Advances in Graphene–Polymer Nanocomposite Foams for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods for Preparation of Graphene–Polymer Nanocomposite Foams
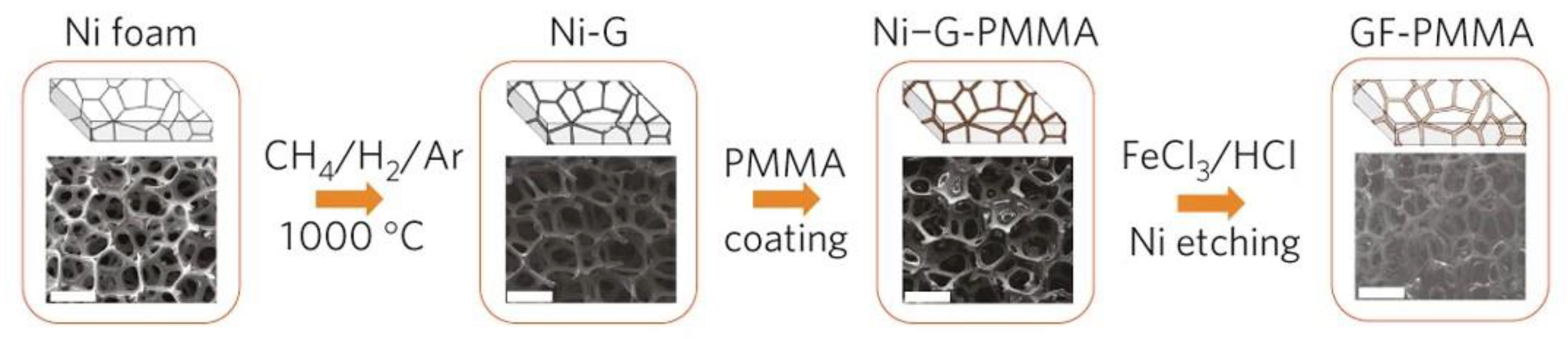
2.1. Coating Graphene onto Polymeric Foams
2.2. Covering Graphene-Based Foams with a Polymer Coating
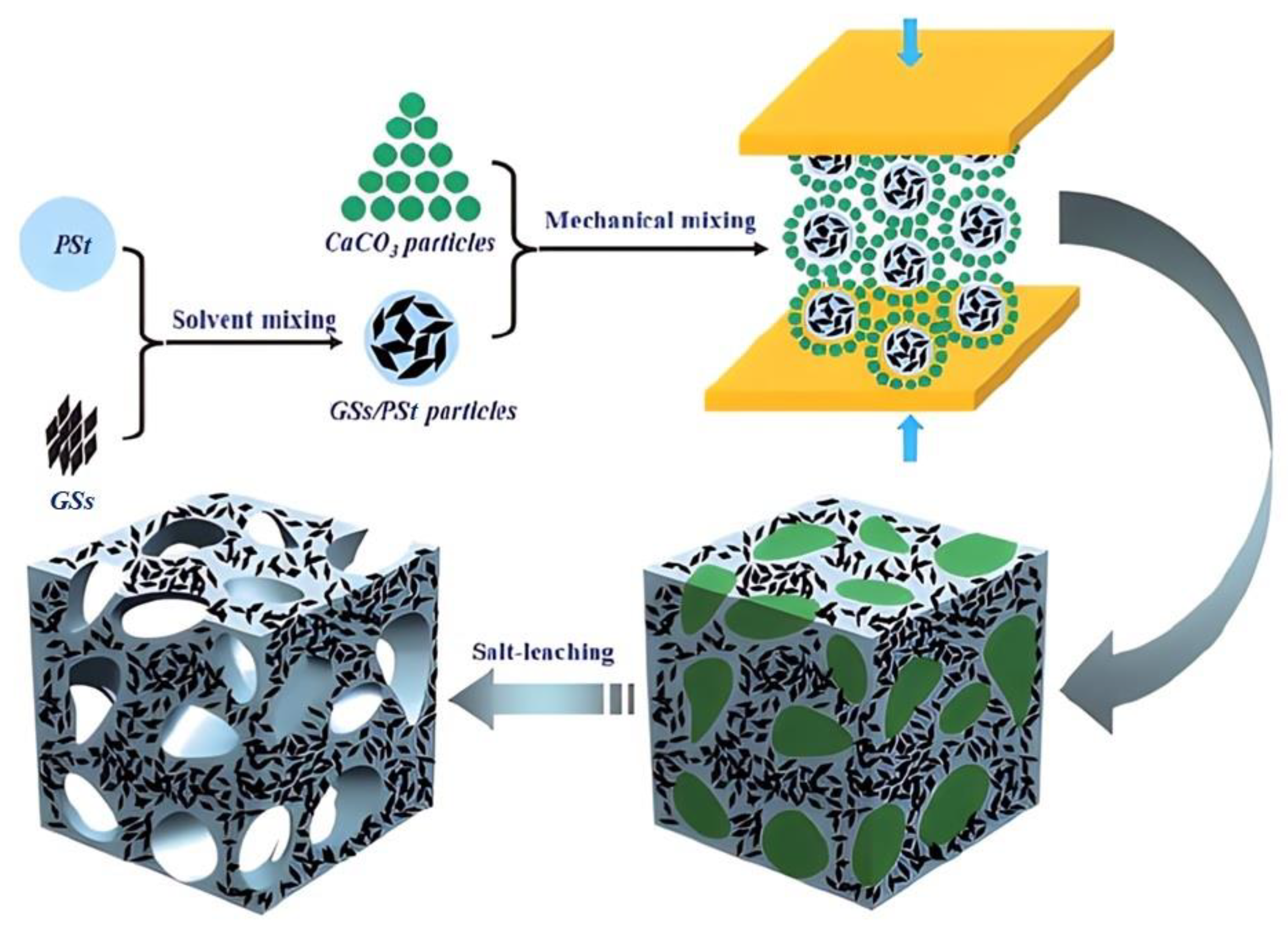
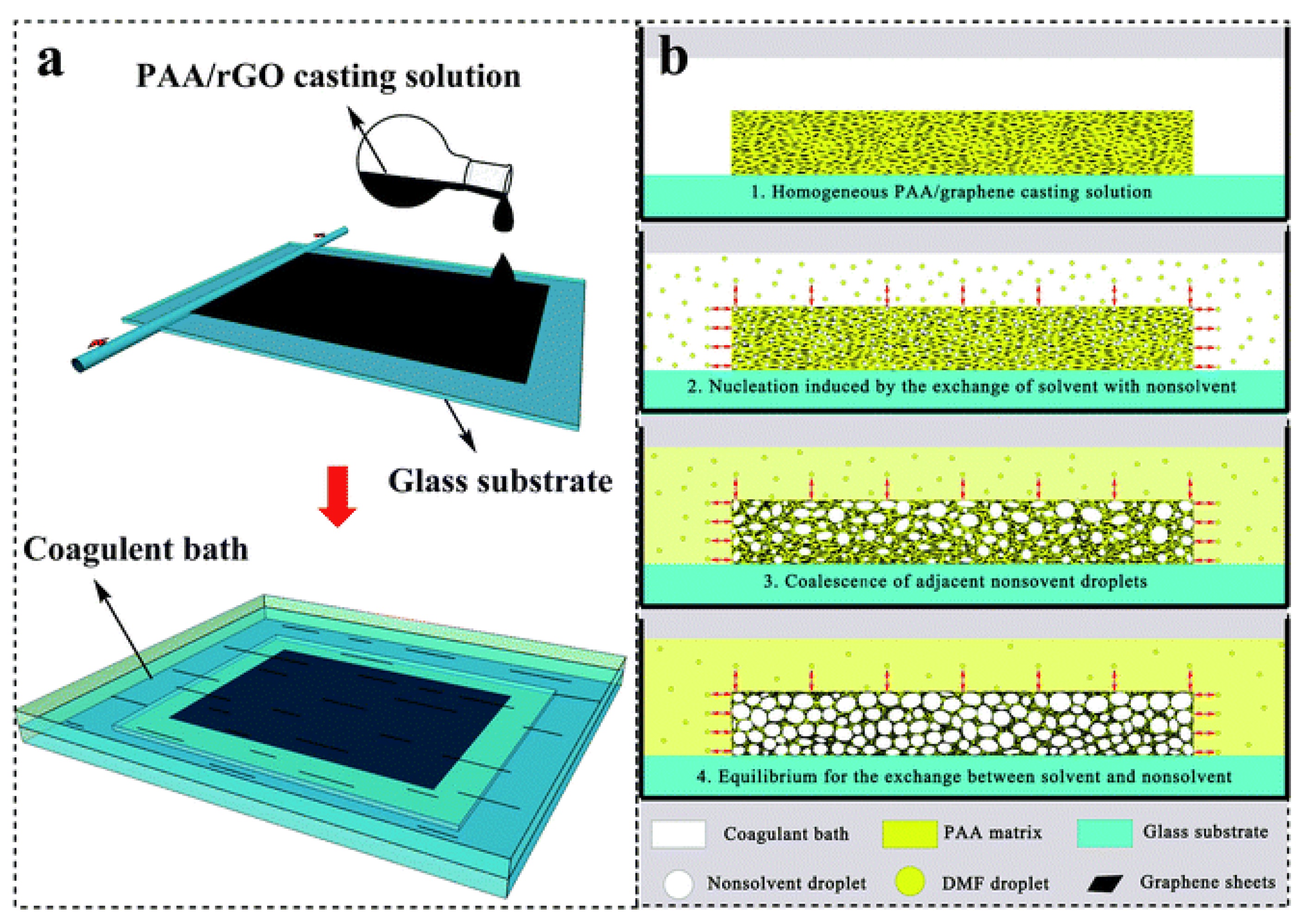
2.3. Dispersion of Graphene within Skeleton of Polymer Foams
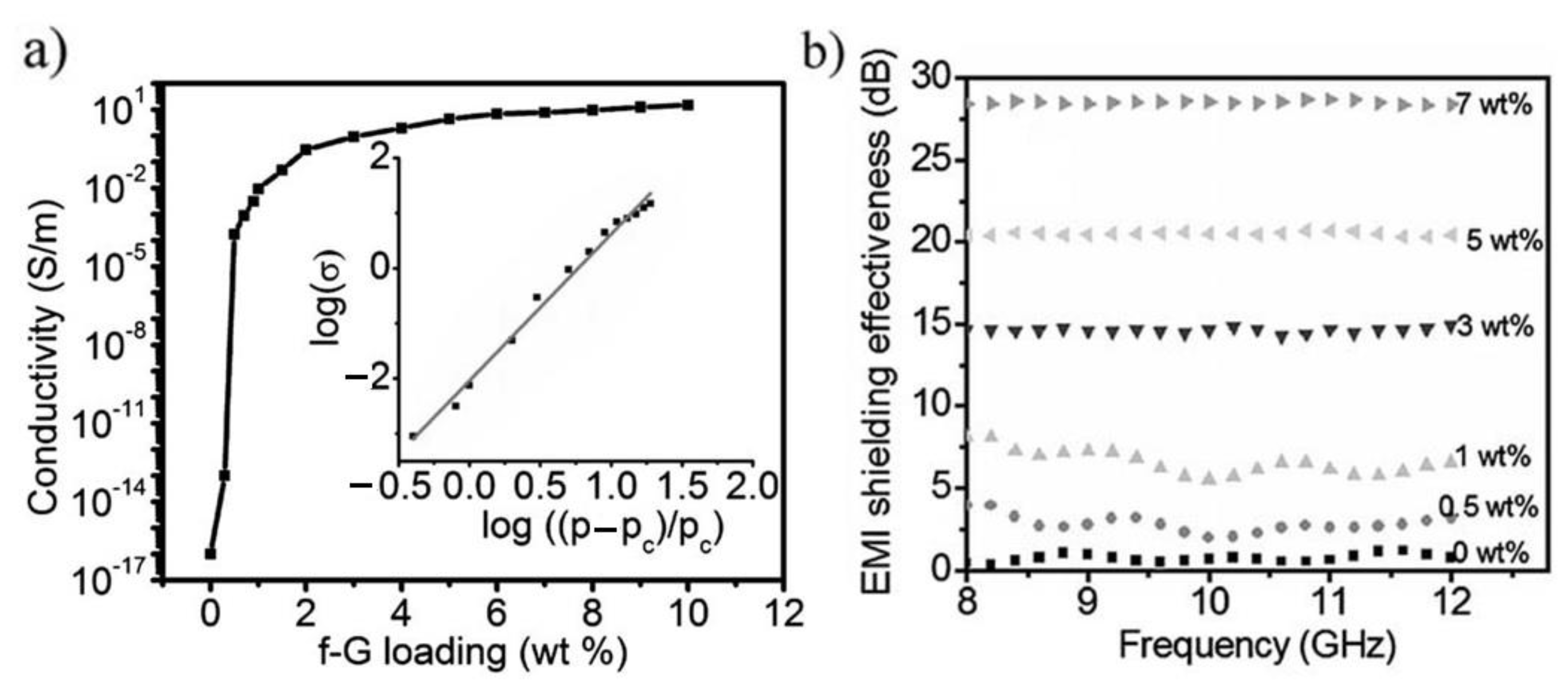
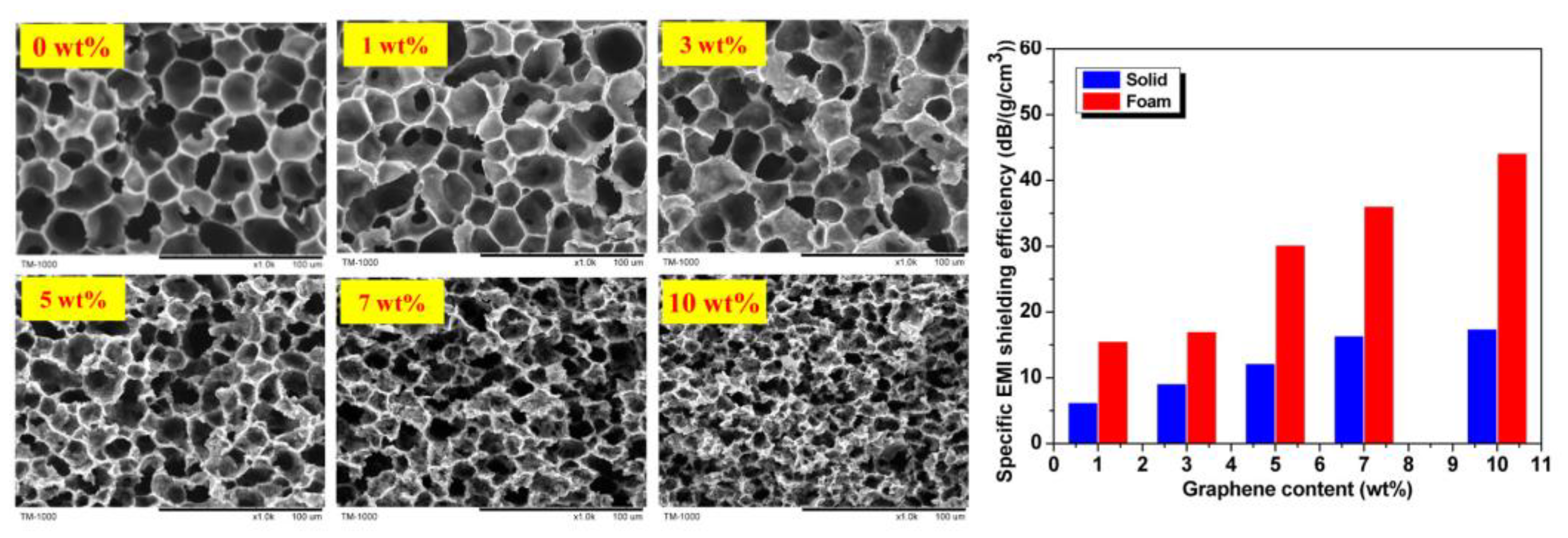
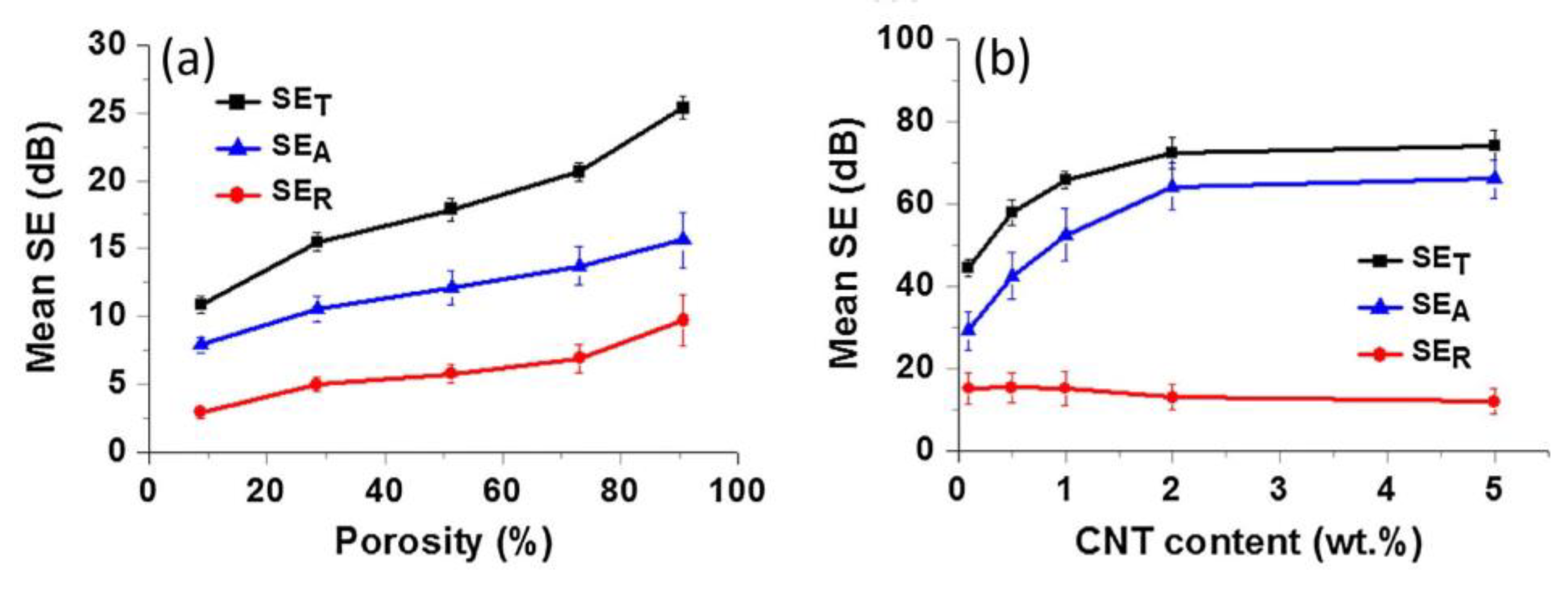
3. Typical Graphene–Polymer Nanocomposite Foams for EMI Shielding
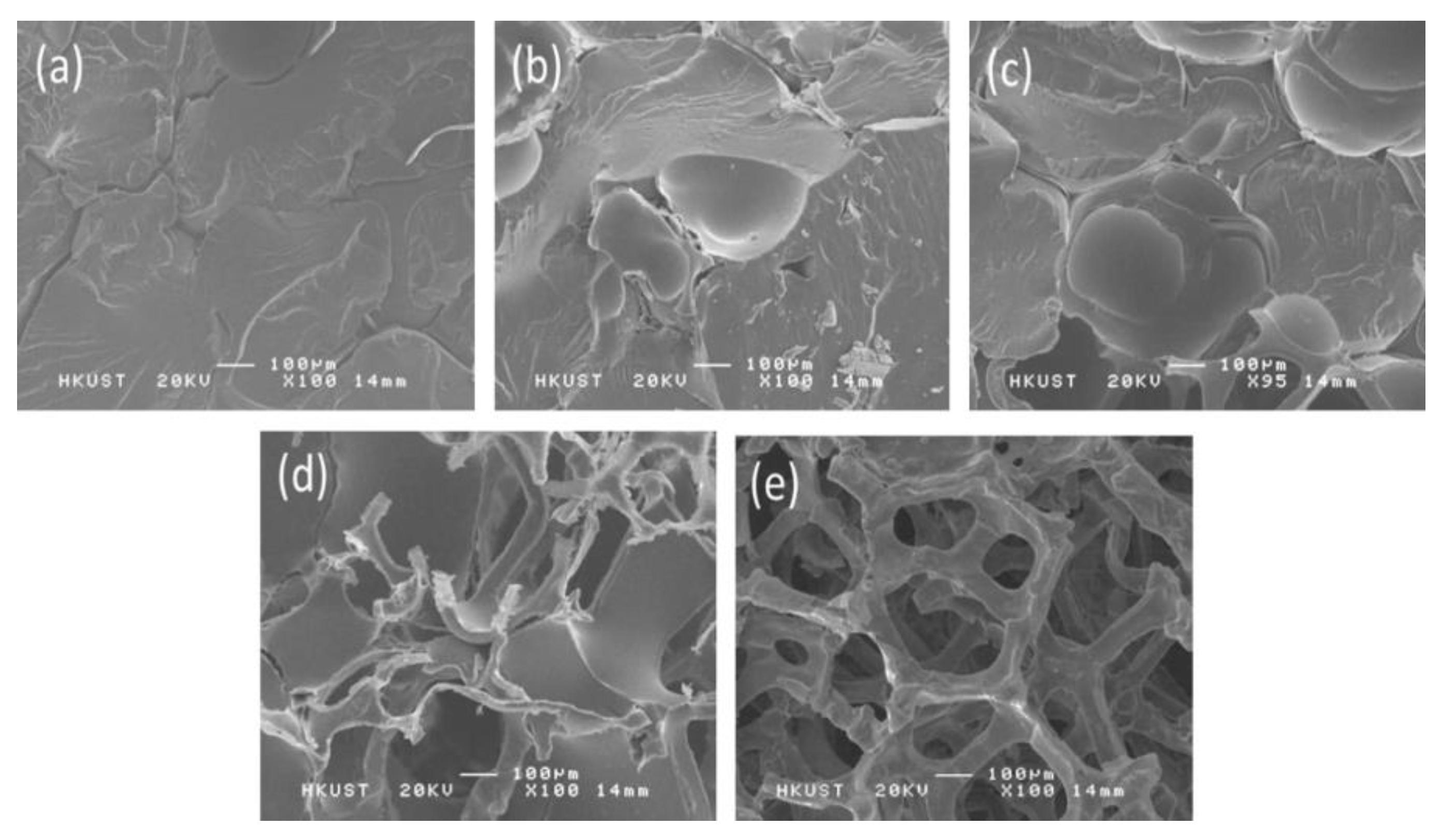
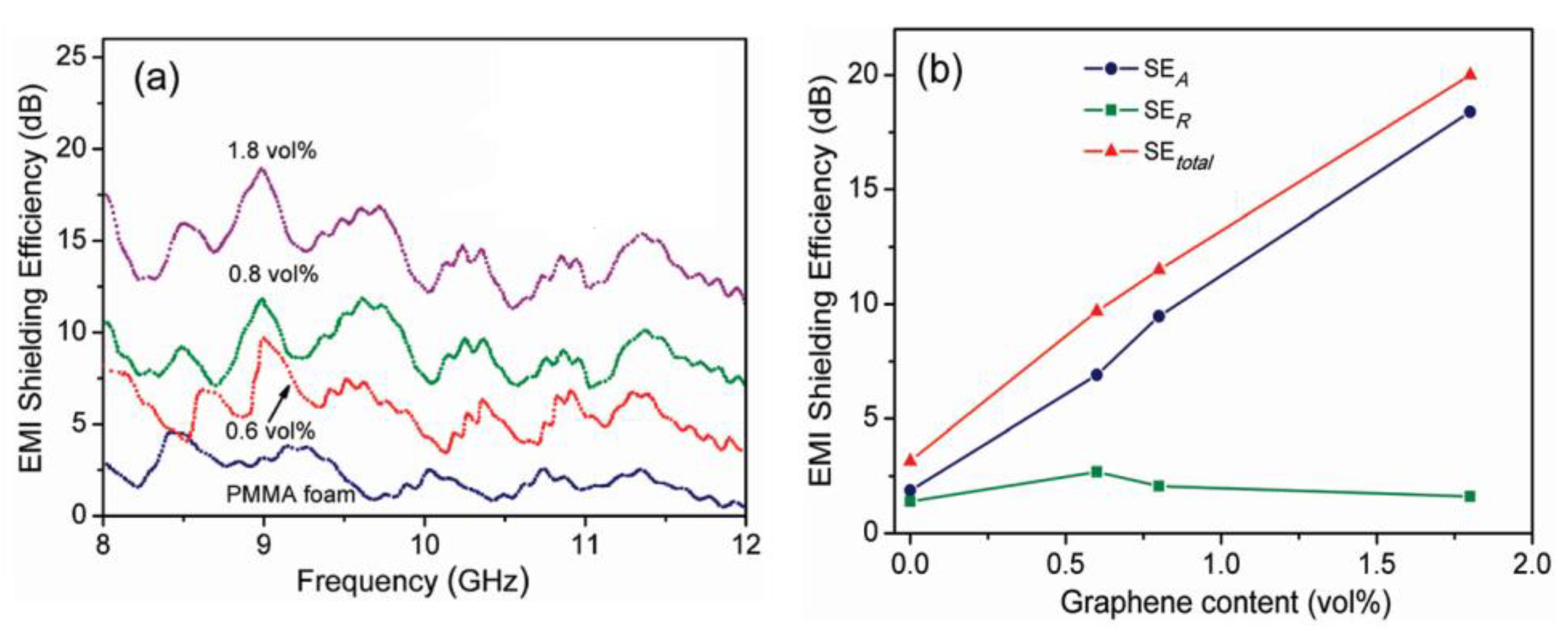
3.1. Graphene–PMMA Nanocomposite Foams
3.2. Graphene–PSt Nanocomposite Foams
3.3. Graphene–Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Nanocomposite Foams
3.4. Graphene–PEI Nanocomposite Foams
3.5. Graphene–Polyimide (PI) Nanocomposite Foams
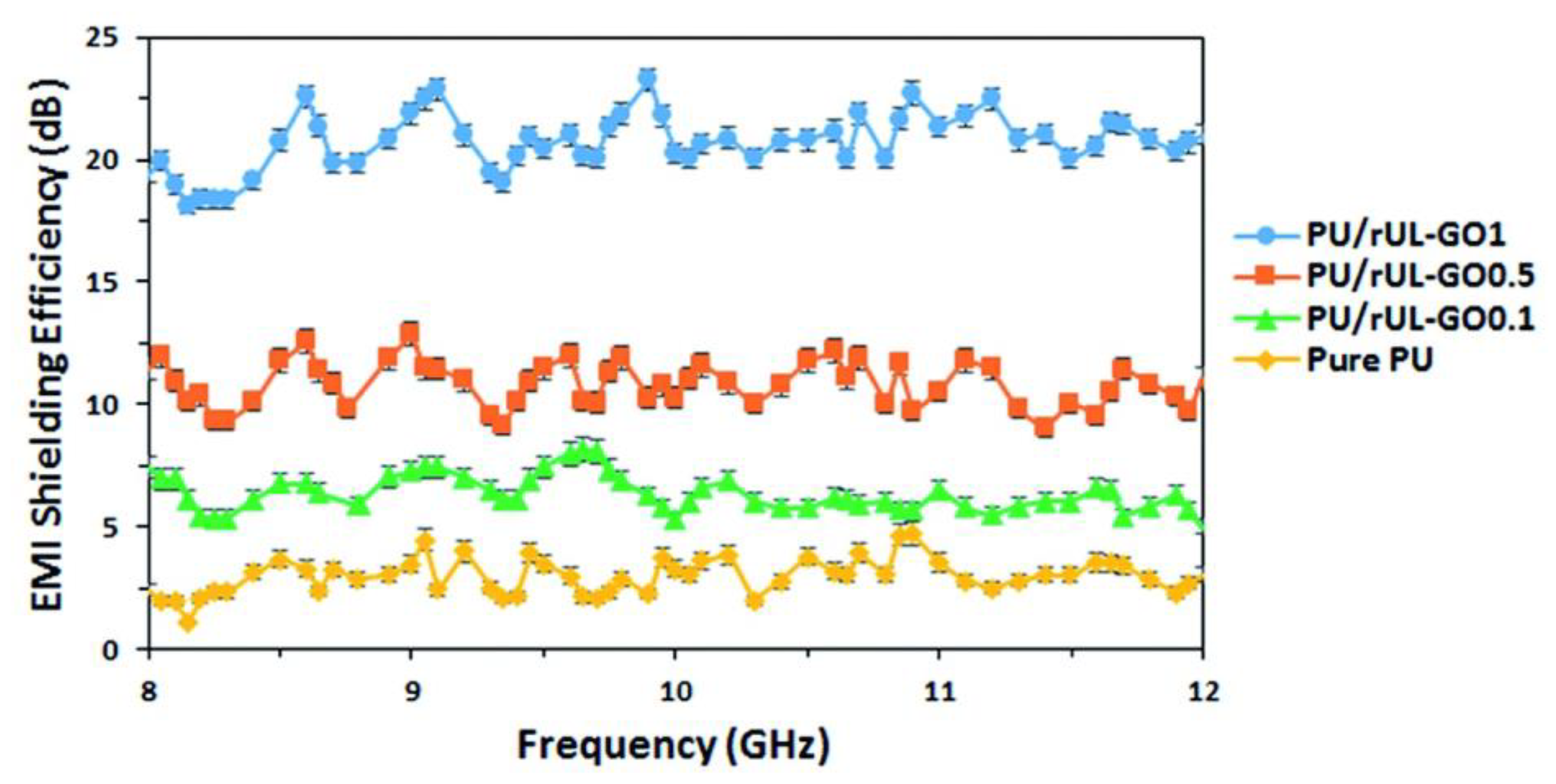
3.6. Graphene–PU Nanocomposite Foams
3.7. Graphene–PDMS Nanocomposite Foam
3.8. Graphene–Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):Poly(Styrene Sulfonate) (PEDOT:PSS) Nanocomposite Foams
3.9. Graphene–Poly(arylene ether nitrile) (PEN) Nanocomposite Foams
4. Conclusions and Outlook
- (1)
- Enhancing the EMI shielding effectiveness of polymers: Although polymers have advantages such as light weight, corrosion resistance, and easy processing, most polymers have weak intrinsic shielding properties against electromagnetic waves. To enhance their EMI shielding effectiveness, conductive polymers such as polyaniline and polypyrrole can be selected as EMI shielding scaffolds.
- (2)
- Incorporating other functional materials: Adding metallic powders, semiconductors, inorganic/organic compounds, and magnetic nanoparticles can improve impedance matching and increase the dissipation capacity of electromagnetic waves. Additionally, new two-dimensional materials such as oxides, nitrides, and black phosphorus can be added as impedance amplitude modulators and media to improve the impedance matching of materials and enhance polarization and multiple reflections at the interface.
- (3)
- Investigating the role of porosity and cell size: Although some studies have mentioned the influence of porosity and cell size on the EMI shielding effectiveness of composite foams, a systematic investigation is still needed to understand the general rules governing how and why the cell density and size affect the reflection or absorption of incident electromagnetic waves.
