Upcycling of HDPE Milk Bottles into High-Stiffness, High-HDT Composites with Pineapple Leaf Waste Materials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Composite Preparation
2.3. Characterizations
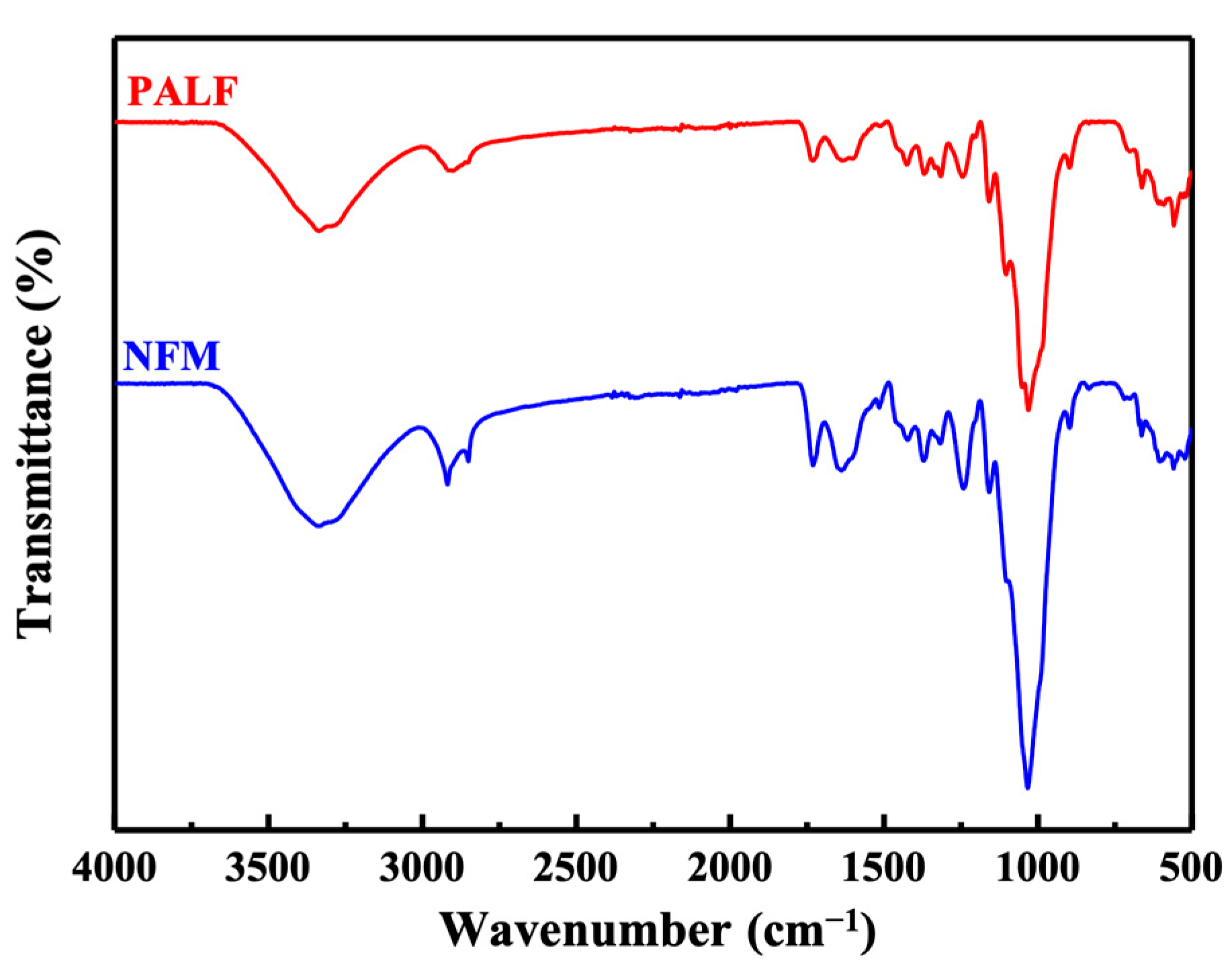
2.3.1. Fiber Chemical Composition
