, 10053–10076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, A.; Zhang, M.; Sharaf, F.; Li, C. Enzymatic degradation of poly (butylene adipate co-terephthalate) (PBAT) copolymer using lipase B from Candida antarctica (CALB) and effect of PBAT on plant growth. Polym. Bull. 2022, 79, 9059–9073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wei, D.; Zheng, A.; Xiao, H. Soil burial biodegradation of antimicrobial biodegradable PBAT films. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 116, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paola Bracciale, M.; De Gioannis, G.; Falzarano, M.; Muntoni, A.; Polettini, A.; Pomi, R.; Rossi, A.; Sarasini, F.; Tirillò, J.; Zonfa, T. Disposable Mater-Bi® bioplastic tableware: Characterization and assessment of anaerobic biodegradability. Fuel 2024, 355, 129361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garalde, R.A.; Thipmanee, R.; Jariyasakoolroj, P.; Sane, A. The effects of blend ratio and storage time on thermoplastic starch/poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) films. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Ye, S.; Liu, Z.; Jing, M.; Liu, C.; Shen, C.; Wang, Y. Self-nucleation in poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) of initially different crystal forms. J. Polym. Sci. 2024, 62, 4101–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.-F.; Bohlén, M.; Lindblad, C.; Hedenqvist, M.; Hakonen, A. Microplastics generated from a biodegradable plastic in freshwater and seawater. Water. Res. 2021, 198, 117123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Wu, G.; Bian, X.; Zeng, J.; Weng, Y. Biodegradation Behavior of Poly(Butylene Adipate-Co-Terephthalate) (PBAT), Poly(Lactic Acid) (PLA), and Their Blend in Freshwater with Sediment. Molecules 2020, 25, 3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshoulles, Q.; Gall Le, M.; Benali, S.; Raquez, J.M.; Dreanno, C.; Arhant, M.; Priour, D.; Cerantola, S.; Stoclet, G.; Le Gac, P.Y. Hydrolytic degradation of biodegradable poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT)—Towards an understanding of microplastics fragmentation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2022, 205, 110122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggero, F.; Carretti, E.; Gori, R.; Lotti, T.; Lubello, C. Monitoring of degradation of starch-based biopolymer film under different composting conditions, using TGA, FTIR and SEM analysis. Chemosphere 2020, 246, 125770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kann, Y.; Shurgalin, M.; Krishnaswamy, R.K. FTIR spectroscopy for analysis of crystallinity of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) polymers and its utilization in evaluation of aging, orientation and composition. Polym. Test. 2014, 40, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Netravali, A.N. A study of physical and mechanical properties of poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) during composting. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2003, 80, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandt, C.; Waeytens, J.; Deniset-Besseau, A.; Nielsen-Leroux, C.; Rejasse, A. Use and misuse of FTIR spectroscopy for studying the bio-oxidation of plastics. Spectrochim Acta. A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 258, 119841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wróbel, M.; Deja-Sikora, E.; Hrynkiewicz, K.; Kowalkowski, T.; Szymanska, S. Microbial Allies in Plastic Degradation: Specific bacterial genera as universal plastic-degraders in various environments. Chemosphere 2024, 363, 142933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyshtva, P.; Voronova, V.; Barbir, J.; Filho, L.; Kroger, S.D.; Witt, G.; Miksch, L.; Saborowski, R.; Gutow, L.; Frank, C.; et al. Degradation of a poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) compound in different environments. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trueba-Santiso, A.; Wimmer, R.; Eskildsen, M.; Cubero-Cardoso, J.; Lema, J.M.; Nielsen, J.L. Reliable methodology to determine biotransformation of PBAT in anaerobic conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 424, 132242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucina, M.; Soggia, G.; De Nisi, P.; Giordano, A.; Adani, F. Assessing the anaerobic degradability and the potential recovery of biomethane from different biodegradable bioplastics in a full-scale approach. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 354, 127224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Biswas, M.K. Management strategies for single-use plastics: Lessons to learn from Indian approach of minimizing microplastic waste. Environ. Sci. Adv. 2023, 2, 1680–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbyszewski, M.; Corcoran, P.L. Distribution and Degradation of Fresh Water Plastic Particles Along the Beaches of Lake Huron, Canada. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 220, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koner, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Chandrasekaran, N. Elucidating the effects of naturally weathered aged-polypropylene microplastics and newly procured polypropylene microplastics on raw 264.7 macrophages. Environ. Sci. Nano. 2024, 11, 983–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Sharma, A.; Batra, N.; Pareek, A. Biodegradation assessment of polythene by microalgae growing on polythene debris from fresh water bodies. Iran. Polym. J. 2025, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample 1 | Sample Code 2 | Features | Thickness (μm) | Tradename and Supplier |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| virgin PLA | PLA-r-X | - Mw = 55.4 kg mol−1 - D-Lactic acid = 1.2% | 120 | Ingeo 3251D NatureWorks |
| PLA-based dish | PLA-d-X | - compostable - composite | ~200 | from market |
| PBAT-based Mater-Bi® shopper | Mb-X | - compostable - composite | 20 | from market |
| virgin PBAT | PBAT-X | - compostable - Mw = 74 kg mol−1 | 120 | Ecoflex® C1200 BASF |
| virgin PHBV | PHBV-X | - HV unit = 3 mol % - Mw = 590 kg mol−1 | 120 | ENMAT Y1000 TianAn Biopolymer |
| Polypropylene | PP-X | - ethylene-propylene copolymer sealable coating | 20 | cigarettes secondary packaging |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bocci, V.; De Vivo, M.; Alfano, S.; Rossetti, S.; Di Pippo, F.; Pietrelli, L.; Martinelli, A. Biodegradation in Freshwater: Comparison Between Compostable Plastics and Their Biopolymer Matrices. Polymers 2025, 17, 2236. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17162236
Bocci V, De Vivo M, Alfano S, Rossetti S, Di Pippo F, Pietrelli L, Martinelli A. Biodegradation in Freshwater: Comparison Between Compostable Plastics and Their Biopolymer Matrices. Polymers. 2025; 17(16):2236. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17162236
Chicago/Turabian StyleBocci, Valerio, Martina De Vivo, Sara Alfano, Simona Rossetti, Francesca Di Pippo, Loris Pietrelli, and Andrea Martinelli. 2025. "Biodegradation in Freshwater: Comparison Between Compostable Plastics and Their Biopolymer Matrices" Polymers 17, no. 16: 2236. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17162236
APA StyleBocci, V., De Vivo, M., Alfano, S., Rossetti, S., Di Pippo, F., Pietrelli, L., & Martinelli, A. (2025). Biodegradation in Freshwater: Comparison Between Compostable Plastics and Their Biopolymer Matrices. Polymers, 17(16), 2236. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17162236









