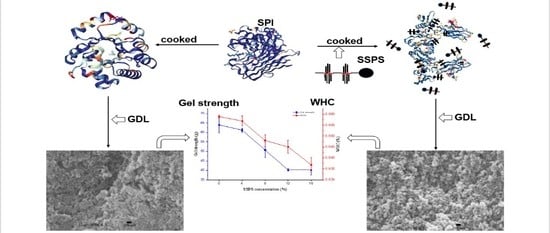
Effect of Soybean Soluble Polysaccharide on the Formation of Glucono-δ-Lactone-Induced Soybean Protein Isolate Gel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of SPI Gels
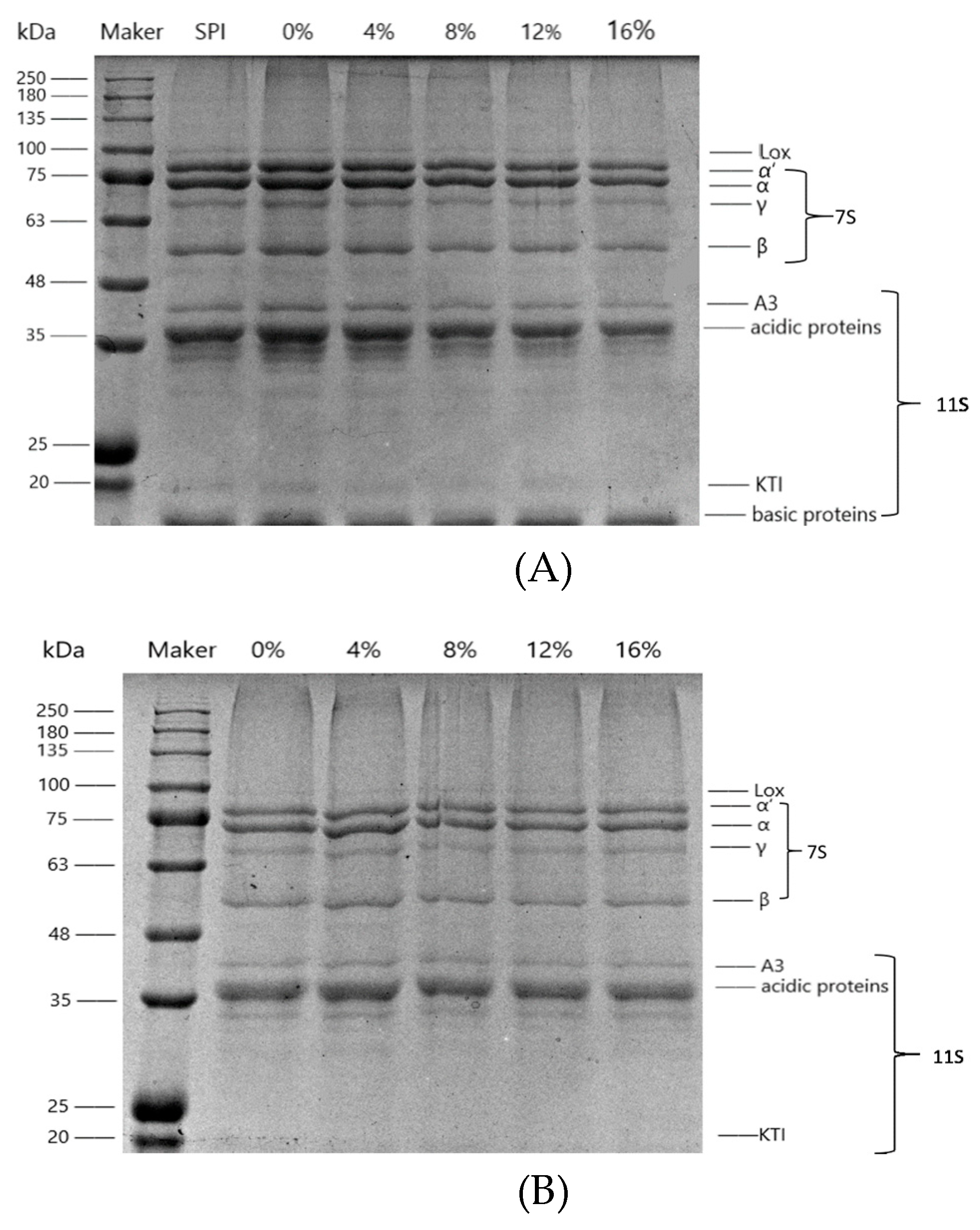
2.3. Electrophoretic Analysis
2.4. Measurement of Sulfhydryl Groups
2.5. Determination of Degree of Grafting (DG) of SPI Gels
2.6. FTIR Spectroscopy Analysis
2.7. Surface Hydrophobicity Measurement
2.8. Determination of Protein Solubility
2.9. Measurement of WHC
2.10. Analysis of Microstructure
2.11. Gel Strength Analysis
2.12. Color Analysis
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of SSPS on the Structure of SPI
3.1.1. Electrophoretic Analysis
3.1.2. Change in Secondary Structure
3.2. Interactions between SSPS and SPI
3.2.1. Change in Protein Solubility
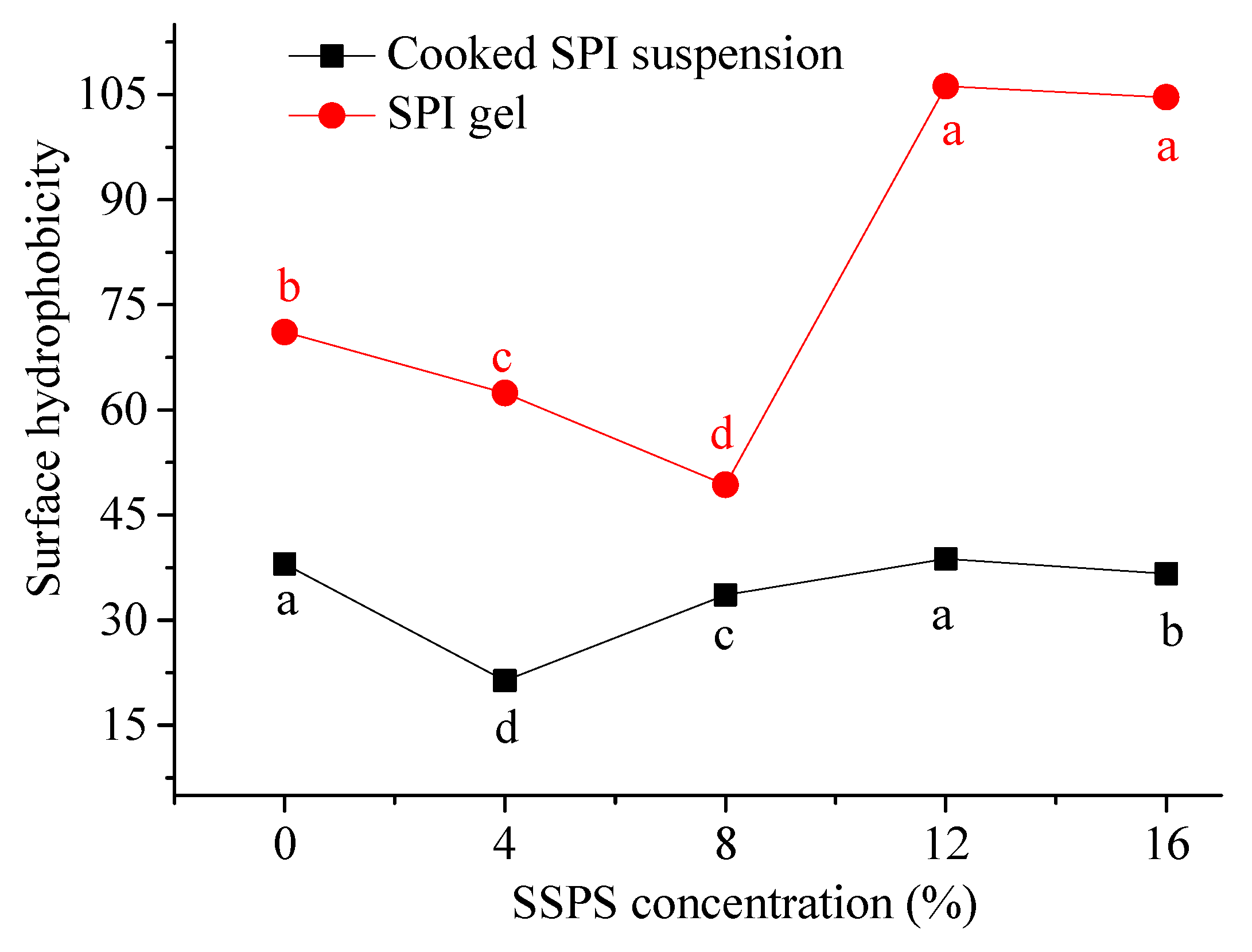
3.2.2. Change in Surface Hydrophobicity
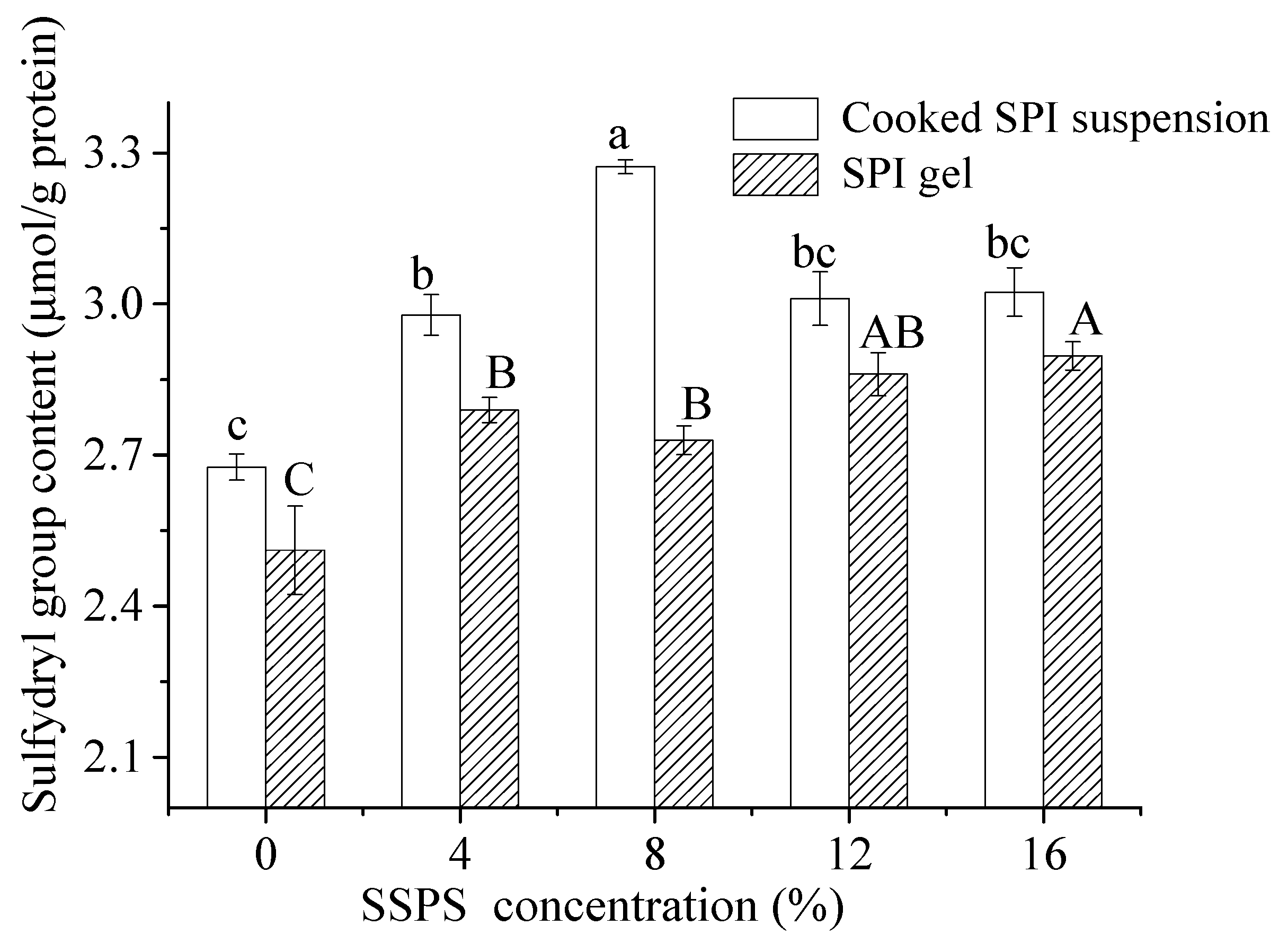
3.2.3. Change in Sulfhydryl Group
3.3. The Occurrence of the Maillard Reaction between SSPS and SPI
3.3.1. Change in Free Amino Groups
3.3.2. Color Variation
3.4. SPI Gel Properties
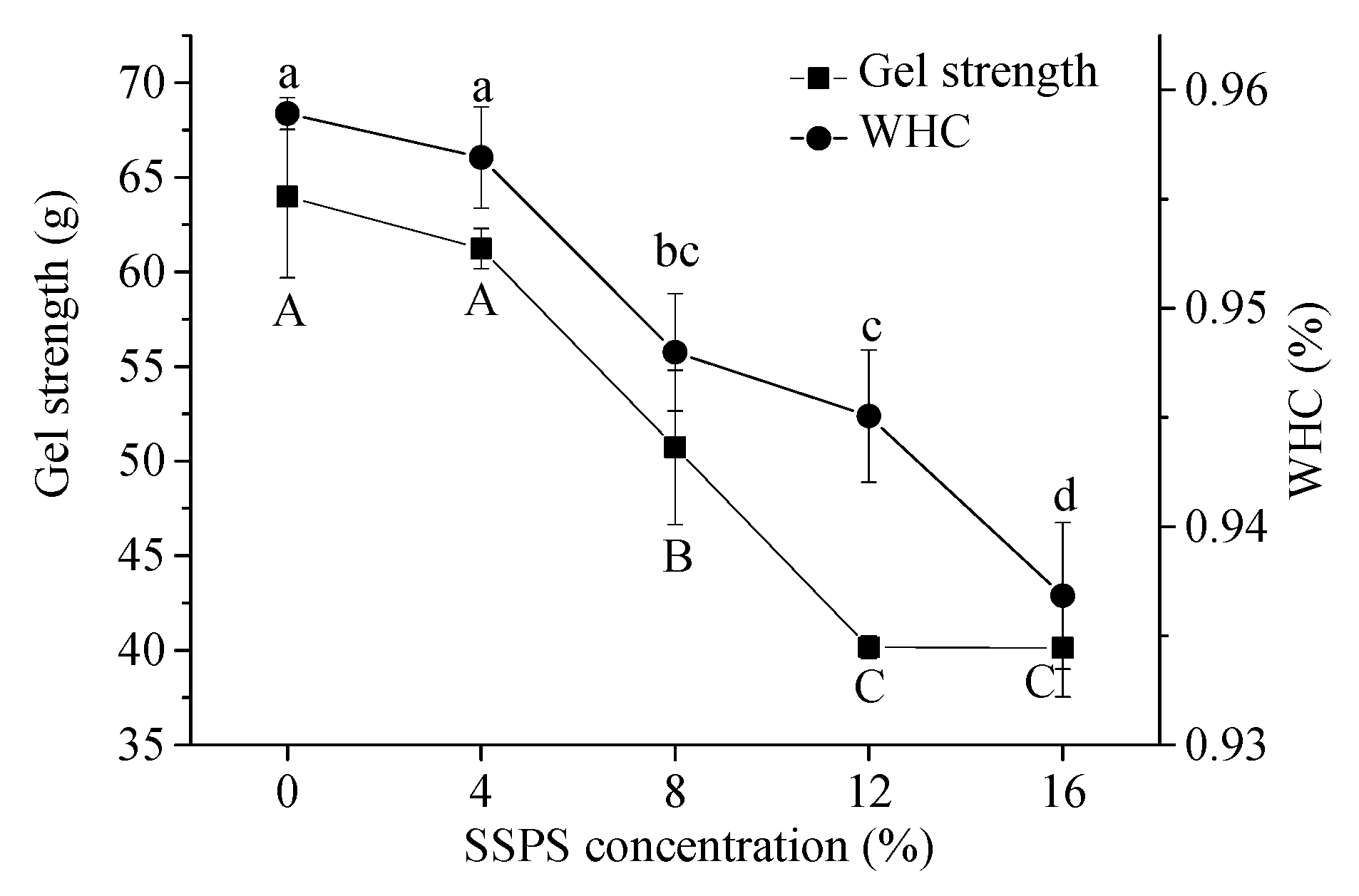
3.4.1. WHC
3.4.2. Gel Strength
3.4.3. Change in the Microstructure of SPI Gels
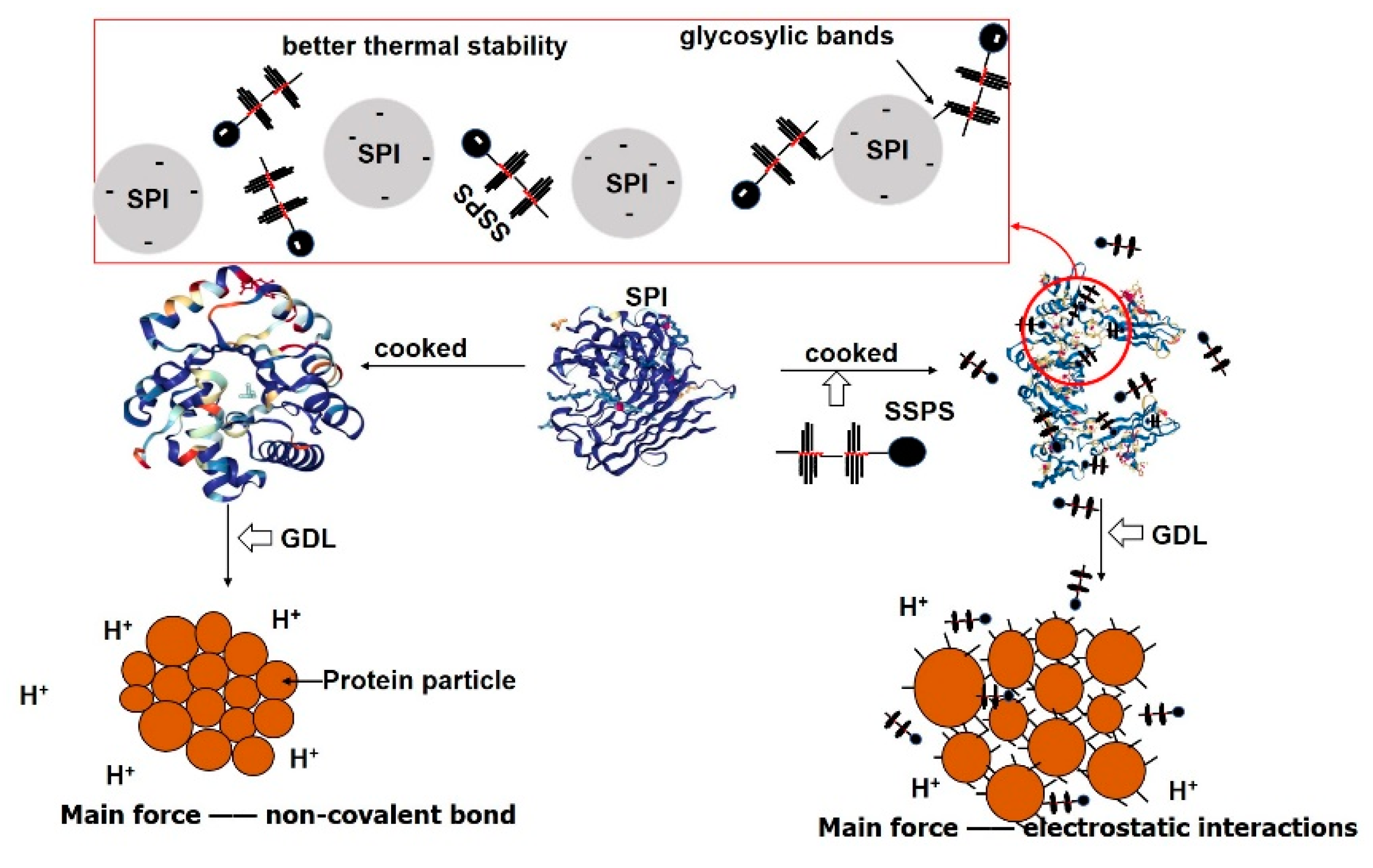
3.5. Effect of SSPS on the Formation of GDL-Induced SPI Gels
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nakamura, T.; Utsumi, S.; Mori, T. Interactions during heat-induced gelation in a mixed system of soybean 7S and 11S globulins. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1986, 50, 2429–2435. [Google Scholar]
- Alting, A.C.; Hamer, R.J.; de Kruif, C.G.; Visschers, R.W. Cold-set globular protein gels: Interactions, structure and rheology as a function of protein concentration. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 3150–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishinari, K.; Fang, Y.; Guo, S.; Phillips, G.O. Soy proteins: A review on composition, aggregation and emulsification. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 39, 301–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, H.; Xiong, Y.L.; Guo, F.; Huang, X.; Adhikari, B.; Chen, J. Gelation enhancement of soy protein isolate by sequential low- and ultrahigh-temperature two-stage preheating treatments. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 2529–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Xiong, Y.L.; Qin, F.; Jian, H.; Huang, X.; Chen, J. Surface properties of heat-induced soluble soy protein aggregates of different molecular masses. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, C279–C287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Agata, K.; Mai, M.; Iino, H. Effects of Brewer’s Yeast Cell Wall on Constipation and Defecation in Experimentally Constipated Rats. J. Agric. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2001, 65, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallieri, Â.L.F.; Cunha, R.L. Cold-Set Whey Protein Gels with Addition of Polysaccharides. Food Biophys. 2009, 4, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, A.; Furuta, H.; Kato, M.; Maeda, H.; Nagamatsu, Y. Effect of soybean soluble polysaccharides on the stability of milk protein under acidic conditions. Food Hydrocoll. 2003, 17, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Campbell, L.J.; Euston, S.R. Influence of sugars on the characteristics of glucono-δ-lactone-induced soy protein isolate gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Fang, Q.; Chen, J. Effects of oligosaccharides and soy soluble polysaccharide on the rheological and textural properties of calcium sulfate-induced soy protein gels. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2016, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Fan, X.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, X.; Fan, G.