2.3.2. Mechanical Properties
2.3.3. Morphological Properties
2.3.4. Thermal Properties
3. Results
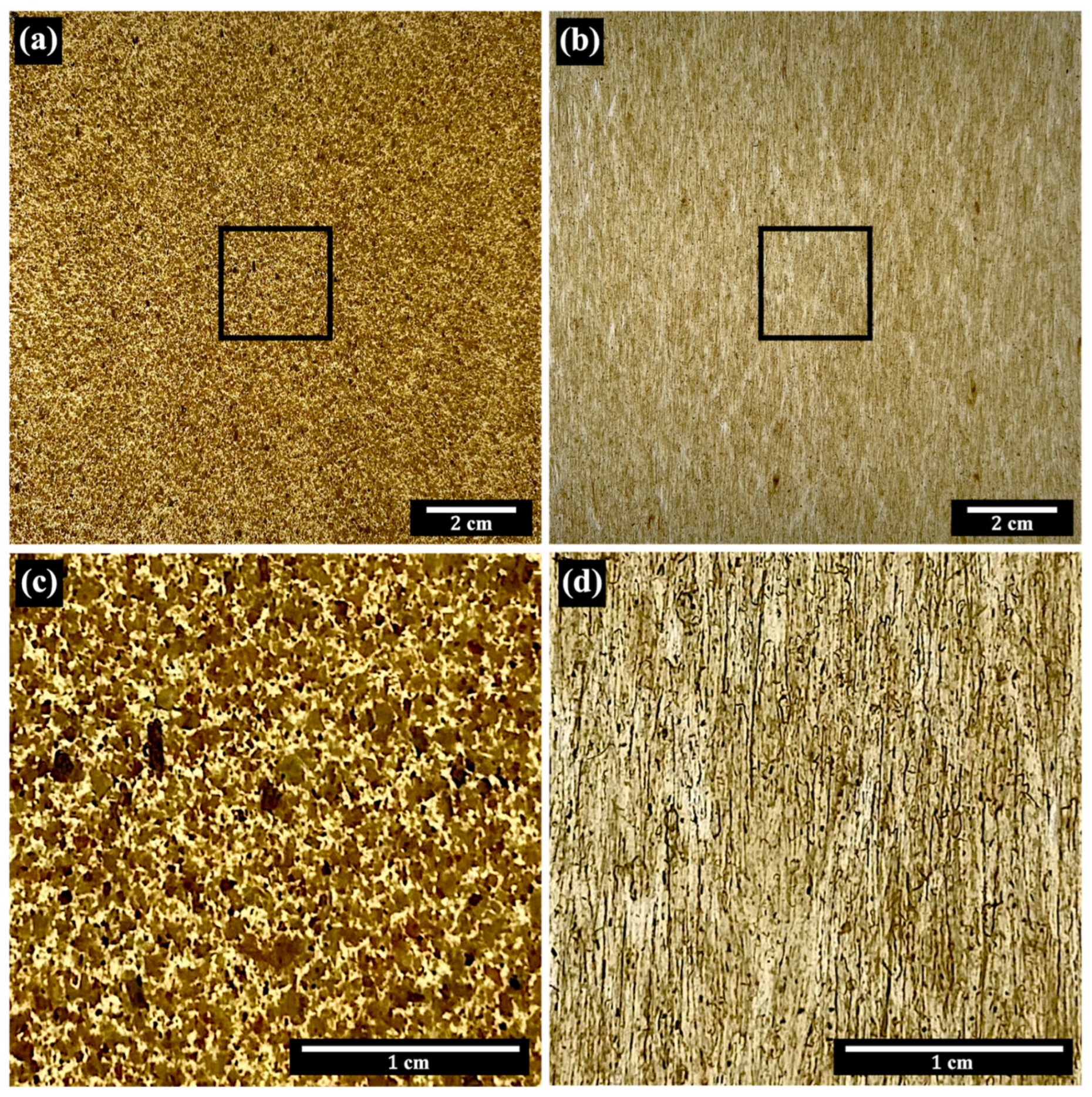
3.1. Pineapple Leaf Waste Material Characteristics
3.2. Prepreg and Sheet Composite Characteristics
