The Effect of Different Atomic Substitution at Mn Site on Magnetocaloric Effect in Ni50Mn35Co2Sn13 Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
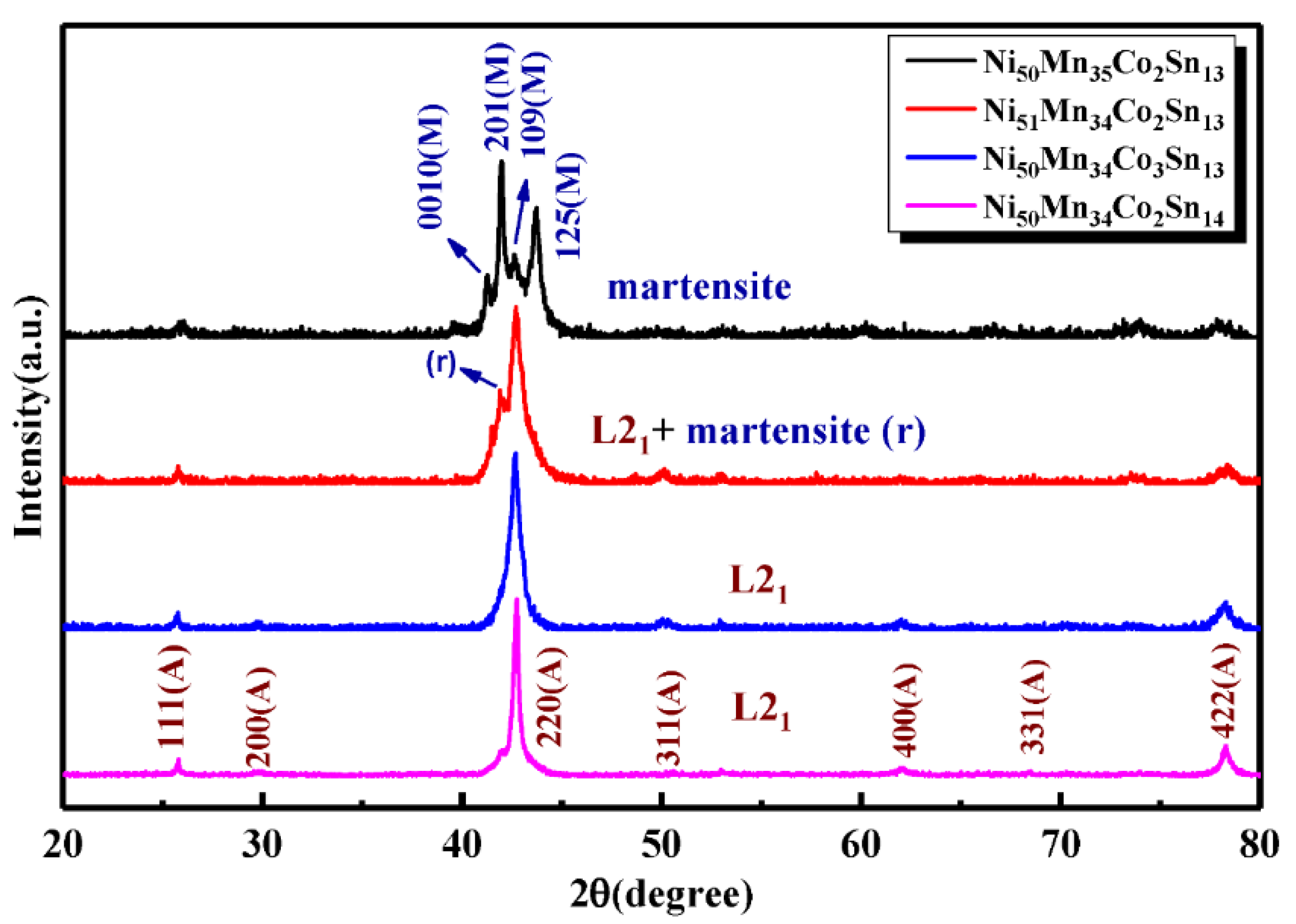
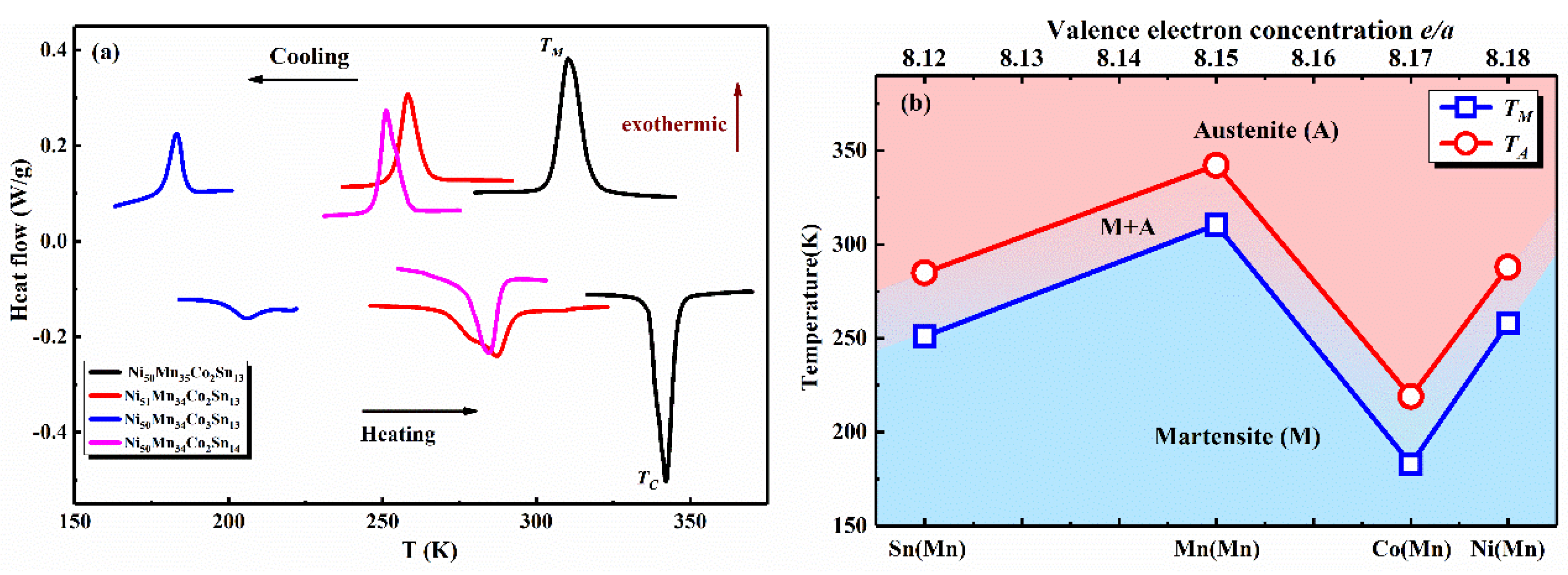
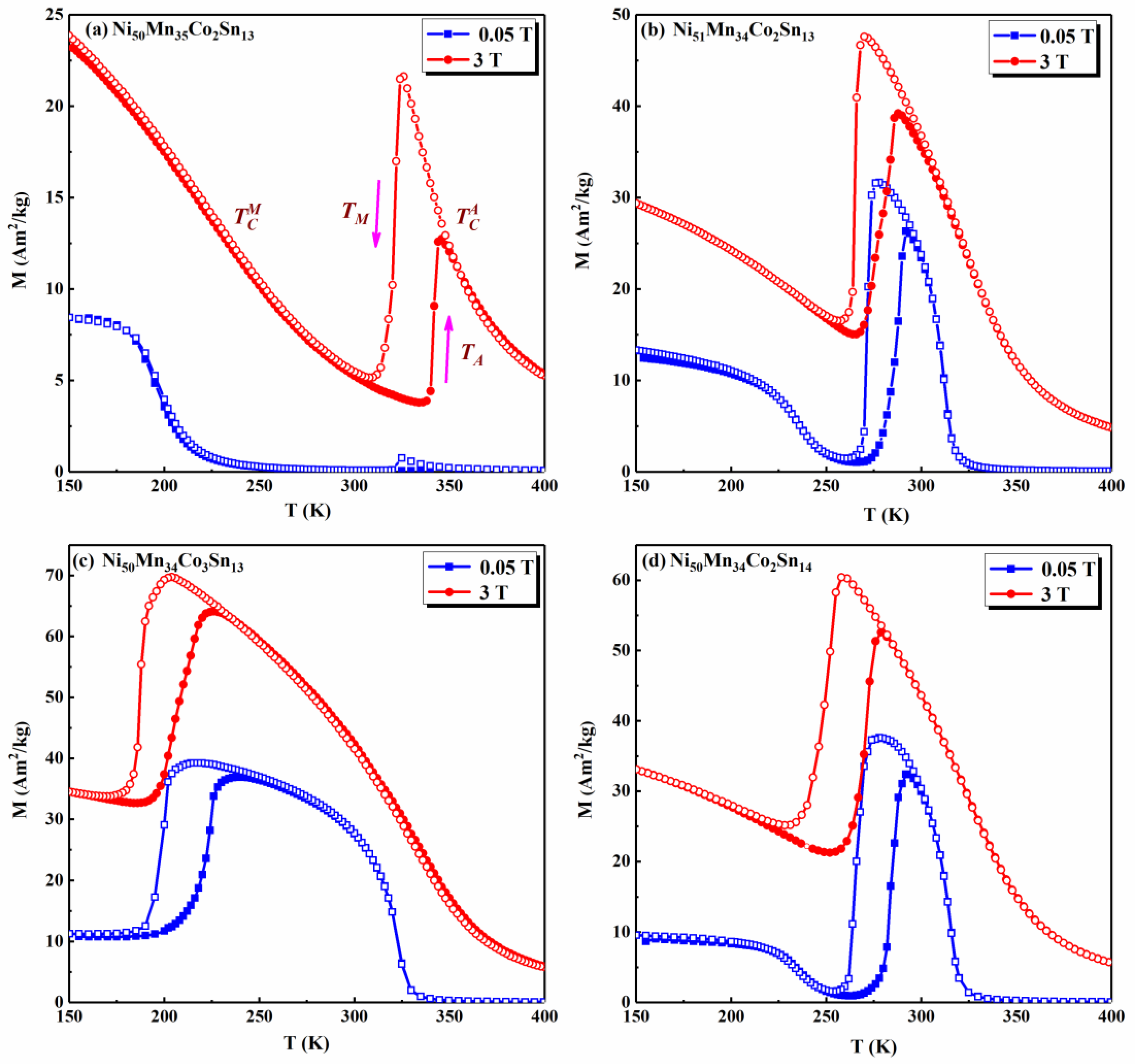
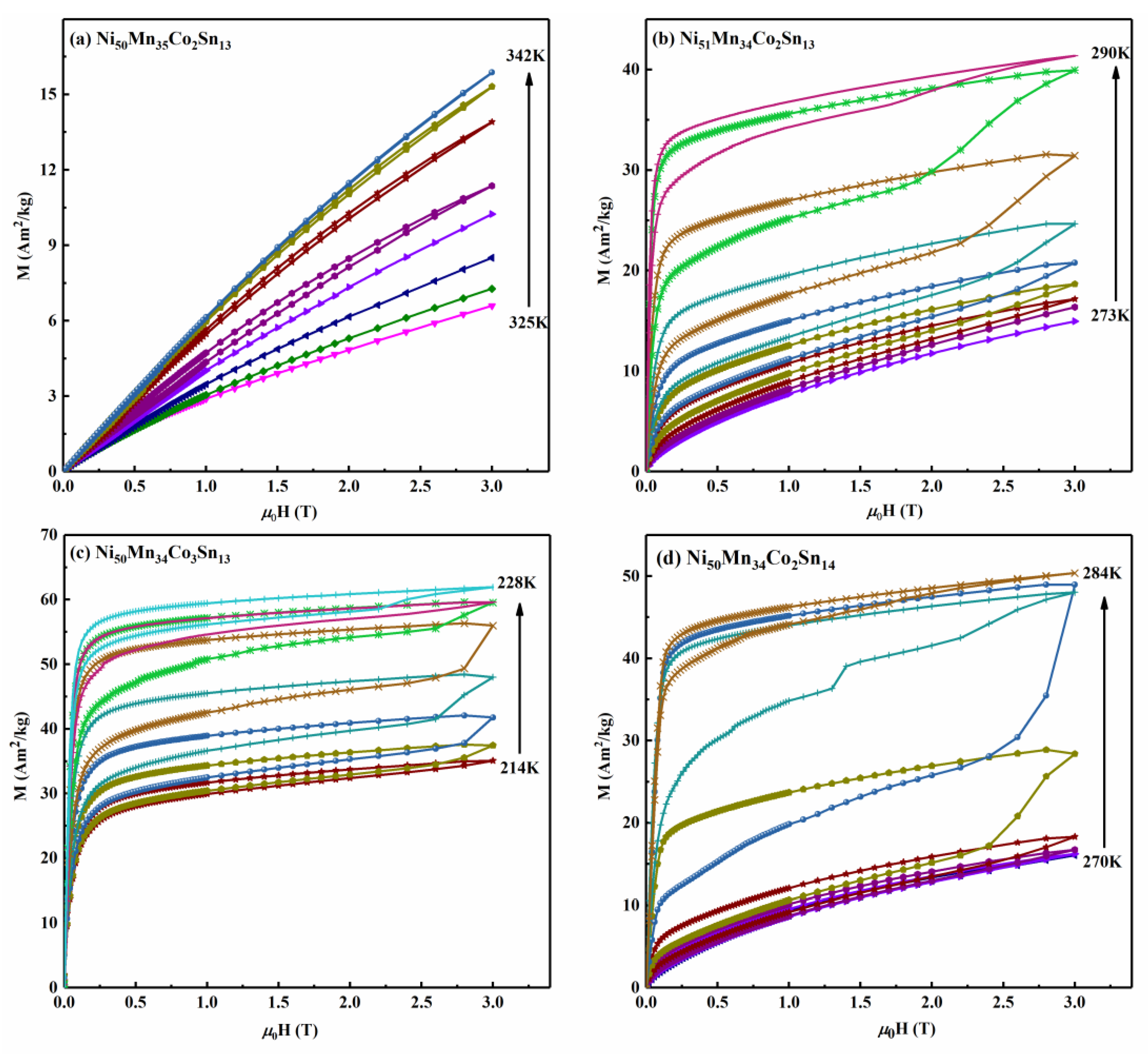
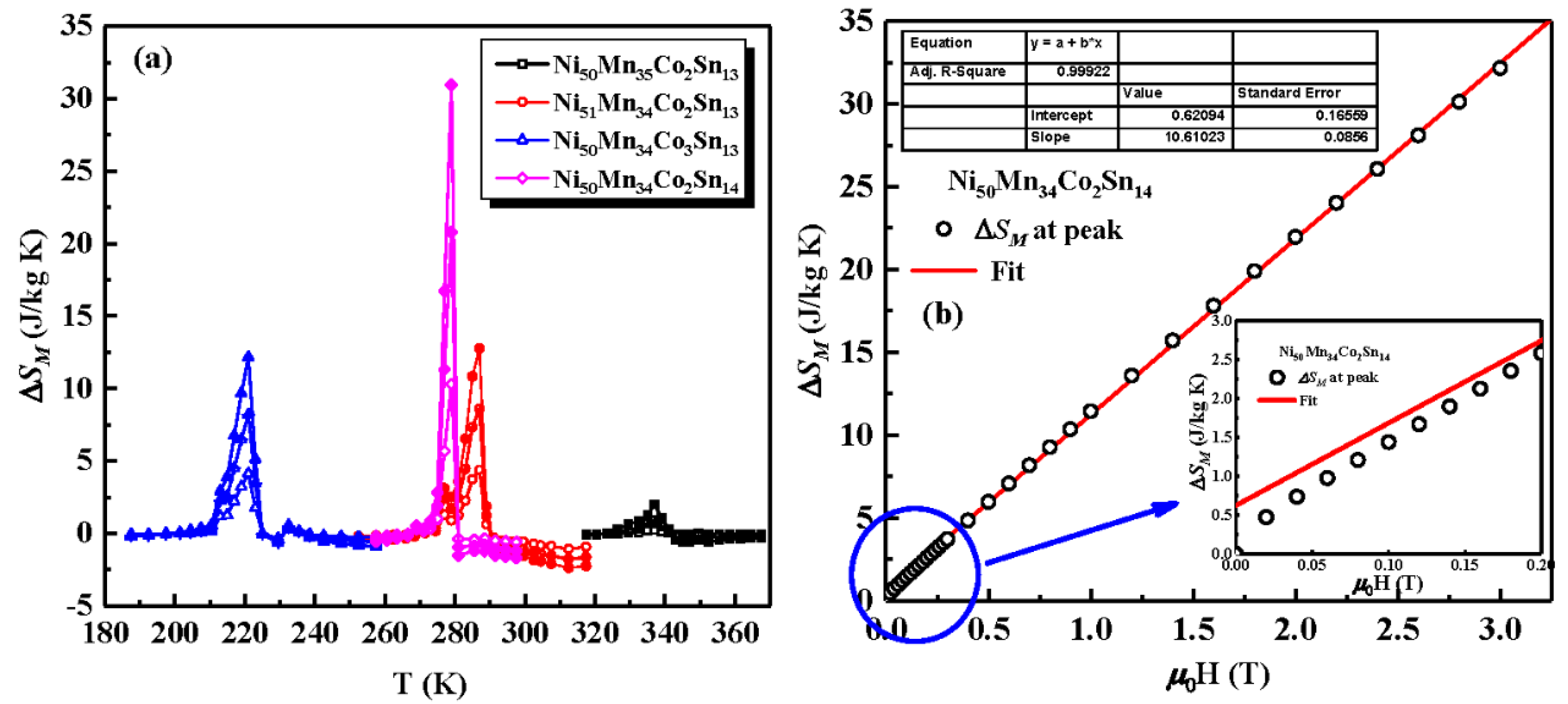
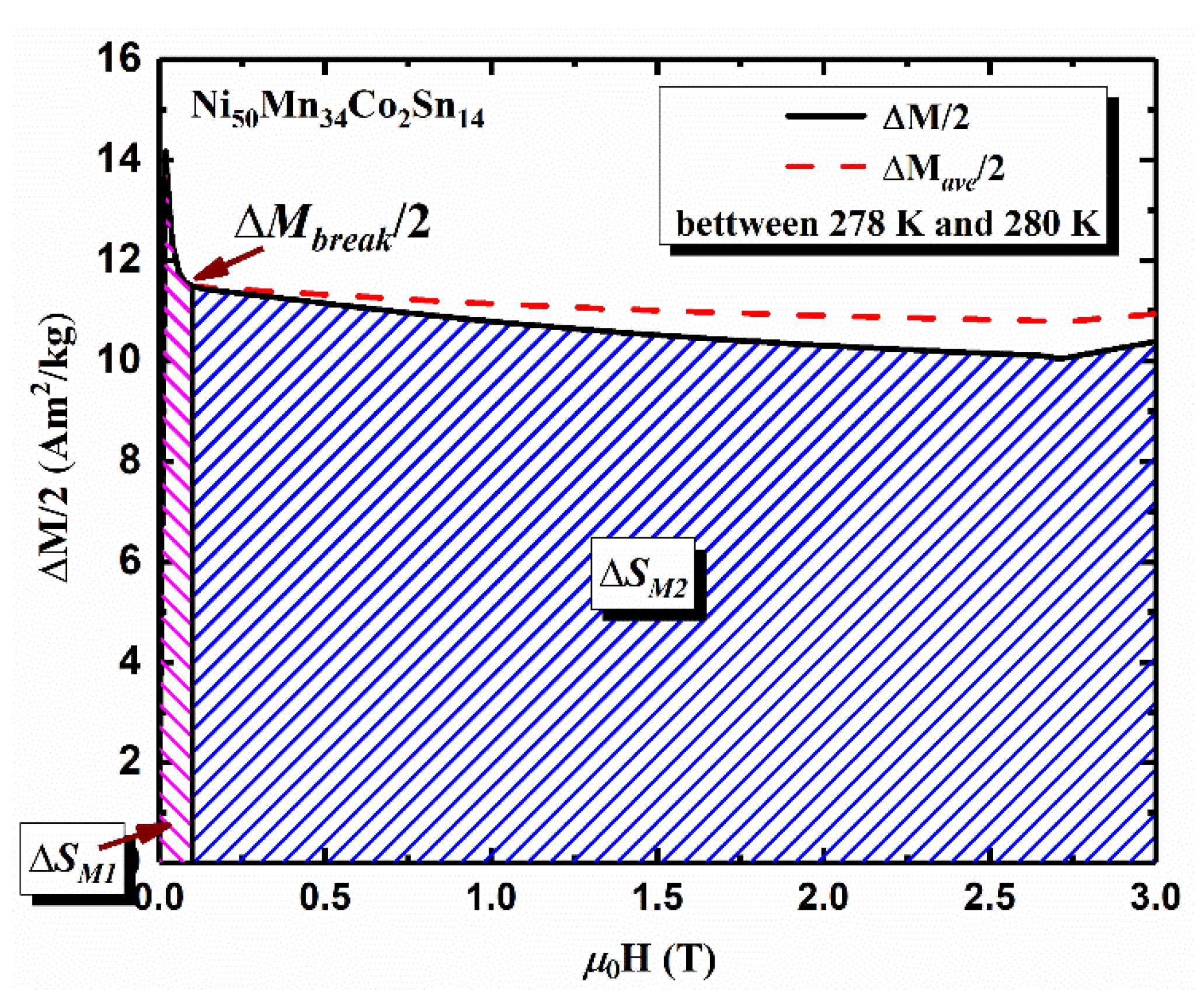
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kainuma, P.; Imano, Y.; Ito, W.; Sutou, Y.; Morito, H.; Okamoto, S.; Kitakami, O.; Oikawa, K.; Fujita, A.; Kanomata, T.; et al. Magnetic-field-induced shape recovery by reverse phase transformation. Nature 2006, 439, 957–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, K.; Okada, H.; Watanabe, K.; Kanomata, T.; Kainuma, R.; Ito, W.; Oikawa, K.; Ishida, K. Observation of large magnetoresistance of magnetic Heusler alloy Ni50Mn36Sn14 in high magnetic fields. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 182510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.Y.; Ma, L.; Liu, G.D.; Liu, Z.H.; Chen, J.L.; Cao, Z.X.; Wu, G.H.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, X.X. Magnetic field-induced martensitic transformation and large magnetoresistance in NiCoMnSb alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 242501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.M.; Liu, Y.; Ren, P.; Xia, B.; Ruan, K.B.; Yi, J.B.; Ding, J.; Li, X.G.; Wang, L. Large exchange bias after zero-field cooling from an unmagnetized state. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 077203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Gottschall, T.; Skokov, K.P.; Moore, J.D.; Gutfleisch, O. Giant magnetocaloric effect driven by structural transitions. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krenke, T.; Duman, E.; Acet, M.; Wassermann, E.F.; Moya, X.; Mañosa, L.; Planes, A. Inverse magnetocaloric effect in ferromagnetic Ni-Mn-Sn alloys. