Surface Fouling Characterization Methods for Polymeric Membranes Using a Short Experimental Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Preparation of Artificial Wastewater
2.2. Preparation of Filtration System
2.3. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amy, G.; Ghaffour, N.; Li, Z.; Francis, L.; Linares, R.V.; Missimer, T.; Lattemann, S. Membrane-based seawater desalination: Present and future prospects. Desalination 2017, 401, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boretti, A.; Rosa, L. Reassessing the projections of the World Water Development Report. NPJ Clean Water 2019, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Xu, N.; Xing, W. Special issue on Membranes and Water Treatment. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2022, 16, 561–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, P.S.; Ismail, A.F. A review on inorganic membranes for desalination and wastewater treatment. Desalination 2018, 434, 60–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quist-Jensen, C.A.; Macedonio, F.; Drioli, E. Membrane technology for water production in agriculture: Desalination and wastewater reuse. Desalination 2015, 364, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanar, N.; Kallem, P.; Son, M.; Park, H.; Kang, S.; Choi, H. A New era of water treatment technologies: 3D printing for membranes. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 91, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanar, N.; Son, M.; Park, H.; Choi, H. Toward greener membranes with 3D printing technology. Environ. Eng. Res. 2021, 26, 200027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanar, N.; Choi, H. Urban Water Management and Quality-Based Water Use. IGLUS Q. 2019, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Sholl, D.S.; Lively, R.P. Seven chemical separations to change the world. Nature 2016, 532, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.; Liang, Y.; Yanar, N.; Kim, M.; Park, H.; Choi, H. Intermolecular cross-linked polymer of intrinsic microporosity-1 (PIM-1)-based thin-film composite hollow fiber membrane for organic solvent nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 671, 121370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.; Park, S.; Kim, Y.; Yanar, N.; Choi, H. Fabrication and Investigation of Acid Functionalized CNT Blended Nanocomposite Hollow Fiber Membrane for High Filtration and Antifouling Performance in Ultrafiltration Process. Membranes 2023, 13, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolaisen, B. Developments in membrane technology for water treatment. Desalination 2003, 153, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Yang, E.; Park, H.; Choi, H. Fabrication of functionalized halloysite nanotube blended ultrafiltration membranes for high flux and fouling resistance. Environ. Eng. Res. 2019, 25, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fareed, H.; Jang, K.; Lee, W.; Kim, I.S.; Han, S. Dehydroxylation-assisted self-crosslinking of MXene-based pervaporation membranes for treating high-salinity water. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 119, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fareed, H.; Jang, K.; Lee, W.; Kim, I.S.; Han, S. Covalently Crosslinked Sulfonated Graphene Oxide Membranes for Alleviation of Silica Scaling and Organic Fouling for Brine Treatment by Pervaporation. SSRN 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliyu, U.M.; Rathilal, S.; Isa, Y.M. Membrane desalination technologies in water treatment: A review. Water Pract. Technol. 2018, 13, 738–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obotey Ezugbe, E.; Rathilal, S. Membrane Technologies in Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Membranes 2020, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lively, R.P.; Sholl, D.S. From water to organics in membrane separations. Nat. Mater. 2017, 16, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Z.; Peng, L.E.; Guo, H.; Qing, W.; Mei, Y.; Tang, C.Y. Seawater pretreatment with an NF-like forward osmotic membrane: Membrane preparation, characterization and performance comparison with RO-like membranes. Desalination 2019, 470, 114115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Zhang, S.; Ling, M.M.; Chung, T.-S. Forward osmosis: An emerging technology for sustainable supply of clean water. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2012, 14, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Phuntsho, S.; Chekli, L.; Hong, S.; Ghaffour, N.; Leiknes, T.; Choi, J.Y.; Shon, H.K. Environmental and economic impacts of fertilizer drawn forward osmosis and nanofiltration hybrid system. Desalination 2017, 416, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Raghupathy, B.P.C.; Sivakumaran, M.; Keshri, A.K. Ceramic membrane for water filtration: Addressing the various concerns at once. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Wang, S.; Xu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, C. Preparation of polyamide thin film nanocomposite membranes containing silica nanoparticles via an In-Situ polymerization of SiCl4 in organic solution. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 565, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanar, N.; Yang, E.; Park, H.; Son, M.; Choi, H. Efficacy of Electrically-Polarized 3D Printed Graphene-blended Spacers on the Flux Enhancement and Scaling Resistance of Water Filtration Membranes. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 6623–6631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madenli, E.C.; Yanar, N.; Choi, H. Enhanced antibacterial properties and suppressed biofilm growth on multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) blended polyethersulfone (PES) membranes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanar, N.; Liang, Y.; Yang, E.; Park, H.; Son, M.; Choi, H. Electrically polarized graphene-blended spacers for organic fouling reduction in forward osmosis. Membranes 2021, 11, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Q.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G.; Tang, C.Y. Membrane fouling in osmotically driven membrane processes: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 499, 201–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tin, M.M.M.; Anioke, G.; Nakagoe, O.; Tanabe, S.; Kodamatani, H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Fujioka, T. Membrane fouling, chemical cleaning and separation performance assessment of a chlorine-resistant nanofiltration membrane for water recycling applications. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 189, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochkodan, V.; Johnson, D.J.; Hilal, N. Polymeric membranes: Surface modification for minimizing (bio)colloidal fouling. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 206, 116–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Feng, C.; Lopez, R.; Coronell, O. Identifying facile and accurate methods to measure the thickness of the active layers of thin-film composite membranes—A comparison of seven characterization techniques. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 498, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyart, Y.; Georges, G.; Deumié, C.; Amra, C.; Moulin, P. Membrane characterization by microscopic methods: Multiscale structure. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 315, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Mutalib, M.; Rahman, M.A.; Othman, M.H.; Ismail, A.F.; Jaafar, J. Chapter 9—Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy-Dispersive X-Ray (EDX) Spectroscopy. In Membrane Characterization; Hilal, N., Ismail, A.F., Matsuura, T., Oatley-Radcliffe, D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 161–179. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, D.; Oatley-Radcliffe, D.L.; Hilal, N. Chapter 7—Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM). In Membrane Characterization; Hilal, N., Ismail, A.F., Matsuura, T., Oatley-Radcliffe, D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 115–144. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.Y.; Yang, Z. Chapter 8—Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM). In Membrane Characterization; Hilal, N., Ismail, A.F., Matsuura, T., Oatley-Radcliffe, D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 145–159. [Google Scholar]
- Tylkowski, B.; Tsibranska, I. Overview of main techniques used for membrane characterization. J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2014, 50, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Chahboun, A.; Coratger, R.; Ajustron, F.; Beauvillain, J.; Aimar, P.; Sanchez, V. Comparative study of micro- and ultrafiltration membranes using STM, AFM and SEM techniques. Ultramicroscopy 1992, 41, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cohen, Y. Fouling resistant and performance tunable ultrafiltration membranes via surface graft polymerization induced by atmospheric pressure air plasma. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 286, 120490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Suwarno, S.R.; Chong, T.H.; McDougald, D.; Kjelleberg, S.; Cohen, Y.; Fane, A.G.; Rice, S.A. Dynamics of biofilm formation under different nutrient levels and the effect on biofouling of a reverse osmosis membrane system. Biofouling 2013, 29, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z.; Kumar, S.; Trinh, C.K.; Shim, J.-J.; Lee, J.-S. Decoupling electrochemical parameters of molecular-level-controlled polypyrrole and graphene oxide nanocomposite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 610, 155464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, T.A.; Ahmad, Z.; Rath, N.; Muneer, M. An environmentally benign approach for the synthesis of 3,4,5-trisubstituted 2-aminofurans under solvent-free conditions via isocyanide-based multicomponent approach. Tetrahedron Lett. 2016, 57, 2638–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Xu, Y.; Cao, X.; Xu, H.; Li, Y. Chapter 18—Advanced characterization of membrane surface fouling. In 60 Years of the Loeb-Sourirajan Membrane; Tseng, H.-H., Al-Ghouti, M.A., Lau, W.J., An, L., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 499–532. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, D.J.; Al Malek, S.; Al-Rashdi, B.; Hilal, N. Atomic force microscopy of nanofiltration membranes: Effect of imaging mode and environment. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 389, 486–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.W.; Monteiro-Riviere, N.A. Use of confocal microscopy for nanoparticle drug delivery through skin. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 18, 061214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrando, M.; Rrzek, A.; Zator, M.; López, F.; Güell, C.; Rŏżek, A. An approach to membrane fouling characterization by confocal scanning laser microscopy. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 250, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Lee, J.; Nghiem, L.D.; Elimelech, M. Role of pressure in organic fouling in forward osmosis and reverse osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 493, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanar, N.; Son, M.; Park, H.; Choi, H. Bio-mimetically inspired 3D-printed honeycombed support (spacer) for the reduction of reverse solute flux and fouling of osmotic energy driven membranes. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 83, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanar, N.; Son, M.; Yang, E.; Kim, Y.; Park, H.; Nam, S.-E.; Choi, H. Investigation of the performance behavior of a forward osmosis membrane system using various feed spacer materials fabricated by 3D printing technique. Chemosphere 2018, 202, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Tang, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Huang, D.; Chen, H.; Zhang, N. Mechanism analysis of membrane fouling behavior by humic acid using atomic force microscopy: Effect of solution pH and hydrophilicity of PVDF ultrafiltration membrane interface. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 487, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrijenhoek, E.M.; Hong, S.; Elimelech, M. Influence of membrane surface properties on initial rate of colloidal fouling of reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 188, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahmatkesh, S.; Rezakhani, Y.; Arabi, A.; Hasan, M.; Ahmad, Z.; Wang, C.; Sillanpää, M.; Al-Bahrani, M.; Ghodrati, I. An approach to removing COD and BOD based on polycarbonate mixed matrix membranes that contain hydrous manganese oxide and silver nanoparticles: A novel application of artificial neural network based simulation in MATLAB. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsaiari, M.; Rozina; Ahmad, M.; Zafar, M.; Sultana, S.; Rizk, M.A.; Almohana, A.I.; Ahmad, Z.; Alsaiari, R.A.; Akhtar, M.S. Treatment of Saussurea heteromalla for biofuel synthesis using catalytic membrane reactor. Chemosphere 2022, 305, 135335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, N.; Ali, Z.; Ullah, S.; Khan, A.S.; Adalat, B.; Nasrullah, A.; Alsaadi, M.; Ahmad, Z. Synthesis of activated carbon-surfactant modified montmorillonite clay-alginate composite membrane for methylene blue adsorption. Chemosphere 2022, 309, 136623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boo, C.; Elimelech, M.; Hong, S. Fouling control in a forward osmosis process integrating seawater desalination and wastewater reclamation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 444, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgın, S.; Takaç, S.; Özdamar, T.H. A Parametric Study on Protein-Membrane-Ionic Environment Interactions for Membrane Fouling. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2005, 40, 1191–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokobi, F. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)—Definition, Principle, Parts, Images. 2022. Available online: https://microbenotes.com/scanning-electron-microscope-sem/ (accessed on 2 December 2023).
- Long, Y.; Yu, G.; Dong, L.; Xu, Y.; Lin, H.; Deng, Y.; You, X.; Yang, L.; Liao, B.-Q. Synergistic fouling behaviors and mechanisms of calcium ions and polyaluminum chloride associated with alginate solution in coagulation-ultrafiltration (UF) process. Water Res. 2021, 189, 116665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellers, T.J.; Davidson, M.W. Introduction to Confocal Microscopy; Olympus Microscopy Resource Center: Tokyo, Japan, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yolcu, E.N.; Tartuk, G.A.; Kaya, S.; Eskibağlar, M. The use of confocal laser scanning microscopy in endodontics: A literature review. Turk. Endod. J. (TEJ) 2021, 6, 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Akin, O.; Temelli, F. Probing the hydrophobicity of commercial reverse osmosis membranes produced by interfacial polymerization using contact angle, XPS, FTIR, FE-SEM and AFM. Desalination 2011, 278, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Cohen, Y.; Moses, K.J.; Sharma, S.; Bilal, M. Polysulfone surface nano-structured with tethered polyacrylic acid. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 470, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machine Makers. Advantages and Disadvantages of Atomic Force Microscopy. 2011. Available online: https://machinemakers.typepad.com/machine-makers/2011/05/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-atomic-force-microscopy.html (accessed on 2 December 2023).
