Electrostatic Self-Assembly of Composite Nanofiber Yarn
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
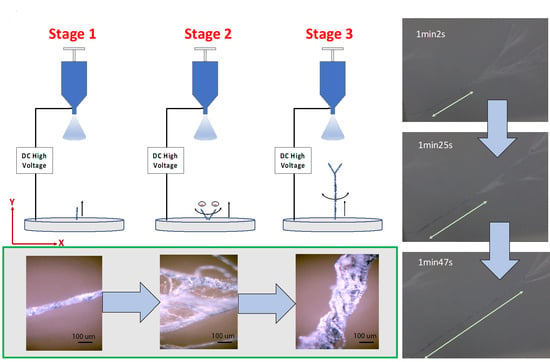
2.1. Yarn Formation
2.2. Experiment Setup
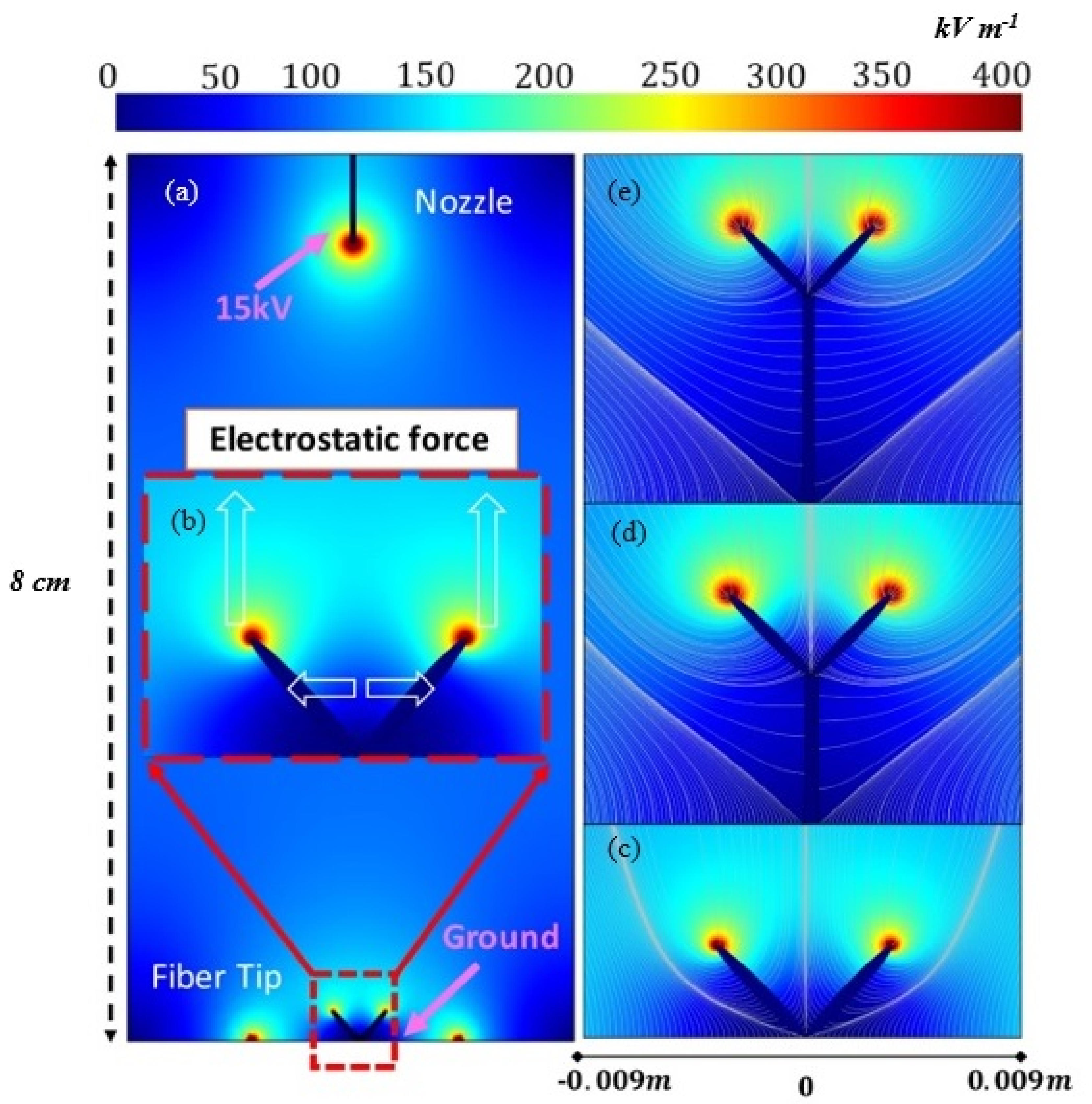
2.3. Finite Element Modelling of Yarn Formation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Field Considerations
3.3. Structural Densification-Electrospinning Time
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, S.L.P.; Stylios, G.K. An overview of smart technologies for clothing design and engineering. Int. J. Cloth. Sci. Technol. 2006, 18, 108–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.V.; Rahman, A.; Kumar, N.S.; Aditi, A.; Galluzzi, M.; Bovio, S.; Barozzi, S.; Montani, E.; Parazzoli, D. Bio-inspired approaches to design smart fabrics. Mater. Des. 2012, 36, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugliuzza, A.; Drioli, E. A review on membrane engineering for innovation in wearable fabrics and protective textiles. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 446, 350–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoppa, M.; Chiolerio, A. Wearable Electronics and Smart Textiles: A Critical Review. Sensors 2014, 14, 11957–11992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honegger, E. Training for technical management in the textile industry at the swiss federal institute of technology. J. Text. Inst. Proc. 1938, 29, P298–P303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Gong, R.-H. Manufacturing technologies of polymeric nanofibres and nanofibre yarns. Polym. Int. 2008, 57, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, D.; Dijkstra, P.J.; Berg, J.W.A.; Feijen, J. Phase separation process in polymer solutions in relation to membrane for-mation, J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 117, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakarvarti, S.; Vetter, J. Template synthesis—A membrane based technology for generation of nano-/micro materials: A review. Radiat. Meas. 1998, 29, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Kotaki, M.; Inai, R.; Ramakrishna, S. Potential of Nanofiber Matrix as Tissue-Engineering Scaffolds. Tissue Eng. 2005, 11, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Brinker, C.J. Annual Review of Nano Research; Cao, G., Brinker, C.J., Eds.; World Scientific: Singapore, 2006; Volume 1, pp. 192–200. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, U.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Electrospinning of Continuous Nanofiber Bundles and Twisted Nanofiber Yarns; InTech: Kwun Tong, China, 2011; pp. 153–174. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning of Polymeric and Ceramic Nanofibers as Uniaxially Aligned Arrays. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazbouz, M.B.; Stylios, G.K. Alignment and optimization of nylon 6 nanofibers by electrospinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 107, 3023–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, W.E.