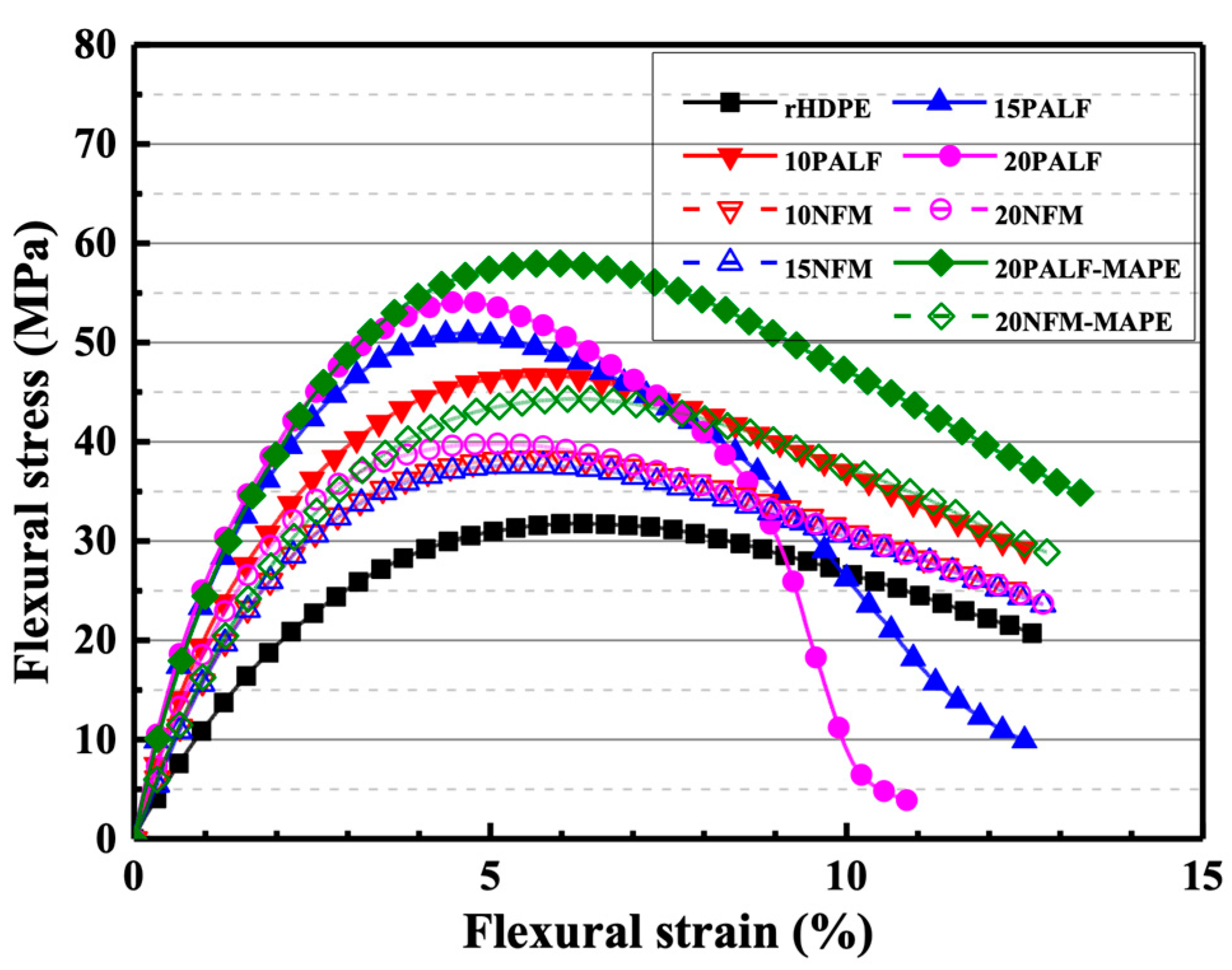
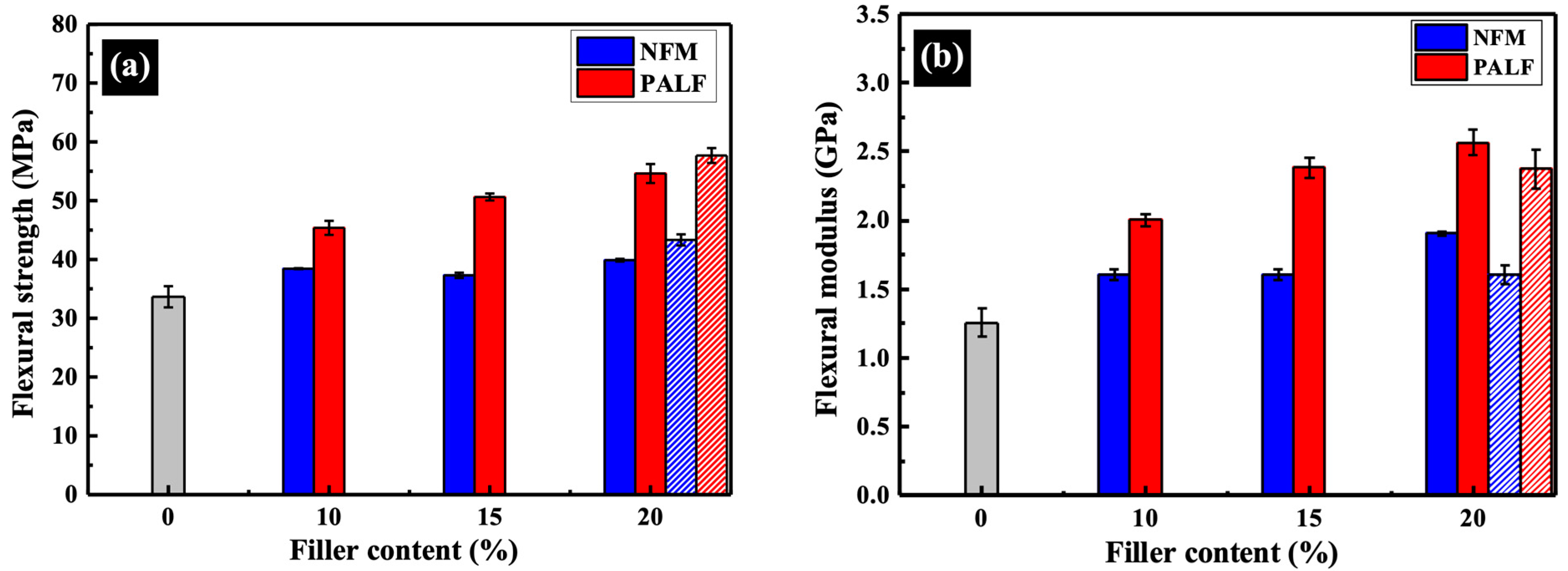
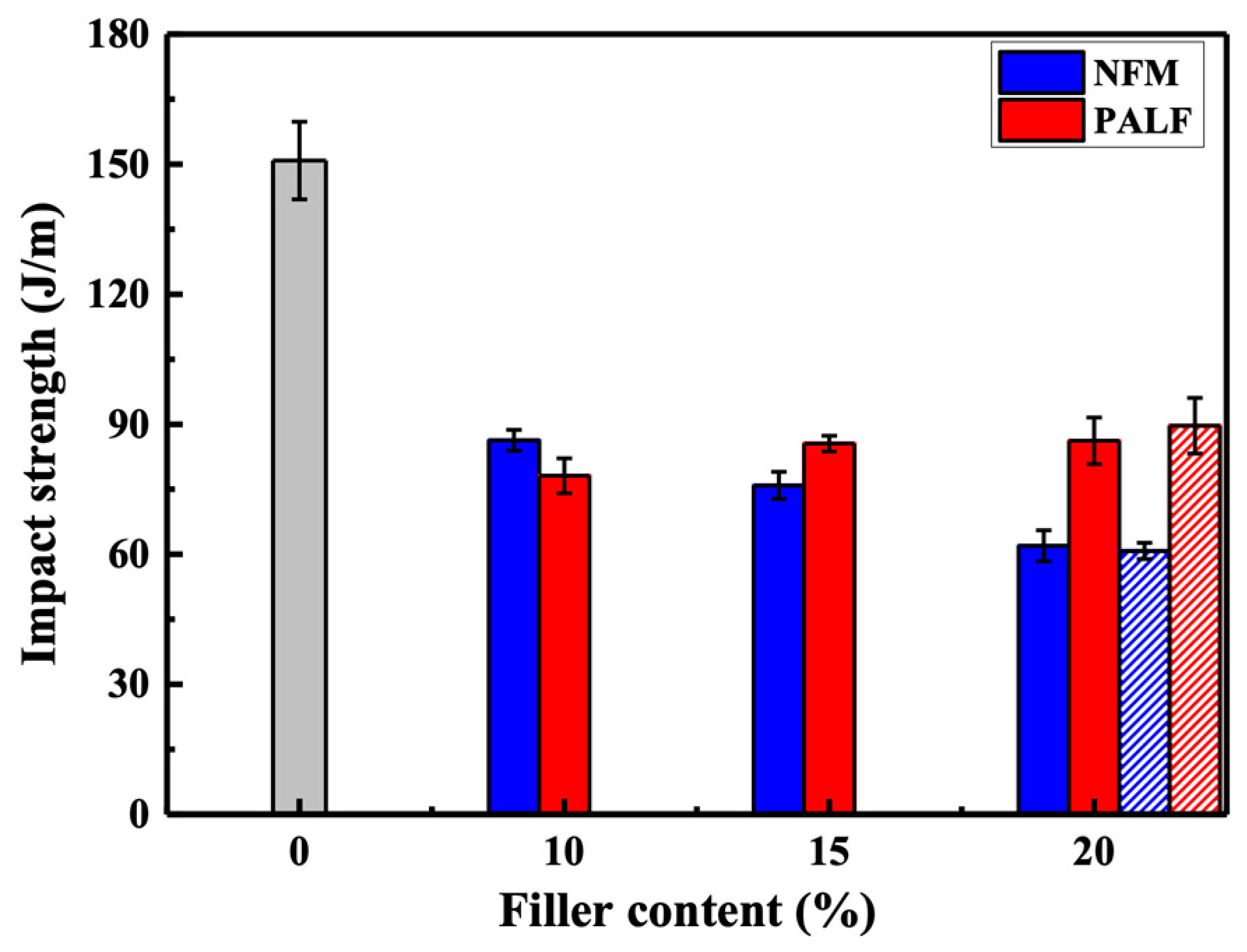
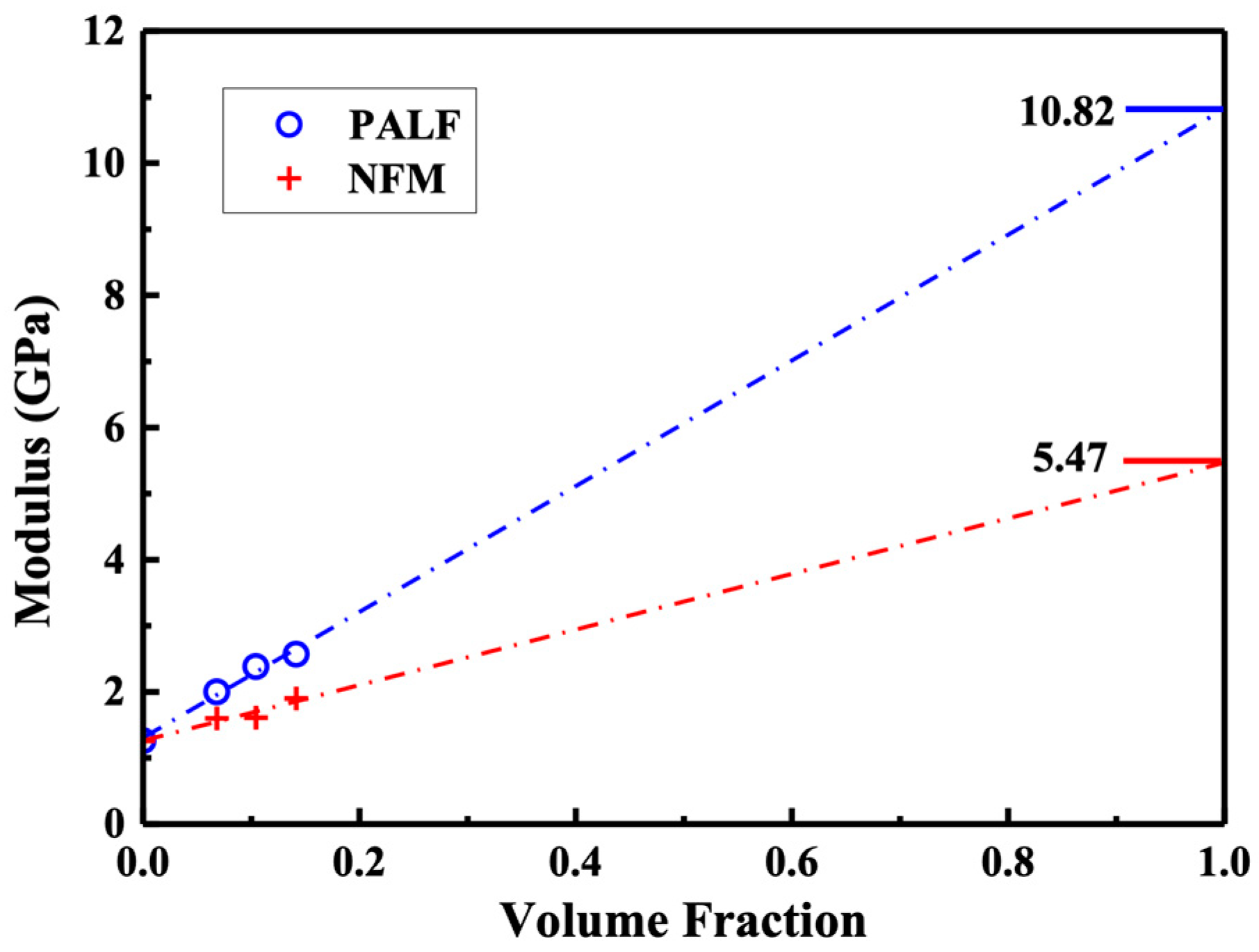
3.3. Mechanical Properties of Composites
3.4. Thermal Properties
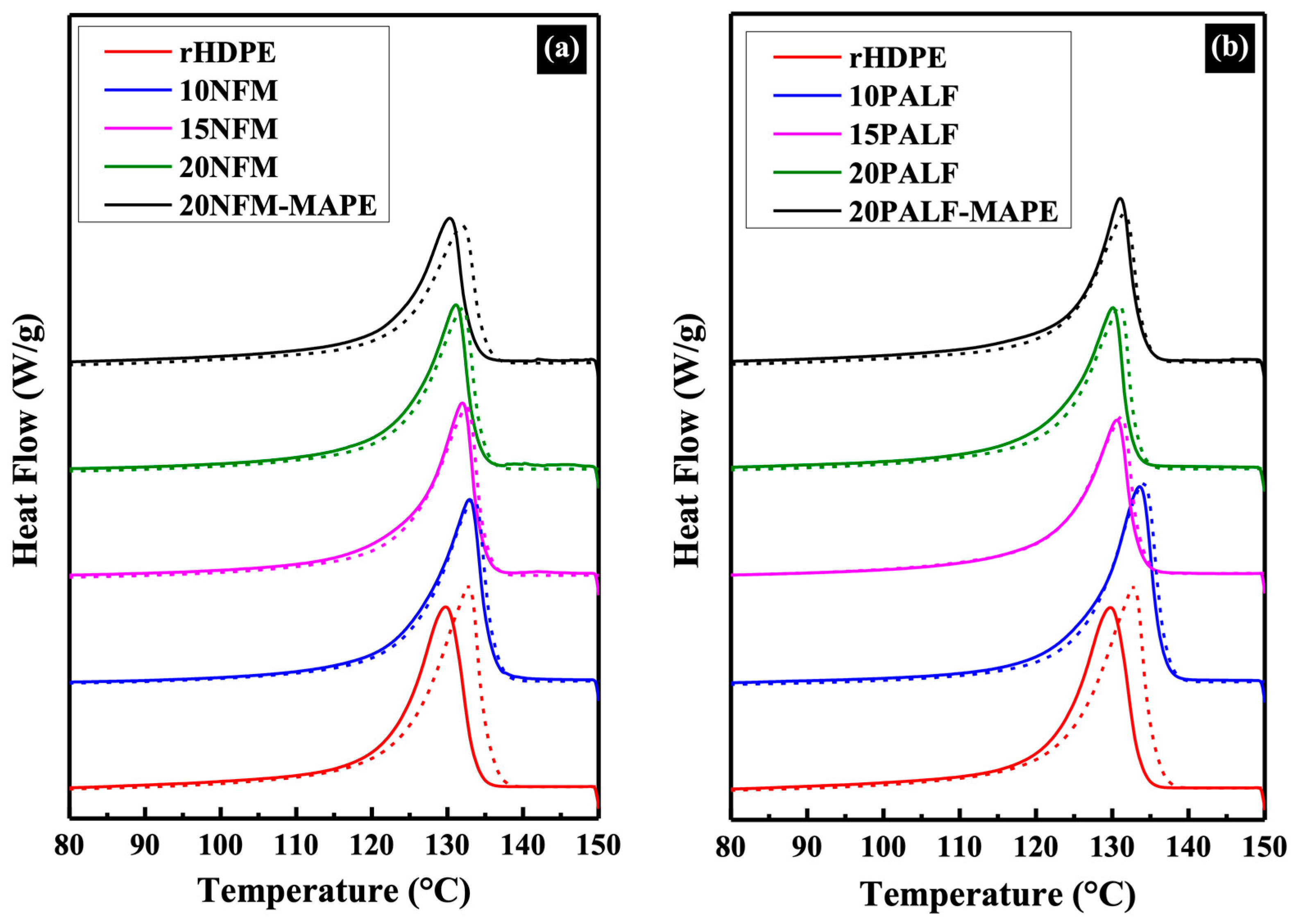