- Nguyen, Q.-M.; Lee, S. Fouling analysis and control in a DCMD process for SWRO brine. Desalination 2015, 367, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyuncu, I.; Brant, J.; Lüttge, A.; Wiesner, M.R. A comparison of vertical scanning interferometry (VSI) and atomic force microscopy (AFM) for characterizing membrane surface topography. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 278, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyence. White Light Interferometer. 2022. Available online: https://www.keyence.eu/ss/products/microscope/roughness/equipment/surface_03.jsp (accessed on 2 December 2023).
- Erickson, A.; Ballinger, T. Ultra-Thin AFM Enables Integration with Light Microscope. Microsc. Today 2018, 26, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ghazanfari, S.; Driessen-Mol, A.; Strijkers, G.J.; Baaijens, F.P.T.; Bouten, C.V.C. The Evolution of Collagen Fiber Orientation in Engineered Cardiovascular Tissues Visualized by Diffusion Tensor Imaging. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepot, K. Microfossils, Analytical Techniques. In Encyclopedia of Astrobiology; Gargaud, M., Irvine, W.M., Amils, R., Claeys, P., Cleaves, H.J., Gerin, M., Rouan, D., Spohn, T., Tirard, S., Viso, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 1570–1576. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, S.M.; Crawshaw, J.P.; Boek, E.S. Three-dimensional imaging of porous media using confocal laser scanning microscopy. J. Microsc. 2017, 265, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
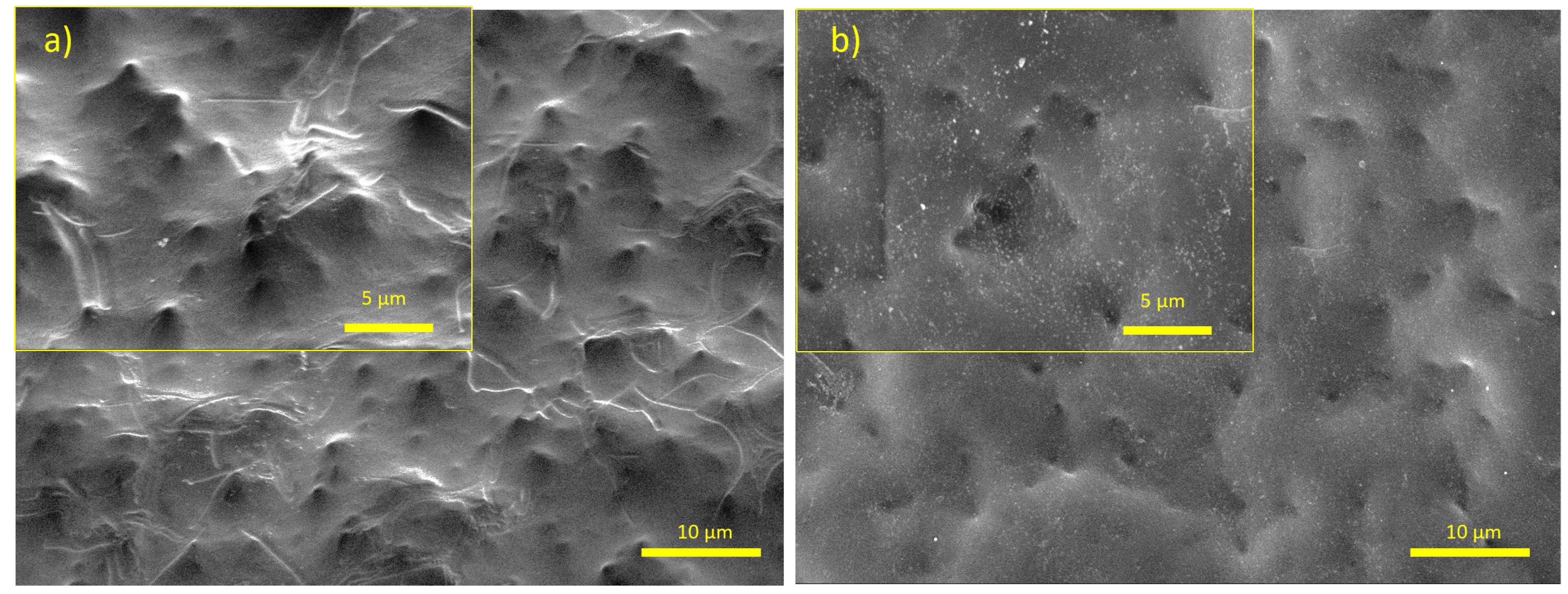
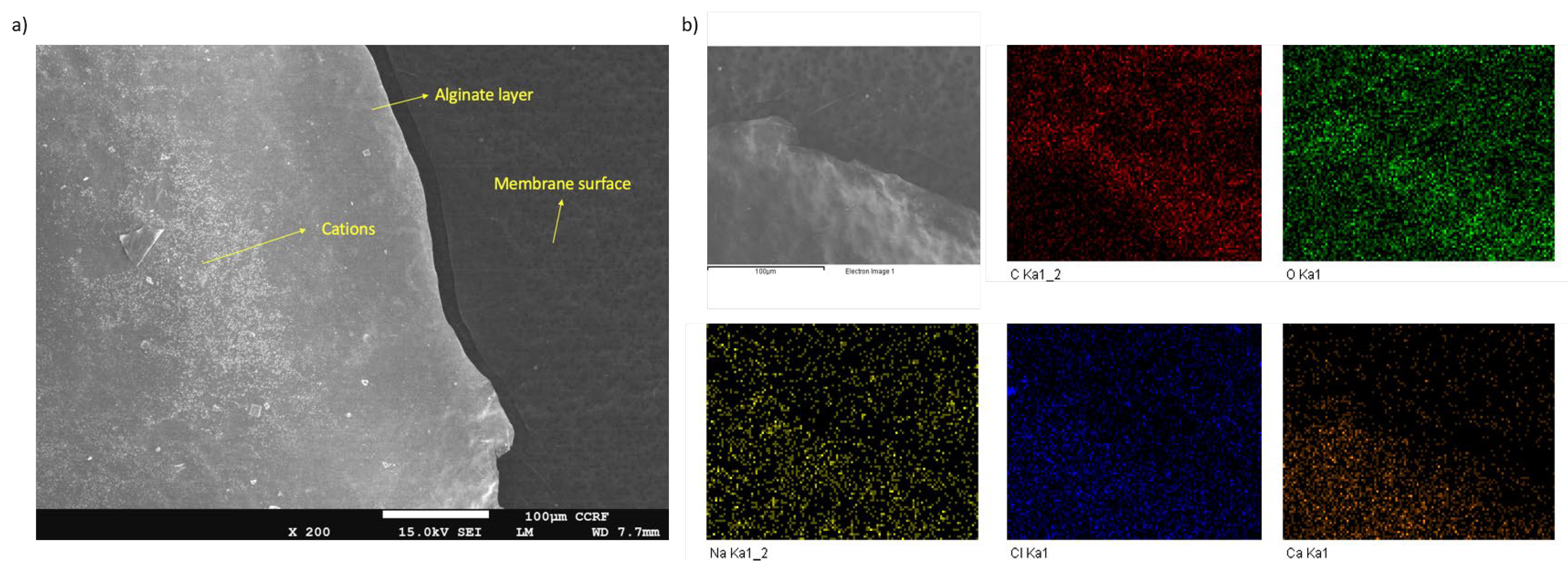

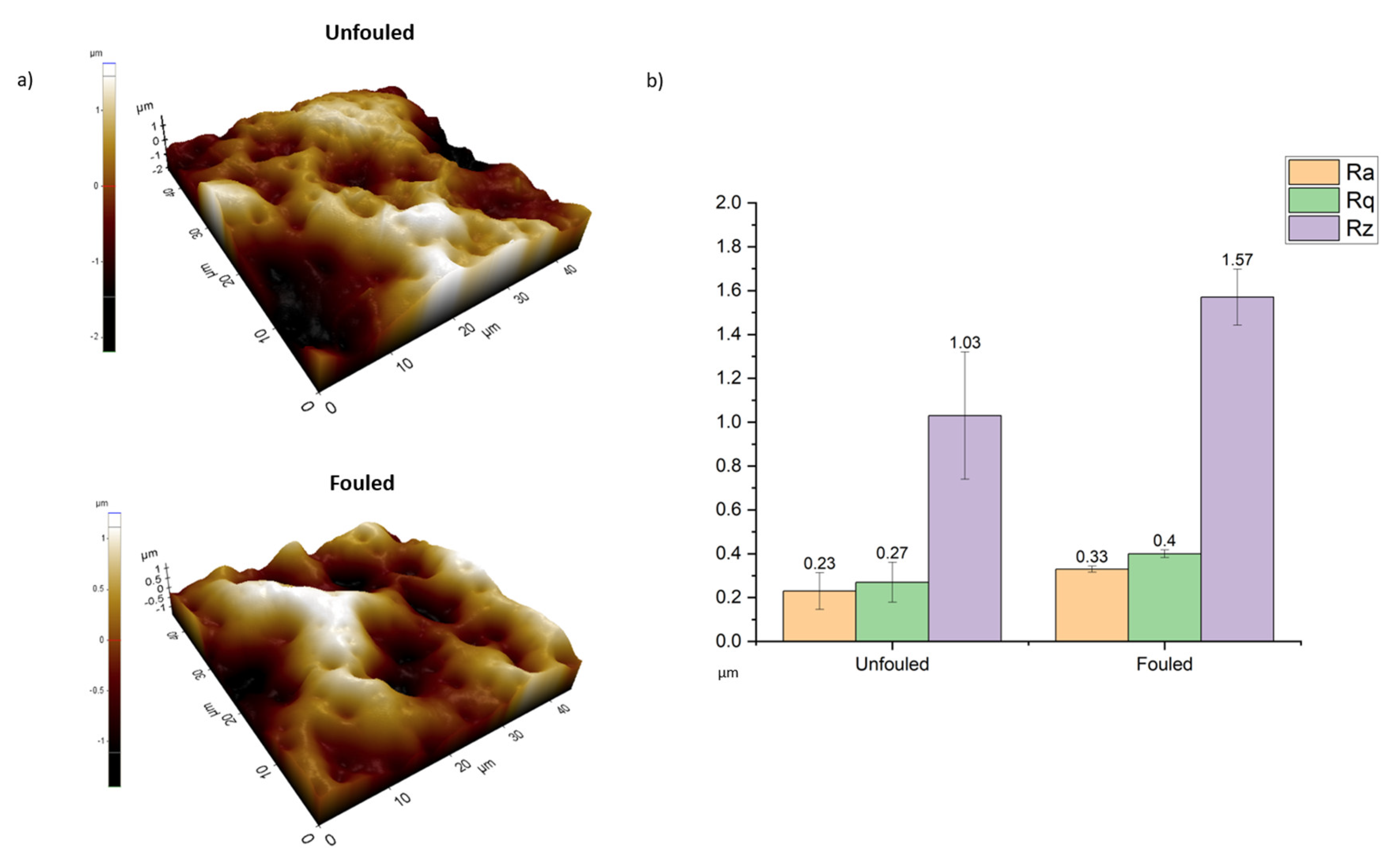
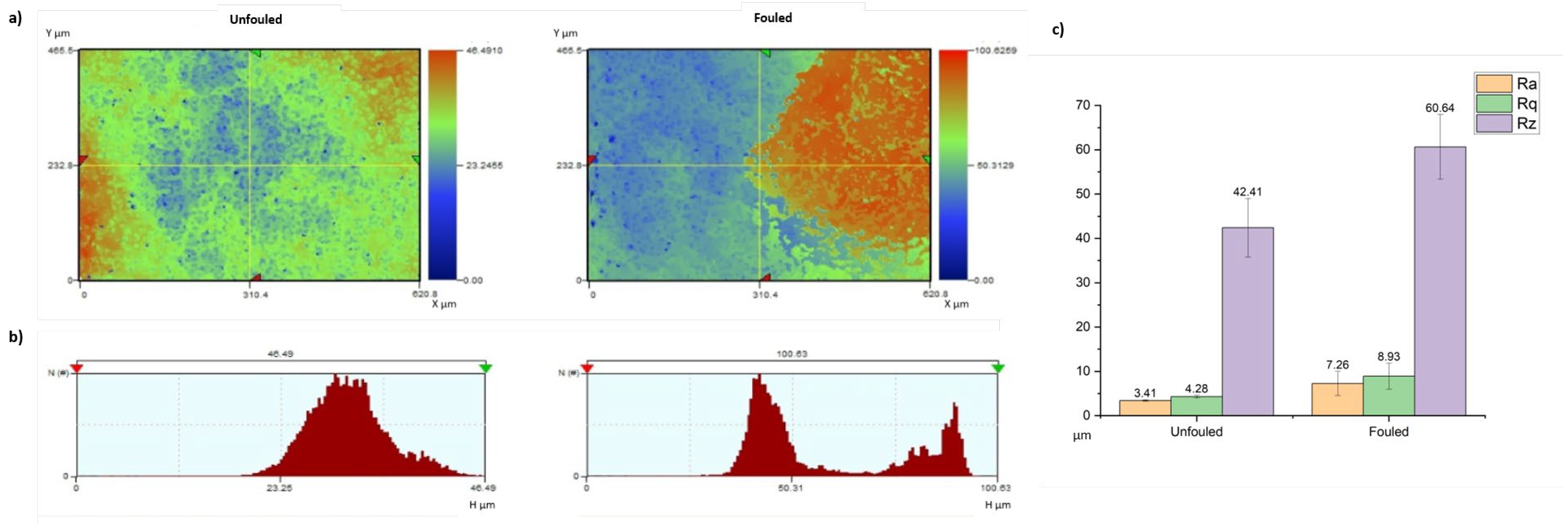
| Material | Concentration | Type |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium alginate | 75 mg/L | Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA), CAS: 9005-38-3 |
| Ammonium chloride | 0.94 mM | Sigma Aldrich, CAS: 12125-02-9 |
| Potassium phosphate, monobasic | 0.45 mM | Oriental Chemical Industry (Cranford, NJ, USA), CAS: 7778-77-0 |
| Calcium chloride dihydrate | 0.50 mM | Duksan (Ansan, Republic of Korea), CAS:10035-048 |