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Pan, S.; Zhu, L. Acid-induced gelation behavior of soybean protein isolate with high intensity ultrasonic pre-treatments. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2013, 20, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Zhong, Q. High temperature-short time glycation to improve heat stability of whey protein and reduce color formation. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 44, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, K.; Cheftel, J.C. Sulfhydryl group/disulfide bond interchange reactions during heat-induced gelation of whey protein isolate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1989, 37, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, F.C.; Swaisgood, H.E.; Porter, D.H.; Catignani, G.L. Spectrophotometric assay using o-phthaldialdehyde for determination of proteolysis in milk and isolated milk proteins. J. Dairy Sci. 1983, 66, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; Biresaw, G.; Xu, J.; Hojilla-Evangelista, M.P.; Rayas-Duarte, P. Oats protein isolate: Thermal, rheological, surface and functional properties. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Nakai, S. Hydrophobicity determined by a fluorescence probe method and its correlation with surface properties of proteins. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 1980, 624, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, K.; Cheftel, J.C. Determination of sulfhydryl groups and disulfide bonds in heat-induced gels of soy protein isolate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1988, 36, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.H.; Chen, L.; Foegeding, E.A. Mechanical and water-holding properties and microstructures of soy protein isolate emulsion gels induced by CaCl2, Glucono-δ-lactone (GDL), and transglutaminase: Influence of thermal treatments before and/or after emulsification. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 4071–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramlan, B.M.S.M.; Maruyama, N.; Takahashi, K.; Yagasaki, K.; Higasa, T.; Matsumura, Y.; Utsumi, S. Gelling properties of soybean β-conglycinin having different subunit compositions. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2004, 68, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelatin Manufacturers Institute of America. Standard Testing Method for Edible Gelatin. Official Procedure of the Gelatin Manufacturers Institute of America; GMIA: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Jing, Z.; Liu, Y. The effect of non-covalent interaction of chlorogenic acid with whey protein and casein on physicochemical and radical-scavenging activity of in vitro protein digests. Food Chem. 2018, 268, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbonaro, M.; Nucara, A. Secondary structure of food proteins by Fourier transform spectroscopy in the mid-infrared region. Amino Acids 2010, 38, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, L.; Lan, Q.; Li, M.; Wu, D.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Lin, D.; Qin, W.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Protein glycosylation: A promising way to modify the functional properties and extend the application in food system. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2506–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, L.; Ma, N.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Ma, G.; Pei, F.; Hu, Q. Characterization and functional evaluation of oat protein isolate-Pleurotus ostreatus β-glucan conjugates formed via Maillard reaction. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, G.; Zhu, T.; Chen, F.; Zhang, N.; Liu, K.; Zhang, L.; Yang, H. Effects of saccharide on the structure and antigenicity of β-conglycinin in soybean protein isolate by glycation. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2014, 240, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.; Rousseau, D. Stabilization of acidic soy protein-based dispersions and emulsions by soy soluble polysaccharides. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Hang, Y.; Yin, X.; Li, Q. Circular dichroism and infrared spectroscopic characterization of secondary structure components of protein Z during mashing and boiling processes. Food Chem. 2015, 188, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Bao, Z.; Xu, W.; Chi, Y. Influence of glycation extent on the physicochemical and gelling properties of soybean β-conglycinin. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015, 240, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou-Wei, Y.; Chuan-He, T.; Qi-Biao, W.; Xiao-Quan, Y. Properties of cast films from hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) and soy protein isolates. A comparative study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 7399–7404. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.T.; Ono, T. The Role of Composition and Content of Protein Particles in Soymilk on Tofu Curding by Glucono-δ-lactone or Calcium Sulfate. J. Food Sci. 2005, 70, C258–C262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achouri, A.; Boye, J.I.; Belanger, D.; Chiron, T.; Yaylayan, V.A.; Yeboah, F.K. Functional and molecular properties of calcium precipitated soy glycinin and the effect of glycation with κ-carrageenan. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1494–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, P.; Zou, M.; Yang, R.; Tian, M.; Gu, Z. Microbial transglutaminase-modified protein network and its importance in enhancing the quality of high-fiber tofu with okara. Food Chem. 2019, 289, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Wang, H.; Hu, T.