3.4.1. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
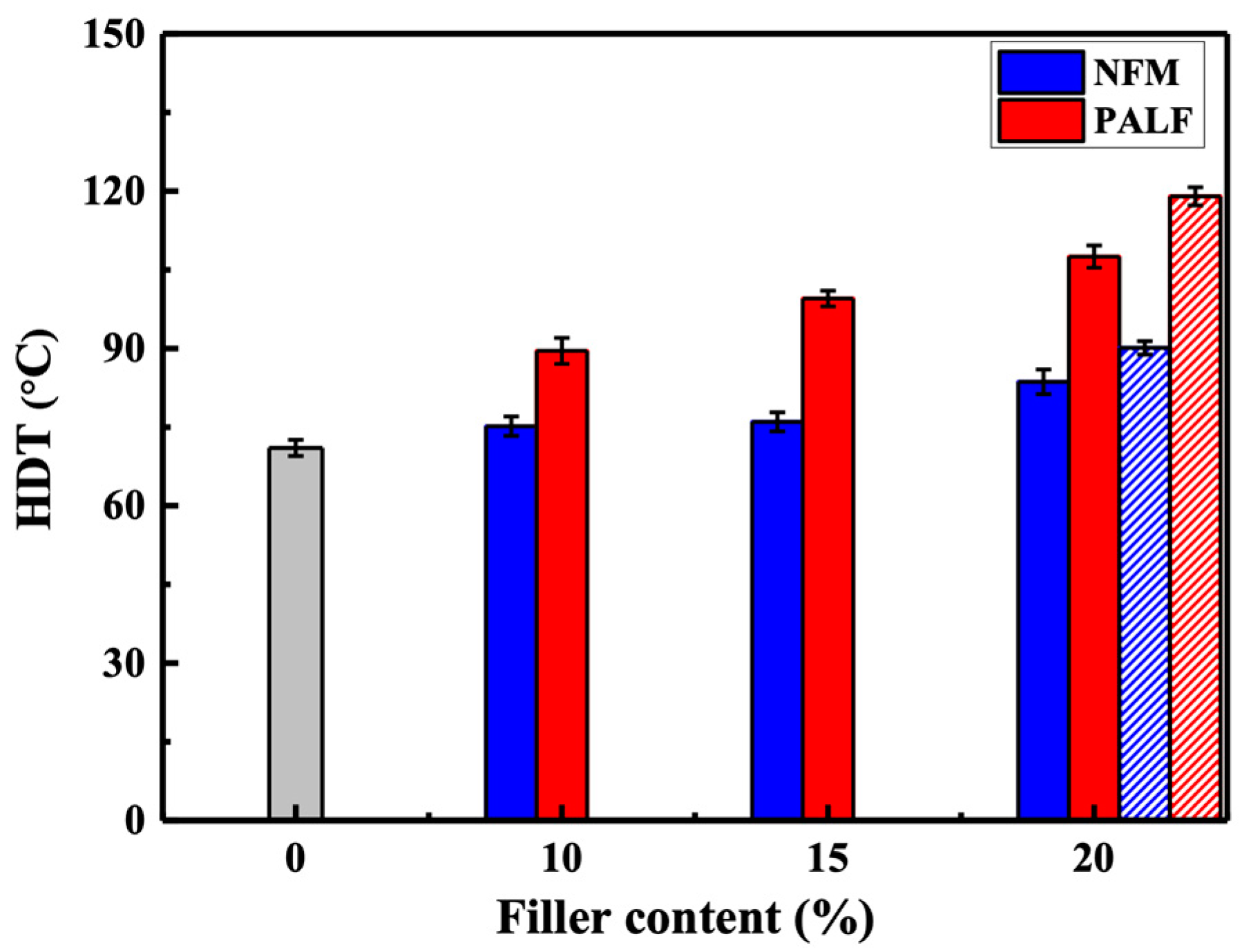
3.4.2. HDT
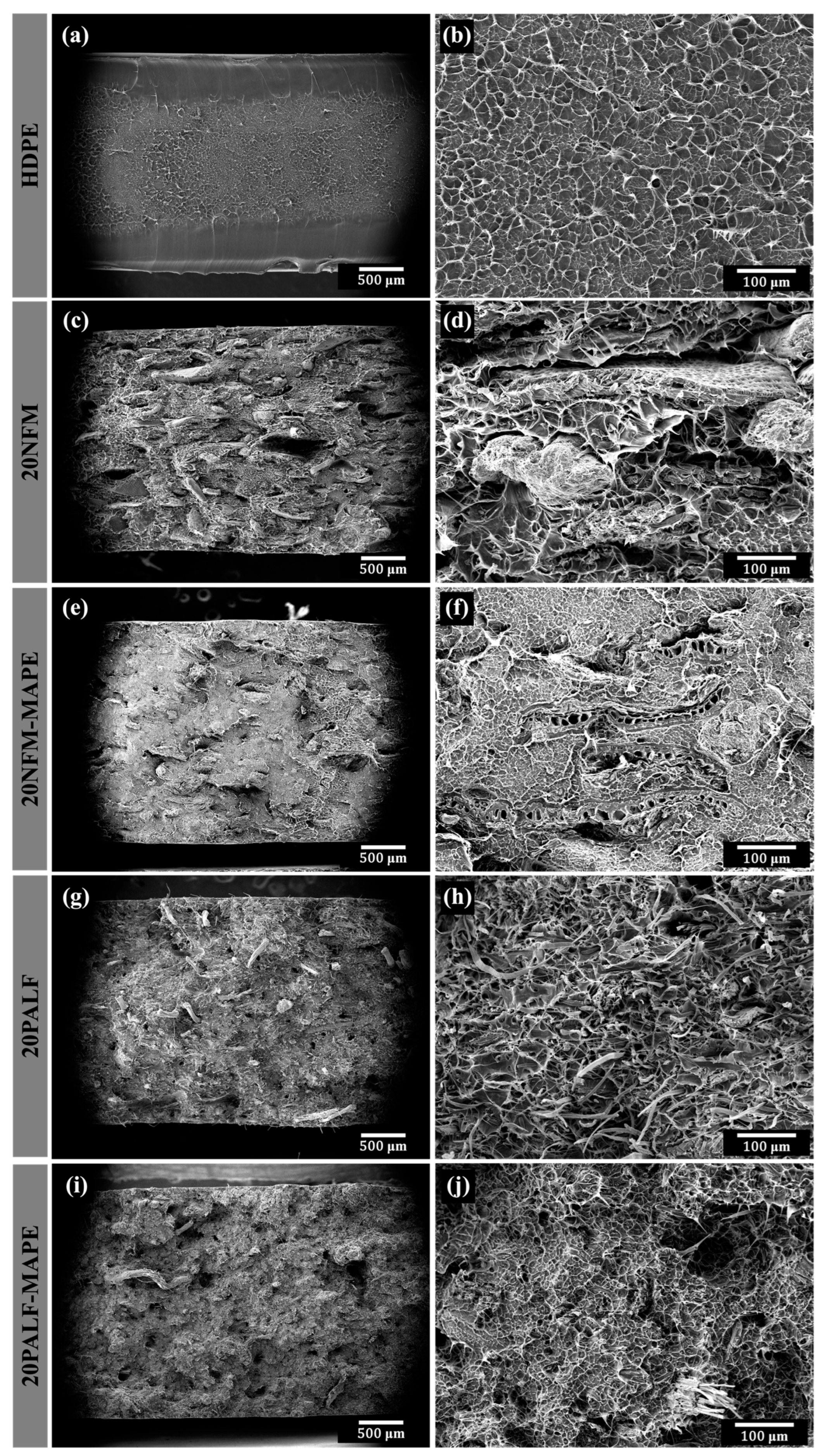
3.5. Fracture Surfaces
4. Discussion and Application Example of rHDPE Composite
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andrady, A.L. Microplastics in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, L. The World’s Plastic Pollution Crisis Explained. Available online: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/environment/article/plastic-pollution (accessed on 12 June 2023).