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.X.; Zhang, H.H.; Qian, M.F.; Geng, L. Enhanced magnetocaloric effect in Ni-Mn-Sn-Co alloys with two successive magnetostructural transformations. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, C.C.M. Hyperfine field systematics in Heusler alloys. J. Phys. F Met. Phys. 1975, 5, 1931–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutou, Y.; Imano, Y.; Koeda, N.; Omori, T.; Kainuma, R.; Ishida, K.; Oikawa, K. Magnetic and martensitic transformations of NiMnX (X = In, Sn, Sb) ferromagnetic shape memory alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 4358–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.D.; Wang, D.H.; Zhang, C.L.; Xuan, H.C.; Gu, B.X.; Du, Y.W. Low-field inverse magnetocaloric effect in Ni50-xMn39+xSn11 Heusler alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 042507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krenke, T.; Acet, M.; Wassermann, F.; Moya, X.; Mañosa, L.; Planes, A. Martensitic transitions and the nature of ferromagnetism in the austenitic and martensitic states of Ni-Mn-Sn alloys. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 014412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Hu, F.X.; Shen, J.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.R.; Shen, B.G. Field-induced structural transition and the related magnetic entropy change in Ni43Mn43Co3Sn11 alloy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 2571–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.D.; Wang, D.H.; Qian, B.; Feng, J.F.; Jiang, X.F.; Du, Y.W. Phase transitions, magnetocaloric effect and magnetoresistance in Ni-Co-Mn-Sn ferromagnetic shape memory alloy. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 49, 010211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleicher, B.; Klar, D.; Ollefs, K.; Diestel, A.; Walecki, D.; Weschke, E.; Schultz, L.; Nielsch, K.; Fähler, S.; Wende, H.; et al. Electronic structure and magnetism of epitaxial Ni-Mn-Ga(-Co) thin films with partial disorder: A view across the phase transition. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 465005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswanath, D.; Körmann, F.; Hickel, T.; Neugebauer, J. Impact of Co and Fe doping on the martensitic transformation and the magnetic properties in Ni-Mn-based Heusler alloys. Phys. Status Solidi B 2018, 255, 1700455. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.S.; Wang, Q.B.; Li, S.P.; Ao, W.Q.; Li, J.Q. Effect of Co substitution on the martensitic transformation and magnetocaloric properties of Ni50Mn35-xCoxSn15. Powder Diffr. 2013, 28, S22–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.H.; Zhang, H.; Hu, F.X.; Sun, J.R.; Pan, L.Q.; Shen, B.G. Magnetocaloric effect and martensitic transition in Ni50Mn36-xCoxSn14. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 588, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, H.C.; Zheng, Y.X.; Ma, S.C.; Cao, Q.Q.; Wang, D.H.; Du, Y.W. The martensitic transformation, magnetocaloric effect, and magnetoresistance in high-Mn content Mn47+xNi43-xSn10 ferromagnetic shape memory alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 108, 103920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, M.K.; Bagani, K.; Banerjee, S. Effect of excess Ni on martensitic transition, exchange bias and inverse magnetocaloric effect in Ni2+xMn1.4-xSn0.6 alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 600, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.L.; Zhang, P.; Dan, N.H.; Yen, N.H.; Thanh, P.T.; Thanh, T.D.; Phan, M.H.; Yu, S.C. Coexistence of conventional and inverse magnetocaloric effects and critical behaviors in Ni50Mn50-xSnx (x = 13 and 14) alloy ribbons. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 212403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Phan, T.L.; Duc, N.H.; Dan, N.H.; Yu, S.C. Magnetocaloric and critical behavior of Ni0.5Mn0.5-xSnx Heusler alloys. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 3753–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, M.F.; Zhang, X.X.; Wei, L.S.; Geng, L.; Peng, H.X. Effect of chemical ordering annealing on martensitic transformation and superelasticity in polycrystalline Ni-Mn-Ga microwires. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 645, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Alarcos, V.; Pérez-Landazábal, J.I.; Recarte, V.; Rodríguez-Velamazán, J.A.; Chernenko, V.A. Effect of atomic order on the martensitic and magnetic transformations in Ni-Mn-Ga ferromagnetic shape memory alloys. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2010, 22, 166001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Zheng, Q.; Zheng, X.Q.; Li, M.; Du, J.; Yan, A.R. Enhanced magnetic refrigeration properties in Mn-rich Ni-Mn-Sn ribbons by optimal annealing. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weise, B.; Dutta, B.; Teichert, N.; Hütten, A.; Hickel, T.; Waske, A. Role of disorder when upscaling magnetocaloric Ni-Co-Mn-Al Heusler alloys from thin films to ribbons. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caron, L.; Ou, Z.Q.; Nguyen, T.T.; Cam Thanh, D.T.; Tegus, O.; Brück, E. On the determination of the magnetic entropy change in materials with first-order transitions. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 3559–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.W.; Zhang, H.; Tao, K.; Wang, Y.X.; Wu, M.L.; Long, Y. Giant magnetocaloric effect induced by reemergence of magnetostructural coupling in Si-doped Mn0.95CoGe compounds. Mater. Des. 2017, 114, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, A.K.; Dubenko, I.; Standler, S.; Ali, N. The effect of partial substitution of In by Si on the phase transitions and respective magnetic entropy changes of Ni50Mn35In15 Heusler alloy. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 202004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.H.; Cong, D.Y.; Sun, X.M.; Nie, Z.H.; Gui, W.Y.; Li, R.G.