Highly Deformable Porous Electromagnetic Wave Absorber Based on Ethylene–Propylene–Diene Monomer/Multiwall Carbon Nanotube Nanocomposites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Compounding and Sample Preparation
2.3. Characterization
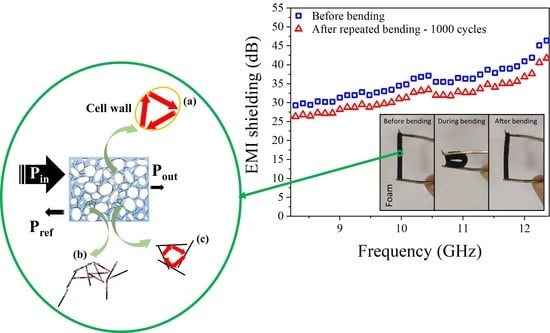
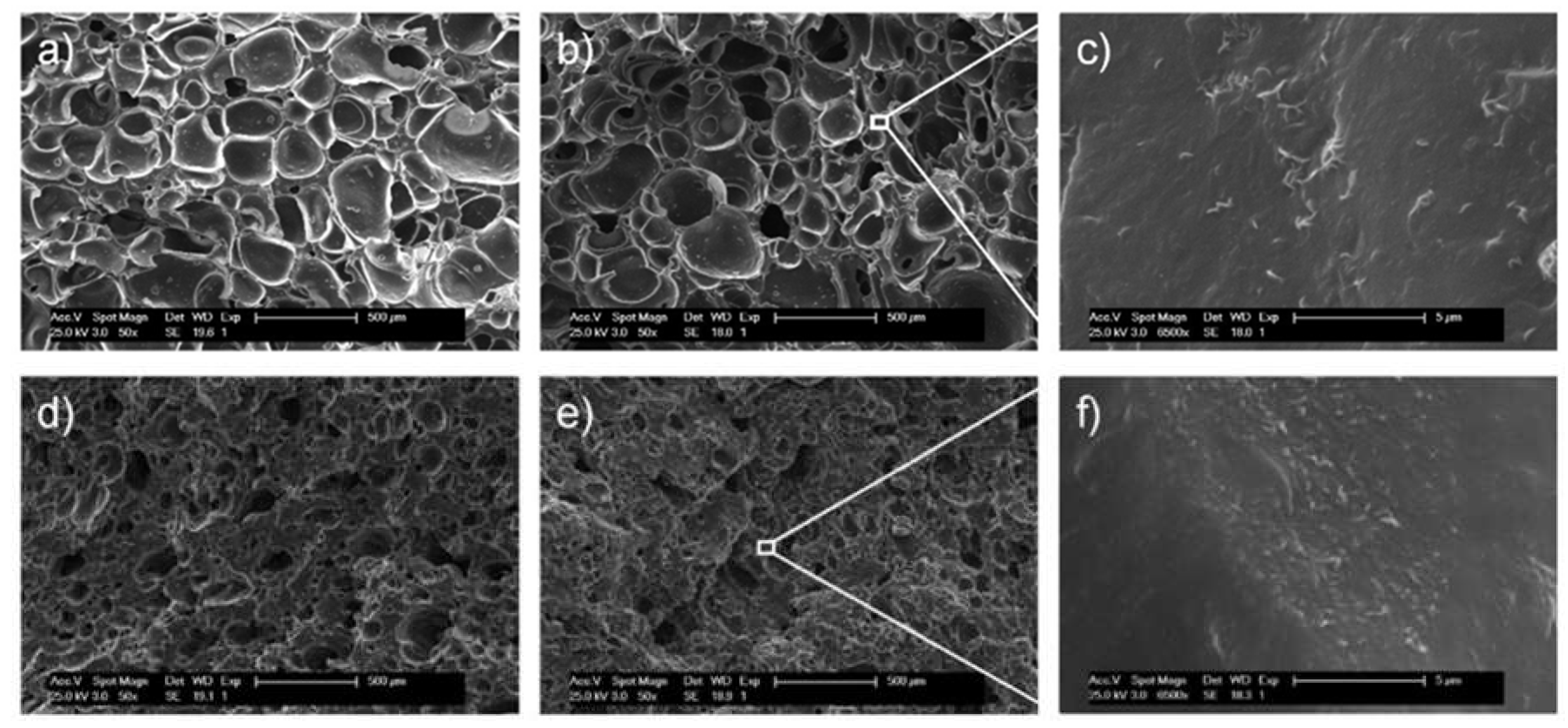
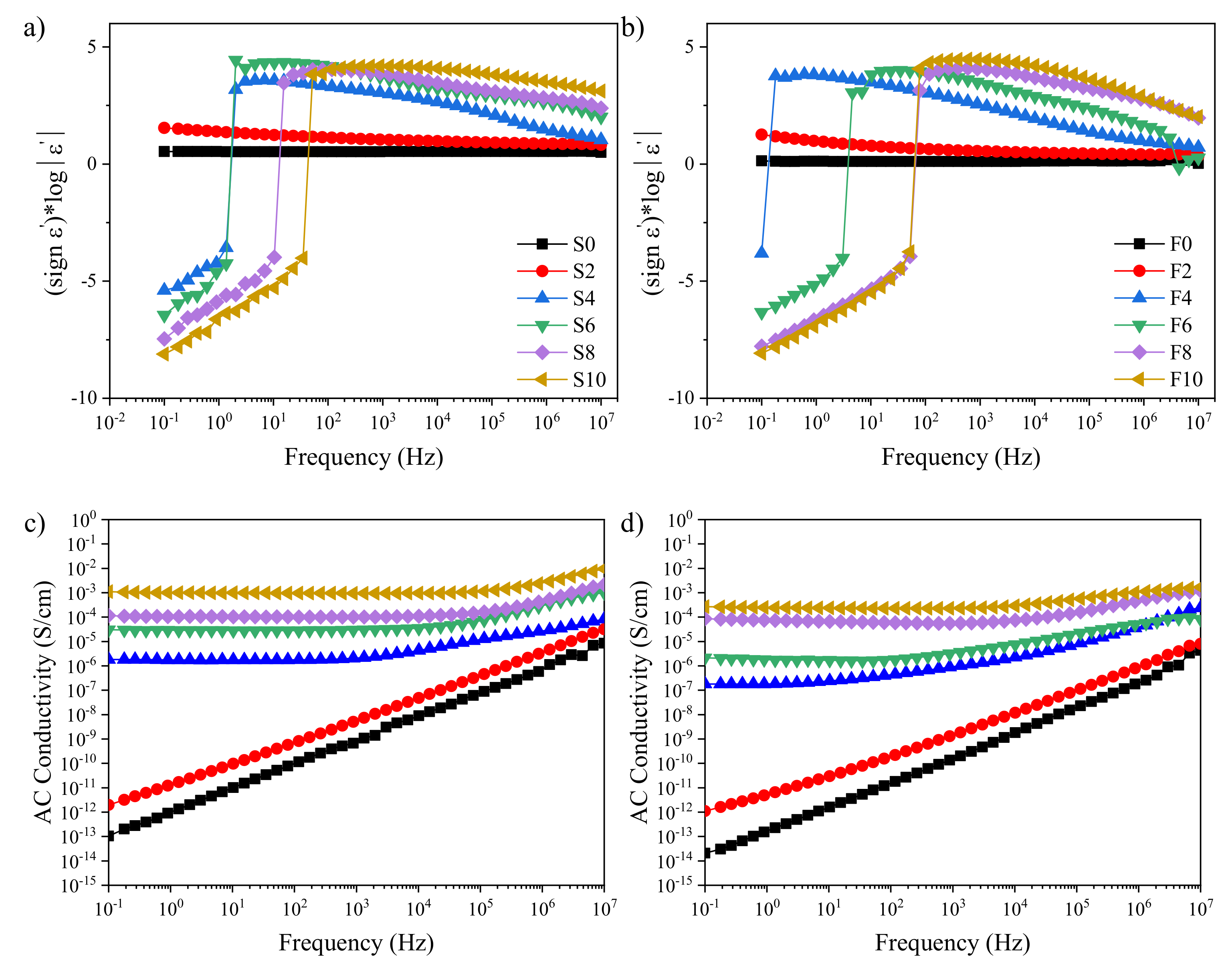
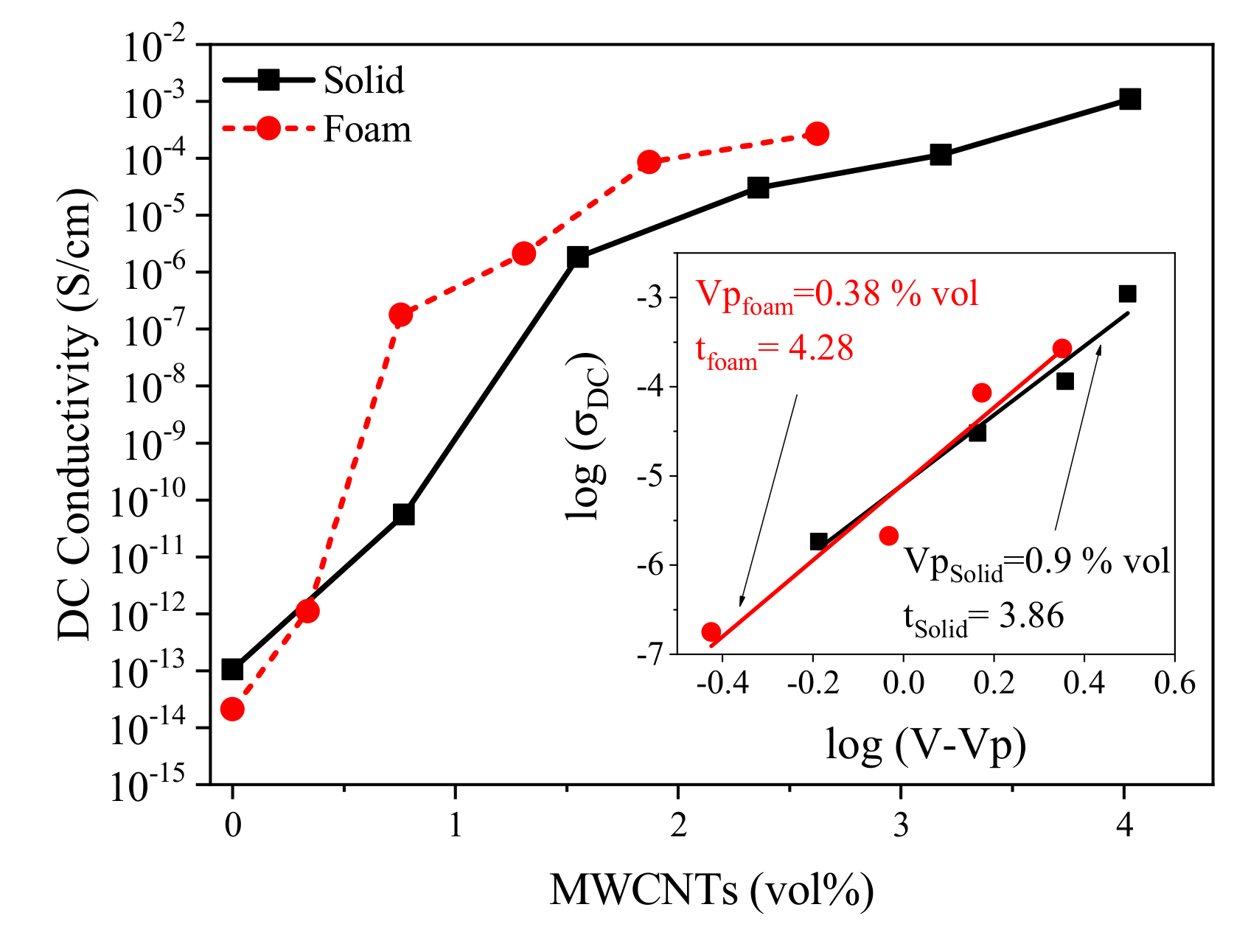
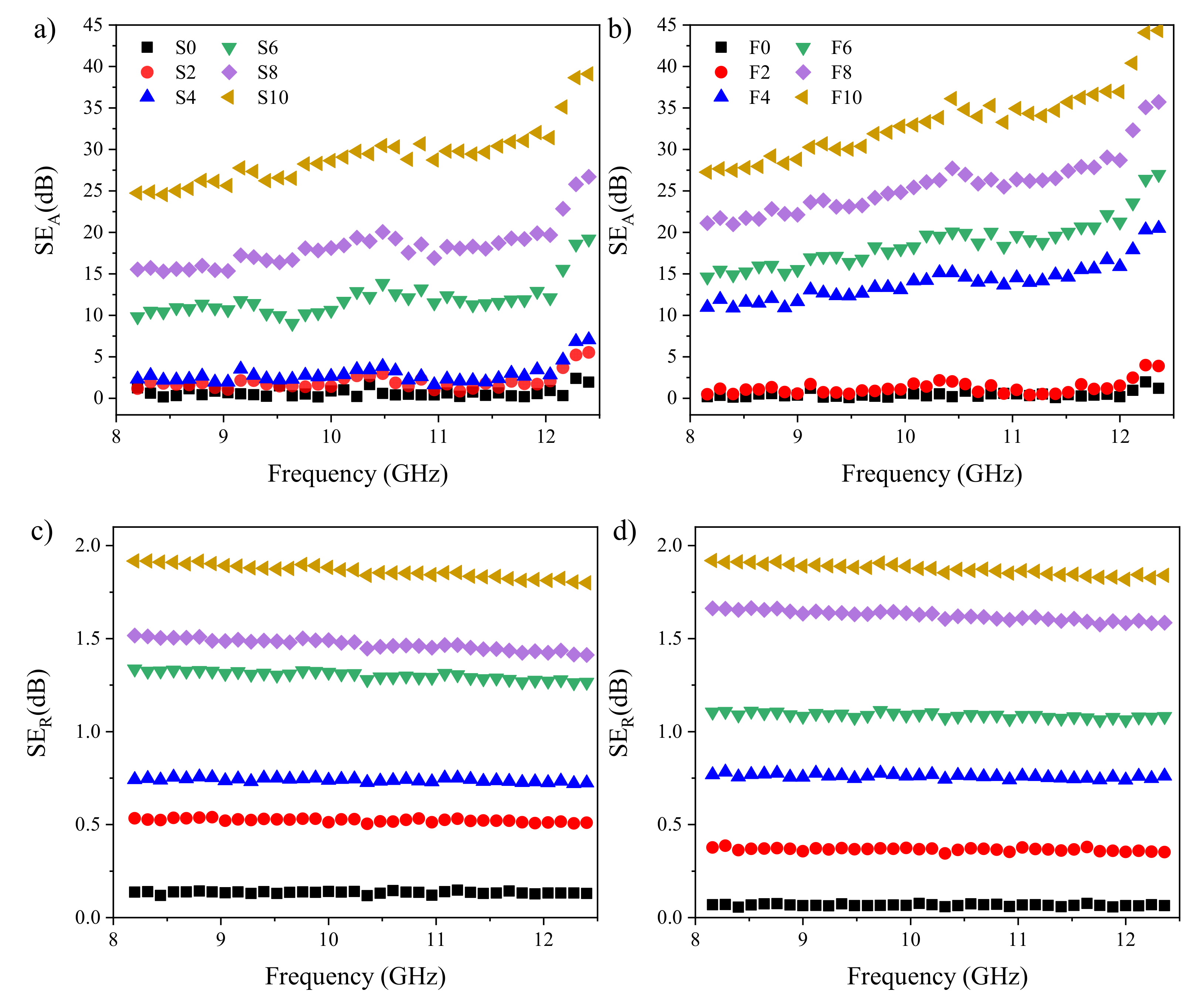
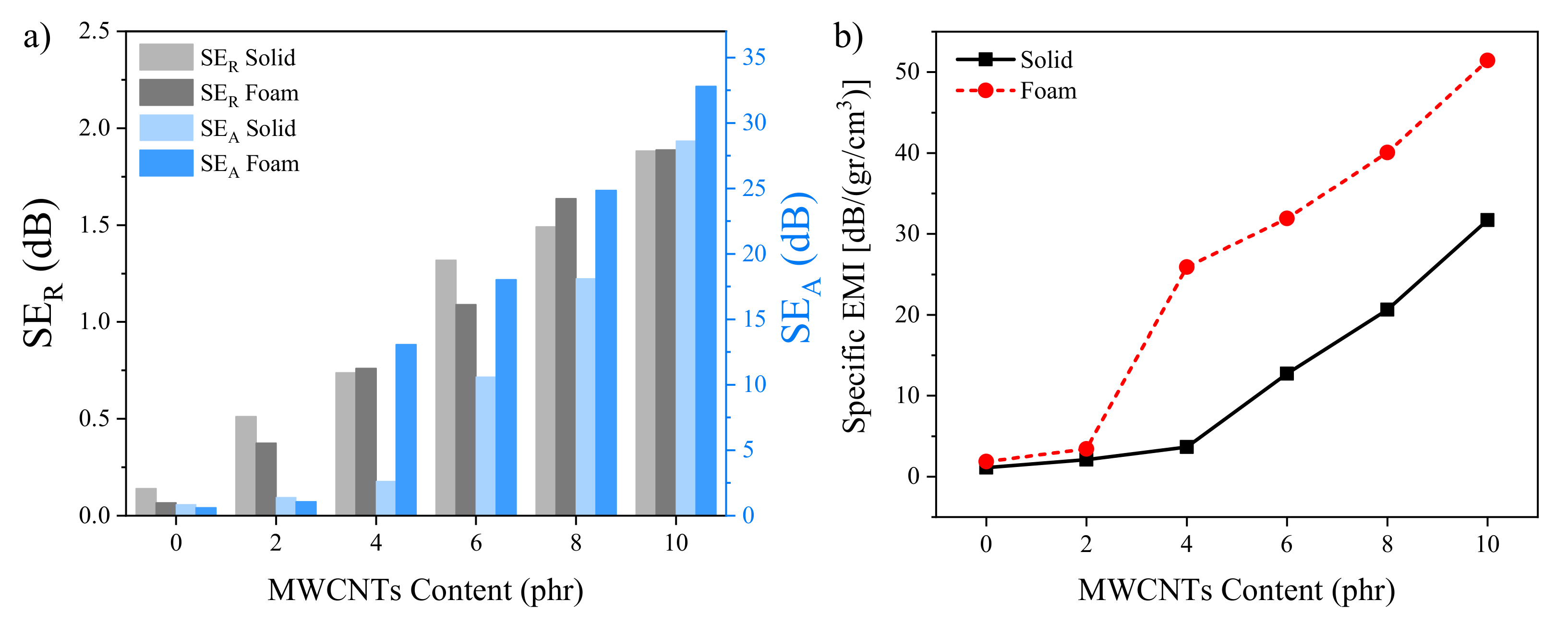
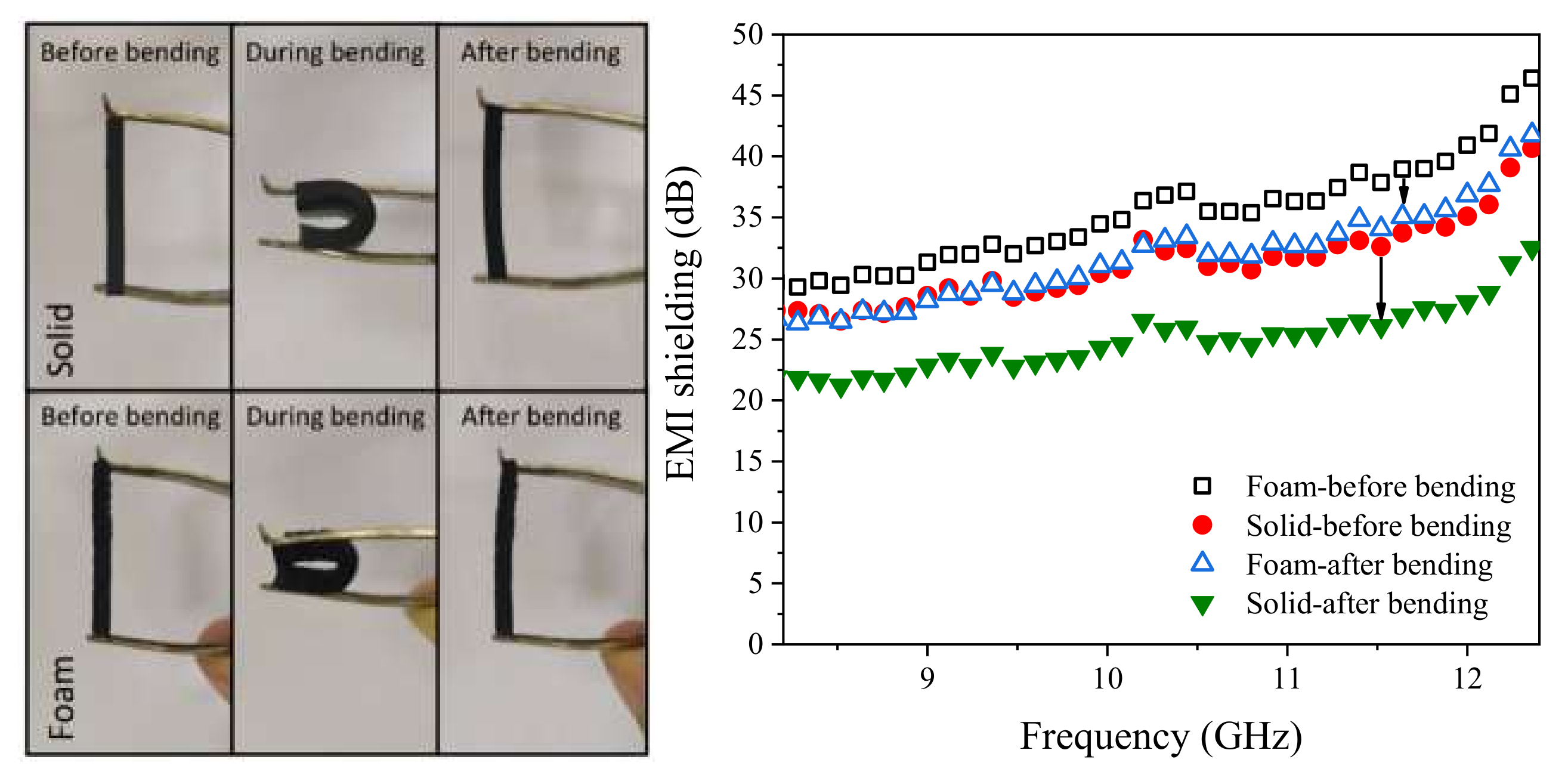
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, J.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Li, B.; Guo, Z.; Song, X.; Lin, L.; Tang, L.-C.; Xue, H.; Gao, J. Mechanically Durable, Highly Conductive, and Anticorrosive Composite Fabrics with Excellent Self-Cleaning Performance for High-Efficiency Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 10883–10894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geetha, S.; Kumar, K.K.S.; Rao, C.R.K.; Vijayan, M.; Trivedi, D.C. EMI shielding: Methods and materials—A review. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 112, 2073–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.C. Advanced Materials and Design for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding; Informa UK Limited: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasi, H.; Antunes, M.; Velasco, J.I. Recent advances in carbon-based polymer nanocomposites for electromagnetic interference shielding. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 103, 319–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gupta, M.C.; Dudley, K.L.; Lawrence, R.W. Conductive Carbon Nanofiber-Polymer Foam Structures. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 1999–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomassin, J.-M.; Pagnoulle, C.; Bednarz, L.; Huynen, I.; Jérôme, C.; Detrembleur, C. Foams of polycaprolactone/MWNT nanocomposites for efficient EMI reduction. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 792–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-B.; Yan, Q.; Zheng, W.-G.; He, Z.; Yu, Z.-Z. Tough Graphene−Polymer Microcellular Foams for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswaraiah, V.; Sankaranarayanan, V.; Ramaprabhu, S. Functionalized Graphene-PVDF Foam Composites for EMI Shielding. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2011, 296, 894–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameli, A.; Jung, P.; Park, C. Electrical properties and electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of polypropylene/carbon fiber composite foams. Carbon 2013, 60, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameli, A.; Nofar, M.; Park, C.; Pötschke, P.; Rizvi, G. Polypropylene/carbon nanotube nano/microcellular structures with high dielectric permittivity, low dielectric loss, and low percolation threshold. Carbon 2014, 71, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, M.M.; Martin-Gallego, M.; Molenberg, I.; Huynen, I.; Lopez-Manchado, M.A.; Verdejo, R. Influence of carbon nanoparticles on the polymerization and EMI shielding properties of PU nanocomposite foams. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 7911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.-B.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zheng, W.-G.; Yu, Z.-Z. Magnetic and electrically conductive epoxy/graphene/carbonyl iron nanocomposites for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 118, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Duan, Y.; Cai, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, D.; Gao, J.; Che, Y. Compressible Fe3O4/MWCNTs-coated polymer foams for high-performance and tunable electromagnetic microwave absorption. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 106114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Ma, Z.; Fan, X.; Fan, X.; Qin, J.; Shi, X. Morphologies and electromagnetic interference shielding performances of microcellular epoxy/multi-wall carbon nanotube nanocomposite foams. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 129, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shen, B.; Yi, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhai, W.; Wei, X.; Zheng, W. The influence of gradient and sandwich configurations on the electromagnetic interference shielding performance of multilayered thermoplastic polyurethane/graphene composite foams. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 138, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizhani, H.; Nayyeri, V.; Katbab, A.; Jalali-Arani, A.; Nazockdast, H. Double percolated MWCNTs loaded PC/SAN nanocomposites as an absorbing electromagnetic shield. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 100, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Liao, X.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, G.; Yi, J.; Yang, Q.; Li, G. Flexible thermoplastic polyurethane/reduced graphene oxide composite foams for electromagnetic interference shielding with high absorption characteristic. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 123, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagotia, N.; Choudhary, V.; Sharma, D.K. Synergistic effect of graphene/multiwalled carbon nanotube hybrid fillers on mechanical, electrical and EMI shielding properties of polycarbonate/ethylene methyl acrylate nanocomposites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 159, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liang, C.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, F.; Wen, F.; Xu, B.; Wang, B. Novel 3D network porous graphene nanoplatelets/Fe3O4/epoxy nanocomposites with enhanced electromagnetic interference shielding efficiency. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 169, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Li, Y.; Zhai, W.; Zheng, W. Compressible Graphene-Coated Polymer Foams with Ultralow Density for Adjustable Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 8050–8057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Oliviero, M.; Wang, J.; Sorrentino, A.; Buonocore, G.G.; Sorrentino, L.; Lavorgna, M.; Xia, H.; Iannace, S. Enhancing the EMI shielding of natural rubber-based supercritical CO2 foams by exploiting their porous morphology and CNT segregated networks. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liao, X.; Li, J.; He, G.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, W.; Wang, G.; Li, G. Light-weight and flexible silicone rubber/MWCNTs/Fe3O4 nanocomposite foams for efficient electromagnetic interference shielding and microwave absorption. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 181, 107670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizhani, H.; Katbab, A.A.; Verdejo, R. Elastomeric nanocomposite foams with improved properties for extreme conditions. In High-Performance Elastomeric Materials Reinforced by Nano-Carbons; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 133–147. [Google Scholar]
