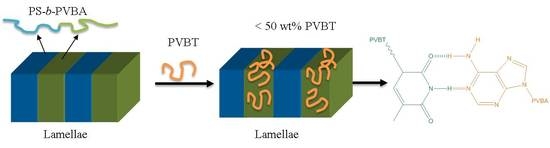
Self-Assembled Structures of Diblock Copolymer/Homopolymer Blends through Multiple Complementary Hydrogen Bonds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
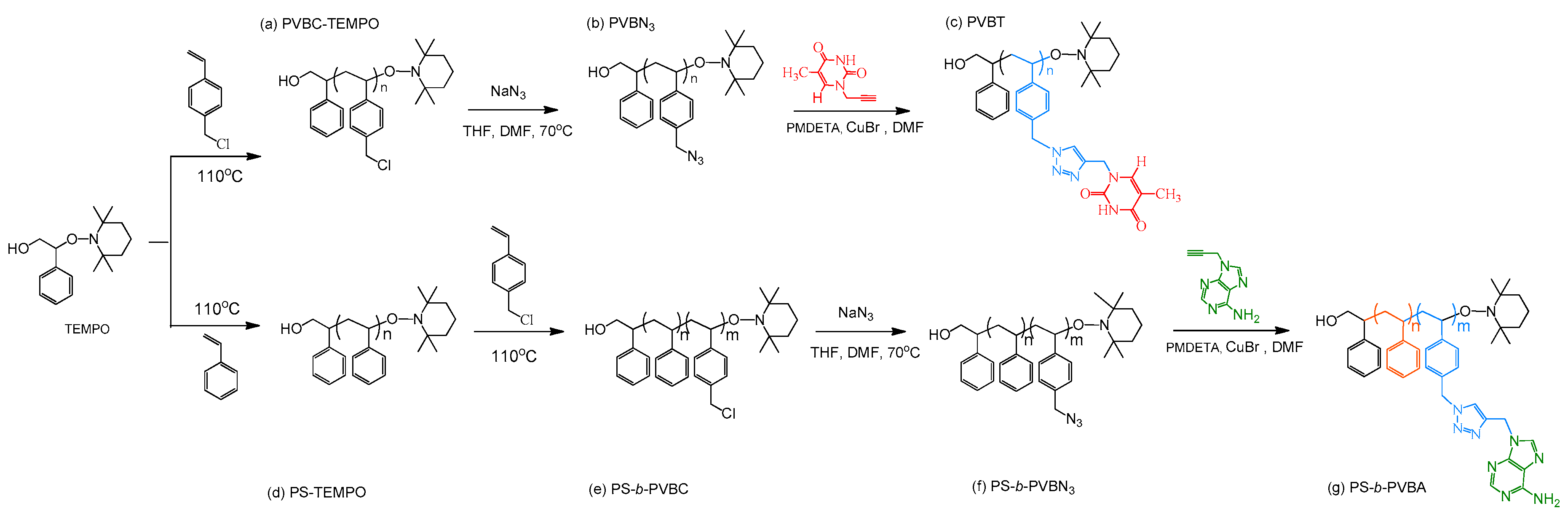
2.2. PS-b-PVBA
2.3. PS-b-PVBA/PVBT Blend Complexes
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
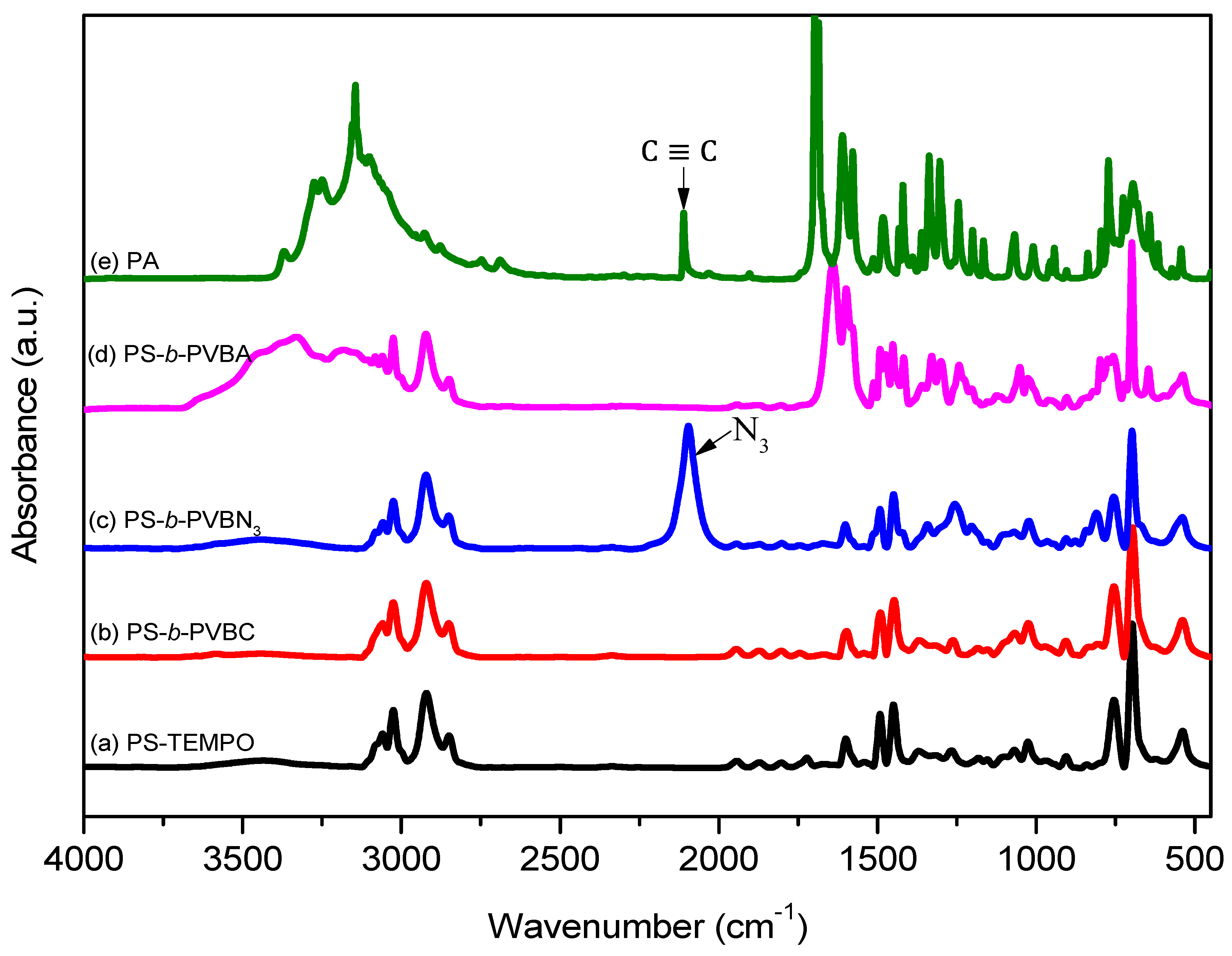
3.1. Synthesis of PS-b-PVBA
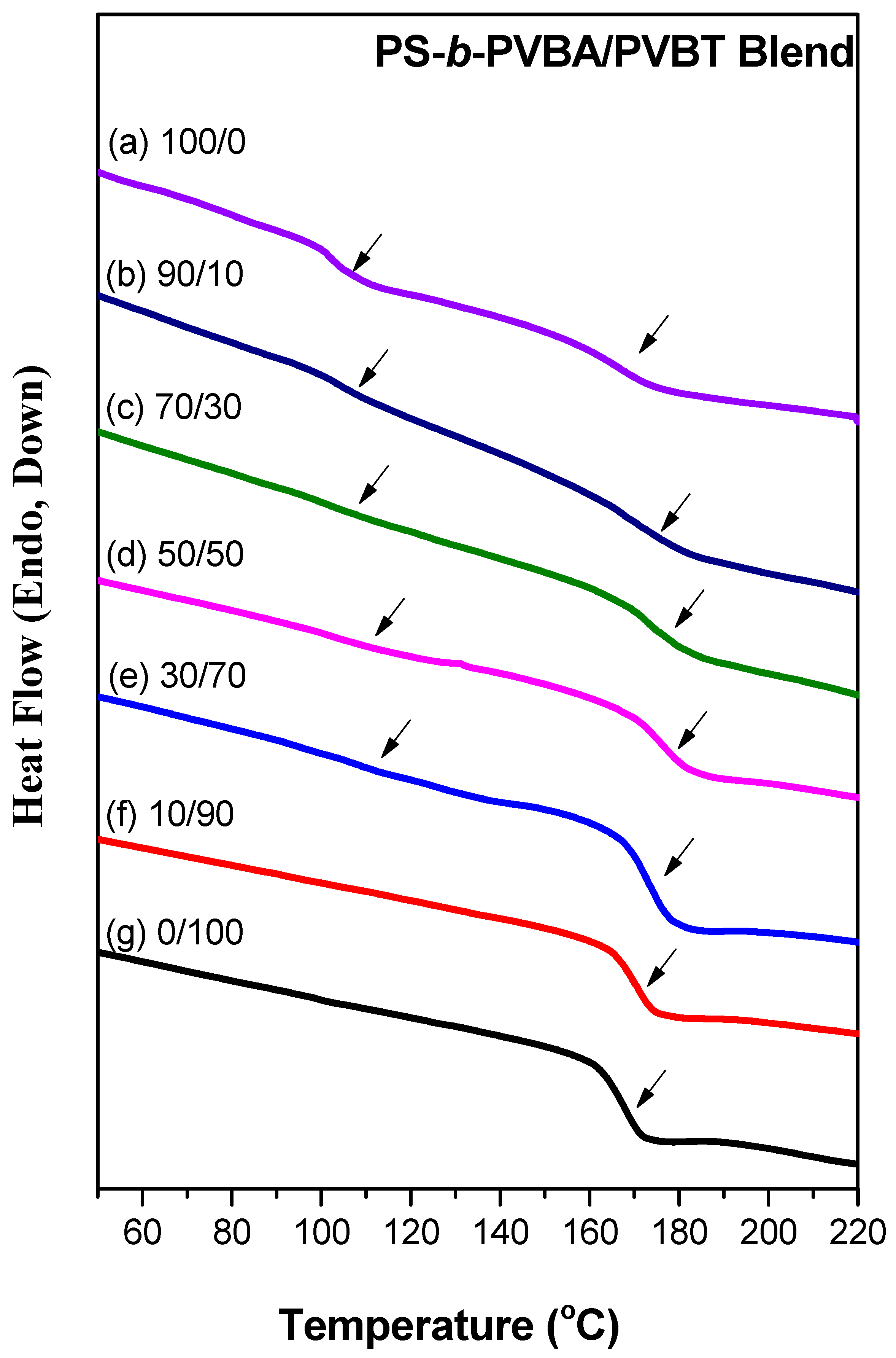
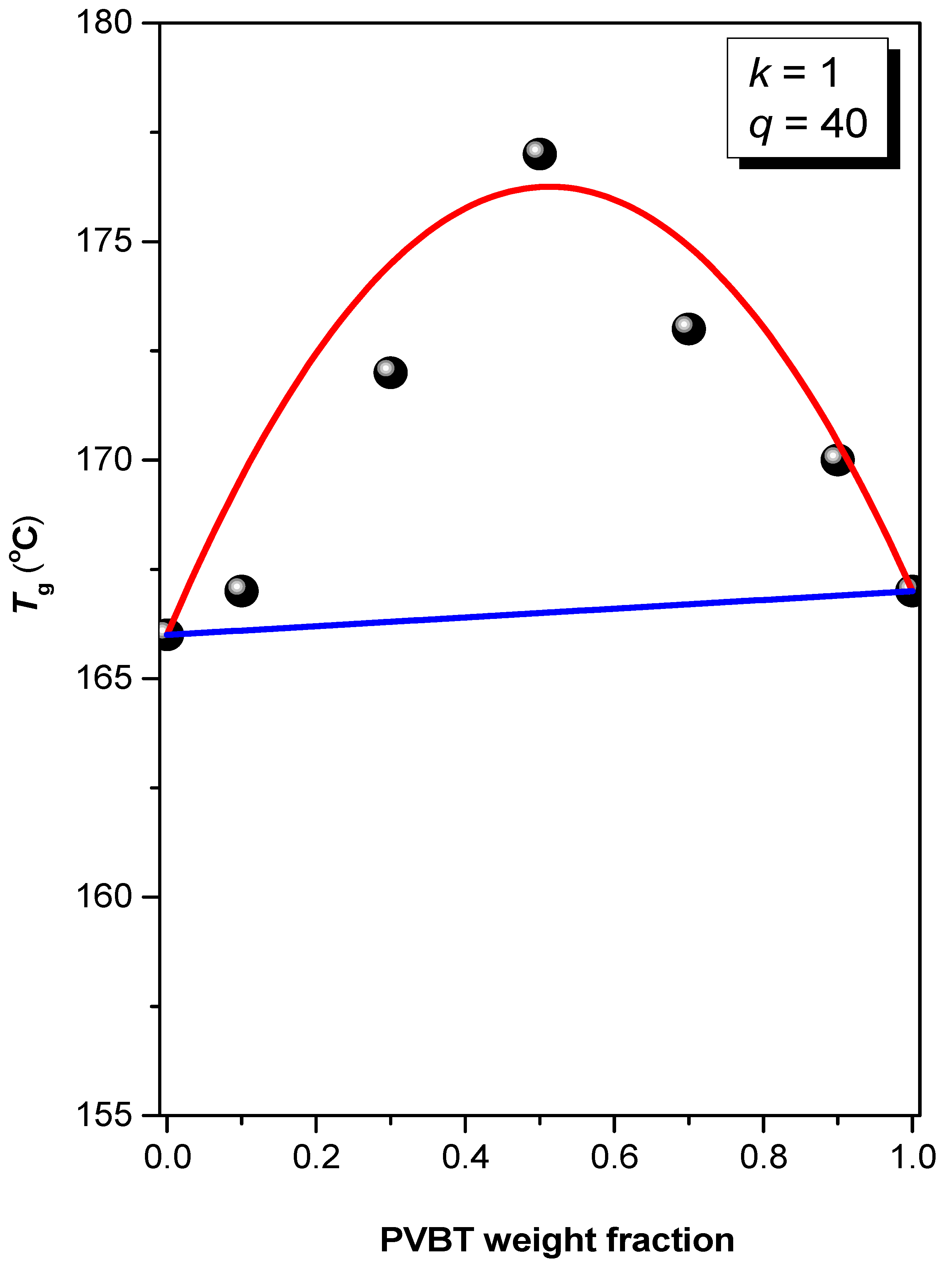
3.2. Thermal Analyses of PS-b-PVBA/PVBT
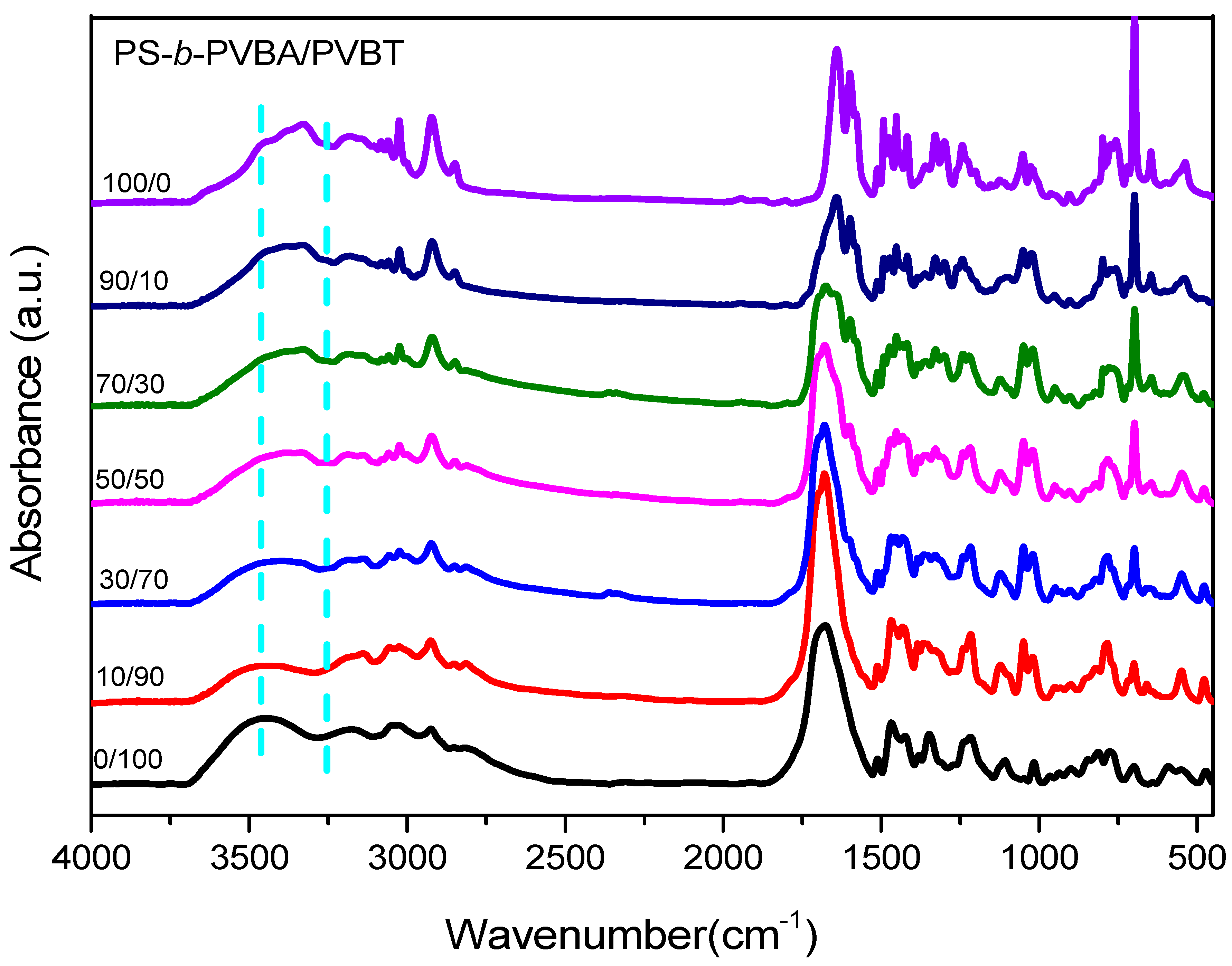
3.3. Hydrogen Bonding in PS-b-PVBA/PVBT Blends
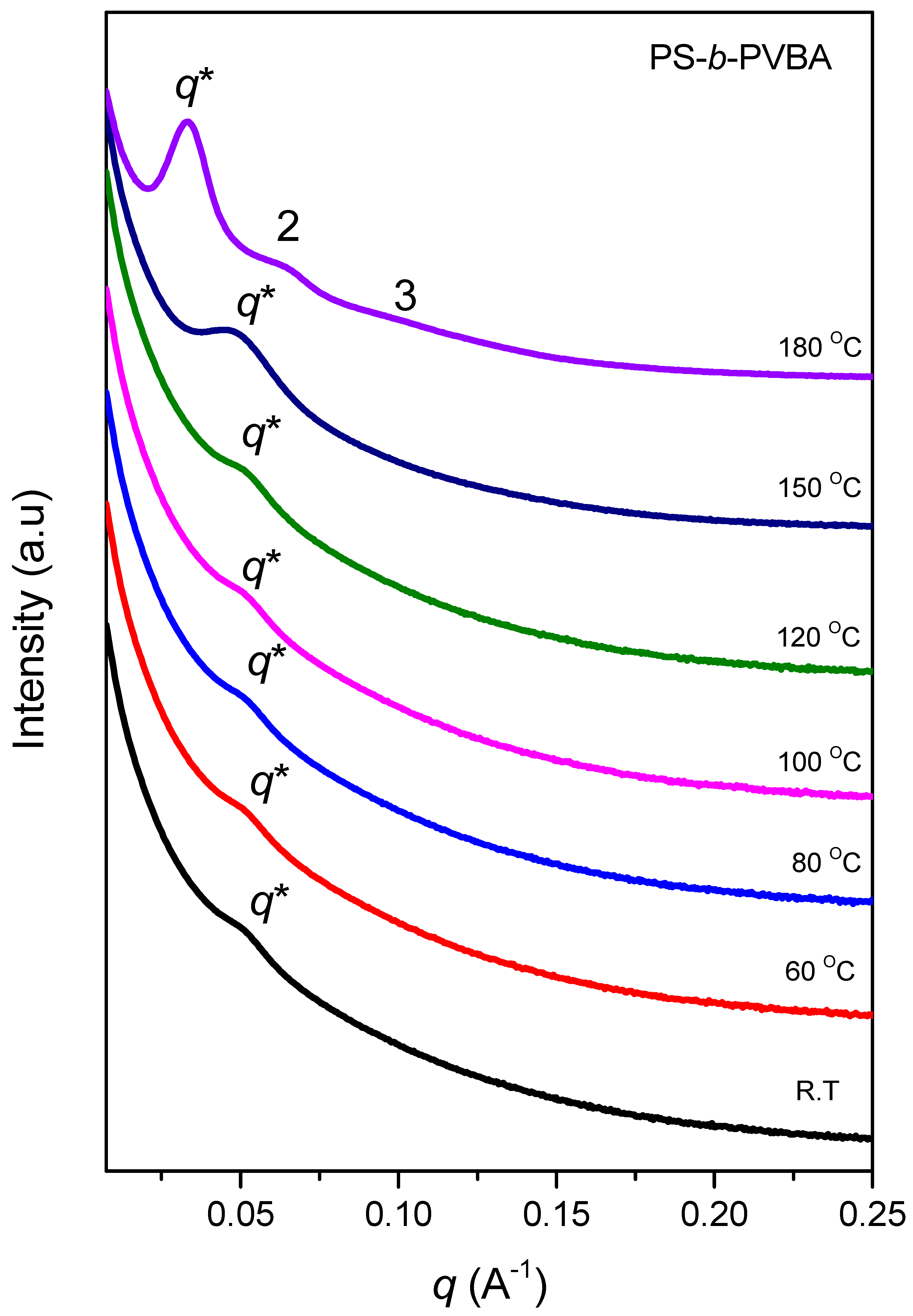
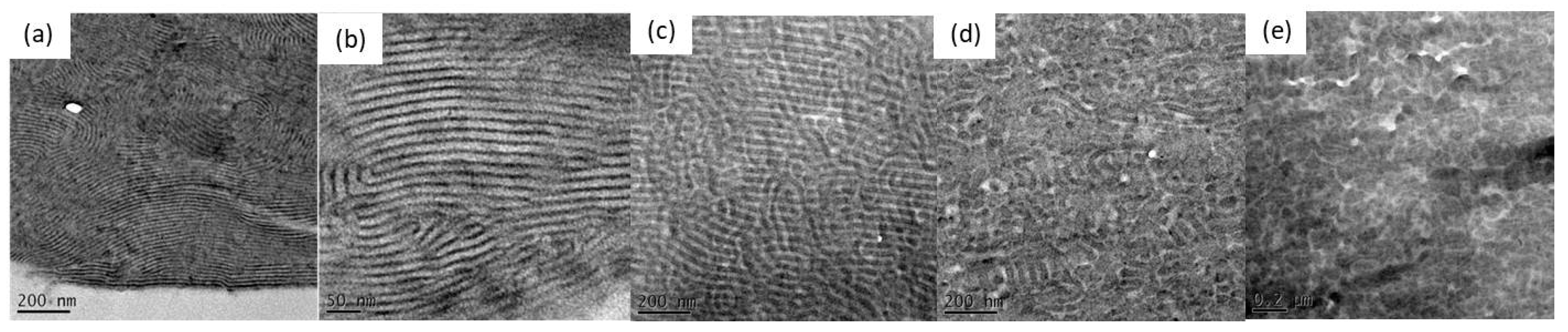
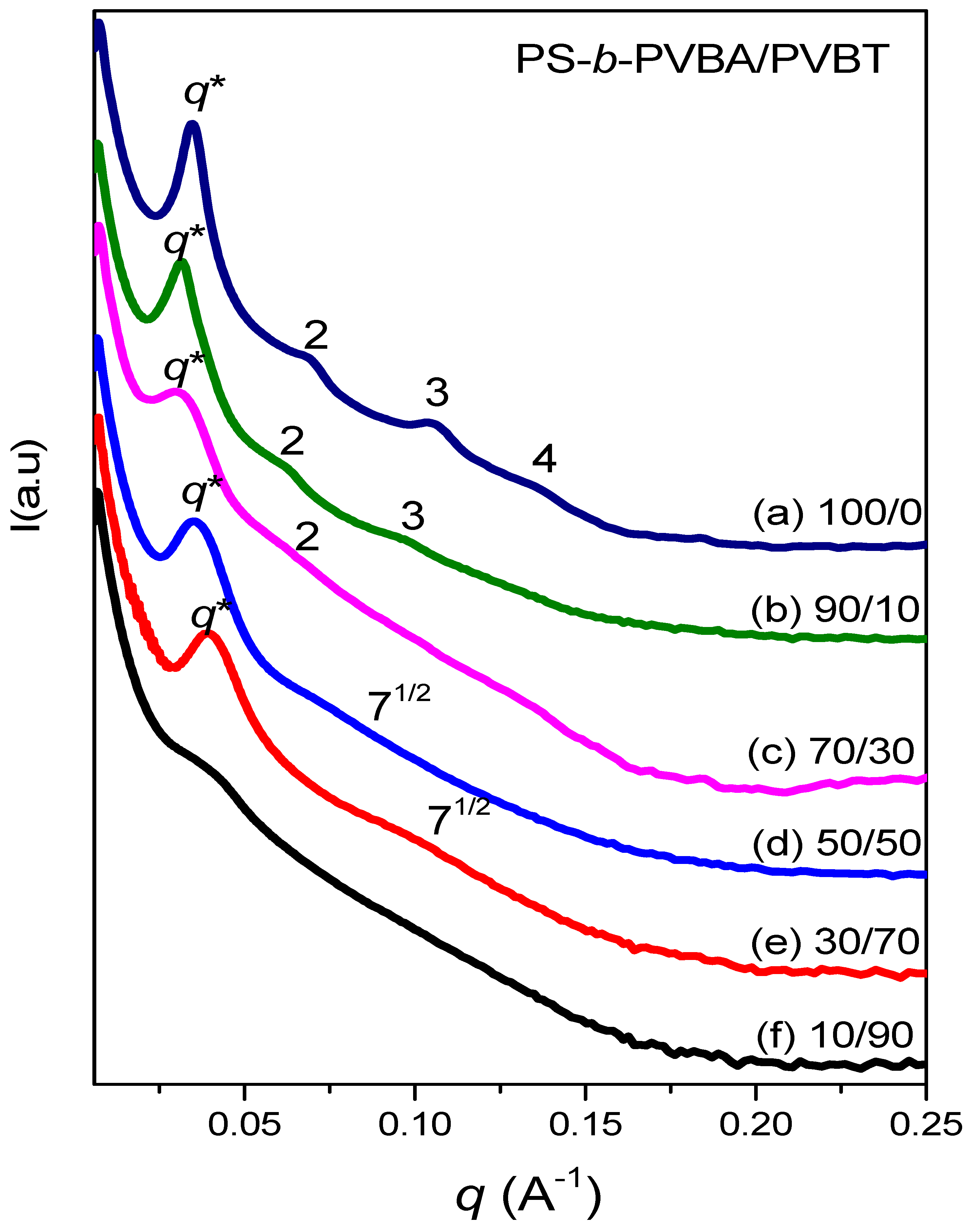
3.4. Self-Assembled Supramolecular Structures of PS-b-PVBA/PVBT Blends
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jenekhe, S.A.; Chen, X.L. Self-assembly of ordered microporous materials from rod-coil block copolymers. Science 1999, 283, 372–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guiod, A.R.; Vandermeulen, W.M.; Klok, V.H. Advanced drug delivery devices via self-assembly of amphiphilic block copolymers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 270–279. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, E.L.; Hsu, W.L.; Chiang, Y.W. Trapping structural coloration by a bioinspired gyroid microstructure in solid state. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Tade, M.O.; Dai, S.; Yamauchi, Y. Synthesis of nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon spheres with extra-large pores through assembly of diblock copolymer micelles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.W. Hydrogen Bonding in Polymeric Materials; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Benoit, H.; Hadiioannou, G. Scattering theory and properties of block copolymers with various architectures in the homogeneous bulk state. Macromolecules 1988, 21, 1449–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shull, K.R. Mean-field theory of block copolymers: Bulk melts, surfaces, and thin films. Macromolecules 1992, 25, 2122–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, Z.G.; Li, R.; Chen, Y.; Zou, H.W.; Liang, M. Preparation of damping structural integration materials via the formation of nanostructure in triblock copolymer modified epoxy resins. J. Polym. Res. 2016, 23, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.K.; Pearce, E.M.; Kwei, T.K. Poly(styrene-b-vinylphenyldimethylsilanol) and its blends with homopolymers. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Xie, H. Miscibility and morphology in block copolymer/homopolymer blends. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1991, 16, 977–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.Q.; Pearce, E.M.; Kwei, T.K. Binary and ternary blends of polystyrene-block-poly(p-hydroxystyrene). Macromolecules 1997, 30, 7119–7126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosoneen, H.; Ruokolainen, J.; Nyholm, P.; Ikkala, O. Self-organized cross-linked phenolic thermosets: Thermal and dynamic mechanical properties of novolac/block copolymer blends. Polymer 2001, 42, 9481–9486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrosielska, K.; Wakao, S.; Takano, A.; Matsushita, Y. Nanophase-separated structures of AB block copolymer/C homopolymer blends with complementary hydrogen-bonding interactions. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 7695–7698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrosielska, K.; Wakao, S.; Suzuki, J.; Noda, K.; Takano, A.; Matsushita, Y. Effect of homopolymer molecular weight on nanophase-separated structures of AB block copolymer/C homopolymer blends with hydrogen-bonding interactions. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 7098–7102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.C.; Kuo, S.W.; Jeng, U.S.; Su, C.J.; Chang, F.C. On modulating the phase behavior of block copolymer/homopolymer blends via hydrogen bonding. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 1083–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan, A.; Shi, A.C. Modeling hydrogen bonding in diblock copolymer/homopolymer blends. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 5796–5805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, S.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Lin, E.L.; Chiang, Y.W.; Kuo, S.W. Hydrogen bonding strength effect on self-assembly supramolecular structures of diblock copolymer/homopolymer blends. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 2395–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, N.; Guo, Q. Nanostructure and hydrogen bonding in interpolyelectrolyte complexes of poly(ε-caprolactone)-block-poly(2-vinyl pyridine) and poly(acrylic acid). Polymer 2008, 49, 5268–5275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, N.; Liu, J.; Guo, Q. Self-assembled complexes of poly(4-vinylphenol) and poly(ε-caprolactone)-block-poly (2-vinylpyridine) via competitive hydrogen bonding. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 7596–7605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, N.; Guo, Q. Selective hydrogen bonding and hierarchical nanostructures in poly(hydroxyether of bisphenol A)/poly(ε-caprolactone)-block-poly(2-vinyl pyridine) blends. Polymer 2008, 49, 922–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.C.; Kuo, S.W.; Lu, C.H.; Jeng, U.S.; Chang, F.C. Self-assembly structures through competitive interactions of crystalline−amorphous diblock copolymer/homopolymer blends: Poly(ε-caprolactone-b-4-vinyl pyridine)/poly(vinyl phenol). Macromolecules 2009, 42, 3580–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, N.V.; Hanley, T.; Guo, Q. Microphase separation through competitive hydrogen bonding in double crystalline diblock copolymer/homopolymer blends. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 7695–7704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.G.; Lin, Y.D.; Kuo, S.W. From microphase separation to self-organized mesoporous phenolic resin through competitive hydrogen bonding with double-crystalline diblock copolymers of poly(ethylene oxide-b-ε-caprolactone). Macromolecules 2011, 44, 9295–9309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, N.V.; Hameed, N.; Guo, Q. Competitive hydrogen bonding and self-assembly in poly(2-vinyl pyridine)-block-poly(methyl methacrylate)/poly(hydroxyether of bisphenol A) blends. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2009, 47, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, N.; Salim, N.V.; Guo, Q. Microphase separation through competitive hydrogen bonding in self-assembled diblock copolymer/homopolymer complexes. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 131, 214905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.F.; Kuo, S.W.; Huang, C.F.; Lu, J.S.; Chan, S.C.; Wang, C.F.; Chang, F.C. Hydrogen-bonding interactions mediate the phase behavior of an AB/C block copolymer/homopolymer blend comprising poly (methyl methacrylate-b-vinylpyrrolidone) and poly (vinylphenol). Macromolecules 2006, 39, 5458–5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.C.; Kuo, S.W.; Jeng, U.S.; Chang, F.C. Self-assembly through competitive interactions of miscible diblock copolymer/homopolymer blends: Poly(vinylphenol-b-methyl methacrylate)/poly (vinylpyrrolidone) blend. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 1401–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Shi, A.C. Microphase separation induced by differential interactions in diblock copolymer/homopolymer blends. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 130, 234904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, I.; Kuo, S.W.; Chang, F.C. Self-Assembly structures through competitive interactions of miscible crystalline–amorphous diblock copolymer/homopolymer blends. Polymer 2009, 50, 5276–5287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, Y. Creation of hierarchically ordered nanophase structures in block polymers having various competing interactions. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyase, H.; Asai, Y.; Takano, A.; Matsushita, Y. Kaleidoscopic tiling patterns with large unit cells from ABC star-shaped terpolymer/diblock copolymer blends with hydrogen bonding interaction. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asari, T.; Matsuo, S.; Takano, A.; Matsushita, Y. Three-phase hierarchical structures from AB/CD diblock copolymer blends with complemental hydrogen bonding interaction. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 8811–8815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asari, T.; Arai, S.; Takano, A.; Matsushita, Y. Archimedean tiling structures from ABA/CD block copolymer blends having intermolecular association with hydrogen bonding. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 2232–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.W. Hydrogen bond-mediated self-assembly and supramolecular structures of diblock copolymer mixtures. Polym. Inter. 2009, 58, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.C.; Kuo, S.W.; Chang, F.C. Self-assembly of an A–B diblock copolymer blended with a C homopolymer and a C–D diblock copolymer through hydrogen bonding interaction. Polymer 2010, 51, 4176–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.W.; Lin, C.L.; Chang, F.C. The Study of Hydrogen Bonding and Miscibility in Poly(vinyl pyridines) with Phenolic Resin. Polymer 2002, 43, 3943–3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.W.; Tung, P.H.; Chang, F.C. Syntheses and the Study of Strong Hydrogen-Bonded Poly(vinyl phenol-b-vinyl pyridine) Diblock Copolymer through Anionic Polymerization. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 9388–9395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Jiang, M.; Ning, F.L.; Chen, D.Y.; Liu, S.Y.; Duan, H.W. Block-copolymer-free strategy for preparing micelles and hollow spheres: Self-assembly of poly(4-vinylpyridine) and modified polystyrene. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 5980–5989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IIhan, F.; Gray, M.; Rotello, V.M. Reversible side chain modification through noncovalent interactions. “Plug and play” polymers. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 2597–2601. [Google Scholar]
- Sherrington, D.C.; Taskinen, K.A. Self-assembly in synthetic macromolecular systems via multiple hydrogen bonding interactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2001, 30, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, K.E.; Kade, M.J.; de Greef, T.F.A.; Meijer, E.W.; Kramer, E.J.; Hawker, C.J. Polymers with multiple hydrogen-bonded end groups and their blends. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakava, S.; Wu, J.; Campo, C.J.; Mather, P.T.; Rowan, S.J. Liquid-crystalline supramolecular polymers formed through complementary nucleobase-pair interactions. Chem. A Eur. J. 2005, 12, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altintas, O.; Schulze-Suenninghausen, D.; Luy, B.; Barner-Kowollik, C. Facile preparation of supramolecular H-shaped (Ter)polymers via multiple hydrogen bonding. ACS Macro Lett. 2013, 2, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.; Zimmerman, S.C. Formation of a miscible supramolecular polymer blend through self-assembly mediated by a quadruply hydrogen-bonded heterocomplex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 11582–11590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mather, B.D.; Baker, M.B.; Beyer, F.L.; Berg, M.A.G.; Green, M.D.; Long, T.E. Supramolecular triblock copolymers containing complementary nucleobase molecular recognition. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 6834–6845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, K.P.; Breedveld, V.; Weck, M. Complementary hydrogen-bonded thermoreversible polymer networks with tunable properties. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 3429–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, B.D.; Lizotte, J.R.; Long, T.E. Synthesis of chain end functionalized multiple hydrogen bonded polystyrenes and poly(alkyl acrylates) using controlled radical polymerization. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 9331–9337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, K.; Yokoyama, T.; Shimasaki, T.; Teramoto, N.; Shibata, M. Bio-based epoxy networks incorporating covalent and melamine cyanurate-type multiple hydrogen-bonding crosslinkages. J. Polym. Res. 2016, 23, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.; Zimmerman, S.C. Interplay of fidelity, binding strength, and structure in supramolecular polymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 14236–14237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.R.; Walter, T. Nucleic acid models. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1996, 21, 209–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.D. The Secret of Life; Knopf: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, S.W.; Cheng, R.S. DNA-Like interactions enhance the miscibility of supramolecular polymer blends. Polymer 2009, 50, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.W.; Tsai, H.T. Complementary multiple hydrogen-bonding interactions increase the glass transition temperatures to PMMA copolymer mixtures. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 4701–4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.W.; Hsu, C.H. Miscibility enhancement of supramolecular polymer blends through complementary multiple hydrogen bonding interactions. Polym. Inter. 2010, 59, 998–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.H.; Huang, K.W.; Kuo, S.W. Heteronucleobase-functionalized benzoxazine: Synthesis, thermal property and multiple hydrogen bonding interactions. Polym. Chem. 2012, 3, 1546–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.C.; Kuo, S.W. Complementary multiple hydrogen bonding interactions mediate the self-assembly of supramolecular structures from thymine-containing block copolymers and hexadecyladenine. Polym. Chem. 2012, 3, 3100–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Altukhov, O.; Cheng, C.C.; Chang, F.C.; Kuo, S.W. Supramolecular structures of uracil-functionalized PEG with multi-diamidopyridine POSS through complementary hydrogen bonding interactions. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 5196–5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.W.; Wu, Y.R.; Kuo, S.W. From random coil to helical structure induced by carbon nanotube through supramolecular interactions. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2013, 34, 1530–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, H.K.; Chen, Y.H.; Chu, Y.L.; Cheng, C.C.; Chang, F.C.; Zhu, C.Y.; Kuo, S.W. Photo-crosslinking of pendent uracil units provides supramolecular hole injection/transport conducting polymers for highly efficient light-emitting diodes. Polymers 2015, 7, 804–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.C.; Bastakoti, B.P.; Pramanik, M.; Yamauchi, Y.; Kuo, S.W. Multiple hydrogen bonding mediates the formation of multicompartment micelles and hierarchical self-assembled structures from pseudo A-block-(B-graft-C) terpolymers. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 5110–5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.W.; Wu, P.W.; Su, W.H.; Zhu, C.Y.; Kuo, S.W. Stimuli-Responsive Supramolecular Materials: Photo-Tunable and Molecular Recognition Behavior. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.W.; Mohamed, M.G.; Zhu, C.Y.; Kuo, S.W. Functional supramolecular polypeptides involving π-π stacking and strong hydrogen-bonding interactions: A conformation study toward carbon nanotubes (CNTs) dispersion. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 5374–5385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.W.; Ji, W.Y.; Kuo, S.W. Water-soluble fluorescent nanoparticles from supramolecular amphiphiles featuring heterocomplementary multiple hydrogen bondings. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 7091–7101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.W.; Ji, W.Y.; Kuo, S.W. Stimuli-responsive supramolecular conjugated polymer with phototunable surface relief grating. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 2813–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; George, S.J. New directions in supramolecular electronics. Mater. Today 2015, 18, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliprandi, A.; Mauro, M.; Cola, L.D. Controlling and imaging biomimetic self-assembly. Nat. Chem. 2016, 8, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Xi, W. Nucleobase-Containing Polymers: Structure, Synthesis, and Applications. Polymers 2017, 9, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, K.; Kanomata, A.; Inoue, T.; Long, T.E. Thermoreversible polyesters consisting of multiple hydrogen bonding (MHB). Macromolecules 2004, 37, 3519–3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.; Beecham, M.P.; Kempe, K.; Haddleton, D.M.; Khan, A.; Marsh, A. Water soluble triblock and pentablock poly(methacryloyl nucleosides) from copper-mediated living radical polymerisation using PEG macroinitiators. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 66, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.C.; Huang, C.F.; Yen, Y.C.; Chang, F.C. A “plug and play” polymer through biocomplementary hydrogen bonding. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2008, 46, 6416–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.S.; Wu, Y.C.; Kuo, S.W. Thymine- and Adenine-Functionalized Polystyrene Form Self-Assembled Structures through Multiple Complementary Hydrogen Bonds. Polymers 2014, 6, 1827–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwei, T. The effect of hydrogen bonding on the glass transition temperatures of polymer mixtures. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Lett. Ed. 1984, 22, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

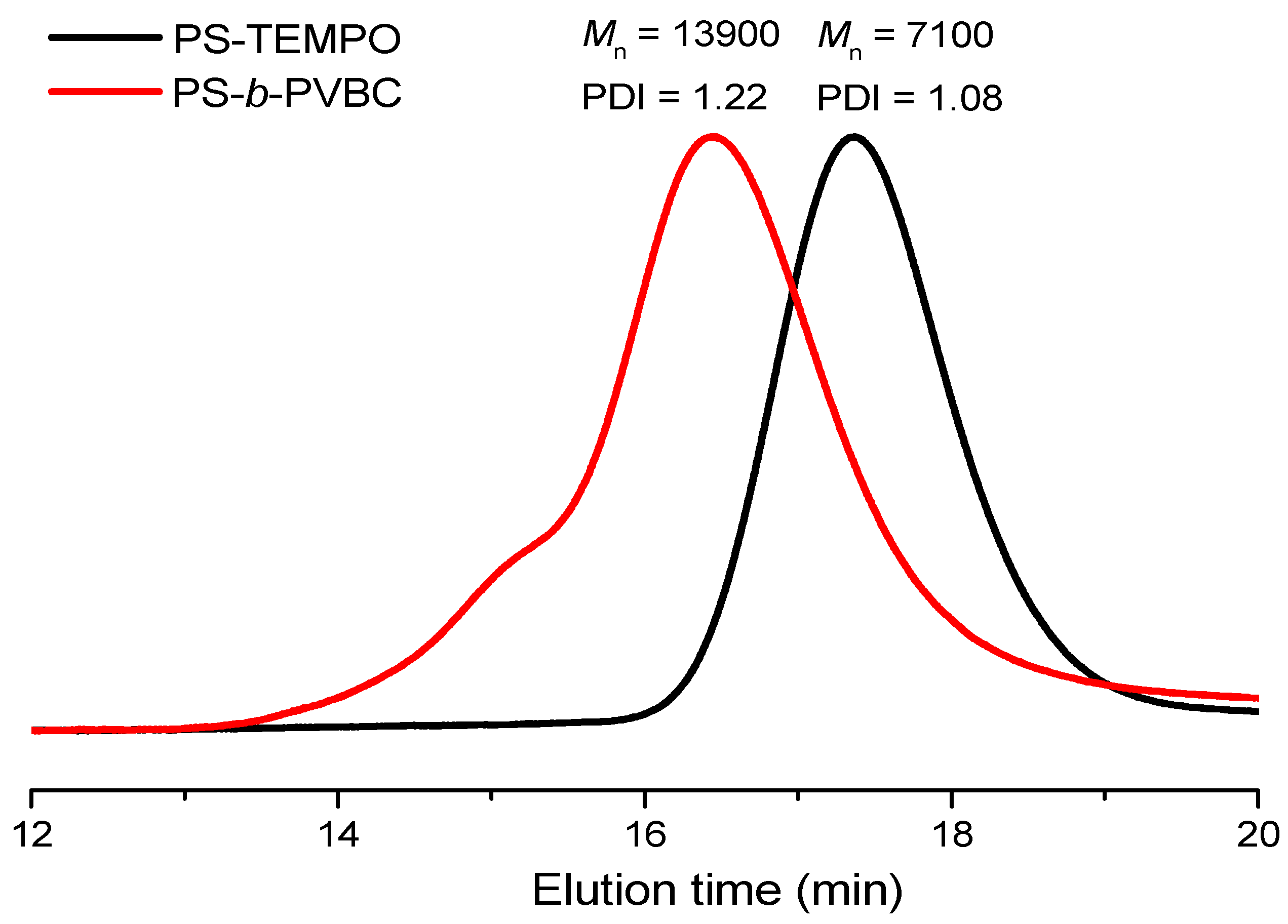
| Sample | PS (Mn) a | PVBC (Mn) a | PVBA (Mn) a | PS Tg (°C) b | PVBA Tg (°C) b | PDI c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PS67-b-PVBA27 | 6900 | 4100 | 8900 | 104 | 166 | 1.22 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, W.-C.; Wu, Y.-S.; Wang, C.-F.; Kuo, S.-W. Self-Assembled Structures of Diblock Copolymer/Homopolymer Blends through Multiple Complementary Hydrogen Bonds. Crystals 2018, 8, 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8080330
Su W-C, Wu Y-S, Wang C-F, Kuo S-W. Self-Assembled Structures of Diblock Copolymer/Homopolymer Blends through Multiple Complementary Hydrogen Bonds. Crystals. 2018; 8(8):330. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8080330
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Wei-Chen, Yu-Shian Wu, Chih-Feng Wang, and Shiao-Wei Kuo. 2018. "Self-Assembled Structures of Diblock Copolymer/Homopolymer Blends through Multiple Complementary Hydrogen Bonds" Crystals 8, no. 8: 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8080330
APA StyleSu, W.-C., Wu, Y.-S., Wang, C.-F., & Kuo, S.-W. (2018). Self-Assembled Structures of Diblock Copolymer/Homopolymer Blends through Multiple Complementary Hydrogen Bonds. Crystals, 8(8), 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8080330