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Y.D. Giant and reversible room-temperature magnetocaloric effect in Ti-doped Ni-Co-Mn-Sn magnetic shape memory alloys. Acta Mater. 2017, 134, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, B.; Long, Y.; Duan, J.F.; Shi, P.J.; Wu, G.H.; Ye, R.C.; Chang, Y.Q.; Zhang, J.; Rong, C.B. Phase transition processes and magnetocaloric effect in Ni2.15Mn0.85−xCoxGa alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 07B335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, H.C.; Han, P.D.; Wang, D.H.; Du, Y.W. Magnetic and magnetocaloric properties in Cu-doped high Mn content Mn50Ni40-xCuxSn10 Heusler alloys. Intermetallics 2014, 54, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Shen, J.; Hu, F.X.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.R.; Shen, B.G. Magnetic properties and magnetic entropy change in Heusler alloys Ni50Mn35−xCuxSn15. Appl. Phys. A 2009, 97, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, R.; Nayak, A.K.; Suresh, K.G.; Nigam, A.K. Effect of Fe substitution on the magnetic, transport, thermal and magnetocaloric properties in Ni50Mn38−xFexSb12 Heusler alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 123904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passamani, E.C.; Xavier, F.; Favre-Nicolin, E.; Larica, C.; Takeuchi, A.Y.; Castro, I.L.; Proveti, J.R. Magnetic properties of NiMn-based Heusler alloys influenced by Fe atoms replacing Mn. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 033919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burch, T.J.; Litrenta, T. Hyperfine studies of site occupation in ternary systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1974, 33, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.Z.; Yang, L.; Liu, B.H.; Meng, F.B.; Liu, E.K. Atomic disorder in Heusler alloy Cr2CoGa. Phys. B 2015, 476, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandpal, H.C.; Fecher, G.H.; Felser, C. Calculated electronic and magnetic properties of the half-metallic, transition metal based Heusler compounds. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, 1507–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Kimura, A.; Miura, Y.; Shirai, M.; Cui, Y.T.; Shimada, K.; Namatame, H.; Taniguchi, M.; Ueda, S.; Kobayashi, K.; et al. Role of electronic structure in the martensitic phase transition of Ni2Mn1+xSn1-x studied by hard-X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and Ab Initio calculation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 176401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Jung, J.; Stoyko, S.S.; Mar, A.; Quetz, A.; Samanta, T.; Dubenko, I.; Ali, N.; Stadler, S.; Chow, K.H. The role of Ni-Mn hybridization on the martensitic phase transitions in Mn-rich Heusler alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 172403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelatt, C.D., Jr.; Williams, A.R.; Moruzzi, V.L. Theory of bonding of transition metals to nontransition metals. Phys. Rev. B 1983, 27, 2005–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.Y.; Liu, E.K.; Chen, J.H.; Li, Y.; Liu, G.D.; Luo, H.Z.; Xi, X.K.; Zhang, H.W.; Wang, W.H.; Wu, G.H. Realization of multifunctional shape-memory ferromagnets in all-d-metal Heusler phases. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 022406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, S.; Ghosh, S.; Ghosh, A.; Devarajan, U.; Kannan, M.; Govindaraj, L.; Mandal, K. Effect of hydrostatic pressure on the magnetic, exchange bias and magnetocaloric properties of Ni45.5Co2Mn37.5Sn15. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 712, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hu, F.X.; Wang, J.; Bao, L.F.; Zheng, X.Q.; Pan, L.Q.; Yin, J.H.; Sun, J.R.; Shen, B.G. Magnetic entropy change and transport properties in Ni45Co5Mn36In13.4. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 549, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschneidner, K.A., Jr.; Pecharsky, V.K.; Tsokol, A.O. Recent developments in magnetocaloric materials. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2005, 68, 1479–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giguère, A.; Foldeaki, M.; Ravi Gopal, B.; Chahine, R.; Bose, T.K.; Frydman, A.; Barclay, J.A. Direct measurement of the “Giant” adiabatic temperature change in Gd5Si2Ge2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 83, 2262–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.R.; Hu, F.X.; Shen, B.G. Comment on “Direct measurement of the ‘Giant’ adiabatic temperature change in Gd5Si2Ge2”. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, J.S.; Amaral, V.S. The effect of magnetic irreversibility on estimating the magnetocaloric effect from magnetization measurements. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 042506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, J.S.; Amaral, V.S. On estimating the magnetocaloric effect from magnetization measurements. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2010, 322, 1552–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.; Bahl, C.R.H.; Bjørk, R.; Engelbrecht, K.; Nielsen, K.K.; Pryds, N. Materials challenges for high performance magnetocaloric refrigeration devices. Adv. Energy Mater. 2010, 2, 1288–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krenke, T.; Duman, E.; Acet, M.; Moya, X.; Mañosa, L.; Planes, A. Effect of Co and Fe on the inverse magnetocaloric properties of Ni-Mn-Sn. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 102, 033903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.Y.; Liu, E.K.; Li, Y.; Xu, G.Z.; Zhang, X.M.; Liu, G.D.; Xi, X.K.; Zhang, H.W.; Wang, W.H.; Wu, G.H.; et al. Unprecedentedly wide Curie-temperature windows as phase-transition design platform for tunable magneto-multifunctional materials. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2015, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecharsky, V.K.; Gschneidner, K.A., Jr. Magnetocaloric effect from indirect measurements: Magnetization and heat capacity. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 86, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Nominal Composition | Final Composition |
