Engineering Additive Manufacturing and Molding Techniques to Create Lifelike Willis’ Circle Simulators with Aneurysms for Training Neurosurgeons
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Fabrication of Simulators
2.1. Circle of Willis Vascular System
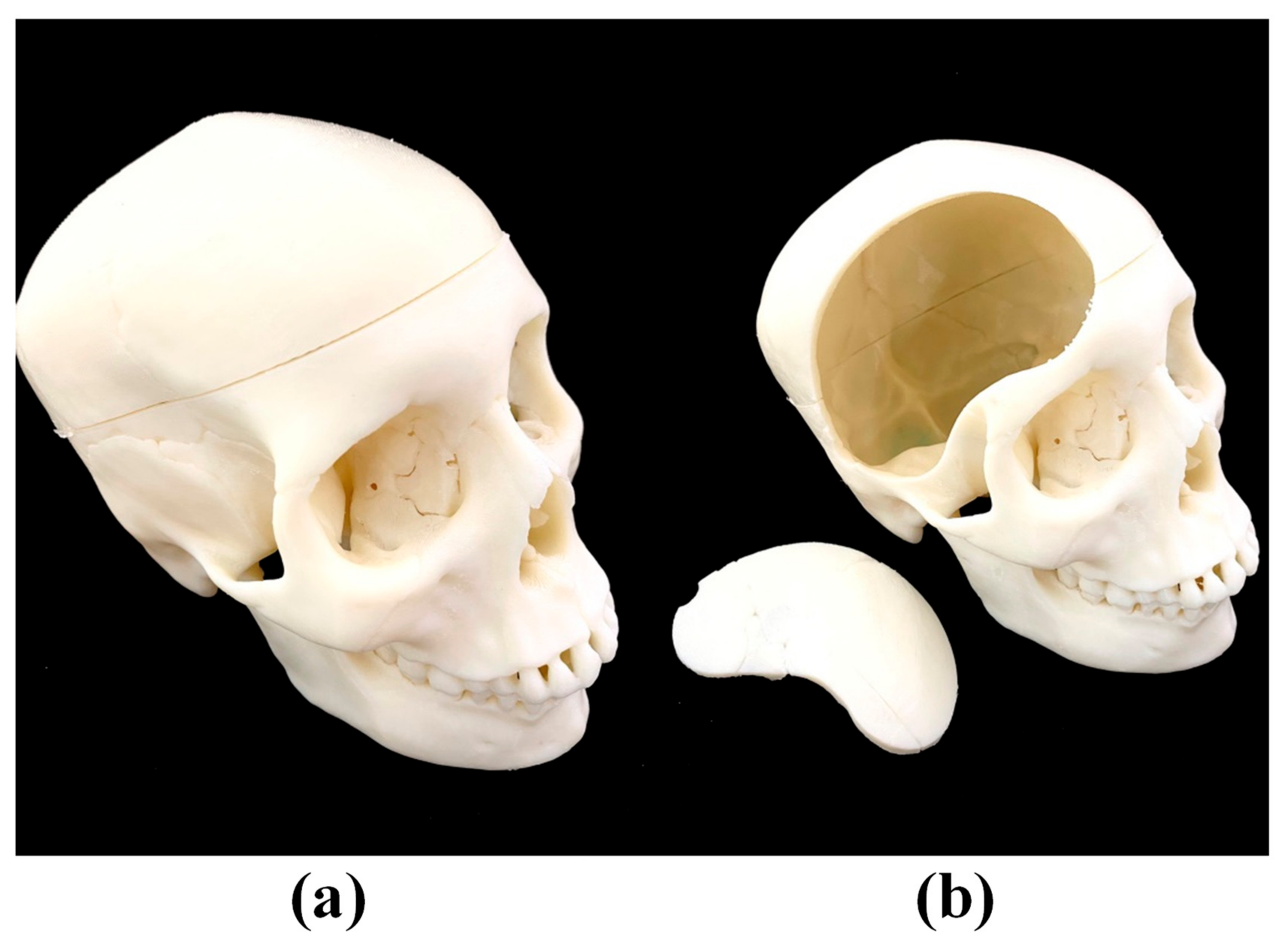
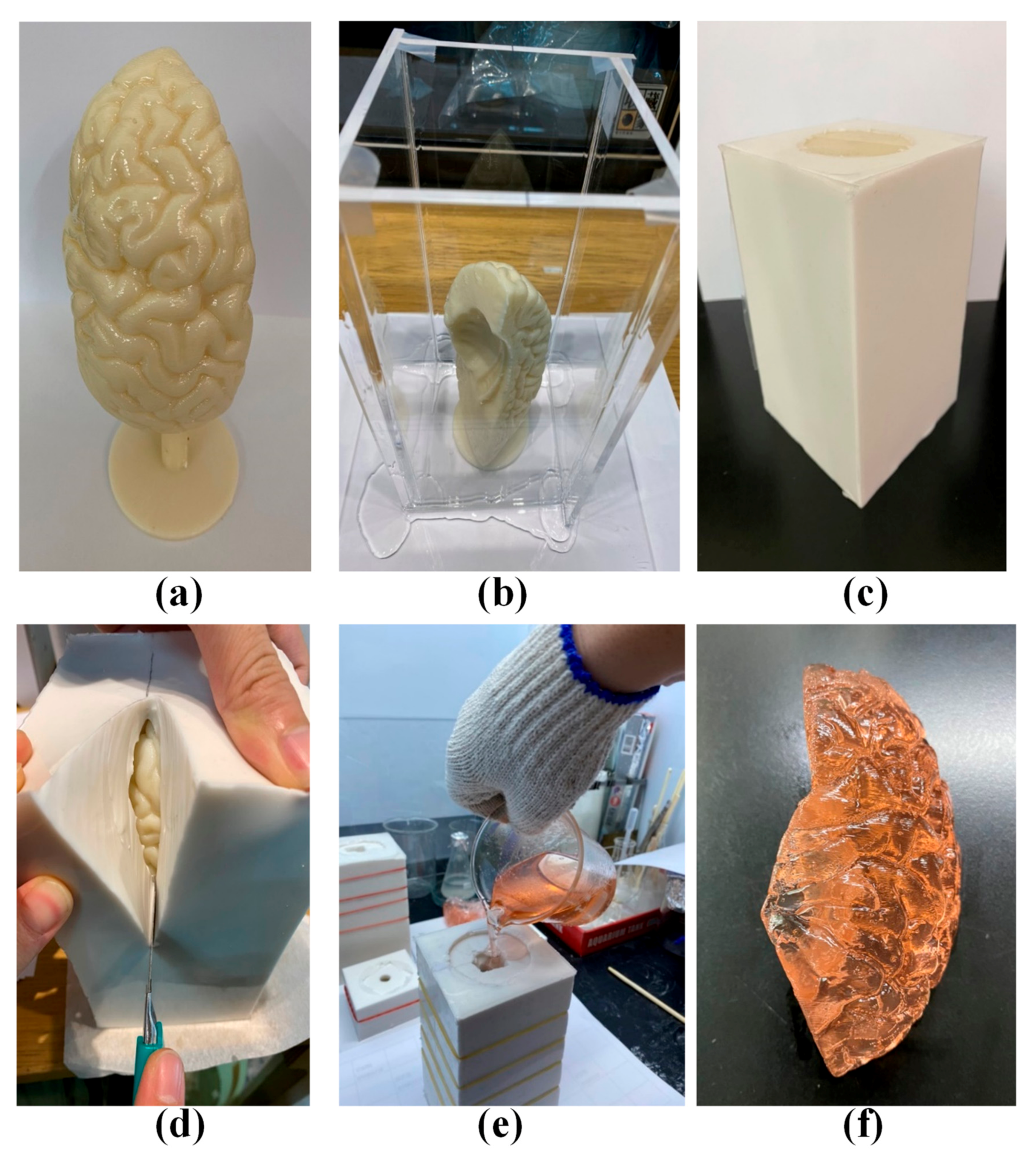
2.2. Brain Lobes and Skull
2.3. Assembly of Complete Simulation Device
3. Experiment Methods
3.1. Materials of Circle of Willis
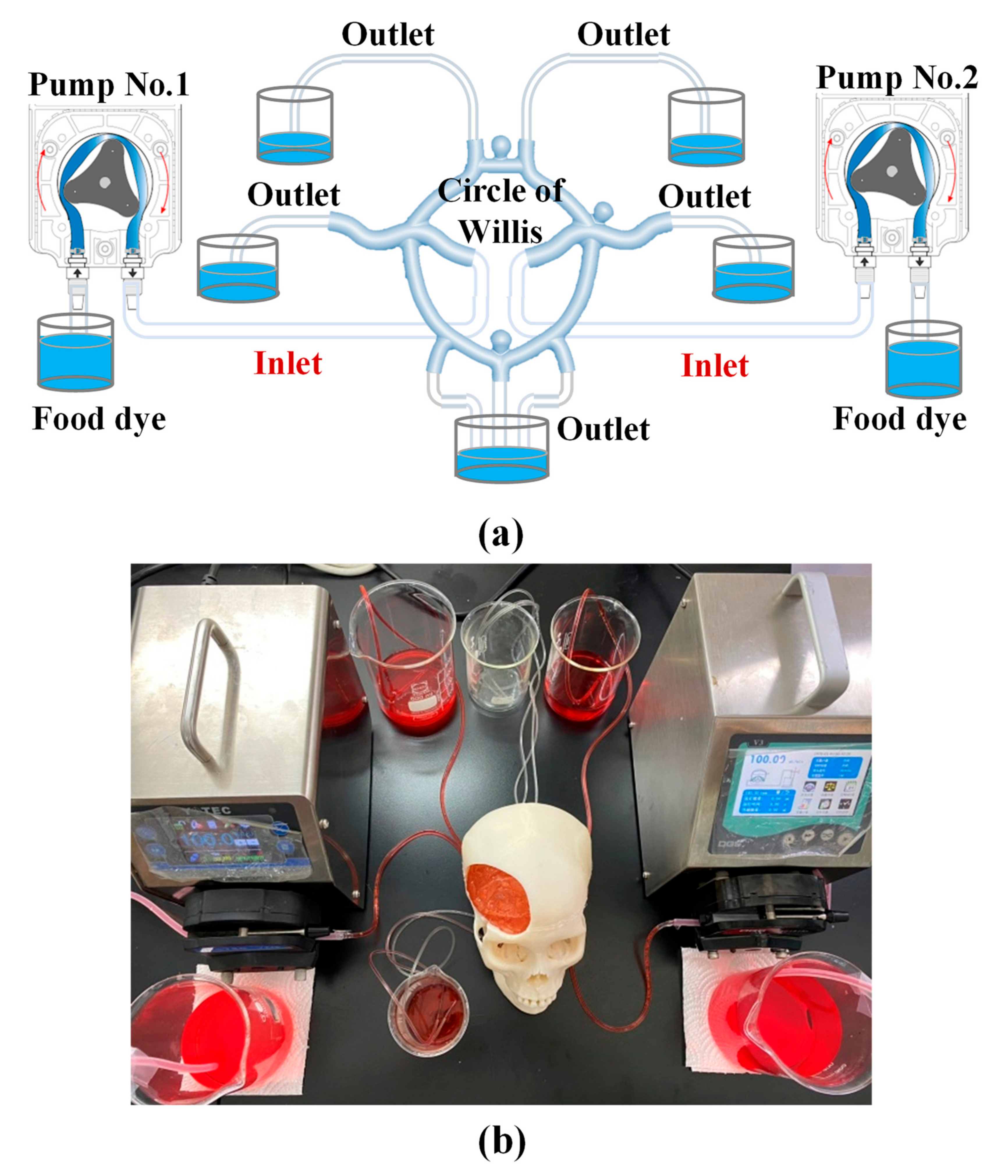
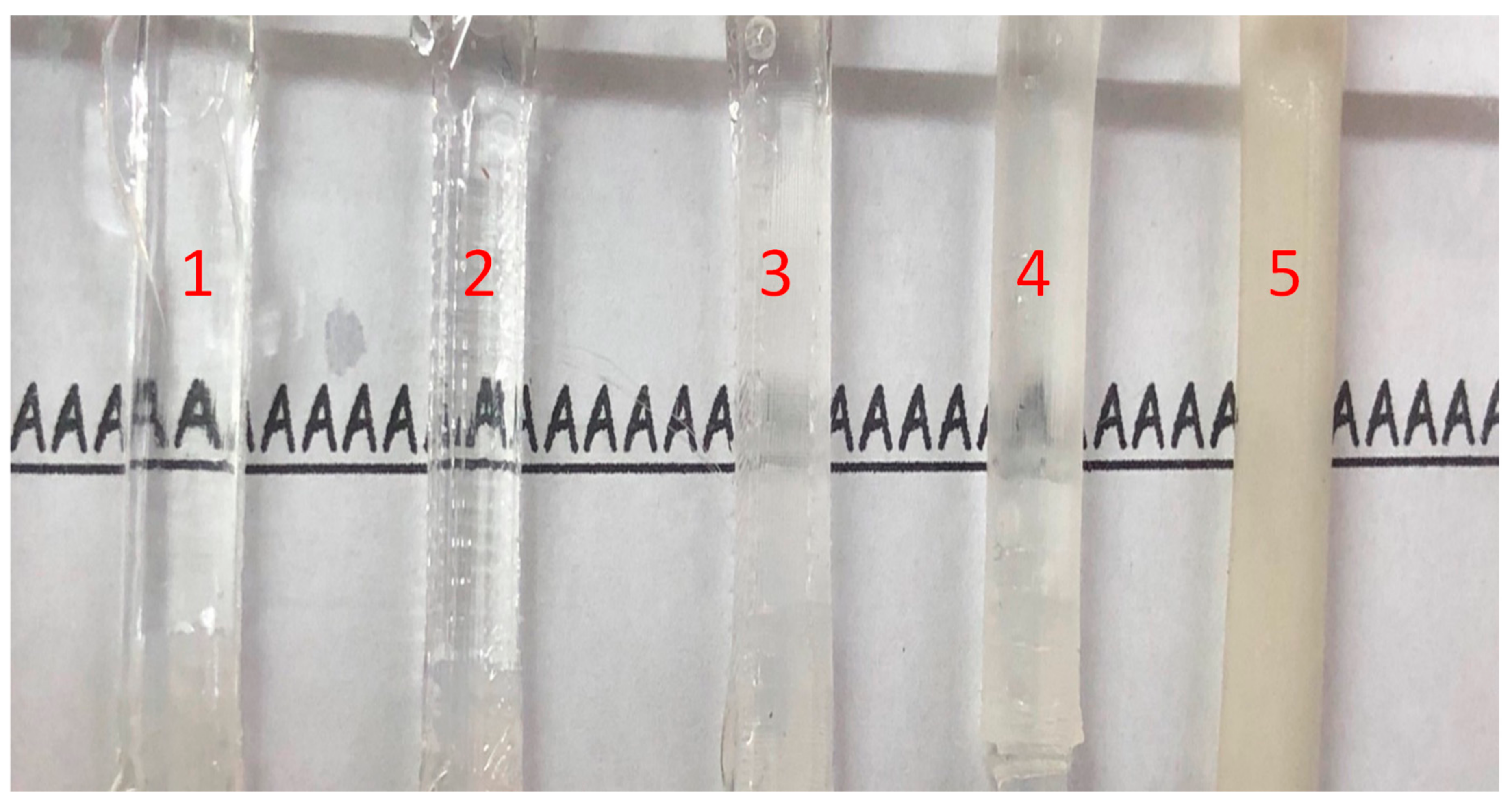
3.2. Visualization of Transparent Vascular System
3.3. Dimensional Accuracy of Vascular System
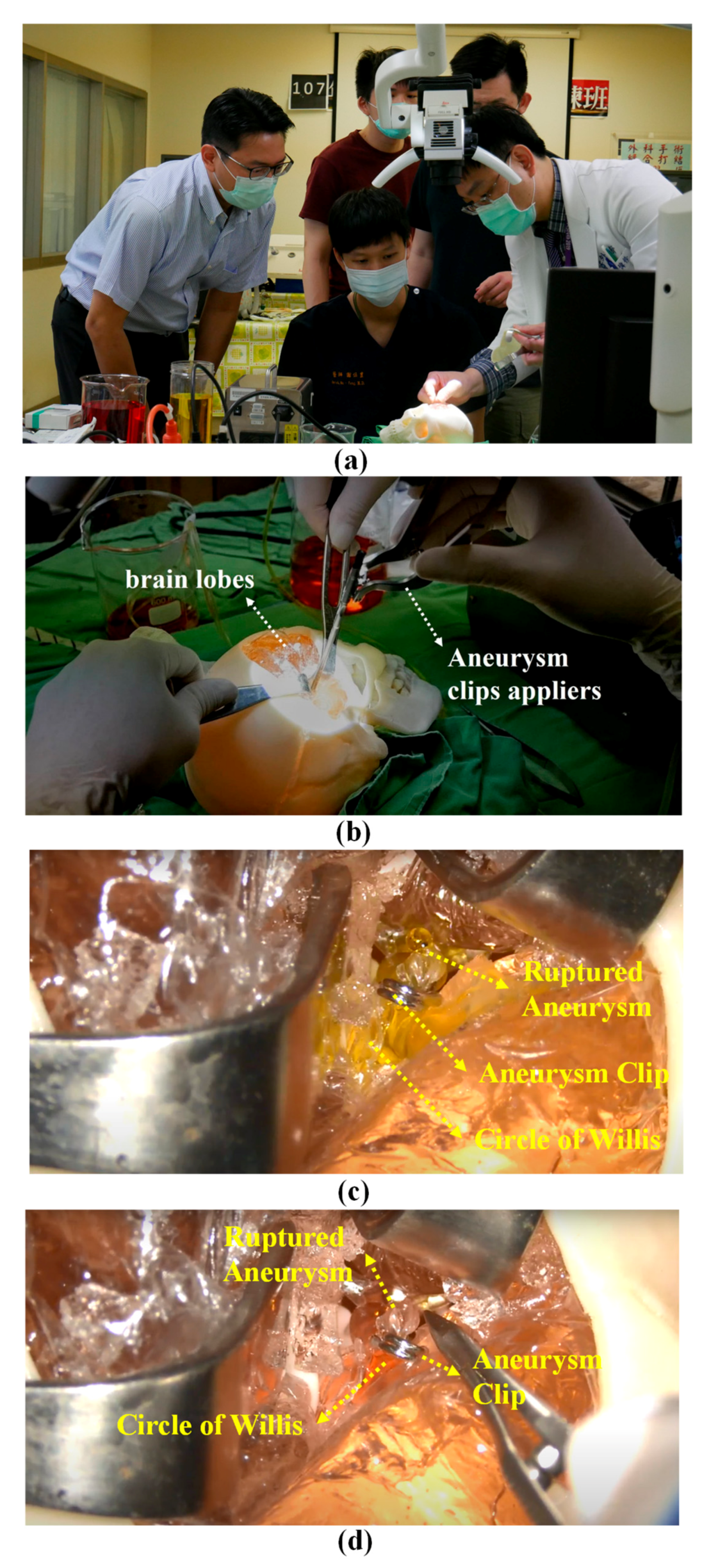
3.4. Training Neurosurgeons in Clipping Aneurysms
4. Experiment Results
4.1. Using Silicone for the Circle of Willis
4.2. Transparency of Simulated Blood Vessels
4.3. Dimensional Accuracy
4.4. Pre-Operative Training
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mashiko, T.; Kaneko, N.; Konno, T.; Otani, K.; Nagayama, R.; Watanabe, E. Training in cerebral aneurysm clipping using self-made 3-dimensional models. J. Surg. Educ. 2017, 74, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganju, A.; Aoun, S.G.; Daou, M.R.; El Ahmadieh, T.Y.; Chang, A.; Wang, L.; Bendok, B.R. The role of simulation in neurosurgical education: A survey of 99 United States neurosurgery program directors. World Neurosurg. 