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, S.; Hu, H. Ball-milling changed the physicochemical properties of SPI and its cold-set gels. J. Food Eng. 2017, 195, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, J.; Shi, J.; Huang, X.; Peng, Q.; Xue, F. Encapsulation of tomato oleoresin using soy protein isolate-gum aracia conjugates as emulsifier and coating materials. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 45, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xue, H.; Chen, Z.; Ding, Q.; Wang, X. Comparative studies on the physicochemical properties of peanut protein isolate–polysaccharide conjugates prepared by ultrasonic treatment or classical heating. Food Res. Int. 2014, 57, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, F.; Luo, S.; Li, P.; Mu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Zhong, X.; Jiang, S.; Zheng, Z. Effects of high hydrostatic pressure on the properties of heat-induced wheat gluten gels. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2018, 12, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.G.; Xiong, Y.L.; Chen, J.; Tang, X.Y.; Zhou, G.H. Rheological and Microstructural Properties of Porcine Myofibrillar Protein-Lipid Emulsion Composite Gels. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, E207–E217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baier, S.; Mcclements, D.J. Impact of preferential interactions on thermal stability and gelation of bovine serum albumin in aqueous sucrose solutions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 9, 2600–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boye, J.I.; Alli, I.; Ramaswamy, H.; Raghavan, V.G.S. Interactive effects of factors affecting gelation of whey proteins. J. Food Sci. 1997, 62, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich, L.M.; Foegeding, E.A. Effects of sugars on whey protein isolate gelation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 5046–5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renkema, J.M.S.; Knabben, J.H.M.; Vliet, T.V. Gel formation by β-conglycinin and glycinin and their mixtures. Food Hydrocoll. 