|---|---|
| Ni50Mn35Co2Sn13 | Ni49.9(8)Mn35.1(4)Co1.9(1)Sn13.1(4) |
| Ni51Mn34Co2Sn13 | Ni50.9(11)Mn34.1(7)Co1.8(1)Sn13.3(9) |
| Ni50Mn34Co3Sn13 | Ni50.1(9)Mn33.9(10)Co2.9(8)Sn13.2(7) |
| Ni50Mn34Co2Sn14 | Ni50.0(10)Mn34.0(8)Co1.9(3)Sn14.1(7) |
| Alloys | ΔS (J/kg K) |
|---|---|
| Ni50Mn35Co2Sn13 | 42.3 |
| Ni51Mn34Co2Sn13 | 28.2 |
| Ni50Mn34Co3Sn13 | 14.9 |
| Ni50Mn34Co2Sn14 | 31.6 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, C.; Zhang, H.; Long, K.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, Z.; He, D.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Long, Y. The Effect of Different Atomic Substitution at Mn Site on Magnetocaloric Effect in Ni50Mn35Co2Sn13 Alloy. Crystals 2018, 8, 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8080329
Xing C, Zhang H, Long K, Xiao Y, Zhang H, Qiu Z, He D, Liu X, Zhang Y, Long Y. The Effect of Different Atomic Substitution at Mn Site on Magnetocaloric Effect in Ni50Mn35Co2Sn13 Alloy. Crystals. 2018; 8(8):329. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8080329
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Chengfen, Hu Zhang, Kewen Long, Yaning Xiao, Hanning Zhang, Zhijie Qiu, Dai He, Xingyu Liu, Yingli Zhang, and Yi Long. 2018. "The Effect of Different Atomic Substitution at Mn Site on Magnetocaloric Effect in Ni50Mn35Co2Sn13 Alloy" Crystals 8, no. 8: 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8080329
APA StyleXing, C., Zhang, H., Long, K., Xiao, Y., Zhang, H., Qiu, Z., He, D., Liu, X., Zhang, Y., & Long, Y. (2018). The Effect of Different Atomic Substitution at Mn Site on Magnetocaloric Effect in Ni50Mn35Co2Sn13 Alloy. Crystals, 8(8), 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8080329