2013, 80, e1–e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passiment, M.; Sacks, H.; Huang, G. Medical simulation in medical education: Results of an AAMC survey 2011. Assoc. Am. Med. Colleges (AAMC) 2011, 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Gaba, D.M. The future vision of simulation in healthcare. Simul. Healthcare 2007, 2, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Ahmadieh, T.Y.; Aoun, S.G.; El Tecle, N.E.; Nanney, A.D., 3rd; Daou, M.R.; Harrop, J.; Bendok, B.R. A didactic and hands-on module enhances resident microsurgical knowledge and technical skill. Neurosurgery 2013, 73 (Suppl. 1), S51–S56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delp, S.L.; Loan, J.P.; Hoy, M.G.; Zajac, F.E.; Topp, E.L.; Rosen, J.M. An interactive graphics-based model of the lower extremity to study orthopaedic surgical procedures. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1990, 37, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, G.R.; Illig, K.A.; Yang, G.; Nguyen, T.H.; Shames, M.L. An approach to EVAR simulation using patient specific modeling. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2014, 28, 1769–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, A. Virtual reality and simulation in neurosurgical training. World Neurosurg. 2017, 106, 1015–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelargos, P.E.; Nagasawa, D.T.; Lagman, C.; Tenn, S.; Demos, J.V.; Lee, S.J.; Bari, A. Utilizing virtual and augmented reality for educational and clinical enhancements in neurosurgery. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 35, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, N.; Gélinas-Phaneuf, N.; Delorme, S.; Del Maestro, R. Fundamentals of neurosurgery: Virtual reality tasks for training and evaluation of technical skills. World Neurosurg. 2013, 80, e9–e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gmeiner, M.; Dirnberger, J.; Fenz, W.; Gollwitzer, M.; Wurm, G.; Trenkler, J.; Gruber, A. Virtual cerebral aneurysm clipping with real-time haptic force feedback in neurosurgical education. World Neurosurg. 2018, 112, e313–e323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’urso, P.S.; Thompson, R.G.; Atkinson, R.L.; Weidmann, M.J.; Redmond, M.J.; Hall, B.I.; Earwaker, W.J.S. Cerebrovascular biomodelling: A technical note. Surg. Neurol. 1999, 52, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurm, G.; Tomancok, B.; Pogady, P.; Holl, K.; Trenkler, J. Cerebrovascular stereolithographic biomodeling for aneurysm surgery. J. Neurosurg. 