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on electrospinning design and nanofibre assemblies. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, R89–R106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazbouz, M.B.; Stylios, G.K. Novel mechanism for spinning continuous twisted composite nanofiber yarns. Eur. Polym. J. 2008, 44, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, J.A.; Wnek, G.E.; Simpson, D.G.; Bowlin, G.L. Electrospinning of Collagen Nanofibers. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.W.; Lee, K.H.; Khil, M.S.; Ho, Y.S.; Kim, H.Y. The effect of molecular weight and the linear velocity of drum surface on the properties of electrospun poly(ethylene terephthalate) nonwovens. Fibers Polym. 2004, 5, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning Nanofibers as Uniaxially Aligned Arrays and Layer-by-Layer Stacked Films. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, W.E.; Gopal, R.; Ramaseshan, R.; Fujihara, K.; Ramakrishna, S. A dynamic liquid support system for continuous elec-trospun yarn fabrication. Polymer 2007, 48, 3400–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, E.; Bűttner, U.; Sanderson, R.D. Continuous yarns from electrospun fibers. Polymer 2005, 46, 2419–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khil, M.S.; Bhattarai, S.R.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, S.Z.; Lee, K.H. Novel Fabricated Matrix Via Electrospinning for Tissue Engi-neering. J. Biomed. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2005, 72, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jee, S.Y.; Lee, J.R.; Kim, H.J.; Hong, Y.T.; Kim, S.; Park, S.J. Method of manufacturing a continuous filament by electrospinning. U.S. Patent 7799262, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Formhals, A. Artificial Thread and Method of Producing Same. U.S. Patent 2187306, 16 January 1940. [Google Scholar]
- Formhals, A. Production of artificial fibers from fiber forming liquids. U.S. Patent 2323025, 29 June 1943. [Google Scholar]
- Dalton, P.D.; Klee, D.; Möller, M. Electrospinning with dual collection rings. Polymer 2005, 46, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.-Q.; Eder, M.; Burgert, I.; Tasis, D.; Prato, M.; Wagner, H.D. One-step electrospun nanofiber-based composite ropes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 83108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effect of incorporation of ethylene glycol into PEDOT:PSS on electron phonon coupling and conductivity. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 215501. [CrossRef]