- Kueseng, P.; Sae-Oui, P.; Rattanasom, N. Mechanical and electrical properties of natural rubber and nitrile rubber blends filled with multi-wall carbon nanotube: Effect of preparation methods. Polym. Test. 2013, 32, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaramontri, Y.; Kummerlöwe, C.; Nakason, C.; Vennemann, N. The effect of surface functionalization of carbon nanotubes on properties of natural rubber/carbon nanotube composites. Polym. Compos. 2014, 36, 2113–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehr, J. Chemical Blowing Agents in the Rubber Industry. Past–Present–and Future? Int. Polym. Sci. Technol. 2016, 43, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdejo, R.; Barroso-Bujans, F.; Rodríguez-Perez, M.A.; De Saja, J.A.; Arroyo, M.; Lopez-Manchado, M.A. Carbon nanotubes provide self-extinguishing grade to silicone-based foams. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdejo, R.; Stämpfli, R.; Alvarez-Lainez, M.; Mourad, S.; Rodríguez-Perez, M.A.; Brühwiler, P.; Shaffer, M.S.P. Enhanced acoustic damping in flexible polyurethane foams filled with carbon nanotubes. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 1564–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.-R.; Kim, G.-H. Effects of multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) content on physical properties and cell structure in ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer (EVA)/MWCNT nanocomposite foams. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2013, 52, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasbakhsh, P.; Ismail, H.; Fauzi, M.A.; Abu Bakar, A. Influence of maleic anhydride grafted ethylene propylene diene monomer (MAH-g-EPDM) on the properties of EPDM nanocomposites reinforced by halloysite nanotubes. Polym. Test. 2009, 28, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dindarloo, A.S.; Karrabi, M.; Hamid, M.; Ghoreishy, R. Various nano-particles influences on structure, viscoelastic, Vulcanization and mechanical behaviour of EPDM nano-composite rubber foam. Plast. Rubber Compos. 