2004, 100, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ripley, B.; Kelil, T.; Cheezum, M.K.; Goncalves, A.; Di Carli, M.F.; Rybicki, F.J.; Blankstein, R. 3D printing based on cardiac CT assists anatomic visualization prior to transcatheter aortic valve replacement. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2016, 10, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Torres, I.O.; De Luccia, N. A simulator for training in endovascular aneurysm repair: The use of three dimensional printers. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2017, 54, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wurm, G.; Lehner, M.; Tomancok, B.; Kleiser, R.; Nussbaumer, K. Cerebrovascular biomodeling for aneurysm surgery: Simulation-based training by means of rapid prototyping technologies. Surg. Innov. 2011, 18, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Morita, A.; Nishimura, K.; Aiyama, H.; Itoh, H.; Fukaya, S.; Ochiai, C. Simulation of and training for cerebral aneurysm clipping with 3-dimensional models. Neurosurgery 2009, 65, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashiko, T.; Otani, K.; Kawano, R.; Konno, T.; Kaneko, N.; Ito, Y.; Watanabe, E. Development of three-dimensional hollow elastic model for cerebral aneurysm clipping simulation enabling rapid and low cost prototyping. World Neurosurg. 2015, 83, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, Q.; Du, S.; Chen, Z.; Fu, J.; Chen, B.; He, Y. Fabrication of cerebral aneurysm simulator with a desktop 3D printer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zammar, S.G.; El Tecle, N.E.; El Ahmadieh, T.Y.; Adelson, P.D.; Veznedaroglu, E.; Surdell, D.L.; Bendok, B.R. Impact of a vascular neurosurgery simulation-based course on cognitive knowledge and technical skills in European neurosurgical trainees. World Neurosurg. 2015, 84, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benet, A.; Plata-Bello, J.; Abla, A.A.; Acevedo-Bolton, G.; Saloner, D.; Lawton, M.T. Implantation of 3D-printed patient-specific aneurysm models into cadaveric specimens: A new training paradigm to allow for improvements in cerebrovascular surgery and research. BioMed. Res. Int. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ngo, T.D.; Kashani, A.; Imbalzano, G.; Nguyen, K.T.; Hui, D. Additive manufacturing (3D printing): A review of materials, methods, applications and challenges. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 143, 172–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Chiang, C.H. Taguchi Method for Investigation of Ultrasonication-Assisted Dissolution of Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) Rod Enclosed within Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) Bulk. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 114910–114915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatel, G. Sonochemistry: New Opportunities for Green Chemistry; World Scientific Publishing Co.: Singapore, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zarrinkoob, L.; Ambarki, K.; Wåhlin, A.; Birgander, R.; Eklund, A.; Malm, J. Blood flow distribution in cerebral arteries. J. Cerebral Blood Flow Metab. 2015, 35, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steiger, H.J.; Aaslid, R.; Keller, S.; Reulen, H.J. Strength, elasticity and viscoelastic properties of cerebral aneurysms. Heart Vessel. 1989, 5, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Zhou, Y.G. Improvement of Transparencies and Mechanical Properties of Poly (cyclohexylene dimethylene cyclohexanedicarboxylate) Parts Using a Compounding Nucleating Agent to Control Crystallization. Materials 2019, 12, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Locations | Average Error (%) | Average Standard Deviation (STD) (%) |
|---|---|---|
| AcomA | 2.75 | 3.5 |
| MCA | 5.5 | 3.5 |
| PcomA | 2.75 | 2.75 |
| PCA | 5 | 2 |
| Aneurysm | 2.25 | 4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, P.-C.; Lin, J.-C.; Chiang, C.-H.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chen, J.-E.; Liu, W.-H. Engineering Additive Manufacturing and Molding Techniques to Create Lifelike Willis’ Circle Simulators with Aneurysms for Training Neurosurgeons. Polymers 2020, 12, 2901. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122901
Chen P-C, Lin J-C, Chiang C-H, Chen Y-C, Chen J-E, Liu W-H. Engineering Additive Manufacturing and Molding Techniques to Create Lifelike Willis’ Circle Simulators with Aneurysms for Training Neurosurgeons. Polymers. 2020; 12(12):2901. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122901
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Pin-Chuan, Jang-Chun Lin, Chung-Hsuan Chiang, Yi-Chin Chen, Jia-En Chen, and Wei-Hsiu Liu. 2020. "Engineering Additive Manufacturing and Molding Techniques to Create Lifelike Willis’ Circle Simulators with Aneurysms for Training Neurosurgeons" Polymers 12, no. 12: 2901. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122901
APA StyleChen, P.-C., Lin, J.-C., Chiang, C.-H., Chen, Y.-C., Chen, J.-E., & Liu, W.-H. (2020). Engineering Additive Manufacturing and Molding Techniques to Create Lifelike Willis’ Circle Simulators with Aneurysms for Training Neurosurgeons. Polymers, 12(12), 2901. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12122901