- Ritchie, H.; Roser, M. Plastic Pollution. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/plastic-pollution (accessed on 12 June 2023).
- Pavlath, A.E.; Robertson, G.H. Biodegradable polymers vs. recycling: What are the possibilities. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 1999, 29, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luckachan, G.E.; Pillai, C.K.S. Biodegradable Polymers—A Review on Recent Trends and Emerging Perspectives. J. Polym. Environ. 2011, 19, 637–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, T.P.; Völker, C.; Kramm, J.; Landfester, K.; Wurm, F.R. Plastics of the Future? The Impact of Biodegradable Polymers on the Environment and on Society. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umesh, M.; Shanmugam, S.; Kikas, T.; Lan Chi, N.T.; Pugazhendhi, A. Progress in bio-based biodegradable polymer as the effective replacement for the engineering applicators. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 362, 132267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Shin, G.; Kwak, H.; Hao, L.T.; Jegal, J.; Kim, H.J.; Jeon, H.; Park, J.; Oh, D.X. Review of polymer technologies for improving the recycling and upcycling efficiency of plastic waste. Chemosphere 2023, 320, 138089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastioli, C. Biodegradable Materials—Present Situation and Future Perspectives. Macromol. Symp. 1998, 135, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volova, T.G.; Boyandin, A.N.; Vasiliev, A.D.; Karpov, V.A.; Prudnikova, S.V.; Mishukova, O.V.; Boyarskikh, U.A.; Filipenko, M.L.; Rudnev, V.P.; Bá Xuân, B.; et al. Biodegradation of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) in tropical coastal waters and identification of PHA-degrading bacteria. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 2350–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniyasamy, S.; Ofosu, O.; John, M.J.; Anandjiwala, R.D. Mineralization of poly(lactic acid) (PLA), Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-valerate) (PHBV) and PLA/PHBV blend in compost and soil environments. J. Renew. Mater. 2016, 4, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandini, F.; Frache, A.; Ferrarini, A.; Taskin, E.; Cocconcelli, P.S.; Puglisi, E. Fate of Biodegradable Polymers Under Industrial Conditions for Anaerobic Digestion and Aerobic Composting of Food Waste. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 2539–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.Z. Biodegradable Plastics: Breaking Down the Facts, Greenpeace East Asia. 2020. Available online: https://www.greenpeace.org/static/planet4-eastasia-stateless/84075f56-biodegradable-plastics-report.pdf (accessed on 14 June 2023).
- Manfra, L.; Marengo, V.; Libralato, G.; Costantini, M.; De Falco, F.; Cocca, M. Biodegradable polymers: A real opportunity to solve marine plastic pollution? J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biodegradable vs. Recyclable Plastics. Available online: https://www.idtechex.com/th/research-article/biodegradable-vs-recyclable-plastics/21022 (accessed on 5 June 2023).
- Which Is Better for the Environment—Biodegradable or Recyclable Plastic? Available online: https://www.plasticstoday.com/sustainability/which-better-environment-biodegradable-or-recyclable-plastic (accessed on 5 June 2023).
- Recycled Content Versus Bioplastics. Available online: https://www.ecoenclose.com/blog/recycled-content-versus-bioplastics/#:~:text=Biodegradable%20plastics%20(meant%20to%20be,or%20virgin%20petroleum%2Dbased%20plastics (accessed on 5 June 2023).