2019, 48, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Hua, W.; Zhang, A.; Bao, J. Light-Weight Silver Plating Foam and Carbon Nanotube Hybridized Epoxy Composite Foams with Exceptional Conductivity and Electromagnetic Shielding Property. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 24131–24142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, G.; Gao, Q.; Tang, M.; Ma, Z.; Qin, J.; Wang, M.; Kim, J.-K. Multifunctional microcellular PVDF/Ni-chains composite foams with enhanced electromagnetic interference shielding and superior thermal insulation performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Hidalgo, R.; Blanco, C.; Menendez, R.; Verdejo, R.; Lopez-Manchado, M.A. Multifunctional Silicone Rubber Nanocomposites by Controlling the Structure and Morphology of Graphene Material. Polym. 2019, 11, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenogin, S. Role of thermal boundary resistance on the heat flow in carbon-nanotube composites. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 95, 8136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klempner, D.; Sendijareviʹc, V.; Aseeva, R.M. Handbook of Polymeric Foams and Foam Technology; Hanser Publishers: Munich, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Solórzano, E.; Lázaro, J.; De Saja, J.A.; Rodríguez-Perez, M.A. Influence of Solid Phase Conductivity and Cellular Structure on the Heat Transfer Mechanisms of Cellular Materials: Diverse Case Studies. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2009, 11, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeddi, J.; Katbab, A.; Mehranvari, M. Investigation of microstructure, electrical behavior, and EMI shielding effectiveness of silicone rubber/carbon black/nanographite hybrid composites. Polym. Compos. 2019, 40, 4056–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Kou, X.; Qiu, J. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes/polyaniline composites with negative permittivity and negative permeability. Carbon 2016, 107, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Qi, S.; Tian, G.; Wu, D. Permittivity transition from highly positive to negative: Polyimide/carbon nanotube composite’s dielectric behavior around percolation threshold. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 012905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlman, R.S.; Joo, J.; Wang, Y.Z.; Pouget, J.P.; Kaneko, H.; Ishiguro, T.; Epstein, A.J. Drude Metallic Response of Polypyrrole. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1995, 74, 773–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, B.V.B.; Kale, N.; Kothavale, B.S.; Kale, S. Fabrication and evaluation of thin layer PVDF composites using MWCNT reinforcement: Mechanical, electrical and enhanced electromagnetic interference shielding properties. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 65107. [Google Scholar]
- Jana, S.; Garain, S.; Sen, S.; Mandal, D. The influence of hydrogen bonding on the dielectric constant and the piezoelectric energy harvesting performance of hydrated metal salt mediated PVDF films. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 17429–17436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duand, H.-J.; Zhu, H.; Yang, J.; Gao, J.; Yang, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhao, G.; Liu, Y. Effect of carbon nanofiller dimension on synergistic EMI shielding network of epoxy/metal conductive foams. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 118, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelkunoff, S. Electromagnetic Waves; Nostrand Company, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1943. [Google Scholar]
- Carpi, F.; Gallone, G.; Galantini, F.; De Rossi, D. Enhancing the dielectric permittivity of elastomers. In Dielectric Elastomers Electromechanical Transducers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 51–68. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, G.; Tang, M.; Zhou, L.; Li, J.; Fan, X.; Shi, X.; Qin, J. Synergistic effect of carbon nanotube and graphene nanoplates on the mechanical, electrical and electromagnetic interference shielding properties of polymer composites and polymer composite foams. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 353, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, N.; Sun, X.; Lin, X.; Shen, X.; Jia, J.; Zhang, B.; Tang, B.; Chan, M.; Kim, J.