Preparation of Chemically Modified Lignin-Reinforced PLA Biocomposites and Their 3D Printing Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Carboxylated Lignin (COOH-Lignin)
2.3. 3D Printing
2.4. Equipment and Experiments
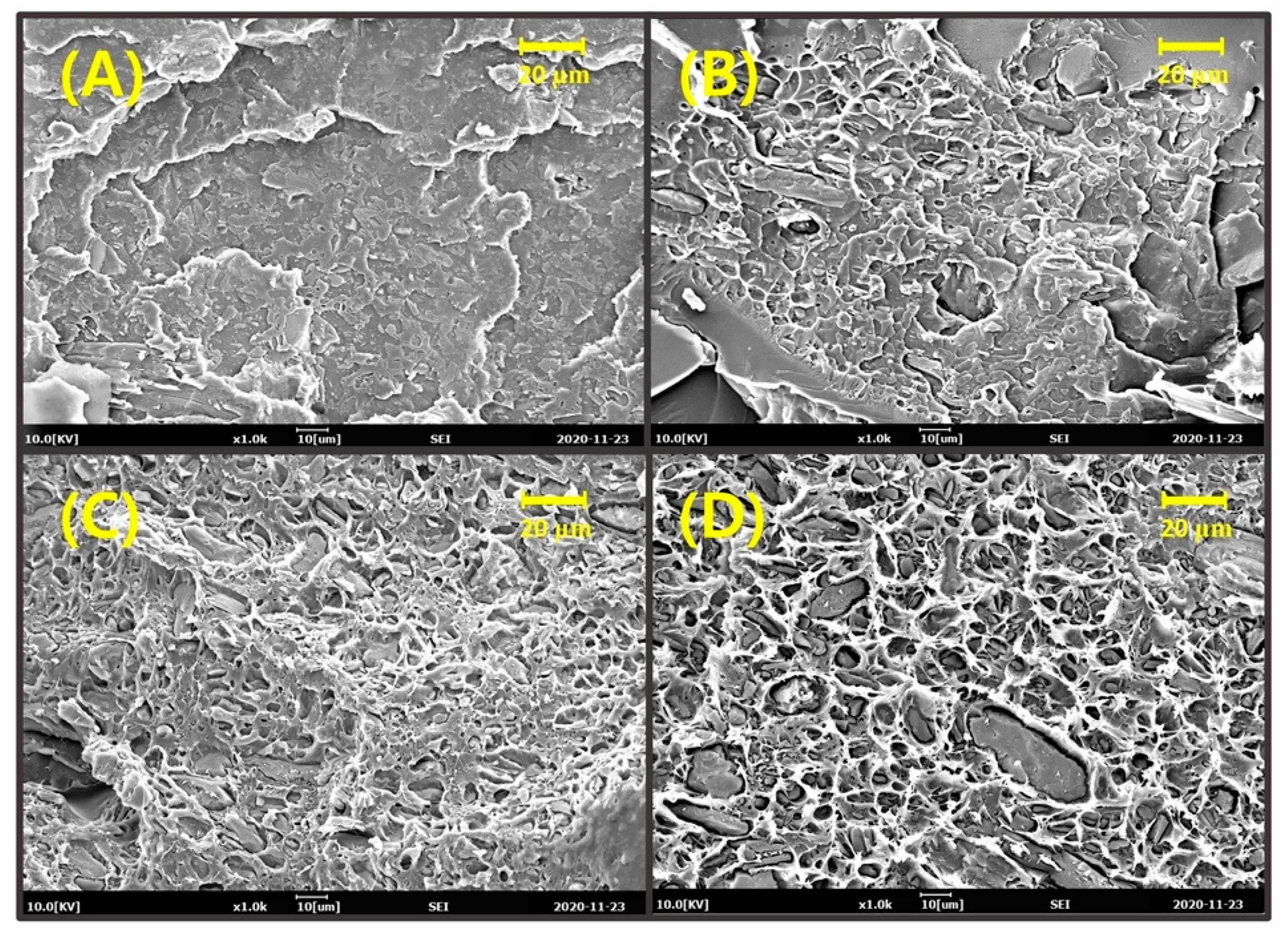
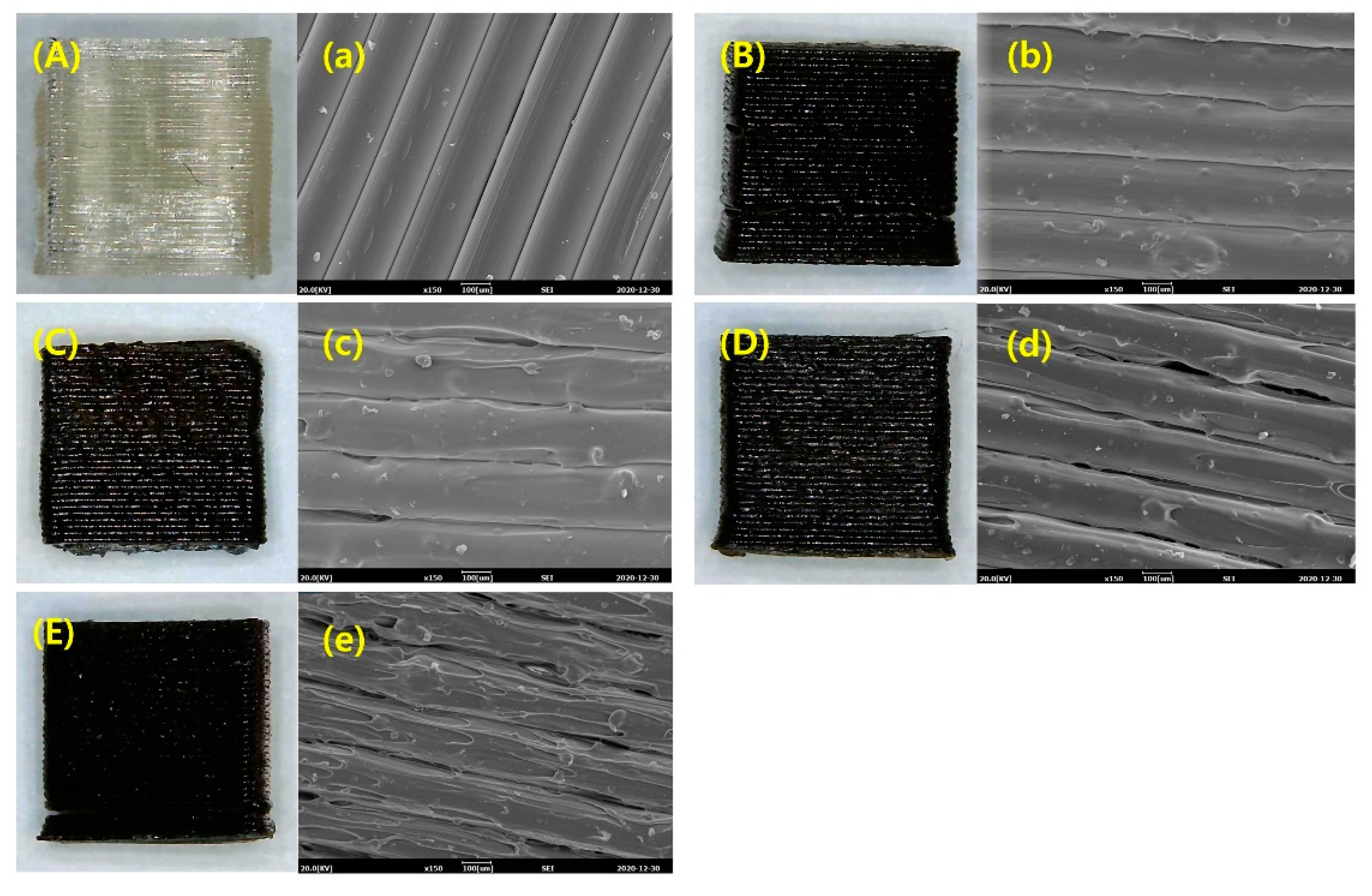
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grisby, W.J.; Scott, S.M.; Plowman-Holmes, M.I.; Middlewood, P.G.; Recabar, K. Combination and processing keratin with lignin as biocomposite materials for additive manufacturing technology. Acta Biomater. 2020, 104, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, N.A.; Bowland, C.C.; Naskar, A.K. A general method to improve 3D-printability and inter-layer adhesion in lignin-based composites. Appl. Mater. Today 2018, 12, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIlroy, C.; Olmsted, P. Disentanglement effects on welding behaviour of polymer melts during the fused-filament-fabrication method for additive manufacturing. Polymer 2017, 123, 376–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dul, S.; Fambri, L.; Pegoretti, A. Fused deposition modelling with ABS–graphene nanocomposites. Compos. Part A: Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 85, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidian, M.; Tehrany, E.A.; Imran, M.; Jacquot, M.; Desobry, S. Poly-Lactic Acid: Production, Applications, Nano-composites, and Release Studies. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. 2010, 9, 552–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSawy, M.A.; Kim, K.-H.; Park, J.-W.; Deep, A. Hydrolytic degradation of polylactic acid (PLA) and its composites. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 79, 1346–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrecque, L.V.; Kumar, R.A.; Gross, R.A.; McCarthy, S.P. Citrate esters as plasticizers for poly(lactic acid). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1997, 66, 1507–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.S.-G.; Liu, H.-J. Effect of soft segment on degradation kinetics in polyethylene glycol/poly(l-lactide) block copolymers. Polym. Bull. 1993, 30, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, H.; Cohn, D. Phase separation in poly(ethylene glycol)/poly(lactic acid) blends. Eur. Polym. J. 1988, 24, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.-C.; He, Y.-S.; Zeng, J.-B.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.-Z. In situ formed crosslinked polyurethane toughened polylactide. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 2530–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojijo, V.; Ray, S.S.; Sadiku, R. Toughening of Biodegradable Polylactide/Poly(butylene succinate-co-adipate) Blends via in Situ Reactive Compatibilization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 4266–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Wolcott, M.P.; Zhang, J. Study of Biodegradable Polylactide/Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) Blends. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Qiao, B.; Wang, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Ma, J.; Coates, P.; Coates, P. Employing a novel bioelastomer to toughen polylactide. Polymer 2013, 54, 2450–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitinis, N.; Verdejo, R.; Cassagnau, P.; Lopez-Manchado, M. Structure and properties of polylactide/natural rubber blends. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 129, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, W.; Huang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Jiang, L.; Dan, Y.; Luo, Y.; Peng, Z. Thermal, mechanical and rheological properties of polylactide toughened by expoxidized natural rubber. Mater. Des. 2013, 45, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, R.; Mohanty, A.K. Modification of Brittle Polylactide by Novel Hyperbranched Polymer-Based Nanostructures. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2476–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phuong, V.T.; Coltelli, M.-B.; Cinelli, P.; Cifelli, M.; Verstichel, S.; Lazzeri, A. Compatibilization and property enhancement of poly(lactic acid)/polycarbonate blends through triacetin-mediated interchange reactions in the melt. Polymer 2014, 55, 4498–4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuryev, Y.; Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M. Novel biocomposites from biobased PC/PLA blend matrix system for durable applications. Compos. Part B: Eng. 2017, 130, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordobil, O.; Egüés, I.; Llano-Ponte, R.; Labidi, J. Physicochemical properties of PLA lignin blends. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 108, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thunga, M.; Chen, K.; Grewell, D.; Kessler, M.R. Bio-renewable precursor fibers from lignin/polylactide blends for conversion to carbon fibers. Carbon 2014, 68, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiridon, I.; Leluk, K.; Resmerita, A.M.; Darie, R.N. Evaluation of PLA–lignin bioplastics properties before and after accelerated weathering. Compos. Part B: Eng. 2015, 69, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, R.K.; Maiti, S.N.; Ghosh, A.K. Crystallization, Morphological, and Mechanical Response of Poly(Lactic Acid)/Lignin-Based Biodegradable Composites. Polym. Technol. Eng. 2015, 55, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimini, V.; Sykacek, E.; Hashim, S.N.A.S.; Holzweber, J.; Hettegger, H.; Fackler, K.; Potthast, A.; Mundigler, N.; Rosenau, T. Compatibility of kraft lignin, organosolv lignin and lignosulfonate with PLA in 3D printing. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2018, 39, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkartzou, E.; Koumoulos, E.P.; Charitidis, C.A. Production and 3D printing processing of bio-based thermoplastic filament. Manuf. Rev. 2017, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanase-Opedal, M.; Espinosa, E.; Rodríguez, A.; Chinga-Carrasco, G. Lignin: A Biopolymer from Forestry Biomass for Biocomposites and 3D Printing. Materials 2019, 12, 3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Robles, J.; Martin, N.K.; Fong, M.L.; Stewart, S.A.; Irwin, N.J.; Rial-Hermida, M.I.; Donnelly, R.F.; Larrañeta, E. Antioxidant PLA Composites Containing Lignin for 3D Printing Applications: A Potential Material for Healthcare Applications. Pharmer 2019, 11, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasti, S.; Triggs, E.; Farag, R.; Auad, M.; Adhikari, S.; Bajwa, D.; Li, M.; Ragauskas, A.J. Influence of plasticizers on thermal and mechanical properties of biocomposite filaments made from lignin and polylactic acid for 3D printing. Compos. Part B: Eng. 2020, 205, 108483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; An, X.; Liu, L.; Tang, S.; Cao, H.; Xu, Q.; Liu, H. Cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin, and their derivatives as multi-components of bio-based feedstocks for 3D printing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 250, 116881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, A.; Zhang, S.; Bhagia, S.; Yoo, C.G.; Ragauskas, A.J. 3D printing of biomass-derived composites: Application and characterization approaches. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 21698–21723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagia, S.; Lowden, R.R.; Erdman, D., III; Rodriguez, M., Jr.; Haga, B.A.; Solano, I.R.M.; Gallego, N.C.; Pu, Y.; Muchero, W.; Kunc, V.; et al. Tensile properties of 3D-printed wood-filled PLA materials using poplar trees. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 21, 100832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, J.F.M.; da Silva, A.L.N.; Escócio, V.A.; da Fonseca Thomé, A.H.M.; De Sousa, A.M.F.; Nascimento, C.R.; Bertolino, L.C. Rheological, mechanical and morphological behavior of polylactide/nano-sized calcium carbonate composites. Polym. Bull. 2016, 73, 3531–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicala, G.; Latteri, A.; Saccullo, G.; Recca, G.; Sciortino, L.; Lebioda, S.; Saake, B. Investigation on Structure and Thermomechanical Processing of Biobased Polymer Blends. J. Polym. Environ. 2016, 25, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Cui, Y.; Gou, G.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, S.; Hui, D.; Gou, J.; Zhou, Z. Liquefaction of lignin in hot-compressed water to phenolic feedstock for the synthesis of phenol-formaldehyde resins. Compos. Part B: Eng. 2017, 112, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdtman, H. Lignins: Occurrence, Formation, Structure and Reactions; Sarkanen, K.V., Ludwig, C.H., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1971; p. 916. [Google Scholar]