- Pattanakul, C.; Selke, S.; Lai, C.; Miltz, J. Properties of recycled high density polyethylene from milk bottles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1991, 43, 2147–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlman, T.A. Effect of cleaning on the properties of recycled milk bottle flake. Annu. Tech. Conf.-ANTEC Conf. Proc. 1998, 3, 3434–3438. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Q.-Z.; Vera, P.; Salafranca, J.; Nerín, C. Decontamination efficiencies of post-consumer high-density polyethylene milk bottles and prioritization of high concern volatile migrants. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2012, 171, 105640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, B.; Jazbec, M.; Florin, N. Increasing packaging grade recovery rates of plastic milk bottles in Australia: A material flow analysis approach. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2023, 37, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghuram, H.; Roitner, J.; Jones, M.P.; Archodoulaki, V.-M. Recycling of polyethylene: Tribology assessment. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 192, 106925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, Y.R.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, J.-S.; Min, K. Recent advances and challenges in the biotechnological upcycling of plastic wastes for constructing a circular bioeconomy. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, R.; Welle, F. Recycling of Post-Consumer Packaging Materials into New Food Packaging Applications—Critical Review of the European Approach and Future Perspectives. Sustainability 2022, 14, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Mohanty, A.K.; Drzal, L.T.; Misra, M.; Hinrichsen, G. A Review on Pineapple Leaf Fibers, Sisal Fibers and Their Biocomposites. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2004, 289, 955–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asim, M.; Abdan, K.; Jawaid, M.; Nasir, M.; Dashtizadeh, Z.; Ishak, M.R.; Hoque, M.E. A Review on Pineapple Leaves Fibre and Its Composites. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2015, 2015, 950567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kengkhetkit, N.; Amornsakchai, T. Utilisation of pineapple leaf waste for plastic reinforcement: 1. A novel extraction method for short pineapple leaf fiber. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2012, 40, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kengkhetkit, N.; Amornsakchai, T. A new approach to “Greening” plastic composites using pineapple leaf waste for performance and cost effectiveness. Mater. Des. 2014, 55, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nopparut, A.; Amornsakchai, T. Influence of pineapple leaf fiber and it’s surface treatment on molecular orientation in, and mechanical properties of, injection molded nylon composites. Polym. Test. 2016, 52, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kengkhetkit, N.; Amornsakchai, T. Effect of Matrix Orientation and Fiber Content on the Properties of Uniaxial Pineapple Leaf Fiber—Polypropylene Composite. KGK-Kaut. Gummi. Kunst. 2020, 72, 44–50. [Google Scholar]
- Wisittanawat, U.; Thanawan, S.; Amornsakchai, T. Remarkable Improvement of Failure Strain of Preferentially Aligned Short Pineapple Leaf Fiber Reinforced Nitrile Rubber Composites with Silica Hybridization. Polym. Test. 2014, 38, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prukkaewkanjana, K.; Thanawan, S.; Amornsakchai, T. High performance hybrid reinforcement of nitrile rubber using short pineapple leaf fiber and carbon black. Polym. Test. 2015, 45, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surajarusarn, B.; Thaiwattananon, S.; Thanawan, S.; Mougin, K.; Amornsakchai, T. Realising the Potential of Pineapple Leaf Fiber as Green and High-performance Reinforcement for Natural Rubber Composite with Liquid Functionalized Rubber. Fibers Polym. 2021, 22, 2543–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yam, K.L.; Gogoi, B.K.; Lai, C.C.; Selke, S.E. Composites from compounding wood fibers with recycled high density polyethylene. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1990, 30, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyasamy, D.; Manoharan, B.; Arockiasamy, F.S.; Aravind, D.; Senthilkumar, K.; Rajini, N.; Muhammed, F.F.; Al-Lohedan, H.A. Exploring the recycling potential of HDPE films reinforced with flax fiber for making sustainable decorative tiles. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 2049–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Wu, Q.; Yao, F.; Xu, Y. Preparation and properties of recycled HDPE/natural fiber composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. 2007, 38, 1664–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Al Talib, A.A.M.; Ee, J.Y.C. Recycling of High Density Polyethylene Plastics (HDPE) Reinforced with Coconut Fibers for Floor Tiles. J. Pharm. Negat. Results 2022, 13, 2136–2143. [Google Scholar]
- Fazli, A.; Stevanovic, T.; Rodrigue, D. Recycled HDPE/Natural Fiber Composites Modified with Waste Tire Rubber: A Comparison between Injection and Compression Molding. Polymers 2022, 14, 3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xanthopoulou, E.; Chrysafi, I.; Polychronidis, P.; Zamboulis, A.; Bikiaris, D.N. Evaluation of Eco-Friendly Hemp-Fiber-Reinforced Recycled HDPE Composites. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Updegraff, D.M. Semimicro determination of cellulose inbiological materials. Anal. Biochem. 1969, 32, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, L.E.; Murphy, M.; Adieco, A.A.D. A chlorite holocellulose, its fractionation and bearing on summative wood analysis and studies on the hemicelluloses. Pap. Trade J. 1946, 122, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Technical Association of the Pulp and Paper Industry. UM 250 Acid–Soluble Lignin in Wood and Pulp; Technical Association of the Pulp and Paper Industry: Atlanta, GA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Technical Association of the Pulp and Paper Industry. T–222 Acid–Insoluble Lignin in Wood and Pulp; Technical Association of the Pulp and Paper Industry: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Hirschberg, V.; Rodrigue, D. Blending Recycled High-Density Polyethylene HDPE (rHDPE) with Virgin (vHDPE) as an Effective Approach to Improve the Mechanical Properties. Recycling 2023, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM-D648; Standard Test Method for Deflection Temperature of Plastics Under Flexural Load in the Edgewise Position. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018.
- Fadzullah, S.H.M.; Mustafa, Z. Fabrication and Processing of Pineapple Leaf Fiber Reinforced Composites. In Green Approaches to Biocomposite Materials Science and Engineering; IGI Global: Hersey, PA, USA, 2017; pp. 125–147. [Google Scholar]