-K. Highly Aligned Graphene/Polymer Nanocomposites with Excellent Dielectric Properties for High-Performance Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5480–5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| S0 | S2 | S4 | S6 | S8 | S10 | F0 | F2 | F4 | F6 | F8 | F10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPDM | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| EPDM-g-MA | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| MWCNTs | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 |
| ZnO | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| STA | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| DCP | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| S | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| OBSH | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Sample | Tensile Stress (MPa) | Strain at Break (%) | Compressive Stress (MPa) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50% | 100% | 300% | 500% | 10% | 30% | 50% | ||
| S0 | 0.62 ± 0.04 | 0.87 ± 0.10 | 1.5 ± 0.1 | 2.1 ± 0.2 | 641 ± 53 | 0.35 ± 0.01 | 1.4 ± 0.02 | 3.6 ± 0.1 |
| S2 | 0.74 ± 0.03 | 1.05 ± 0.03 | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 2.8 ± 0.3 | 630 ± 31 | 0.39 ± 0.02 | 1.5 ± 0.03 | 4.0 ± 0.2 |
| S4 | 0.83 ± 0.05 | 1.19 ± 0.07 | 2.5 ± 0.1 | 3.6 ± 0.1 | 600 ± 39 | 0.52 ± 0.04 | 1.7 ± 0.06 | 4.2 ± 0.1 |
| S6 | 1.05 ± 0.03 | 1.59 ± 0.05 | 3.6 ± 0.1 | 5.2 ± 0.2 | 560 ± 42 | 0.63 ± 0.01 | 2.0 ± 0.07 | 5.3 ± 0.1 |
| S8 | 1.27 ± 0.06 | 1.98 ± 0.07 | 4.6 ± 0.1 | 6.6 ± 0.2 | 520 ± 39 | 0.64 ± 0.04 | 2.2 ± 0.1 | 5.5 ± 0.3 |
| S10 | 1.56 ± 0.07 | 2.51 ± 0.09 | 5.9 ± 0.1 | - | 483 ± 28 | 0.72 ± 0.08 | 2.4 ± 0.1 | 5.8 ± 0.2 |
| F0 | 0.15 ± 0.02 | 0.23 ± 0.03 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | - | 344 ± 40 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.1 ± 0.01 | 0.22 ± 0.02 |
| F2 | 0.29 ± 0.03 | 0.47 ± 0.05 | 1.0 ± 0.2 | - | 351 ± 21 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.15 ± 0.02 | 0.33 ± 0.06 |
| F4 | 0.50 ± 0.05 | 0.77 ± 0.07 | 1.5 ± 0.1 | - | 361 ± 75 | 0.11 ± 0.04 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 0.70 ± 0.19 |
| F6 | 0.70 ± 0.07 | 1.09 ± 0.07 | 2.3 ± 0.2 | - | 377 ± 54 | 0.18 ± 0.03 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 1.25 ± 0.03 |