- Yarin, A.L.; Koombhongse, S.; Reneker, D.H. Bending instability in electrospinning of nanofibers. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 89, 3018–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.; Chen, S.; Chiang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Chao, C. Highly conductive PEDOT:PSS films by post-treatment with dimethyl sulfoxide for ITO-free liquid crystal display. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 3760–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriev, O.; Grinko, D.; Noskov, Y.; Ogurtsov, N.; Pud, A. PEDOT:PSS films—Effect of organic solvent additives and annealing on the film conductivity. Synth. Met. 2009, 159, 2237–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Johansson, M.; Andersson, M.; Hummelen, J.; Inganäs, O. Polymer Photovoltaic Cells with Conducting Poly-mer Anodes. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 662–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Chu, C.; Chen, F.; Xu, Q.; Yang, Y. High-Conductivity Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene): Poly(styrene sul-fonate) Film and Its Application in Polymer Optoelectronic Devices. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-C.; Chiang, Y.-H.; Wu, C.-W.; Estroff, B. Inkjet-printed multi-parameter measuring sensor. Nanosens. Biosens. Info-Tech Sens. 3D Syst. 2017, 10167, 1016713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seekaew, Y.; Lokavee, S.; Phokharatkul, D.; Wisitsoraat, A.; Kerdcharoen, T.; Wongchoosuk, C. Low-cost and flexible printed graphene–PEDOT:PSS gas sensor for ammonia detection. Org. Electron. 2014, 15, 2971–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample # | Material A (6% PVA Dissolved in PEDOT:PSS) | DMSO | Ethylene Glycol (EG) | CNC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 93.7% | 6.3% | ||
| 2 | 95% | 5% | ||
| 3 | 100% | |||
| Material B (7% PVA dissolved in PEDOT:PSS) | ||||
| 4 | 93.1% | 4.9% | 2% | |
| 5 | 93.1% | 4.9% | 2% |
| Test # | Voltage (kV) | Distance (cm) | Sample # | E field (kV cm−1) | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 15 | 8.0 | 1 | 1.875 | Yarn |
| B | 15 | 8.0 | 2 | 1.875 | Yarn |
| C | 17 | 7.0 | 3 | 2.43 | No yarn |
| D | 17 | 8.0 | 4 | 2.13 | No yarn |
| E | 17 | 7.0 | 4 | 2.42 | Yarn |
| F | 19 | 8.5 | 4 | 2.24 | No yarn |
| G | 19 | 7.5 | 4 | 2.53 | Yarn |
| H | 17 | 8.0 | 5 | 2.13 | Yarn |
| I | 15 | 8.0 | 5 | 1.87 | Yarn |
| J | 15 | 8.5 | 5 | 1.76 | Yarn generated after 3 min |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.-C.; Cheng, Y.-T.; Estroff, B. Electrostatic Self-Assembly of Composite Nanofiber Yarn. Polymers 2021, 13, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010012
Wang W-C, Cheng Y-T, Estroff B. Electrostatic Self-Assembly of Composite Nanofiber Yarn. Polymers. 2021; 13(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wei-Chih, Yen-Tse Cheng, and Benjamin Estroff. 2021. "Electrostatic Self-Assembly of Composite Nanofiber Yarn" Polymers 13, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010012
APA StyleWang, W.-C., Cheng, Y.-T., & Estroff, B. (2021). Electrostatic Self-Assembly of Composite Nanofiber Yarn. Polymers, 13(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13010012