2001, 15, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, S.L.; Xu, G.Q.; Perera, C.O. Aggregation profile of 11S, 7S and 2S coagulated with GDL. Food Chem. 2005, 91, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, T. Contribution of disulfide bonding to viscoelastic properties and microstructures of 11S globulin gels from soybeans: Magnesium chloride-induced gels. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2013, 19, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nagano, T.; Mori, H.; Nishinari, K. Effect of heating and cooling on the gelation kinetics of 7S globulin from soybeans. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 1415–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| SSPS Concentration (%) | Cooked SPI Suspension | SPI Gels | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-Sheet | Random Coil | α-Helix | β-Turns | β-Sheet | Random Coil | α-Helix | β-Turns | |
| 0 | 22.99 | 28.24 | 23.17 | 25.6 | 24.63 | 2.79 | 45.14 | 27.44 |
| 4 | 27.86 | 21.33 | 10.25 | 40.56 | 37.08 | 0.06 | 36.71 | 26.15 |
| 8 | 35.66 | 20.83 | 14.06 | 29.45 | 38.72 | 0 | 28.79 | 32.49 |
| 12 | 36.33 | 14.7 | 13.62 | 35.35 | 42.55 | 0.01 | 29 | 28.44 |
| 16 | 42.14 | 7.43 | 5.67 | 44.76 | 33.07 | 0 | 39.01 | 27.92 |
| SSPS Concentration (%) | Cooked SPI Suspension | SPI Gels | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S2–S1 | S3–S2 | S1 | S2 | S3 | S2–S1 | S3–S2 | |
| 0 | 28.6 ± 0.3c | 68.9 ± 0.5a | 80.2 ± 0.8d | 40.2 | 11.3 | 16.1 ± 0.2d | 37.8 ± 1.5b | 80.5 ± 1.8c | 21.7 | 42.7 |
| 4 | 23.7 ± 1.5d | 63.2 ± 0.7b | 88.0 ± 1.2b | 39.5 | 24.8 | 19.2 ± 1.3c | 81.2 ± 2.9a | 82.8 ± 0.5c | 62.1 | 1.6 |
| 8 | 24.6 ± 1.4d | 63.2 ± 0.4b | 93.5 ± 1.5a | 38.5 | 30.4 | 28.7 ± 0.2a | 83.9 ± 1.8a | 82.7 ± 0.3c | 55.2 | 1.2 |