| F8 | 0.91 ± 0.07 | 1.40 ± 0.09 | 3.2 ± 0.1 | - | 392 ± 65 | 0.25 ± 0.06 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 1.94 ± 0.33 |
| F10 | 0.97 ± 0.10 | 1.54 ± 0.14 | 3.5 ± 0.2 | - | 405 ± 37 | 0.33 ± 0.01 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 2.94 ± 0.4 |
| Material | Foam Fabrication Procedure | Filler Content (wt.%) | EMI Shielding | Mechanical Properties | Other Characteristics | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specific EMI SE (dB/gr cm-3) | Thickness (mm) | ||||||
| NR/MWCNTs | ScCO2 | 6.4 | 40 | 1.3 | Compressive stress at 30%: 0.14 MPa | Segregated CNT network | [21] |
| PDMS/MWCNTs | ScCO2 | 10 | 72 | 2 | N/A | Flexible-Retained EMI shielding properties after bending | [22] |
| EPDM/MWCNTs | OBSH foaming agent | 10 | 52 | 25 | Compressive stress at 30%: 1.06 MPa, tensile stress at 300%: 3.46 MPa, strain at break: 405% | Chemical, moisture, and ozone resistive-Retained EMI shielding properties after bending | This work |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bizhani, H.; Katbab, A.A.; Lopez-Hernandez, E.; Miranda, J.M.; Verdejo, R. Highly Deformable Porous Electromagnetic Wave Absorber Based on Ethylene–Propylene–Diene Monomer/Multiwall Carbon Nanotube Nanocomposites. Polymers 2020, 12, 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040858
Bizhani H, Katbab AA, Lopez-Hernandez E, Miranda JM, Verdejo R. Highly Deformable Porous Electromagnetic Wave Absorber Based on Ethylene–Propylene–Diene Monomer/Multiwall Carbon Nanotube Nanocomposites. Polymers. 2020; 12(4):858. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040858
Chicago/Turabian StyleBizhani, Hasti, Ali Asghar Katbab, Emil Lopez-Hernandez, Jose Miguel Miranda, and Raquel Verdejo. 2020. "Highly Deformable Porous Electromagnetic Wave Absorber Based on Ethylene–Propylene–Diene Monomer/Multiwall Carbon Nanotube Nanocomposites" Polymers 12, no. 4: 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040858
APA StyleBizhani, H., Katbab, A. A., Lopez-Hernandez, E., Miranda, J. M., & Verdejo, R. (2020). Highly Deformable Porous Electromagnetic Wave Absorber Based on Ethylene–Propylene–Diene Monomer/Multiwall Carbon Nanotube Nanocomposites. Polymers, 12(4), 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12040858