P(LMA-co-tBMA-co-MAA) Copolymers Bearing Amphiphilic and Polyelectrolyte Characteristics: Synthetic Aspects and Properties in Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of P(LMA-co-tBMA) Copolymers
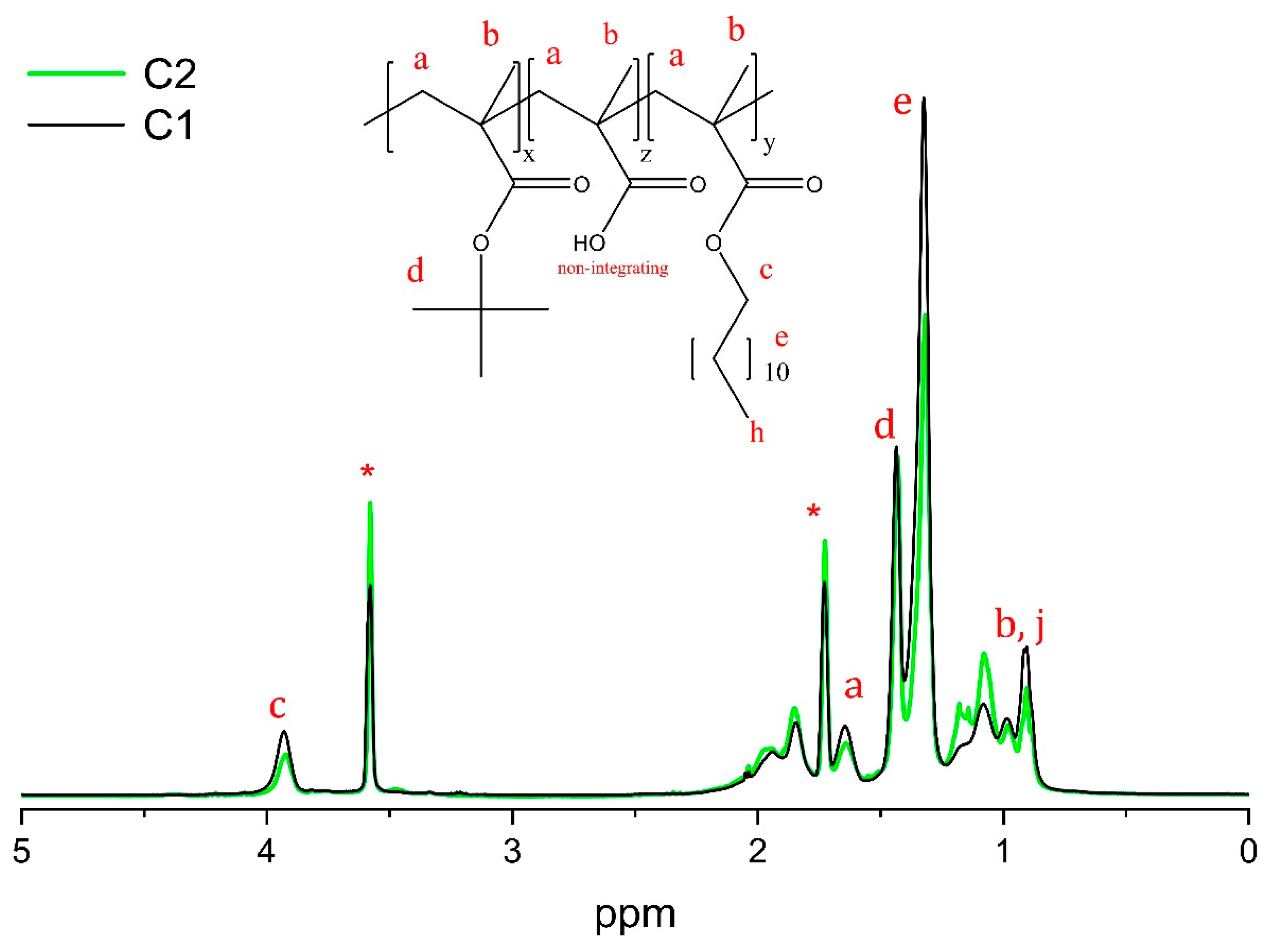
2.3. Selective Acid Hydrolysis of P(LMA-co-tBMA) Copolymers
2.4. Preparation of P(LMA-co-tBMA-co-MAA) Copolymer Nanoassemblies in Aqueous Solutions
2.5. Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC)
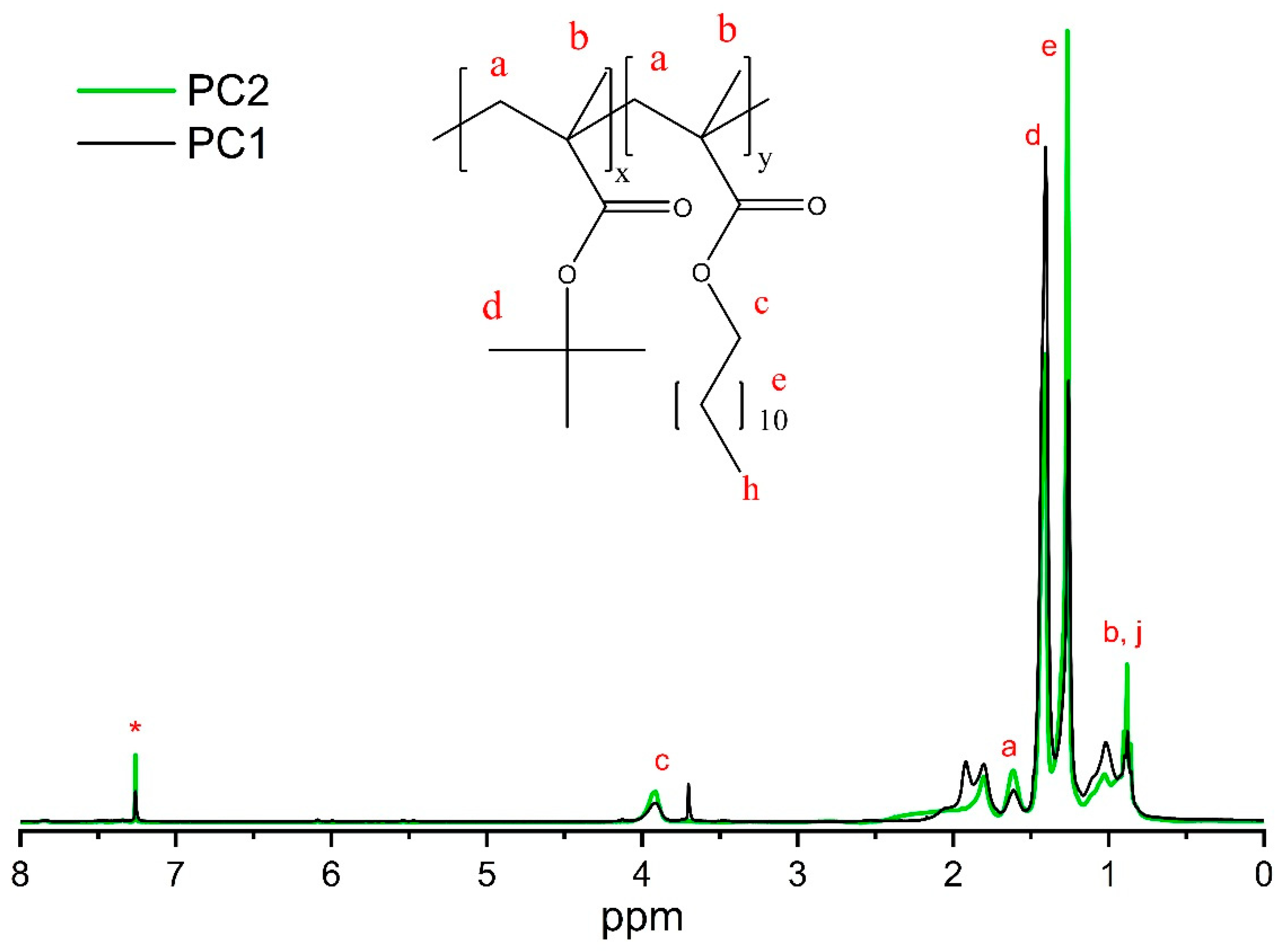
2.6. Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (1H-NMR) Spectroscopy
2.7. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
2.8. Fluorescence Spectroscopy
2.9. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of P(LMA-co-tBMA-co-MAA) Copolymers
3.2. Self-Assembly Studies of P(LMA-co-tBMA-co-MAA) Copolymers in Aqueous Solutions
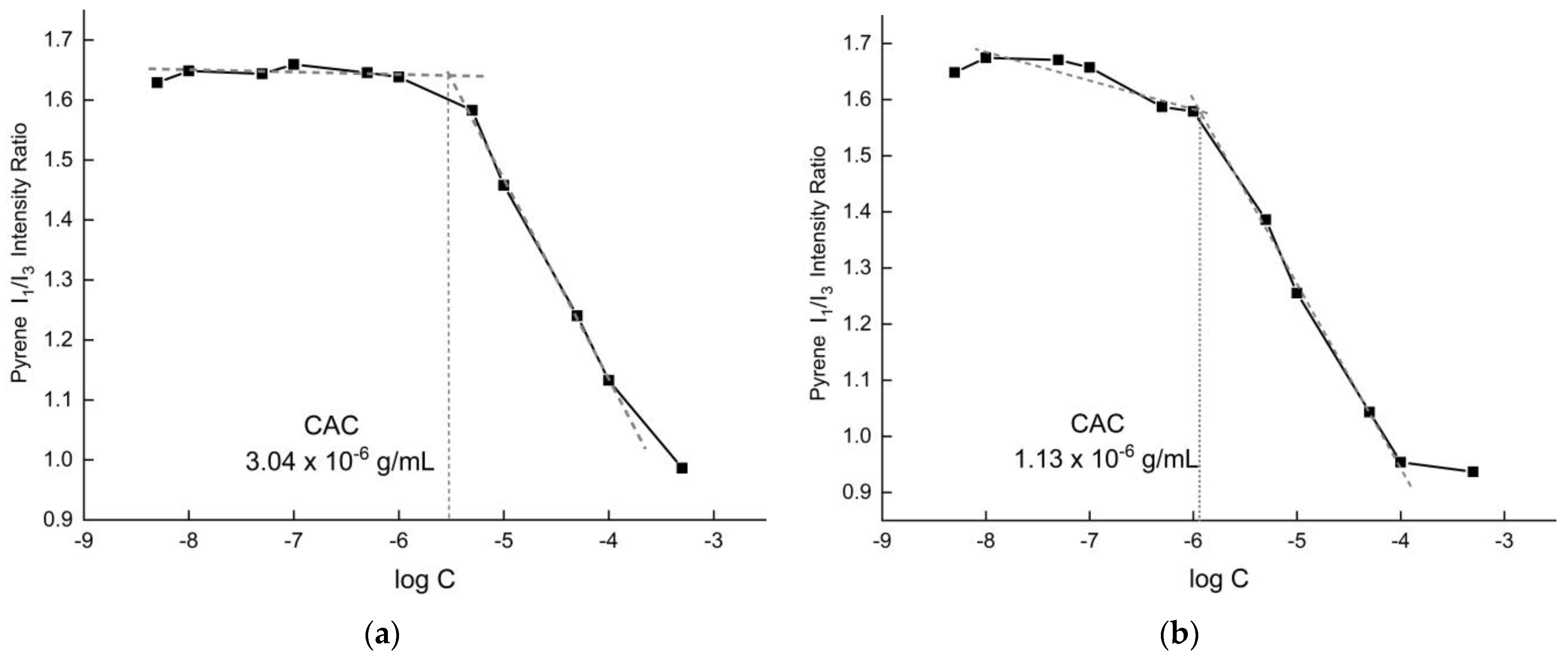
3.2.1. CAC Determination
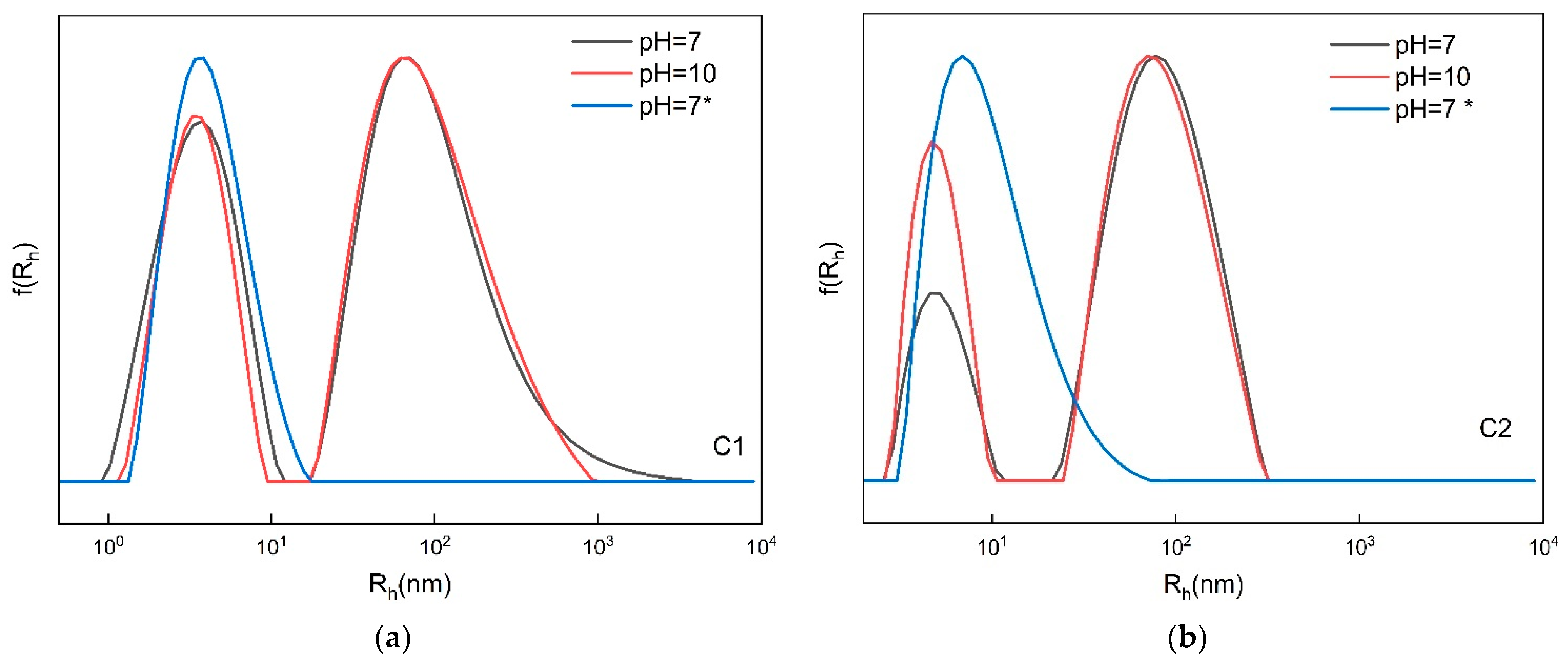
3.2.2. pH-Responsive Self-Assembly
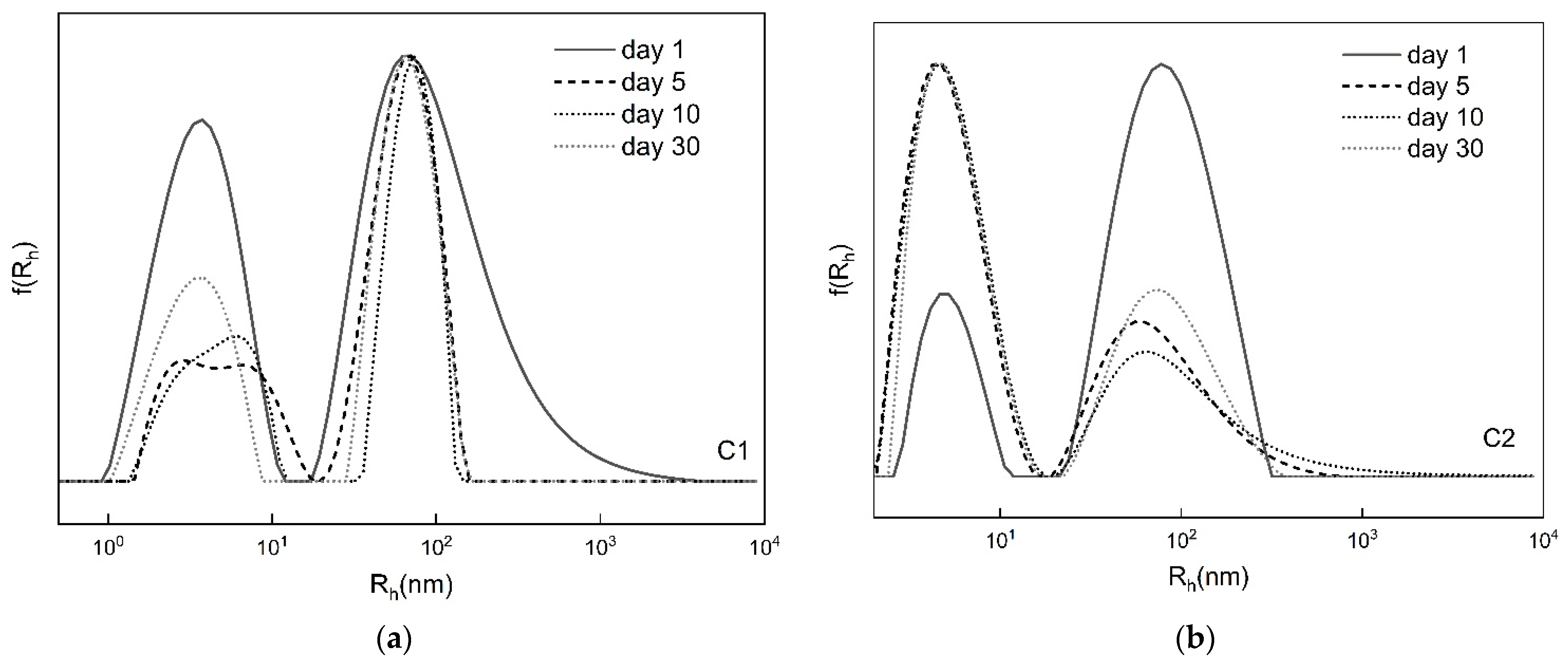
3.2.3. Time-Dependent Self-Assembly
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| C1 | Copolymer 1 |
| C2 | Copolymer 2 |
| PC | Precursor copolymer |
| MAA | Methacrylic acid |
| LMA | Lauryl methacrylate |
| tBMA | Tert-Butyl methacrylate |
| RAFT | Reversible-addition fragmentation chain transfer |
References
- Begines, B.; Ortiz, T.; Pérez-Aranda, M.; Martínez, G.; Merinero, M.; Argüelles-Arias, F.; Alcudia, A. Polymeric Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery: Recent Developments and Future Prospects. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sur, S.; Rathore, A.; Dave, V.; Reddy, K.R.; Chouhan, R.S.; Sadhu, V. Recent Developments in Functionalized Polymer Nanoparticles for Efficient Drug Delivery System. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2019, 20, 100397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karayianni, M.; Pispas, S. Block Copolymer Solution Self-Assembly: Recent Advances, Emerging Trends, and Applications. J. Polym. Sci. 2021, 59, 1874–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, Y.; Eisenberg, A. Self-Assembly of Block Copolymers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 5969–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Jin, B.; Luo, Y.; Li, X. Amphiphilic Block Copolymer Micelles for Gene Delivery. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2022, 38, 1368–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, J.; Mishra, V.; Singh, S.K.; Gulati, M.; Kapoor, B.; Chellappan, D.K.; Gupta, G.; Dureja, H.; Anand, K.; Dua, K.; et al. Harnessing Amphiphilic Polymeric Micelles for Diagnostic and Therapeutic Applications: Breakthroughs and Bottlenecks. J. Control. Release 2021, 334, 64–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trimaille, T.; Lacroix, C.; Verrier, B. Self-Assembled Amphiphilic Copolymers as Dual Delivery System for Immunotherapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 142, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Guo, X.; Choi, B.; Feng, A.; Wei, X.; Thang, S.H. A Facile Synthesis of pH Stimuli Biocompatible Block Copolymer Poly(Methacrylic Acid)-: Block-Poly(N-Vinylpyrrolidone) Utilizing Switchable RAFT Agents. Polym. Chem. 2019, 10, 2083–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsaro, C.; Neri, G.; Santoro, A.; Fazio, E. Acrylate and Methacrylate Polymers’ Applications: Second Life with Inexpensive and Sustainable Recycling Approaches. Materials 2022, 15, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Chan, J.M.; Farokhzad, O.C. pH-Responsive Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 1913–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, A.M.L.; Oliveira, E.E.; Machado, B.A.S.; Marcelino, H.R. Eudragit®-Based Nanoparticles for Controlled Release through Topical Use. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2023, 25, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vshivkov, S.A.; Soliman, T.S.; Kluzhin, E.S.; Kapitanov, A.A. Structure of Poly(Acrylic Acid), Poly(Methacrylic Acid) and Gelatin Solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 294, 111551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yao, W.D.; Rao, Y.F.; Lu, X.Y.; Gao, J.Q. pH-Responsive Carriers for Oral Drug Delivery: Challenges and Opportunities of Current Platforms. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.L.; Yu, W.; Xu, F. pH-Responsive PMAA-b-PEG-b-PMAA Triblock Copolymer Micelles for Prednisone Drug Release and Release Kinetics. Polym. Bull. 2012, 69, 597–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamenova, K.; Radeva, L.; Konstantinov, S.; Petrov, P.D.; Yoncheva, K. Copolymeric Micelles of Poly(ε-Caprolactone) and Poly(Methacrylic Acid) as Carriers for the Oral Delivery of Resveratrol. Polymers 2023, 15, 3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, J.L.; You, H.; Tirrell, D.A. Tuning the Response of a pH-Sensitive Membrane Switch. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 2949–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Ling, P.; Zhang, T. Polymeric Micelles, a Promising Drug Delivery System to Enhance Bioavailability of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs. J. Drug Deliv. 2013, 2013, 340315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, A.; Roy, S.; Menon, S. Amphiphilic Block Copolymers: From Synthesis Including Living Polymerization Methods to Applications in Drug Delivery. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 172, 111224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmelmann, M.; Kurzbach, D.; Koynov, K.; Hinderberger, D.; Zentel, R. Aggregation Behavior of Amphiphilic p(HPMA)-Co-p(LMA) Copolymers Studied by FCS and EPR Spectroscopy. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 4065–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wannasarit, S.; Wang, S.; Figueiredo, P.; Trujillo, C.; Eburnea, F.; Simón-Gracia, L.; Correia, A.; Ding, Y.; Teesalu, T.; Liu, D.; et al. A Virus-Mimicking pH-Responsive Acetalated Dextran-Based Membrane-Active Polymeric Nanoparticle for Intracellular Delivery of Antitumor Therapeutics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1905352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevimli, S.; Knight, F.C.; Gilchuk, P.; Joyce, S.; Wilson, J.T. Fatty Acid-Mimetic Micelles for Dual Delivery of Antigens and Imidazoquinoline Adjuvants. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Xu, C.; Lu, C.; Liu, Q.; Wang, J.; Chu, F. Synthesis of pH-Sensitive and Self-Fluorescent Polymeric Micelles Derived From Rosin and Vegetable Oils via ATRP. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 753808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrier, S. 50th Anniversary Perspective: RAFT Polymerization—A User Guide. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 7433–7447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukova, O.V.; Zaitsev, S.D.; Ryabov, S.A.; Arkhipova, E.V.; Kovaleva, T.F.; Mukhina, I.V. Effect of (co) polymers based on methacrylic acid on the state of cells of the immune system. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2020, 69, 1579–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukova, O.V.; Sergeeva, T.F.; Gavrina, A.I. Modified Poly(T-Butyl Methacrylate) as a Doxorubicin Carrier for Targeted Delivery. Pharm. Chem. J. 2018, 52, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezgin-bayindir, Z.; Ergin, A.D.; Parmaksiz, M.; Elcin, A.E.; Elcin, Y.M.; Yuksel, N. Evaluation of Various Block Copolymers for Micelle Formation and Brain Drug Delivery: In Vitro Characterization and Cellular Uptake Studies. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2016, 36, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.W.; Cui, Z.M.; Ge, X.; Luo, Y.L.; Xu, F. Polymers Prepared through an “ATRP Polymerization-Esterification” Strategy for Dual Temperature-And Reduction-Induced Paclitaxel Delivery. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 28891–28901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Hanson, J.; Shi, Y.; Yao, Y.; Robertson, M.L. Enhancing Mechanical Properties of Sustainable Thermoplastic Elastomers through Incorporating Ionic Interactions. Macromolecules 2024, 57, 8306–8319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairbanks, B.D.; Gunatillake, P.A.; Meagher, L. Biomedical Applications of Polymers Derived by Reversible Addition-Fragmentation Chain-Transfer (RAFT). Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 91, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, M.; Babaei, M.; Zolfaghari, R.; Abnous, K.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Ramezani, M.; Alibolandi, M. Synthesis of a Therapeutic Amphiphilic Copolymer of SN38 via RAFT Polymerization and Its Self-Assembly to Peptomicelles for Fighting against Colon Adenocarcinoma. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 6252–6264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Sun, W.; Liang, X.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, H. The Role of Carboxylic Groups in Heparin-Mimicking Polymer-Functionalized Surfaces for Blood Compatibility: Enhanced Vascular Cell Selectivity. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 201, 111653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chytil, P.; Kostka, L.; Etrych, T. Hpma Copolymer-Based Nanomedicines in Controlled Drug Delivery. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pissuwan, D.; Boyer, C.; Gunasekaran, K.; Davis, T.P.; Bulmus, V. In Vitro Cytotoxicity of RAFT Polymers. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janata, M.; Čadová, E.; Angelisová, P.; Charnavets, T.; Hořejší, V.; Raus, V. Tailoring Butyl Methacrylate/Methacrylic Acid Copolymers for the Solubilization of Membrane Proteins: The Influence of Composition and Molecular Weight. Macromol. Biosci. 2022, 22, e2200284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moad, G. RAFT Polymerization to Form Stimuli-Responsive Polymers. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 177–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iborra, A.; Díaz, G.; López, D.; Giussi, J.M.; Azzaroni, O. Copolymer Based on Lauryl Methacrylate and Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Methyl Ether Methacrylate as Amphiphilic Macrosurfactant: Synthesis, Characterization and Their Application as Dispersing Agent for Carbon Nanotubes. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 87, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.; Heuser, T.; Weyandt, E.; Wang, B.; Walther, A. Polyacid Microgels with Adaptive Hydrophobic Pockets and Ampholytic Character: Synthesis, Solution Properties and Insights into Internal Nanostructure by Cryogenic-TEM. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 8342–8352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Q.; Guo, X.D.; Lin, W.J.; Zhang, L.J.; Zhang, C.Y.; Qian, Y. Amphiphilic Copolymer Brush with Random pH-Sensitive/Hydrophobic Structure: Synthesis and Self-Assembled Micelles for Sustained Drug Delivery. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Simpson, J.D.; Fuchs, A.V.; Rolfe, B.E.; Thurecht, K.J. Effects of Surface Charge of Hyperbranched Polymers on Cytotoxicity, Dynamic Cellular Uptake and Localization, Hemotoxicity, and Pharmacokinetics in Mice. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 4485–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazares-Cortes, E.; Baker, B.C.; Nishimori, K.; Ouchi, M.; Tournilhac, F. Polymethacrylic Acid Shows Thermoresponsivity in an Organic Solvent. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 5995–6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Liu, Y. Self-Assembly of Carbon Nanotubes Modified by Amphiphilic Block Polymers in Selective Solvent. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2009, 210, 2070–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivorotova, T. Synthesis of Polyelectrolytes Containing Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Side Chains by Living Radical Polymerization. Ph.D. Thesis, Vilnius University, Vilnius, Lithuania, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.L.; Huang, R.J.; Xu, F.; Chen, Y.S. pH-Sensitive Biodegradable PMAA2-b-PLA-b-PMAA2 H-Type Multiblock Copolymer Micelles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Drug Release Applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 7730–7741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, F.; Zeng, L. Graphic for Table of Contents Design of Yolk-Shell Fe3O4 @PMAA Composite Microspheres for Adsorption of Metal Ions and pH-Controlled Drug Delivery. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 7065–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ALOthman, Z.A. Preparation and Characterization of Alkyl Methacrylate Capillary Monolithic Columns. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2012, 16, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sert, Y.; Singer, L.M.; Findlater, M.; Doǧan, H.; Çirak, Ç. Vibrational Frequency Analysis, FT-IR, DFT and M06-2X Studies on Tert-Butyl N-(Thiophen-2yl)Carbamate. Spectrochim. Act. A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 128, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Q.; Zheng, L.S.; Guo, X.D.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, L.J. pH-Sensitive Micelles Self-Assembled from Amphiphilic Copolymer Brush for Delivery of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yue, Z.; Xie, J.; Wang, W.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, E.; Cao, Z. Micelles with Ultralow Critical Micelle Concentration as Carriers for Drug Delivery. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 2, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topuzogullari, M.; Bulmus, V.; Dalgakiran, E.; Dincer, S. pH- and Temperature-Responsive Amphiphilic Diblock Copolymers of 4-Vinylpyridine and Oligoethyleneglycol Methacrylate Synthesized by RAFT Polymerization. Polymer 2014, 55, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohy, J.F. Block Copolymer Micelles. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2005, 190, 65–136. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Li, X.; Dong, J. Self-Assembly of Well-Defined Amphiphilic Poly(N-(2-Methacryloylxyethyl)Pyrrolidone)-Poly(Lauryl Methacrylate) Diblock Copolymers in Non-Polar Solvent. Colloid. Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 577, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabanov, A.V.; Batrakova, E.V.; Alakhov, V.Y. Pluronic Block Copolymers as Novel Polymer Therapeutics for Drug and Gene Delivery. J. Control. Release 2002, 82, 189–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öztürk, K.; Kaplan, M.; Çalış, S. Effects of Nanoparticle Size, Shape, and Zeta Potential on Drug Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 666, 124799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atukorale, P.U.; Guven, Z.P.; Bekdemir, A.; Carney, R.P.; Van Lehn, R.C.; Yun, D.S.; Silva, P.H.J.; Demurtas, D.; Yang, Y.-S.; Alexander-Katz, A.; et al. Structure-Property Relationships of Amphiphilic Nanoparticles That Penetrate or Fuse Lipid Membranes. Bioconjugate Chem. 2018, 29, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soo Choi, H.; Liu, W.; Misra, P.; Tanaka, E.; Zimmer, J.P.; Itty Ipe, B.; Bawendi, M.G.; Frangioni, J.V. Renal Clearance of Quantum Dots. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teulère, C.; Ben-Osman, C.; Barry, C.; Nicolaÿ, R. Synthesis and Self-Assembly of Amphiphilic Heterografted Molecular Brushes Prepared by Telomerization. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 141, 110080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, S.A.; Dolui, S.; Kumar, D.; Mane, S.R.; Banerjee, S. Facile Access to Functional Polyacrylates with Dual Stimuli Response and Tunable Surface Hydrophobicity. Polym. Chem. 2021, 12, 3042–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Hirai, Y.; Takenaka, M.; Sawamoto, M.; Terashima, T. Intramolecular Folding or Intermolecular Self-Assembly of Amphiphilic Random Copolymers: On-Demand Control by Pendant Design. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 3738–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| PC/C | Mw a (g/mol) (×104) | Mw/Mn a | %wt LMA | %wt tBMA b Before Hydrolysis | %wt tBMA b After Hydrolysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.14 | 1.16 | 32 | 68 | 20 |
| 2 | 1.02 | 1.19 | 47 | 53 | 19 |
| Copolymer | pH | I90° (a.u.) | Rh (nm) | PDI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 7 | 35 | 95 (62%)/3 (38%) | 0.531 |
| 10 | 30 | 90 (66%)/4 (34%) | 0.552 | |
| 7* | 20 | 4 | 0.490 | |
| C2 | 7 | 165 | 82 (80%)/5 (20%) | 0.542 |
| 10 | 108 | 80 (70%)/5 (30%) | 0.549 | |
| 7* | 138 | 10 | 0.342 |
| Copolymer | Day | I90° (a.u.) | Rh (nm) | PDI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 1 | 35 | 95 (62%)/3 (38%) | 0.531 |
| 5 | 52 | 64 (62%)/5 (38%) | 0.550 | |
| 10 | 46 | 71 (60%)/5 (40%) | 0.521 | |
| 30 | 43 | 66 (60%)/3 (40%) | 0.544 | |
| C2 | 1 | 165 | 82 (80%)/5 (20%) | 0.542 |
| 5 | 70 | 75 (36%)/5 (64%) | 0.492 | |
| 10 | 50 | 79 (32%)/5 (68%) | 0.476 | |
| 30 | 65 | 80 (39%)/5 (61%) | 0.494 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balafouti, A.; Pispas, S. P(LMA-co-tBMA-co-MAA) Copolymers Bearing Amphiphilic and Polyelectrolyte Characteristics: Synthetic Aspects and Properties in Aqueous Solutions. Polymers 2025, 17, 1473. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111473
Balafouti A, Pispas S. P(LMA-co-tBMA-co-MAA) Copolymers Bearing Amphiphilic and Polyelectrolyte Characteristics: Synthetic Aspects and Properties in Aqueous Solutions. Polymers. 2025; 17(11):1473. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111473
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalafouti, Anastasia, and Stergios Pispas. 2025. "P(LMA-co-tBMA-co-MAA) Copolymers Bearing Amphiphilic and Polyelectrolyte Characteristics: Synthetic Aspects and Properties in Aqueous Solutions" Polymers 17, no. 11: 1473. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111473
APA StyleBalafouti, A., & Pispas, S. (2025). P(LMA-co-tBMA-co-MAA) Copolymers Bearing Amphiphilic and Polyelectrolyte Characteristics: Synthetic Aspects and Properties in Aqueous Solutions. Polymers, 17(11), 1473. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17111473