- Graupner, N.; Fischer, H.; Ziegmann, G.; Müssig, J. Improvement and analysis of fibre/matrix adhesion of regenerated cellulose fibre reinforced PP-, MAPP- and PLA-composites by the use of Eucalyptus globulus lignin. Compos. Part B: Eng. 2014, 66, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiss-Blanquet, S.; Zheng, D.; Ferreira, N.L.; Lapierre, C.; Baumberger, S. Effect of pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis of wheat straw on cell wall composition, hydrophobicity and cellulase adsorption. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 5938–5946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisperguer, J.; Perez, P.; Urizar, S. Structure and thermal properties of lignins: Characterization by infrared spectroscopy and differential scanning calorimetry. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2009, 54, 460–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelwahab, M.A.; Taylor, S.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. Thermo-mechanical characterization of bioblends from polylactide and poly(buthylene adipate-co-terephthalate) and lignin. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2015, 300, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Lignin Content (wt.%) | Pristine Lignin | COOH-Lignin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tm (°C) | Tg (°C) | Tm (°C) | Tg (°C) | |
| 5 | 152.2 | 63.4 | 152.1 | 64.4 |
| 10 | 150.1 | 60.6 | 152.5 | 63.9 |
| 15 | 151.7 | 62.5 | 151.5 | 63.4 |
| 20 | 149.2 | 60.3 | 152.2 | 65.0 |
| Std. Dev. | 1.4 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 0.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, S.-H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, O.Y.; Hwang, S.-H. Preparation of Chemically Modified Lignin-Reinforced PLA Biocomposites and Their 3D Printing Performance. Polymers 2021, 13, 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040667
Hong S-H, Park JH, Kim OY, Hwang S-H. Preparation of Chemically Modified Lignin-Reinforced PLA Biocomposites and Their 3D Printing Performance. Polymers. 2021; 13(4):667. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040667
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Seo-Hwa, Jin Hwan Park, Oh Young Kim, and Seok-Ho Hwang. 2021. "Preparation of Chemically Modified Lignin-Reinforced PLA Biocomposites and Their 3D Printing Performance" Polymers 13, no. 4: 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040667
APA StyleHong, S.-H., Park, J. H., Kim, O. Y., & Hwang, S.-H. (2021). Preparation of Chemically Modified Lignin-Reinforced PLA Biocomposites and Their 3D Printing Performance. Polymers, 13(4), 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040667