| Sodium bicarbonate | 0.50 mM | DC Chemical Co. Ltd. (Shanghai, China), CAS:144-55-8 |
| Sodium chloride | 2.00 mM | Sigma Aldrich, CAS: 7647-14-5 |
| Magnesium sulfate | 0.60 mM | Oriental Chemical Industry, CAS: 7487-88-9 |
| SEM | AFM | CLSM | WLI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Principle | Detect intensity of emitted secondary electron | Measure forces between probe and surface | Detect emitted fluorescence signals from a single point of focus | Detect light interference occurring in the distance traveled by white light |
| Resolution | 0.5–1 nm | ~1 nm | Lateral: ~140 nm Vertical: ~1 µm | Lateral: ~1 nm Vertical: ~160 nm |
| Vertical scanning range | Not applicable | Up to 20 µm | Up to 500 µm | Up to 20 mm |
| Sample preparation | Dry and metallic coating steps | Dry step | Proper fluorescent stain and dry steps | Dry step |
| Challenges for membrane fouling characterization |
|
|
| Low accuracy for extremely rough, tortuous, or non-reflecting surfaces |
| Destructive /Non-destructive | Dynamic destructive | Static non-destructive | Destructive | Static non-destructive |
| Relative cost | Medium | Medium | High | Low |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yanar, N.; Park, S.; Yang, E.; Choi, H. Surface Fouling Characterization Methods for Polymeric Membranes Using a Short Experimental Study. Polymers 2024, 16, 2124. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16152124
Yanar N, Park S, Yang E, Choi H. Surface Fouling Characterization Methods for Polymeric Membranes Using a Short Experimental Study. Polymers. 2024; 16(15):2124. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16152124
Chicago/Turabian StyleYanar, Numan, Shinyun Park, Eunmok Yang, and Heechul Choi. 2024. "Surface Fouling Characterization Methods for Polymeric Membranes Using a Short Experimental Study" Polymers 16, no. 15: 2124. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16152124
APA StyleYanar, N., Park, S., Yang, E., & Choi, H. (2024). Surface Fouling Characterization Methods for Polymeric Membranes Using a Short Experimental Study. Polymers, 16(15), 2124. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16152124