| 12 | 30.5 ± 0.2b | 61.8 ± 0.1c | 84.3 ± 1.2c | 31.3 | 22.5 | 23.2 ± 0.4b | 85.4 ± 1.2ab | 86.5 ± 1.9a | 63.3 | 1.1 |
| 16 | 36.7 ± 1.3a | 62.7 ± 0.1bc | 81.1 ± 0.5d | 25.9 | 18.4 | 23.3 ± 0.8b | 86.1 ± 0.5a | 87.5 ± 1.5a | 64.2 | 1.4 |
| SSPS Concentration (%) | Color of SPI Gels | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DG of SPI Gels | L* | a* | b* | |
| 0 | 0 | 41.5 ± 0.3c | 3.5 ± 0.5c | 6.5 ± 0.2c |
| 4 | 2.4 ± 0.2d | 41.6 ± 0.3c | 3.3 ± 0.5c | 7.4 ± 0.3b |
| 8 | 3.8 ± 0.02c | 43.3 ± 0.7b | 4.9 ± 0.5b | 7.6 ± 0.2b |
| 12 | 4.5 ± 0.1b | 44.4 ± 0.5a | 7.3 ± 0.7a | 9.1 ± 0.3a |
| 16 | 8.5 ± 0.2a | 44.4 ± 0.5a | 7.4 ± 0.6a | 9.2 ± 0.3a |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lan, Q.; Li, L.; Dong, H.; Wu, D.; Chen, H.; Lin, D.; Qin, W.; Yang, W.; Vasanthan, T.; Zhang, Q. Effect of Soybean Soluble Polysaccharide on the Formation of Glucono-δ-Lactone-Induced Soybean Protein Isolate Gel. Polymers 2019, 11, 1997. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11121997
Lan Q, Li L, Dong H, Wu D, Chen H, Lin D, Qin W, Yang W, Vasanthan T, Zhang Q. Effect of Soybean Soluble Polysaccharide on the Formation of Glucono-δ-Lactone-Induced Soybean Protein Isolate Gel. Polymers. 2019; 11(12):1997. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11121997
Chicago/Turabian StyleLan, Qiuyu, Lin Li, Hongmin Dong, Dingtao Wu, Hong Chen, Derong Lin, Wen Qin, Wenyu Yang, Thava Vasanthan, and Qing Zhang. 2019. "Effect of Soybean Soluble Polysaccharide on the Formation of Glucono-δ-Lactone-Induced Soybean Protein Isolate Gel" Polymers 11, no. 12: 1997. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11121997
APA StyleLan, Q., Li, L., Dong, H., Wu, D., Chen, H., Lin, D., Qin, W., Yang, W., Vasanthan, T., & Zhang, Q. (2019). Effect of Soybean Soluble Polysaccharide on the Formation of Glucono-δ-Lactone-Induced Soybean Protein Isolate Gel. Polymers, 11(12), 1997. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11121997