- Neto, A.R.; Araujo, M.A.; Barboza, R.M.; Fonseca, A.D.; Tonoli, G.H.; Souza, F.V.; Mattoso, L.H.; Marconcini, J.M. Comparative study of 12 pineapple leaf fiber varieties for use as mechanical reinforcement in polymer composites. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 64, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanpichai, S.; Witayakran, S. All-cellulose composite laminates prepared from pineapple leaf fibers treated with steam explosion and alkaline treatment. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2017, 36, 073168441770492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil, M.A.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Parvez, M.S.; Siddika, A.; Gafur, M.A.; Repon, M.R.; Hossain, M.T. A novel approach for pineapple leaf fiber processing as an ultimate fiber using existing machines. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, H.N.Q.; Leu, J.H.; Tran, K.T.; Nguyen, V.N.D.; Nguyen, T.T. Rapid Fabrication of Pineapple Leaf Fibers from Discarded Leaves by Using Electrolysis of Brine. Textiles 2023, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najeeb, M.I.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Andou, Y.; Shah, A.U.M.; Eksiler, K.; Jawaid, M.; Ariffin, A.H. Characterization of silane treated Malaysian Yankee Pineapple AC6 leaf fiber (PALF) towards industrial applications. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 3128–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, K.L. Discontinuous-Fibre Reinforced Composites: Fundamentals of Stress Transfer and Fracture Mechanics; Springer: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, X.; Shen, C.; Xu, S. The effects of coupling/grafting modification of wood fiber on the dimensional stability, mechanical and thermal properties of high density polyethylene/wood fiber composites. Mater. Res. Express. 2019, 6, 115328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Fan, M. Revealing the Interface Structure and Bonding Mechanism of Coupling Agent Treated WPC. Polymers 2018, 10, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cestari, S.P.; Mendes, L.C.; Altstädt, V.; Lopes, L.M.A. Upcycling polymers and natural fibers waste—Properties of a potential building material. Recycling 2016, 1, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez Fletes, R.C.; Rodrigue, D. Effect of wood fiber surface treatment on the properties of recycled hdpe/maple fiber composites. J. Compos. Sci. 2021, 5, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cestari, S.P.; Albitres, G.A.V.; Mendes, L.C.; Altstädt, V.; Gabriel, J.B.; Avila, G.C.B.; Silveira, I.D.S.D.S. Advanced properties of composites of recycled high-density polyethylene and microfibers of sugarcane bagasse. J. Compos. Mater. 2018, 52, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-B.; Huang, Z.-H. Micromechanical prediction of elastic-plastic behavior of a short fiber or particle reinforced composite. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 134, 105889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentges, N.; Çelik, H.; Hopmann, C.; Fagerström, M.; Mirkhalaf, S.M. Micromechanical modelling of short fibre composites considering fibre length distributions. Compos. Part B. Eng. 2023, 264, 110868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, H.L. The elasticity and strength of paper and other fibrous materials. Br. J. Appl. Phys. 1952, 3, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seculi, F.; Espinach, F.X.; Julián, F.; Delgado-Aguilar, M.; Mutjé, P.; Tarrés, Q. Evaluation of the Strength of the Interface for Abaca Fiber Reinforced Hdpe and Biope Composite Materials, and Its Influence over Tensile Properties. Polymers 2022, 14, 5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Deepak, D.; Aggarwal, L.; Gupta, V.K. Tensile and Flexural Behavior of Hemp Fiber Reinforced Virgin-Recycled HDPE Matrix Composites. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 6, 1696–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaro, S.L.; Ganzerli, T.A.; de Carvalho Neto, A.G.; da Silva, O.R.R.F.; Radovanovicet, E. Chemical, morphological and mechanical analysis of sisal fiber-reinforced recycled high-density polyethylene composites. Express Polym. Lett. 2010, 4, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seculi, F.; Julián, F.; Llorens, J.; Espinach, F.X.; Mutjé, P.; Tarrés, Q. Methodologies to Evaluate the Micromechanics Flexural Strength Properties of Natural-Fiber-Reinforced Composites: The Case of Abaca-Fiber-Reinforced Bio Polyethylene Composites. Polymers 2023, 15, 3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surajarusarn, B.; Traiperm, P.; Amornsakchai, T. Revisiting the morphology, microstructure, and properties of cellulose fibre from pineapple leaf so as to expand its utilization. Sains Malays. 2019, 48, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bualek-Limcharoen, S.; Samran, J.; Amornsakchai, T.; Meesiri, W. Effect of Compatibilisers on Mechanical Properties and Morphology of In-Situ Composite Film of Thermotropic Liquid Crystalline Polymer/Polypropylene. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1999, 39, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample Code | rHDPE (wt.%) | Filler (wt.%) | MAPE (wt.%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NFM | PALF | |||
| rHDPE | 100 | - | - | - |
| 10NFM | 90 | 10 | - | - |
| 15NFM | 85 | 15 | - | - |
| 20NFM | 80 | 20 | - | - |
| 20NFM-MAPE | 70 | 20 | - | 10 |
| 10PALF | 90 | - | 10 | - |
| 15PALF | 85 | - | 15 | - |
| 20PALF | 80 | - | 20 | - |
| 20PALF-MAPE | 70 | - | 20 | 10 |
| Sample | Cellulose (%) | Holocellulose (%) | Lignin (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acid Soluble | Acid Insoluble | |||
| NFM | 32.56 | 72.62 | 3.04 | 18.50 |
| PALF | 57.19 | 85.49 | 2.61 | 7.82 |
| Sample | Content (%) | First Heating | Cooling | Second Heating | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tm (°C) | Tc (°C) | Tm (°C) | Xc (%) | ||
| rHDPE | 0 | 129.8 | 119.6 | 132.8 | 73.9 |
| NFM | 10 | 133.0 | 119.6 | 133.5 | 78.2 |
| 15 | 132.0 | 119.3 | 132.6 | 76.6 | |
| 20 | 131.2 | 119.1 | 132.1 | 75.8 | |
| 20 * | 130.3 | 119.4 | 131.9 | 69.9 | |
| PALF | 10 | 133.5 | 120.0 | 134.2 | 79.4 |
| 15 | 130.6 | 118.3 | 131.1 | 75.6 | |
| 20 | 130.1 | 118.3 | 131.0 | 75.3 | |
| 20 * | 131.1 | 119.2 | 131.5 | 70.5 | |
| Fiber | Preparation Method (Mixing/Molding) | Flexural Strength | Flexural Modulus | Ref. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matrix (MPa) | Composite (MPa) | Increment (%) | Matrix (MPa) | Composite (MPa) | Increment (%) | |||
| PALF (20 wt.%) | TRM/CM | 33.7 | 54.6 (57.7) | 62 (71) | 1256 | 2567 (2375) | 104 (89) | This work |
| NFM (20 wt.%) | TRM/CM | 33.7 | 39.8 (43.3) | 18 (28) | 1256 | 1905 (1607) | 52 (28) | This work |
| Coconut (20 wt.%) * | ITM/CM | 19.9 | 16.5 | −17 | 581 | 647 | 11 | [37] |
| Flax (20 wt.%) | TSW/IM | - | - | - | 592 | 636 | 7 | [38] |
| Maple (30 wt.%) ** | Dry blending/CM | 19.6 | 26.2 | 34 | 953 | 1323 | 39 | [56] |
| Hemp (20 wt.%) *** | IM | 22.6 | 22.6 | 0 | - | - | - | [62] |
| Sisal (10 wt.%) | SSE/IM | 20.3 | 25.4 | 25 | 714 | 1123 | 57 | [63] |
| Abaca (30 wt.%) | ITM/IM | 21.3 | 30.1 (50.3) | 41 (136) | - | - | - | [64] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amornsakchai, T.; Duangsuwan, S. Upcycling of HDPE Milk Bottles into High-Stiffness, High-HDT Composites with Pineapple Leaf Waste Materials. Polymers 2023, 15, 4697. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15244697
Amornsakchai T, Duangsuwan S. Upcycling of HDPE Milk Bottles into High-Stiffness, High-HDT Composites with Pineapple Leaf Waste Materials. Polymers. 2023; 15(24):4697. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15244697
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmornsakchai, Taweechai, and Sorn Duangsuwan. 2023. "Upcycling of HDPE Milk Bottles into High-Stiffness, High-HDT Composites with Pineapple Leaf Waste Materials" Polymers 15, no. 24: 4697. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15244697
APA StyleAmornsakchai, T., & Duangsuwan, S. (2023). Upcycling of HDPE Milk Bottles into High-Stiffness, High-HDT Composites with Pineapple Leaf Waste Materials. Polymers, 15(24), 4697. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15244697