- (4)
- Considering thickness-specific efficiency: Currently, the weight-specific shielding efficiency of foams is often emphasized, while the thickness-specific efficiency is usually ignored. It would be more reasonable to evaluate the shielding efficiency by dividing it by the thickness dimension of samples.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shahzad, F.; Alhabeb, M.; Hatter, C.; Anasori, B.; Hong, S.; Koo, C.; Gogotsi, Y. Electromagnetic interference shielding with 2D transition metal carbides (MXenes). Science 2016, 353, 1137–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudary, V.; Dhawan, S.K.; Saini, P. Polymer based nanocomposites for electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding. In EMI Shielding Theory and Development of New Materials; Research Signpost: Kerala, India, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, S.; Sun, Z.; Huang, P.; Li, Y.; Hu, N. Some basic aspects of polymer nanocomposites: A critical review. Nano Mater. Sci. 2019, 1, 2–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Zheng, Q.; Kim, J. Rational design of two-dimensional nanofillers for polymer nanocomposites toward multifunctional applications. Prog. Mater Sci. 2021, 115, 100708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gupta, M.C.; Dudley, K.; Lawrence, R. Conductive Carbon Nanofiber–Polymer Foam Structures. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 1999–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lin, S.; Huang, K.; Jia, C.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Song, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Lei, M.; et al. A large-area AgNW-modified textile with high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. NPJ Flex. Electron. 2020, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhan, M.; Wang, K. Ultralightweight silver nanowires hybrid polyimide composite foams for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2015, 7, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaran, S.; Deshmukh, K.; Ahamed, M.B.; Khadheer Pasha, S.K. Recent advances in electromagnetic interference shielding properties of metal and carbon filler reinforced flexible polymer composites: A review. Compos. Part A Appl. S. 2018, 114, 49–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shu, J.; Cao, W.; Zhang, M.; Yuan, J.; Cao, M. Eco-mimetic nanoarchitecture for green EMI shielding. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 369, 1068–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qi, Q.; Yin, G.; Wang, W.; Yu, D. Flexible, Ultralight, and Mechanically Robust Waterborne Polyurethane/Ti3C2Tx MXene/Nickel Ferrite Hybrid Aerogels for High-Performance Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2021, 13, 21831–21843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Cai, Y.; He, P.; Shu, J.; Cao, W.; Yuan, J. 2D MXenes: Electromagnetic property for microwave absorption and electromagnetic interference shielding. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 1265–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Jang, C.; Xiao, S.; Ishigami, M.; Fuhrer, M.S. Intrinsic and extrinsic performance limits of graphene devices on SiO2. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, B.; Zhai, W.T.; Zheng, W.G. Ultrathin flexible graphene film: An excellent thermal conducting material with efficient EMI shielding. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 4542–4548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Sahoo, S.; Joanni, E.; Singh, R.K.; Tan, W.K.; Kar, K.K.; Matsuda, A. Recent progress on carbon-based composite materials for microwave electromagnetic interference shielding. Carbon 2021, 177, 304–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Tang, X.; Cai, J.; Wu, H.; Shen, J.; Guo, S. Construction, mechanism and prospective of conductive polymer composites with multiple interfaces for electromagnetic interference shielding: A review. Carbon 2021, 177, 377–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, H.; Antunes, M.; Velasco, J.I. Recent advances in carbon-based polymer nanocomposites for electromagnetic interference shielding. Prog. Mater Sci. 2019, 103, 319–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Hu, Q.; Wei, R.; Mai, X.; Naik, N.; Pan, D.; Guo, Z.; Shi, Z. Review on the electromagnetic interference shielding properties of carbon based materials and their novel composites: Recent progress, challenges and prospects. Carbon 2021, 176, 88–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Qin, S.; Jiang, Y.; Song, P.; Wang, H. Lightweight high-performance carbon-polymer nanocomposites for electromagnetic interference shielding. Compos. Part A Appl. S. 2021, 145, 106376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Shao, Q.; Ji, G.; Liang, X.; Cheng, Y.; Quan, B.; Du, Y. Metal-organic-frameworks derived porous carbon-wrapped Ni composites with optimized impedance matching as excellent lightweight electromagnetic wave absorber. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Yang, L.; Da, Y.; Zhai, W.; Zheng, W. Microcellular graphene foam for improved broadband electromagnetic interference shielding. Carbon 2016, 102, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Chang, H.; Xiao, P.; Chen, H.; Huang, Z.; Chen, Y. Broadband and Tunable High-Performance Microwave Absorption of an Ultralight and Highly Compressible Graphene Foam. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2049–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Zhai, W.; Lu, D.; Zheng, W.; Yan, Q. Fabrication of microcellular polymer/graphene nanocomposite foams. Polym. Int. 2012, 61, 1693–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhai, T.; Verdolotti, L.; Xia, H. Nanocomposite polymeric materials with 3D graphene-based architectures: From design strategies to tailored properties and potential applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 89, 213–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Huang, X.; Wu, X.; Qian, R.; Jiang, P. Mechanically Flexible and Multifunctional Polymer-Based Graphene Foams for Elastic Conductors and Oil-Water Separators. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5658–5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Li, Y.; Fei, T.; Gong, W. Facile one-pot synthesis of superhydrophobic reduced graphene oxide-coated polyurethane sponge at the presence of ethanol for oil-water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 345, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodlur, R.M.; Rabinal, M.H. Self assembled graphene layers on polyurethane foam as a highly pressure sensitive conducting composite. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 90, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, S.; Hong, A.; Choi, Y.; Ha, C.; Park, W. A tactile sensor using a conductive graphene-sponge composite. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 9185–9192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, J.; Wu, T.; Wang, X.; Huang, G.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Gao, J. Cost-effective reduced graphene oxide-coated polyurethane sponge as a highly efficient and reusable oil-absorbent. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2013, 5, 10018–10026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ren, W.; Gao, L.; Liu, B.; Pei, S.; Cheng, H. Three-dimensional flexible and conductive interconnected graphene networks grown by chemical vapour deposition. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Wan, Y.; Yu, S.; Yang, W.; Zhu, P.; Sun, R.; Wong, C.; Liao, W.H. Tuneable cellular-structured 3D graphene aerogel and its effect on electromagnetic interference shielding performance and mechanical properties of epoxy composites. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 56589–56598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xu, C.; Ma, C.; Ren, W.; Cheng, H.M. Lightweight and flexible graphene foam composites for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 1296–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Liu, X.; Shen, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Kim, J. Graphene foam/carbon nanotube/poly(dimethyl siloxane) composites for exceptional microwave shielding. Compos. Part A Appl. S. 2016, 92, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Duan, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, C. Three-dimensional porous stretchable and conductive polymer composites based on graphene networks grown by chemical vapour deposition and PEDOT:PSS coating. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 3169–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.K.; Xiong, G.M.; Zhu, M.; Özyilmaz, B.; Castro Neto, A.H.; Tan, N.S.; Choong, C. Polymer-Enriched 3D Graphene Foams for Biomedical Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 8275–8283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, Y.; Dong, X.; Chan-Park, M.B.; Song, H.; Chen, P. Macroporous and monolithic anode based on polyaniline hybridized three-dimensional graphene for high-performance microbial fuel cells. ACS Nano 2015, 6, 2394–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, P.; Zhao, X.; Huang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q. Free-standing three-dimensional graphene and polyaniline nanowire arrays hybrid foams for high-performance flexible and lightweight supercapacitors. J. Mater. Chem. 2014, 2, 14413–14420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Li, L.; Wang, Q. Fabrication of three-dimensional polyetherimide bead foams via supercritical CO2/ethanol co-foaming technology. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 4072–4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauceau, M.; Fages, J.; Common, A.; Nikitine, C.; Rodier, E. New challenges in polymer foaming: A review of extrusion processes assisted by supercritical carbon dioxide. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 749–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Rende, D.; Schadler, L.S.; Ozisik, R. Polymer nanocomposite foams. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 3837–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, M.; Velasco, J.I. Multifunctional polymer foams with carbon nanoparticles. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 486–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavgani, J.N.; Adelnia, H.; Zaarei, D.; Gudarzi, M.M. Lightweight flexible polyurethane/reduced ultralarge graphene oxide composite foams for electromagnetic interference shielding. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 27517–27527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswaraiah, V.; Sankaranarayanan, V.; Ramaprabhu, S. Functionalized Graphene–PVDF Foam Composites for EMI Shielding. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2011, 296, 894–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdejo, R.; Barroso-Bujans, F.; Rodríguez-Pérez, M.Á.; Saja, J.A.; López-Manchado, M.A. Functionalized graphene sheet filled silicone foam nanocomposites. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 2221–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.C.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, H.; Kang, Y.S. Membrane formation by water vapor induced phase inversion. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 156, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, J.; Zhai, W.; Feng, W.; Shen, B.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, W. Facile preparation of lightweight microcellular polyetherimide/graphene composite foams for electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2013, 5, 2677–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Zhai, W.; Tao, M.; Ling, J.; Zheng, W. Lightweight, multifunctional polyetherimide/graphene@Fe3O4 composite foams for shielding of electromagnetic pollution. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2013, 5, 11383–11391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Ren, P.; Pang, H.; Fu, Q.; Yang, M.; Li, Z. Efficient electromagnetic interference shielding of lightweight graphene/polystyrene composite. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 18772–18774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-B.; Yan, Q.; Zheng, W.-G.; He, Z.; Yu, Z.-Z. Tough Graphene−Polymer Microcellular Foams for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2011, 3, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Yang, B.; Wang, X.; Zuo, Y.; Chen, P.; Xia, R.; Miao, J.; Zheng, Z.; Qian, J.; Ke, Y.; et al. Composites of an Epoxy Resin (EP)/PVDF/NiCo-Graphene Nanosheet (GNS) for Electromagnetic Shielding. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 7731–7744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Pei, X.; Shen, B.; Zhai, W.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, W. Polyimide/graphene composite foam sheets with ultrahigh thermostability for electromagnetic interference shielding. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 24342–24351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, Z.; Zou, H.; Liu, P. Preparation of porous polyimide/in-situ reduced graphene oxide composite films for electromagnetic interference shielding. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2017, 28, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; He, X.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Y. Flexible Polyimide Foams Coated with Graphene Nanoplatelets/Fe3O4 for Absorption-Dominated Electromagnetic Interference Shielding, Broad-Band Microwave Absorption, and Sensor Applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 11424–11434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Li, Y.; Zhai, W.; Zheng, W. Compressible graphene-coated polymer foams with ultralow density for adjustable electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2016, 8, 8050–8057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Hou, G.; Su, X.; Bi, S.; Tang, J. Compressible Ni and Reduced Graphene Oxide (Ni-rGO) Coated Polymer Foams for Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Shielding. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 186, 012031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Feng, Y.; Wang, J. Asymmetric conductive structure design for stabilized composites with absorption dominated ultra-efficient electromagnetic interference shielding performance. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2023, 236, 110006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Shen, X.; Zheng, Q.; Xue, Q.; Kim, J.-K. Ultralight graphene foam/conductive polymer composites for exceptional electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2017, 9, 9059–9069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, X. In Situ Growth of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles in Poly(arylene ether nitrile)/Graphene/Carbon Nanotube Foams for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 7802–7813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Hamidinejad, M.; Wang, S.; Bai, P.; Che, R.; Zhang, R.; Park, C.B. Advances in electromagnetic shielding properties of composite foams. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 8896–8949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Qiu, H.; Gu, J. Structural Design Strategies of Polymer Matrix Composites for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding: A Review. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, A.R.; Puthiyaveettil Azeez, N.; Thankan, B.; Gopakumar, N.; Jaroszewski, M.; Paoloni, C.; Kalarikkal, N.; Thomas, S. Recent Progress in Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Performance of Porous Polymer Nanocomposites—A Review. Energies 2022, 15, 3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachariah, S.M.; Grohens, Y.; Kalarikkal, N.; Thomas, S. Hybrid materials for electromagnetic shielding: A review. Polym. Compos. 2022, 43, 2507–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahi-Sarmad, M.; Noroozi, M.; Xiao, X.; Park, C.B. Recent Advances in Graphene-Based Polymer Nanocomposites and Foams for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 1545–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, R.; Gebrekrstos, A.; Orasugh, J.T.; Ray, S.S. Nanocarbon-Containing Polymer Composite Foams: A Review of Systems for Applications in Electromagnetic Interference Shielding, Energy Storage, and Piezoresistive Sensors. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 6807–6842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yan, X.; Xu, X.L.; Chen, Y.; Han, W.; Chai, X.; Liu, X.L.; Liu, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, H.; et al. Progress in the foaming of polymer-based electromagnetic interference shielding composite by supercritical CO2. Chem. Asian J. 2023, 18, e202201000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orasugh, J.T.; Ray, S.S. Functional and Structural Facts of Effective Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Materials: A Review. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 8134–8158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, J.; Zhou, D. Advances in Graphene–Polymer Nanocomposite Foams for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. Polymers 2023, 15, 3235. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153235
Sun J, Zhou D. Advances in Graphene–Polymer Nanocomposite Foams for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. Polymers. 2023; 15(15):3235. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153235
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Jiaotong, and Dan Zhou. 2023. "Advances in Graphene–Polymer Nanocomposite Foams for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding" Polymers 15, no. 15: 3235. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153235
APA StyleSun, J., & Zhou, D. (2023). Advances in Graphene–Polymer Nanocomposite Foams for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. Polymers, 15(15), 3235. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153235





